MODULE 15A - [Anatomy 1.0] GENERAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Excitable cells that are specialized for the reception of stimuli and the conduction of the nerve impulse
NEURON
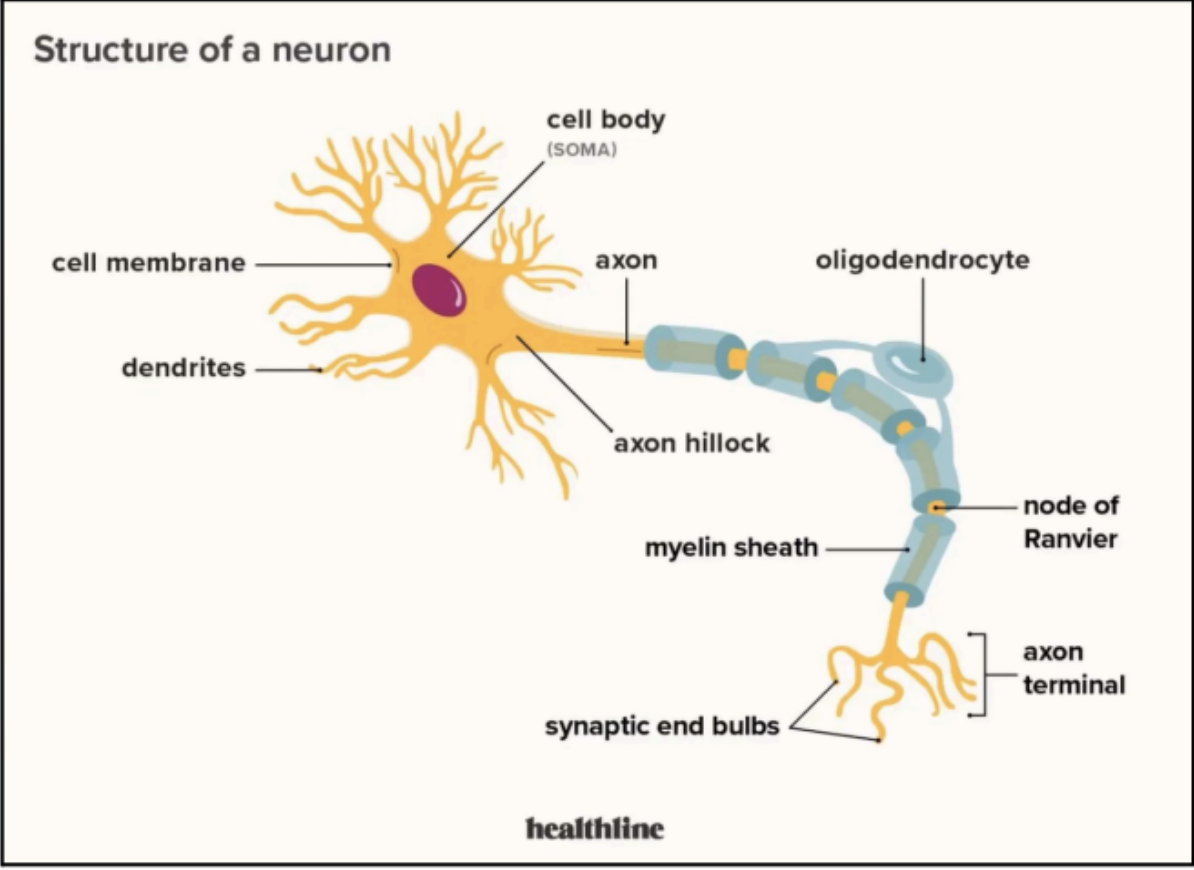
Consists essentially of a mass of cytoplasm in which a nucleus is embedded
Bounded externally by a plasma membrane
Surface projects one or more processes called neurites (e.g. dendrites and axons)
CELL BODY
neurites responsible for receiving information
Dendrites
a single, long tubular neurite that conducts impulses away from the cell body
Axons
Dendrites and axons are often referred to as ______ ______
nerve fibers
Clumps of rough endoplasmic reticulum that are found throughout the cytoplasm of the cell body
synthesizes proteins within the cell body
Nissl Bodies (Nissl Substance)
Nissl Bodies are absent in _____ and within the _____
Axon Hillock; Axon
A small conical elevation on the cell body that gives rise to the axon
Region of the cell body close to the axon
Axon Hillock
Short processes of the cell body
Often branch profusely to increase the surface area of the reception of axons from other neurons.
Cytoplasm resembles that of the cell body
Function: receive nerve impulse toward the cell body.
DENDRITES
Longest process of the cell body
Arises from axon hillock
branches profusely before their termination
Function: always conducts impulses away from the cell
body
Except for axons of unipolar neurons which may also carry an impulse toward the body
AXON
Outer covering of the axon
Multi-layered phospholipid
Function: increases the conduction velocity of the nerve impulses along the axon
Myelin Sheath
Enumerate the morphological classification of neurons based on the number of its neurites
Unipolar
Bipolar
Multipolar
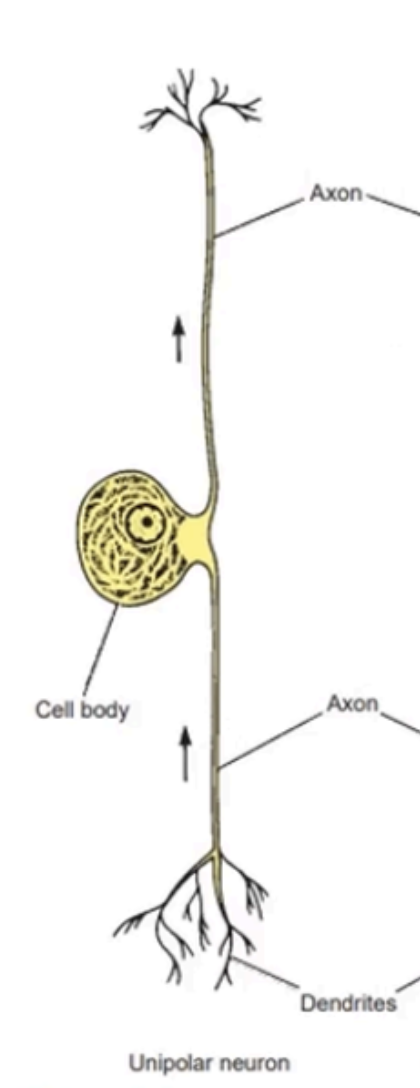
Cell body has a single neurite (or axon) that branches within a short distance from the cell body
One end is preceding to some peripheral structure and the other end enters the central nervous system (CNS)
The fine terminal branches at the peripheral end of the axon are often referred to as the dendrites.
Single neurite divides a short distance from cell body
Location: Posterior root ganglion
UNIPOLAR NEURONS
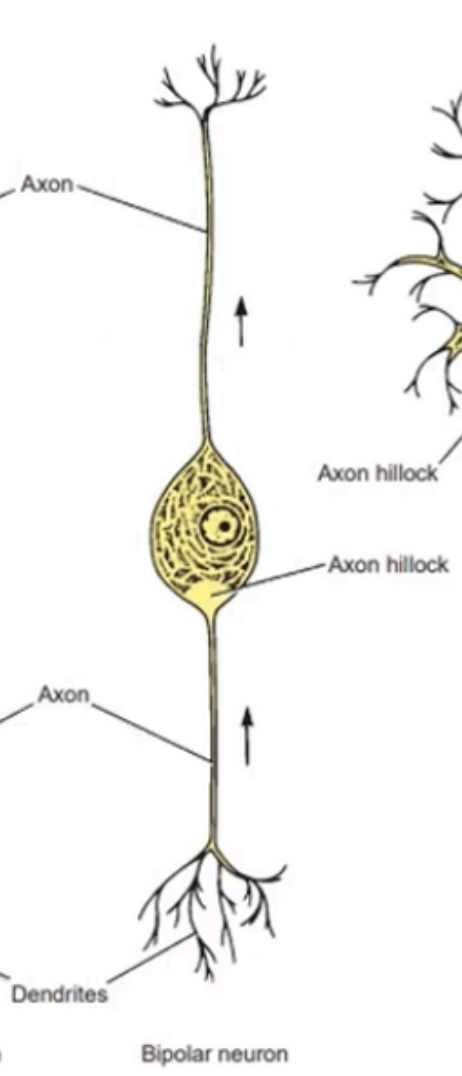
Have an elongated cell body
From each end emerges a single neurite
A total of 2 neurites, which are both axons, with the fine terminal branches at the peripheral end of one of the axons, also being referred to as dendrites
Single neurite emerges from either end of cell body
Location: Retina, sensory cochlea, and vestibular ganglia
BIPOLAR NEURONS
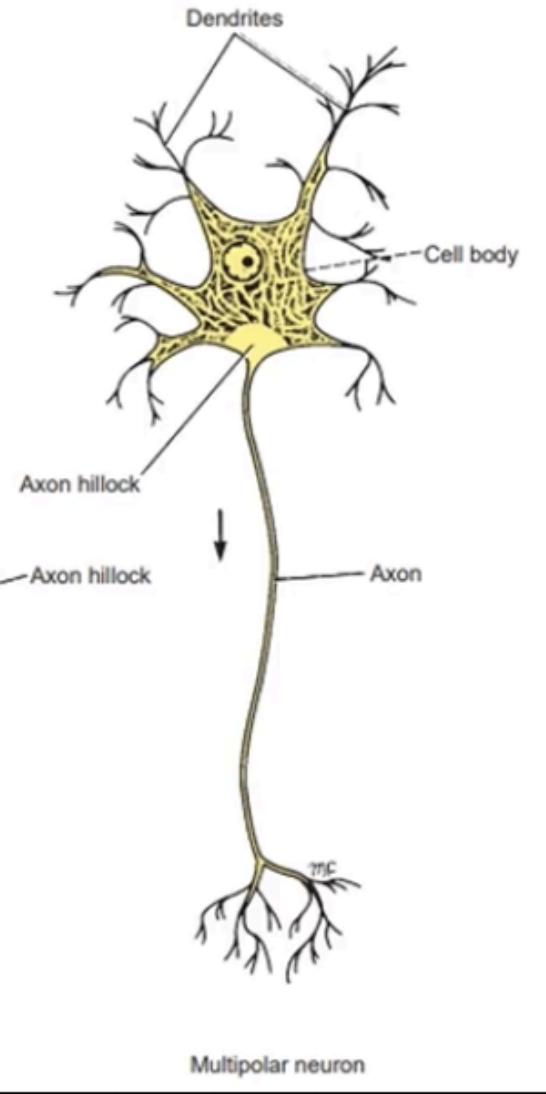
Most common kind
Have several neurites arising from the cell body, which are mostly dendrites and one long axon
Many dendrites and one long axon
Location: Fiber tracts of the brain and spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and motor cells of spinal cord
MULTIPOLAR NEURONS
Enumerate the morphological classification of neurons based on the number of its size
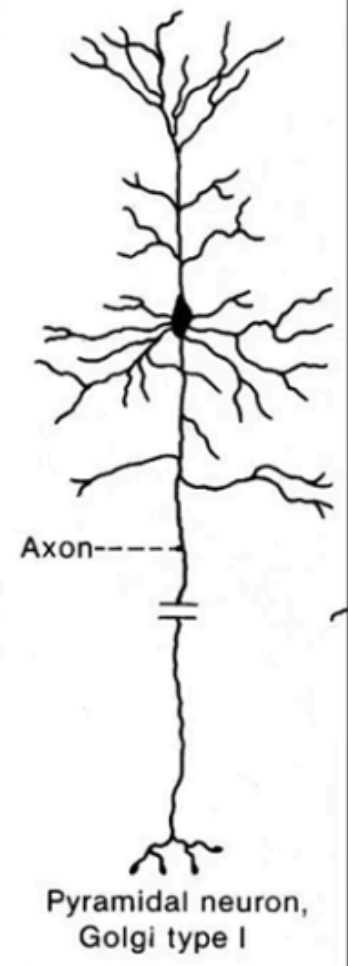
Golgi Type I
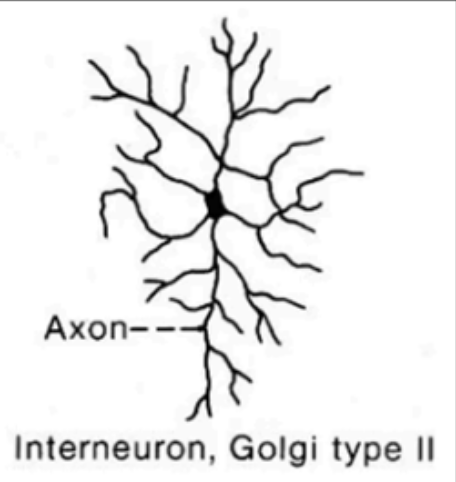
Golgi Type II
Size: Medium to large
Arrangement of Neurites: Single long axon
Location: Fiber tracts of brain and spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and motor cells of spinal cord
Golgi Type I
Size: Small to Medium
Arrangement of Neurites: Short axon that often resemble its dendrites
Location: Cerebral and cerebellar cortex
Golgi Type II
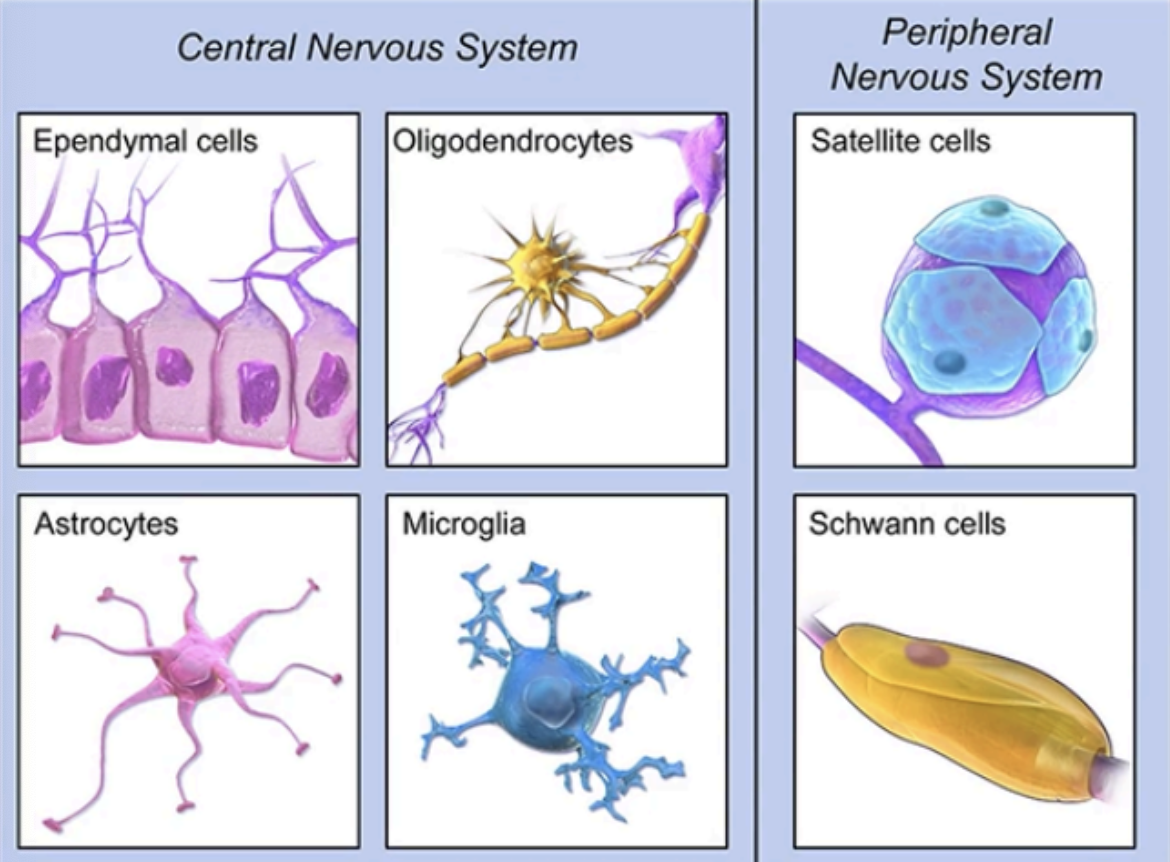
Enumerate the types of Neuroglia in the CNS and PNS
CNS
Ependymal Cells
Oligodendrocytes
Astrocytes
Microglia
PNS
Satelite Cells
Schwann Cells
Line the fluid filled cavities of the brain and the central
canal of the spinal cord.
Made up of:
Ependymocytes
Choroidal epithelial cells
EPENDYMAL CELLS
Assist in the circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the cavities by the movements of their cilia
Ependymocytes
Involved in the production and secretion of the CSF from the choroid plexuses
Choroidal epithelial cells
Phagocytes that arise from macrophages
Aid in removal of damaged neurons and infectious
agents within the CNS
MICROGLIAL CELLS
Further divided into 4 cell types
Two are found within the CNS:
Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes
The other two are found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS):
Schwann cells and Satellite (or capsular) cells
MACROGLIAL CELLS
Most numerous cells in the CNS
Have small cell bodies with branching processes
that extend in all directions.
Has two types
Fibrous
Protoplasmic
Contains Perivascular Feet
Functions:
Serve as a supporting framework for neurons and nerve fibers
Serve as “electrical insulators” between neurons → prevent axon terminals from influencing neighboring and unrelated neurons
Serve as phagocytes by taking up degenerating
synaptic axon terminals.
Astrocytes
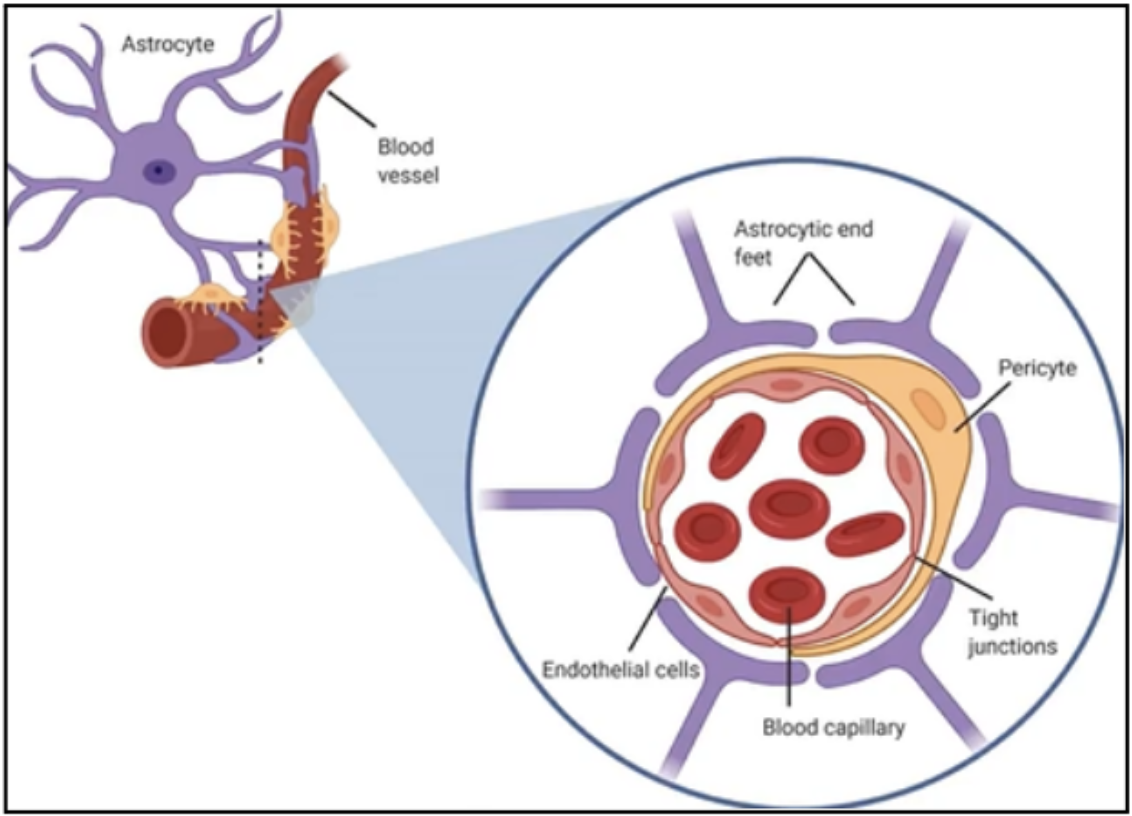
Expanded processes of astrocytes on blood vessels
Form an almost complete covering on the external surface of the capillaries
Important for the blood-brain barrier
Perivascular feet
selectively allow and block the passage of materials from the blood to the CNS.
blood-brain barrier
Mechanisms of how astrocytes serves as electrical insulators between neurons
Covering the synaptic contacts between neurons; forming barriers
Taking up neurotransmitter substances
Controlling the electrolyte balance of the
CNS
Process where astrocytes fill in the spaces previously occupied by the neurons following the death of neurons due to disease,
replacement gliosis
Forms the myelin sheath of axons of neurons in the CNS
Oligodendrocytes
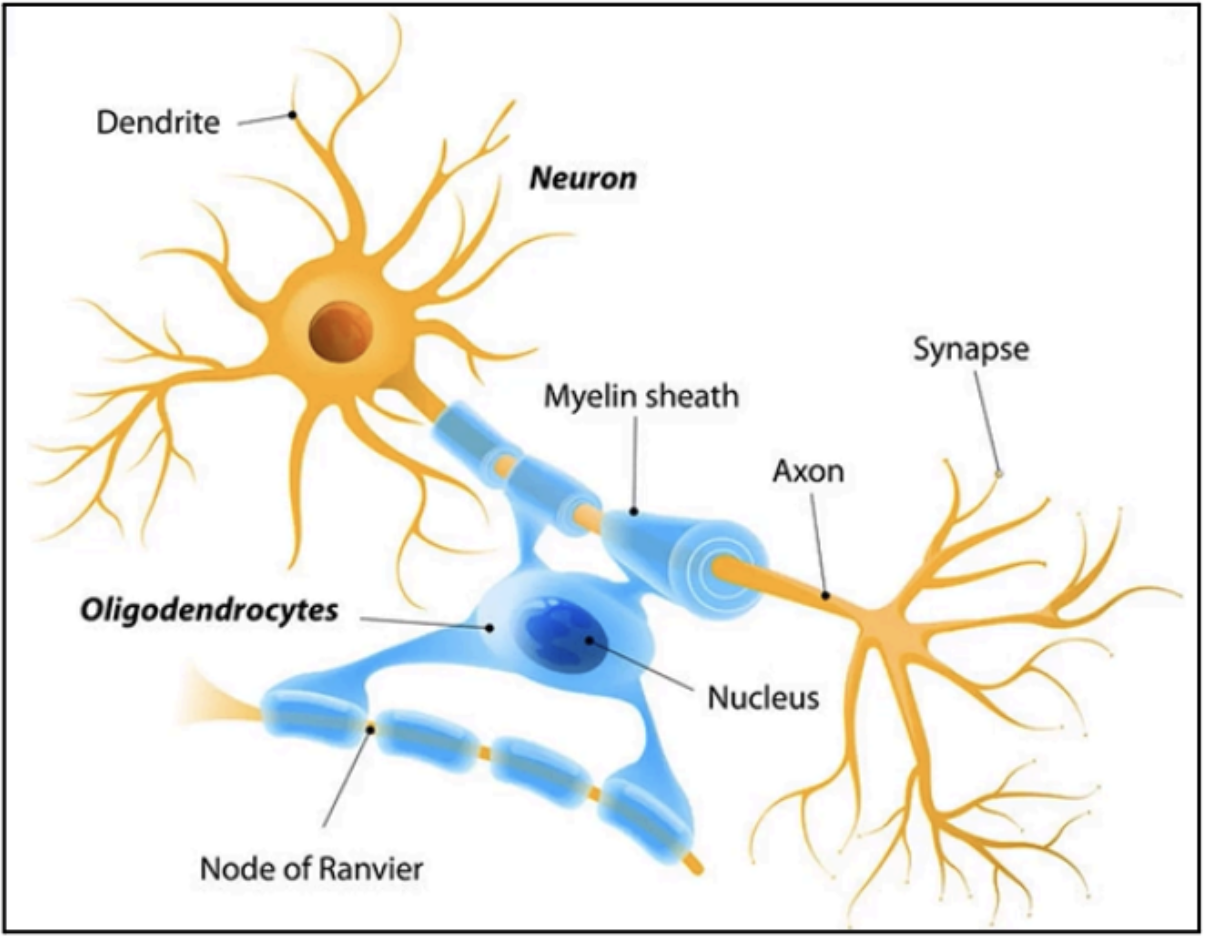
Provides axons with an insulating coat and greatly increases the speed of nerve conduction
myelin sheath
How many nerve fibers (axons) can 1 oligodendrocyte myelinate
60 nerve fibers (axons)
Produce myelin for the nerves of the
Schwann Cells
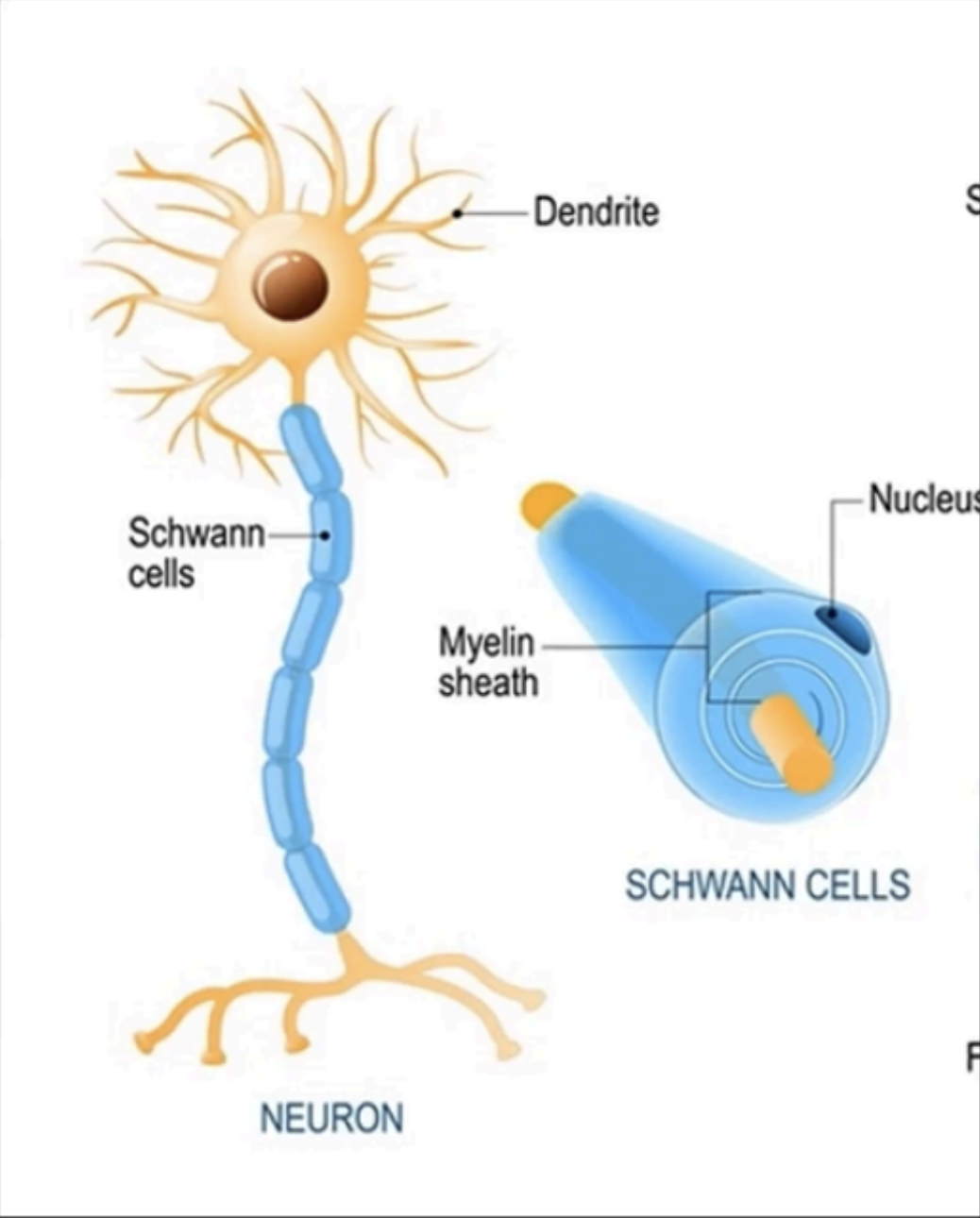
How many nerve fibers (axons) can 1 Schwann cell myelinate
1 segment of an axon
Areas of interruption or gaps along the myelin sheath that covers the axons of neurons
Essential in the speed and timing of delivery of impulses from 1 neuron to another
Nodes of Ranvier
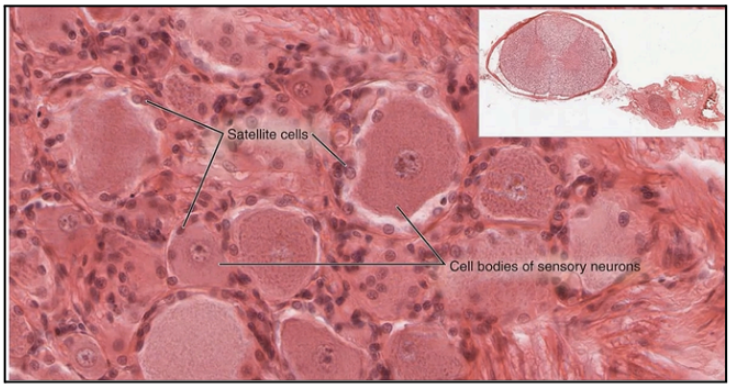
Glial cells that envelope the peripheral and central processes of each neuron from the autonomic ganglia
Satellite Cells (Capsular Cells)
Tumors of Neuroglia are also called?
Gliomas
Tumors of Neuroglia account for _____ to _____ of intracranial tumors and are highly invasive except for _____
40% to 50% ; ependymomas
Most common tumors of neuroglia
Tumors of astrocytes (astrocytomas and glioblastomas)
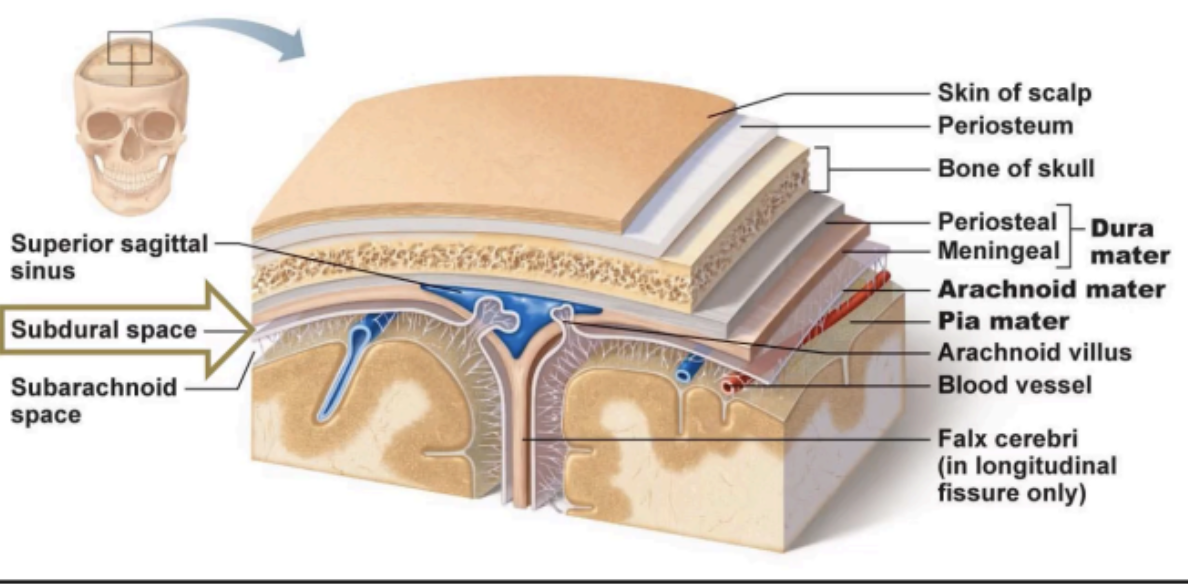
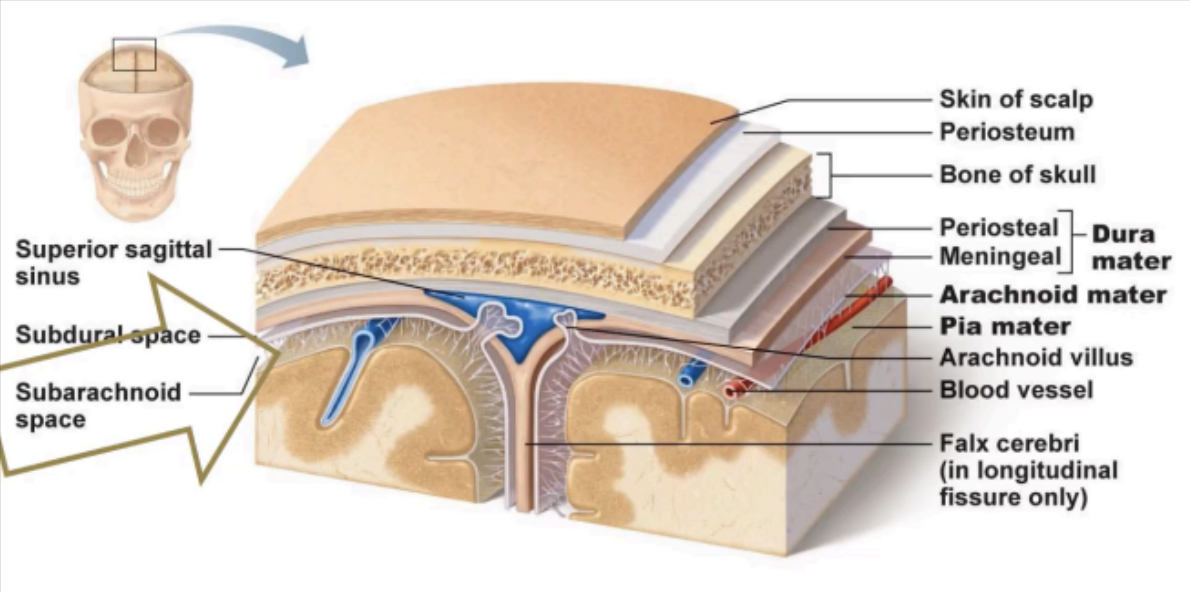
The brain and spinal cord are surrounded by supporting membranes called _____
Meninges
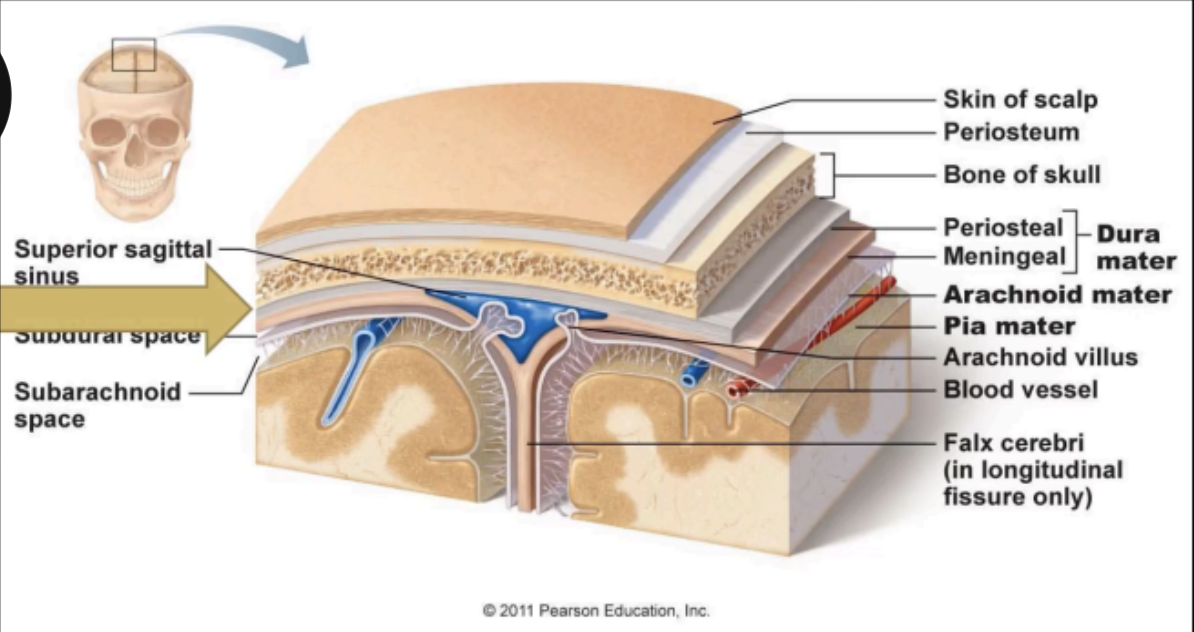
Enumerate the meninges from the outermost to the innermost membrane
Dura mater → Arachnoid mater → Pia mater
PAD = Padding of the Brains
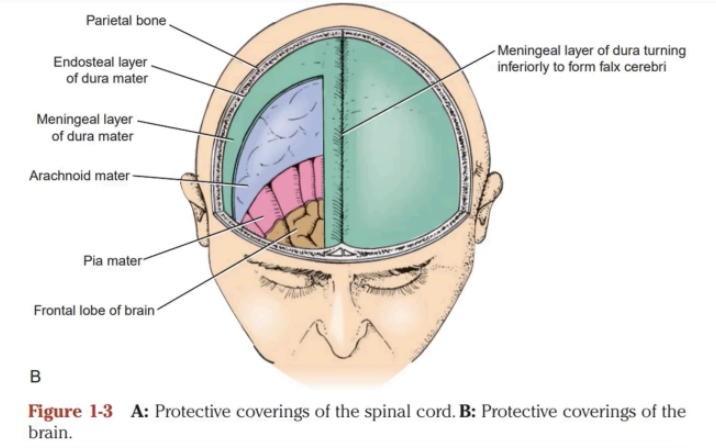
Outermost meninx
A strong fibrous membrane that consists of two layers:
Endosteal layer
Meningeal layer
DURA MATER
a periosteum surrounding the inner surface of the cranial bones
Endosteal layer (Dura Mater)
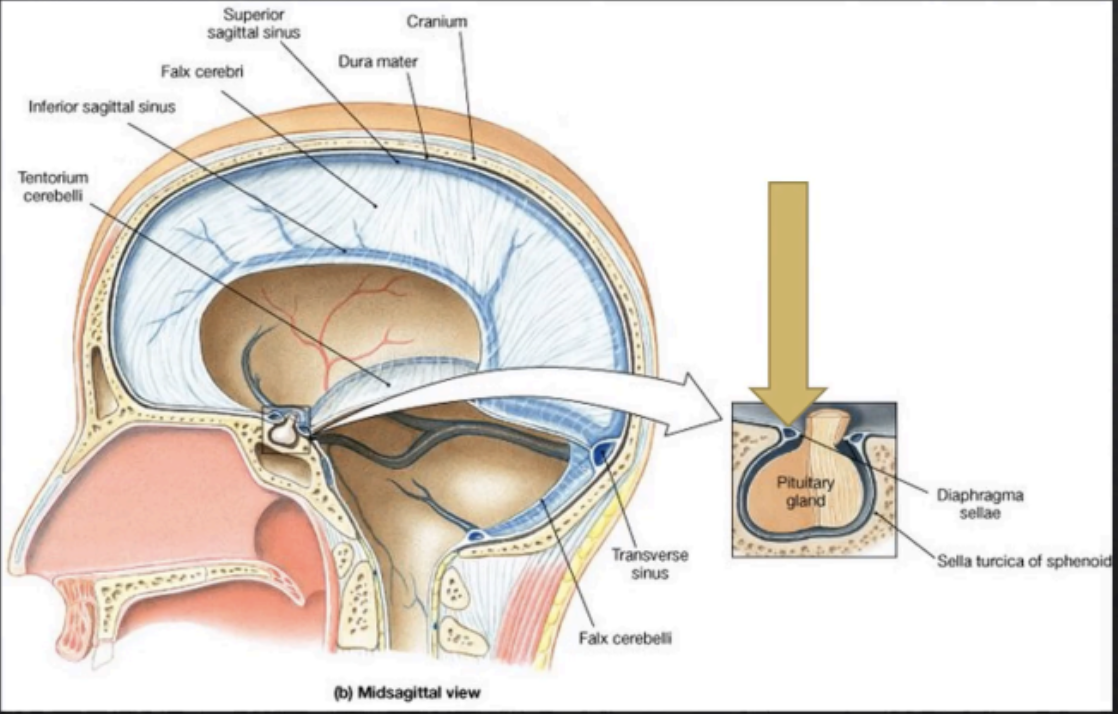
Forms 4 folds within the cranium, which are the Falx Cerebri, Falx Cerebelli, Tentorium Cerebelli, and Diaphragma Sellae
Meningeal layer (Dura Mater)
Enumerate the folds of the meningeal layers of the Dura Mater
Falx Cerebri
Falx Cerebelli
Tentorium Cerebelli
Diaphragma Sellae
Located at the midline between the two cerebral hemispheres
Falx Cerebri
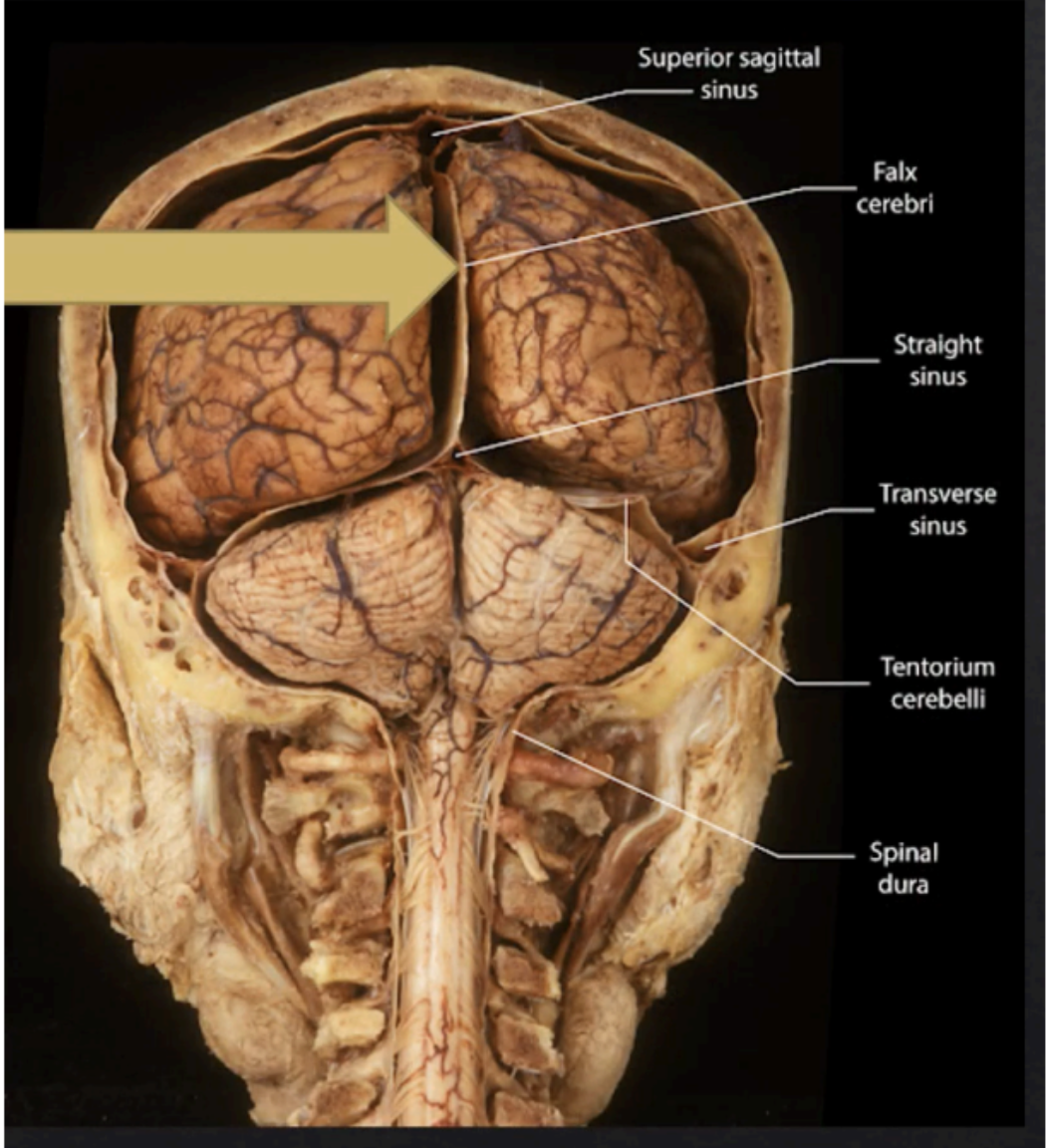
Separates the two cerebellar hemispheres and lies inferior to the tentorium cerebelli
Falx Cerebelli
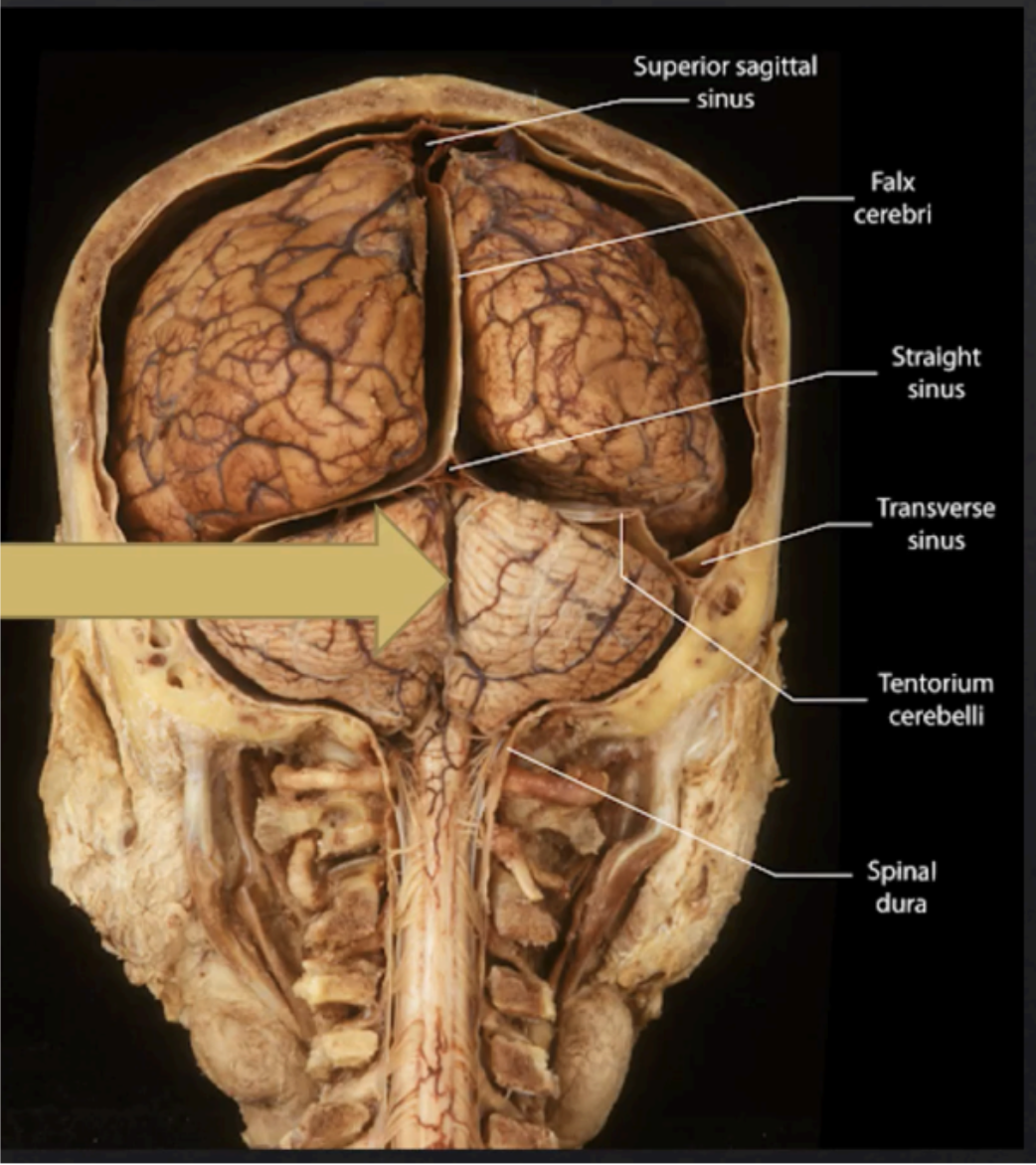
Forms a roof over the posterior cranial fossa, shielding the superior surface of the cerebellum, and supports the occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres
Tentorium Cerebelli
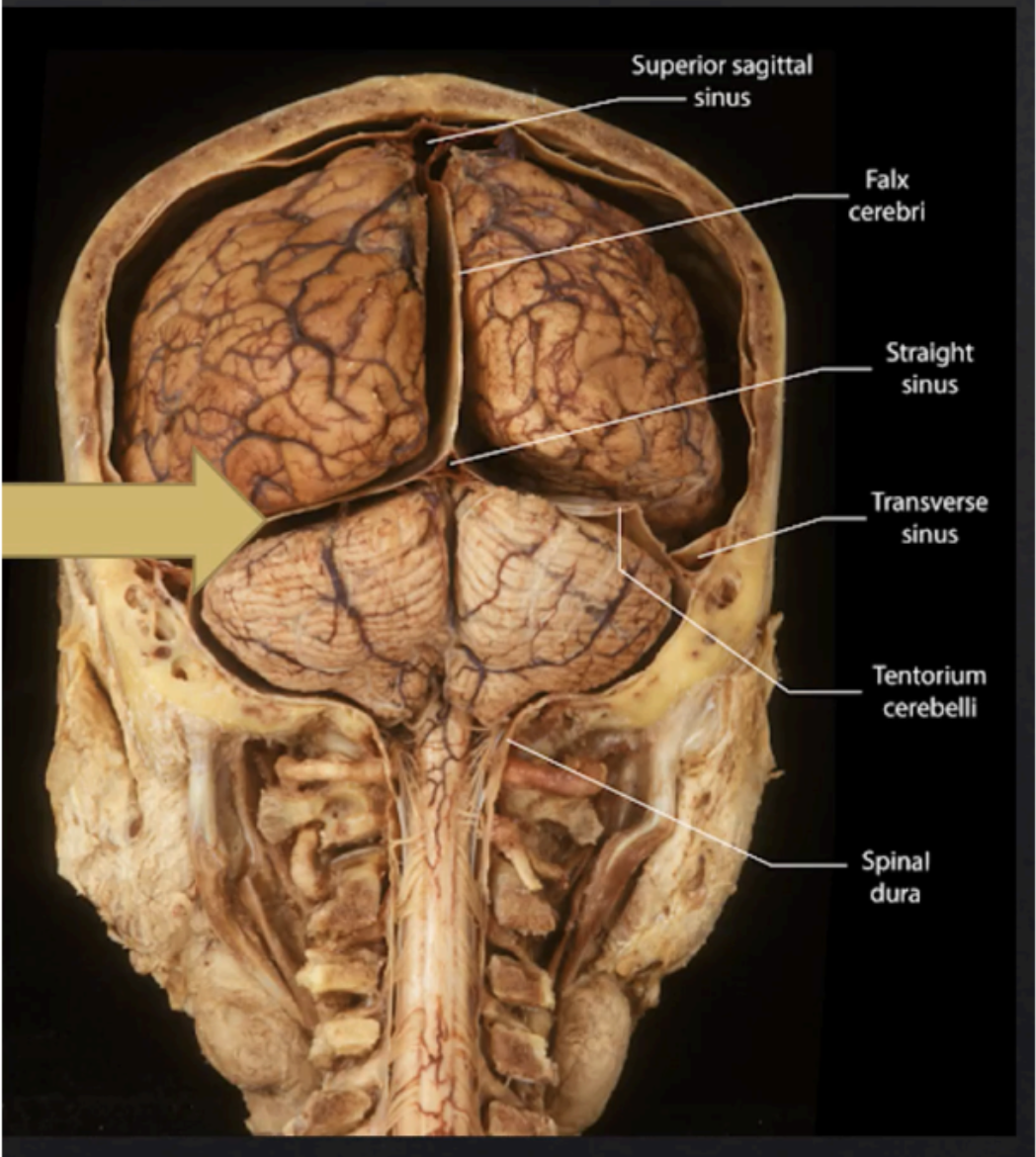
Small circular fold of dura that forms the roof of the sella turcica, protecting the superior surface of the pituitary gland.
It has a tiny opening in the middle segment that allows the passage of the stalk of the pituitary gland.
Diaphragma Sellae
A thin, delicate membrane that loosely surrounds the
brain and the spinal cord.
Lies between the dura mater and the pia mater.
ARACHNOID MATER
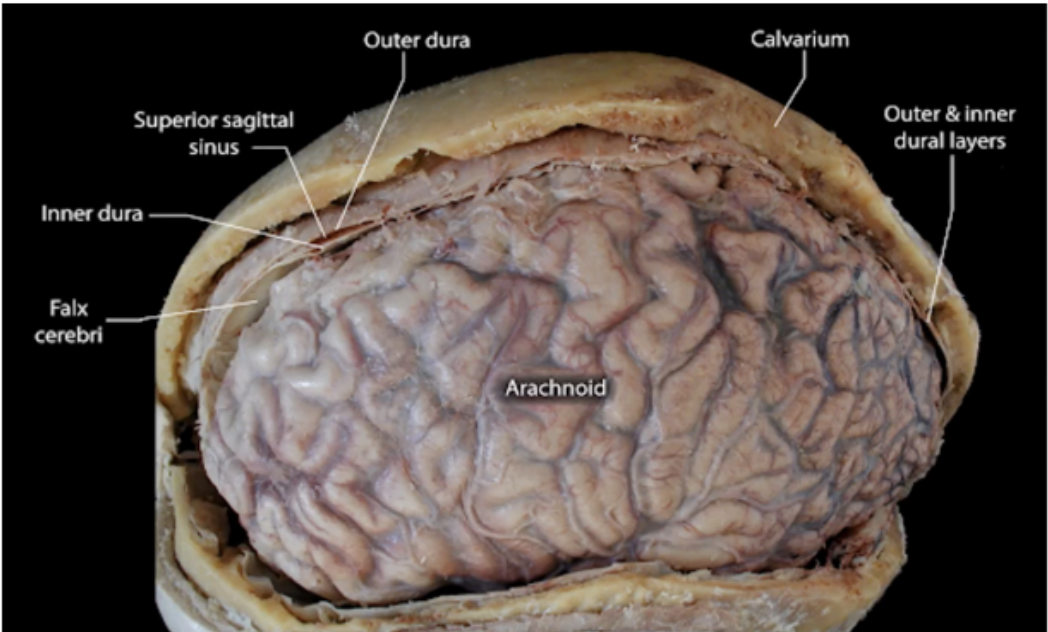
A membrane that closely invests the brain, covering
the gyri and descending into the deepest sulci.
Highly vascular and contains the cerebral arteries
entering the substance of the brain and spinal cord.
PIA MATER
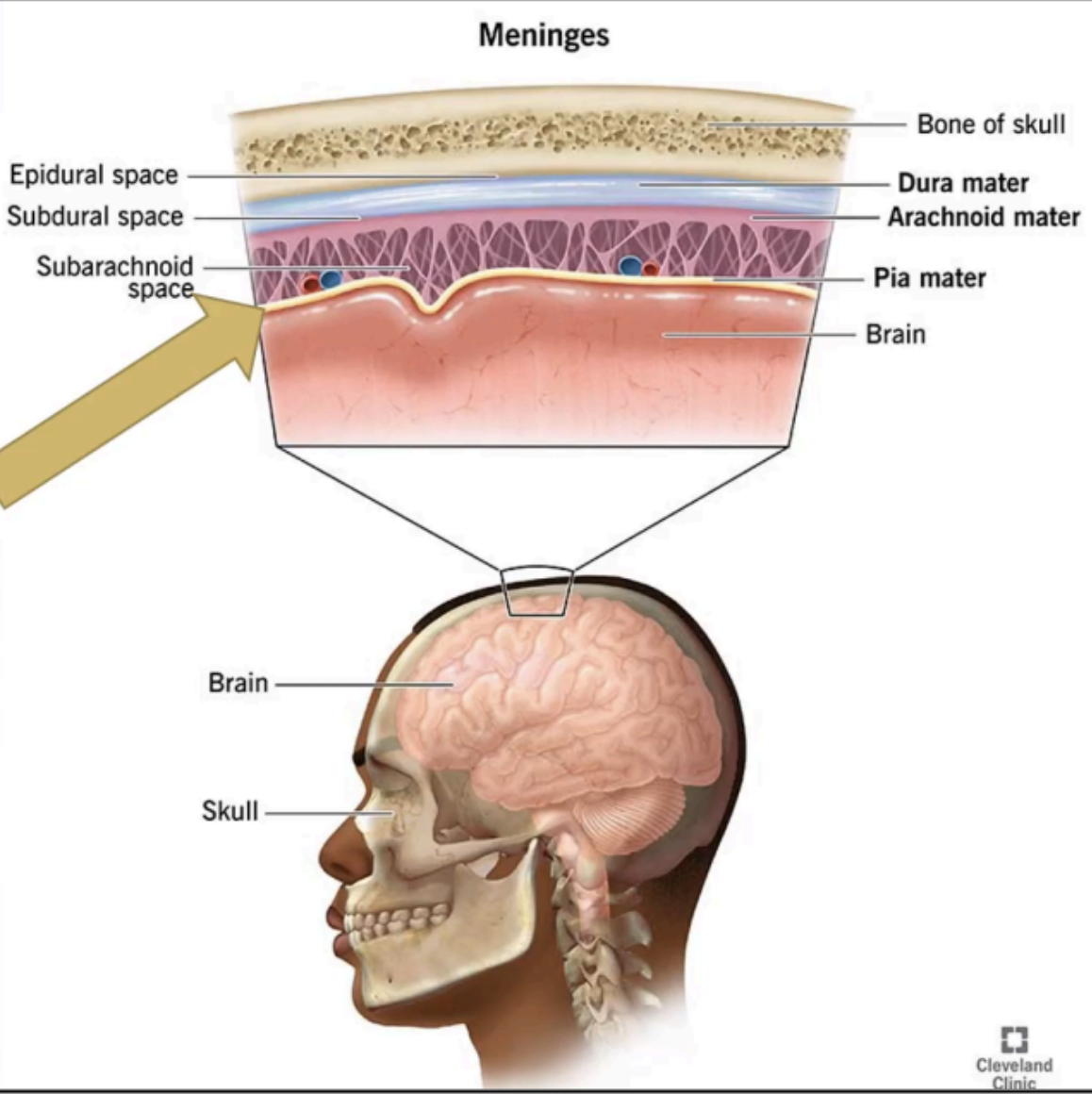
Enumerate the Meningeal spaces
EPIDURAL SPACE
SUBDURAL SPACE
SUBARACHNOID SPACE
A potential space located between the bone and the dura mater.
Potential spaces that may be filled with blood due to traumatic tearing of blood vessels located in these spaces.
EPIDURAL SPACE
The presence of blood inside the epidural space
Epidural Hemorrhage
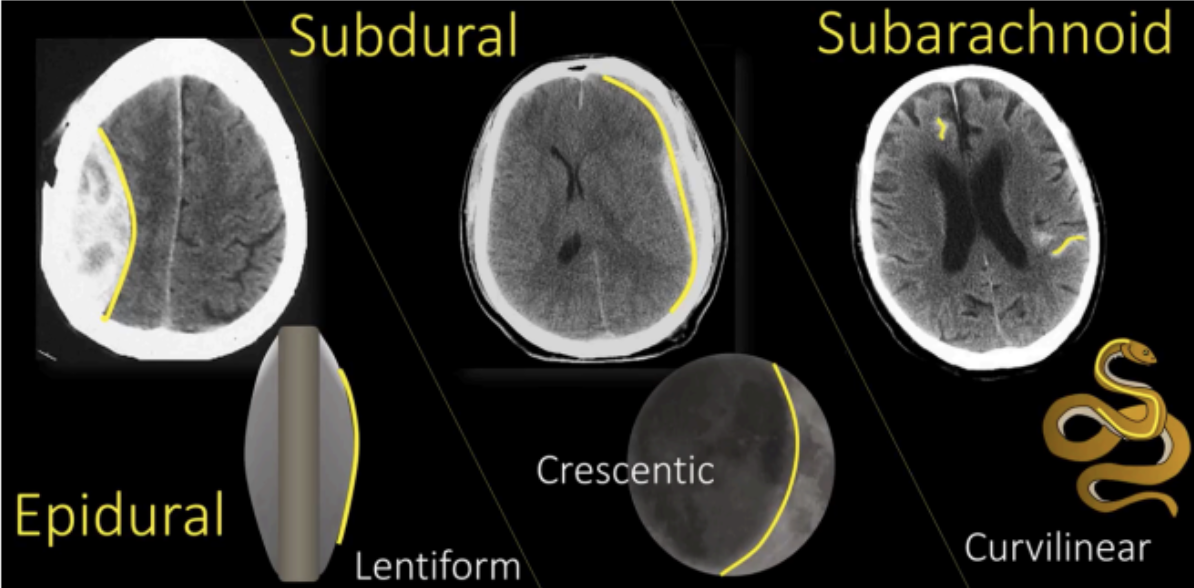
Potential space located between the dura and the arachnoid.
Potential spaces that may be filled with blood due to traumatic tearing of blood vessels located in these spaces.
SUBDURAL SPACE
The presence of blood inside the Subdural space
Subdural hemorrhage
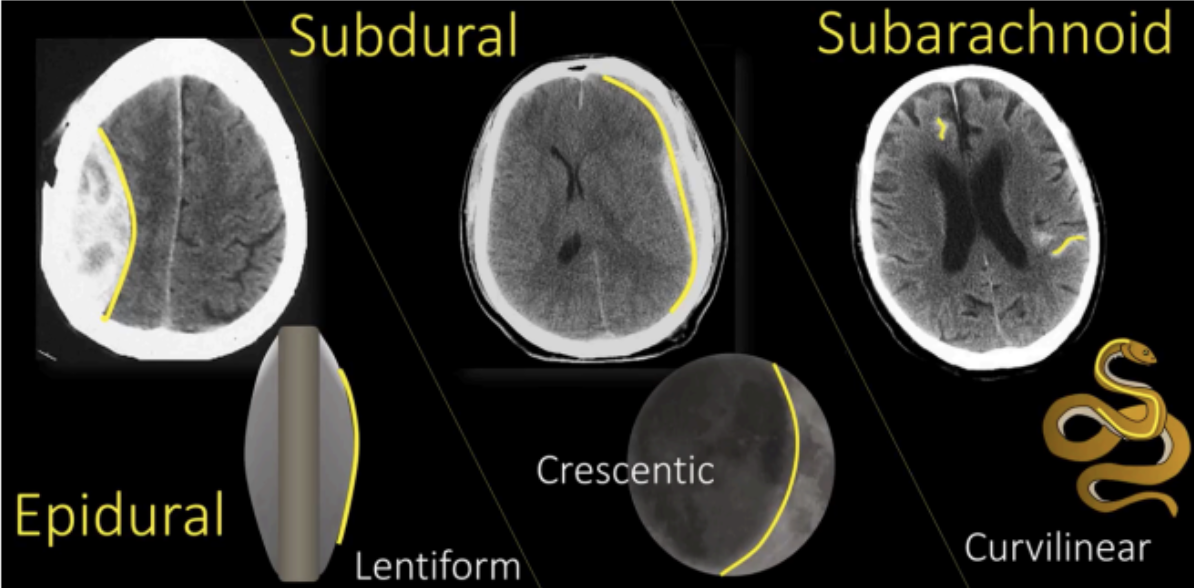
Between the arachnoid and the pia mater
Contains CSF and communicates with the ventricles of the brain where CSF is formed.
SUBARACHNOID SPACE
The presence of blood inside the subarachnoid space
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
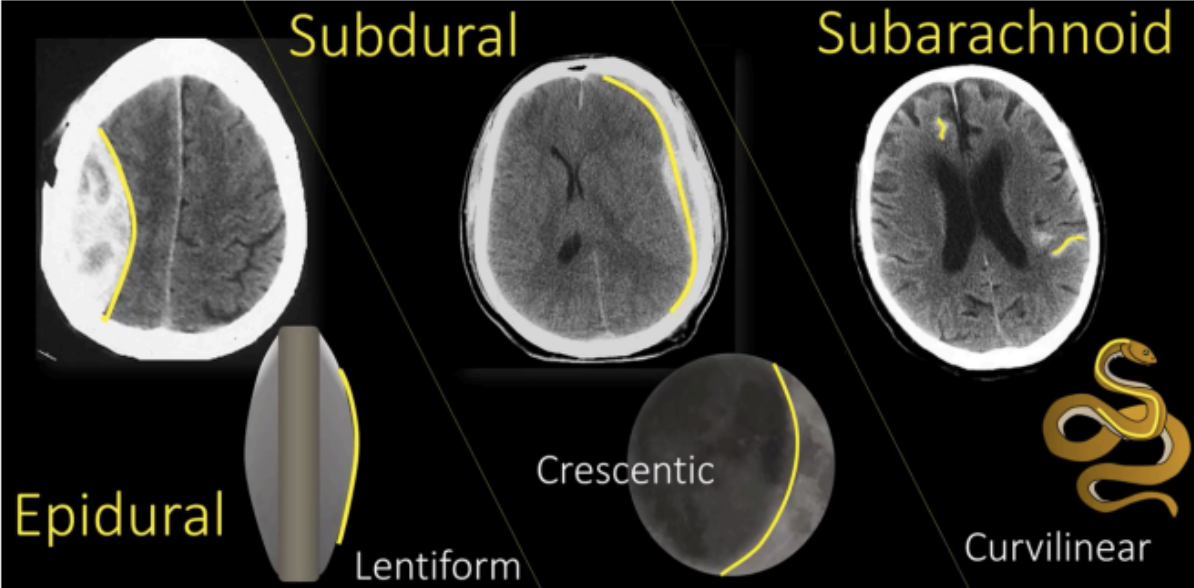
Consists of the brain and spinal cord
Main centers for correlation and integration of nervous information
Covered by meninges and suspended in the CSF
Protected by the skull and vertebral column
Interior of the CNS is organized into gray and white
matter
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Consists of nerve cells (neural body) embedded in neuroglia, thus the gray color
GRAY MATTER
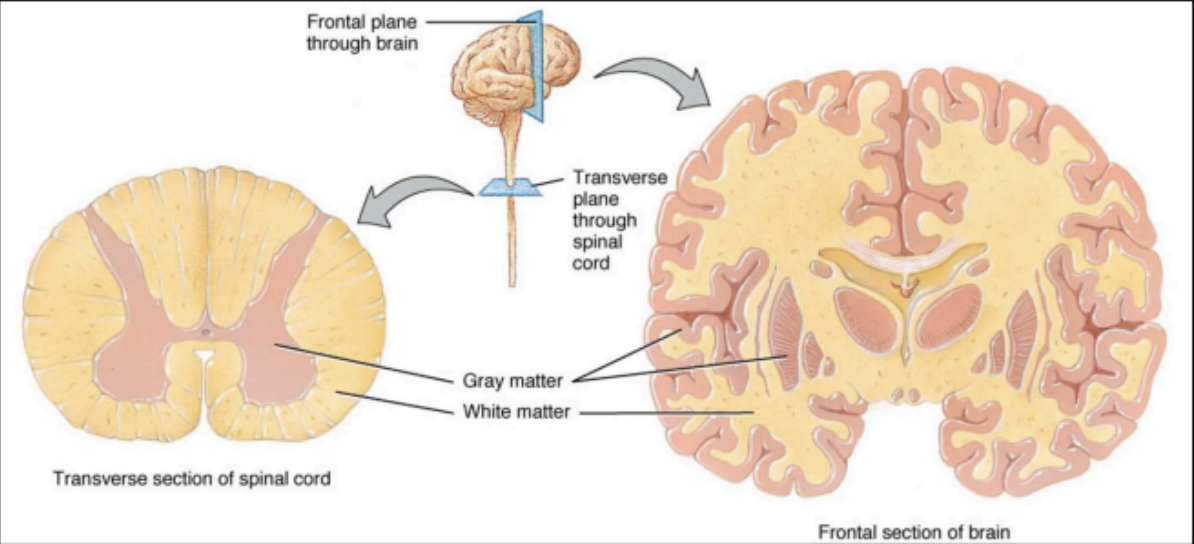
Consists of nerve fibers (neural axons and dendrites) embedded in neuroglia
The white color is due to the presence of lipid material in the myelin sheath
WHITE MATTER
Lies in the cranial cavity and is continuous with the spinal cord through the foramen magnum
It is conventionally divided into three major divisions
BRAIN
Enumerate the three divisions of the brain
Forebrain
Midbrain
Hindbrain
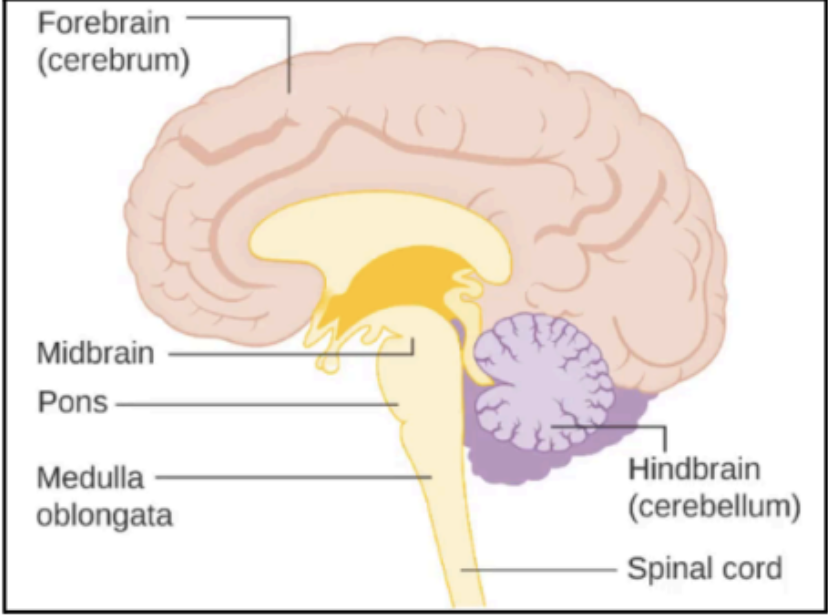
Enumerate the two parts of the forebrain
Cerebrum
Diencephalon
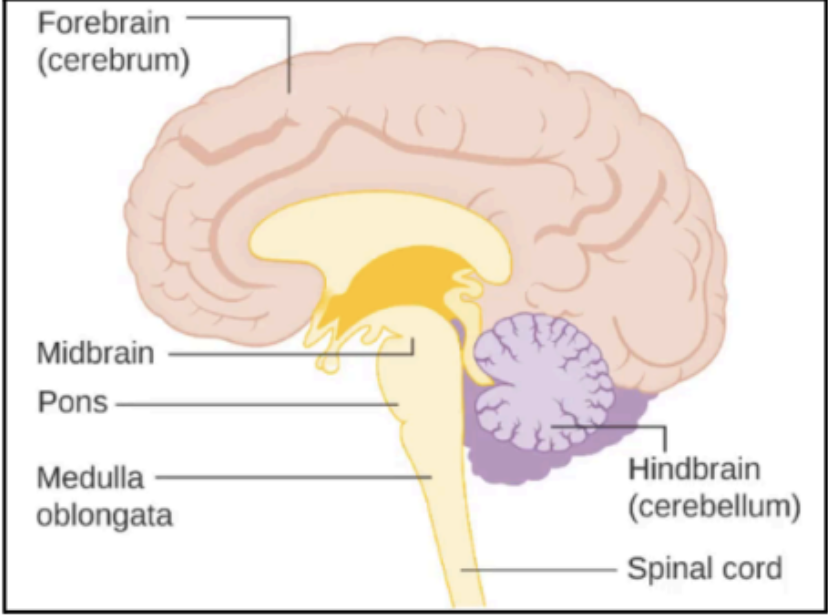
Enumerate the parts of the Hindbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
Cerebellum
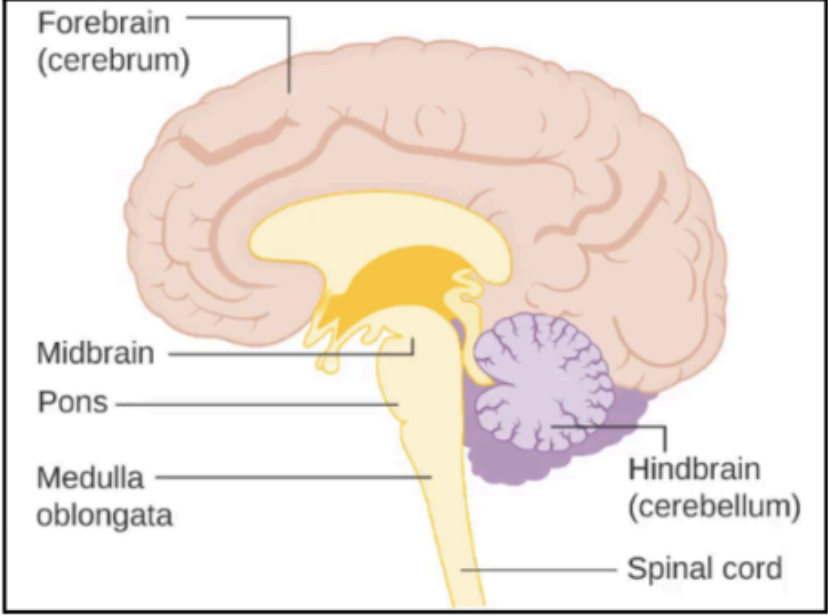
Enumerate the parts of the Brainstem (Note this is different from the three major divisions of the brain)
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
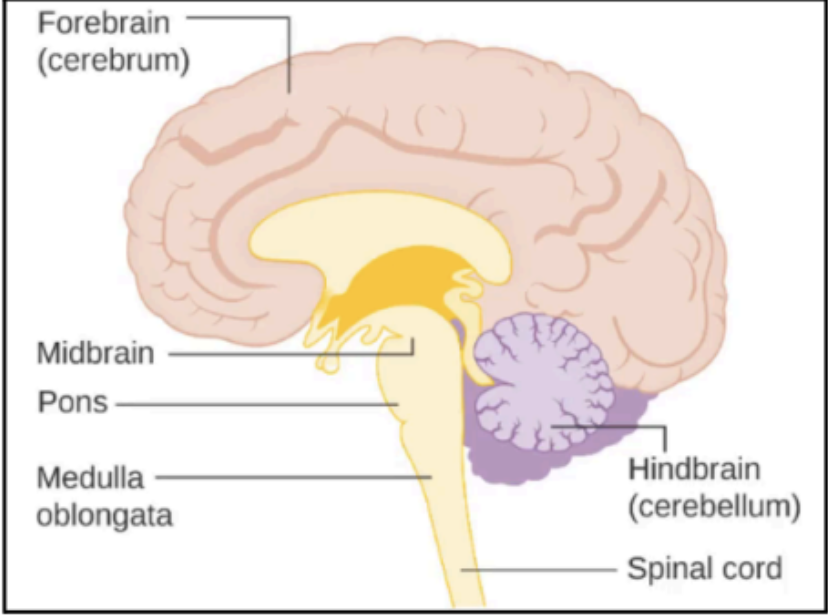
The largest part of the brain
Consists of two cerebral hemispheres (left and right)
Each hemisphere extends from the frontal to the occipital bones in the skull, superior to the anterior and middle cranial fossae, and posteriorly it lies above the tentorium cerebelli.
The two cerebral hemispheres are separated by a deep
medial longitudinal fissure, into which projects the falx cerebri.
CEREBRUM
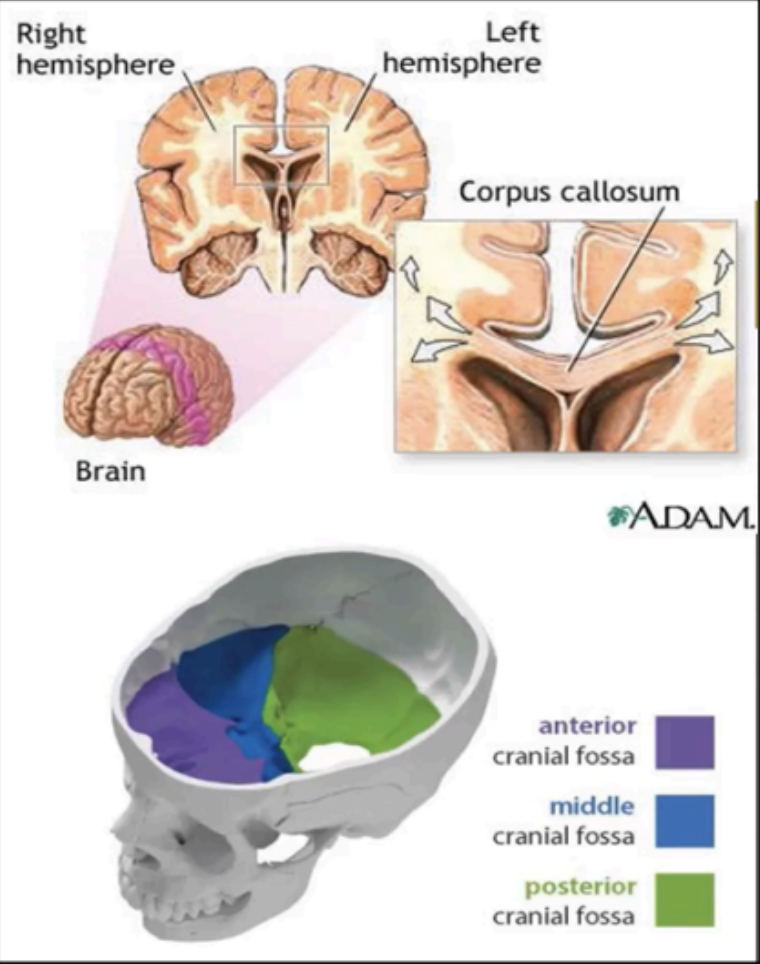
The white matter that connects the two hemispheres of the brain
corpus callosum
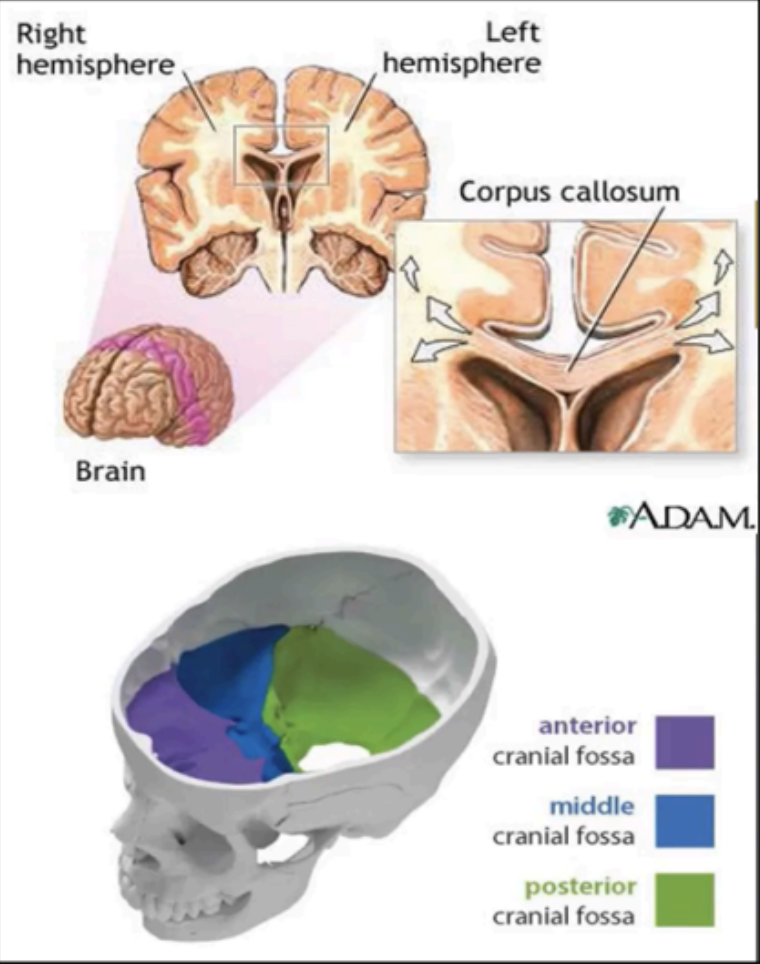
Surface layer of the cerebral hemispheres
Composed of gray matter.
It has folds called gyri or gyrus
Several large sulci are used to subdivide the cerebral hemispheres into lobes, which are named from the bones under which they lie.
Part of the cerebrum
Cortex
This greatly increases the surface area of the cortex.
Part of the cerebrum
gyri or gyrus
The gyri or gyrus are separated by folds called
Part of the cerebrum
Sulcus or sulci
Consist of white matter which contains several masses of gray matter, called basal nuclei or ganglia.
Part of the cerebrum
Inner Core of the Brain
Fan shaped collection of nerve fibers passing in the
white matter to and from the cerebral cortex to the brain stem.
Converges on the basal nuclei
Part of the cerebrum
Corona Radiata
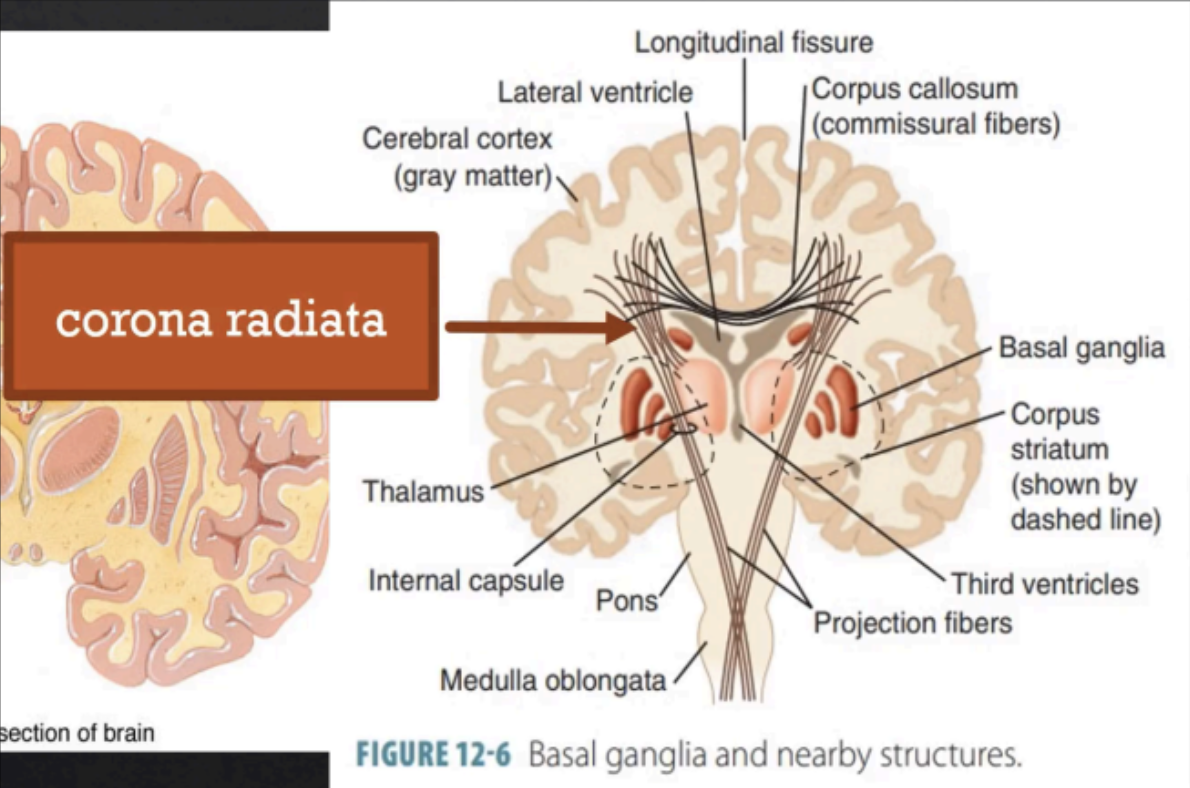
Convergence of corona radiata on the basal nuclei which passes in between the basal nuclei
Part of the cerebrum
Internal Capsule
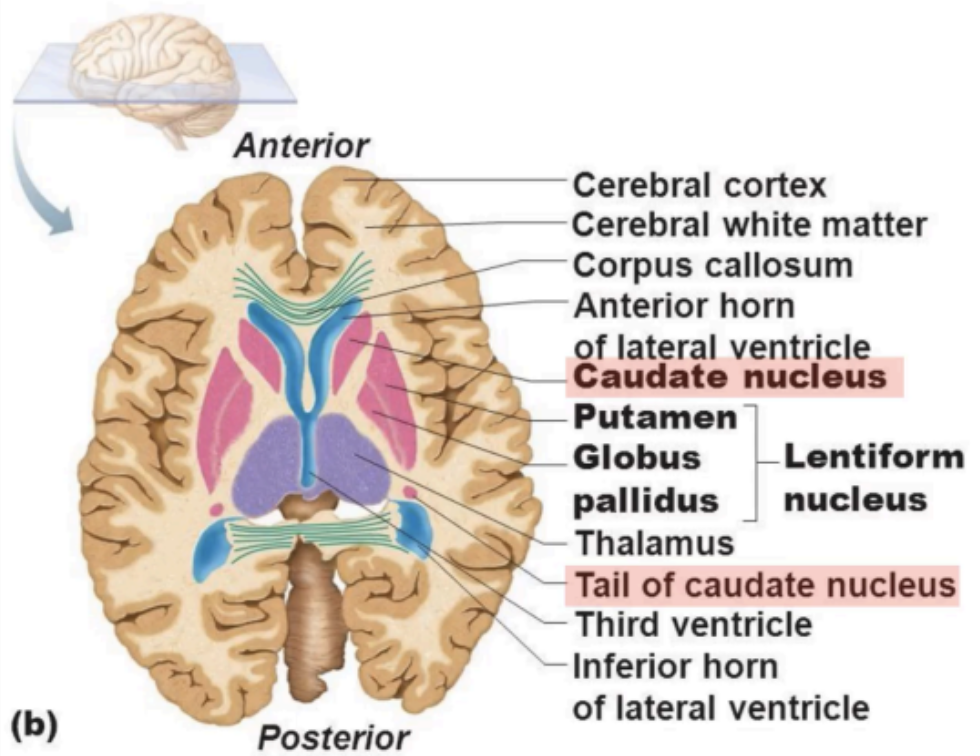
Tailed nucleus on the medial side of the internal capsule
Part of the cerebrum
Caudate Nucleus
Lens-shaped nucleus on the lateral side of the internal capsule
Part of the cerebrum
Lentiform Nucleus
The cavities within each cerebral hemisphere (anterior horn and inferior horn).
Part of the cerebrum
Lateral Ventricles
Lies below the cerebral hemispheres and consists of a dorsal thalamus and a ventral hypothalamus.
DIENCEPHALON
A large egg-shaped mass of gray matter that lies on either side of the third ventricle.
Part of the Diencephalon
Thalamus
Forms the lower part of the lateral wall and floor of
the third ventricle.
Part of the Diencephalon
Hypothalamus
A narrow part of the brain that connects the forebrain to the hindbrain.
MIDBRAIN
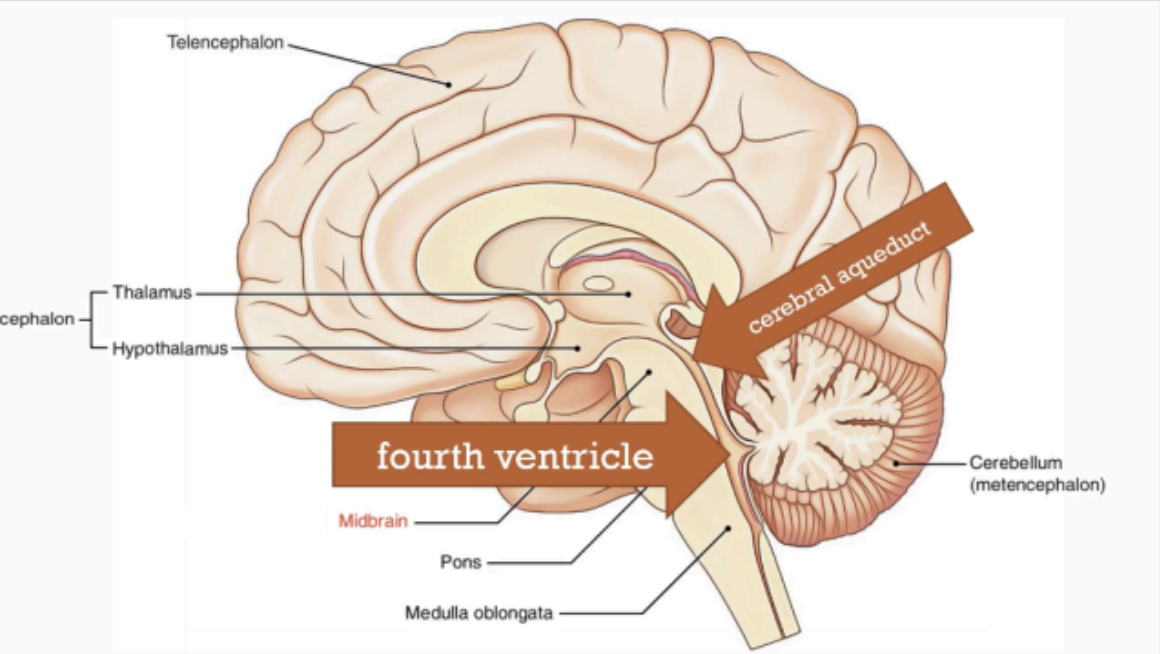
narrow cavity which connects the 3rd and the 4th ventricles.
Part of the Midbrain
cerebral aqueduct
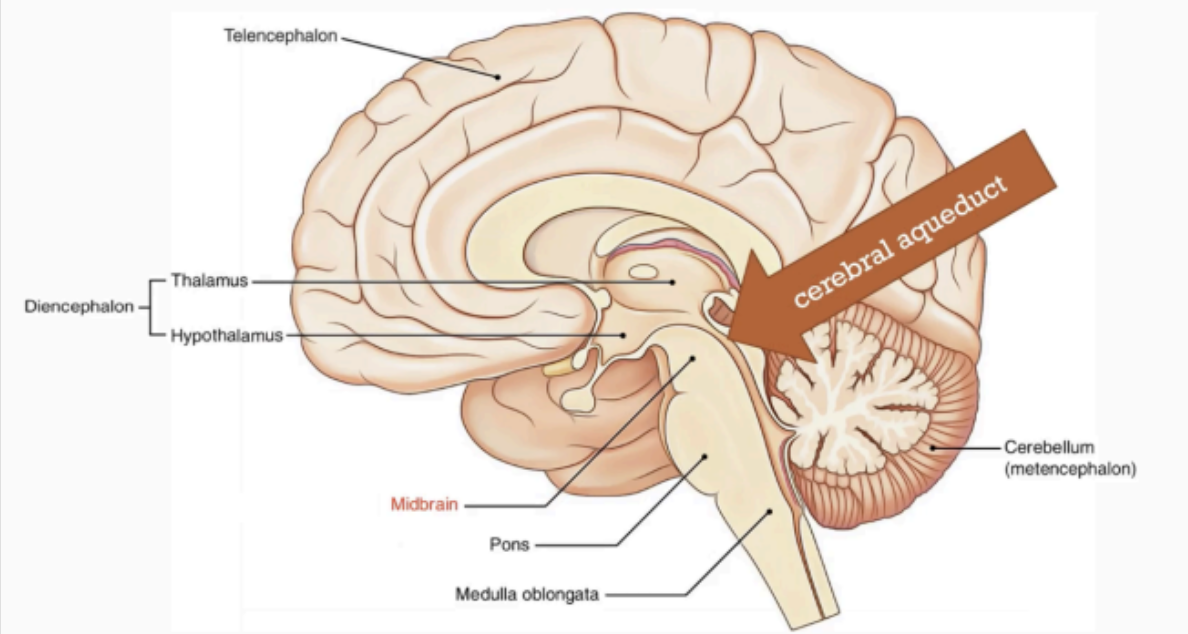
Part of the hindbrain
Situated between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
Its name means “bridge”
Comes from the large number of transverse fibers that connect the two cerebellar hemispheres on its anterior aspect.
PONS
Conical in shape
Connects the pons to the spinal cord
Conduit for ascending and descending nerve
fibers
MEDULLA OBLONGATA
Lies within the posterior cranial fossa, posterior to the pons and medulla oblongata.
It consists of two hemispheres
Also known as the “little brain”
It also has a cortex composed of gray matter and an inner core of white matter, with several masses of gray matter or nuclei.
CEREBELLUM
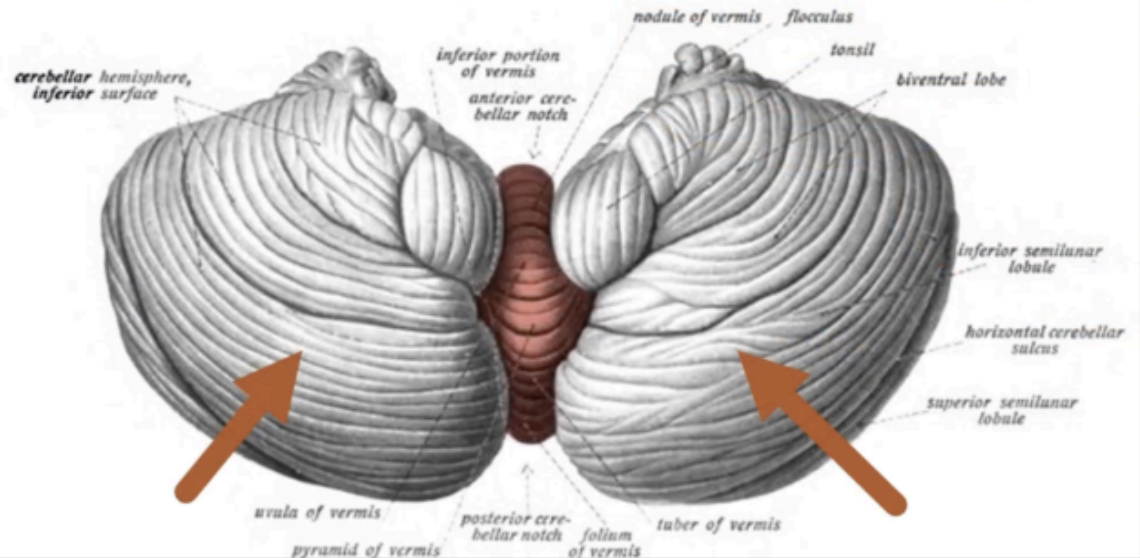
The two hemispheres of the cerebellum is connected by a median portion called
vermis
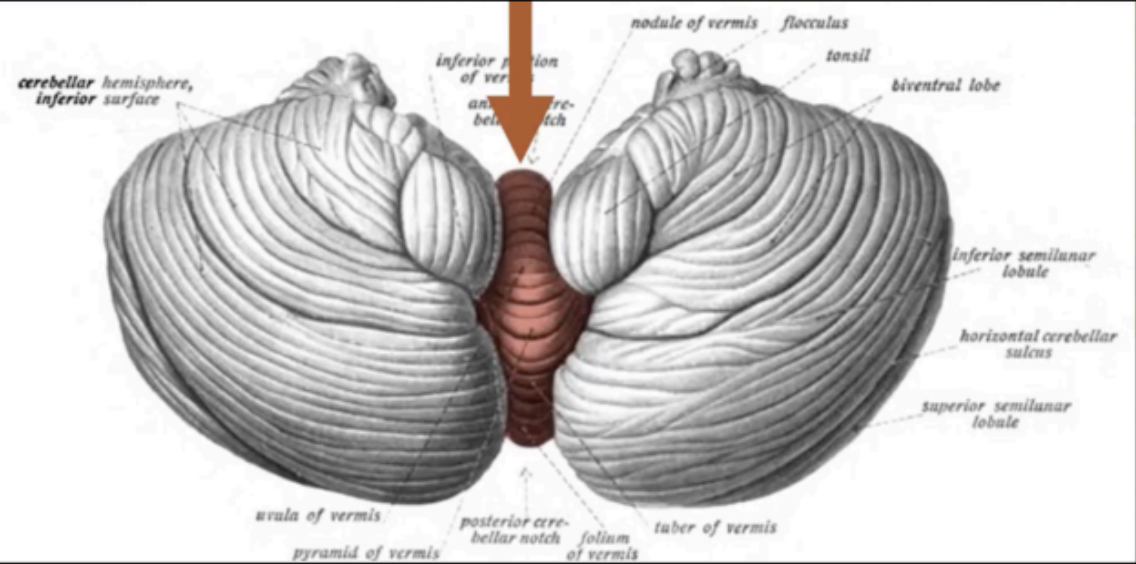
The medulla pons and cerebellum surround the cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid called the
4th ventricle
Connected superiorly to the 3rd ventricle through the
cerebral aqueduct
Inferiorly, it is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord.
FOURTH VENTRICLE
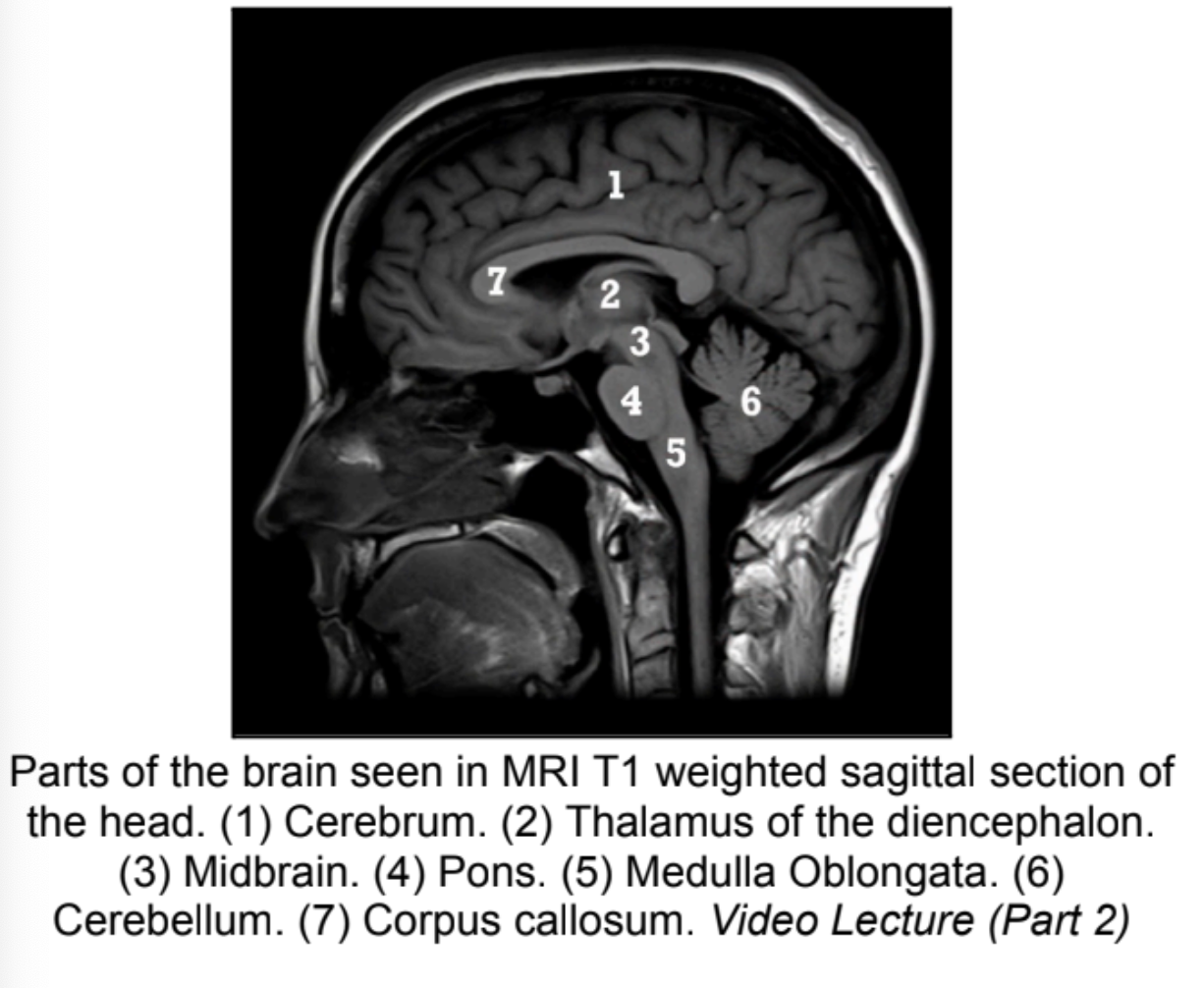
Parts of the brain seen in MRI T1 weighted sagittal section of the head
*No Answer*
Lies below the brain
Situated within the vertebral canal and is also surrounded by three meninges, the dura, arachnoid, and pia mater.
SPINAL CORD
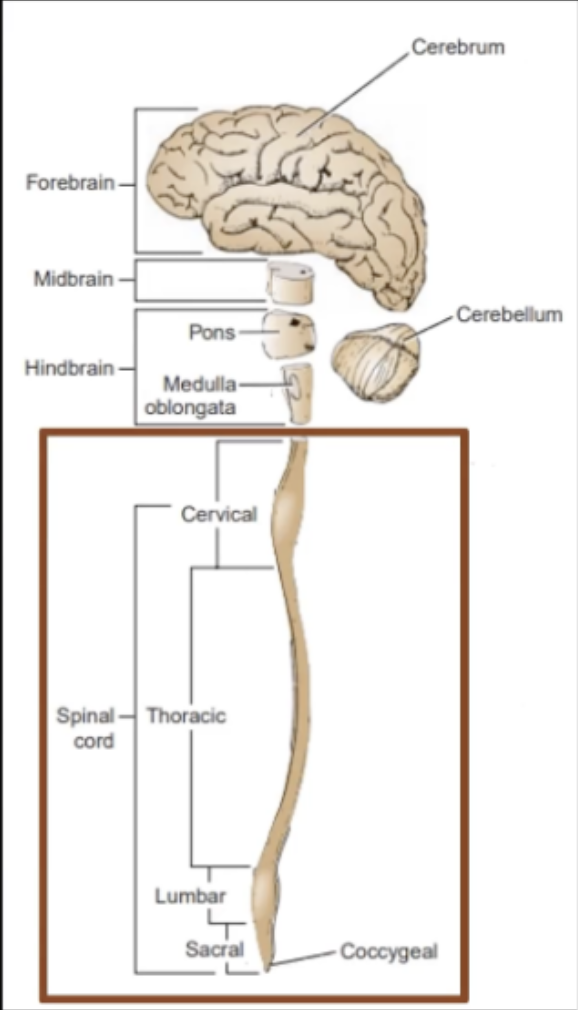
The Spinal Cord begins superiorly at the _____ below the _____ and terminates inferiorly in the _____ into the _____.
Foramen Magnum; Medulla Oblongata; Lumbar Region; Conus Medullaris
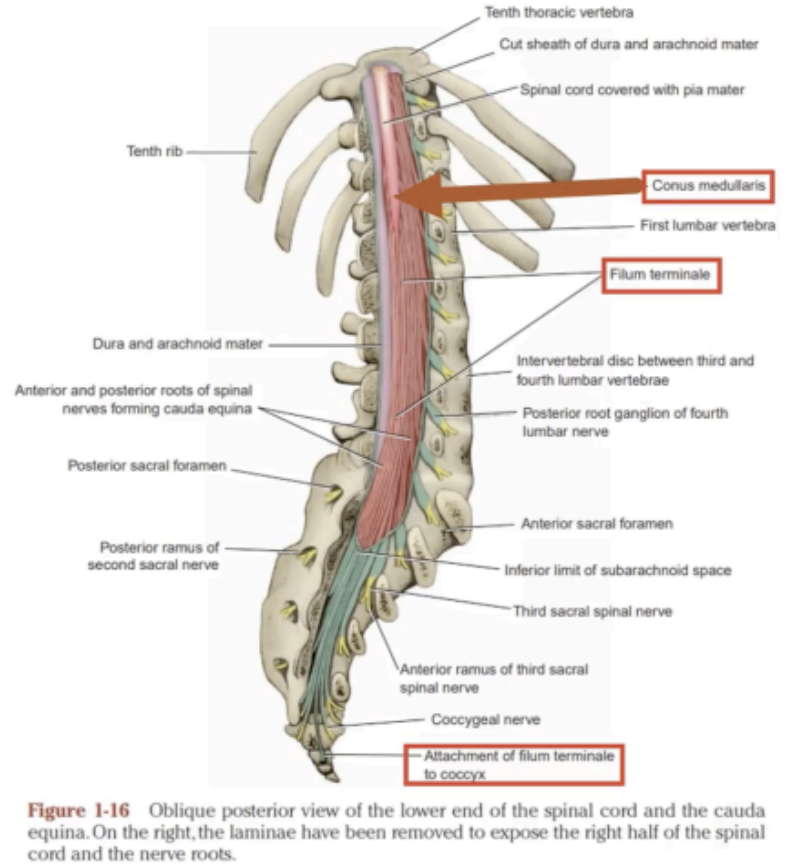
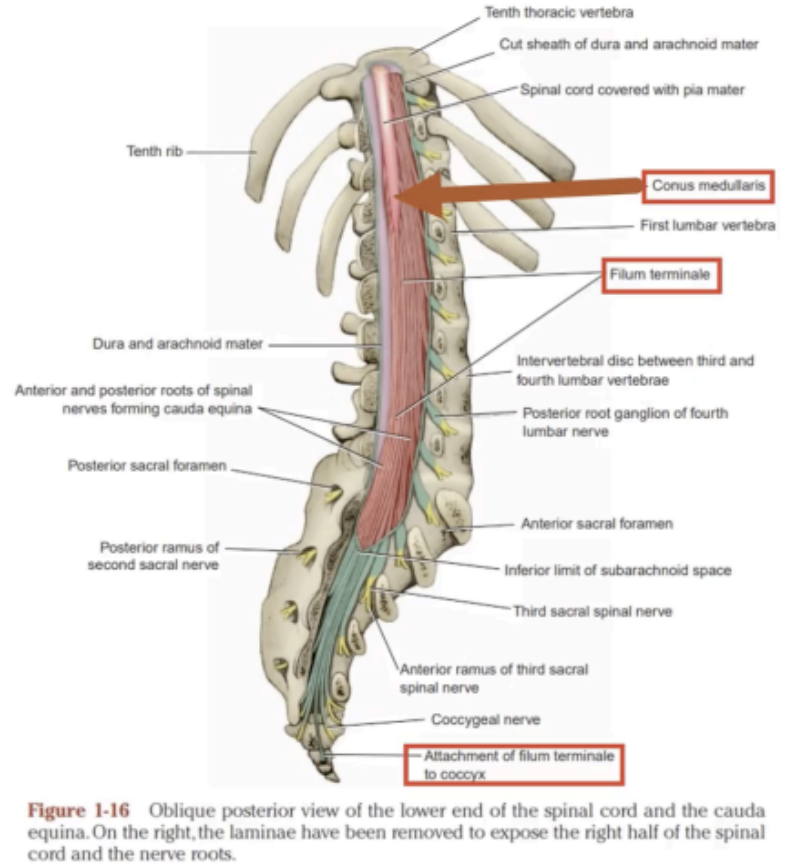
Prolongation of the pia mater that attaches the conus medullaris to the back of the coccyx.
Phylum terminal
Unlike the brain's structure, the spinal cord has an inner core of _____ and an outer covering of _____.
gray matter; white matter
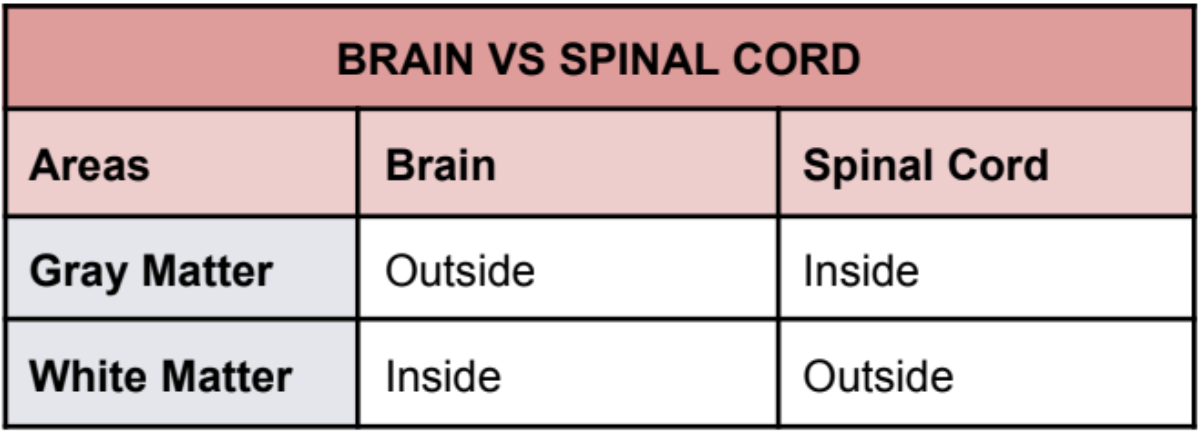
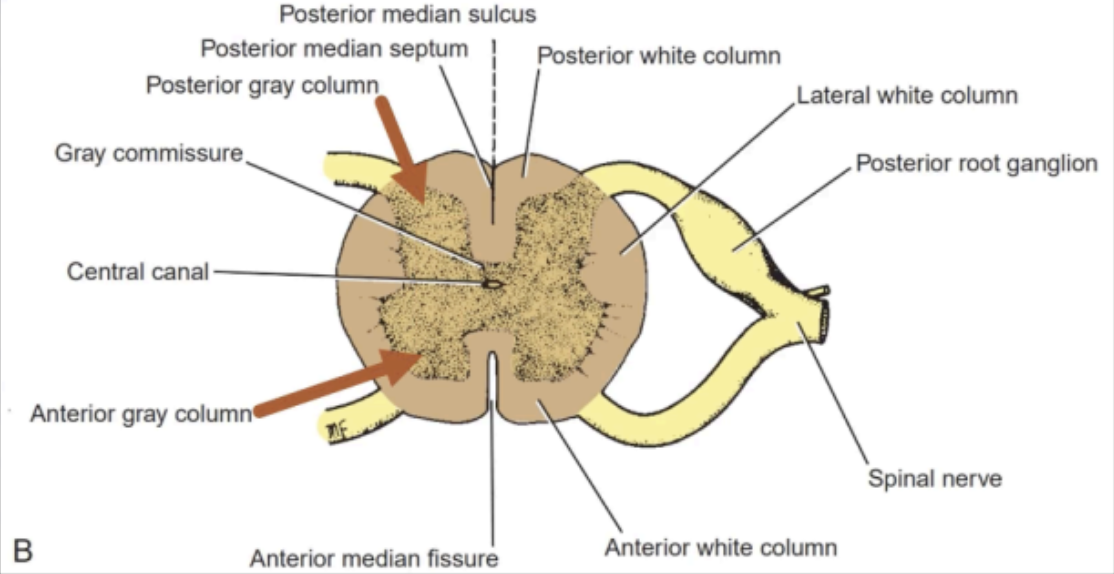
seen as an H-shaped pillar with anterior and posterior gray horns or columns.
GRAY MATTER
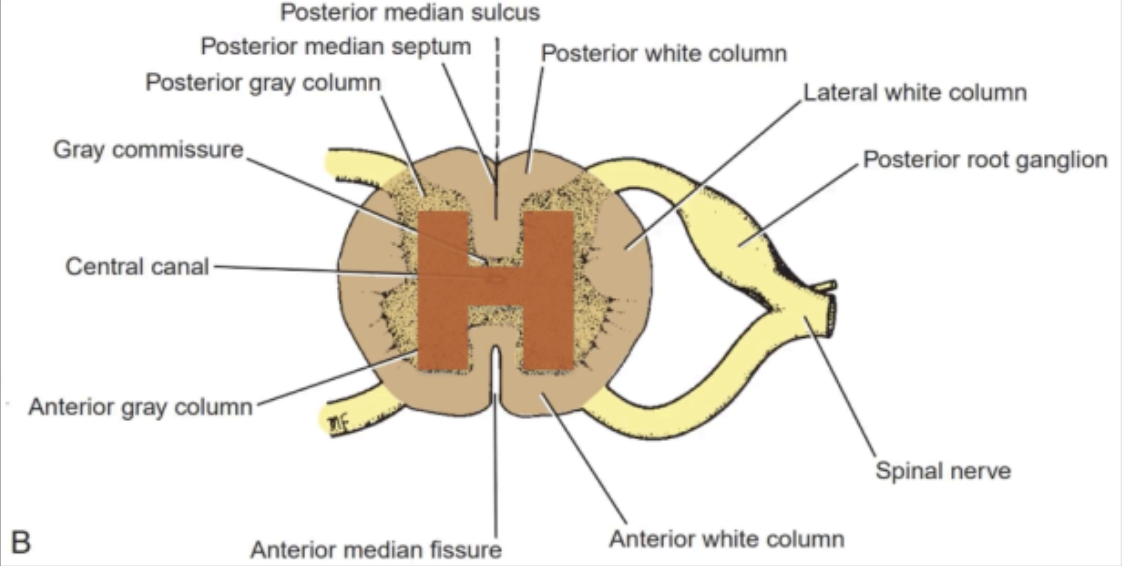
The Anterior and Posterior gray horn of the gray matter of the spinal cord is connected by
This part also contains the central canal
Gray commissure
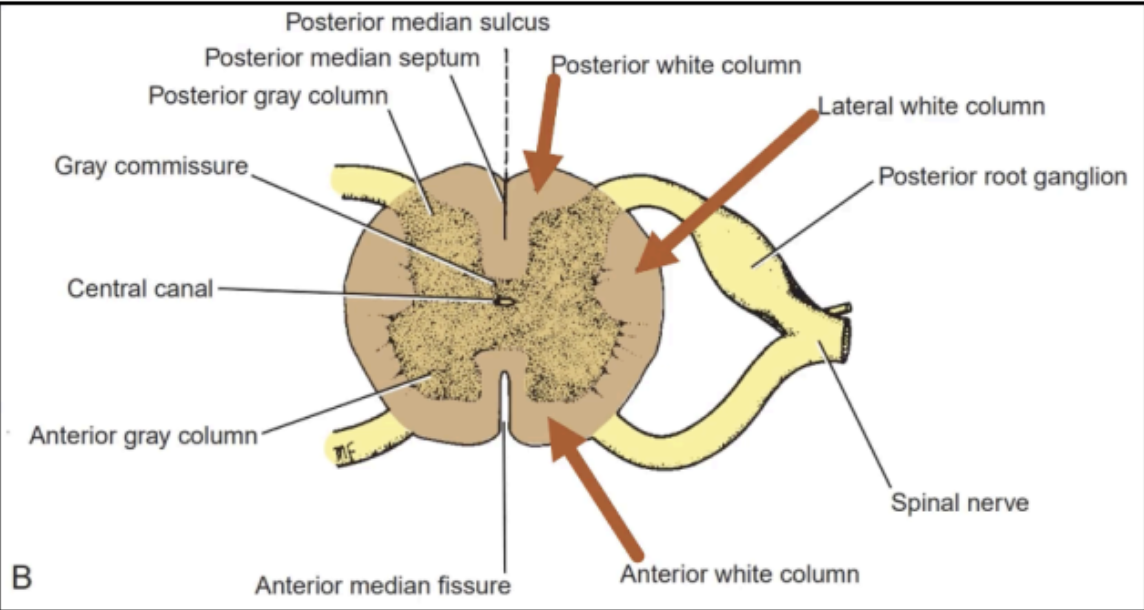
Divided into anterior, lateral, and posterior columns
WHITE MATTER
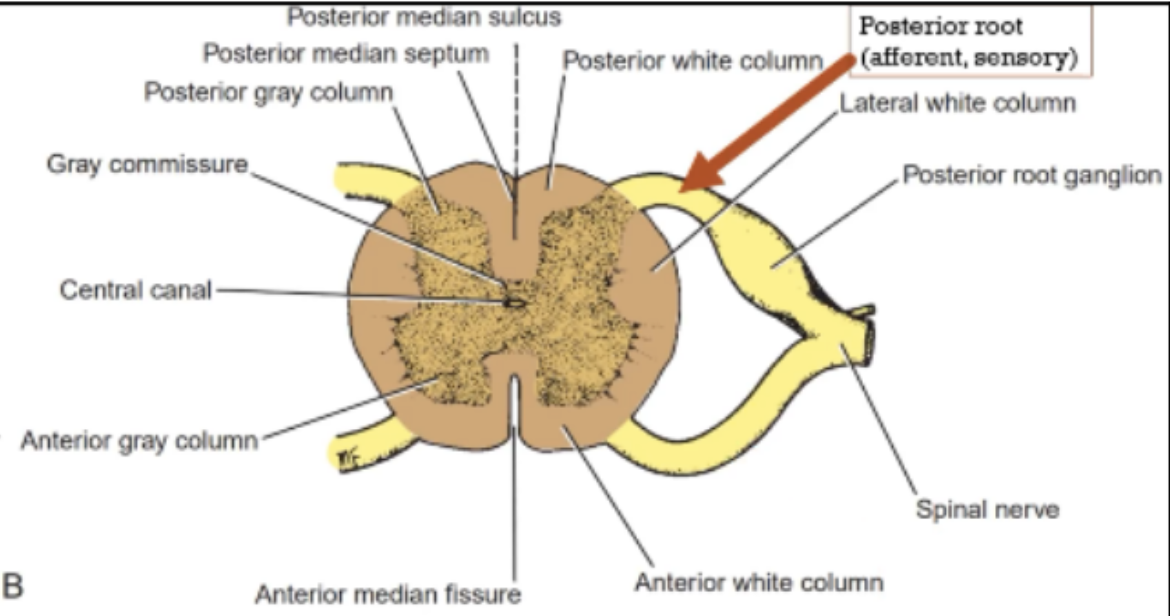
Along the entire length of the spinal cord are attached _____ of spinal nerves by the anterior roots and posterior roots.
31 pairs
Efferent/Motor fibers
Carry nerve impulses away from the CNS
Anterior Roots
Afferent/Sensory fibers
Carry nerve impulses toward the CNS
Has a posterior root ganglion
A swelling that contains cell bodies of sensory nerve fibers.
Posterior Roots
Anterior and Posterior roots unite to form a _____ that exits through its respective ____.
spinal nerve; intervertebral foramen