Human Excretion (LC Biology)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Excretion:
The removal of waste products of metabolism from the cell.
Homeostasis:
The maintenance of a constant internal body environment.
How we excrete:
• Lungs - Excrete water & CO2.
• Kidneys - Excrete water & urea.
• Skin - Excrete water & salt.
diagram of urinary system:
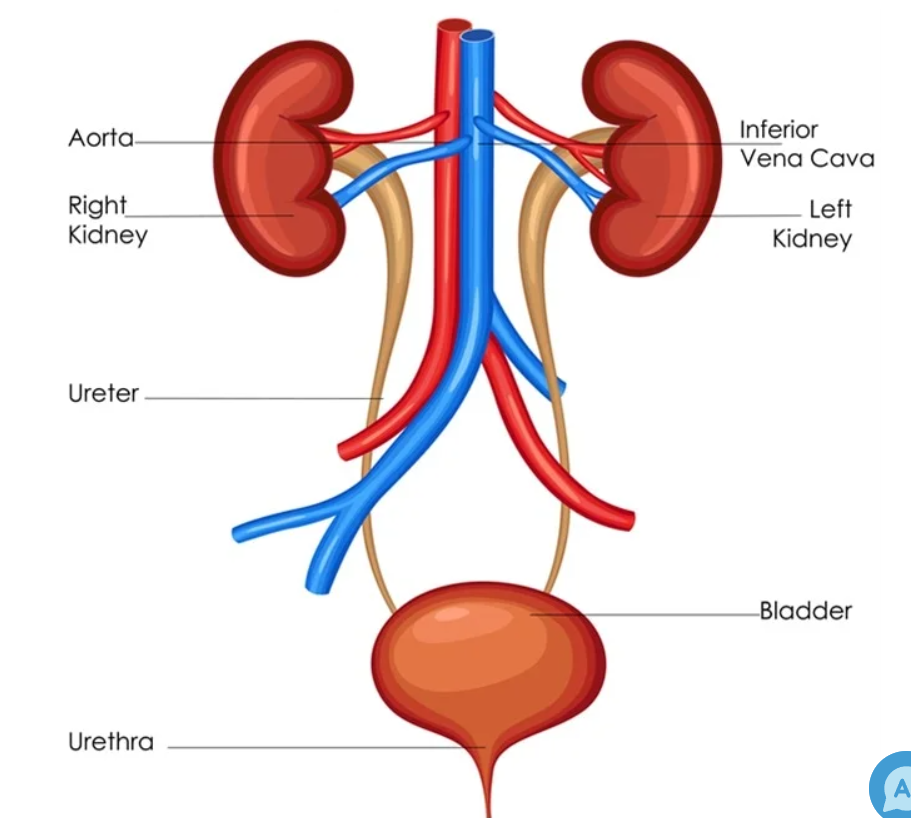
Ureters:
Carry urine from kidneys -> Bladder.
Bladder:
Muscular organ that stores urine.
Kidney:
Filters blood to remove unwanted material.
Urethra:
Tube to carry urine from bladder out of body during urination.
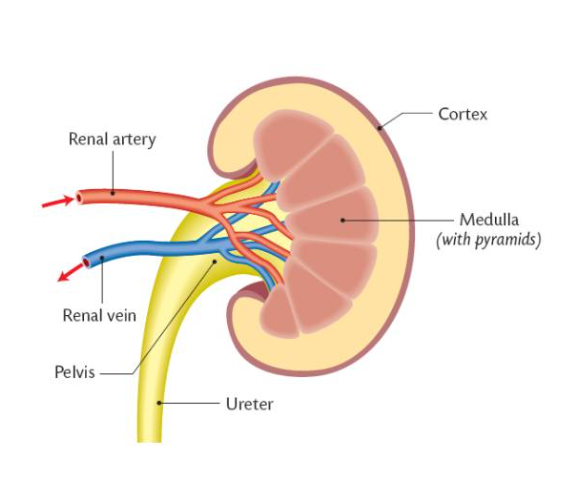
Diagram of the kidney:
Location of the kidneys in the human body:
Lower abdomen
Cortex function:
Filters blood (Outer layer)
Medulla function:
Reabsorption.
Function/role of kidneys:
Filter blood that comes through them.
Absorbs back in what it needs to keep.
Passing the waste products to the bladder for storage/secretion.
Function/role of kidneys:
• Blood is filtered in the outer cortex to remove small pigments; Glucose, amino acids, water & urea.
Filtering of blood
Filtering of blood from kidneys:
• Blood arrives in kidneys from aorta & vena cava.
• Once these vessels enter the kidney they are called the renal gland artery & the renal gland vein.
Function/role of kidneys: Reabsorption of substances
• Occurs in medulla.
• Only desired substances can be reabsorbed into bloodstream.
• EG: Glucose & amino acids.
Function/role of kidneys: Secretion
• Undesired substances that were filtered from blood are transported through tubes of the kidney . They reach the kidneys pelvic area.
• These undesired items are taken to the bladder.
• Finally, they are excreted in the form of urine.
Urination:
The passing of urine in the body.
Urine:
Composed of water & urea.
Path of urine leaving body =
Urine passed from bladder, through urethra & excreted from body.
Osmoregulation:
The process by which an organism regulates the water balance in its body and maintains the homeostasis of the body
Osmoregulation in the body?
• Kidneys are the osmoregulatory organs of the body.
• Water is taken in through food, the water we drink but also formed inside during respiration.
• Water is lost from body via lungs, kidneys & skin.
Nephron:
The functional role of the kidney.
Diagram of the Nephron:
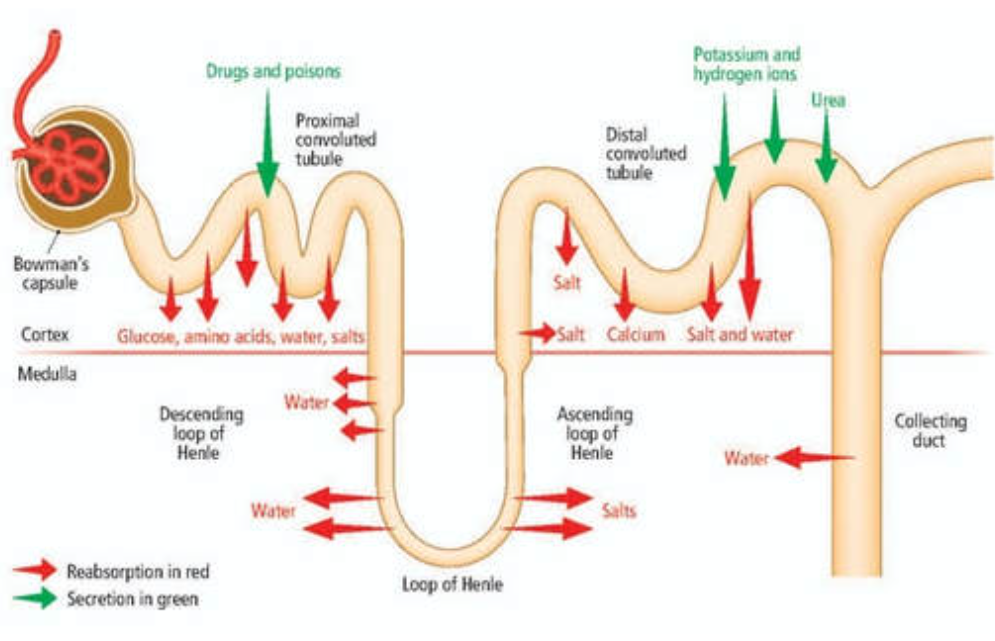
Filteration:
OCCURS IN THE BOWMANS CAPSULE.
• The renal artery divides into different artioles & then into a capillary network (Glomerulus) at the top of each nephron.
• The bowman's capsule surrounds each glomerulus & it is here that small molecules are forced into blood under pressure out of the plasma & into lumen of bowman's capsule...forming glomerular filtrate.
Explain the importance of blood entering the glomerulus under pressure:
As efferent artioles are narrower than afferent atrioles & as a result, force filtering the plasma.
State two reasons why there are many capillaries surrounding the PCT, loop of Henle and DCT:
Re-absorption & secretion
Reabsorption:
OCCURS IN THE DCT.
Glomerular filtrate passes from bowman's capsule into the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) & elements (Glucose, water, salt) are reabsorbed back into blood in Efferent arteriole.
- Water = osmosis
- Salt ect = Active transport (energy)
Everything gets filtered except...
Large proteins & blood cells!
Some substances are not reabsorbed...
EG: Urea & some water.
• They pass as urine, into pelvis of kidney & for bladder for storage.
ADH (anti-diuretic Hormone)
-> Controls reabsorption of water in the distal convoluted tubule.
- Produced by pituitary gland.
How does ADH work?
ADH works by making the walls of the Distal Convoluted Tubule more permeable, thus more H20 is reabsorbed into blood.
Two gases excreted from body:
CO2 & H20.