Unit 4
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
State
A political unit with defined boundaries, a population, recognition, and sovereignty
2
New cards
Nation
A cultural unit in a specific territory with a shared identity due to history/heritage
3
New cards
Nation-State
**The political boundaries (state) and cultural boundaries (nation) match. Nation-states are homogeneous.**
* This is not very common. Some of the best current examples are Iceland and Japan.
* The main advantage of a nation-state is that since there is cultural unity it is often easier to maintain political unity as well (since the population already identifies together).
* This is not very common. Some of the best current examples are Iceland and Japan.
* The main advantage of a nation-state is that since there is cultural unity it is often easier to maintain political unity as well (since the population already identifies together).
4
New cards
Multinational State
**A state (country) with more than one cultural group. Multinational states are heterogenous (diverse).**
* This is much more common than nation-states, most countries are multinational states.
* Advantages of a multinational state can include-
* Openness to immigrants
* Political links to other countries
* Economic links to other countries
* Improved perspectives
\
* This is much more common than nation-states, most countries are multinational states.
* Advantages of a multinational state can include-
* Openness to immigrants
* Political links to other countries
* Economic links to other countries
* Improved perspectives
\
5
New cards
Multi-state nation
When a nation stretches across state boundaries.
* The Kurdish people are found within the boundaries of six states.
* The Kurdish people are found within the boundaries of six states.
6
New cards
Stateless nation
**When a nation lacks control of a state.**
* The Kurds are also an example of a stateless nation. They wish to create the country of Kurdistan shown on the map, but have received international recognition for the proposed state.
* Stateless nations can sometimes undermine established governments as they seek establishment of a state.
* The Kurds are also an example of a stateless nation. They wish to create the country of Kurdistan shown on the map, but have received international recognition for the proposed state.
* Stateless nations can sometimes undermine established governments as they seek establishment of a state.
7
New cards
Semi Autonomous and Autonomous Regions
**Self-determination**
* Sometimes countries might do this because the region is geographically distinct OR, more commonly, that there is a dominant minority group (majority-minority) in the region.
* The creation of autonomous regions can help manage competing forces in multinational states and can help appease stateless nations so that the country can remain unified.
* Sometimes countries might do this because the region is geographically distinct OR, more commonly, that there is a dominant minority group (majority-minority) in the region.
* The creation of autonomous regions can help manage competing forces in multinational states and can help appease stateless nations so that the country can remain unified.
8
New cards
Self-determination
Ability of a country to make their own political choices
9
New cards
Political Power
Political Power is expressed geographically as control over people, land, and resources. Those who hold Political Power control the behavior of people through laws and regulations.
10
New cards
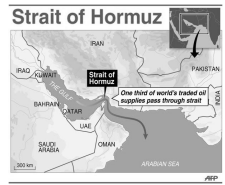
Choke Point
* A strategic strait or canal (geographical feature) which could be controlled by a country
* Makes it harder for an area to be captured
* Can be closed/blocked to stop or prohibit trade
* EX: The Strait of Hormuz which connects the Gulf of Oman with the Persian Gulf
* Makes it harder for an area to be captured
* Can be closed/blocked to stop or prohibit trade
* EX: The Strait of Hormuz which connects the Gulf of Oman with the Persian Gulf
11
New cards
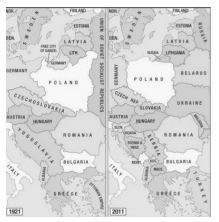
Shatterbelt
* An area of instability between regions with opposing political and/or cultural views
* A region under persistent stress or tension, and often fragmented by rivals
* EX: Israel and Kashmir today + Eastern Europe during the Cold War
* A region under persistent stress or tension, and often fragmented by rivals
* EX: Israel and Kashmir today + Eastern Europe during the Cold War
12
New cards
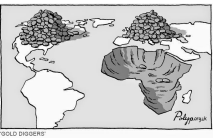
Neocolonialism
* The use of economic, political, cultural, or other means to control or influence other countries, especially those of former colonies
* When nations and corporations dominate subject nations
* Can be applied to multinational corporations in MDCs controlling resources in LDCs
* EX: DeBeers is based in the UK but controls a large number of the diamond mines in African countries
* When nations and corporations dominate subject nations
* Can be applied to multinational corporations in MDCs controlling resources in LDCs
* EX: DeBeers is based in the UK but controls a large number of the diamond mines in African countries
13
New cards
Relic Boundary
**Boundary that existed as an official boundary but does not anymore**
* Ex. Berlin Wall between East and West Germany & Great Wall of China
* Ex. Berlin Wall between East and West Germany & Great Wall of China
14
New cards
Consequent Boundary(Cultural/Ethnographic)
**Boundary between different cultures, languages, or religions**
* Ex. border between India (Hinduism) and Pakistan (Islam) & Ireland (mostly Catholic) and Northern Ireland (mostly Protestant)
* Ex. border between India (Hinduism) and Pakistan (Islam) & Ireland (mostly Catholic) and Northern Ireland (mostly Protestant)
15
New cards
Superimposed Boundary
**Boundary imposed by an outside power or force ignores existing cultures around the area**
* Ex. Many African countries (Berlin Conference)
* Ex. Many African countries (Berlin Conference)
16
New cards
Antecedent Boundary
Boundary that existed before human settlement and (cultural) changes in landscape
* Ex. Western States in the U.S.
* Ex. Western States in the U.S.
17
New cards
Subsequent Boundary
Boundary created during human settlement with changes in culture of landscape \n usually not geometric
* Ex. Northeast U.S. (colonization)
* Ex. Northeast U.S. (colonization)
18
New cards
Defining Boundary
Deciding the geographic location of the boundary
19
New cards
Delimiting Boundary
The recording of the boundary on a map
20
New cards
Demarcating Boundary
**Marking the boundary somehow physically**
* Usually involves regulation of trade and passage across the boundary
* Usually involves regulation of trade and passage across the boundary
21
New cards
Administering Boundary
Maintaining the boundary
22
New cards
Reasons for conflict over Borders
* Area is contested
* Political instability Between neighboring states
* Distribution of resources as a result of the border
* Political instability Between neighboring states
* Distribution of resources as a result of the border
23
New cards
Territorial Waters
Are waters that are enclosed by boundaries off the shore of costal and island states which are considered part of the state's territory.
24
New cards
Defined by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLONS)
Is a belt of costal water extending, at most, 12 nautical miles (22.2 km or 13.8 mi) from the baseline (normally the average low-water mark) of a costal state
25
New cards
Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZs)
Sea zone over which a state has special rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources.
* For example: Any energy production, from wind or water, in these areas will be under control of the state which boundary it is within
* Unlike territorial waters, EEZs have a reduced sovereign right on the resources in them
* For example: Any energy production, from wind or water, in these areas will be under control of the state which boundary it is within
* Unlike territorial waters, EEZs have a reduced sovereign right on the resources in them
26
New cards
Landlocked Countries
Landlocked countries are at a huge disadvantage because their international trade depends on transit through other countries.
27
New cards
Reapportionment
Reassigning legislative seats among districts after census reports so they each represent the same amount of people
28
New cards
Redistricting
Redrawing voting district lines (usually due to population change)
29
New cards
Gerrymandering
* Manipulating voting district boundaries to make people favor one political party over another
* Process is disliked, but not illegal
* Common tactics = packing and cracking
* Process is disliked, but not illegal
* Common tactics = packing and cracking
30
New cards
Packing
* Creating district where support for opposition is overwhelming Why: While they may win those districts, they aren't in others, so they can't win majority control.
* (access vote gerrymandering: since the opposition has more votes than needed in districts they're packed in)
* (access vote gerrymandering: since the opposition has more votes than needed in districts they're packed in)
31
New cards
Cracking
Disperses the opposition among districts so that they lose everywhere (wasted vote gerrymandering: the votes for opposition are all wasted since none of them are expressed)
32
New cards
Unitary System
**Central government is supreme Operates as one unit Centralized**
* Ex. China
* Ex. China
33
New cards
Federal System
**Divides power between the different subdivisions Not as Centralized**
* Ex. USA
* Ex. USA
34
New cards
Unitary Government Pros and Cons
* Pros
* People follow same laws, have same policies
* Decisions are more efficient
* Cons
* Disconnects with minority regions within the country
* Can't respond to unique needs as wel
* People follow same laws, have same policies
* Decisions are more efficient
* Cons
* Disconnects with minority regions within the country
* Can't respond to unique needs as wel
35
New cards
Federal Government Pros and Cons
* Pros
* Can help prevent disintegration of a state due to diverse interests
* Subnational units can create their own solutions that are more effective in meeting localized needs
* Cons
* Inequalities between subunits; not the same throughout the country
* Less unified, conflict between the different levels; redundancy in services (ie. state police and local police
* Can help prevent disintegration of a state due to diverse interests
* Subnational units can create their own solutions that are more effective in meeting localized needs
* Cons
* Inequalities between subunits; not the same throughout the country
* Less unified, conflict between the different levels; redundancy in services (ie. state police and local police
36
New cards

Devolution
**The movement of power from the central government to a smaller, self-identified community within it.**
* In the sub-units formed by devolution, the power is not evenly divided.
* In the sub-units formed by devolution, the power is not evenly divided.
37
New cards
\[Physical Geography\] Factors that can lead to the devolution of states
Isolated villages, rugged topography, and islands often want to separate from the country
38
New cards
\[Ethnic Separatism\] Factors that can lead to the devolution of states
Groups with ethno-nationalist views often want independence and to control their own area within a country, the compromise being devolution
39
New cards
\[Ethnic Cleansing \] Factors that can lead to the devolution of states
A country may want to wipe a certain ethnic group out of the state but grant them power over their territory instead
40
New cards
\[Terrorism\] Factors that can lead to the devolution of states
Violent uprising of a group can lead political powers to grant them some autonomy over their concentration within an area of a country
41
New cards
\[Economic and Social Problems\] Factors that can lead to the devolution of states
Poorer areas of the country can often feel disadvantaged and at the same time, richer areas don't want to provide for the poor
42
New cards
\[Irredentism\] Factors that can lead to the devolution of states
An state may want to claim or influence an area within another state that has a majority of people from that ethnicity, especially if it was part of it in the past.
43
New cards
Examples of Devolution
* The United Kingdom- Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland have some degree of authority over their own territories but they are still a part of a larger country, the UK
* Belgium- The federal government divides power among different areas. These “communities” represent divided languages and cultures.
* Nigeria- The use of federalism in Nigeria refers to the devolution of self-governance of Nigeria to its federal states who share sovereignty with the federal government.
* Canada- devolution occurred in regards to the Northwest Territories (largely native peoples) by giving people in those areas decision-making power over resources and land use; Canada is also noted for giving Quebec concessions regarding language laws (French).
* Belgium- The federal government divides power among different areas. These “communities” represent divided languages and cultures.
* Nigeria- The use of federalism in Nigeria refers to the devolution of self-governance of Nigeria to its federal states who share sovereignty with the federal government.
* Canada- devolution occurred in regards to the Northwest Territories (largely native peoples) by giving people in those areas decision-making power over resources and land use; Canada is also noted for giving Quebec concessions regarding language laws (French).
44
New cards
Disintegration
**The process of a state breaking up into two or more independent parts**
* Often disintegration is not only about politics within the country, but also the influence of other countries
* Often disintegration is not only about politics within the country, but also the influence of other countries
45
New cards
Examples of Disintegration
* Sudan- South Sudan separated from Sudan in 2011 largely due to religious differences. The South was largely Christian and Animist and the North largely Islamic
* Soviet Union- It was broken into 15 different states. Different cultures, ideas, and poverty mainly caused the downfall of the Soviet Union.
* East Timor- Once part of Indonesia, they separated from the rest of Timor and they now have their own independence. Although, Timor is still part of Indonesia.
* Soviet Union- It was broken into 15 different states. Different cultures, ideas, and poverty mainly caused the downfall of the Soviet Union.
* East Timor- Once part of Indonesia, they separated from the rest of Timor and they now have their own independence. Although, Timor is still part of Indonesia.
46
New cards
Supranationalism
Supranationalism is where 3 or more states work together for a common political, economic, military or cultural purpose.
47
New cards
Advantage and Disadvantage of Supranationalism
* KEY ADVANTAGE
* More collective power, increase trade, political security.
* KEY DISADVANTAGE
* When a state joins a supranational org they give up some of their own power to the org.(loss of sovereignty)
* More collective power, increase trade, political security.
* KEY DISADVANTAGE
* When a state joins a supranational org they give up some of their own power to the org.(loss of sovereignty)
48
New cards
The United Nations
* Formed after WWII to promote peace in world
* Mission is to build peaceful relationships among states
* Conflict is resolved peacefully
* Has many agencies or organs w/in it (ex: World Health Org)
* Mission is to build peaceful relationships among states
* Conflict is resolved peacefully
* Has many agencies or organs w/in it (ex: World Health Org)
49
New cards
North Atlantic Treaty Organization
* Largest military budget in world
* Main goal ls to protect the states involved through military
* Main goal ls to protect the states involved through military
50
New cards
Association of Southeast Asian Nations
* Set up to promote cultural, economic and political development in the region
* Manages the water resource issues in the seas in the region
* Manages the water resource issues in the seas in the region
51
New cards
Arctic Council
* cooperation between Arctic states
* involvement of the many indigenous communities of the Arctic
* concerned with sustainable development and environmental issues of the Arctic
* involvement of the many indigenous communities of the Arctic
* concerned with sustainable development and environmental issues of the Arctic
52
New cards
Centripetal Forces
**Events or circumstances that help unite the people of a state**
* Equality
* Cultural Homogeneity
* Shared Language
* Patriotism
* Good Leadership
* Geographic Boundaries keeping people inside
* Flourishing Economy
* Uniform Government Policies
* Strong Infrastructure
* Raison D'etre
* Equality
* Cultural Homogeneity
* Shared Language
* Patriotism
* Good Leadership
* Geographic Boundaries keeping people inside
* Flourishing Economy
* Uniform Government Policies
* Strong Infrastructure
* Raison D'etre
53
New cards
Raison D'etre
**The purpose or reason for the initial existence of a state**
* Literally translated in French as "the reason for being
* It is the most significant centripetal force
* Example: Israel's Raison D'etre➔ to create a homeland for the Jews
* Literally translated in French as "the reason for being
* It is the most significant centripetal force
* Example: Israel's Raison D'etre➔ to create a homeland for the Jews
54
New cards
Centrifugal Forces
**Events or circumstances that divide and split the people of a state,**
* Discrimination & Inequality
* Cultural Diversity
* Various Languages
* Various Religions
* Economic Disparities
* Government policies that exclude one or more groups
* Geographic Boundaries splitting a country
* Multinational States
* Poor Leadership
* Poverty
* Weak Infrastructure
* Lack of a Raison D'etre
* Ex: Yugoslavia was created as a multinational state with split religions and languages and did not have a Raison D'etre. Eventually, the country broke apart.
* Discrimination & Inequality
* Cultural Diversity
* Various Languages
* Various Religions
* Economic Disparities
* Government policies that exclude one or more groups
* Geographic Boundaries splitting a country
* Multinational States
* Poor Leadership
* Poverty
* Weak Infrastructure
* Lack of a Raison D'etre
* Ex: Yugoslavia was created as a multinational state with split religions and languages and did not have a Raison D'etre. Eventually, the country broke apart.