Anatomy Exam 4: Conduction Pathways, Spinal Nerves, Reflexes, and Senses
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Sensory pathways
Signals from sensory receptors ascending to brain
Motor pathways
Signals from brain to muscles or glands
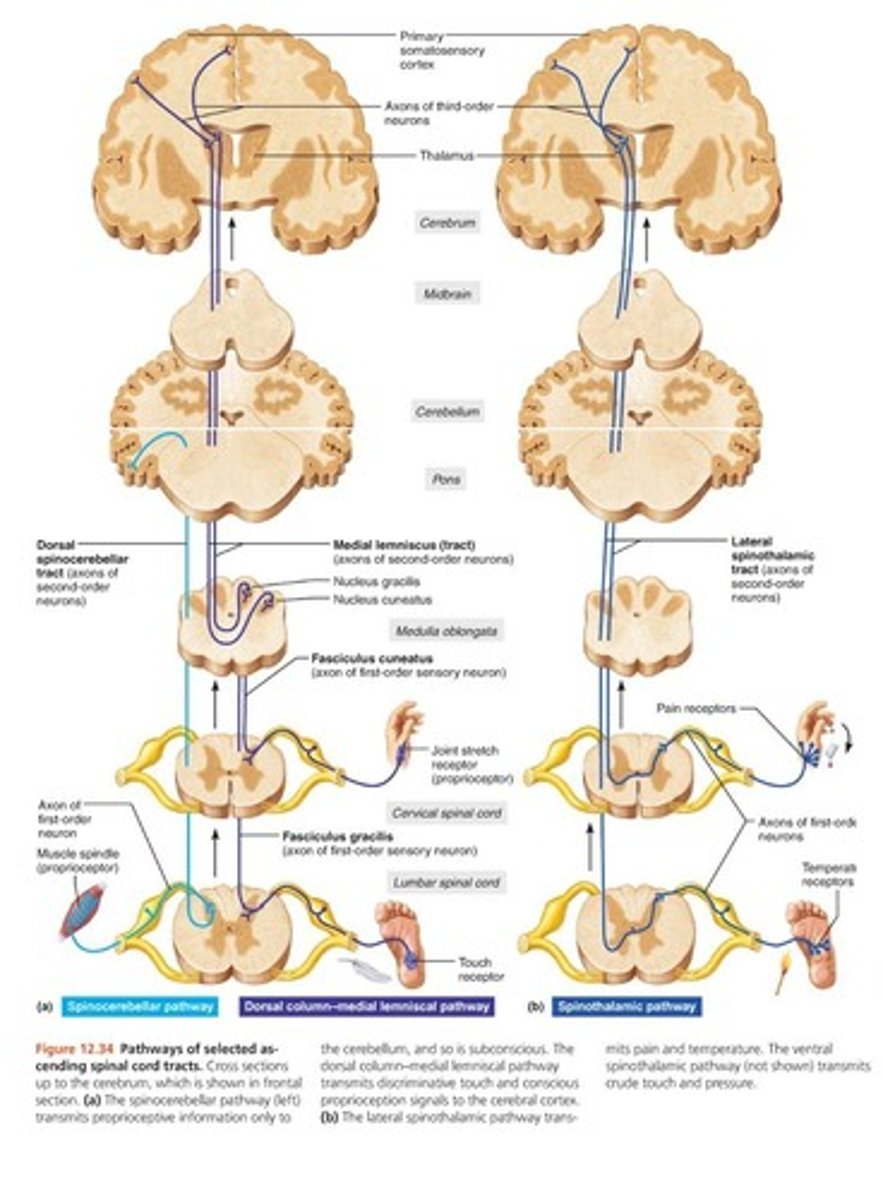
Spinothalamic pathway
pain (nociception) and temperature-lateral; "crude touch"-anterior
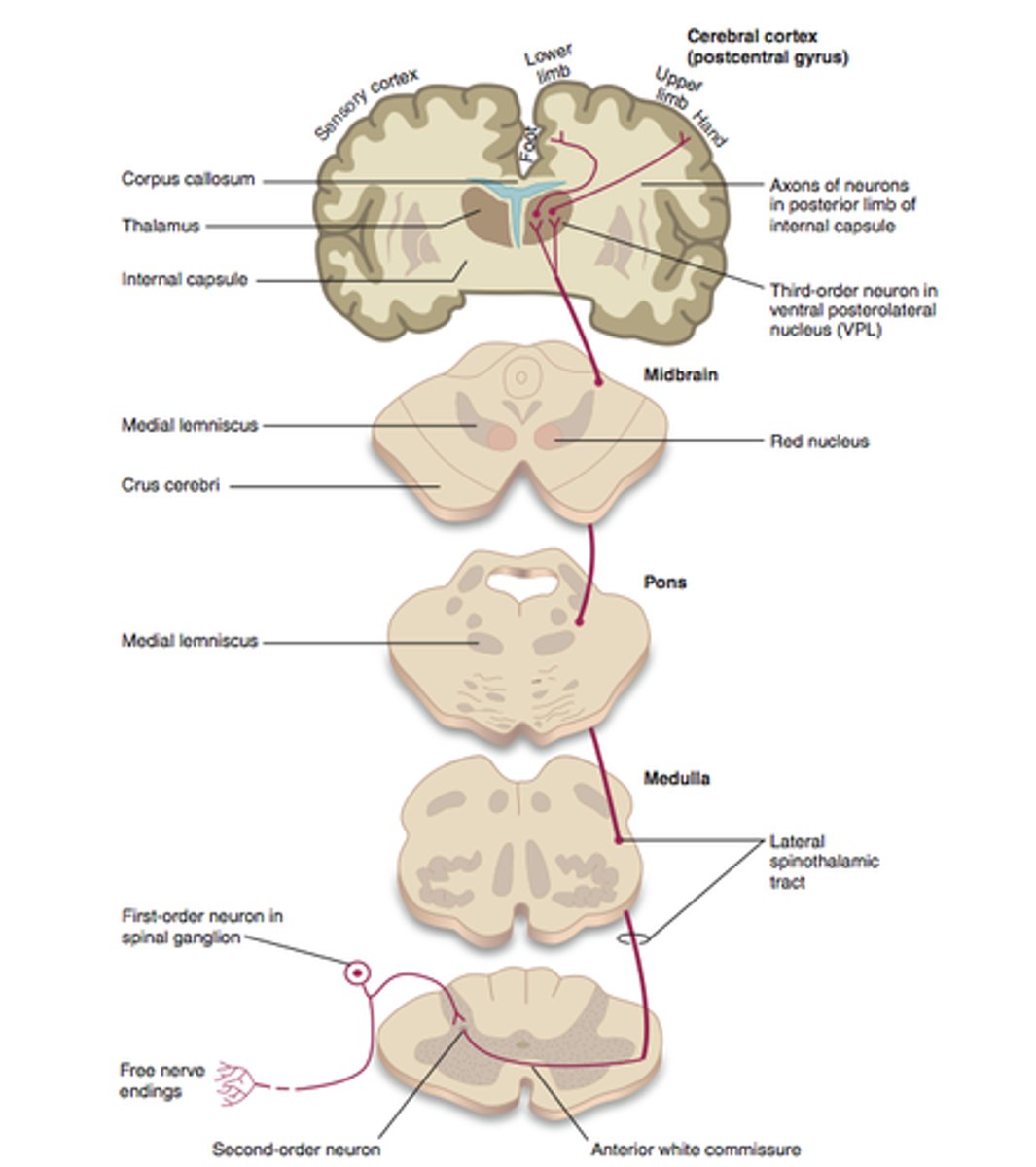
Spinocerebellar tract
Propioception (orientation of body parts)
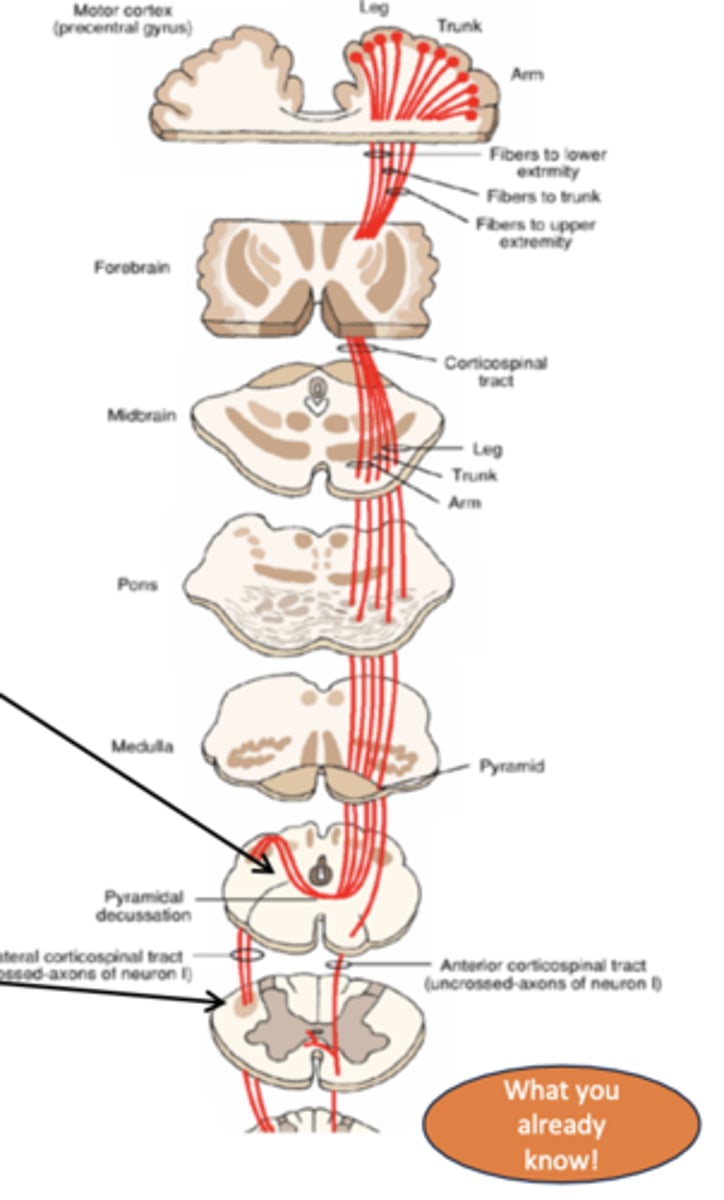
Cotricospinal pathway
Motor (voluntary): walking, writing, reaching, typing
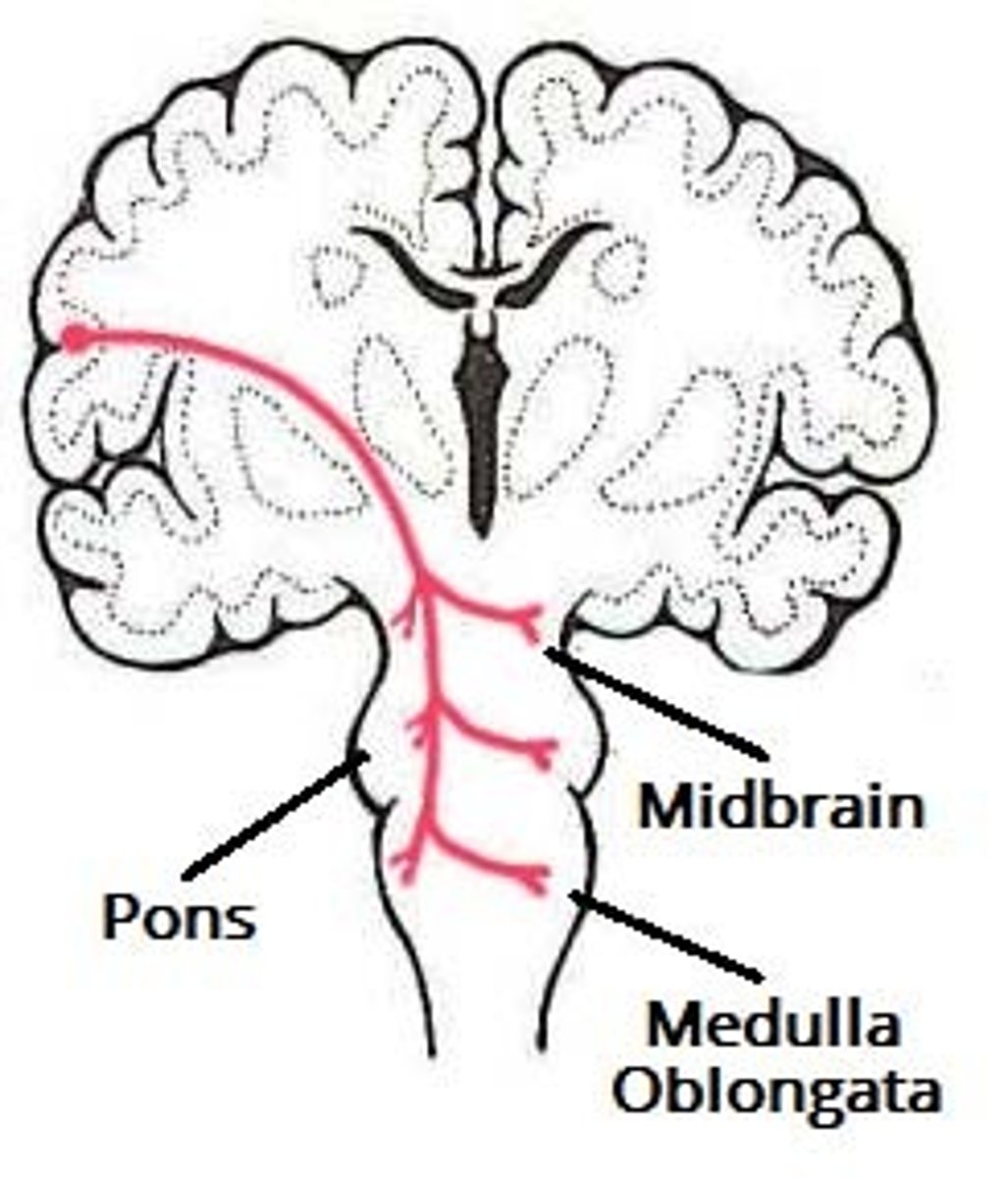
Corticobulbar
Motor: cranial nerves (trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, hypoglossal)
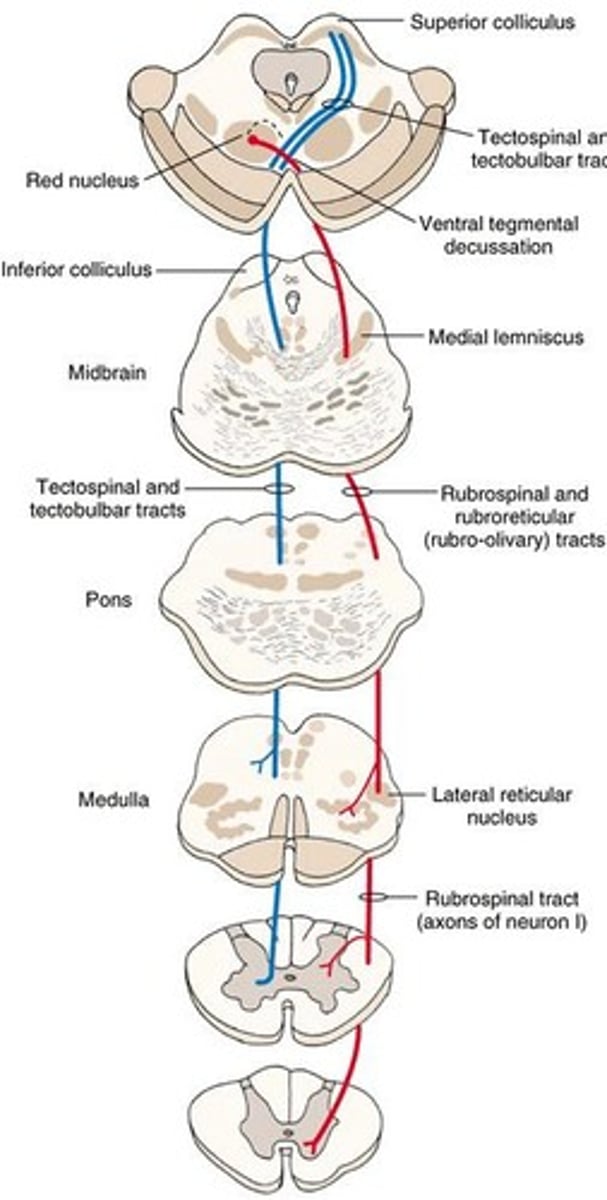
Rubrospinal pathway
Motor: reflexes, posture. Red nucleus + spinal cord.
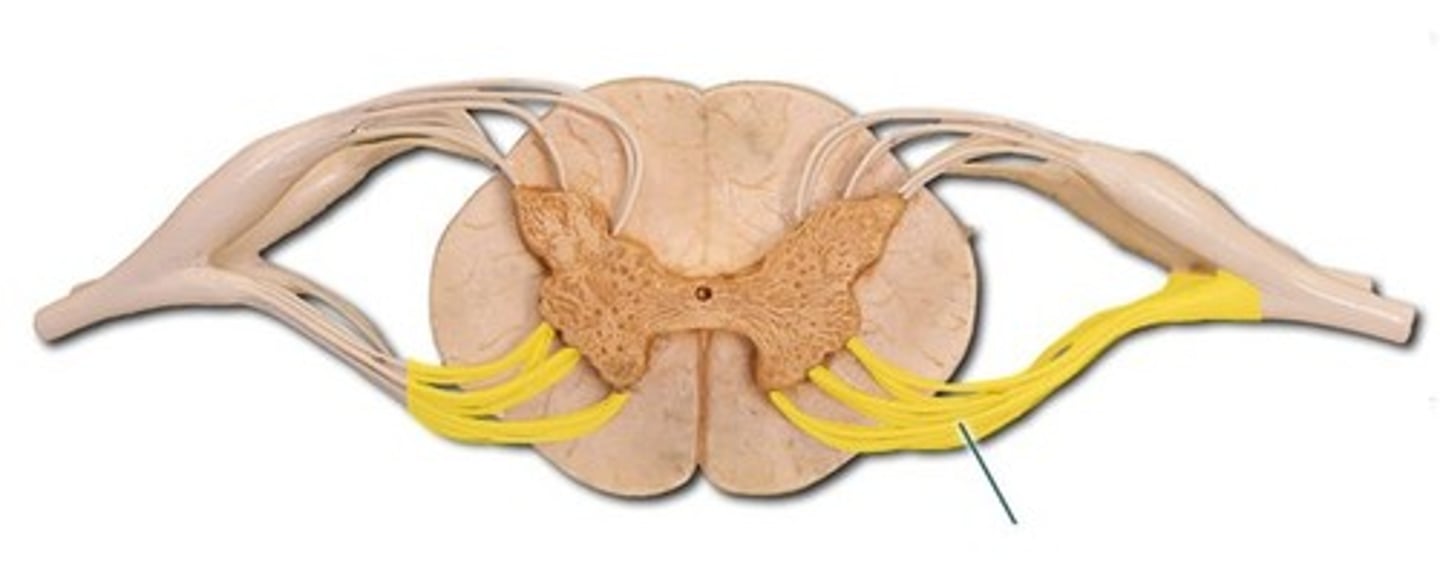
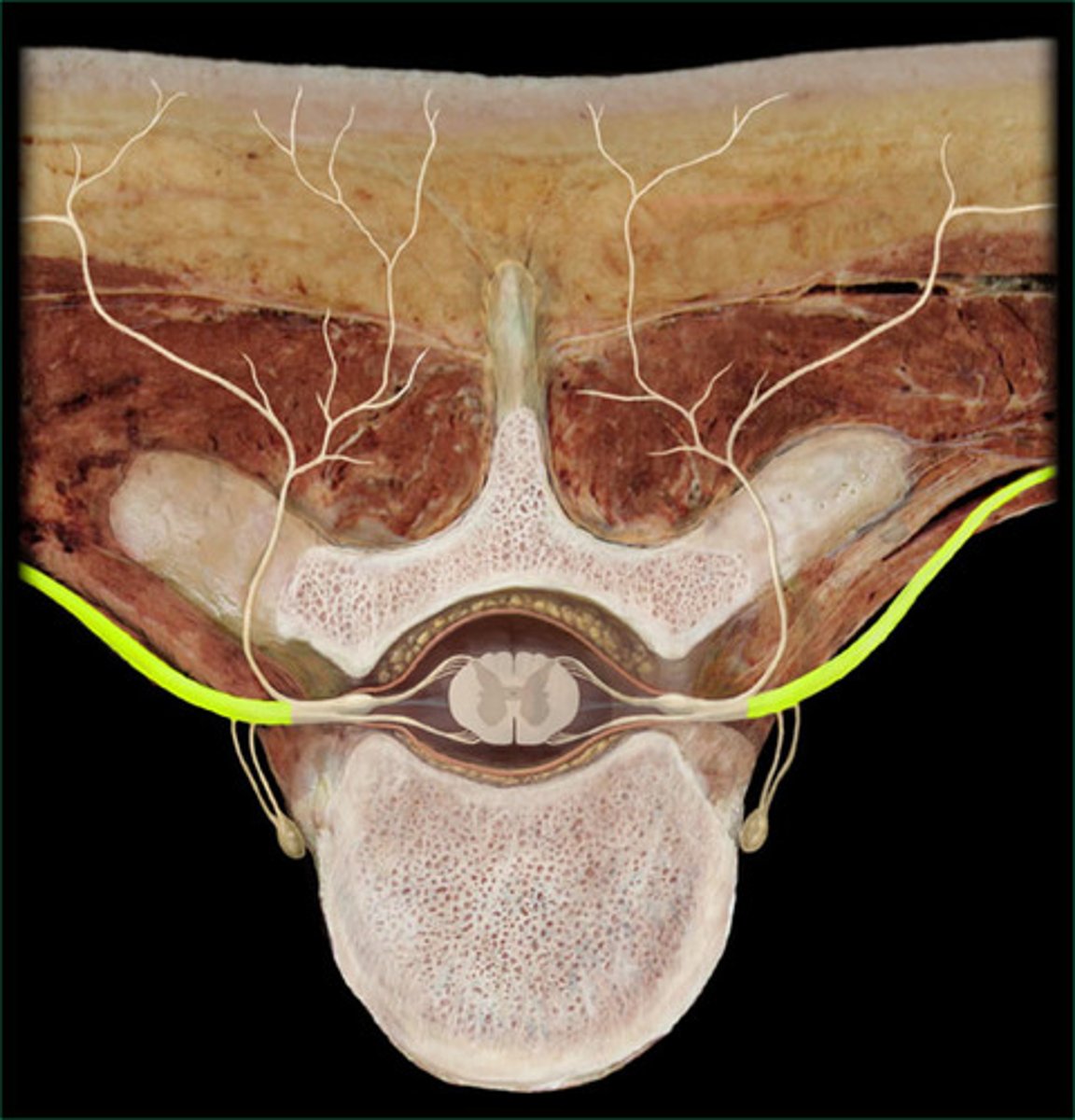
Anterior root
contains motor neurons
Posterior root
contains sensory neurons
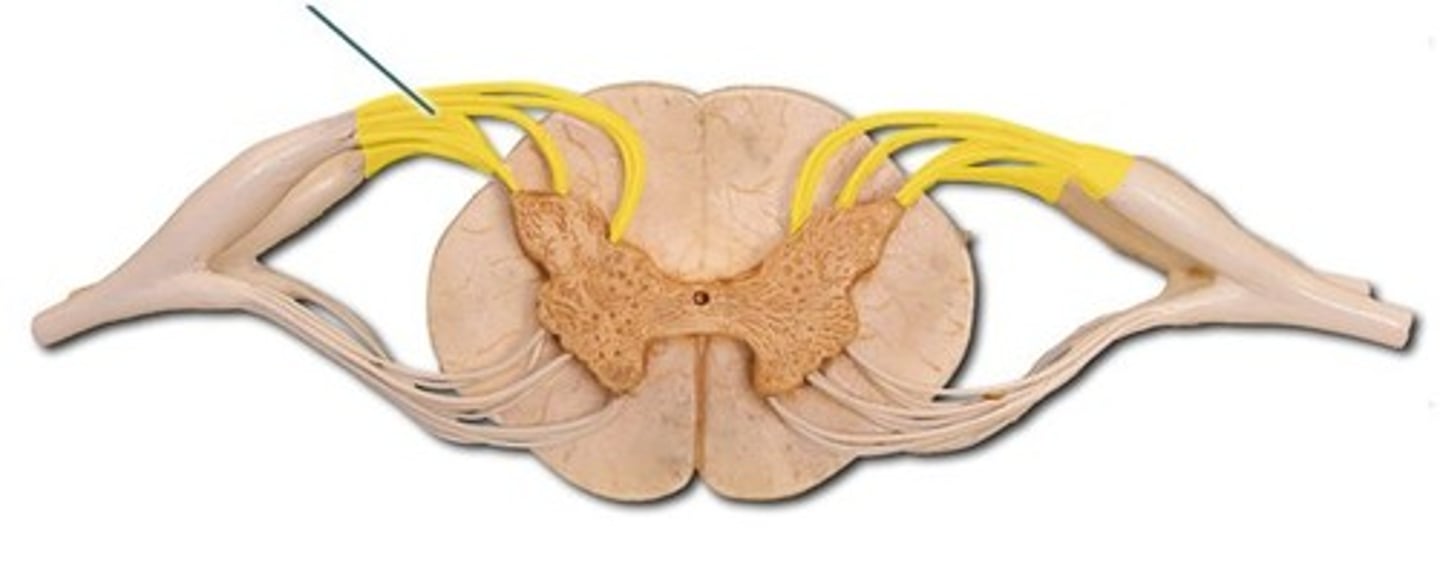
Posterior root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
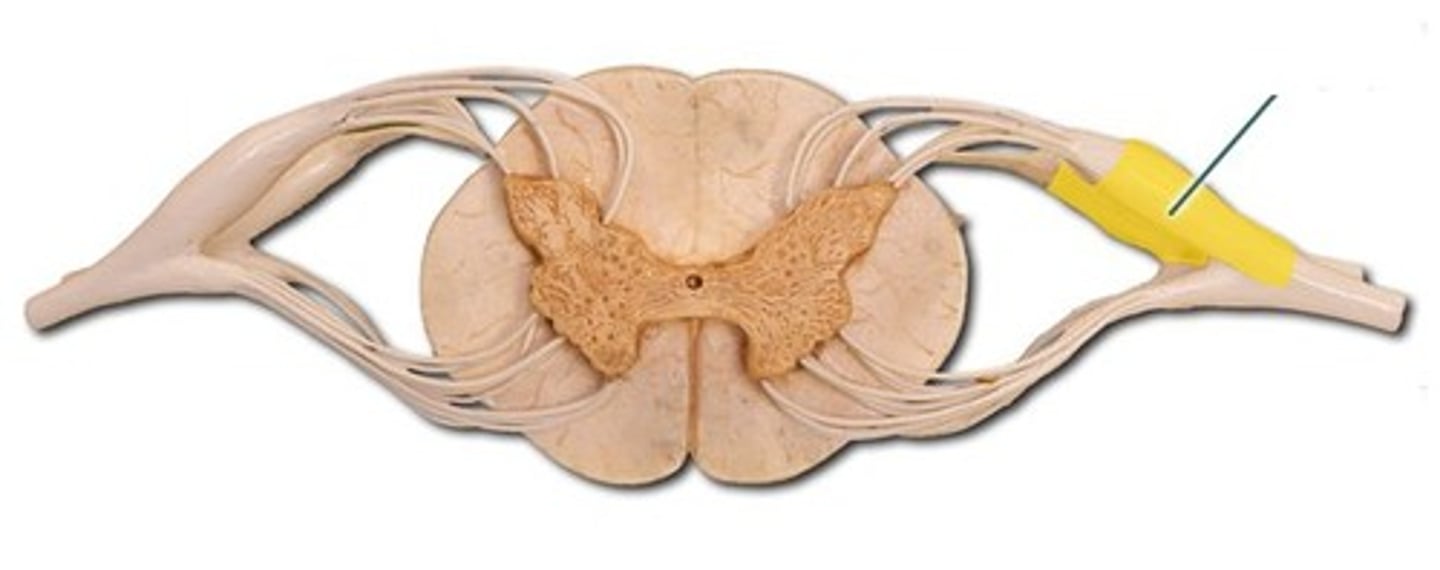
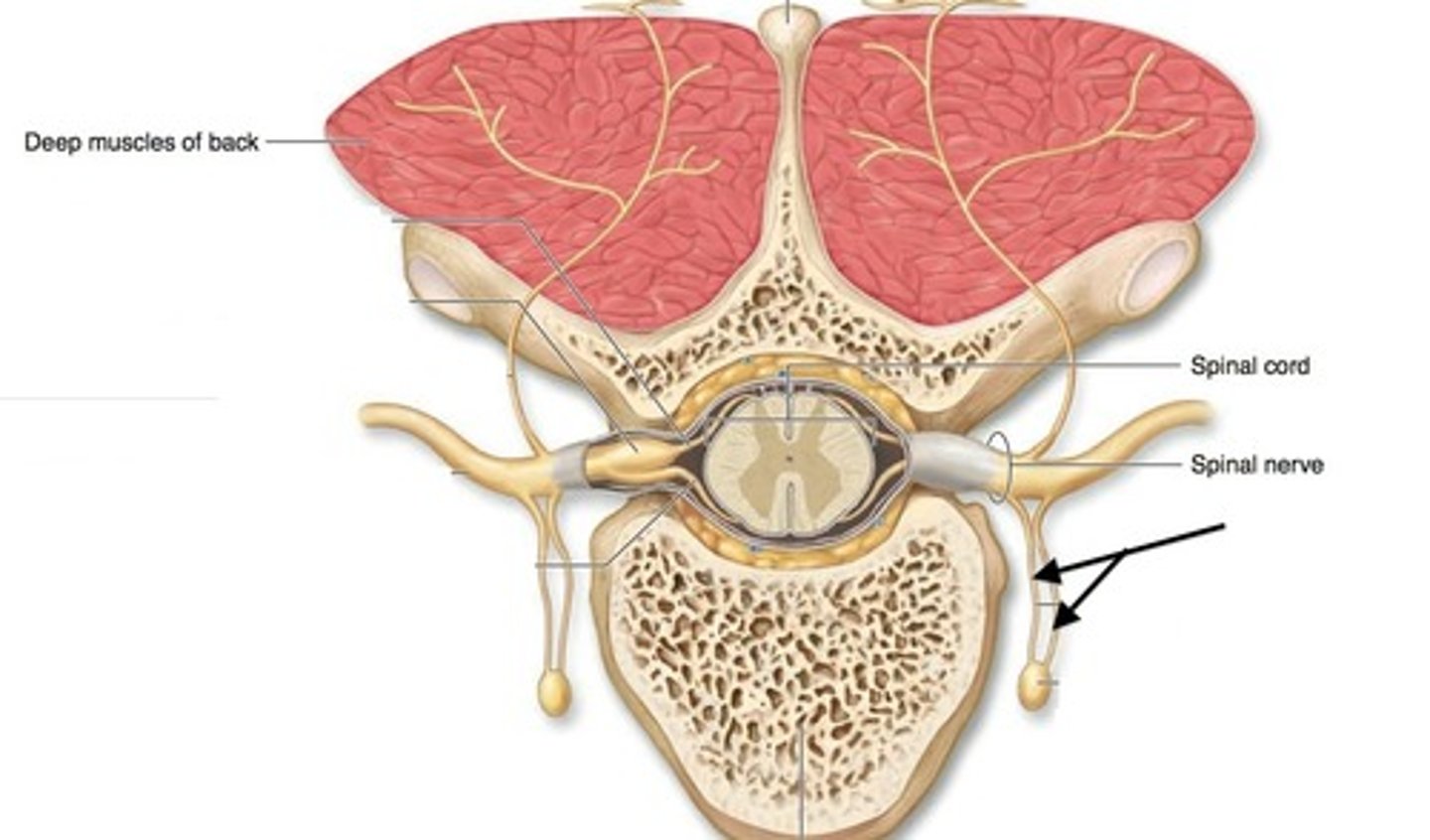
Posterior ramus
innervates the muscles and joints in that region of the spine and the skin of the back
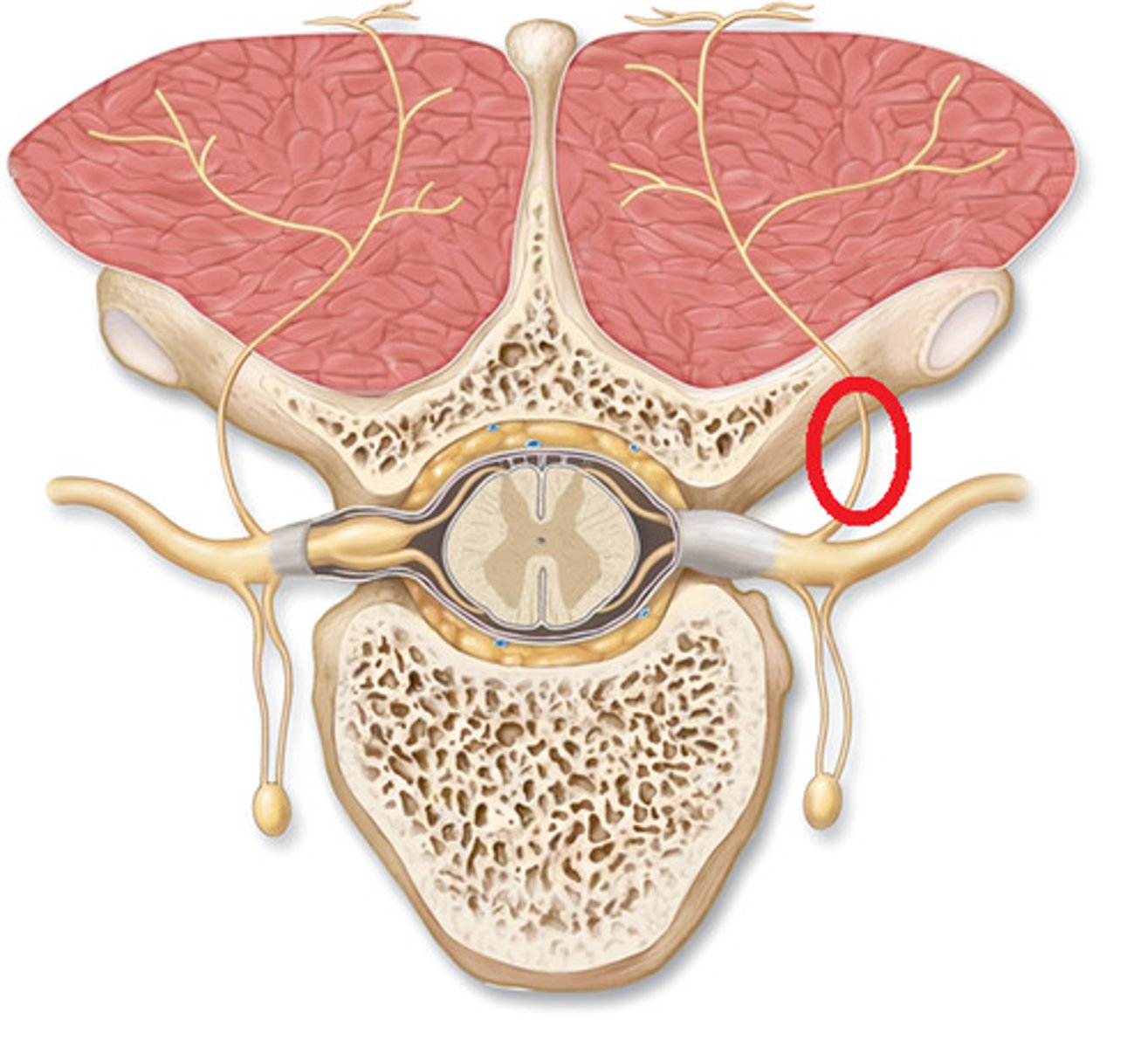
Anterior ramus
innervates the anterior and lateral skin and muscles of the trunk and gives rise to nerves of the limbs
Rami communicantes
autonomic nerve fibers that attach to ventral rami
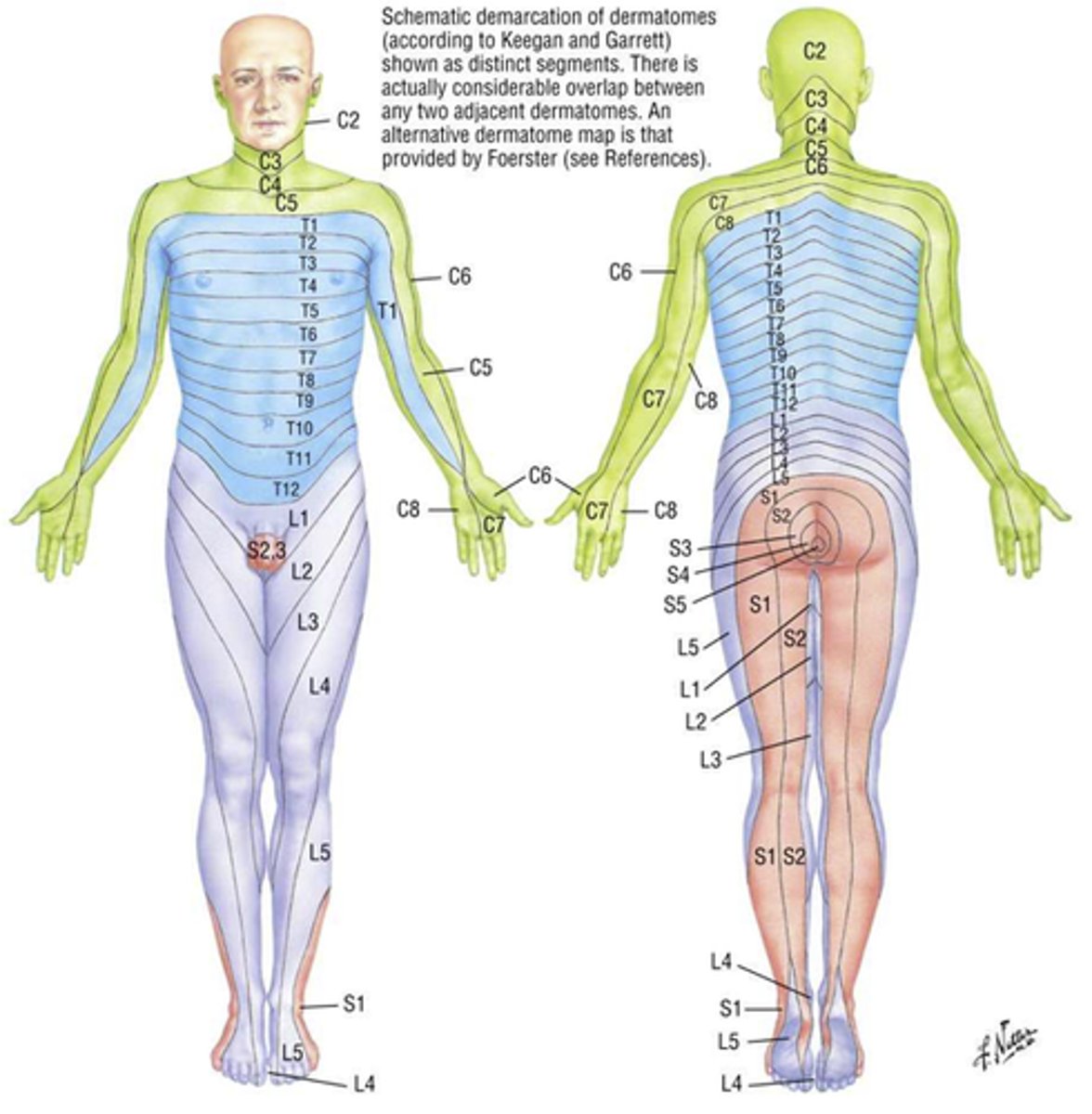
Dermatome
Segments of skin supplied by single spinal nerves; can help localize damage to one or more spinal nerves
Nerve plexus
axons from anterior rams extend through different branches to different body structures
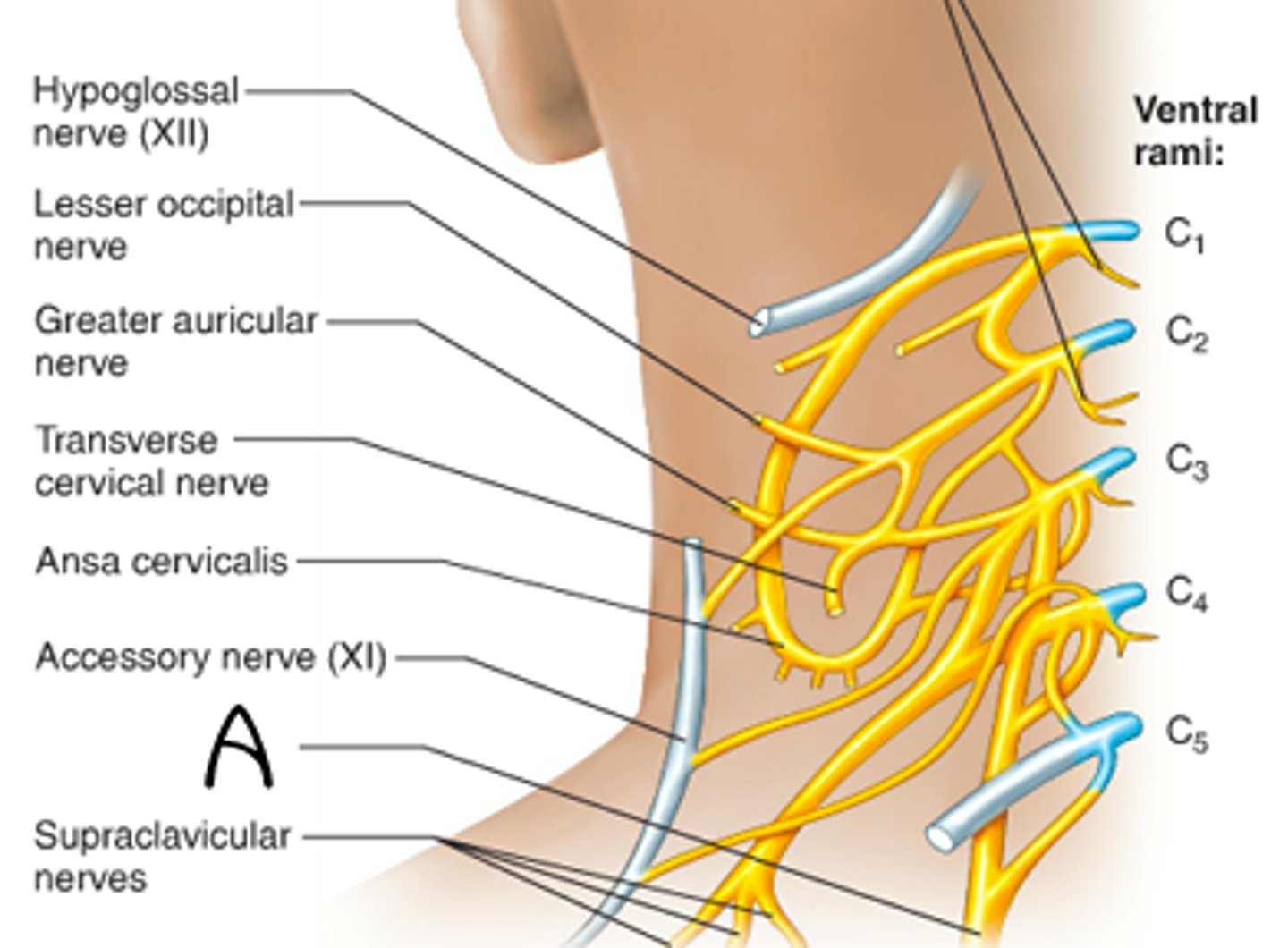
ansa cervicalis
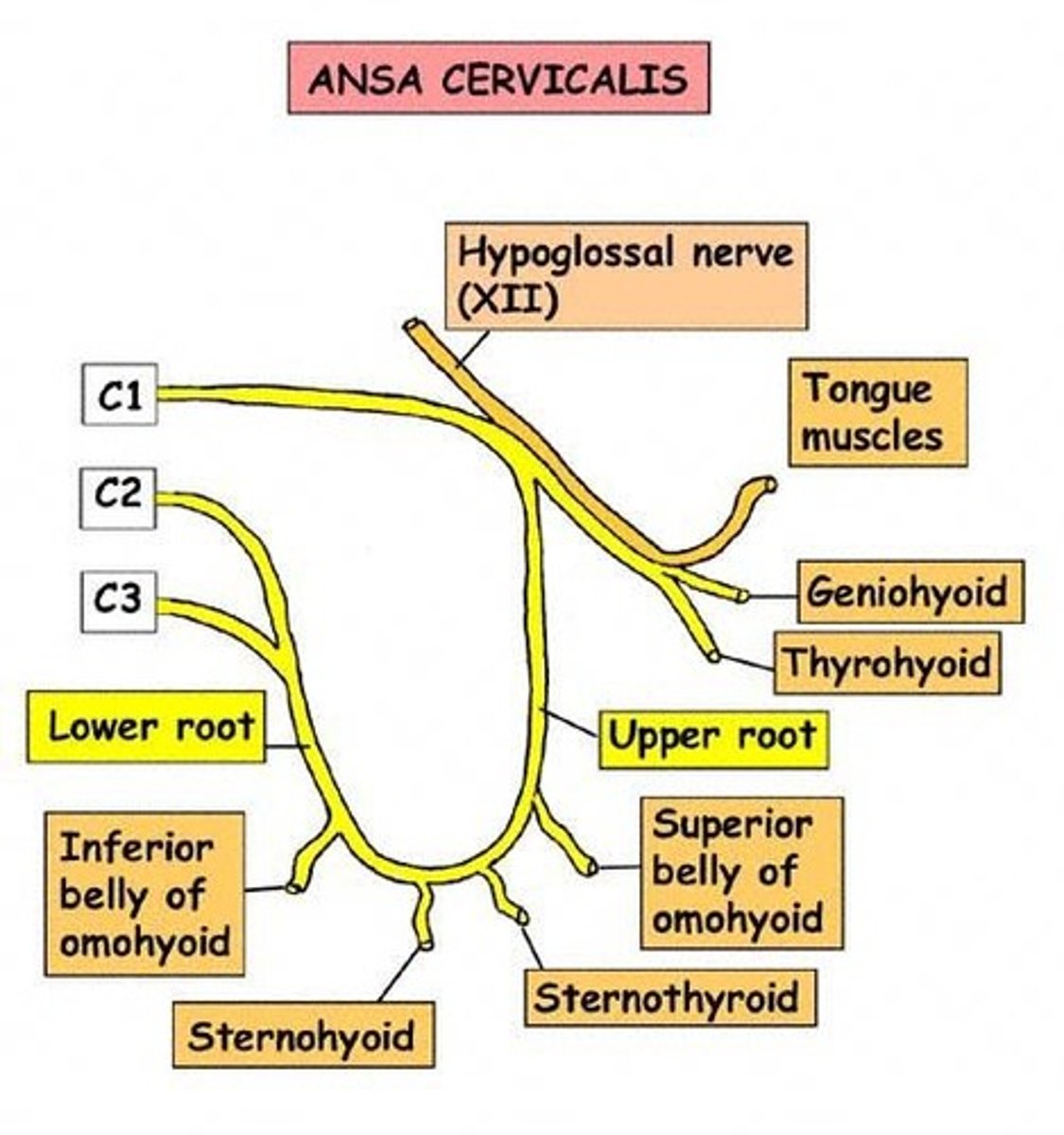
phrenic nerve
controls diaphragm, signals diaphragmatic contraction
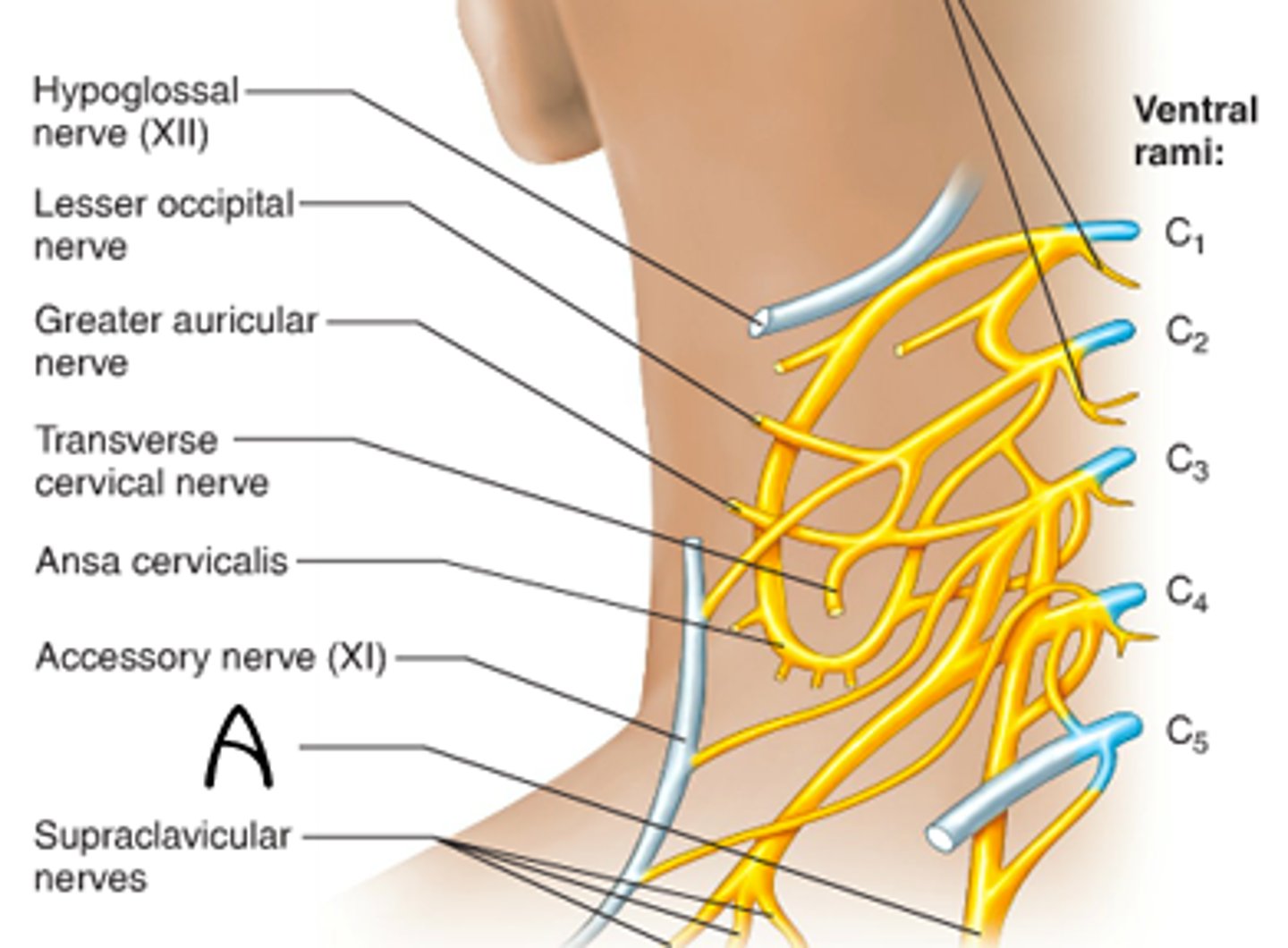
segmental branches
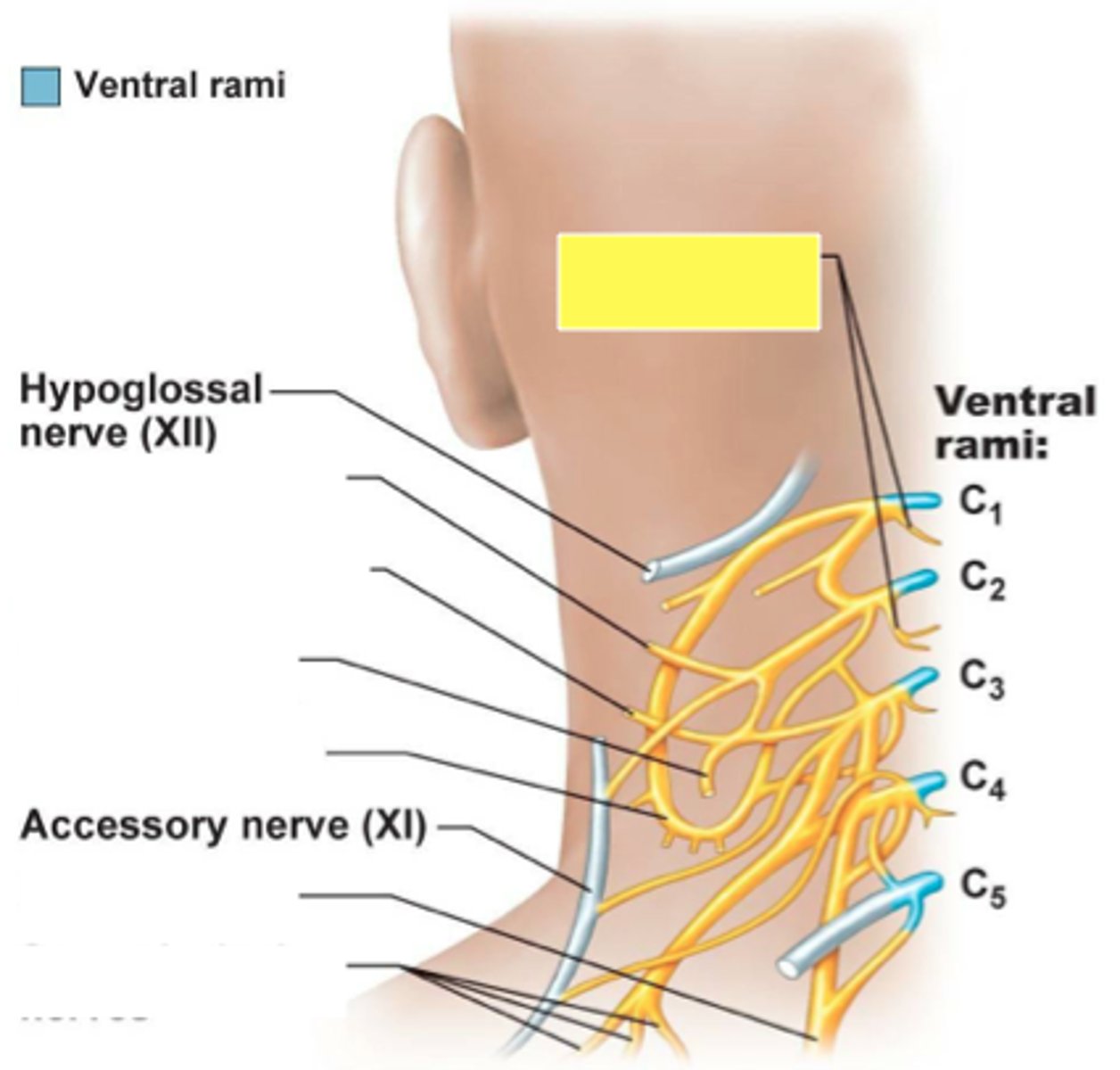
greater auricular
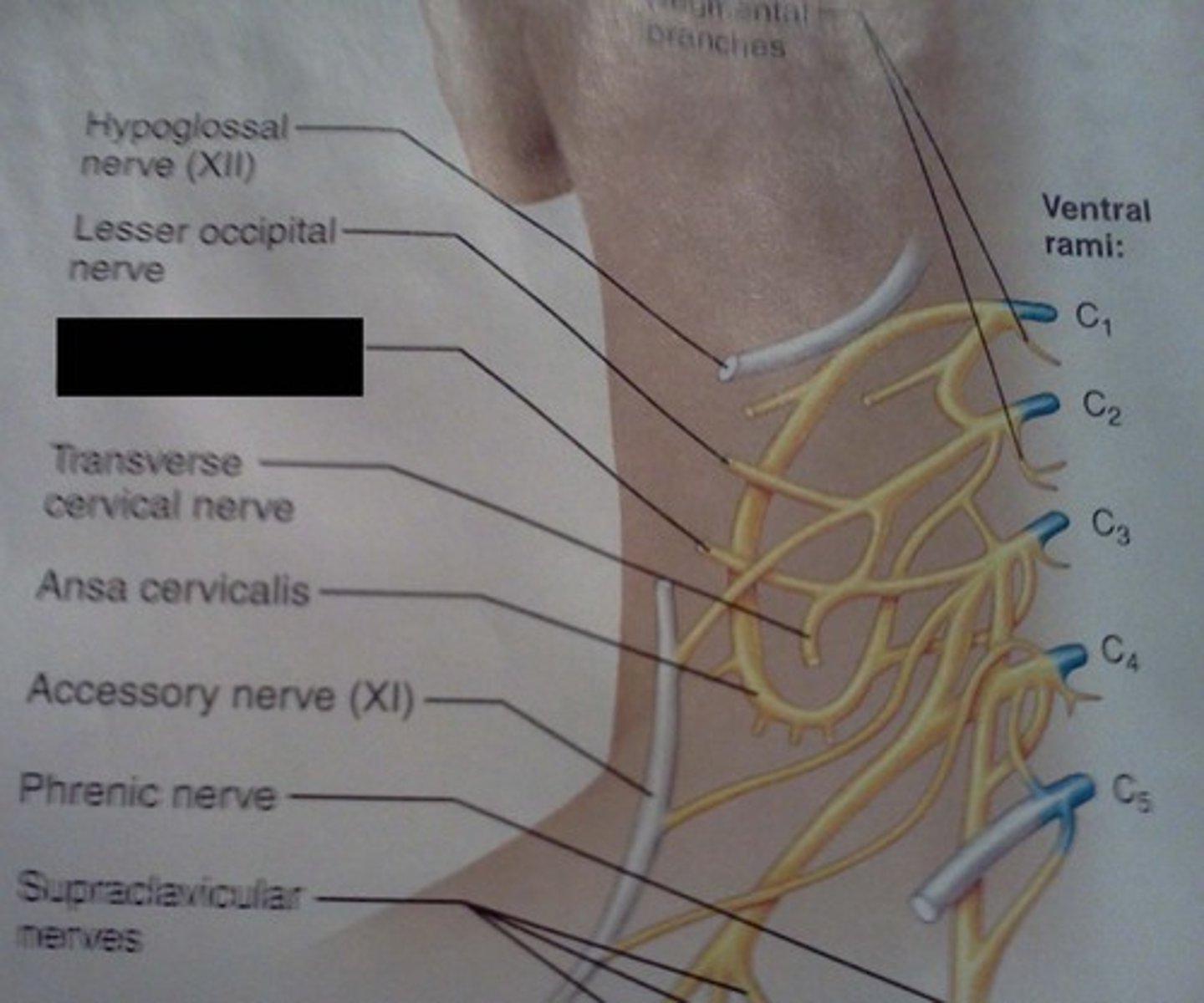
lesser occipital
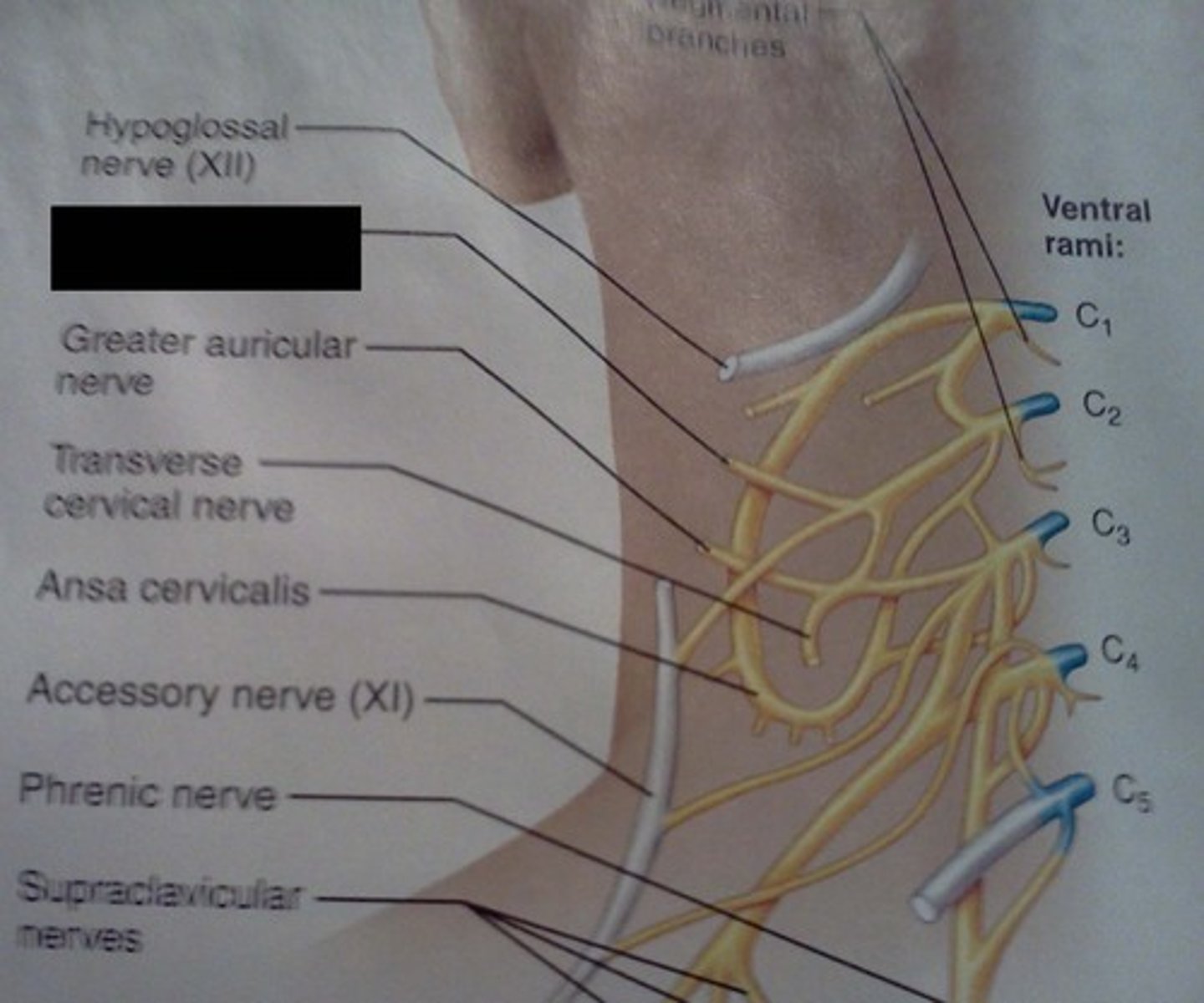
supraclavicular
Innervate area over clavicle, parts of the shoulder, and proximal chest
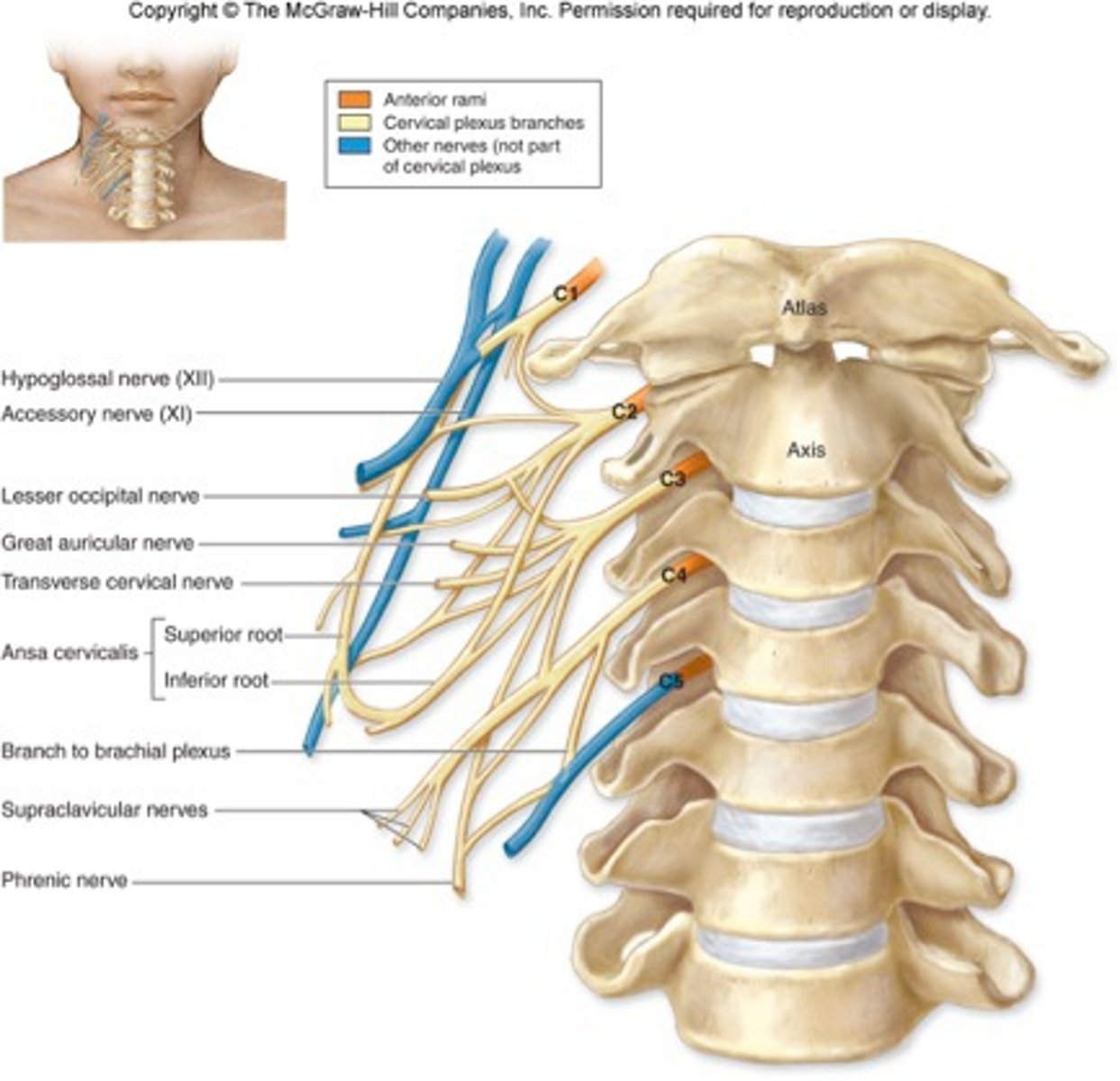
transverse cervical nerve
Brachial plexus
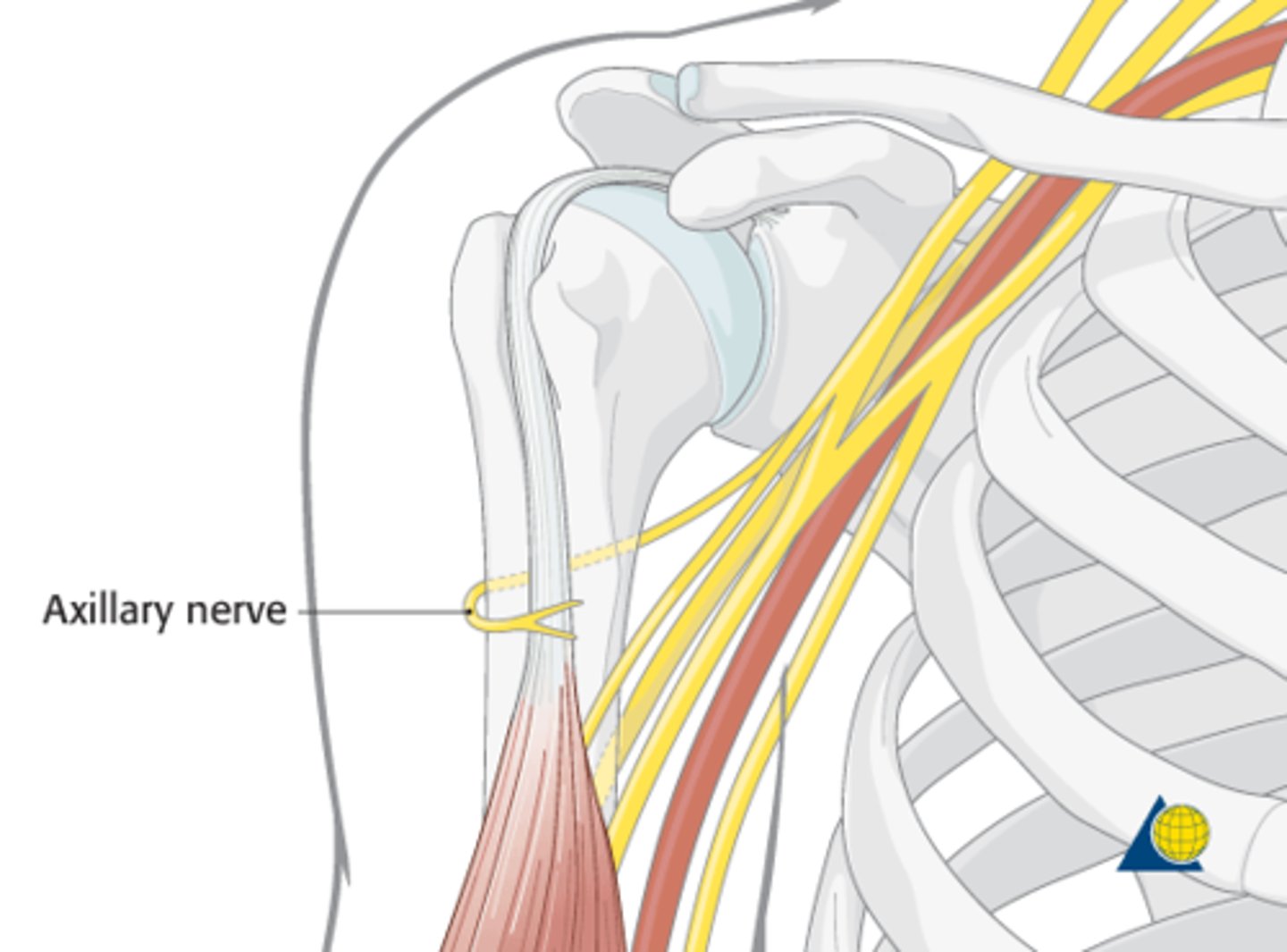
Axillary nerve
posterior cord: innervates deltoid and teres minor muscles
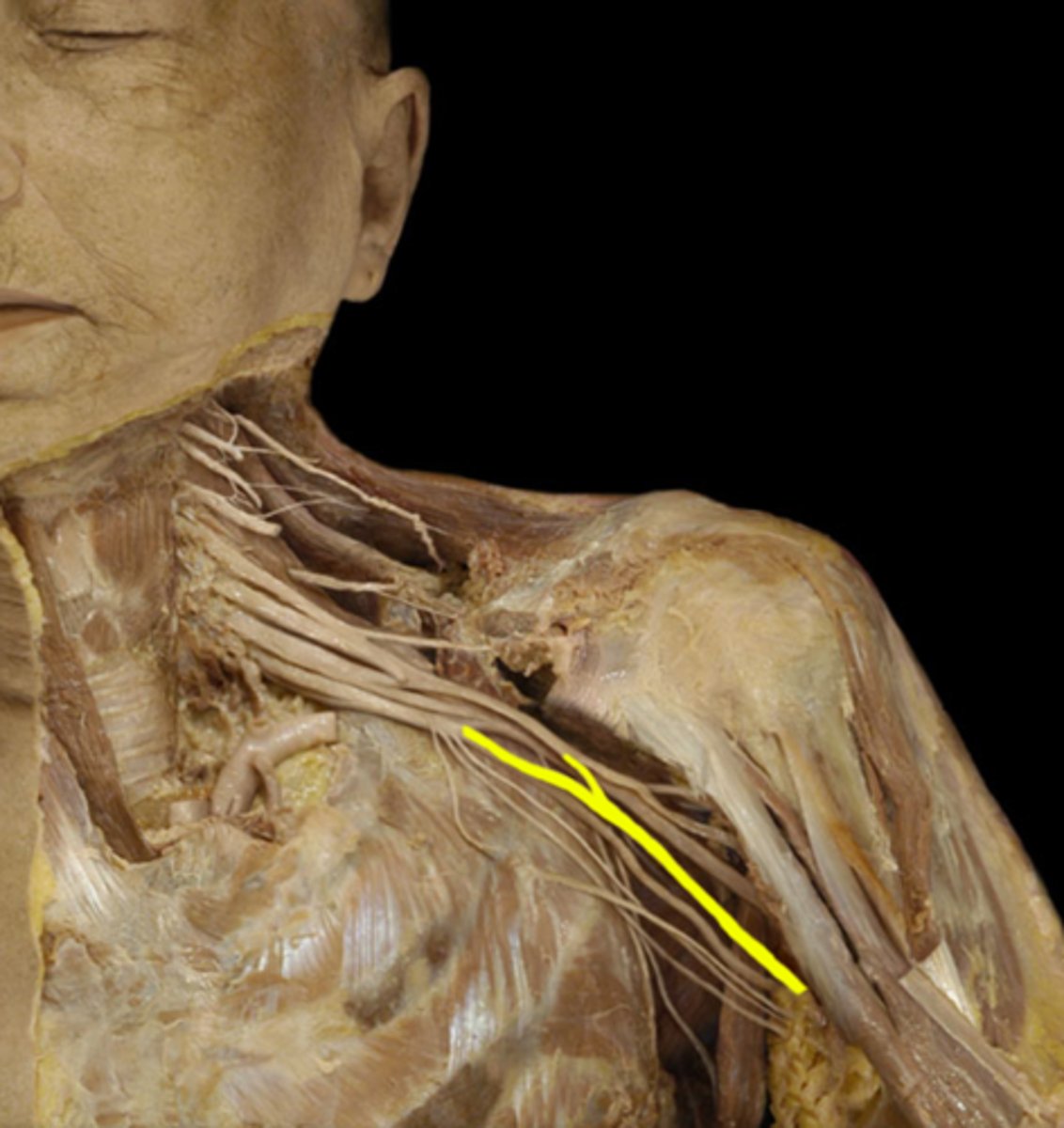
Median nerve
medial cord: innervates flexor muscles of forearm (lateral palm)
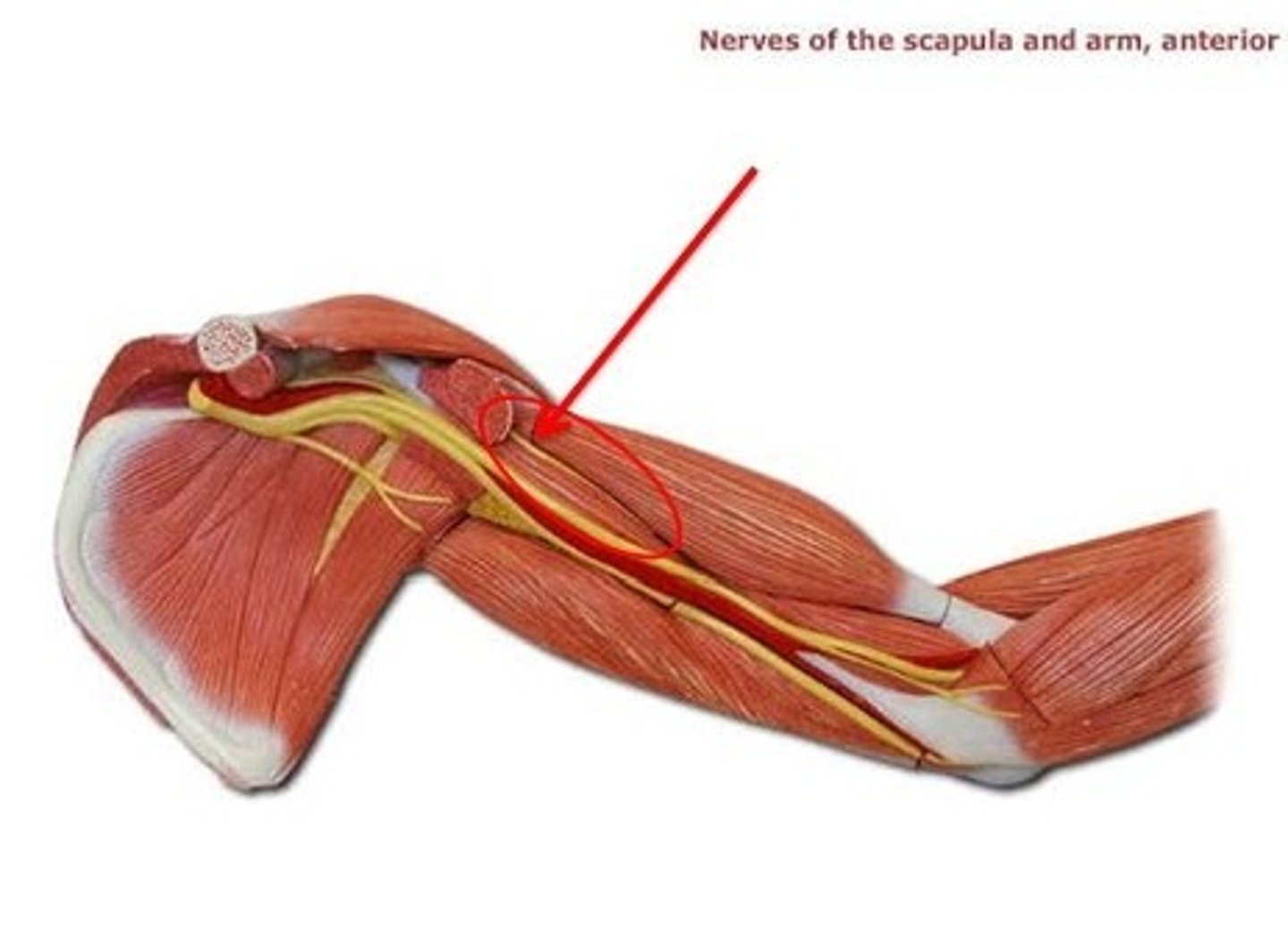
Musculocutaneous nerve
lateral cord that innervates biceps brachii, brachialis, and corocobrachialis
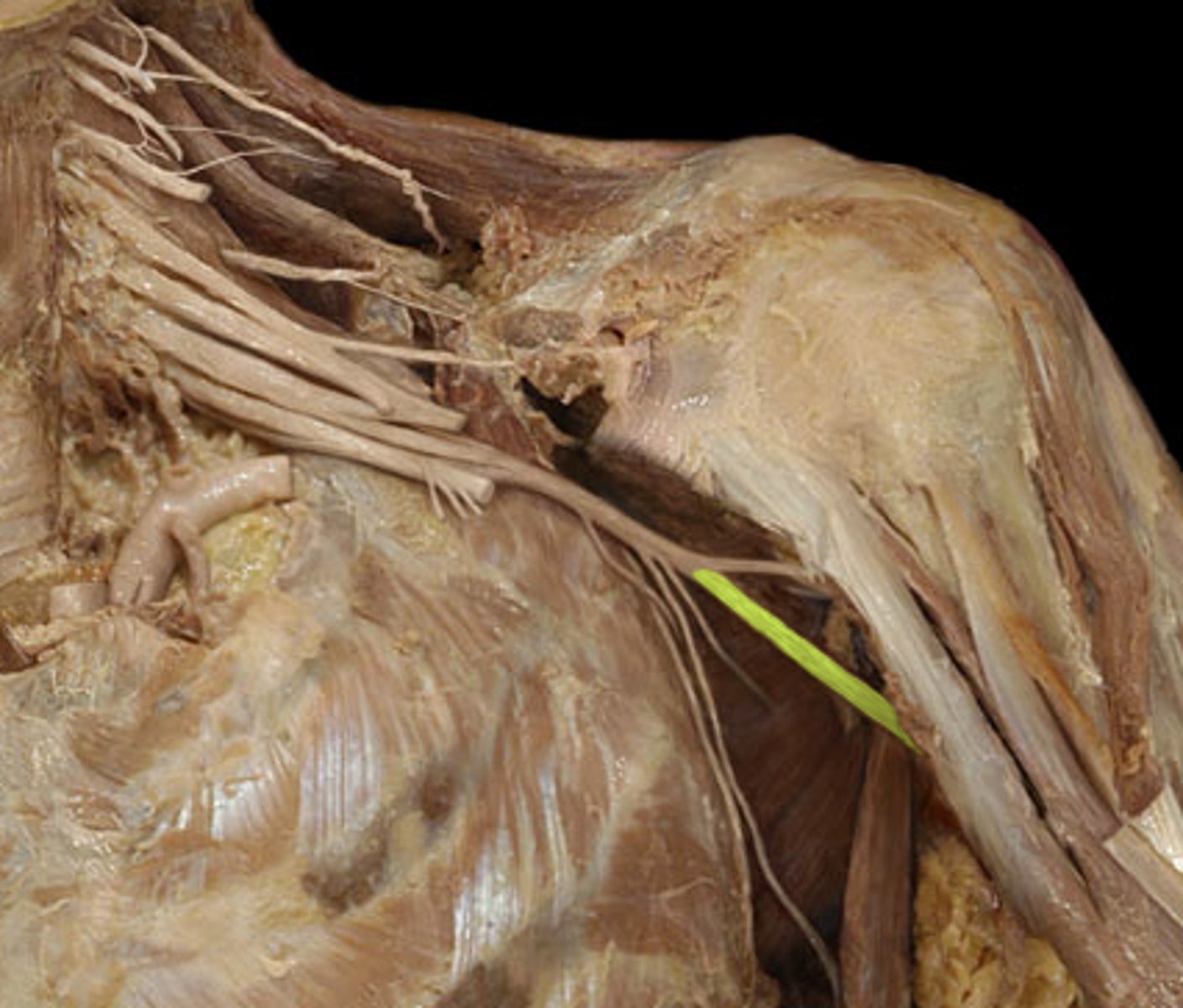
Radial nerve
posterior cord that innervates most extensor muscles of the upper limb
Ulnar nerve
Medial cord that innervates flexor muscles of forearm (lateral palm)
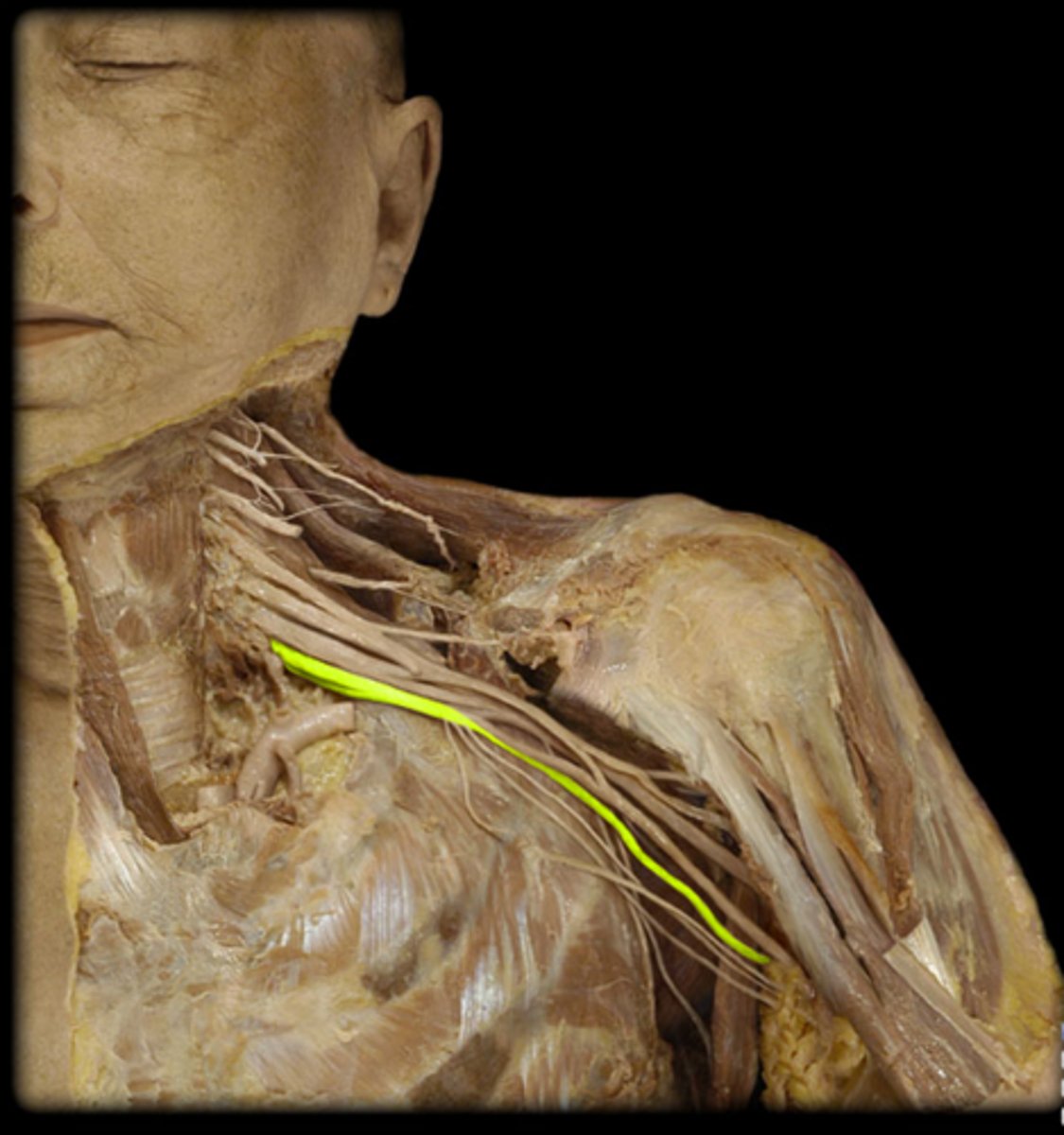
Femoral nerve
Innervates the quadriceps muscles
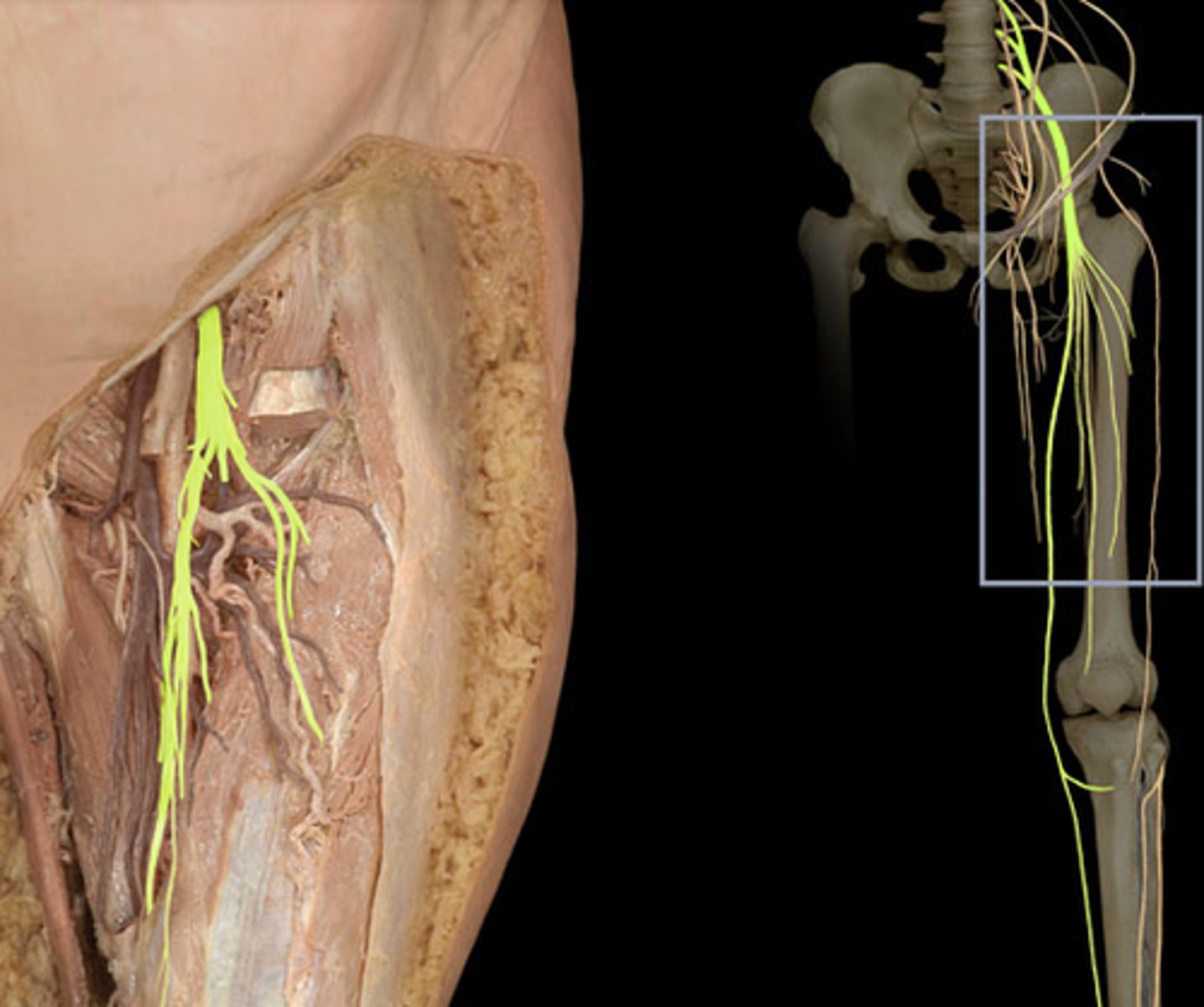
Obturator nerve
innervates the adductor muscles
Tibial nerve
-Supplies the posterior compartment muscles
-sural nerve
-medial and lateral plantar nerve
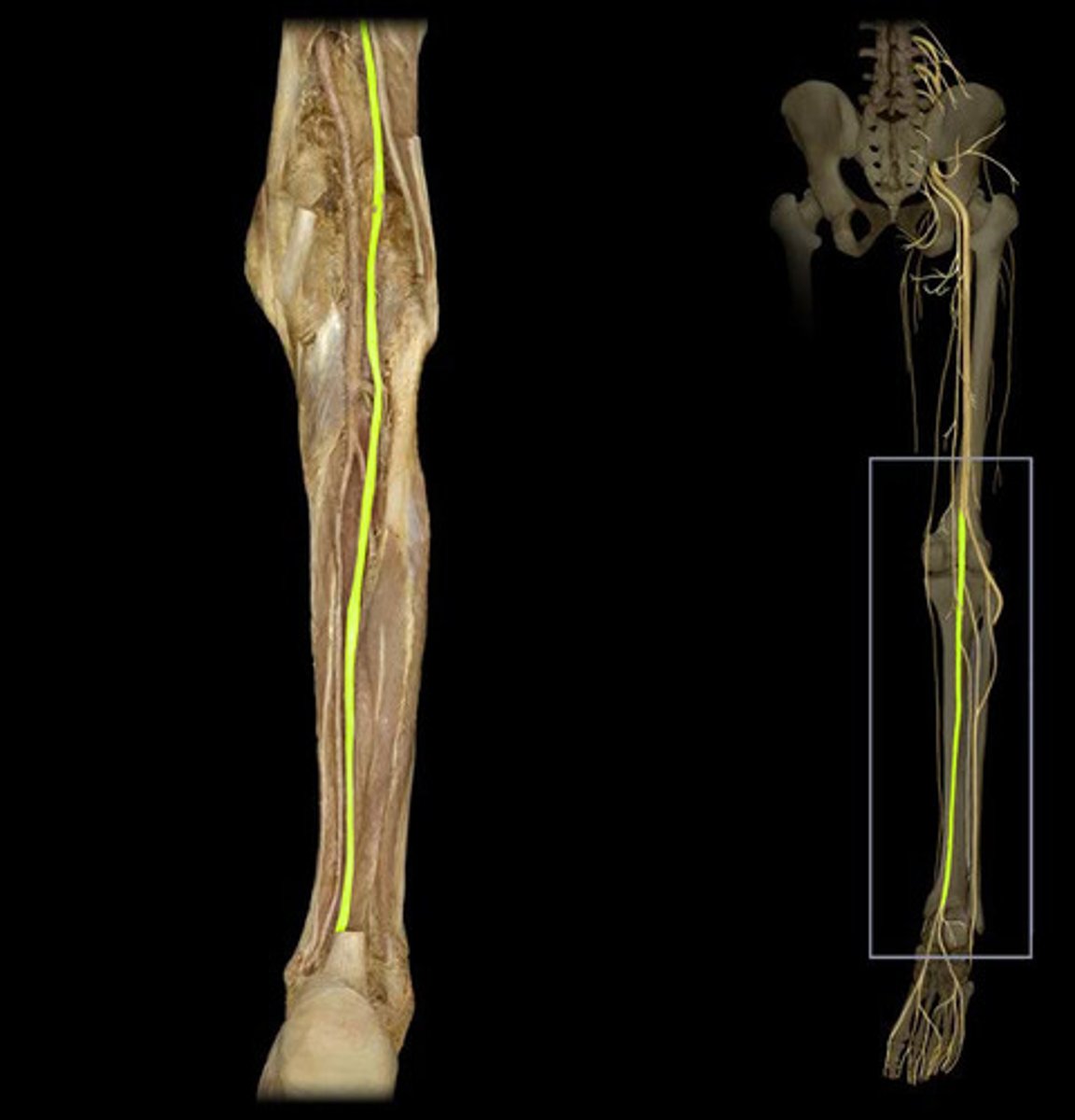
Sciatic nerve
tibial and common fibular nerves in one sheath
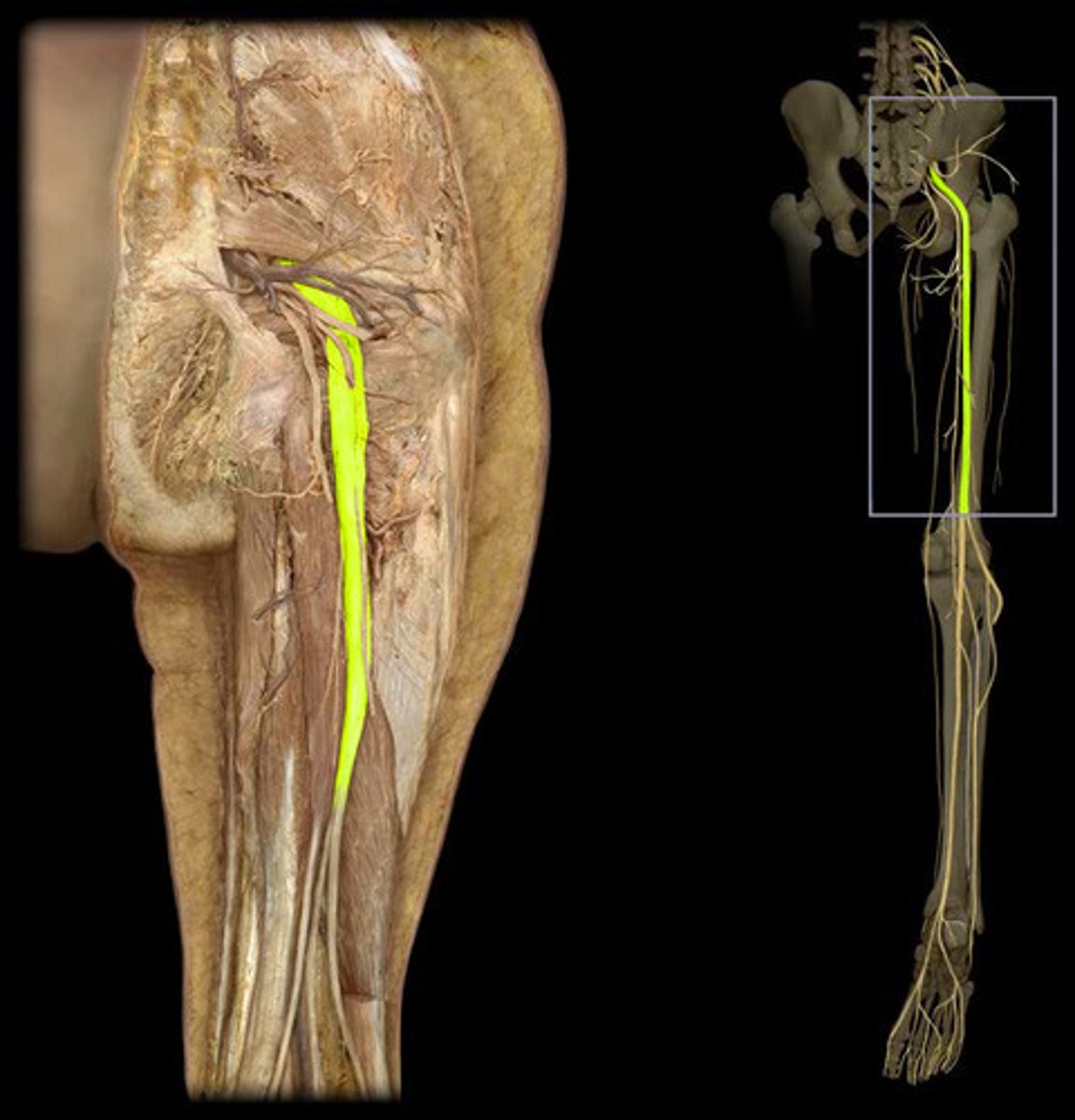
common fibular
Innervate knee joint
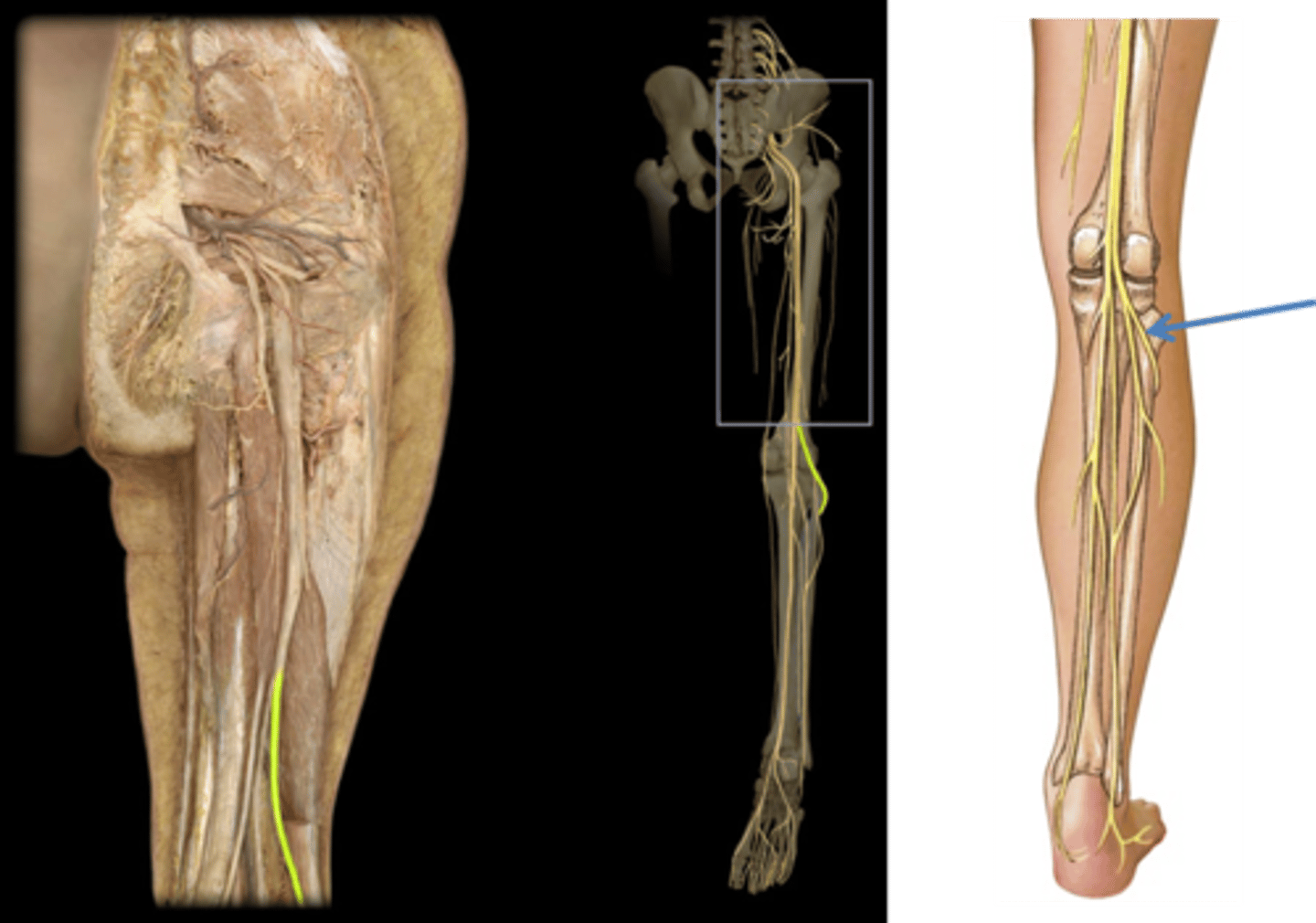
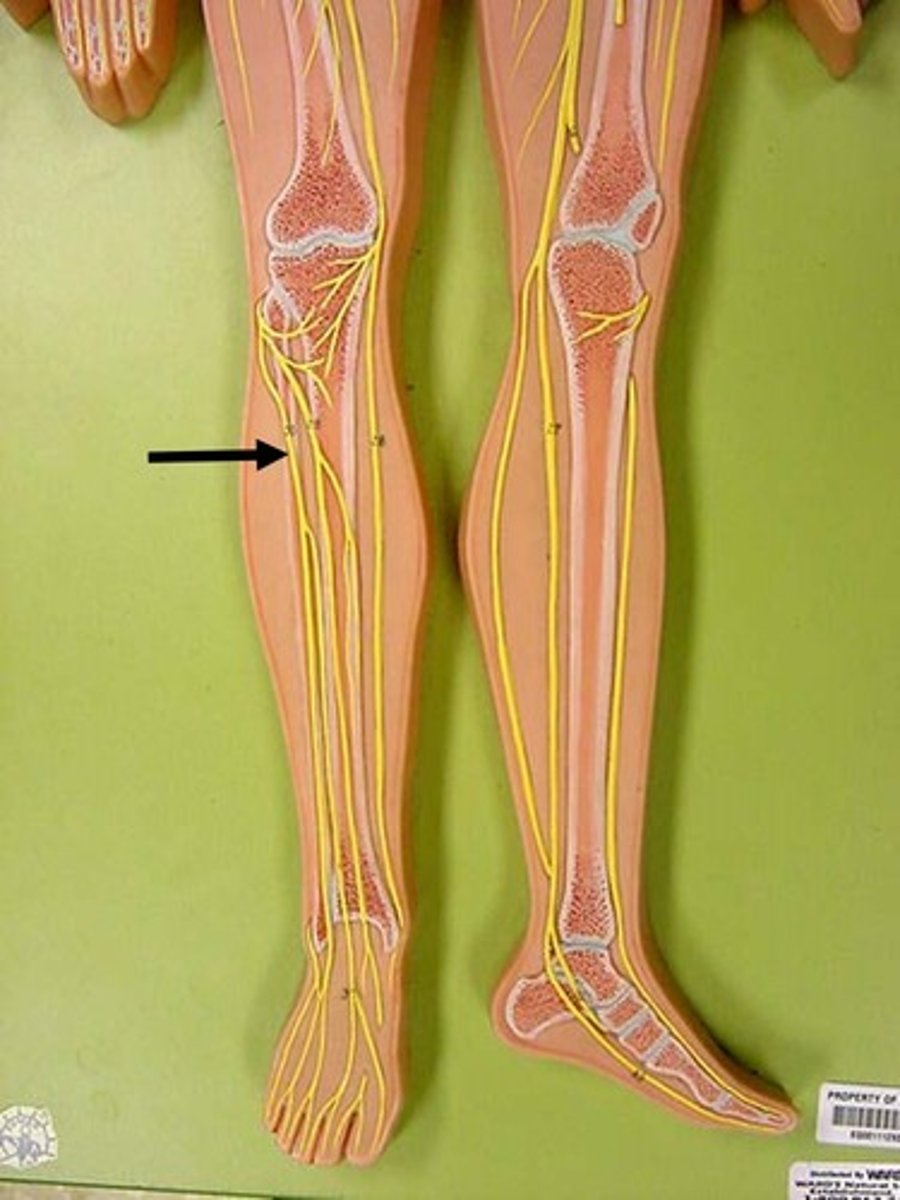
deep fibular
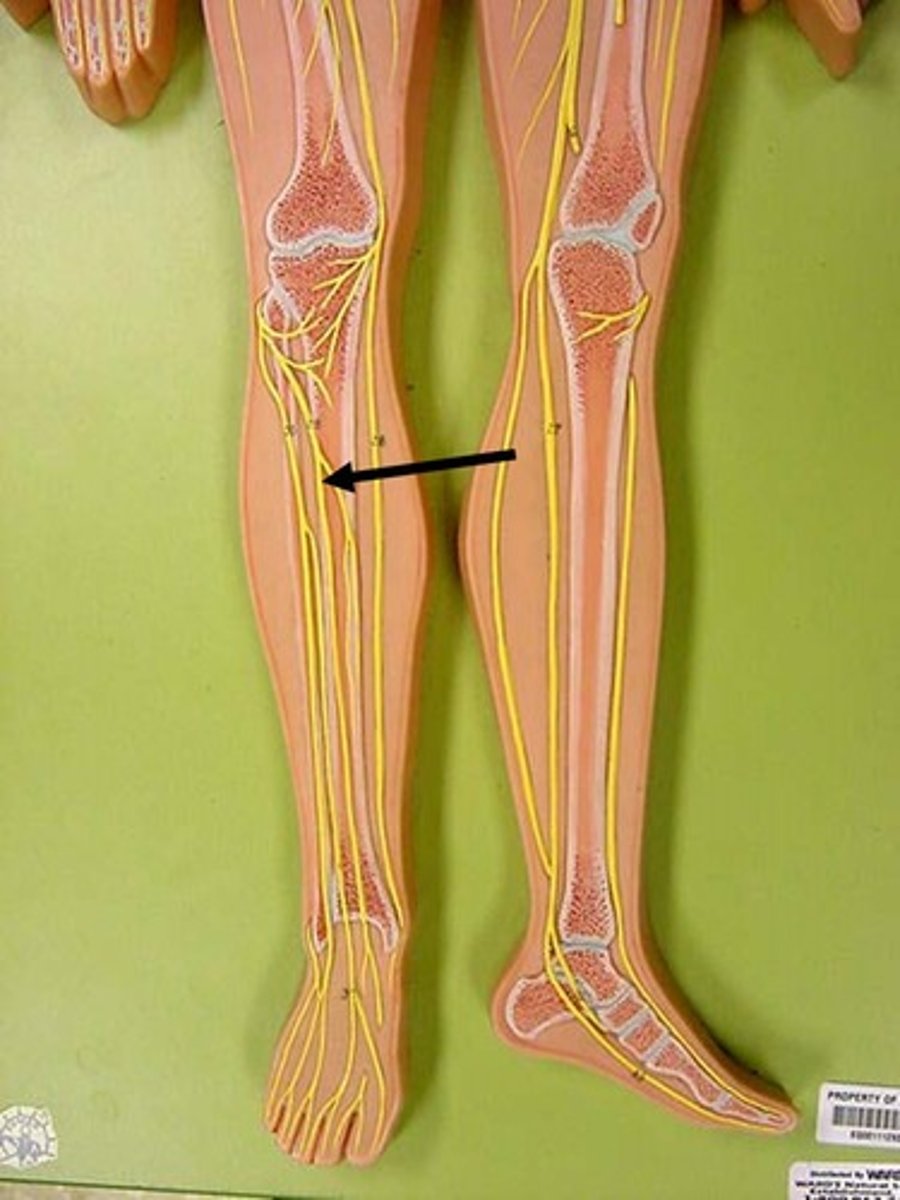
Superficial fibular
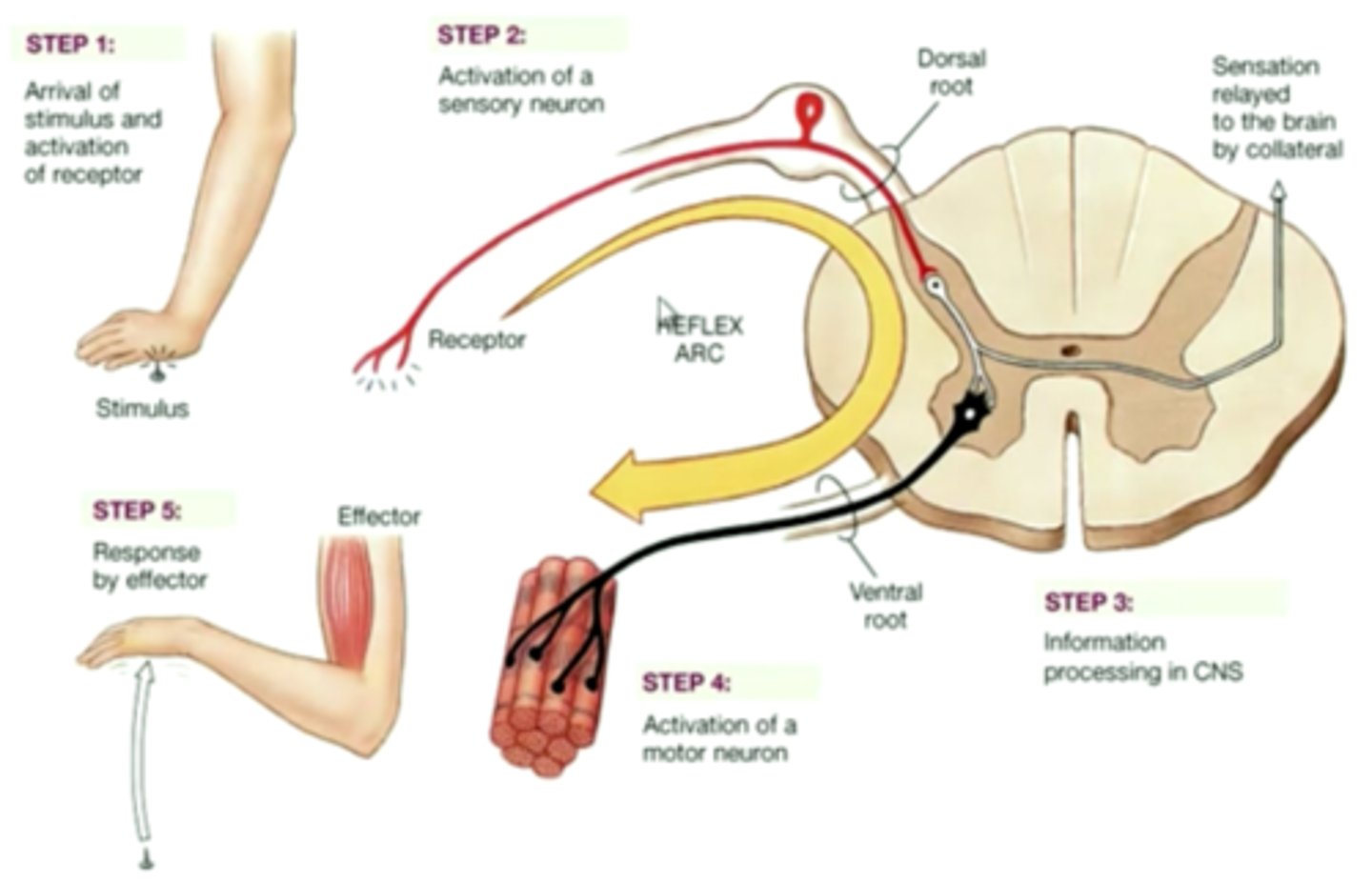
Reflex arc
A relatively direct connection between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron that allows an extremely rapid response to a stimulus, often without conscious brain involvement.
Ipsilateral
receptor and effector organs on same side of spinal cord
Contralateral
sensory impulses from receptor organ cross over through SC to activate effector organs in opposite limb
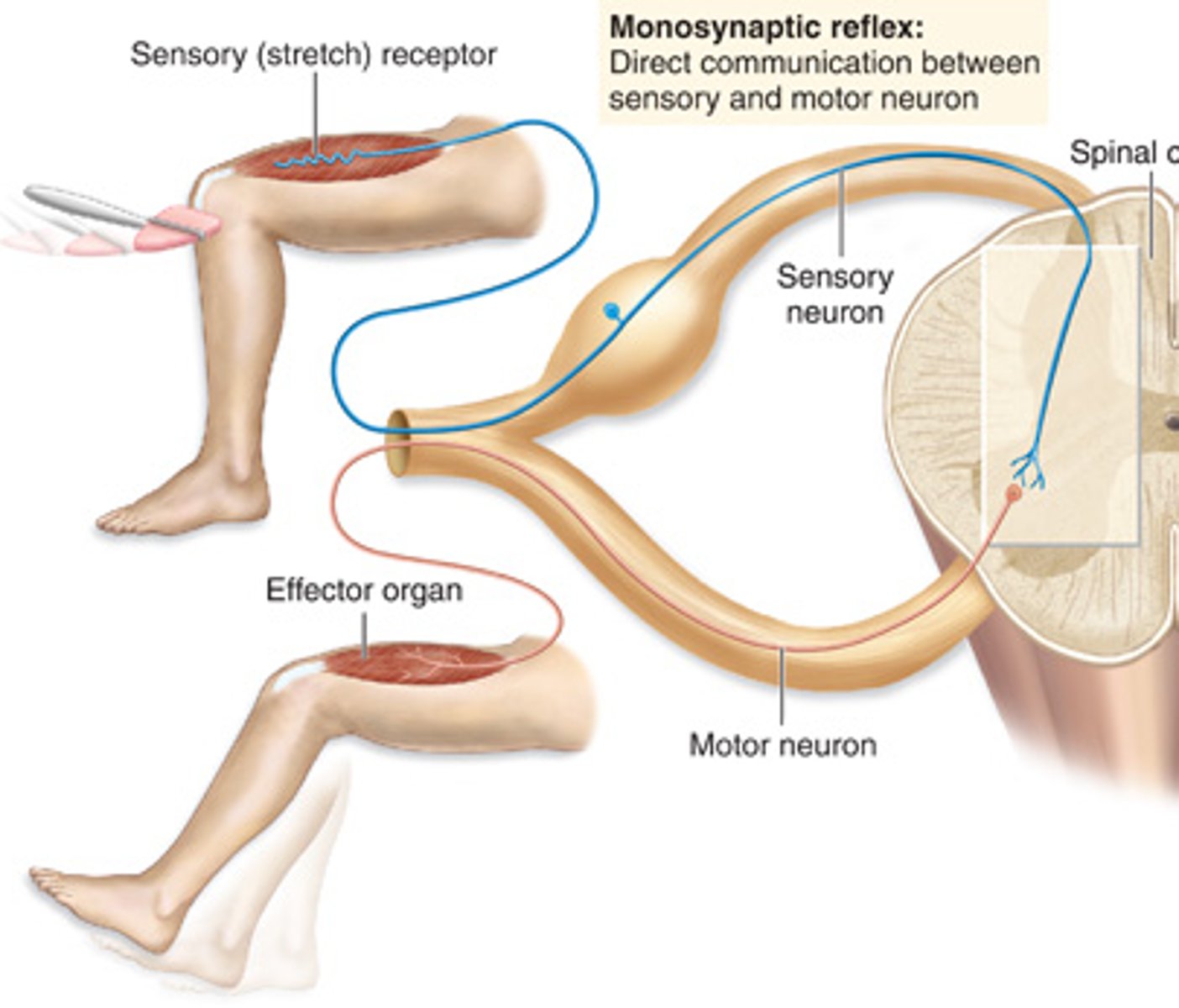
Monosynaptic reflex
direct communication between sensory and motor neuron (e.g., stretch reflex)
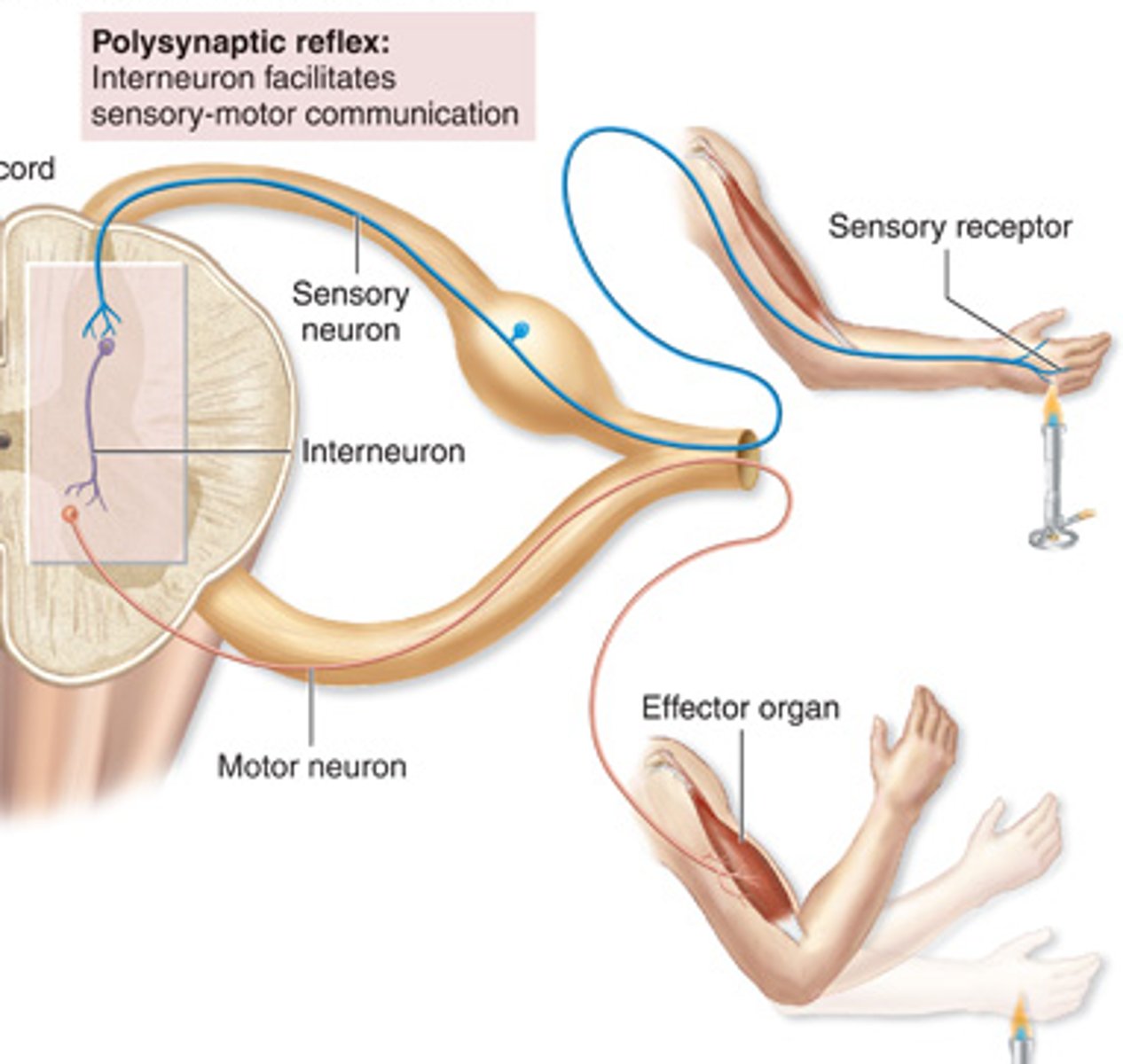
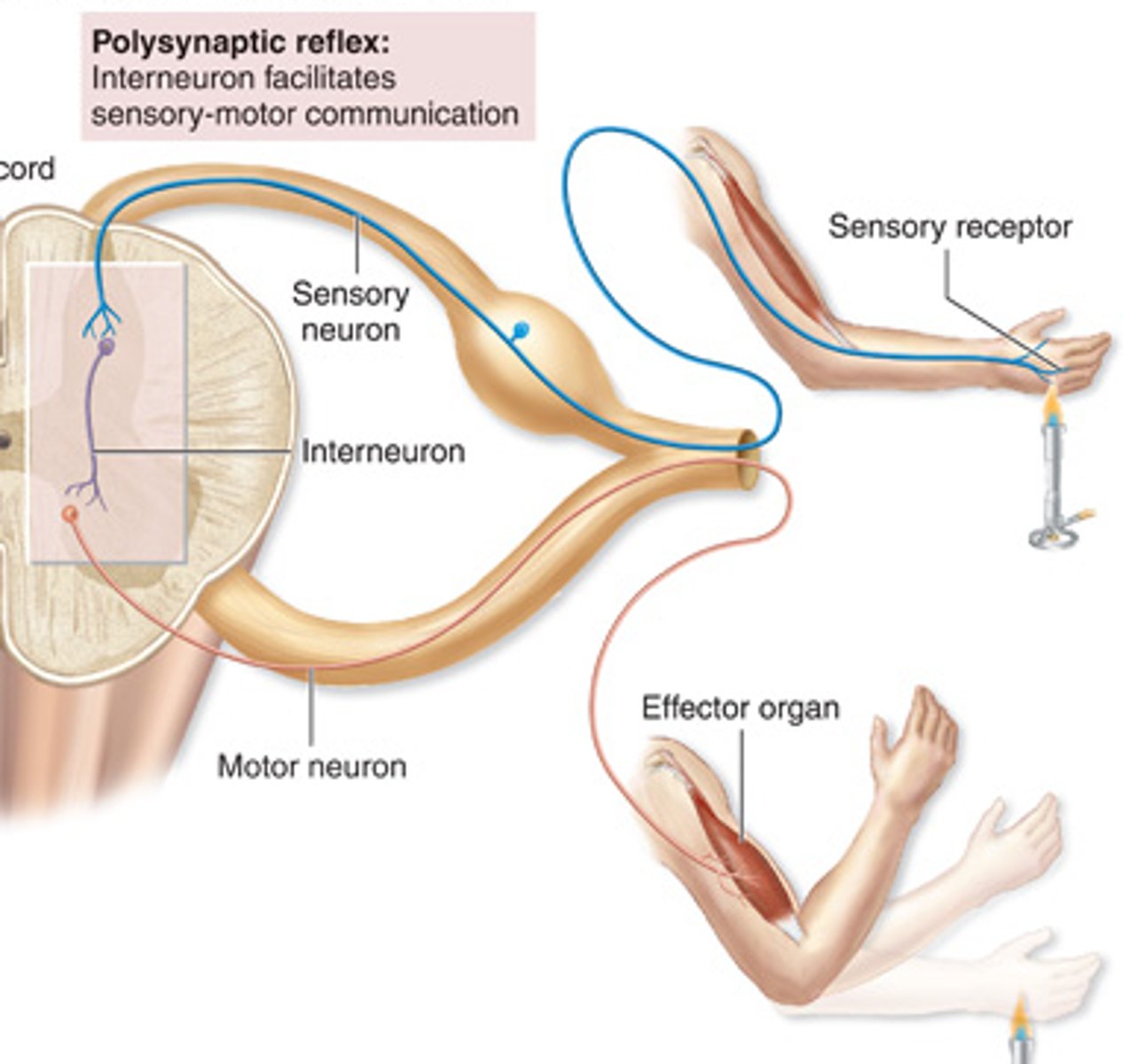
Polysynaptic reflex
Interneuron facilitates sensory-motor communication (e.g., withdrawal reflex)
Spinal reflex
A simple automatic action of the spinal cord not requiring involvement of the brain, such as the knee-jerk reflex
Cranial reflex
reflex that is processed in the brain
Somatic reflex
Involve skeletal muscles as the effectors
Visceral reflex
Cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, or gland as the effector
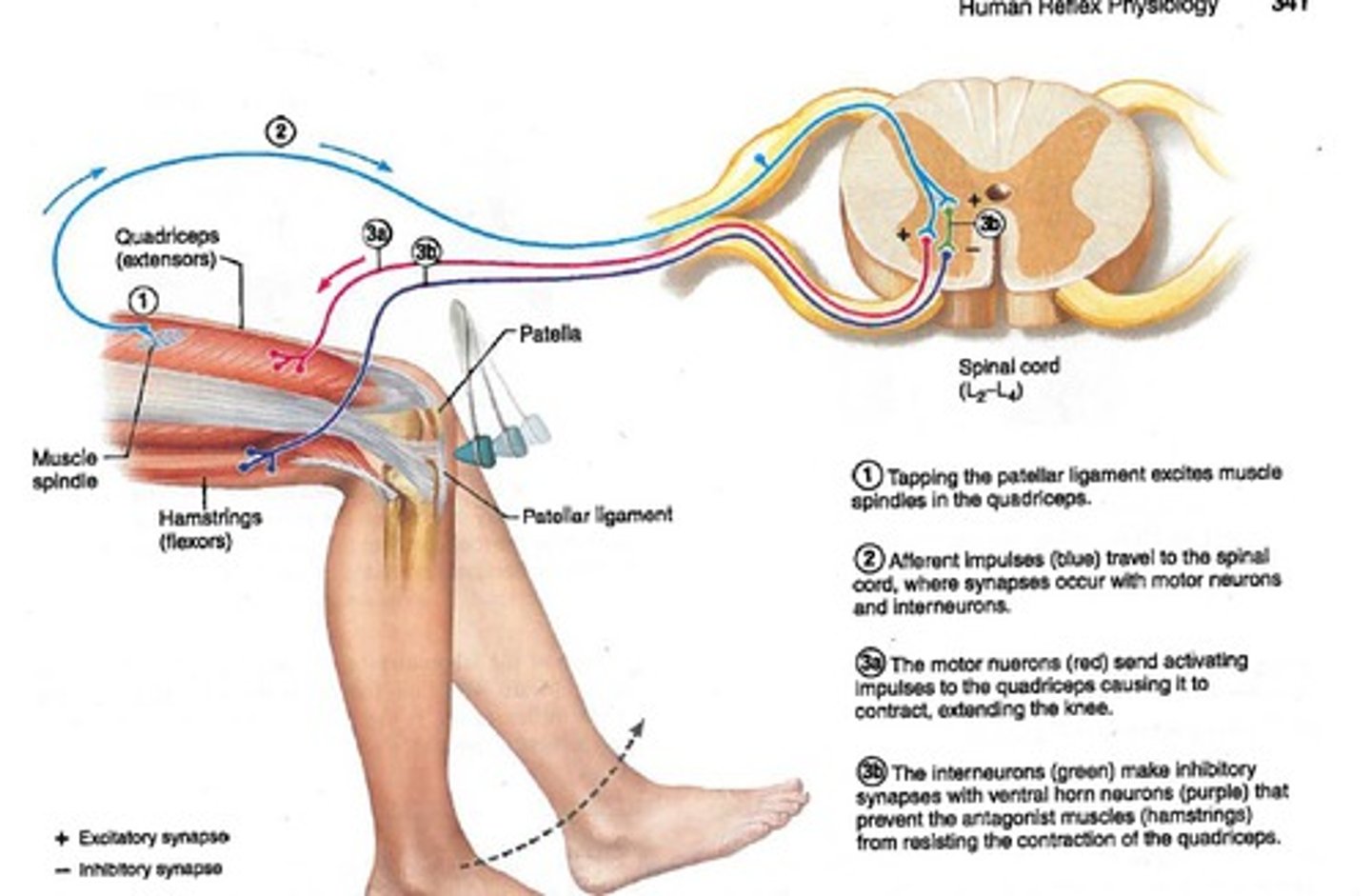
Stretch reflex
Monosynaptic reflex; shortest latency among spinal reflexes
(Patellar reflex is example of this as tendon stretches when hammer strikes)
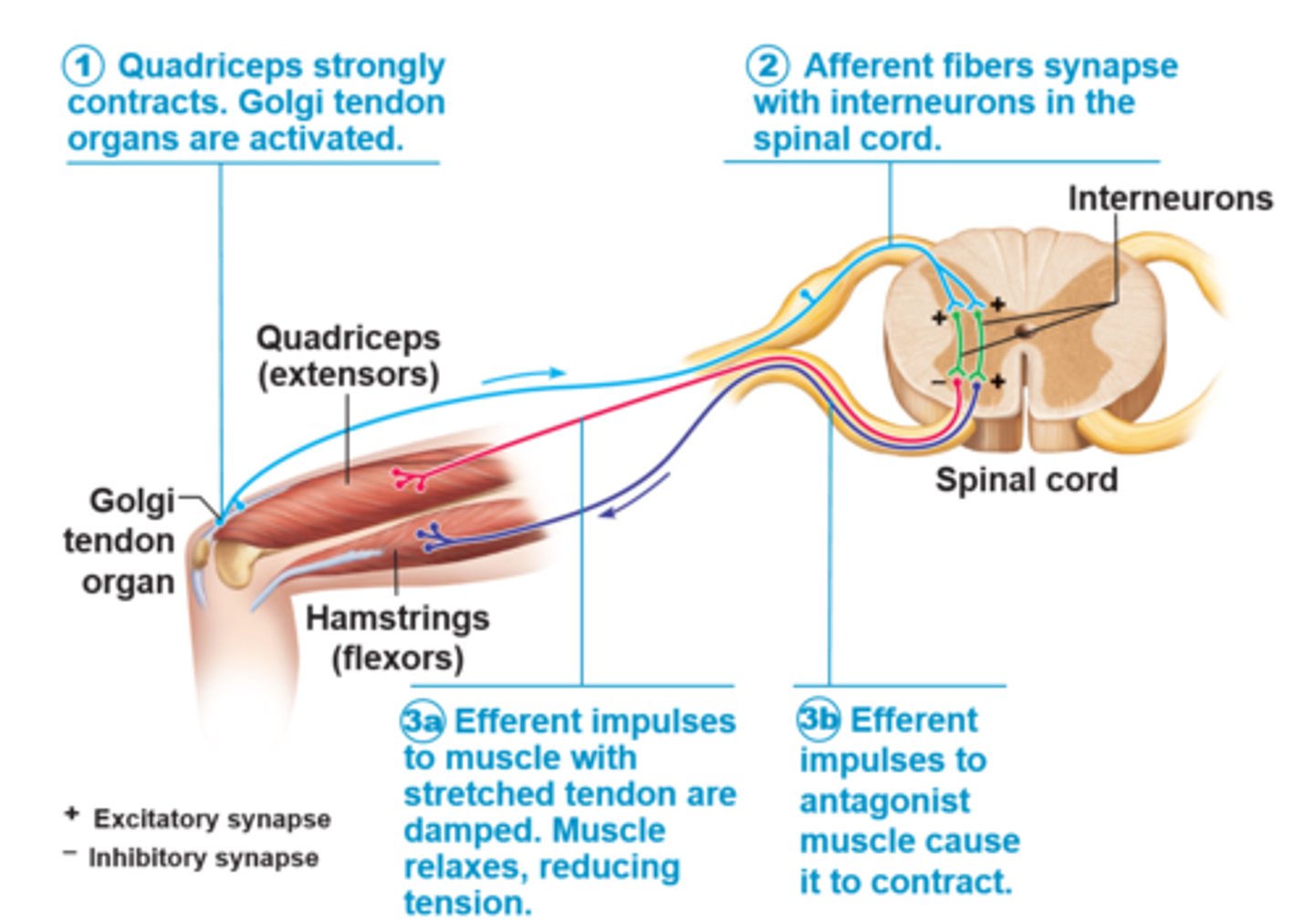
Golgi tendon reflex
Polysynaptic reflex; prevents muscles from contracting excessively; responds to tension (results in muscle lengthening)
Withdrawal reflex
• polysynaptic reflex initiated by painful stimulus
• transmitted by sensory neuron to spinal cord
• received by interneurons
• motor neurons signaled to flex
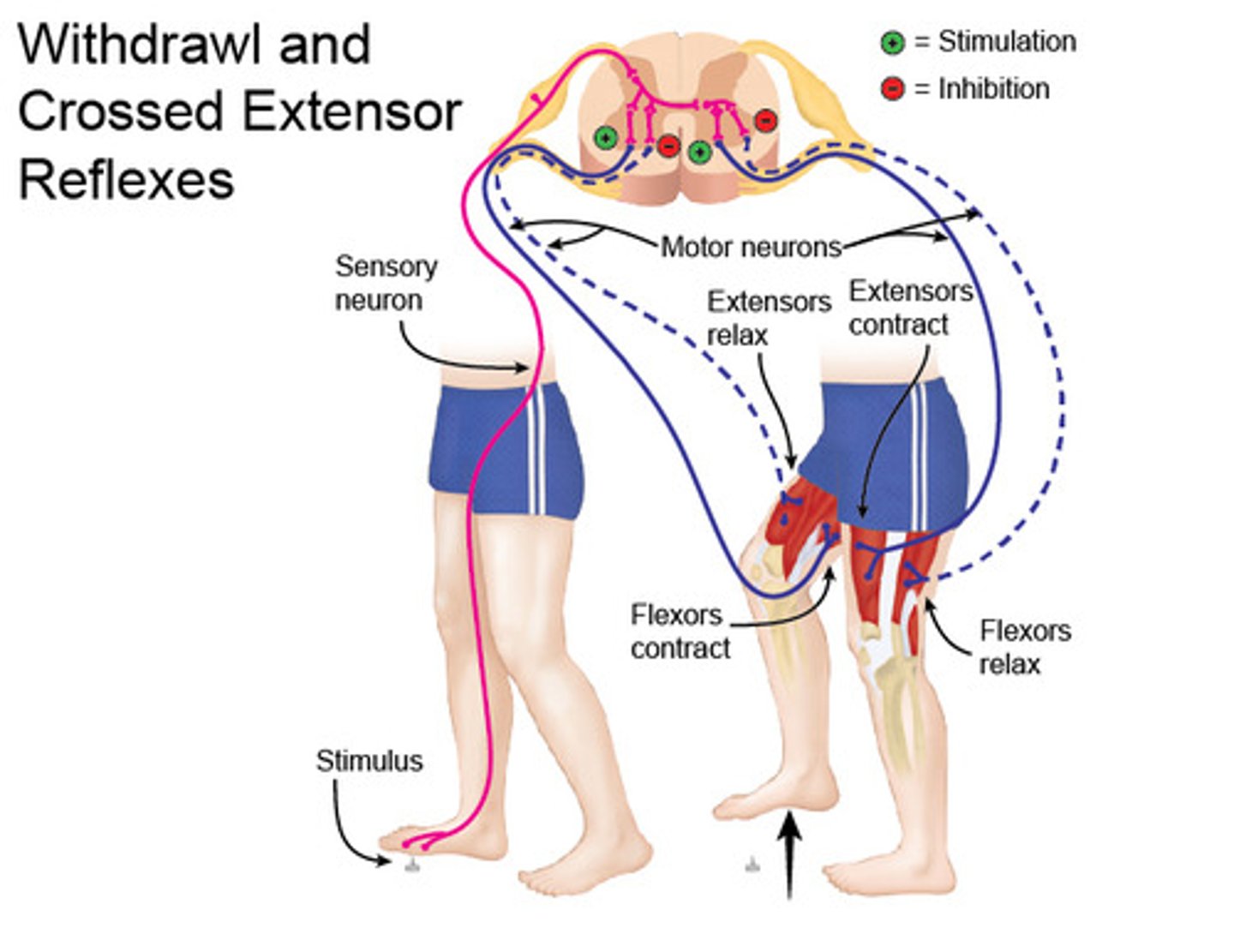
Crossed extensor reflex
-sensory transmission to spinal cord
-synapse with interneurons in stretch and crossed-extensor reflex
-Synapse with motor neurons on antagonistic muscle in opposite limb
Stimuli
events in the environment that can be detected and that might produce responses
Sensation
stimulus that we are consciously aware of
General senses
distributed throughout the body; structurally simple
Special senses
located only in head; structurally complex sense organs. Sensory receptors for smell, taste, vision, hearing, and equilibrium
Receptors
convey signals to CNS by sensory neurons
Receptor field
distribution area of the endings of a sensory neuron
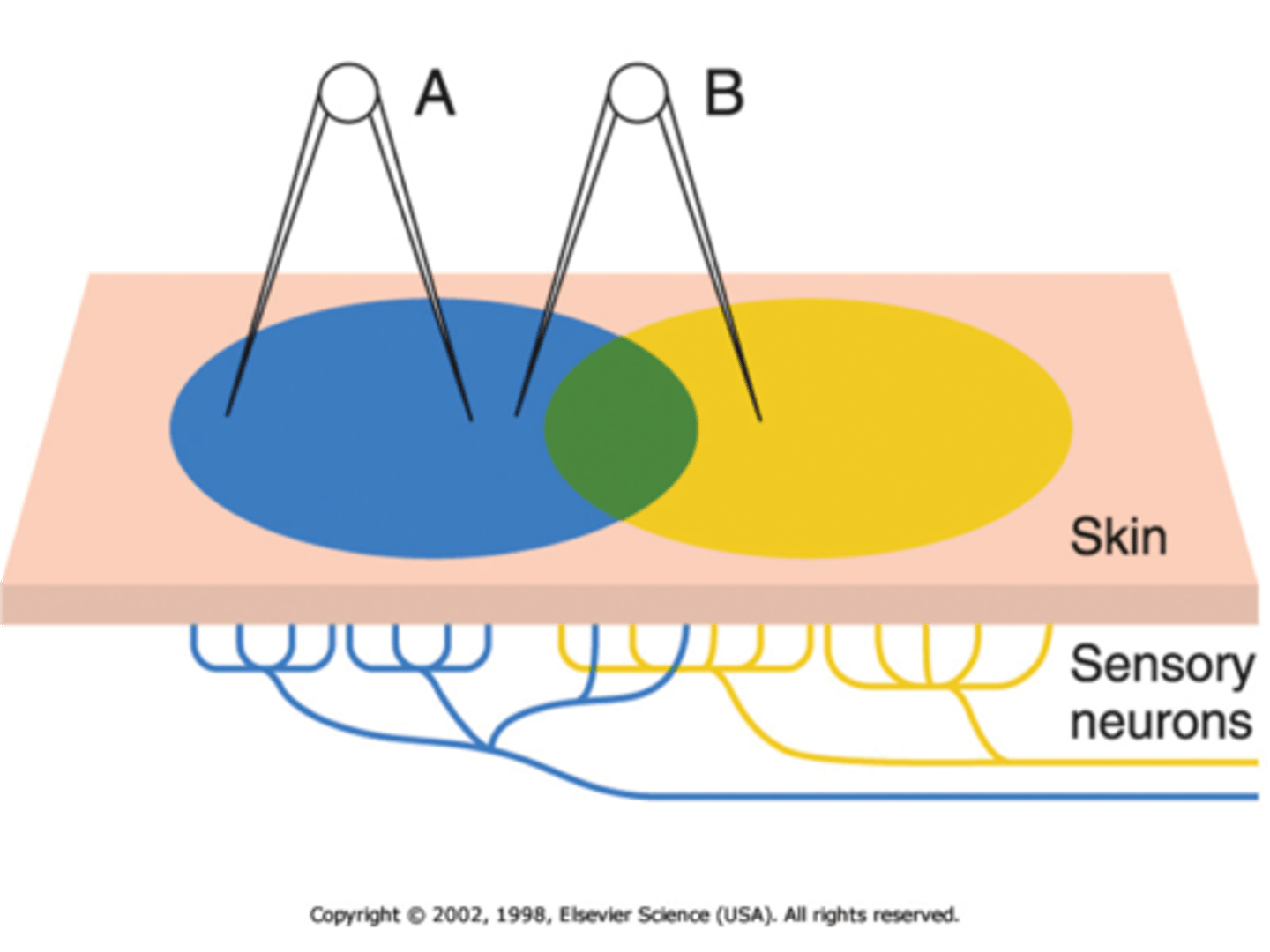
exteroreceptors
detect stimuli from external environment, receptors in skin for special senses (membranes lining nasal cavity, oral cavity, vagina, anal canal
interoreceptors
detect stimuli in internal organs, primarily stretch receptors in smooth muscle walls (mostly unaware of these sensations)
proprioceptors
detect body and limb movements, skeletal muscle contraction and stretch, provide awareness of body joint position and skeletal muscle contraction
somatic sensory receptors
provide position, touch, pressure, pain, and temperature sensations
visceral sensory receptors
found in walls of internal organs, they monitor stretch, chemical environment, temperature, pain
Special sensory receptors