ekg/ecg
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
ekg/ecg
electrokardiogram/electrocardiogram
interchangeable
typical conduction pathway
SA node: 60-100bpm (intrinsic closer to 100, parasympathetic brings number down)
AV node: 40-60 bpm (can also pace the heart at a slower rate if SA node is compromised)
Bundle of His
Bundle branches: 25-40bpm
Purkinje fibers: 25-40bpm
each segment can take over pacing if normal conduction is interrupted higher in the pathway
EKG represents ?
electrical activity (y axis) against time (x axis)
cardiac action potential triggers flows of what ions across the cell membrane?
potassium, calcium, sodium
myocardial depolarization
wave spreads quickly and should cause synchronized contraction of heart muscle
refractory period
each cell has a period where additional electrical stimulation will not cause another depolarization
vector of electrical activity toward an EKG lead
positive deflection (above the line)
vector of electrical activity away from EKG lead
negative deflection (below the line)
12 lead EKG
leads represent different views of heart
limb leads: bipolar (I, II, III); unipolar (aVR, aVL, aVF)
chest leads: V1-V6
10 electrodes give 12 views
telemetry
5 electrodes
provides bipolar leads (I, II, III) and 1 unipolar lead
typically used in hospital setting for quick identification of HR and rhythm
does not diagnose ischemia
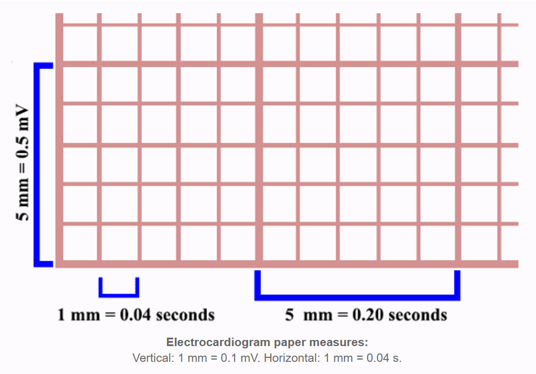
EKG paper
x-axis is time
each small box = 0.04 seconds
5 small boxes=1 big box
1 big box=0.20 seconds
5 big box=1 second
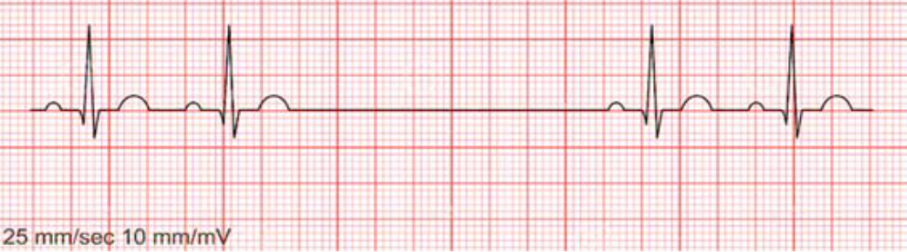
phases of cardiac cycle on EKG
P wave
PR interval
QRS complex
ST segment
T wave
R-R interval=1 complete cardiac cycle
P wave
SA node impulse starts atrial depolarization
impulse→AV node→ventricles
heart events: atrial depolarization and contraction (atrial kick)
PR interval
time between atrial depolarization and ventricular depolarization
normal=0.12-0.20 seconds
QRS complex
impulse spreads from AV node→bundle of His→bundle branches→purkinje fibers
heart events: ventricular depolarization and contraction (systole)
should happen quickly
normal=0.06-0.10 se
T wave
pause in electrical activity followed by ventricular repolarization
ST segment and T wave are both sensitive to mismatch btwn myocardial oxygen supply and demand
heart events: ventricular repolarization and relaxation (diastole)
QT interval
represents time btwn start & end of ventricular repolarization
should be <½ of RR interval when rhythm is regular
decr w/ higher HR
short interval is insignificant
long interval=long refractory period=more risk for dysrhythmias
possible causes of long QT interval
ischemia, electrolyte imbalances, medications, hypothermia, heredity
estimating heart rate on EKG for regular rhythms only
find an R that is close to a heavy line
count how many large boxes until the next R
more accurate estimate of HR on EKG
mark a 6-second strip: 30 large boxes
count how many R’s present
multiply by 10 to get beats/min
works for regular and irregular heart rhythms
systematic interpretation of EKGs
is the R-R interval the same for each beat?: indicates whether rhythm is regular/irregular
estimate/calculate HR
is there a P wave for every QRS complex?
QRS complex fore very P wave?
what is the PR interval?
are the QRS complexes narrow, do they all look the same?
does anything else look abnormal?
normal sinus rhythm
R-R interval is the same for each beat
HR btwn 60-100 bpm
every P wave has a QRS complex, PR interval between 0.12-0.20 seconds (<1 large box)
every QRS complex has a P wave
every QRS complex is narrow and looks consistent (duration <0.12 seconds or <3 small boxes)
sinus tachycardia
sinus rhythm >100bpm
occurs in response to excs, stress, anxiety, pain, dehydration, stimulants
less common causes: hyperthyroidism, anemia, blood loss
incr myocardial O2 demand (workload on the heart)
sinus bradycardia
sinus rhythm <60 bpm
may occur in highly conditioned athletes
other potential causes: infection, hypothyroidism, sleep apnea, beta blockers, rheumatoid conditions, TBI
may decr CO
sinus dysrhythmia/sinus arrhythmia
all features of normal sinus rhythm except irregular R-R intervals
normal variant of sinus rhythm that occurs w/ respiratory pattern
may be due to fluctuating stimulation of vagus nerve during breathing cycle
sinus arrest/sinus block
SA node fails to initiate an impulse—missing P wave
P waves are normal, identical, occur before every QRS
PR interval normal
QRS complex is narrow, normal
R-R interval is regular except for when pause occurs
caused by sudden incr in para activity, diseased SA node, infection, digoxin toxicity
implications: long pauses can reduce CO and cause syncope
supraventricular arrhythmias/dysrhythmias
abnormal conduction occurs above the ventricles
QRS complexes remain narrow and normal
ventricular arrhythmias/dysrhythmias
ectopic pacemaker occurs w/in ventricle
QRS complexes are wide and abnormal shape
conduction blocks
normal conduction is interrupted
types of supraventricular arrhythmias
premature atrial complexes (PACs)
atrial tachycardia
supraventricular tachycardia
atrial fibrillation
atrial flutter
premature atrial complex
early beat initiated w/in atria but not SA node
“ectopic”
rhythm: skipped/early beat may be felt by pt or on palpation
P wave present for every QRS complex, but different size/shape or buried in T wave from previous beat
PR interval normal
QRS narrow and normal
implications: usually benign; incr freq may lead to atrial fibrillation or SVT; may be caused by stress, nicotine, caffeine, alcohol, hypoxemia
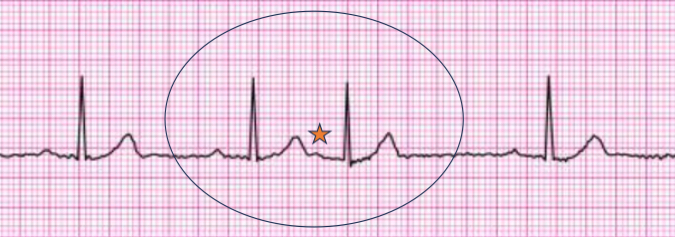
multiple PACs
atrial bigeminy
atrial tachycardia
atrial bigeminy
alternating regular beats and PACs
atrial tachycardia
3 or more PACs consecutively
may be paroxysmal—comes on spontaneously and self-resolves
may be sustained w/ HR 140-250 bpm
supraventricular tachycardia
ectopic pacemaker in atria
rhythm: very regular
rate >100bpm, often higher
P waves: hidden in preceding T waves
PR interval: unable to measure
QRS complex narrow and normal
implications: high HR→reduced ventricular filling time; impaired CO; syncope
atrial fibrillation
inconsistent, irregular R-R intervals w/o clear P waves
multiple simultaneous impulses from different locations in atria
rhythm: very irregular w/o clear pattern
rate: may be normal (rate controlled) or tachycardia (rapid ventricular response)
P waves not present, may see fibrillation wave
PR interval NA
QRS narrow and normal
implications: incr risk of embroils stroke, loss of atrial kick→impair ventricular filling, esp. at higher HR
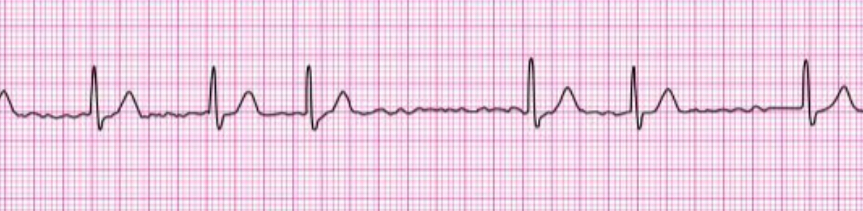
atrial flutter
P waves replaced by F waves with sawtooth appearance
ectopic focus in atria depolarizes repetitively at a rate of 250-350 bpm
rhythm: regular
rate: normal or elevated, determined only by ventricular depolarization, conduction ratio can be 2:1 up to 8:1
P waves replaced by rapid F waves
no PR interval
normal narrow QRS
implications: hemodynamically stability depends on ventricular rate
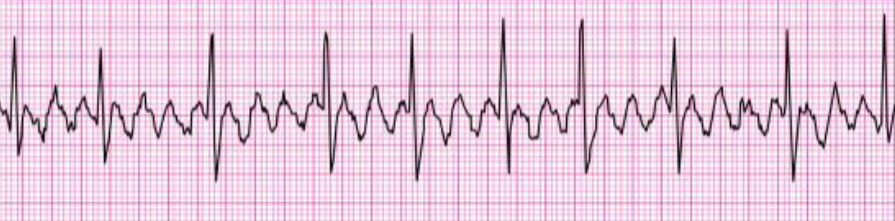
junctional rhythm
no impulse from SA node
AV node takes over pacing
rhythm: regular
rate: 40-60 bpm (intrinsic AV node rate)
P waves not present, may be inverted or hidden in QRS
PR interval unmeasurable
QRS normal and narrow
implications: loss of atrial kick, lower HR can impact CO
ventricular arrhythmias
premature ventricular complexes (PVCs)—unifocal, multifocal, ventricular bigeminy/trigeminy/quadrigeminy, couplets
premature ventricular complexes
ectopic focus in the ventricle causes early QRS
QRS wide and abnormal shape bc impulse doesn’t follow normal conduction pathway
ventricular contraction slower, less synchronized
PVCs may be followed by a pause before normal rhythm resumes
implications: impaired ventricular filling and contraction, decr SV→decr CO
more=potential to deteriorate to VT or V fib
unifocal PVC
all look the same
multifocal PVC
PVCs look different
couplets PVC
2 consecutive PVCs
bigeminy PVC
alternating normal beats and PVCs
trigeminy PVCs
2 normal beats followed by PVC
quadrigeminy PVC
3 normal beats followed by PVC
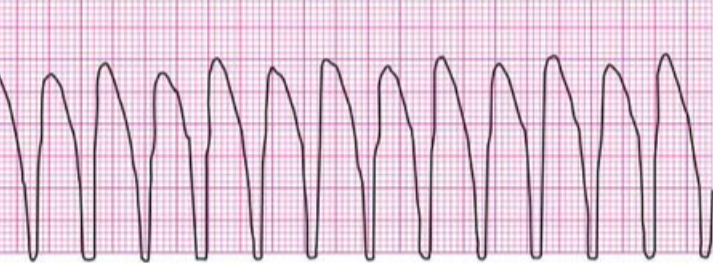
ventricular tachycardia
3+ consecutive PVCs
may be sustained or non-sustained, w or w/o pulse
rhyth: regular
rate: 100-250 bpm
no P wave
no PR interval
QRS wide and abnormal
potential causes: electrolyte abnormality, ischemic heart disease, meds, hypoxemia
implications: significant impairment in CO, potential to degenerate to V fib
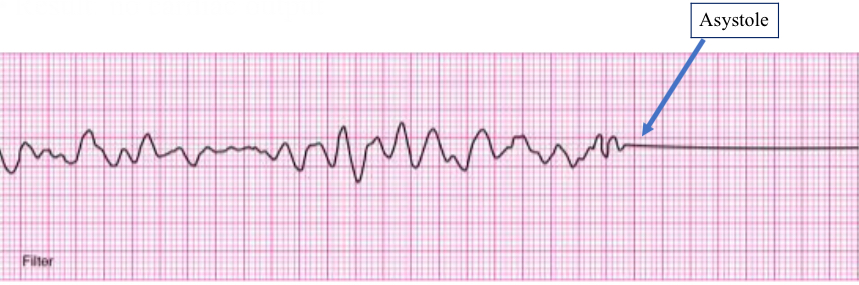
ventricular fibrillation
irregular quivering of ventricle/myocardium
result: no CO
rhythm: irregular w/o discernible P wave, QRS complex, T wave
pt has no pulse
medical emergency, requires immediate CPR and defibrillation
conduction blocks
first degree AV block
second degree AV block, type 1 and 2
third degree/complete heart block
bundle branch blocks
first degree AV block
PR interval abnormally long
rhythm: regular
rate; usually normal
P wave normal
PR interval >0.20 seconds
QRS occurs after each P wave, narrow and normal
potential causes; ischemia, electrolyte abnormalities, incr vaal tone, rheumatoid conditions
implications: slowed transmission of impulses from atria to ventricles
typically asymptomatic