R3.2.9 Oxidation reactions of the alcohols
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
1
New cards
Oxidizing agents for alcohols
Acidified potassium dichromate or potassium manganate.
Color change: orange to green (Cr₂O₇²⁻ → Cr³⁺).
2
New cards
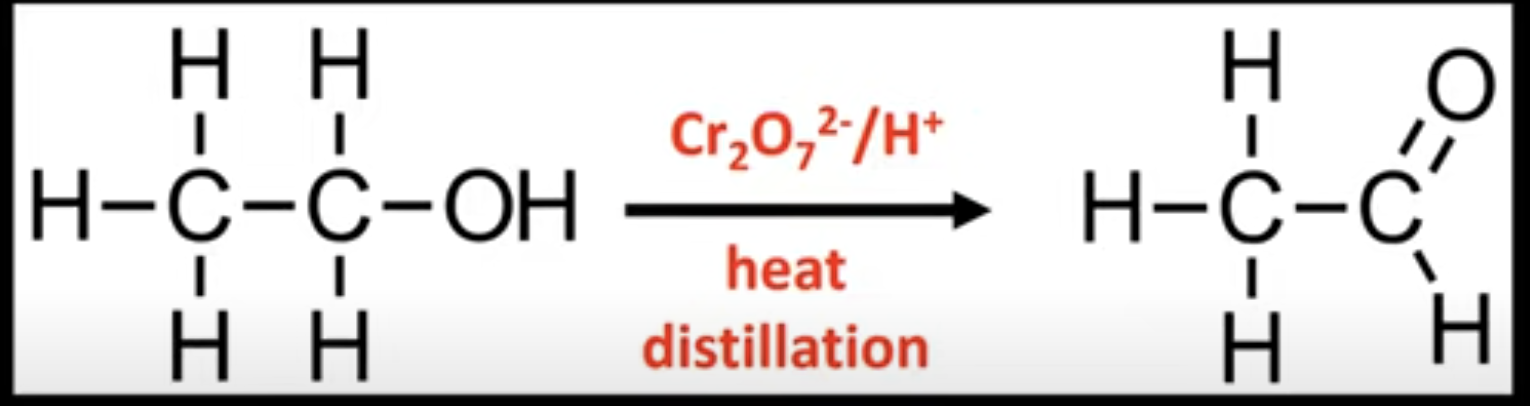
Partial oxidation of primary alcohols
Forms aldehydes.
Conditions: heat and distillation, excess alcohol.
Aldehyde is distilled off.
3
New cards
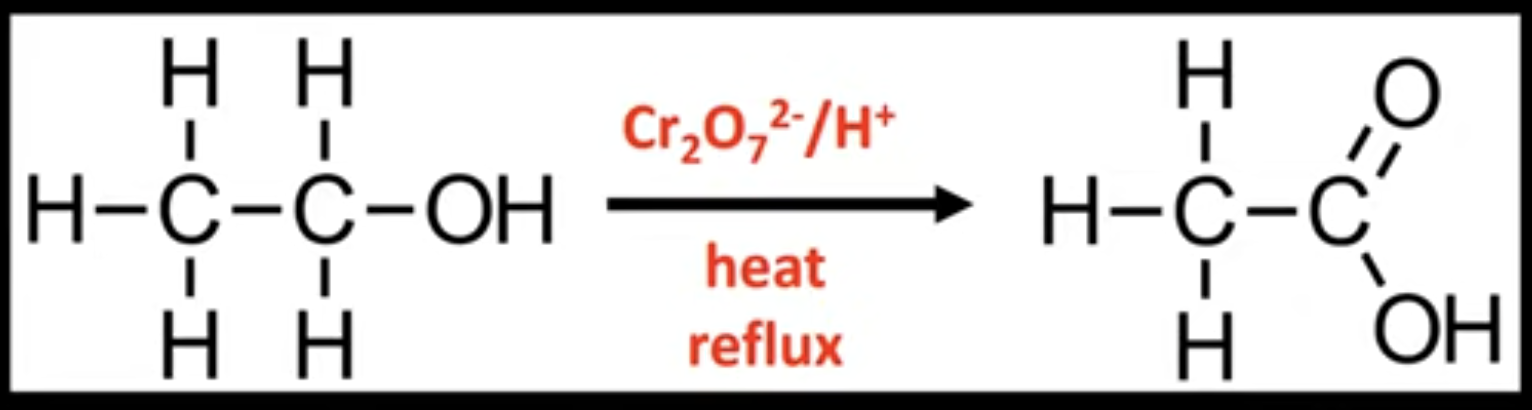
Complete oxidation of primary alcohols
Forms carboxylic acids.
Conditions: heat under reflux, excess oxidizing agent.
Uses reflux condenser.
4
New cards
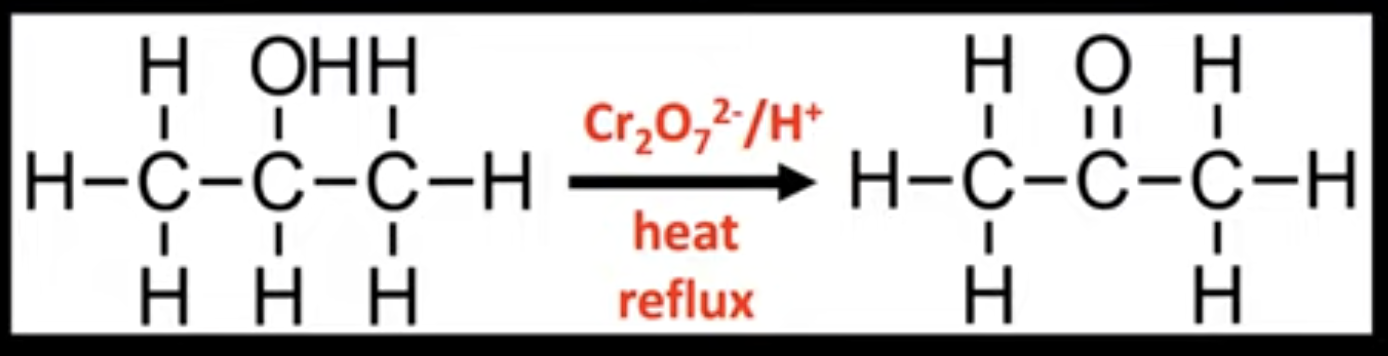
Oxidation of secondary alcohols
Forms ketones.
Conditions: heat under reflux.
Uses acidified potassium dichromate.
5
New cards
Oxidation of tertiary alcohols
Does not occur.
No H on carbon with –OH group.
Tertiary alcohols resist oxidation.
6
New cards
Function of distillation and reflux
Distillation: separates aldehyde.
Reflux: ensures complete oxidation by prolonged contact.