Karyotypes: variation, types, causes
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is aneuploidy?
Chromosome number differs from normal euploid cells by part of a chromosome set
What are 2n, 2n+1, 2n-1, 2n-2?
Euploid, trisomic, monosomic, nullisomic
How is aneuploidy different from polyploidy?
Organisms with more than 1 COMPLETE sets of chromosomes are an example of polyploidy
Polyploidy occurs when the genome of a species is duplicated during meiosis or when the genomes of two species are hybridised
Aneuploidy involves the duplication of only 1+ chromosomes when an organism usually only has two copies (3 copies of a chromosome instead of 2, for instance)
How can structural variations of the chromosome lead to aneuploidy?
Chromosomes can undergo:
deletions
duplications
inversions- pericentric or paracentric
translocations
What is a deletion?
Part of a chromosome is deleted- deletes the genes on this part of the chromosome
What is duplication?
Part of a chromosome is duplicated- leads to having more than one copy of the same gene on a chromosome
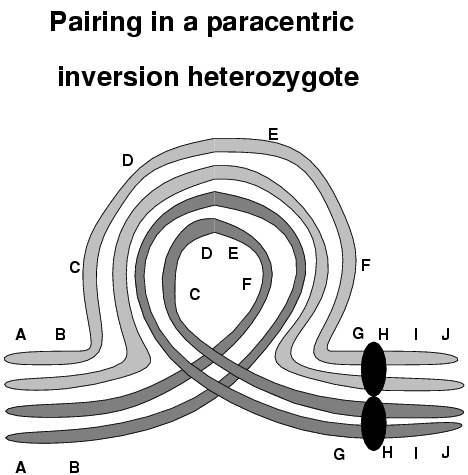
What is a pericentric inversion?
An inversion that spans the centromere- the order of genes on a chromosome gets inversed
Can form an inversion loop= loop is required otherwise pairing cannot occur properly, phenotype of individual likely normal but pairing and segregation affected.
Offspring can have recombinant DNA
What is a translocation?
Parts of a chromosome translocate to another chromosome and the genes with it. Can be reciprocal or nonreciprocal
Outline aneuploidy caused by nondisjunction
Spindle fibres from a single pole attach to the centromeres of BOTH homologous chromosomes of a pair
Spindle fibres from a single pole attach to the centromere of BOTH sister chromatids
Leads to one cell having too many copies of the chromosome and one cell having not enough (or none)
Why does age increase the risk of nondisjunction?
Eggs (meiocytes) arrested at diplotene during prophase I before birth
Bivalents held together by chiasma
Chiasma must remain intact until meiosis resumes during the menstrual cycle
As time passes, the chance of bivalent breakdown increases
Most nondisjunction occurs at Anaphase I
How do deletions and duplications occur?
May occur spontaneously in the gonads of parents with otherwise normal sets of chromosomes
More likely to occur if there are pre-existing structural variants, eg recombination in a parent with a heterozygous inversion
What are two causes of spontaneous chromosomal rearrangements?
Breaking and rejoining- breaks and rejoins of broken ends causes rearrangement
Crossing over between repetitive DNA- non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR), homologues misalign while pairing
How do chromosomal rearrangements change pairing structures?
Can lead to inversion loo[s, cross-shaped quadrivalents, for instance