Lecture Exam 1 Content (in progress)
1/38
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
what is the afferent pathway
the pathway before the “control centre” in homeostatic feedback loops
what is the efferent pathway
the pathway after the “control centre” in homeostatic feedback loops
extrinsic regulation
regulation that occurs in the nervous and/or endocrine system.
autoregulation (intrinsic regulation)
when an internal structure reacts to the stimulus. a change in the cell, tissue or organ. happening within.
Negative feedback consists of the system “shutting off” whereas positive feedback systems consist of "overloading” the system.
explain the difference between positive and negative feedback mechanisms
increased risk of disease
complications with aging
increased risk of destructive positive feedback loops
what are some of the issues associated with chronic homeostatic imbalance
Labour and Blood clotting
what are two examples of a positive feedback loop
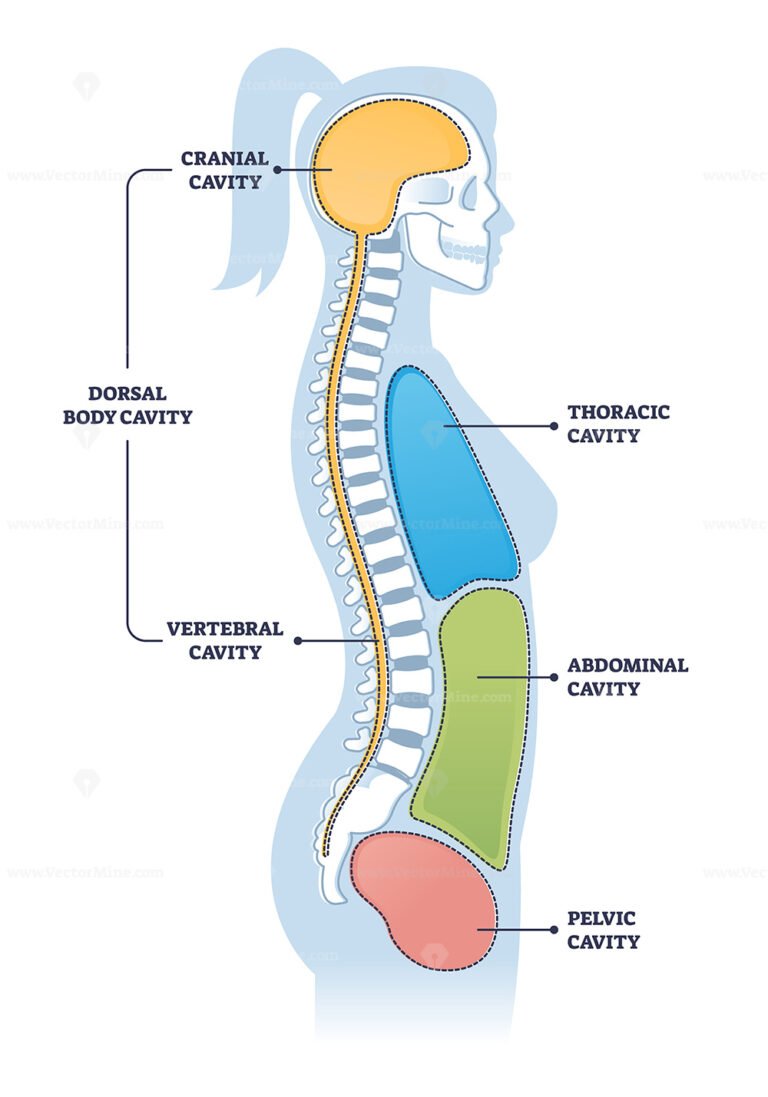
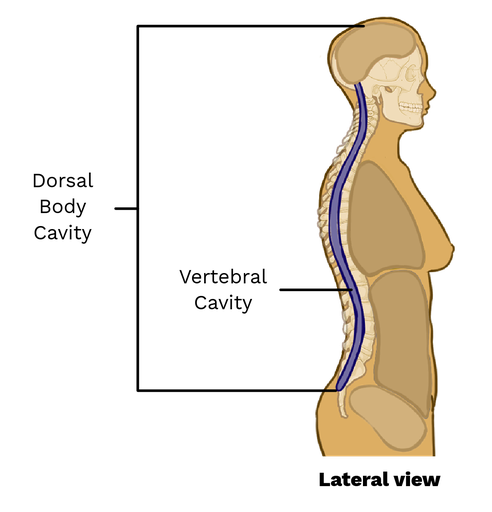
dorsal cavity
consists of the vertebral cavity and the cranial cavity which protects the central nervous system.
ventral cavity
consists of the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities which protects the viscera
vertebral cavity
the cavity within the vertebral column that houses the spinal cord.
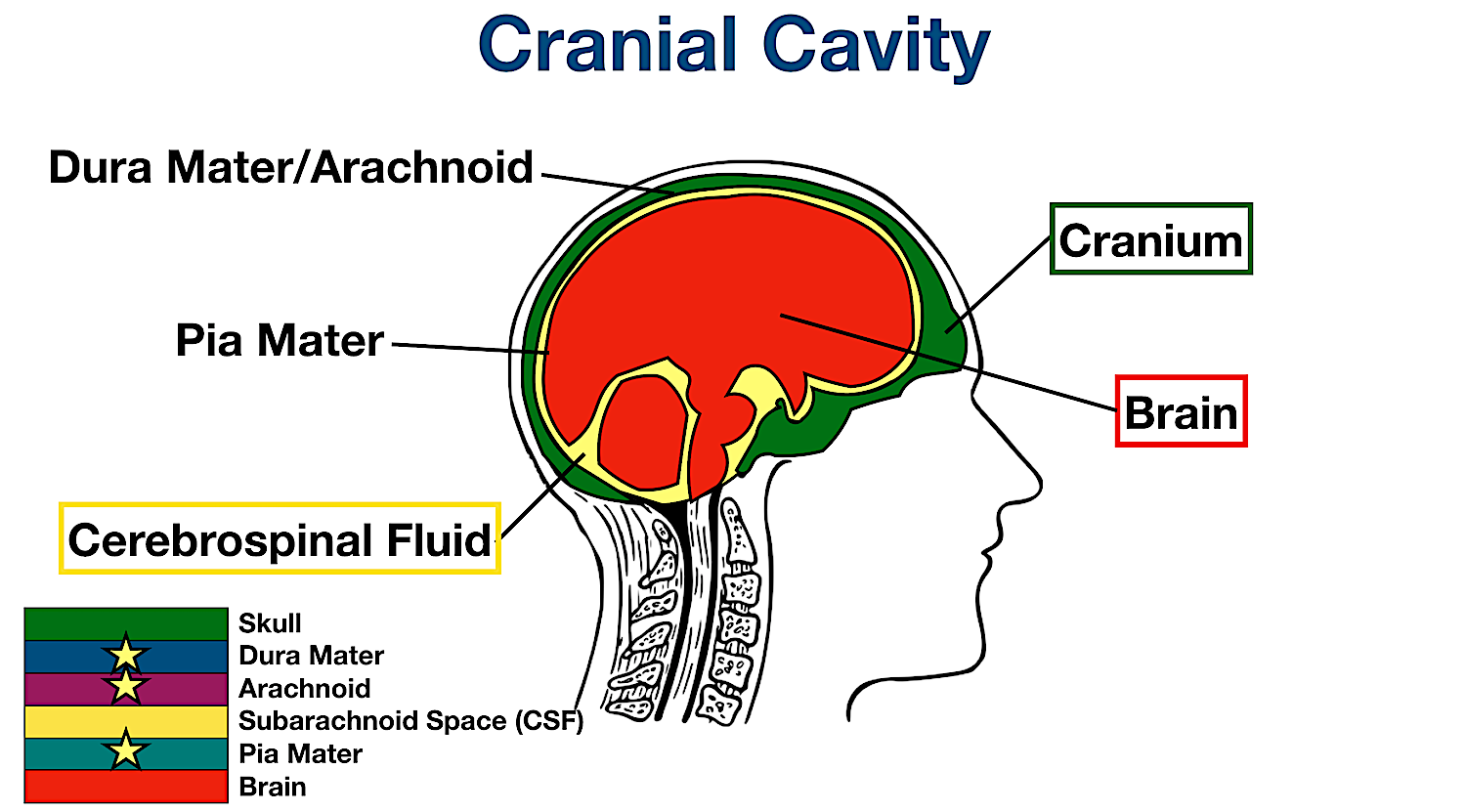
cranial cavity
the cavity that houses the brain and is surrounded by the skull.
thoracic cavity
The part of the ventral cavity located above the diaphragm, containing the lungs and heart.
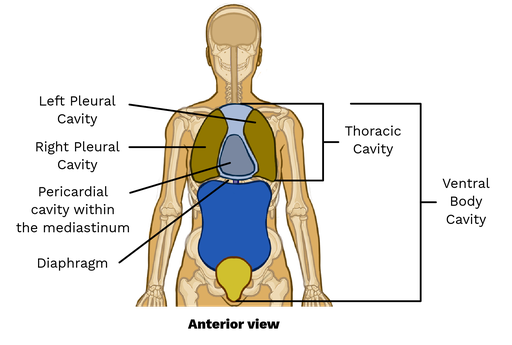
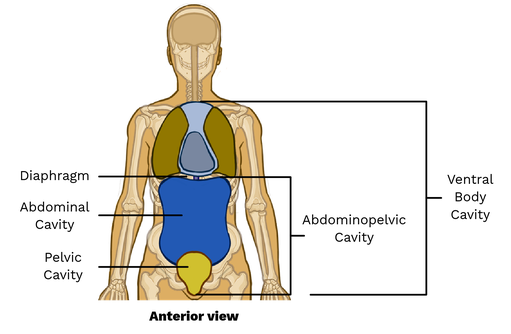
abdominopelvic cavity
the cavity located below the diaphragm that contains the digestive organs, urinary bladder, and reproductive organs.
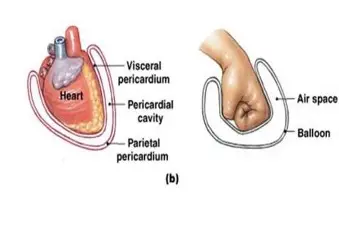
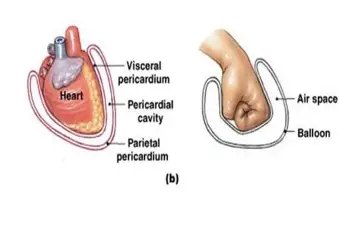
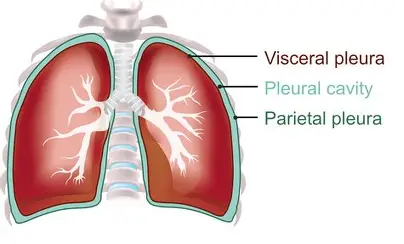
visceral
referring to the serous membrane directly touching the organ(s)
parietal
reffering to the serous membrane lining the cavity
pleura
a serous membrane lining the thoracic cavity and covering the lungs.
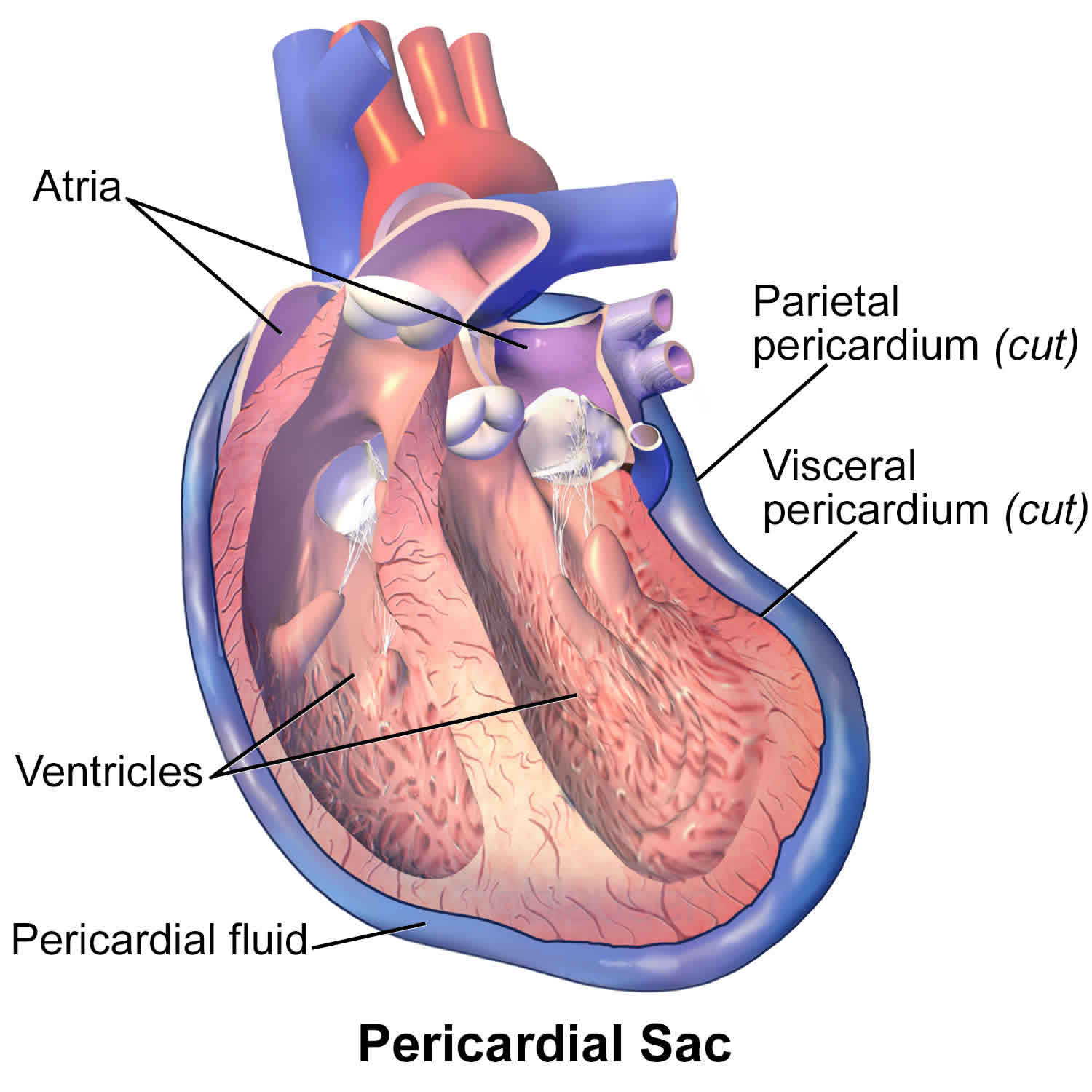
pericardial
referring to the serous membrane around the heart
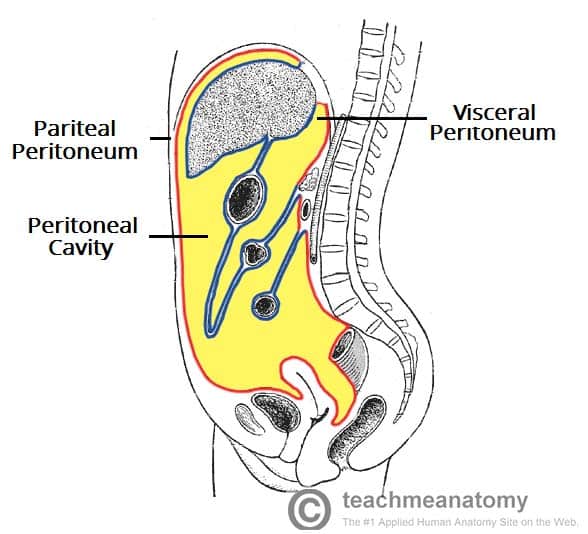
peritoneum
relating to the serous membrane around the digestive organs
perspiration and thermoregulation
what function does high heat vapourization provide for humans?
prevents accessive fluctuation in core body temperature to prevent things like frostbite.
what is the function of a high heat capacity in the human body
Carbohydrates (sugars)
which macromolecules are hydrophilic
Lipids (fats)
which Macromolecules are Hydrophobic
Diabetes Mellitus
What is the cause of Ketoacidosis
bicarbonate buffer system
respiratory compensation
carbonic acid- bicarbonate
what are the three types of buffer systems
Acidosis
when the blood pH drops below 7.35
Alkalosis
when the blood pH rises above 7.45
7.35-7.45
What is the homeostatic range of blood pH
Monosaccharides
What is the monomer of a Carbohydrate?
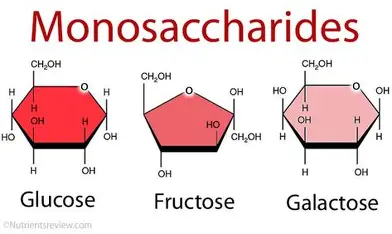
Glucose, Fructose and Galactose
What are the three monosaccharides?
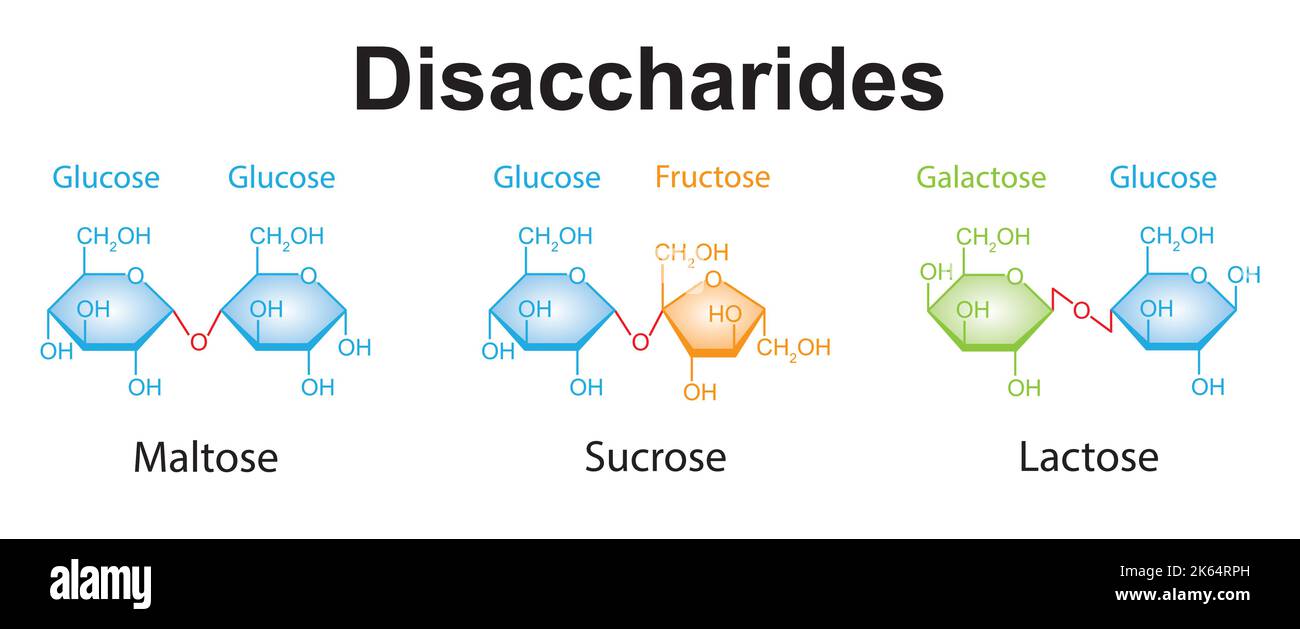
Sucrose, Lactose and Maltose
What are the three Disaccharides that we need to know?
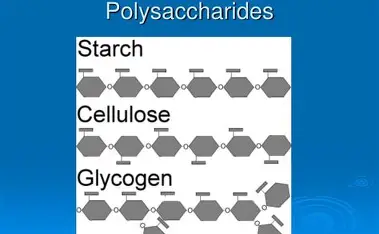
Cellulose, Glycogen, and Starch
What are the three polysaccharides that we need to know?
The middle Monomer in cellulose is mirrored which makes it difficult for animals to digest.
What is the difference between Cellulose and Starch?
Saturated fats contain only single bonds and are found in solid form at room temperature
unsaturated fats contain double bonds and are liquid at room temperature
Trans fats contain an extra Hydrogen (hydrogenated fats) to “fix” the structure of an unsaturated fat to remain solid at room temperature (ex. margarine)
What are the differences between a saturated, unsaturated and trans fats
fatty acids
eicosanoids
glycerides
phospholipids
glycolipids
steroids
what are the 6 classes of Lipids
Amino Acids
What are the monomers of Proteins?
Nucleotides
What are the monomers of Nucleic Acids?
an unsaturated fat has a bend at the double bond between carbons
What is the difference in structure between saturated and unsaturated fats?
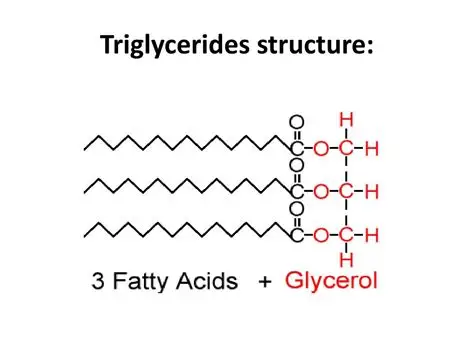
a glycerol and three fatty acid groups
What are triglycerides formed from
Cholesterol
What is the most important steroid in the body