Cell Division and Mitosis: Part 1/2 (Combined Part 1 and Part 2): Cellular Reproduction
1/31
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What distinguishes living organisms from nonliving matter?
The ability to produce more of their own kind.
What is the continuity of life based on?
The reproduction of cells, or cell division.
List the functions of cell division in multicellular organisms.
Cell division functions in reproduction, growth, and repair.
What does cell division enable in unicellular organisms?
It reproduces an entire organism, thereby increasing the population.
How does cell division function in multicellular organisms?
It enables development from a single cell and repairs and renews cells that die.
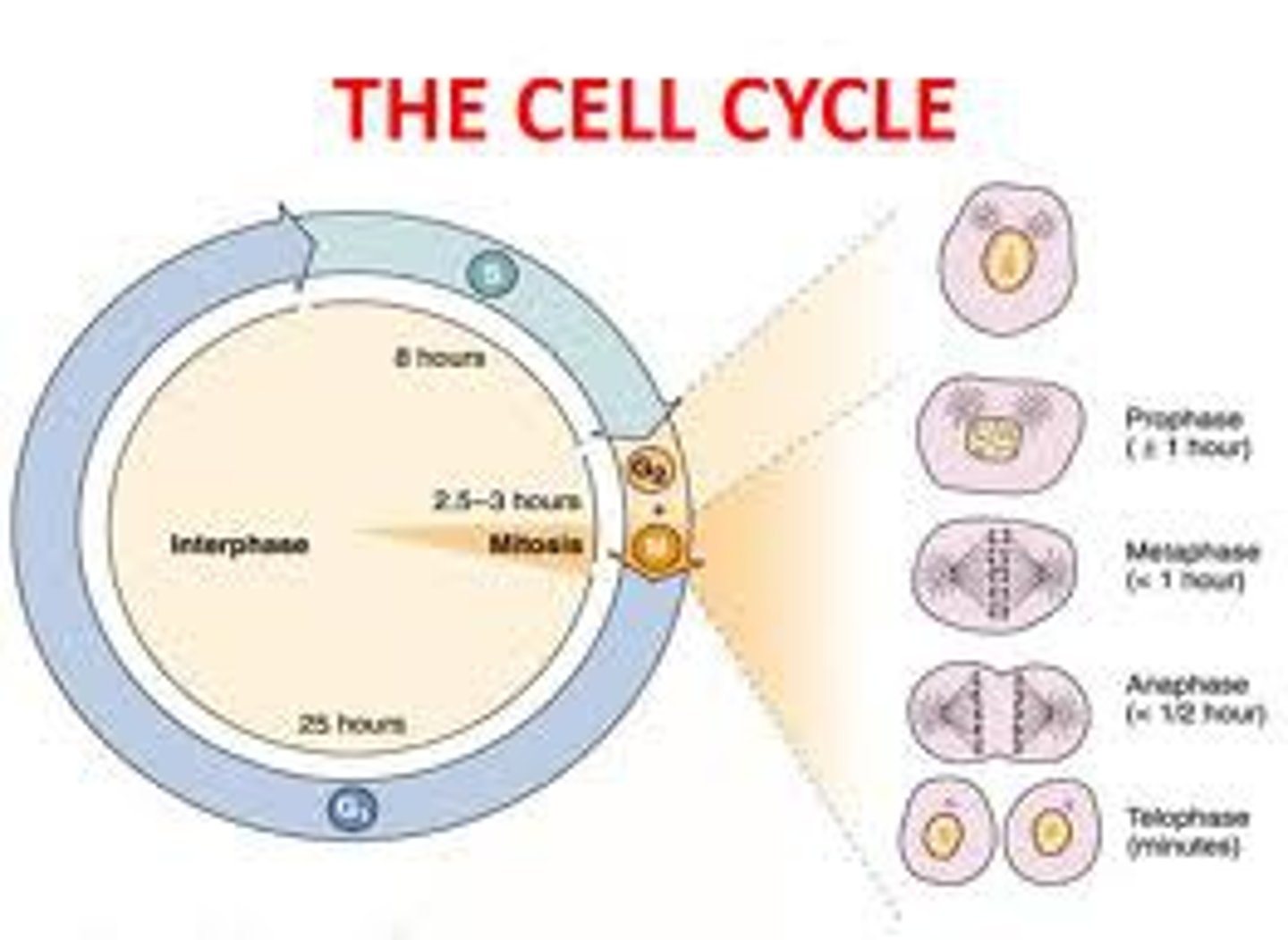
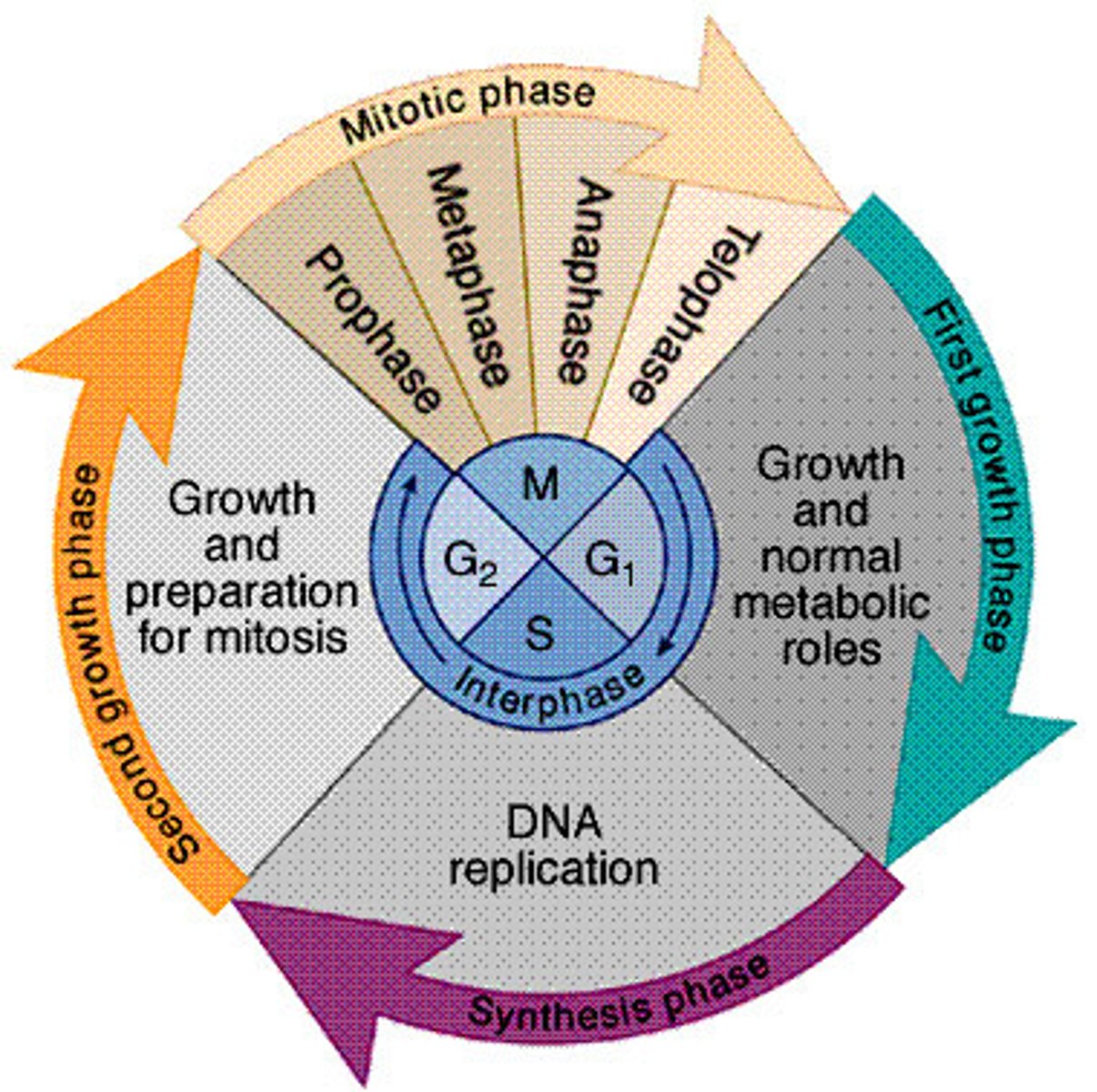
What is the cell cycle?
The life of a cell from its origin in the division of a parent cell until its own division into two daughter cells.
What is the outcome of most cell division in terms of genetic material?
Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells.
What is the exception to the rule of genetically identical daughter cells?
Meiosis, which produces sperm and eggs.
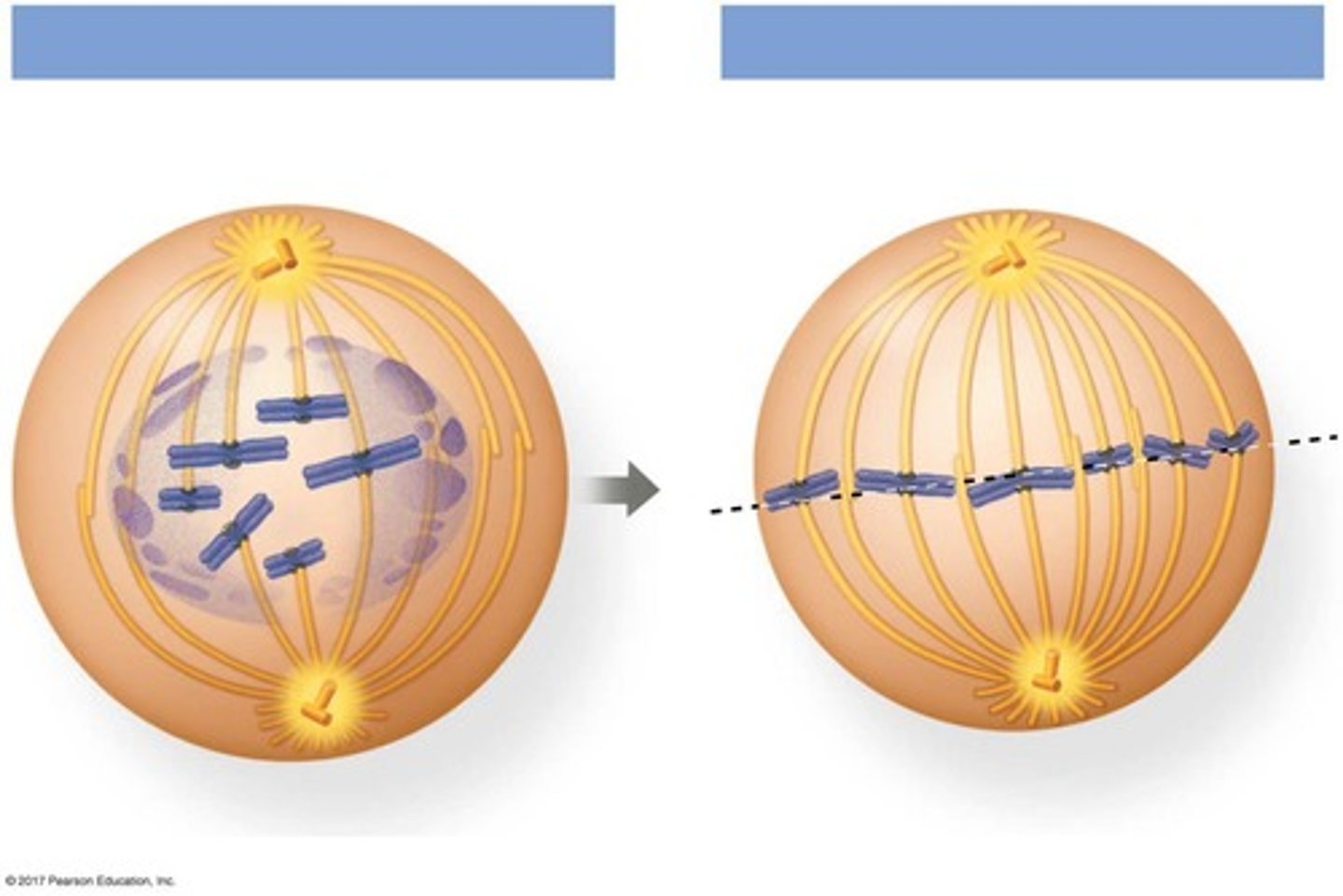
How does a dividing cell ensure genetic fidelity during division?
It duplicates its DNA, allocates the copies to opposite ends, and then splits into daughter cells.
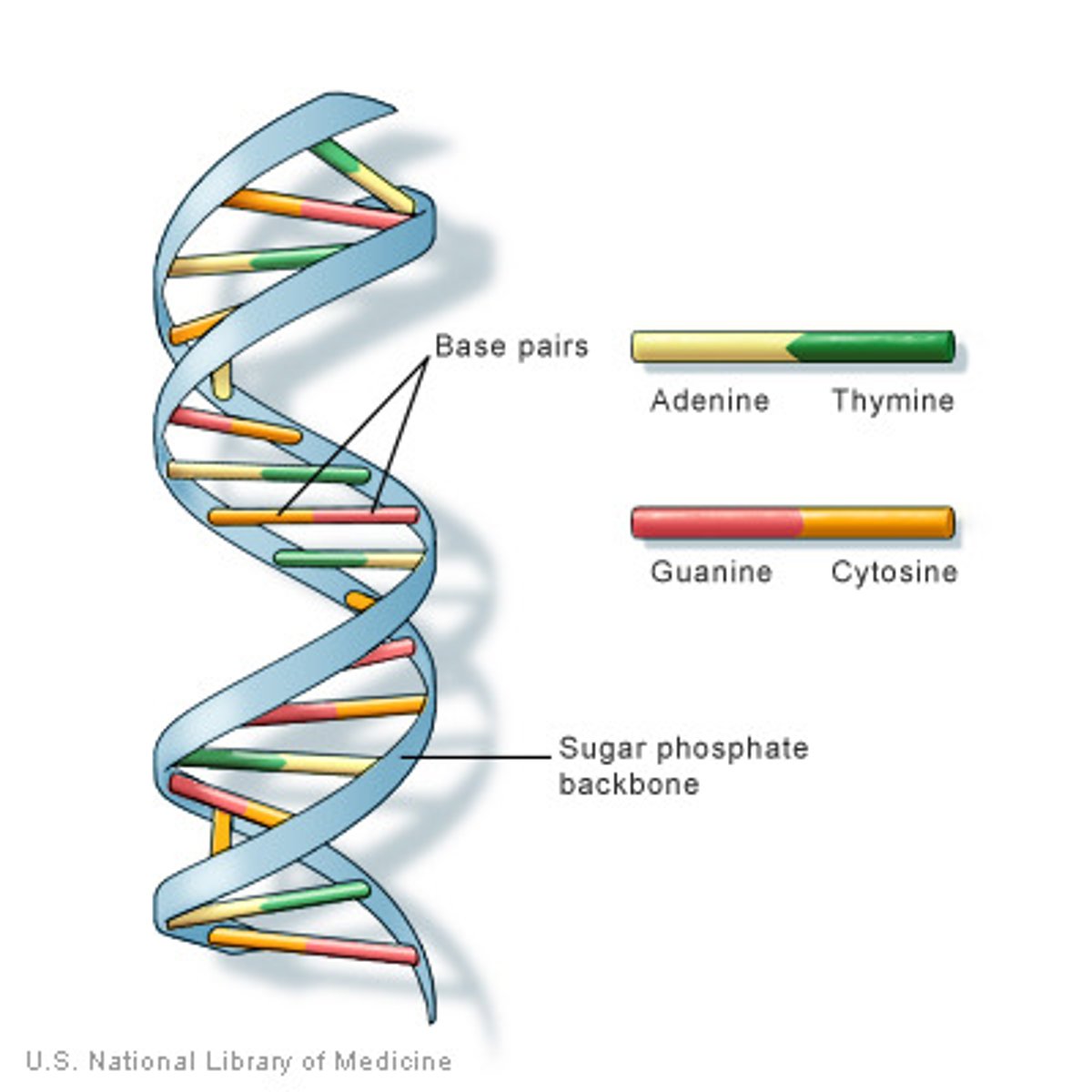
What is a genome?
A cell's genetic information, packaged as DNA.
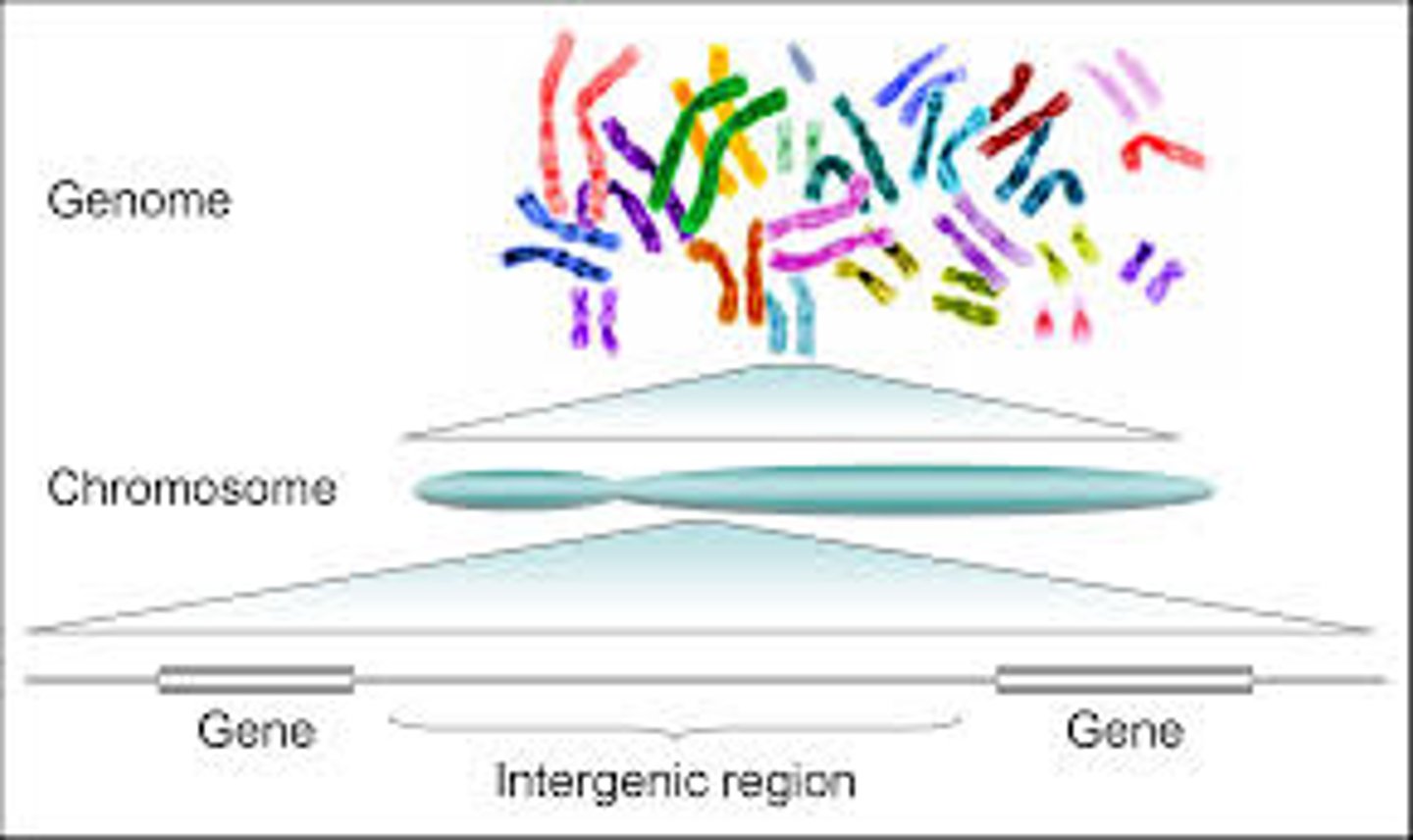
How is the genome structured in prokaryotes versus eukaryotes?
In prokaryotes, it is often a single long DNA molecule; in eukaryotes, it consists of multiple DNA molecules.
How much DNA must a human cell replicate for division?
About 2 meters of DNA.
What are chromosomes?
DNA molecules packaged into structures that contain genetic information.
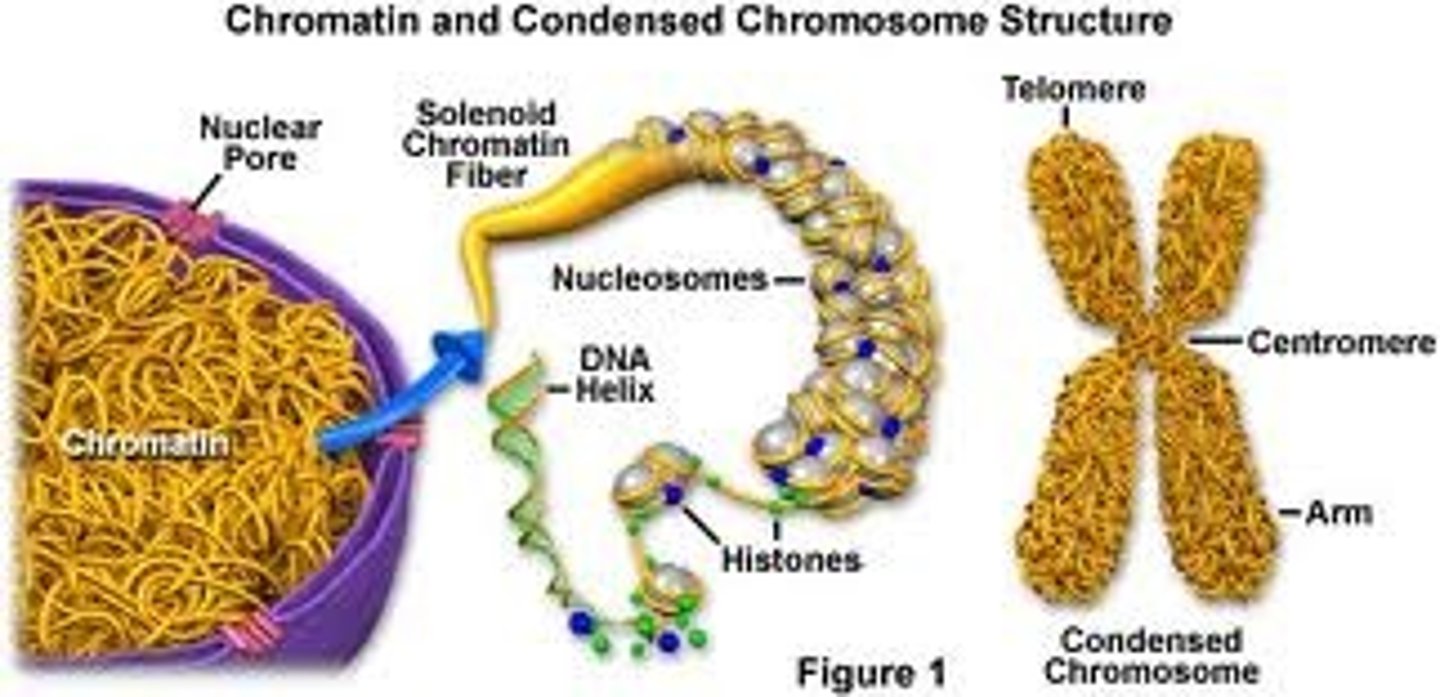
What is chromatin?
A complex of DNA and proteins that make up eukaryotic chromosomes.
What is the typical number of chromosomes in human somatic cells?
46 chromosomes, made up of two sets of 23.
How many chromosomes do human reproductive cells (gametes) have?
One set of 23 chromosomes.
What happens to chromosomes when a cell is not dividing?
Each chromosome is in the form of a long, thin chromatin fiber.
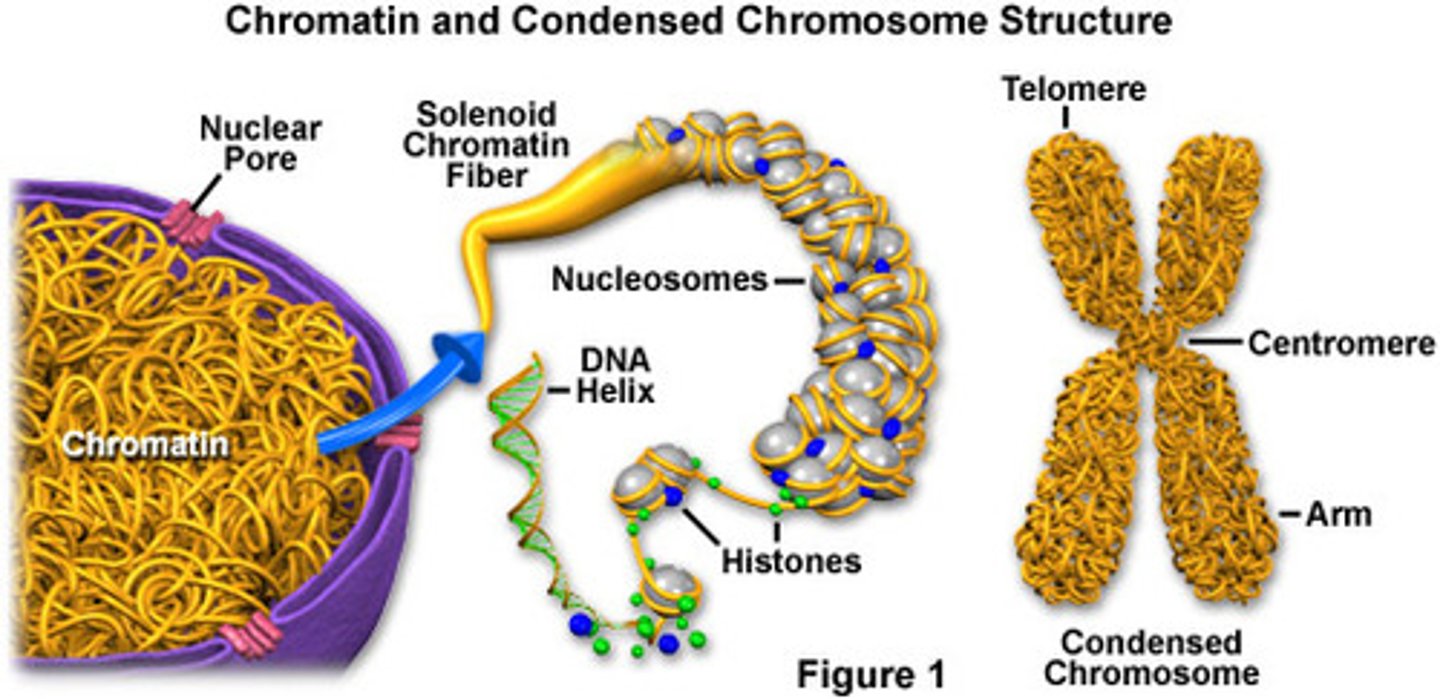
What occurs to chromatin before cell division?
It condenses, coiling and folding to form a smaller package.
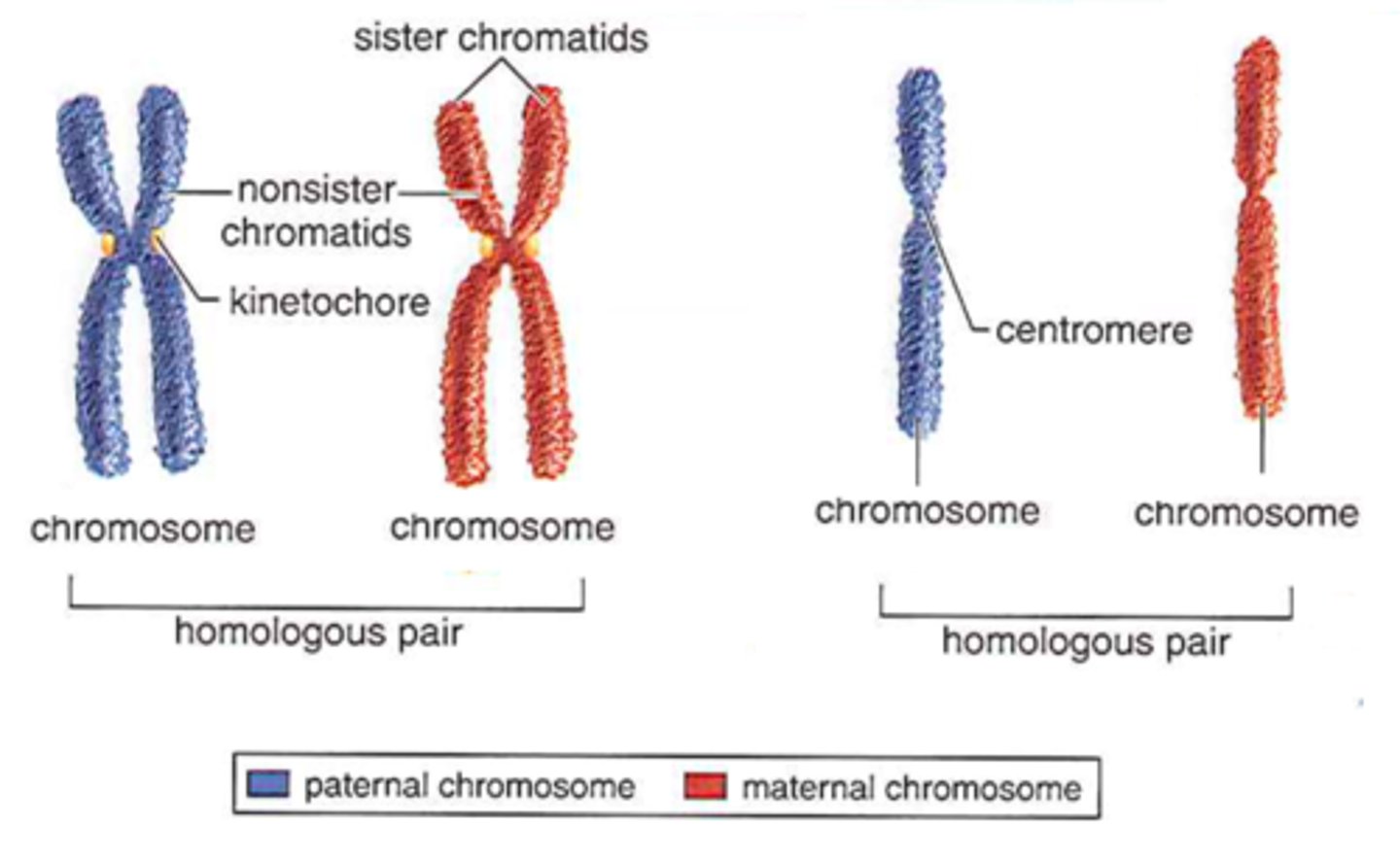
What are sister chromatids?
Duplicated chromosomes consisting of two identical copies of the chromosomes' DNA.
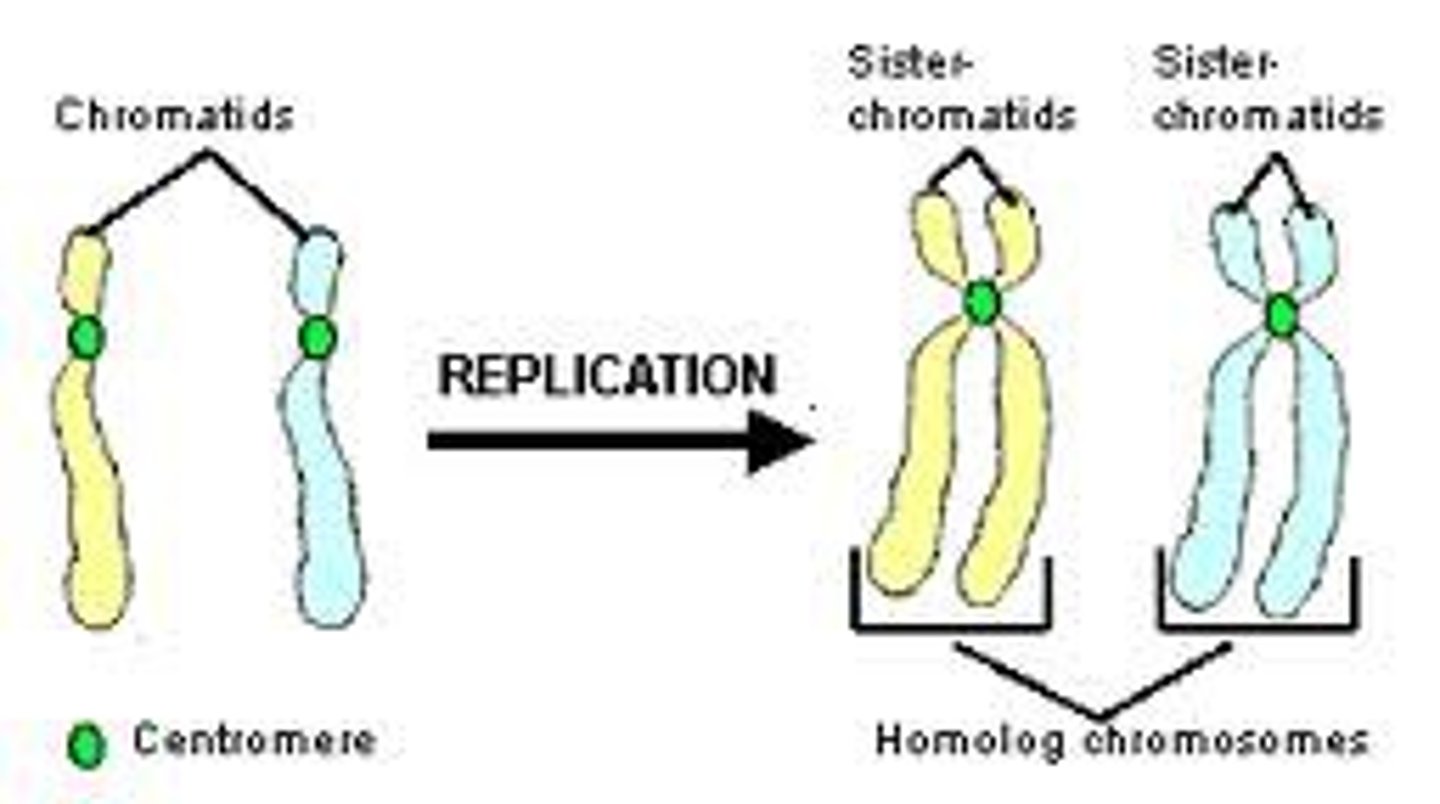
What is sister chromatid cohesion?
The attachment of sister chromatids along their lengths by protein complexes called cohesins.
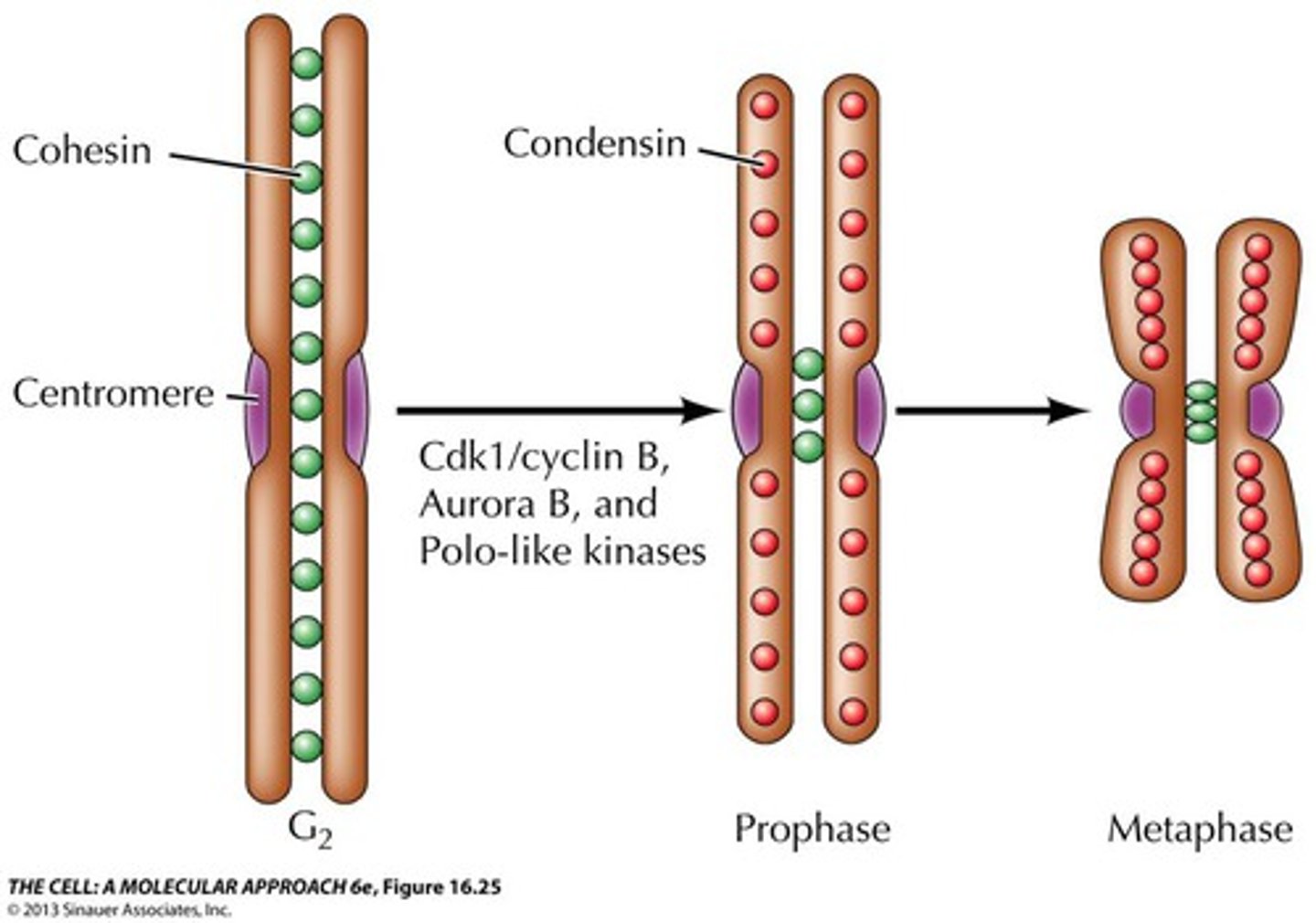
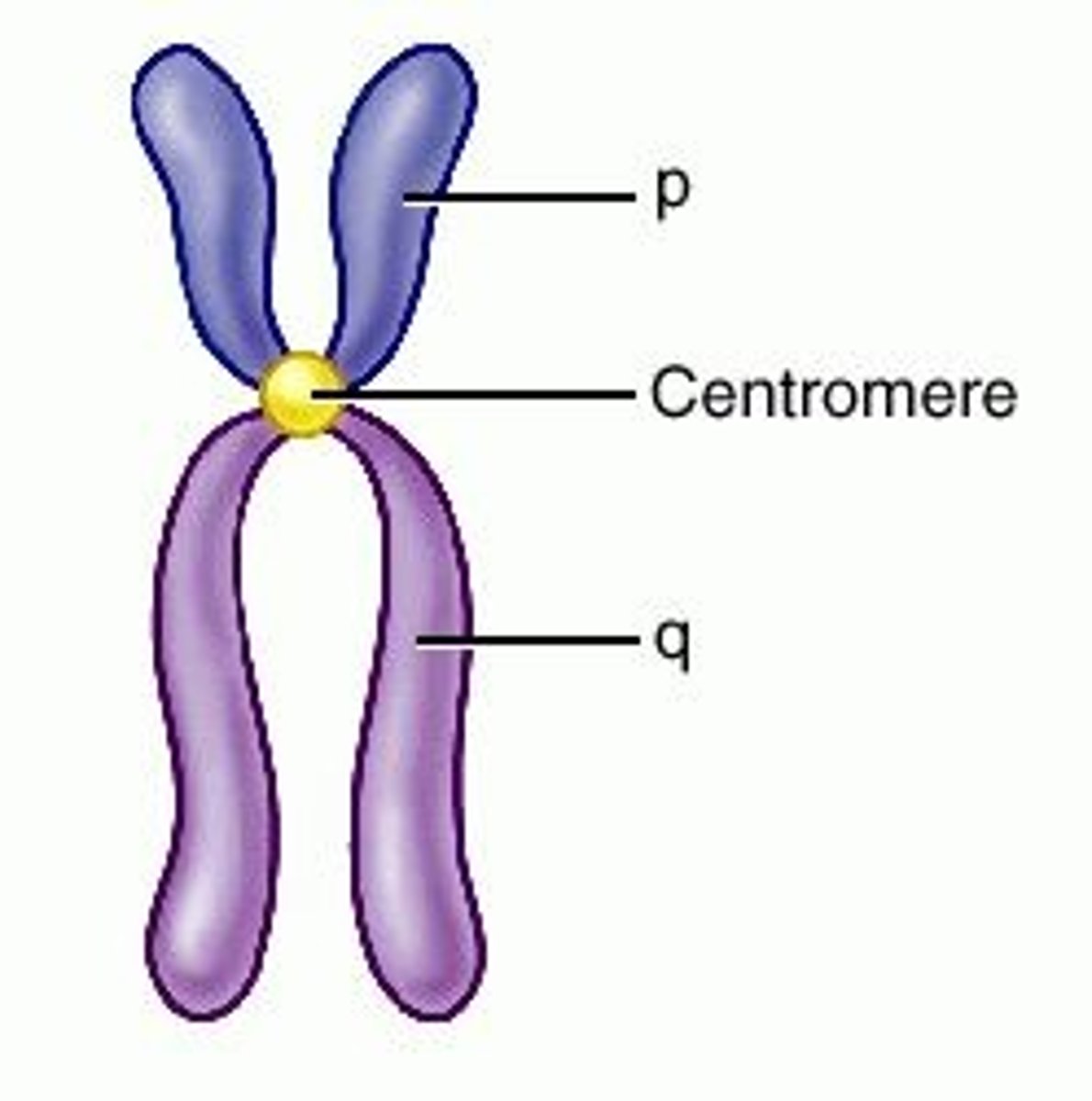
What is a centromere?
A specialized region of one chromatid where the two chromatids are most closely attached.
What happens to sister chromatids during cell division?
They separate and move into two new nuclei at opposite ends of the parent cell.
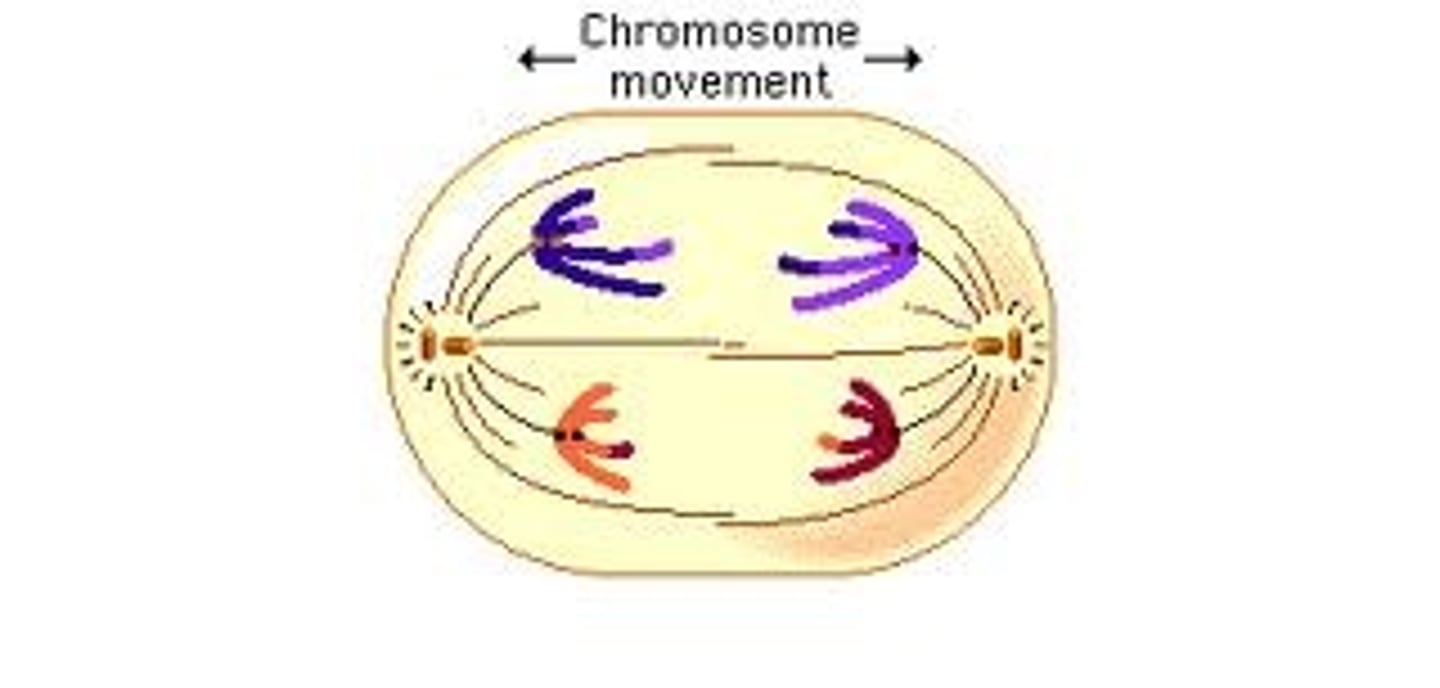
What do the new nuclei receive after sister chromatids separate?
A group of chromosomes identical to the original group in the parent cell.
What is mitosis?
The division of the nucleus, usually followed by cytokinesis, producing two genetically identical cells.
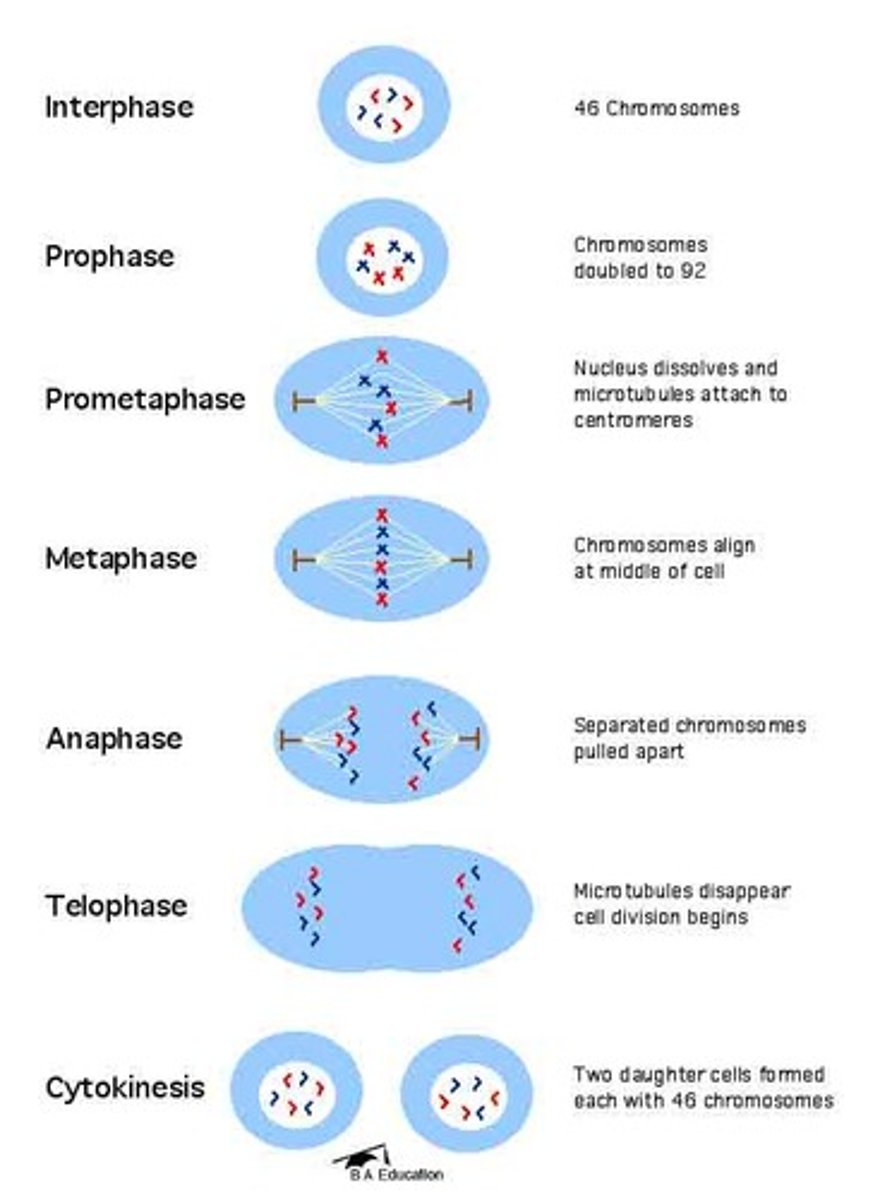
What is cytokinesis?
The division of the cytoplasm that follows mitosis.
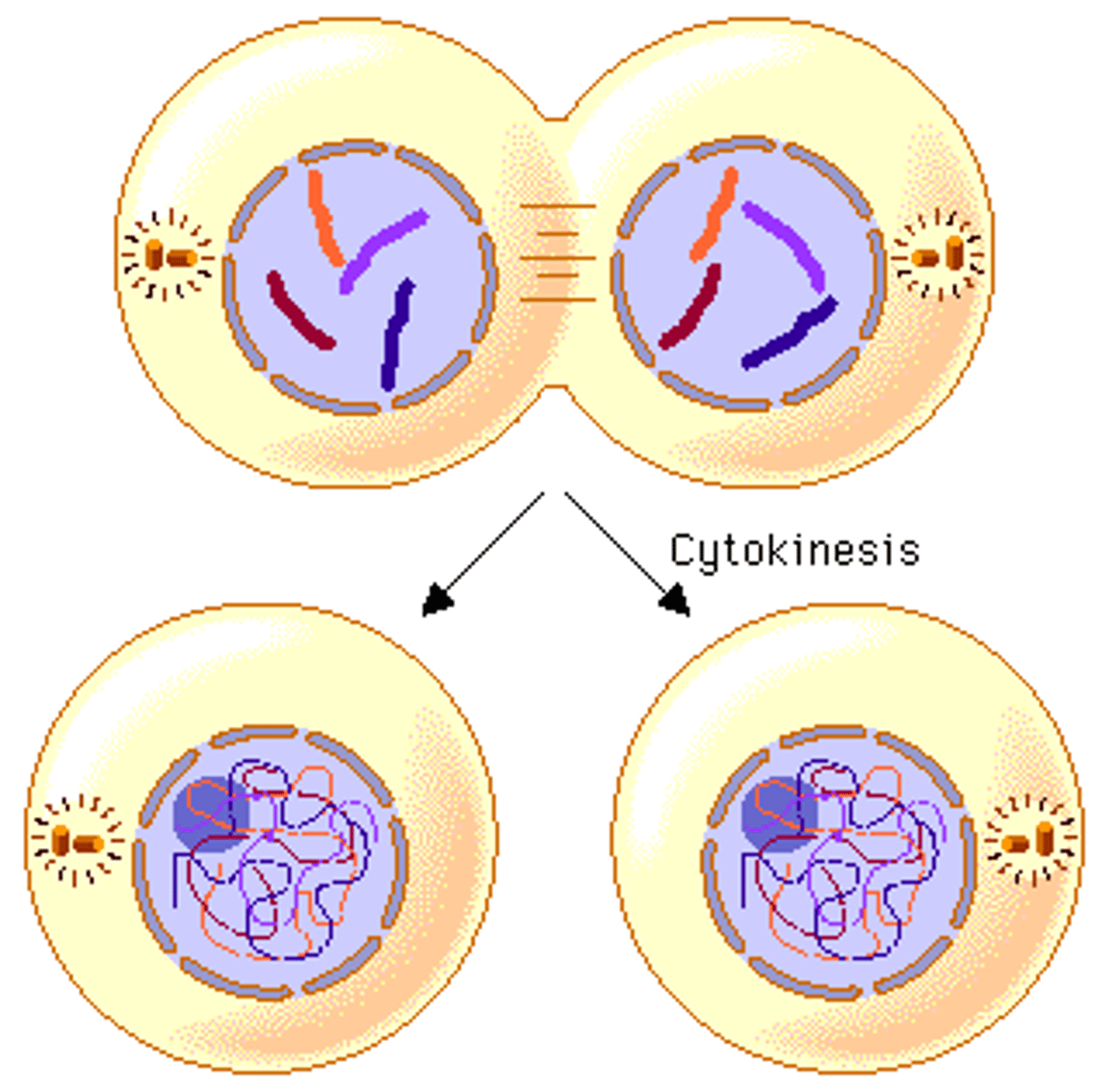
What is the total number of chromosomes inherited from both parents?
46 chromosomes (23 from each parent).
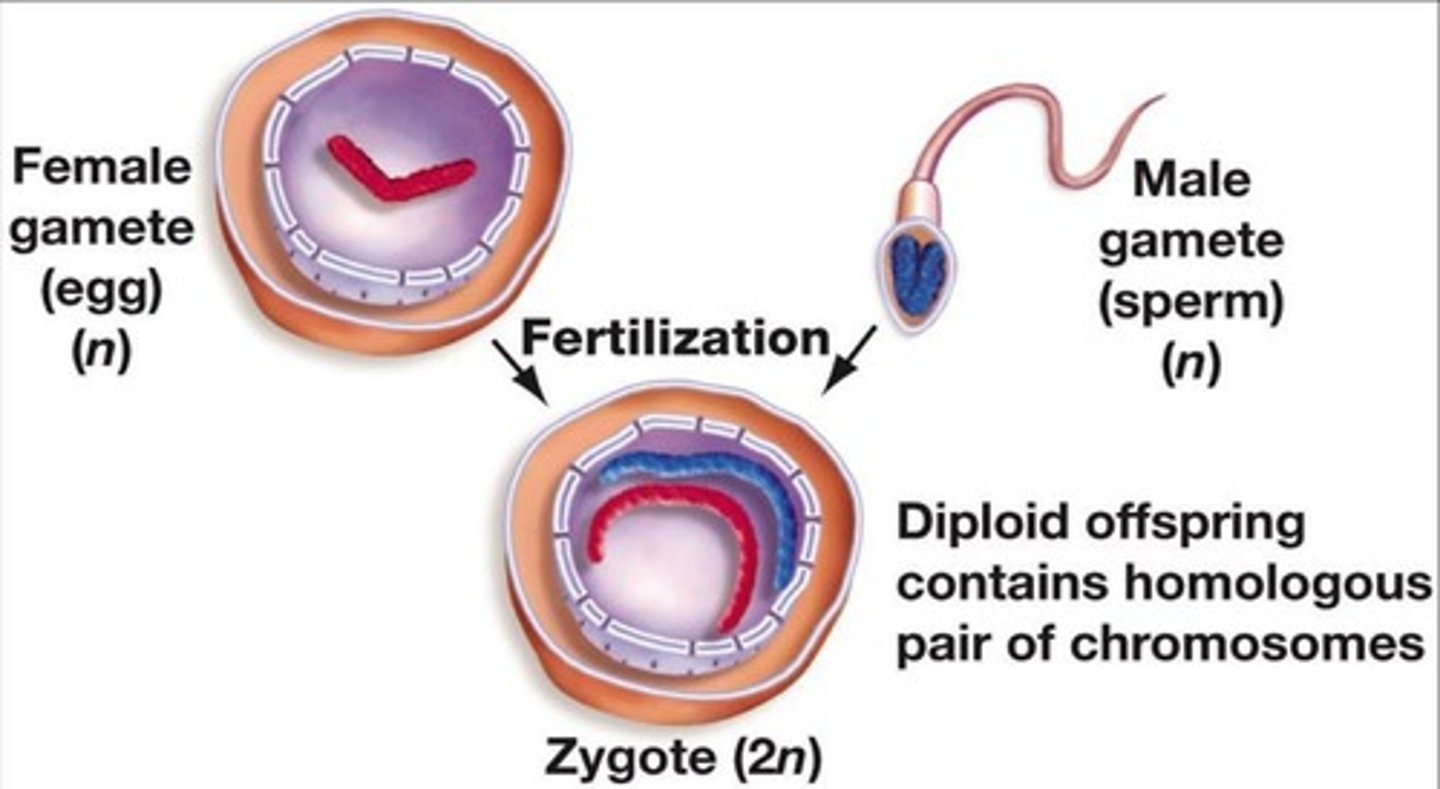
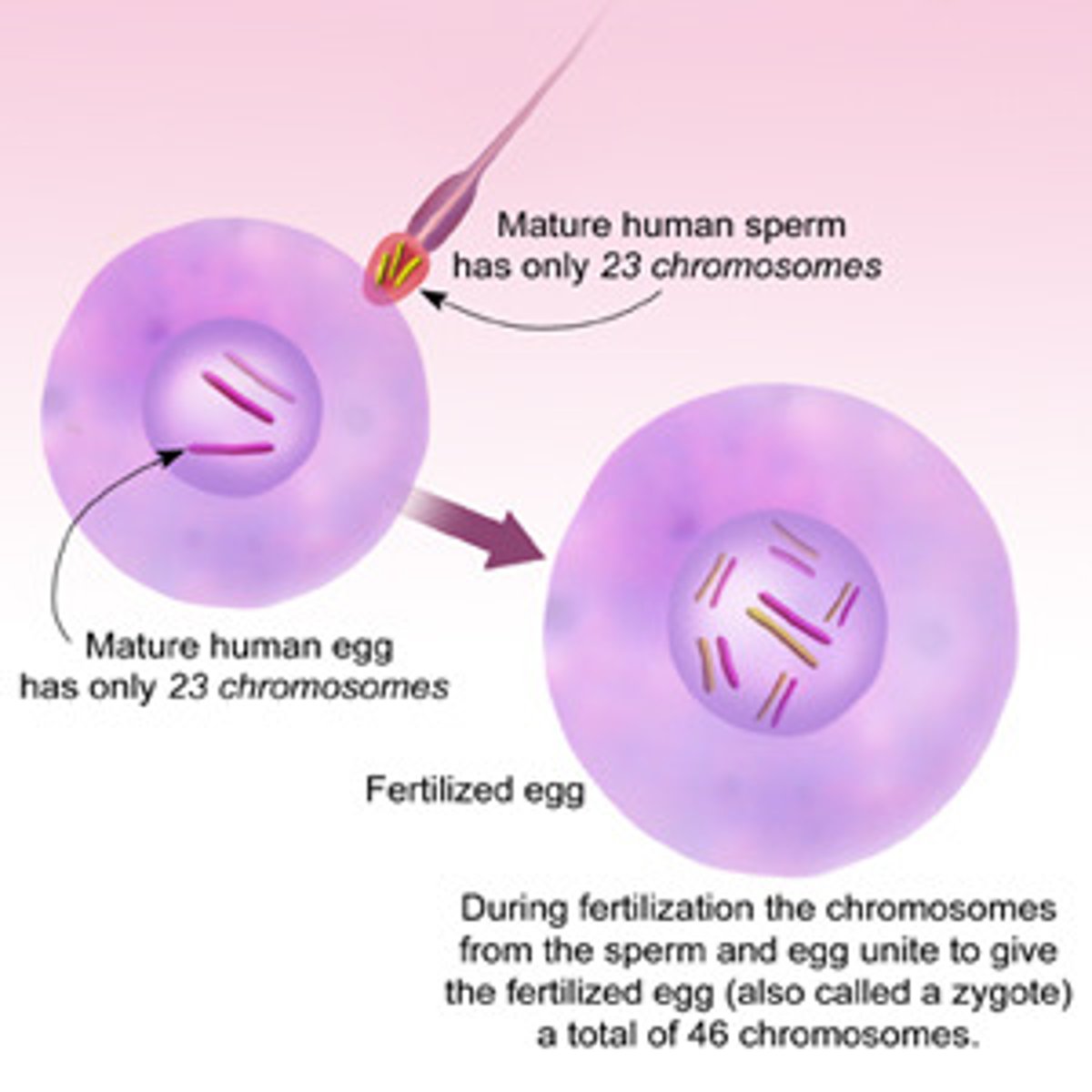
What is a zygote?
A fertilized egg formed when a sperm unites with an egg, which undergoes mitosis and cytokinesis to develop into a multicellular organism.
How many somatic cells does a fully developed human have?
Approximately 200 trillion somatic cells.
What is the role of mitosis in the body?
To replace dead and damaged cells, producing clones with identical genetic information.
What type of cell division produces gametes?
Meiosis.
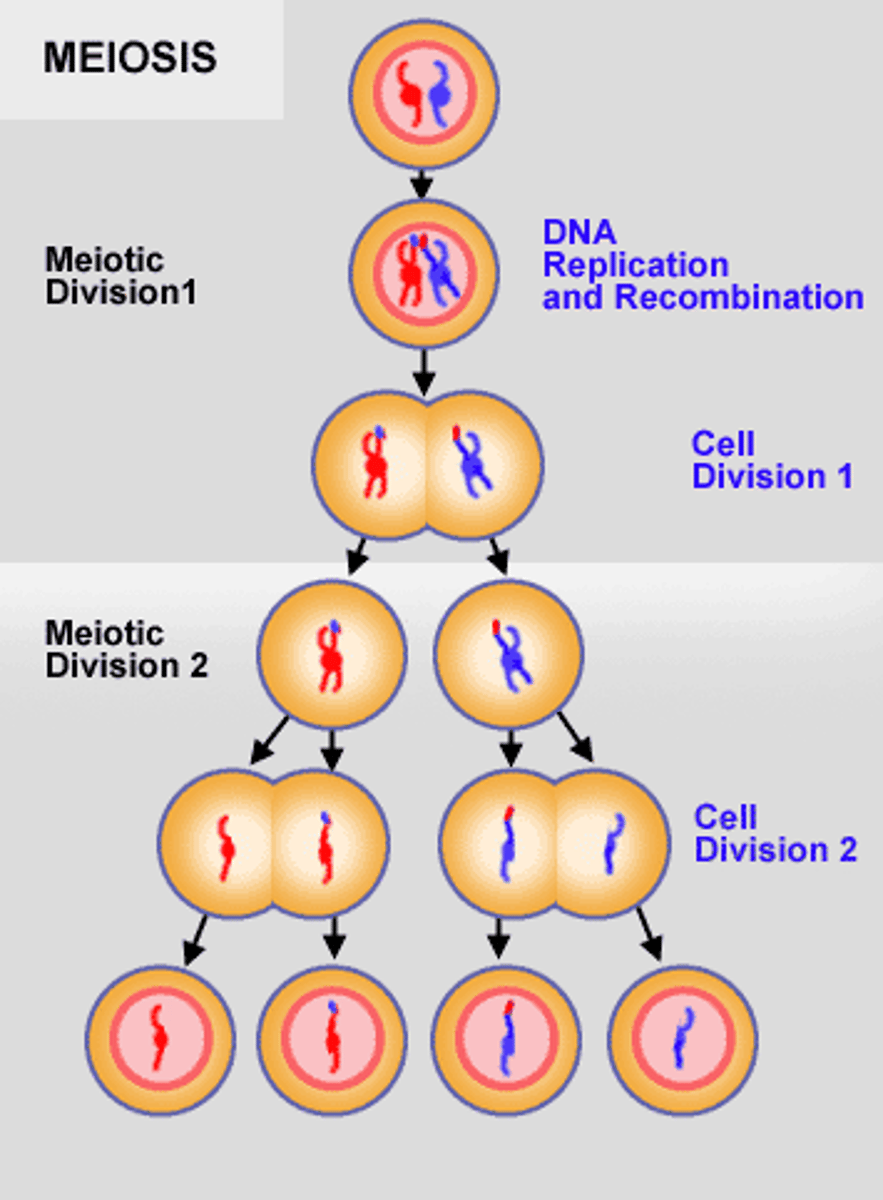
How many daughter cells does meiosis produce, and how do they differ from the parent cell?
Meiosis produces four non identical daughter cells, each with half the parent cell's chromosomes.
What is the chromosome number after fertilization?
46 chromosomes, restored by the fusion of two gametes.