Intro to digital marketing - Chapter 4: On site SEO
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
URL
Gets heavy ratings in relevance calculation, and thus keywords should be used
e.g. If an owner picks the keyword of chicken for a category page, then the page’s URL should be http://www.foodworld.com/chicken.html
On-site
Formatting of content on the website
Search engine optimization
Designing and making a site with webpages that are relevant to consumers are searching for (search terms)
The goal of search engine optimization
To naturally rank webpages as highly as possible in the search engine results page to make traffic
The goal of search engine optimization (con’t)
To rank well for as many searches as possible by improving a site’s search ranking on already existing searches, as well as begin new rankings on new searches
Title tag
Shows up at the top of a browser when one gets to that page; also gets heavy weightings in calculating relevance
e.g. Women’s Sandals + FREE SHIPPING | Shoes | Zappos.com
Main content
Using a target keyword at least once in the page’s main content
Keyword stuffing
An ineffective tactic of inserting a keyword phrase too often
Image alt text and file name
Properly labelling images so search engines can “see” the content of an image
Alternative text
A label/tag that indicates an image’s content and should describe the image as well as incorporate keywords
Anchor text
An objective third-party description of a web page
Internal link
Links from one page to another; should use the linked to page’s target keyword phrase as the anchor text of that link
How should sites use links
A site should use several links among its pages for SEO purposes and to increase navigability of the site
Ranking
The position a site shows up in the SERP within the natural search results
The first step in conducting on-site SEO
Picking a list of search phrases to target for improvement in search rankings
The 4 factors choice of target search phrases should be based on
Relevance of Search Intent
Traffic
Competition
Current ranking
Relevance of search intent
A site that sells one thing shouldn’t try to rank for the search phrase of another thing
Relevance of search intent (con’t)
A company that sells sheds would want to rank highly in relevant search phrases like “Quality sheds.”
The desired phrase should be relevant to the product but broad enough to capture a large number of searches
Traffic
Balancing keyword relevance with keyword search demand
Google’s Keyword planner
Provides free estimates of the monthly search volume of a search phrase
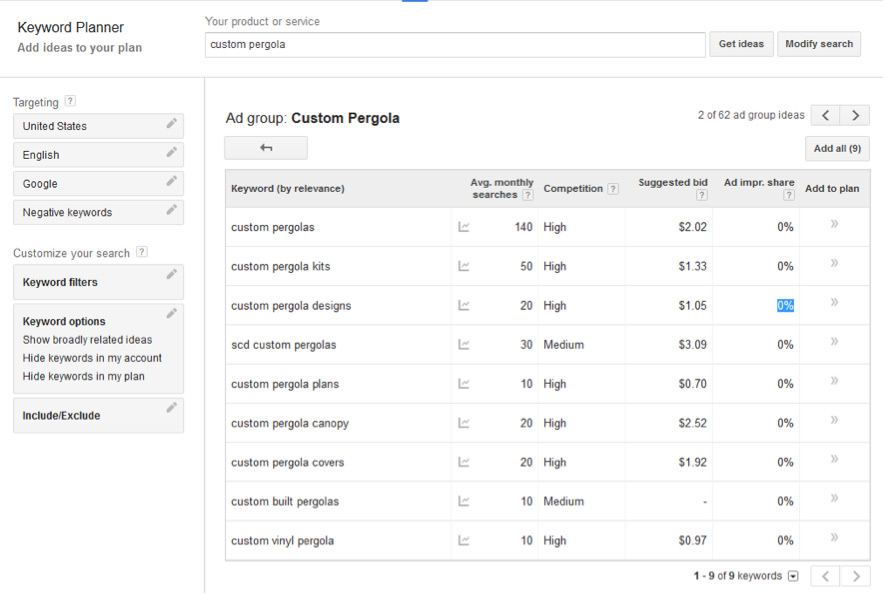
How to gage competition
See what sites show up
If the links to those sites are optimized perfectly for a keyword
Small websites and competition
Smaller sites have more chances of success when going after long-tail keyword phrases
e.g. Gold Rolex watch
Long tail keywords
Multi-word phrases which are extended or more specific versions of fat head terms; sites can rank similarly for multiple long tail terms when the words are alike
e.g. White Nike shoes
Fat head term
Highly popular, short, and broad keywords that receive a massive amount of search volume; has more competition
How to improve current ranking
Improve the key phrases that will yield higher rankings and search results
Mapping keywords to pages
Matching each target keyword phrase to a page in the website to maximize the relevance of the page to the keyword, or sometimes making entirely new pages dedicated to keywords
Mapping keywords to pages example
A jeweller would place handmade earrings on the homepage and product categories (e.g. hoop earrings, drop earrings, etc) on the category pages, which would further link to a subcategory page that eventually go to product pages
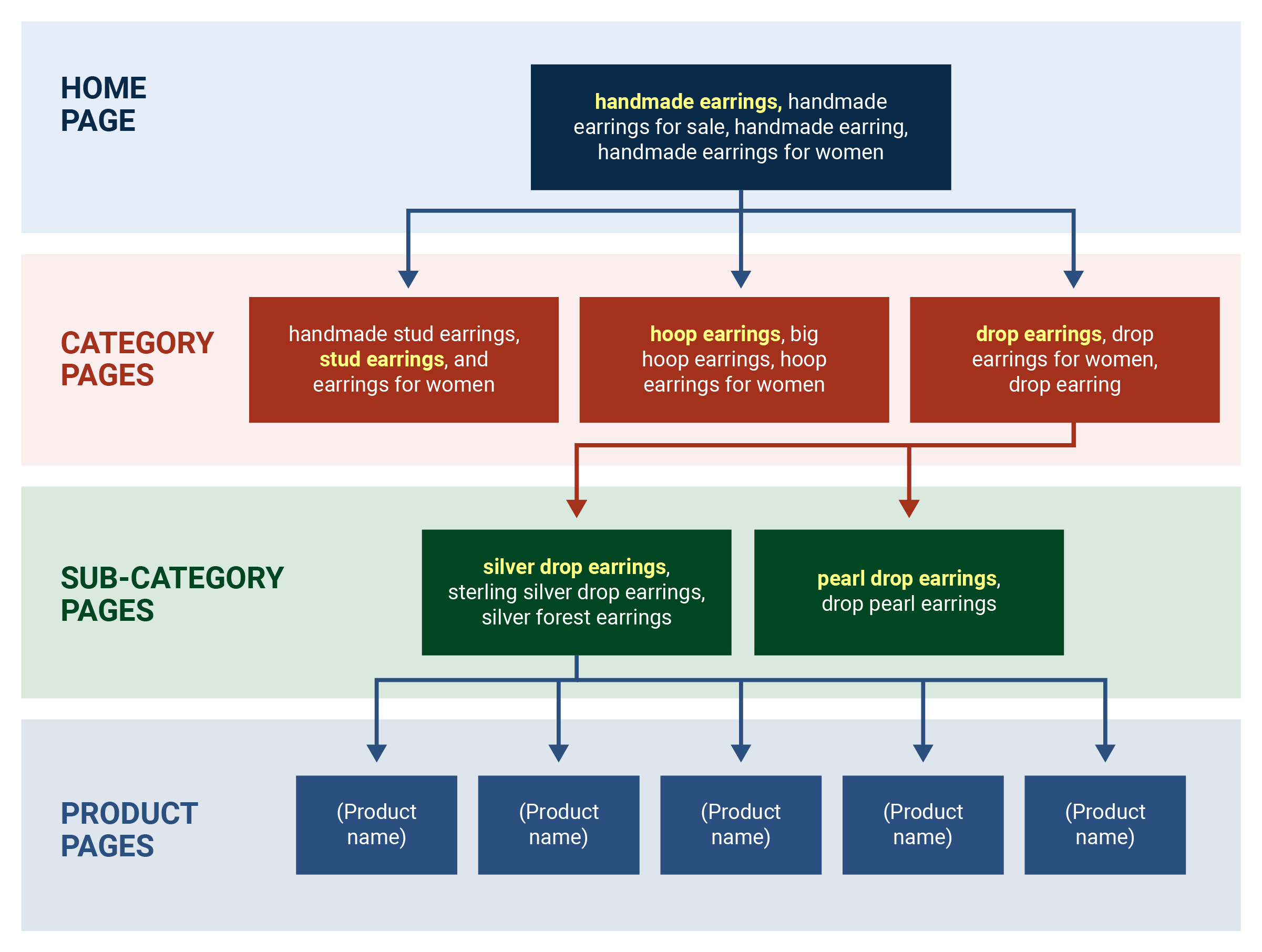
Three reasons for importance mapping individual keyword phrases to individual pages
Reminds the site devs which keywords need to be put into the page content to ensure high relevancy scores
Ensures the right web page is displayed for the right search
Ensures a site isn’t unintentionally multiple pages for the same keyword (keyword cannibalization
How to show original content
Use the rel=”canonical” tag in the page code to signify the original version of content to avoid punishment for unoriginal content from search engines
Meta descriptions
A short, 160 character description of a web page’s content; is included in the <HEAD> data and is hidden from viewers; unique metas are a quality signal
Short load times
Cater to the short attention span of users by finding the cause of and fixing long load times
Fresh content
Providing users with news and regular updates to show search engines that the site belongs to active and regular users
e.g, sales, new products, articles, Q&As, etc
Quantity content
Having at least 100 words of content, as users are likely to find good info on a site with lots of content
Bounce rate
The % of sessions that start on a page that has only 1 view, should be kept low by having good content on the site and search relevance to the search term
Quality content
Creating quality content instead of crafting content for search engines in light of AI and other similar tools
URL Inspection Tool
A tool in the Google Search Console site that allows webmasters to assess if Google is properly loading pages
Insufficient internal linking
If pages on a site have no inbound links from other pages which may lead to engines not having a way to find those pages
Punishment for past crimes
When a site receives consequences for manipulating a search engine into giving it good rankings, can be fixed by complying with search engine guidlines
Dirty sitemaps
If XML sitemap (a map that helps search engines properly index a site) is broken or otherwise has errors, then it can be a sign the site isn’t trustworthy or poorly managed
Poor mobile optimization
A site that has poor usability on mobile devices won’t rank well on searches done on a mobile device; sites that aren’t mobile-optimized will be at a disadvantage, given the rise of mobile web traffic
The three core web vitals
Large colourful paint (LCP)
First input delay (FID)
Cumulative layout shift (CLS)
These three metrics should be kept as low as possible
Large colourful paint (LCD)
How long it takes for a site’s content to appear
First input delay (FID)
How long it takes for a user to interact with anyone
Cumulative layout shift (CLS)
If the content is shifted when another piece loaded later on the page
Poor security
When a site doesn’t have transport layer security encryption and is marked as “non-secure”
Local intent
When a user wants search results which are close by
Local pack
A list of three local businesses that match the search and are shown on the map
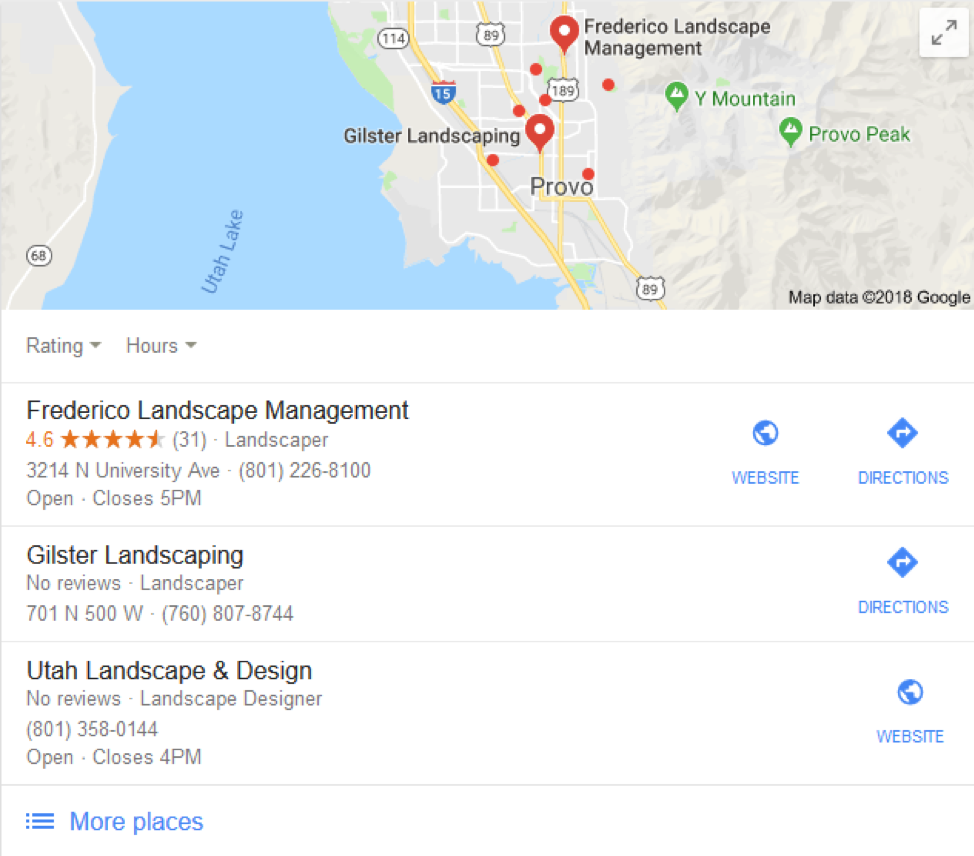
Local pack (con’t)
It can vary depending on what’s searched up
e.g.
Snack local pack (for restaurants),
ABC local pack (Branded terms like Starbucks and Gas stations)
Sponsored local pack
Organic search results and the results page
A results page will show organic results, but in a usual but localized manner
e.g. A search on Richmond Pizza joints will show a local pack on top, but have the second result be a Yelp article on Richmond Pizza joints
Reviews
Companies should get reviews from customers, as reviews have great weight in local rankings
Structured citations
References and listings from other websites; consistency is important and thus firms should check for it and ask for corrections when inaccuracies are found
e.g. Yelp
Name, Address, and Phone number (NAP)
Providing similar info about a firm across locations
e.g, Toys R Us, shouldn’t be referred to as “Toys r us”
My Business
Registering and verifying a business with Google so they know of the firm’s validity and thus show the firm on search results
The Panda Update
An algorithm change that collects data from users to see what makes a page appealing, and then ranks sites accordingly after running that info through machine learning algorithms
The Pigeon Update
An overhaul of Google’s local rankings by improving the accuracy of results based on the user’s locations and including traditional quality signals like links in local search results
The Hummingbird Update
An algorithm replacement that’s faster and more precise by interpreting the intent and meaning of a search phrase (contextual interpretation)
e.g. If you looked up Mount Everest’s elevation, Google will see that you want to know it’s actual elevation
RankBrain
Helps determine a site’s ranking
Mobile-first ranking
Giving favour to mobile-friendly sites by showing them in search results and removing sites that weren’t mobile-friendly
Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT)
An algorithm made by AI researchers at Google that provides more accurate search query responses
Knowledge graph
An info repository about people, places, and topics that can be shown directly on the results page
Featured Snippets and their caveats
Needs a lot of sophistication as the search engine needs to understand the specific piece of info being searched up by the user and separate it from the other info about that topic
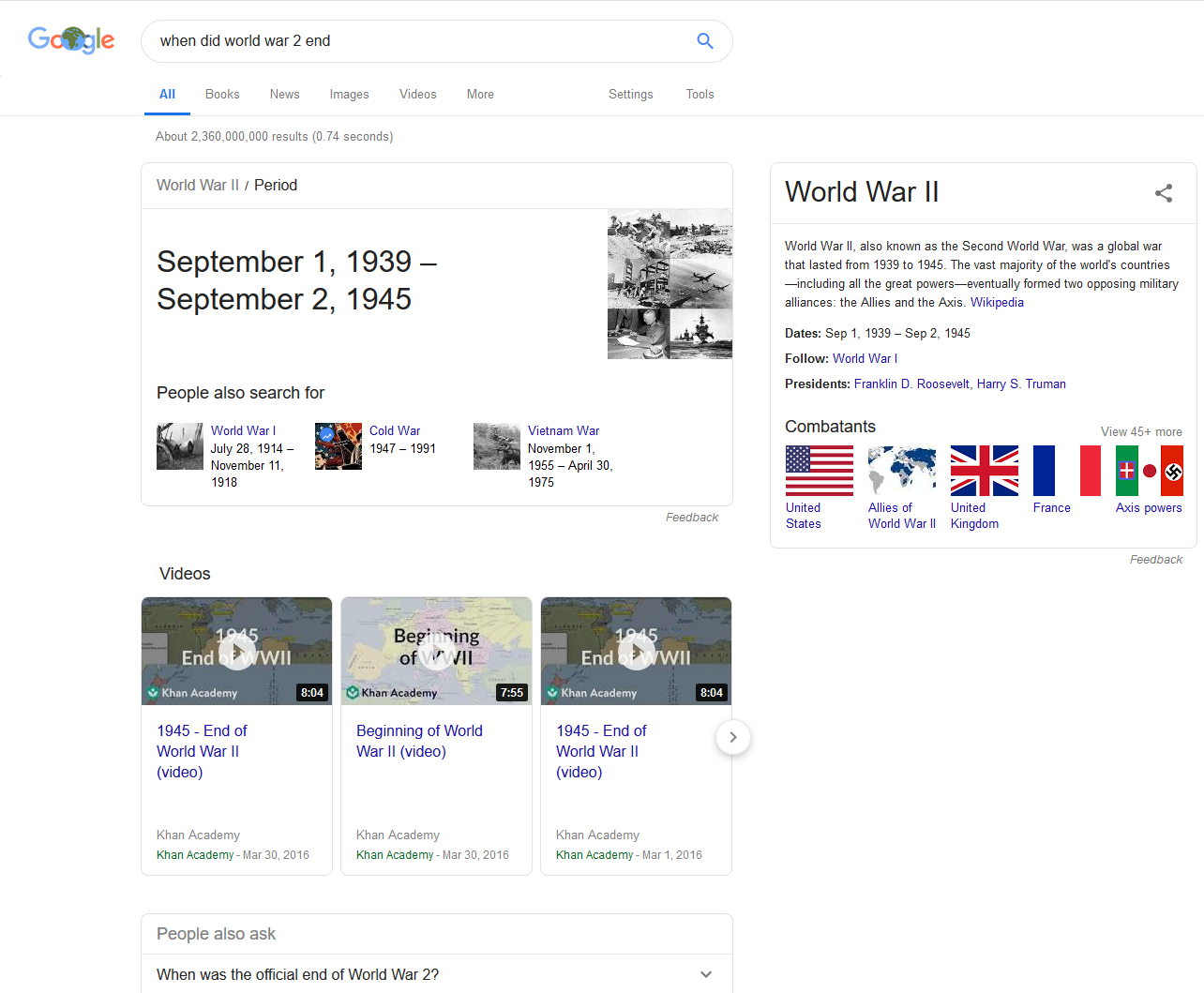
Featured Snippets and their caveats (con’t)
Firms can format their info in plain HTML text and add schema mark-up to ensure featured snippets provide accurate info about their business
Voice search
Using the voice to input searches and give commands like “Focus on long tail keywords” and “Keep Google My Business up-to-date
Crawling
Finding and updating web content
Caching
The HTML code of a webpage that gets sent to a repository
Indexing
Reconfiguring each web page as a hit list
What determines Google’s SERP rank?
Relevance + Quality
Breadcrumbs
Shows were you came from and how you initially got to the page
How to locate alt text
Right click on any given image, header, or anchor text and selecting “inspect to bring up the HTML code