Unit 2 Exam (NUR 116) (copy)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Intentional tort
Examples:
- Invasion of privacy
- Defamation
- Assault
- Battery
Assault
Assault: occurs when a client is made to feel fearful of harm or offensive contact
(e.x. being threatened with restraints)
Battery
An act that that results in harm or injury to a client
(e.x. illegally retraining a client, operating on the wrong body part)
Ethical Principles
standards of what is right/wrong with regard to important social values and norms
Autonomy (ethical principle)
(my body my choice)
Nurse's obligation to respect the clients right to make their own decisions regarding their health care, including the right to refuse care.
Beneficence
(going above and beyond)
The nurse's obligation to minimize harm and practice in a way that benefits the client
Nonmaleficence
(least amount of harm)
Nurse's obligation to do no harm or the least amount of harm to the client while trying to achieve the best possible outcome.
Veracity
Refers to the nurse's obligation to provide truthful and accurate information to the client-telling the truth.
Justice
(equal treatment)
Nurse's obligation to provide treatment that is fair and equitable to all clients regardless of age, sex, race, or economic status.
Urinary Retention
a condition in which the bladder does not completely empty with urination.
Health problems:
- Prostate enlargement
- Prolapsed prostate
Signs and symptoms:
- Difficulty urinating
- Pain
- Abdominal distention
- Urinary frequency
- Urinary hesitancy
- Weak or slow urine stream
- Urinary leakage condition
Stress incontinence
Coughing, sneezing, laughing, or physical activity that increases pressure on the bladder, resulting in urine leakage.

Urge incontinence
A strong need or urge to urinate, but leakage occurs before the client gets to the toilet.

Reflex incontinence
Urinary leakage as a result of nerve damage
Overflow incontinence
incomplete bladder emptying that results in the bladder overfilling when full, leading to urine leakage
Functional incontinence
physical inability to reach the toilet in time.
[*This may be due to a physical impairment such as being wheelchair-bound or having arthritis of the hands, which can hinder the fine motor skills needed to unbutton clothing*.]
Nocturnal enuresis
(nighttime bedwetting)
common in children but may occur in adults who have consumed too much alcohol, who consume caffeine at night, or who take certain medications.
Feeding
-Pay attention to patient
-Check for pocketing
- Sit upright
-Bend chin to chest
-Cue swallowing ("Okay! Time to swallow!)
-Follow bites of food with liquid
Urine Culture
Used to evaluate urine for the presence of bacteria and yeast that may cause a UTI.
- Wipe 3 times
- Urinate into the toilet
- Stop quickly
- Continue to urinate in the collection cup
What can alter the result of a urine culture?
Antibiotics
Where do you collect a sterile urine sample?
Foley catheter
24 hour urine collection
Urine is collected over a 24-hour period, placed in a special container, and kept in ice or refrigerated
-Check for kidney function
-Throw away the first void
-Collect every drop of urine for the next 24 hours ("Which the client won't do" - Kennedy)
Diarrhea
Caused by:
- Antibiotics (disrupt normal flora)
- Infection
-Medication use
- GI disorders
- Diet
- Alcohol
- Caffeinated beverages and food
- Dairy (milk, cheese, cream, and ice cream)
- foods that are high in fat or are highly greasy
- Beverages that contain fructose
- Spicy foods
- Apples, peaches, and pears
- Products that contain sweeteners, such as sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol, and maltitol
Full Liquid Diet
Contains only fluids, foods that are liquids, and foods that are liquids at room temperature.
Examples include:
- Ice cream
- Juices
- Pudding
- Milkshake
- Tea
- Strained soups
- Protein shakes
- Gelatin
Clear Liquid Diet
Contains only clear liquids. Foods that can be seen through as well as foods that partly or completely melt at room temperature.
examples include:
-Broth
-Gelatin
-Water
What kind of clear liquid foods should patients avoid after a colon procedure or tonsillectomy?
Liquids or gelatin with red coloring should be avoided to prevent confusion with possible bleeding.
What kind of diet would be appropriate for clients experiencing nausea, vomiting or diarrhea?
Clear liquid diet
Trans fats
Trans fats:
Raise low-density lipoprotein (LDL) Bad colesterol
Lowers high-density lipoprotien (HDL) good cholesterol
Found in processed foods
Not safe for human consumption (made in lab)

Saturated fats
Found in full-fat dairy products.
-Cheese
-Butter
-Whole milk
Diet high in saturated fat can increase the risk of heart disease and raise total blood cholesterol levels.

Monounsaturated fats
Healthy fats
-Nuts
-Olives
-Olive oil
-Seeds
-Avocados
Lower cholesterol while decreasing the risk of heart disease

Constipation
Infrequent bowel movements, often defined as fewer than 3 bowel movements in a week. Additionally, these stools are hard, lumpy, and difficult to pass

Constipation symptoms that require medical attention:
-Fever
-Bleeding from the GI tract
-Abdominal pain
-Vomiting
-Low back pain
-Weight loss
Interventions for constipation:
-High-fiber diet (Only works if patient is deficient in fiber. High fiber diet can also cause more clog)
-staying well hydrated
-exercise
-bowel training
-Medications to soften stools
Fecal impaction
An extreme form of constipation:
the hardened stool clumps together, preventing the client from evacuating the bowel, and leading to intestinal obstruction or rectal injury.
What is the procedure if constipation has advanced to an impaction?
A warm mineral oil enema can be used to loosen the stool and allow for its manual removal.
What is the procedure if complete obstruction occurs?
Surgery may be needed.
Findings of needing medical intervention include:
- Abdominal pain
- Cramping with the inability to pass stool or only passing liquid or very thick segments of stool that can move around the impaction.
BMI (Underweight client)
Less than 18.5
BMI (Healthy client)
18.5 - 24.9
BMI (Overweight client)
25 - 29.9
BMI (Obese client)
30 or greater
Labs
Albumen (protein): The normal range is 3.4 to 5.4 g/dL
HDL- Over 60 (good cholesterol)
LDL- Under 100 (bad cholesterol)
Cholesterol- Under 200
Informed Consent
Permission to provide care given by the client after relevant information is provided. consent must be given by a client or a legal representative voluntarily, without coercion by others.
What is the nurse's role with informed consent?
VERIFY and WITNESS that the client or a legal representative signs the consent form in their presence. Also, verify that the client has adequate knowledge to make the treatment decision referred to in the consent process
Parenteral nutrition
IV (your vein)
Dietary intake that is administered intravenously (IV)
-Prevents malnutrition in clients or, if the client is already malnourished, can help correct it.
- Clients with a digestive system that cannot absorb or tolerate adequate food eaten by mouth can utilize parenteral nutrition.
- Only administered into a large vein (central vein)
- For clients without a functioning GI tract, total parenteral nutrition may be the only option.
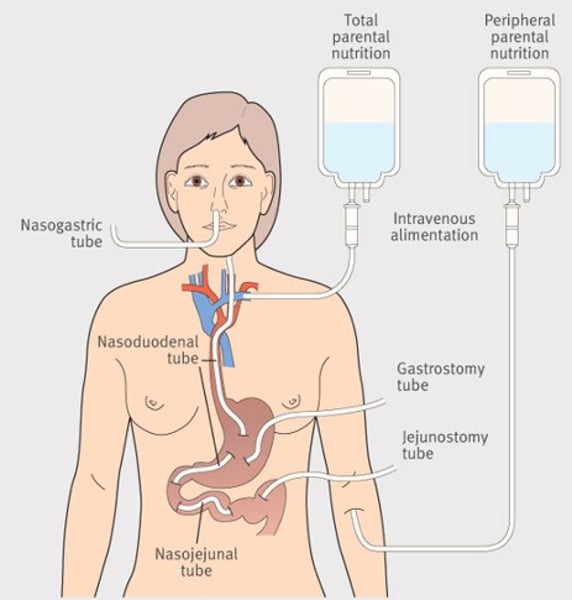
What does Parenteral nutrients provide to a patient?
Proteins, Fats, Carbohydrates, Minerals, electrolytes, and Vitamins.
Bladder training
Assists with retraining the bladder by setting a schedule to use the bathroom. This technique focuses on accident avoidance. Gradually increase the time between bathroom visits to urinate.
- Attempt to extend the time between bathroom trips- first by only 15 minutes, and then advancing the time slowly.
Advance Directives
A written statement of a person's wishes regarding medical treatment.
Two types of advance directives:
- Living will- document where a client can clearly state which life-sustaining treatment(s) they wish to have performed if they become unable to make decisions for themselves.
-Power of attorney/ health proxy- A client can appoint an individual to make health care decisions on their behalf if they are unable to do so.
Urinary catheters
Placed into the bladder to allow urine to drain. Placed in the bladder through the urethra or through a surgically created opening in the lower abdomen
**Bag should be below the bladder. Not on the floor and hung from a non-movable part of the bed. Tube should be secured to the patient's thigh by tape or stat-lock
Kubler-Ross Stages of Grieving
1. Denial
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. Depression
5. Acceptance
Normal Grief
Also known as uncomplicated grief, is caused by the loss of someone very close, through death or the ending of a relationship - Typically lessons over time as feelings decrease in intensity

Anticipatory Grief
grief that is experienced before the loss of someone or something. This kind of grief arises when a loss is experienced.

Prolonged Grief Disorder
Previously known as complicated grief; lasts >6 months and can be so significant, it affects the client's ability to function. unable to accept the death of a loved one.

Disenfranchised Grief
Grief related to a relationship that does not coincide with what is considered by by society to be recognized or justified loss. "Not worthy of loss"

Fecal Occult Blood Testing
Check stool for the presence of blood.
+Blood=Blue
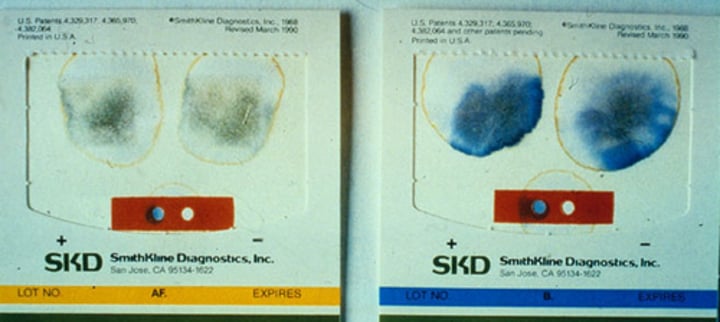
What can cause a false positive for fecal occult blood testing?
Consuming foods such as red meat, beets, broccoli, and turnips can affect the results of FOBT.
What should patients avoid for fecal occult blood testing?
Medications and supplements such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and Vitamin C. Lead to a false positive.
Supplementation
Vegans need B12 supplementation- B12 comes from animal sources.
-Vitamin C- Good for wound healing
-Vitamin K- Aids in clotting
NG tubes
Initial placement checked by X-ray
-Subsequent placement checked by aspirating stomach contents
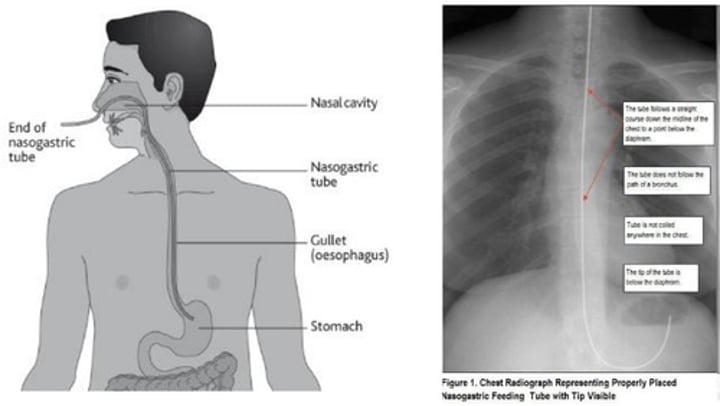
If patient starts coughing during implementation of NG tube, what should the nurse do?
Remove NG tube and try again!
Response to stress
-Tachycardia
- Increased blood pressure and increased cardiac output
- Dilation of bronchial airways
- Pupil dilation
- Increase in blood glucose levels
Situational stressors
Created by personal, family, or work-related issues
Examples include:
- Being diagnosed and living with a chronic illness
- Financial strain
- Being a victim of a motor vehicle accident
Developmental stressors
occurs as an individual moves though life
Adventitious stressors
Stress that results from events of disaster; they are generally rare, unexpected, and can result from natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, and war.
Socioeconomic stressors
Stress that occurs from factors such as poverty, socioeconomic status (SES), and homelessness.
Cultural stressors
Stress that individuals may experience by living within a society in which they do not culturally fit and/or receive care that ignores their cultural beliefs.
Accute Stress Disorder
Results from an overwhelming event that causes an intense and dysfunctional reaction.
- If the symptoms of ASD last beyond a month, post-traumatic disorder will be diagnosed.
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
Prolonged and heightened stress reaction to a traumatic event that lasts more than a month.
-Characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, numbness of feeling, and/or insomnia.

Irritable bowel syndrome
A common, chronic gastrointestinal condition manifested by symptoms of abdominal discomfort, cramping, bloating, diarrhea, and/or constipation.
-Stress is a common trigger for IBS, so treatment planning should include stress-reducing techniques and activities.

Urine Analysis
-Color- pale yellow to amber
-pH- 5.0-9.0
-Specific gravity- 1.002-1.030
-Clarity -clear
-Oder- mild
-Protein- under 20 mg/dl
-Glucose- negative
-Ketones- negative
-Bilirubin- negative
-Nitrate- negative
-Leukocyte esterase- negative (under microscope less than 5 per high power field)
-Renal cells- none
-Transitional cells- none
-Squamous cells- rare
-Casts- rare
-Crystals- none
-Bacteria, yeast, parasites- none
Purewick would be used for which type of incontinence?
Overflow incontinence
What kind of device would work great for patients with functional incontinence?
Bedside commode
LDL
low density lipoprotein (bad cholesterol)
HDL
high density lipoprotein (good cholesterol)