ACE University Wrong Answers/Struggle
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Section I - Which of the following is WITHIN the ACE Certified Personal Trainer scope of practice regarding training clients with weight-loss goals?
Creating therapeutic exercise programs to help clients with low-back pain to improve core stability
Evaluating a client's nutrient intake to guide meal planning
Recommending nutritional supplements only after conducting extensive research on their effectiveness and safety
Designing exercise programs that lead ot increased energy expenditure and positive changes in body composition
Designing exercise programs that lead ot increased energy expenditure and positive changes in body composition
Section I - Which of the following would be OUTSIDE the scope of practice for ACE Certified Personal Trainers?
Offering solutions to a client who exhibits signs of depression that impact exercise adherence
Teaching a client techniques for self-myofascial release
Leading a client through exercises ot improve shoulder stability
Discussing proper techniques and appropriate uses for dynamic stretching
Offering solutions to a client who exhibits signs of depression that impact exercise adherence
Section I - A client has soreness after a weekend tennis tournament. Which of the following is an appropriate action that is WITHIN the scope of practice for ACE Certified Personal Trainers?
Provide deep tissue massage to the affected area
Discuss proper techniques for stretching the affected muscles
Suggest using common, low-dosage anti-inflammatory medications
Implement a therapeutic exercise program to reduce soreness and improve function
Discuss proper techniques for stretching the affected muscles
Section I - A client has been released from physical therapy for shoulder impingement and si now working with an ACE Certified Personal Trainer. Which course of action would be MOST appropriate for the personal trainer to take?
Continue to implement the physical therapy exercises
Progress the client to strength and power training for the upper body
Build on the work done in physical therapy
Evaluate the progress of the client's rehabilitation
Build on the work done in physical therapy
Section I - What is the MOST appropriate solution for an ACE Certified Personal Trainer to provide to a client who has tight illotibial (IT) bands?
Refer the client to a physical therapist
Teach the client to perform self-deep tissue massage
Teach the client self-myofascial release techniques
Prescribe a series of ballistic stretches
Teach the client self-myofascial release techniques
Section I - Which exercise would be MOST appropriate in the Movement Training phase of the ACE IFT Model Muscular Training component?
High marches
Plyometric squat
Butt kicks
Body-weight lunges
Body-weight lunges
Section I - An ACE Certified Personal Trainer begins working with a new client who has obesity and is apprehensive about beginning an exercise program. Which of the following approaches would be MOST effective in helping the client achieve early success in this first session?
Administer the Rockport Fitness Walking Test to determine the client's cardiovascular fitness
Conduct the push-up and body-weight squat tests to determine upper- and lower-body strength to inform exercise program design
Have the client perform exercises that provide the trainer with basic feedback about the client's current movement abilities and fitness
Assess the client's body composition using skinfold measurements to record the client's baseline body-fat percentage
Have the client perform exercises that provide the trainer with basic feedback about the client's current movement abilities and fitness
Section V - Which of the following risk-management approaches involves modifying the risk by removing part of the activity?
Reduction
Avoidance
Transfer
Retention
Reduction
Section V - The breach of duty directly caused the injury or harm — not just coincidentally, but as a foreseeable outcome of the trainer’s actions or inactions.
Proximate Causation
Section V - Which of the following scenarios BEST describes an ACE Certified Personal Trainer working as an independent contractor?
The personal trainer typically only works for one employer
The health club provides continuing education on a quarterly basis for personal trainers
The personal trainer receives a salary plus commission from a health club
Personal-training services are not a core function of the health club's business operations
Personal-training services are not a core function of the health club's business operations
Section V - Which of the following would provide the BEST security when storing client exercise programs online?
A password-protected file in a virtual training program or app
A folder at the membership desktop ot be entered into the facility's computer
A folder in the filing cabinet in the shared personal-training office
A shared tablet owned by the health club facility located behind the front desk
A password-protected file in a virtual training program or app
Section V - Which of the following is WITHIN the scope of practice for an ACE Certified Personal Trainer?
Informing a client that a certain food contains a high amount of a specific vitamin
Recommend that a client increase caloric intake of a particular food
Providing a client with a sample food log of what the trainer eats
Recommending a specific shoe brand in response to a client’s request
Informing a client that a certain food contains a high amount of a specific vitamin
Section V - Which of the following scenarios would pose the HIGHEST chance for legal action?
A personal trainer asking another trainer to conduct a client session on their behalf
A personal trainer asking a client to sign a photography release waiver
A personal trainer conducting the same fitness assessments for all clients
A personal trainer cancelling a session at the last minute
A personal trainer conducting the same fitness assessments for all clients
Section II - An ACE Certified Personal Trainer is working with a new client who has had a consistent exercise history. During the interview, the client explains that they enjoy all types of exercise and loves the way a workout makes them feel. Which of the following BEST describes this client's motivation?
Associative motivation
Controlled motivation
Autonomous motivation
Extrinsic motivation
Autonomous motivation
Section II - Which of the following client types is MOST likely ot exhibit positive health behaviors?
A client with an internal locus of control
A client with strong willpower
A client with an external locus of control
A client with a strong emotional state
A client with an internal locus of control
Section II - Which of the following will MOST strongly influence a client's current self-efficacy levels?
Positive feedback from others
Physiological state
Past performance experiences
Mood state and emotional belief
Past performance experiences
Section II - According to the health belief model, which of the following refers to people's perceptions of how likely they are to develop an illness?
Perceived benefits
Perceived seriousness
Perceived susceptibility
Perceived barriers
Perceived susceptibility
Section II - During a training session, a client begins talking about intimate personal issues and problems at home. Which of the following actions is MOST appropriate for the ACE Certified Personal Trainer to take?
Provide some solutions to the problem
Listen and sympathize
Offer advice to the client
Redirect the conversation
Redirect the conversation
Section II - During a training session, an ACE Certified Personal Trainer asks the client to explain what benefits might be gained by increasing their exercise frequency from 2 days/week to 3 days/week. Which of the following BEST identifies the type of communication skill used by the trainer?
Closed questioning
Offering affirmation
Summarizing
Open-ended questioning
Open-ended questioning
Section II - Which of the following is a key consideration when setting goals with a client?
Goals should be positive
Numerous goals should be set to offer many options and choices
Once set, revisiting goals is a waste of time
Goals should be set by the trainer and agreed upon by the client
Goals should be positive
Section II - A client who is beginning to master the hip-hinge basics of a squat and is ready to receive more specific feedback so the movement can be refined and perfected is in which stage of learning?
Cognitive stage
Autonomous stage
Motor stage
Associative stage
Associative stage
Section II - Which of the following components of motivational interviewing is being displayed when an ACE Certified Personal Trainer deliberately pursues the welfare and best interests of the client?
Collaboration
Acceptance
Evocation
Compassion
Compassion
Section II - Which of the following could cause a barrier to exercise fi included in the exercise preparticipation health-screening process for a client?
Time commitment
Current level of physical activity
Desired exercise intensity
Risk-factor profiling or classification
Risk-factor profiling or classification
Section II - Which of the following is a factor identified as an important risk modulator of exercise-related cardiovascular events?
Past physical-activity levels
Current weight
Body mass index
Desired intensity level
Desired intensity level
Section II - If an ACE Certified Personal Trainer makes the following statement early in a preparticipation health screening, which of the following are they trying to accomplish? "Managing your diabetes is important to you. How do you envision me helping to support your goals?"
Breaking down any possible barriers
Asking open-ended questions to get more detail
Trying to collaborate on the client's goals
Creating rapport with the client
Asking open-ended questions to get more detail
Section II - Which of the following forms collects more detailed medical and health information beyond the preparticipation health screening?
Medical release
Lifestyle and health-history questionnaire
Informed consent
Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire for Everyone (PAR-Q+)
Lifestyle and health-history questionnaire
Section II - For the past two months, a client has been following their healthcare provider's exercise guidelines of 30 minutes of indoor cycling at a rating of perceived exertion of 8 (on the 6 to 20 scale), followed by mild stretching. The client has asked the ACE Certified Personal Trainer to add the elliptical machine to incorporate upper-body movements. Which would be the MOST appropriate response?
Explain that, for their safety, a new medical release would be necessary to incorporate additional exercise
Explain that increasing the resistance will increase the RPE above 8 and allow the client's legs to get stronger in preparation for a standing cardiorespiratory exercise machine
Suggest that extending the time on the bicycle to 45 minutes would help better prepare the client for the elliptical
Suggest adding light upper-body muscular training while keeping the stationary biking the same
Explain that, for their safety, a new medical release would be necessary to incorporate additional exercise
Section II - An ACE Certified Personal Trainer's client states they are interested ni using an over-the-counter diuretic for rapid weight loss. Which of the following would be the MOST appropriate response?
Explain the dangers of using such a product
Suggest they maintain adequate water intake to avoid dehydration
Suggest they talk to a pharmacist
Explain that there are other products that are safer to use
Explain the dangers of using such a product
Difficulty or discomfort in breathing; shortness of breath
What is Dyspnea
Temporary loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain — essentially, fainting.
What is Syncope
Difficulty breathing while lying flat; breathing improves when sitting or standing.
What is Orthopnea
Section II - During an initial exercise session, a client presents with symptoms of dizziness and mentions this occasionally occurs during workouts. Which would be the MOST appropriate action by an ACE Certified Personal Trainer?
Continue exercise with caution and seek a healthcare provider's clearance
Modify the current program to a more suitable activity level
Discontinue exercise and have the client seek a qualified healthcare provider's clearance
Create a new program to help address the issues identified
Discontinue exercise and have the client seek a qualified healthcare provider's clearance
Key Characteristics of the DASH Plan
High in:
• Fruits and vegetables
• Whole grains
• Low-fat dairy products
• Lean protein (fish, poultry, beans)
• Nuts and seeds
• Potassium, magnesium, and calcium (blood
pressure-regulating minerals)
Low in:
Sodium (typically ≤2,300 mg/day, or 1,500 mg/ day for more significant effect)
Saturated fat and cholesterol
Red meat, sweets, sugary drinks, and processed
foods
Section II - An ACE Certified Personal Trainer working with a client makes the following statement: "You want to make these changes to manage your blood pressure, avoid medication, and improve your quality of life. What obstacles do you think might get in the way of these goals?" Which of the following BEST identifies the approach the personal trainer is taking?
Communicating openly
Breaking down barriers
Assessing the outcomes
Determining the stage of change
Breaking down barriers
Section II - Which of the following antihypertensive medications increases the excretion of water and electrolytes through the kidneys?
Beta blockers
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
Diuretics
Calcium channel blockers
Diuretics
Drugs that reduce the effects of adrenaline and noradrenaline on the body
What is Beta Blockers?
Section III - Which of the following refers to a resting heart rate (RHR) that is less than 60 beats per minute?
Normal sinus rhythm
Sinus bradycardia
Sinus tachycardia
Elevated sinus rhythm
Sinus bradycardia
A condition where the heart beats faster than normal, with the heart rate typically exceeding 100 beats per minute
What is Sinus tachycardia
Section III - A long-standing client has significantly increased their exercise frequency and intensity to break through a recent plateau. Over the past week, their resting heart rate has averaged 78 beats per minute compared to their typical 70 beats per minute. Which of the following might BEST explain this increase?
Overtraining syndrome
Increased stroke volume
Increased hemoglobin production
Sinus node syndrome
Overtraining syndrome
Section III - According to the ACC/AHA blood pressure guidelines, which ACE uses:
Category Systolic (top) Diastolic (bottom)
_______ - <120 and <80
_______ - 120-129 and <80
_______ - 130-139 or 80-89
_______ - ≥140 or ≥90
Normal
Elevated
Stage 1 Hypertension
Stage 2 Hypertension
EVEN IF one value falls under normal level, if the other value (systolic or diastolic) is over the guideline value, it is elevated or hypertension
The minimum amount of fat required for normal physiological function
Purpose: Hormone production, Thermoregulation, rotection of internal organs, ervous system and reproductive function
What is Essential Fat?
Fat stored under the skin
• Visible fat — contributes to skinfold thickness
• Van be used as an energy reserve and offers insulation, but not critical to survival
What is Subcutaneous Fat?
The general term for body fat tissue
Stores energy, produces hormones (like leptin) and cushions organs
What is Adipose Tissue?
Fat stored around internal organs in the abdominal cavity
High-risk fat — associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease, Type diabetes, and inflammation
What is Visceral Fat?
Section III - Which of the following indicates the average resting heart rate in males?
72 to 76 beats per minute
54 to 59 beats per minute
79 to 82 beats per minute
60 to 70 beats per minute
60 to 70 beats per minute
Section III - Insufficient blood flow to tissues, usually due to blockage or narrowing of arteries
It can affect the heart, brain, limbs, etc.
If prolonged, leads to tissue damage or death
What is Ischemia?
Complete blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle, resulting in tissue death
Usually caused by a ruptured plaque leading to a blood clot in a coronary artery
What is myocardial infarction (heart attack)?
Section III - Which of the following describes the point at which ventilation begins to increase in a nonlinear fashion?
Respiratory exchange ratio (RER)
Heart-rate reserve (HRR)
Second ventilatory threshold (VT2)
First ventilatory threshold (VT1)
First ventilatory threshold (VT1)
Section III - Which of the following is the RECOMMENDED fluid intake prior to exercise?
12-15 mL/kg (0.41-0.51 oz/lb)
2-4 mL/kg (0.68-0.14 oz/b)
5-7 mL/kg (0.08-0.11 oz/lb)
8-10 mL/kg (0.27-0.34 oz/lb)
5-7 mL/kg (0.08-0.11 oz/lb)
Section III - What is the RECOMMENDED weekly or biweekly exercise duration progression for cardiorespiratory training over the first four to six weeks of training a new client?
5%
20%
15%
10%
10%
When to progress to Fitness Training?
A minimum of 20 minutes of steady-state cardiorespiratory exercise in zone 1 on at least three days per week
Cardiorespiratory interval training is typically introduced during which stage of training?
Fitness Training
Anaerobic power is typically performed during which of the following stages of training?
Performance Training
Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
What is Cardiac Output?
Section III - An ACE Certified Personal Trainer is working with a client who wants to run a 10K. Which of the following conditions would MOST likely prohibit the client from participating in a ventilatory threshold assessment?
Asthma
Diabetes
Overweight
Allergies
Asthma
Asthma is the only condition listed that:
Directly affects the respiratory system
Can interfere with breathing during exercise
Section III - Which portion of the spine consists of five fused vertebrae?
Cervical
Соссух
Sacrum
Lumbar
Sacrum
Region - # of Vertebrae Function
Cervical | 7 (C1-C7) | Supports the head and allows for neck mobility (nodding, rotation) |
Thoracic | 12 (T1-T12) | Anchors the rib cage, provides upper back stability |
Lumbar | 5 (L1-L5) | Handles most of the body's weight; involved in lifting & movement |
Sacrum | 5 fused (S1-S5) | Forms the posterior pelvic wall; connects spine to lower body |
Coccyx | 3-5 fused | The tailbone; provides attachment for pelvic floor muscles |
Exercises that involve contracting muscles without changing their length.
What is Isometric Exercise?
A series of connected joints where the distal (end) joint is fixed or restricted in movement.
What is Closed kinetic chain?
Section III - An ACE Certified Personal Trainer is working with a client who has a bench press repetition range of 12-15. The client had been consistently bench pressing 175 pounds (79 kg) for 12 repetitions, and can now complete 15 repetitions at the same weight. Utilizing the double-progression training protocol, which of the following would be the MOST appropriate progression?
Perform 10 repetitions of 195 pounds (88 kg)
Perform 10 repetitions of 185 pounds (84 kg)
Perform 12 repetitions of 195 pounds (88 kg)
Perform 12 repetitions of 185 pounds (84 kg)
Perform 12 repetitions of 185 pounds (84 kg)
When the top of the rep range is reached with proper form, increase the weight by ~5%; Return to the lower end of the rep range and repeat the progression cycle
Step 1: Progress Repetitions
Keep the same weight
Build reps up to the top of the target rep range (12-15 reps)
Step 2: Increase Load (Weight)
When the top of the rep range is reached with proper form, increase the weight by
Return to the lower end of the rep range and repeat the progression cycle
Load increase formula:
New Load = Current Load x 1.05 (5% increase)
Week 1-4 - 175 lbs, 12-15 reps
Week 5 - After mastering 15 reps, 185 lbs, back to 12 reos
What is Double-Progression Formula?
Section III - Which of the following training principles refers to loss of muscle strength due to termination of a regular muscular-training program?
Overload
Overtraining
Reversibility
Atrophy
Reversibility
Recommended repetition tempo for beginners learning new exercises, especially in resistance training
What is 6 seconds per rep?
2-3-1 Tempo:
Eccentric (2 seconds): The lowering phase of the movement.
Isometric (3 seconds): The pause or hold at the bottom of the movement.
Concentric (1 second): The lifting phase of the movement.
Section III - Which of the following is a correctible factor for a client whose assessment identifies muscular imbalances and postural deviations?
Structural deviation
Lack of joint stability
Joint trauma from injury
Congenital condition
Lack of joint stability
Anterior pelvic tilt = when the pelvis tilts forward, causing:
The lumbar spine to arch excessively
The hip flexors to tighten and the glutes/abdominals to weaken • A visible “swayback” or deep low-back curve
What is Lordosis?
Excessive outward curvature of the thoracic spine (upper back)
What is Kyphosis?
A bone disease where bones become weak and brittle
What is Osteoporosis?
Lateral (side-to-side) curvature of the spine
What is Scoliosis?
Section III - Which of the following assessments would MOST likely be contraindicated for a client with low-back pain?
Unipedal stance test
Static postural assessment
Y-balance test
McGill's Torso Muscular Endurance Battery Test
McGill's Torso Muscular Endurance Battery Test
List of Static Balance Assessments:
Assessment | Safe for Low-Back Pain? | Why? |
Unipedal Stance Test | Usually safe | Tests balance - minimal spinal loading |
Static Postural Assessment | Very safe | Observational only |
Y Balance Test | Maybe — depends | Mild core activation, but can stress low back slightly |
McGill Test Battery | Contraindicated | Involves sustained trunk loading and spinal stress |
Section III - Which of the following identifies the PRIMARY purpose of the Thomas test?
To evaluate the length of the muscles involved in hip flexion
To evaluate the length of the muscles involved with trunk flexion
To evaluate the length of the muscles involved with trunk extension
To evaluate the length of the muscles involved in hip extension
To evaluate the length of the muscles involved in hip flexion
The central part of the human body, excluding the head, neck, and limbs. It encompasses the following anatomical regions:
Thorax: The chest cavity containing organs such as the heart, lungs, and diaphragm.
Abdomen: The area below the thorax, containing organs like the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas.
Pelvis: The lower part of the trunk, supporting the reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum.
Trunk
Section III - During a squat pattern assessment, the ACE Certified Personal Trainer observes the client is driving the knees forward during the descent of the squat. Which of the following is MOST likely causing this compensation?
Quadriceps dominance
Lumbar dominance
Hamstring dominance
Glute dominance
Quadriceps dominance
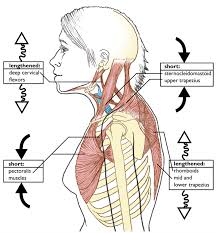
Section III - From the side view of a standing row assessment, the ACE Certified Personal Trainer notices the client's head migrates forward. Which of the following muscles are MOST likely underactive?
Levator scapulae
Mid and lower trapezius
Cervical spine flexors
Rhomboid major and minor
Cervical spine flexors
Epley Formula - Measuring 1RM (rep max)
This formula is reasonably accurate for 10 reps or fewer
1RM = Weight x (1 + {Reps/30})
Section III - An ACE Certified Personal Trainer is developing a Performance Training program for a client. What percentage of time should be spent training in zone 1?
70 to 80%
40 to 50%
85 to 95%
55 to 65%
70 to 80%
Section III - Which of the following is a PRIMARY characteristic of Functional Training for muscular fitness?
Focus on establishing/reestablishing postural stability and kinetic chain mobility
Section III - Which of the following describes the MOST appropriate time for a client to perform plyometric drills in a training session?
In the middle, to serve as the highest effort before working back down
At the beginning, following a dynamic warm-up
At the beginning, following self-myofascial release and static stretching
At the end, before static stretching and after self-myofascial release
At the beginning, following a dynamic warm-up
Why?
Plyometric drills are explosive, high-intensity movements that
require:
Maximal neuromuscular effort
Full central nervous system (CNS) readiness
Proper joint preparation
Stored elastic energy from tendons and muscles
So they need to be performed: Early in the workout, when the client is not fatigued and fully primed — after a dynamic warm-up.
Section III - Which of the following is the recommended plyometric training volume for a client with some plyometric experience?
100 to 120 contacts per session
80 to 99 contacts per session
140 to 160 contacts per session
121 to 139 contacts per session
100 to 120 contacts per session
What the heck is a “contact”?
One foot or hand striking the ground or a surface during a landing or jump.
Experience Level & Plyometric Volume
Beginner - 80–100 Contacts (recommended)
Intermediate - 100–120 Contact (recommended)
Advanced - 120–140+ (recommended)
Section III - An ACE Certified Personal Trainer is facilitating a stretching session with a client. The client performs a passive 10-second pre-stretch, then pushes against the force provided by the personal trainer. Which of the following BEST identifies this type of stretching?
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF)
Myofascial release
Ballistic
Dynamic
Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF)
Wrong: Ballistic - Considered risky and outdated for most general populations
A stretching technique that combines static stretching with isometric contractions to improve flexibility and range of motion.
It involves stretching a muscle group, then contracting the muscle against resistance while still stretched, followed by stretching the muscle further.
What is Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF)?
Section IV - Which hormone facilitates energy intake when energy storage is too low
Leptin
Insulin and glucagon
Send blood glucose into the body for use
RDA’s recommended protein amount
1.2 to 1.7 grams per kg of body weight per day
Section IV - Which of the following is the MOST appropriate cardiorespiratory assessment to determine intensity levels for a deconditioned client?
Physician-supervised VOmax test
Submaximal cycle ergometer test
Talk test
Rockport walking test
Talk test
It’s safe, easy, and requires no equipment
It’s done in real time during any activity (walking, cycling, etc.)
It helps identify the first ventilatory threshold (VT1) — the point where speaking becomes noticeably harder
RPE 4
Start of discomfort
Talking becomes slightly strained
Approaching VT1
ACE’s RPE Scale (0–10)
RPE | Perceived Exertion | Corresponds to |
|---|---|---|
0 | Nothing at all | Resting, sitting |
1–2 | Very light | Easy walking, casual pace |
3–4 | Light to moderate | Breathing heavier but still comfortable | Approaching VT1 |
5–6 | Moderate | Noticeably increased breathing, can still talk |
7–8 | Vigorous | Challenging, can speak but with effort | Approaching VT2 |
9 | Very hard | Nearly max effort |
10 | Maximal effort | Exhausting, can’t sustain |
Section IV - Which of the following is the MOST important factor for an ACE Certified Personal Trainer to consider when designing an initial exercise program for a client with overweight or obesity?
Selecting exercises that the client will enjoy
Collaborating with a registered dietician to include a proper nutrition plan
Creating a program that will yield a 10% weight loss in the first 6 months
Establishing a social support system
Selecting exercises that the client will enjoy
Intensity
Force per movement (e.g., speed, load, impact)
Section IV - When increased too much or too soon, which of the following factors MOST increases the risk of potential musculoskeletal injury in a client with overweight or obesity?
Volume
Intensity
Time
Frequency
Intensity
Section IV - Which of the following types of exercise would be CONTRAINDICATED for a client with overweight or obesity?
Jumping
Recumbent cycling
Water exercise
Walking
Jumping
High impact on joints
Jumping increases ground reaction forces, which scale with body weight
Can stress knees, ankles, hips, especially if there's already poor joint alignment or mobility
Lower neuromuscular control
Clients with overweight may lack coordination or strength for safe landings
This increases risk of sprains, falls, or compensatory patterns
Higher injury risk without greater benefit
Section IV - A new client with low-risk coronary artery disease wants to start a muscular-training program with an ACE Certified Personal Trainer. Which of the following is the BEST initial program design?
Using selectorized machines (40-60% of 1-RM), complete 2-3 sets of exercises for all major muscle groups
Using free weights (40-60% of 1-RM), complete one set of exercises for ail major muscle groups
Using free weights (65-80% of 1-RM), complete one set of exercises for all major muscle groups
Using selectorized machines (65-80% of 1-RM), complete one set of exercises for all major muscle groups
Using free weights (40–60% of 1-RM), complete one set of exercises for all major muscle groups
Low-to-moderate intensity (40–60% 1-RM)
Helps build muscular endurance without spiking blood pressure or heart rate
One set minimizes initial volume
Allows the trainer to monitor response and tolerance closely
Reduces risk of overexertion early on
Section IV - Which of the following would be a recommended muscular-training program for a client with osteoarthritis?
Frequency: 1-2 days/week, Intensity: 30-40% of 1-RM, Time: 2-4 sets of 6-7 exercises
Frequency: 5-6 days/week, Intensity: 50-80% of 1-RM, Time: 2-4 sets of 8-12 exercises
Frequency: 2-3 days/week, Intensity: 30-40% of 1-RM, Time: 2-4 sets of 6-7 exercises
Frequency: 2-3 days/week, Intensity: 50-80% of 1-RM, Time: 2-4 sets of 8-12 exercises
Frequency: 2-3 days/week, Intensity: 50-80% of 1-RM, Time: 2-4 sets of 8-12 exercises
Clients with osteoarthritis (OA) benefit from progressive resistance training — it:
Strengthens muscles around the joints, which reduces pain and improves function
Enhances joint stability and mobility
Maintains bone density, which is key for aging populations
Chronic, inflammatory, autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and potential joint damage. It's considered an autoimmune disease because the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, leading to inflammation in the lining of the joints.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)?
Section IV - Which of the following BEST defines exercise-induced bronchoconstriction?
Permanent narrowing of the airways following moderate to vigorous exercise
Permanent narrowing of the airways following very light to light exercise
Temporary narrowing of the airways following very light to light exercise
Temporary narrowing of the airways following moderate to vigorous exercise
Temporary narrowing of the airways following moderate to vigorous exercise
Section IV - Which of the following puts children at greater risk of heat-related illnesses compared to adults?
Lower ratio of body surface area to mass
Higher cardiac output
Diminished sweating capacity
Higher exercise economy
Diminished sweating capacity
What is the recommended frequency of aerobic activity for children and adolescents?
Four days per week
Five days per week
Six days per week
Seven days per week
Seven days per week
Section IV - Which of the following should be the focus of a training program performed early in a pregnancy when designing a program for a pregnant woman?
Posterior leg and trunk strength
Upper-body strength
Body-weight exercises
Low-back discomfort
Posterior leg and trunk strength
Section IV - What are the ACOG recommendations for a woman to resume exercise after delivery?
Begin slowly and gradually increase duration, frequency, and then intensity
5-10 minutes three times per week
Daily activity of 5-10 minutes
20-30 minutes three times per week
Begin slowly and gradually increase duration, frequency, and then intensity