Biology Terms for Micro Exam 3: Drug Toxicity & More
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
sterilization
the mechanical removal of most microbes from an animate or inanimate surface
ex. heat (autoclave), sterilants
disinfection
the destruction or removal of vegetative pathogens but not bacterial endospores
usually used only on inanimate objects
ex. bleach, iodine, heat (boiling)
decontamination
the mechanical removal of most microbes
ex. soaps, detergents, dishwashers
antisepsis
reduces the number of microbes on the human skin
a form of decontamination but on living tissues
ex. alcohol swabs, surgical hand scrubs
types of physical control
heat, radiation, filtration
heat
elevated temperatures are microbicidal
lower temperatures are microbiostatic
moist heat
hot water, boiling water, or steam between 60-135C
boiling water --> disinfects
dry heat
hot air or an open flame, which ranges from 160-1000C
thermal death time
shortest length of time required to kill all test microbes at a specified temperature
thermal death point
the lowest temperature required to kill all microbes in a sample in 10 min
radiation- ionizing
gamma rays and x-rays
highly effective alternative for sterilizing materials that are sensitive to heat or chemicals
radiation-nonionizing
UV rays
not as penetrating as ionizing, the object is disinfected
filtration
effective method to remove microbes from air and liquids
fluid is strained through a filter with openings large enough for the fluid to pass but not microbes
pore sizes can be controlled to permit true sterilization
uses of filtration
Used to prepare liquids that cannot withstand heat such as serum, blood products, vaccines, drugs, IV fluids, enzymes, and media
Alternative method for decontaminating milk and beer without altering their flavor
Important step in water purification
High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are used in hospital rooms and sterile rooms
chemical control
can be liquid, gaseous, or solid
germicides and sterilants
ex. Lysol sanitizing wipes, Purell instant hand sanitizer
antimicrobial chemotherapy
the use of drugs to control infection and kill infected cells without killing the host's cells
antibiotics
originally metabolic products of bacteria and fungi
produced to inhibit the growth of competing microbes in their habitat
before starting antimicrobial therapy you must
1. identify the microorganism
2. identify the degree of the microorganism's susceptibility to various drugs
3. the overall medical condition of the patient
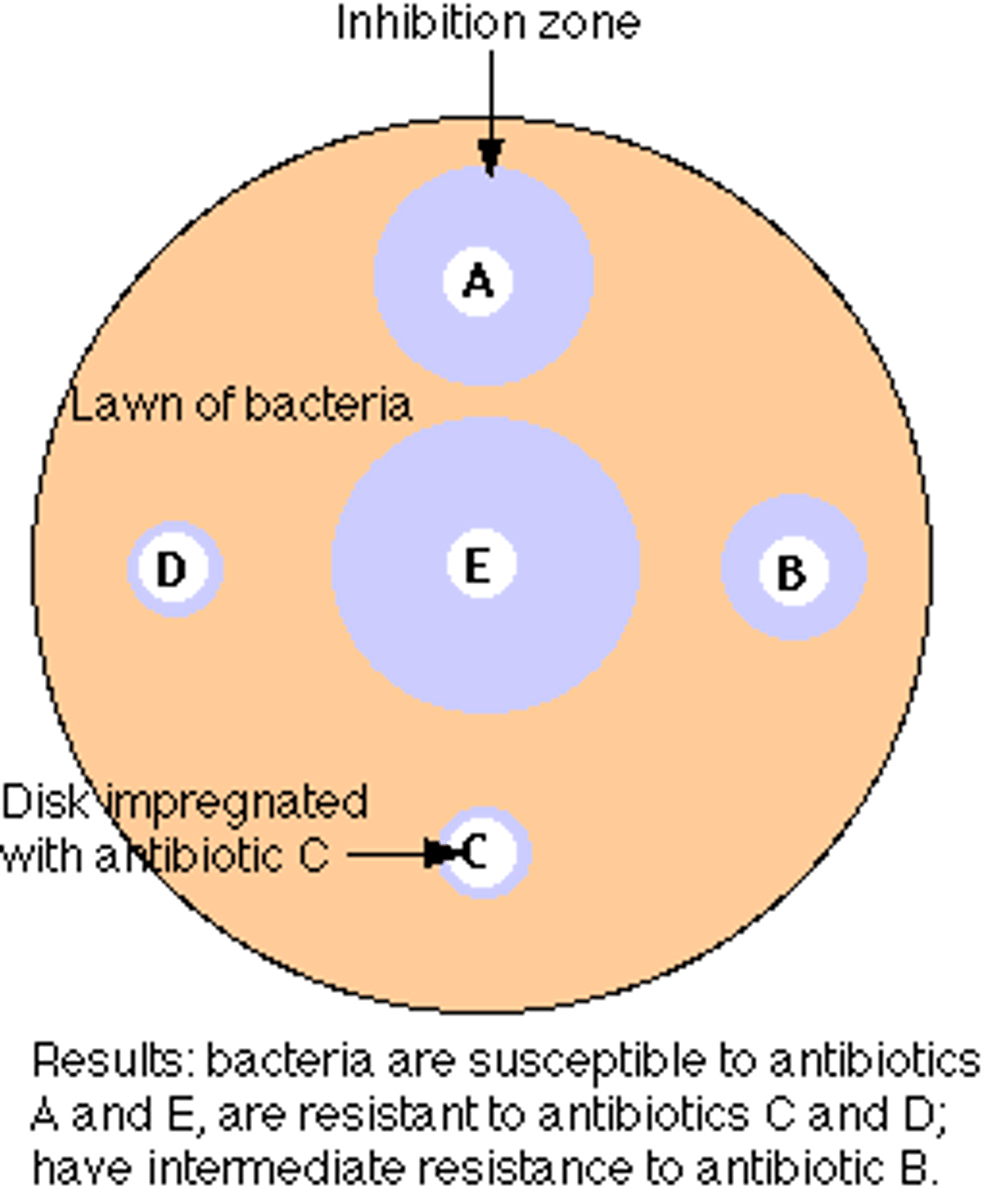
Kirby-Bauer Technique
surface of an agar plate is spread with test bacterium
small discs containing a prepared amount of antibiotic are placed on the plate
zone of inhibition surrounding the disc s is measured and compared with a standard for each drug
therapeutic index
the ratio of the dose of the drug that is toxic to humans as compared to its minimum effective dose
the smaller the ratio, the greater the potential for toxic drug reactions
the drug with the highest therapeutic index has the widest margin of safety
selective toxicity
antimicrobial drugs are selectively toxic
this means that they kill or inhibit microbial cells without damaging host tissues
selective toxicity application
drugs with excellent selective toxicity block the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall (penicillin)
human cells lack the chemical peptidoglycan and are therefore unaffected by the drug
selective toxicity decreases when the infectious agent is closer in structure to the host cell
antimicrobial drugs get classified into 5 categories
1. inhibition of cell wall synthesis
2. inhibition of nucleic acid (RNA and DNA) structure and function
3. inhibition of the ribosome in protein synthesis
4. interference with cytoplasmic membrane structure or function
5. inhibition of folic acid synthesis
broad-spectrum
effective against more than one group of bacteria
narrow-spectrum
target a specific group
penicillin
Antibiotic that interferes with the synthesis of the peptidoglycan portion of bacterial cell walls
original penicillin was narrow-spectrum but molecule has been altered and improved on over the years
antifungal
an agent that destroys or inhibits the growth of fungi
fungal cells are eukaryotic; therefore, present special problems in drug treatment
similarities between fungal and human cells mean that drugs toxic to fungi will also harm human tissues
anti-protozoal
an example of an anti-protozoal drug is metronidazole, a widely used drug for amoebas
anti-helminthic
A drug used to treat helminth infections
ex. Ivermectin
the most effective drugs immobilize, disintegrate, or inhibit the metabolism of all stages of the helminth life cycle
antiviral
drug used to treat viral infections
infectious agent relies on a host cell for most of its metabolic functions. Therefore, disrupting viral metabolism requires disruption of cellular metabolism of host
ex. measles, mumps, hepatitis are prevented with vaccines
actions of antiviral drugs
1. Inhibition of virus entry
2. Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
3. Inhibition of viral assembly/release
antiretroviral
used to manage HIV infections
drug resistance
an adaptive response in which microorganisms begin to tolerate an amount of the drug that would be normally inhibitory
spontaneous mutations
how resistance develops in chromosomal genes
acquisition of entire new genes or sets of genes via horizontal transfer from another species
horizontal transfer
The transfer of DNA from one species to another by conjugation, transformation, or transduction
new gene transfer causes slowing or stopping of metabolism so that the microbe cannot be harmed by the antibiotic
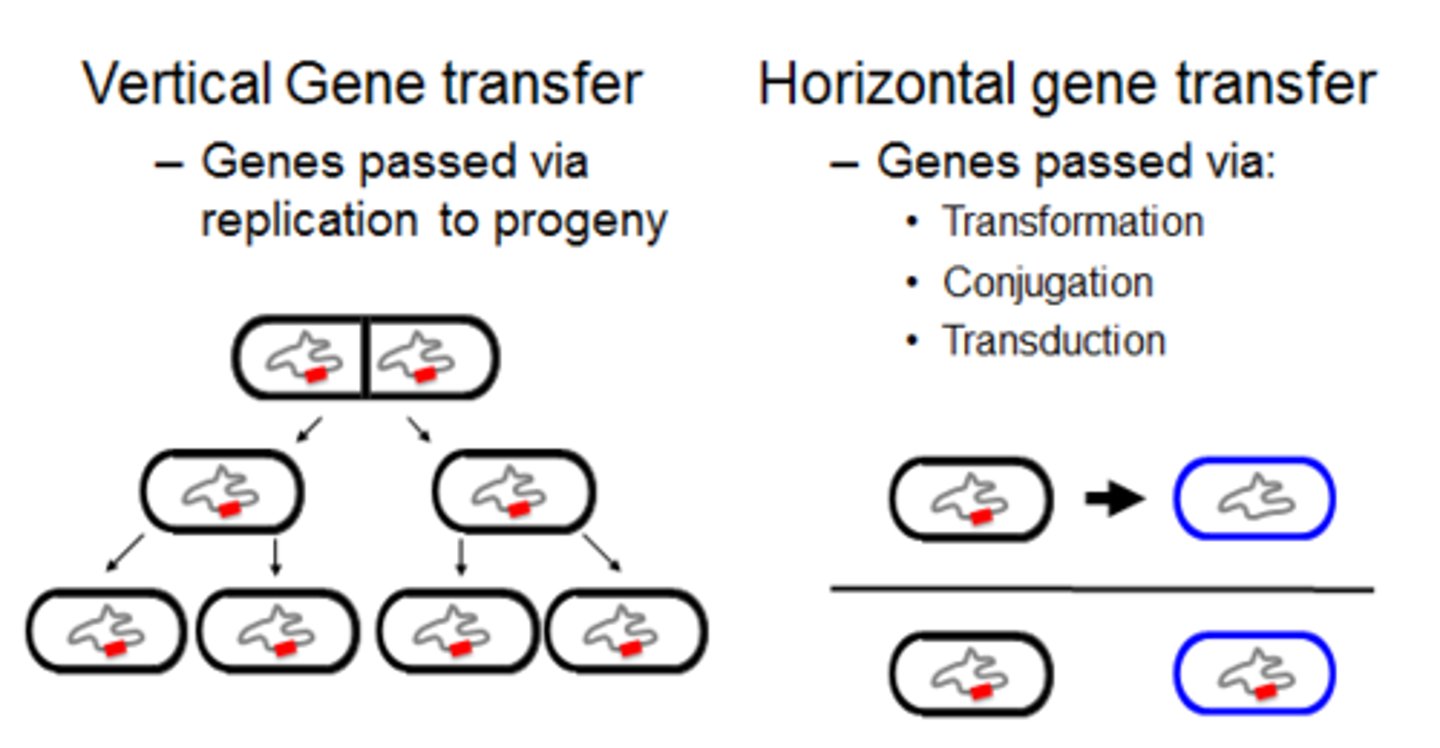
development of resistance and it's long-term therapeutic consequences
any large population of microbes will contain a few individual cells that are already drug-resistant
if the population is exposed to drugs, the drug-resistant population will have a selective advantage
offspring inherit drug resistance
replacement populations evolve to have the drug-resistance form as the dominant species
probiotics
preparations of live microorganisms fed to animals and humans to improve intestinal biota
can replace microbes lost during antimicrobial therapy
augment biota already there
safe, and In some cases, effective
useful in the management of food sensitivities
prebiotics
nutrients like carbohydrates that encourage the growth of beneficial microbes in the intestine that are already there
drug allergy
drug acts as an antigen that stimulates an allergic response
can be provoked by the intact molecule or by substances that develop from the body's metabolic alteration of the drug
penicillin allergy is most common
first exposure sensitizes, second exposure can lead to hives, respiratory inflammation, or anaphylaxis
drug toxicity
drugs can be toxic to different organs in the human body causing adverse reactions
ex. hemolysis, hepatotoxic, nephrotoxic, neurotoxic
infection
microbes that get past "host defenses", enter tissues, and multiply
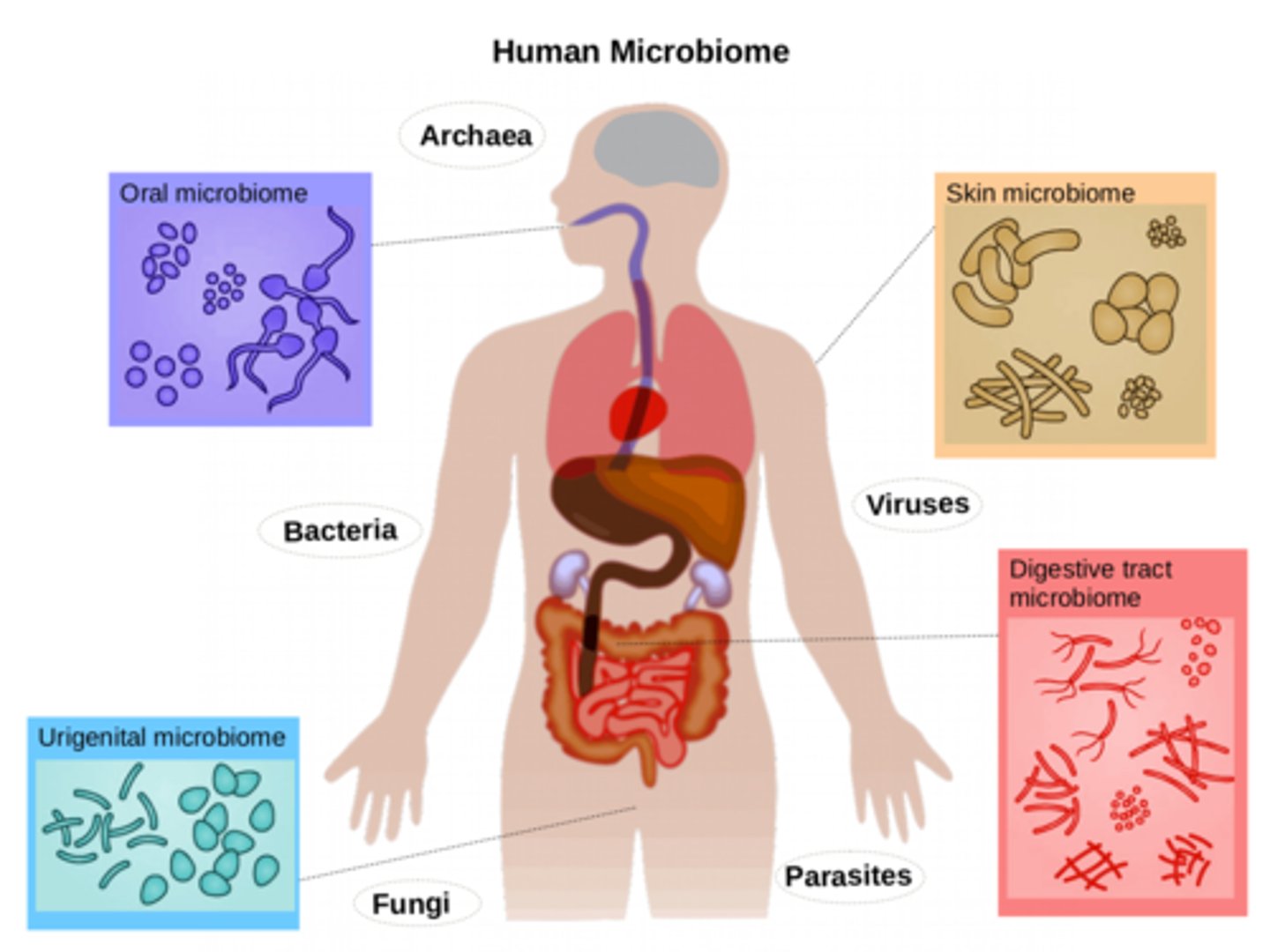
human microbiome
the sum of all microbes (bacteria) found on and in a human
(skin, mucous membranes, URI, GI tract, urethra, genitalia, vagina, ear canal, external eye, lungs, urine, breast milk, amniotic fluid and fetus)
pathogen
a microbe whose relationship with its host is parasitic and results in infection and disease
true pathogens
capable of causing disease in healthy persons with normal immune defenses
opportunistic pathogens
cause disease when the host's defenses are compromised or when the pathogens become established in a part of the body that is not natural to them
exogenous infectious agents
organisms coming from outside the body
endogenous infectious agents
organisms coming from somewhere in the same human host
infectious dose
the minimum number of microbes "bacteria" necessary to cause an infection to proceed
microorganisms with smaller "infectious doses" have greater virulence
symptom
subjective evidence of disease as sensed by the patient
ex. pain, soreness, swelling
signs
objective evidence of disease as noted by an observer
ex. edema, granulomas, lymphadenitis
incubation period
time from initial contact with the infectious agent to the appearance of first symptoms
agent is multiplying at the portal of entry but has not caused enough damage to elicit symptoms or disease
prodromal stage
1-2 day period when the earliest notable symptoms of infection appear
acute stage
infectious agent multiplies at high levels, exhibits its greatest virulence, becomes well established in its target tissue
marked by fever and other prominent and specific signs and symptoms
convalescent period
patient begins to respond to the infection and symptoms decline
patient's strength and health gradually return due to the healing nature of the immune response
many patients stop taking their antibiotics during this period
continuation period
**Only some infections have this phase
Either the organism lingers for months, years, or indefinitely after the patient is well or the organism is gone but symptoms continue
zoonotic infections
infections that are transmitted from animals
human-human infections
a great number of infections that affect humans have their reservoirs in other humans
communicable infections
a disease in which an infected host can transmit the infectious agent to another host and establish infection in that host
noncommunicable infections
an infectious disease that does not arise through transmission of the infectious agent from host-host
infected persons cannot spread to another host
horizontal transmission
disease is spread through a population from one infected individual to another
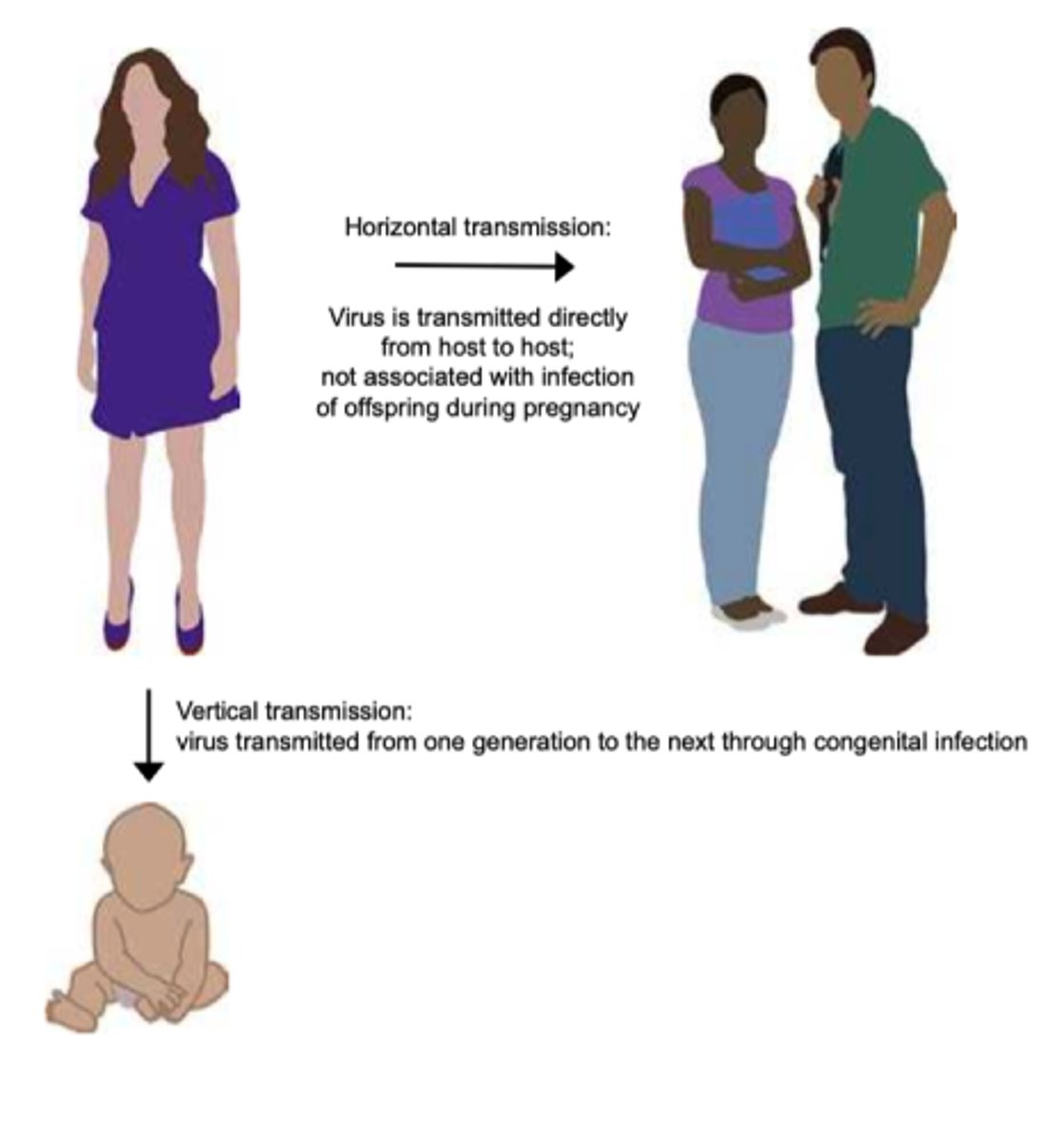
vertical transmission
disease transmitted from parent to offspring
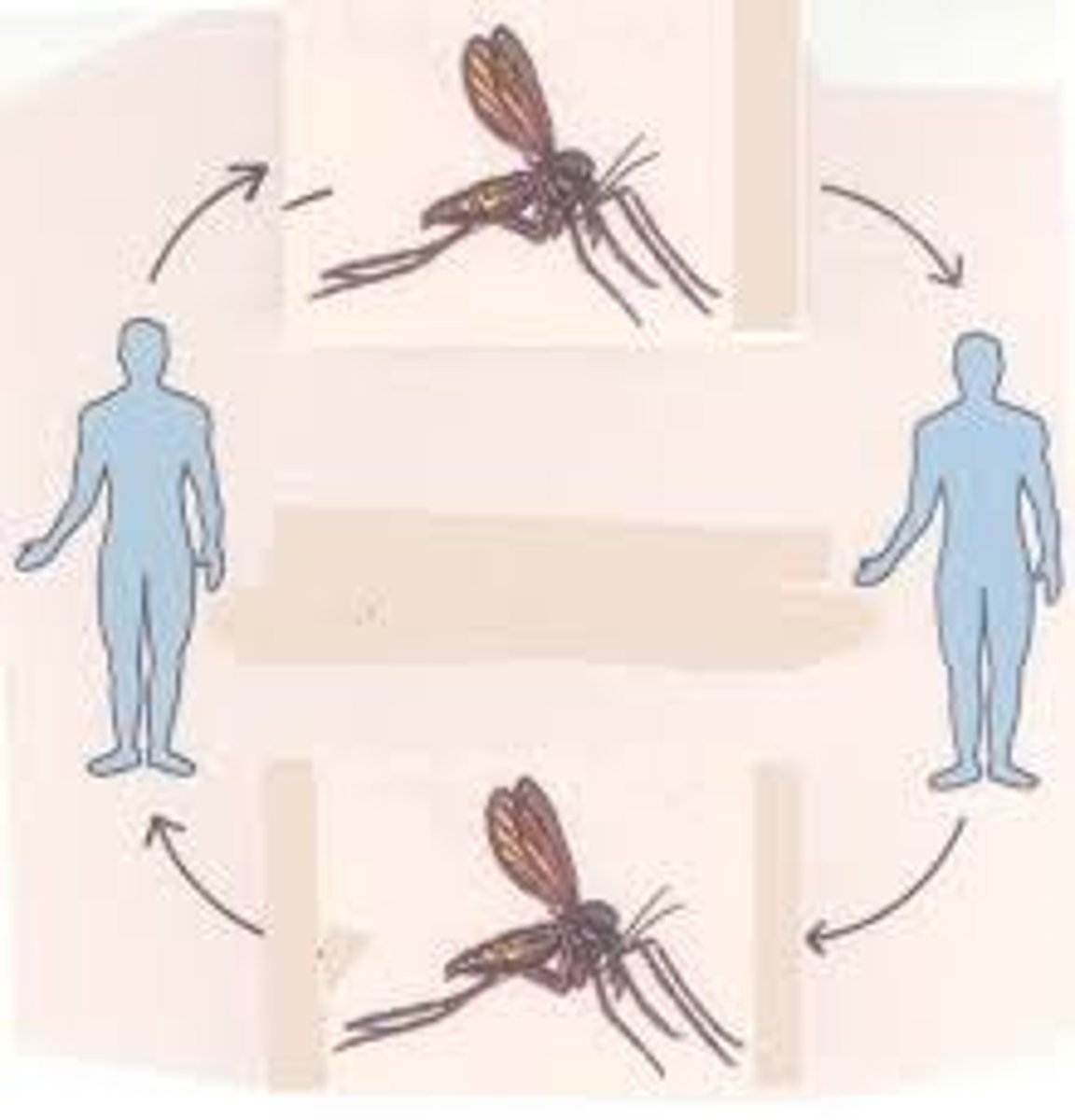
vector transmission
arthropods harbor an infectious agent and transfer it to a human
stages of microbe disease
1. finding a portal of entry
2. attaching firmly and negotiating the microbiome
3. surviving host defenses
4. causing damage/disease
5. exiting host
finding a portal of entry
skin, GI tract, respiratory tract, urogenital tract, endogenous biota
attaching to host
fimbriae, capsules, surface proteins, viral spikes
surviving host defenses
avoiding phagocytosis, avoiding death inside phagocyte, absence of adaptive immunity
causing disease
direct damage via enzymes or toxins, inducing excessive host response, causing epigenetic changes in host chromosome
exiting host
portals of exit: respiratory tract, salivary glands, skin cells, fecal matter, urogenital tract, blood
antibiotic resistance
the evolution of populations of pathogenic bacteria that antibiotics are unable to kill
immunopathology
the study of disease states associated with the overreactivity or underactivity of the immune response
hypersensitivity
allergy and autoimmunity
the tissues are innocent bystanders attacked by immune components that can't distinguish one's own tissues from foreign material
hyposensitivity
immune system is incompletely developed, suppressed, or destroyed
Type 1 hypersensitivity
common allergy and anaphylaxis
ex. anaphylaxis, hay fever, asthma
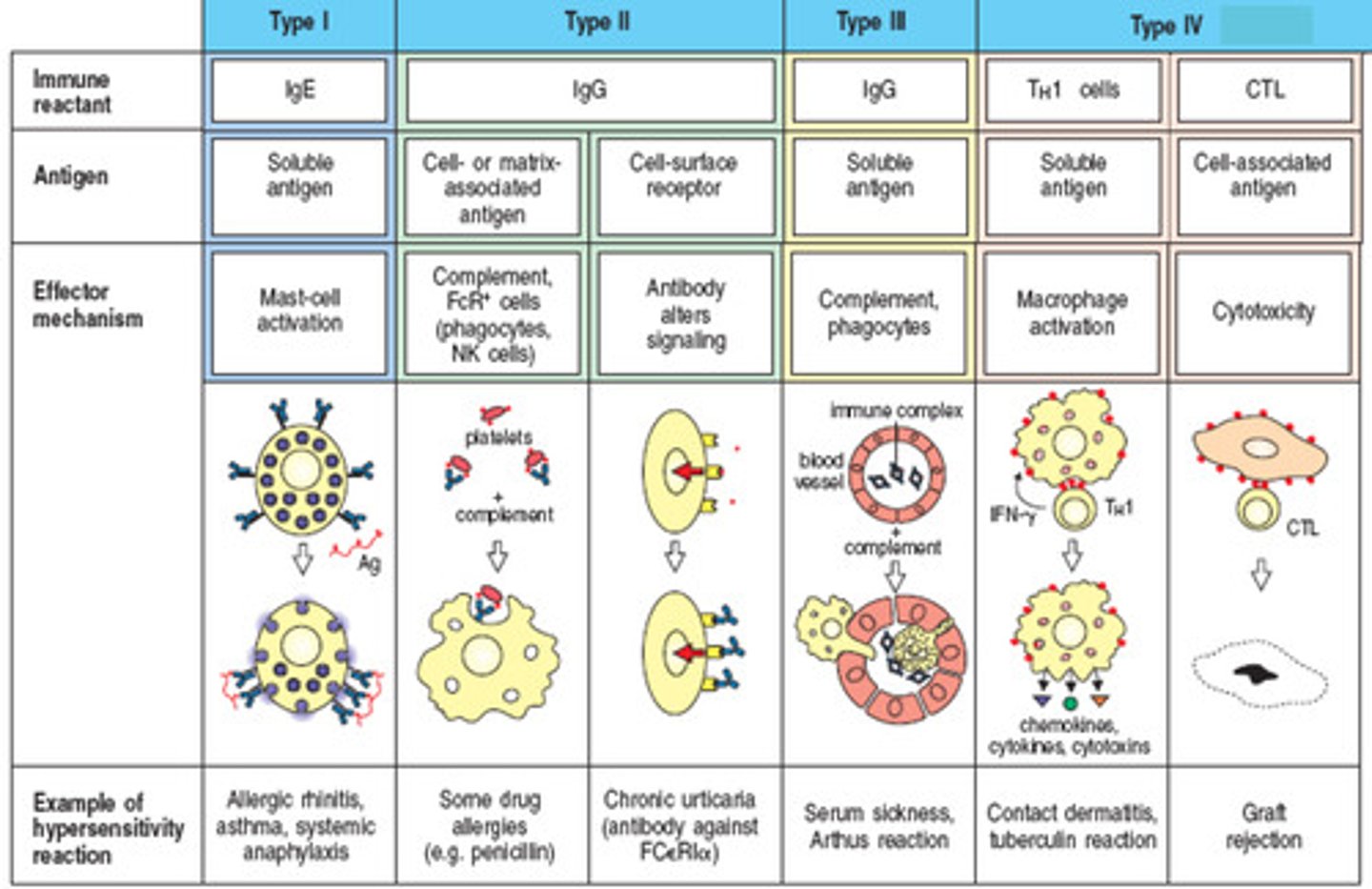
Type II hypersensitivity
IgG and IgM mediated cell damage
ex. blood group incompatibility, pernicious anemia, myasthenia gravis
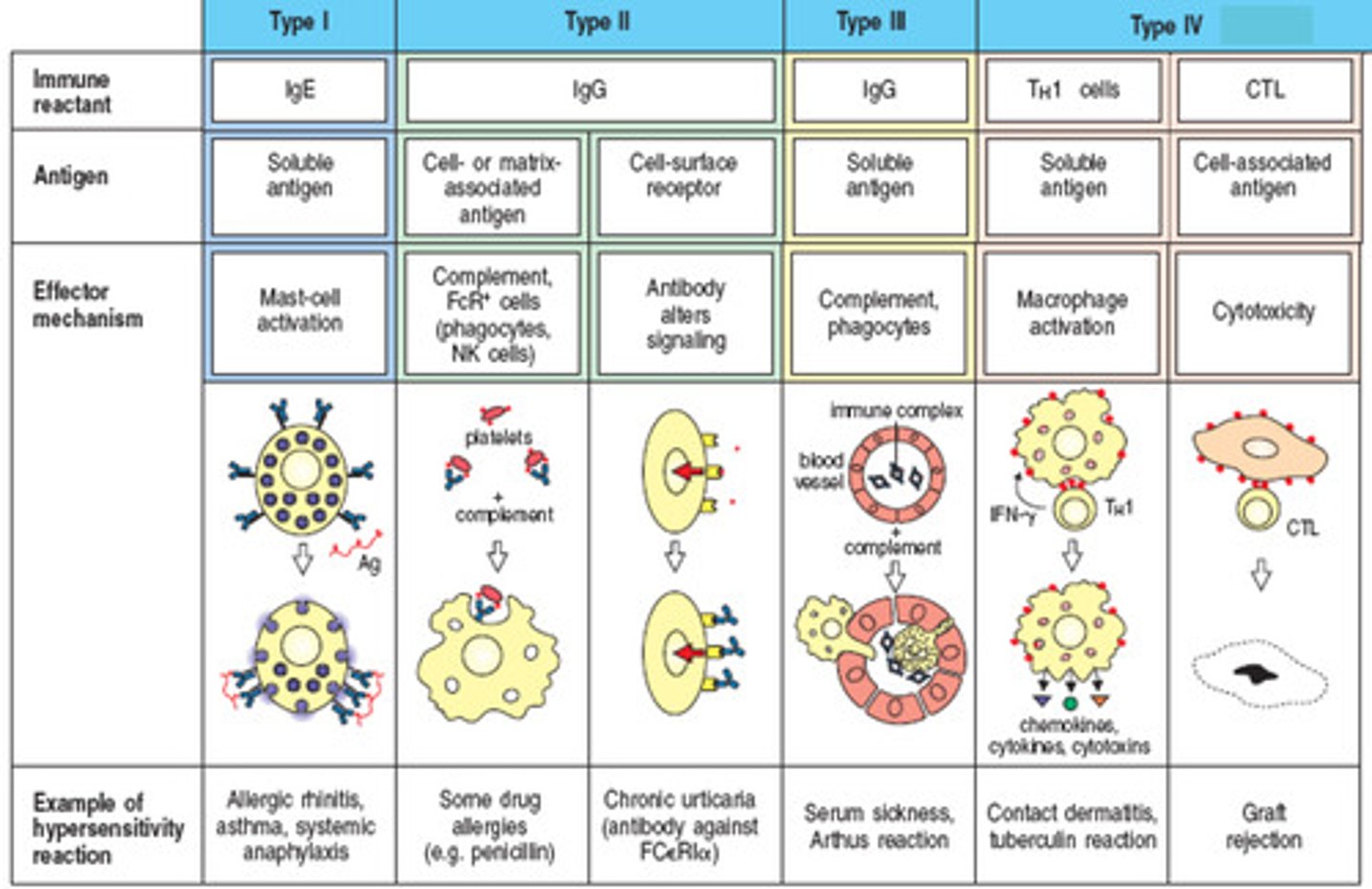
Type III hypersensitivity
Immune complexes deposit in tissues causing inflammation
ex. systemic lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, serum sickness, rheumatic fever
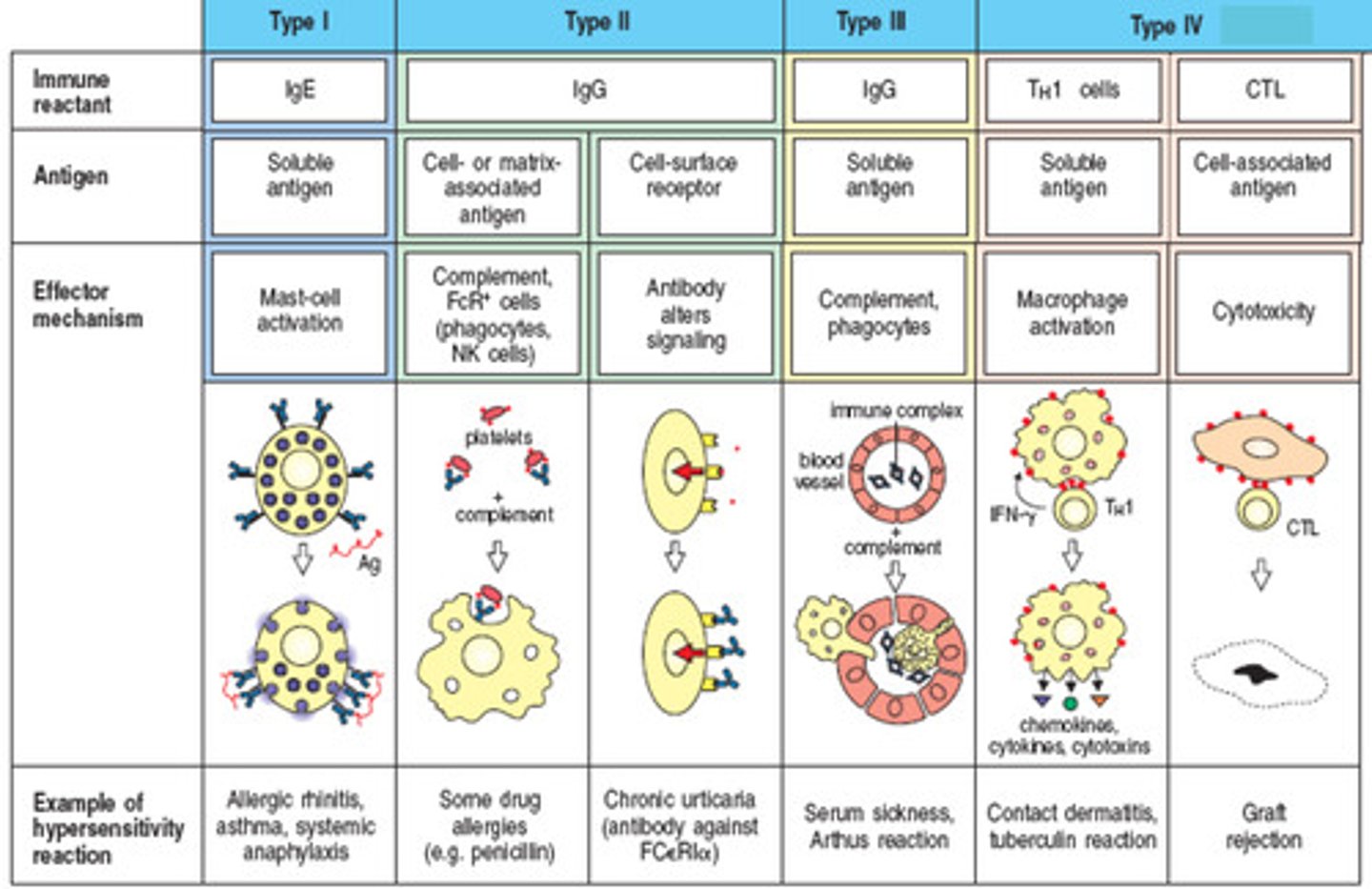
Type IV hypersensitivity
T-cell response
ex. infection reactions, contact dermatitis, graft rejection

atopy
chronic local allergy such as hay fever and asthma
genetic basis for atopy
1. increased IgE production
2. increased reactivity of mast cells
3. increased susceptibility of target tissue to allergic mediators
Anaphylaxis
systemic, sometimes fatal, reaction that involves airway obstruction and circulatory collapse

degranulation
the release of the contents of mast cell granules that release inflammatory cytokines
Rh factor
Rhesus antigen
Rh+ represent the dominant gene that codes for the antigen; Rh- represents the recessive gene that does not code for the antigen
the only way to develop antibodies against this factor is through exposure to a fetus's antigens while pregnant or transfusion
hemolytic disease of the newborn
happens in a second pregnancy in which the mother's blood type is Rh- and the fetus is Rh+
autograft
tissue transplanted from one site on an individual's body to another site
isograft
tissue from an identical twin is used
allograft
exchanges between genetically different individuals belonging to the same species; the most common types of grafts
xenograft
a tissue exchange between individuals or a different species
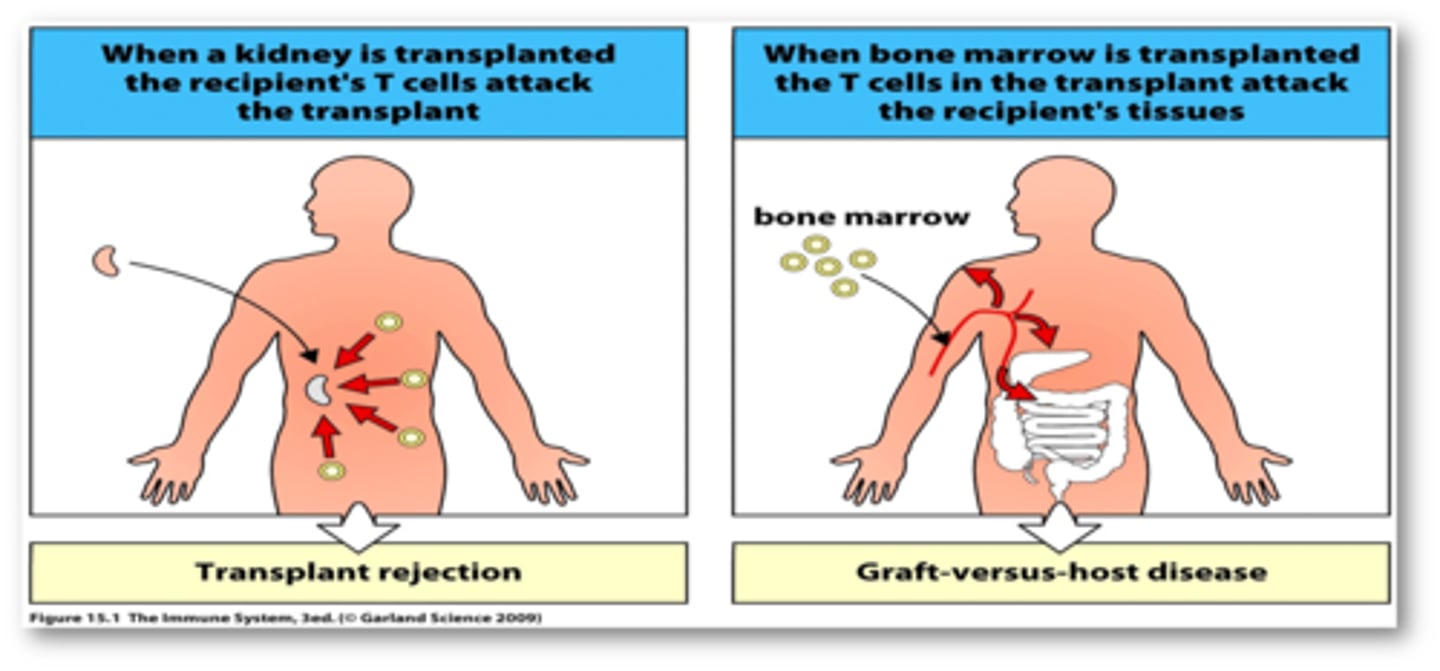
graft vs host
graft attacks any host tissue bearing foreign MHC markers
effects are systemic and toxic
occurs within 100-300 days of the graft
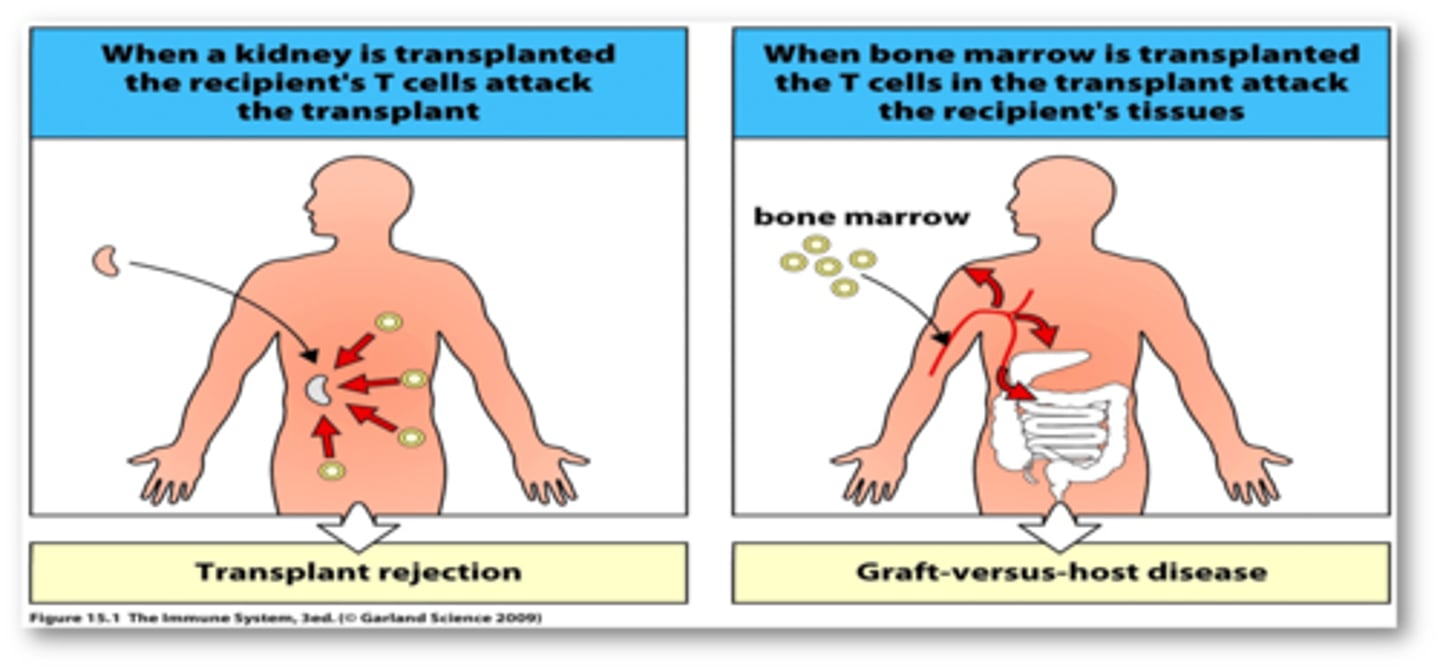
host vs graft
cytotoxic T cells of a host recognize foreign class. I MHC markers on the surface of a grafted cells
helper and cytotoxic T cells bind to the grafted tissue and secrete lymphokines that begin the rejection process within 2 weeks of transplantation
antibodies formed against the transplanted tissue contributes to damage
the result is destruction of the vascular supply and death of the graft
phenotypic
observations of traits that an organism is expressing
involves remaining microbe appearance and behavior
considers macroscopic and microscopic morphology, physiology, and biochemistry
stains used: gram stain, acid-fast, KOH.
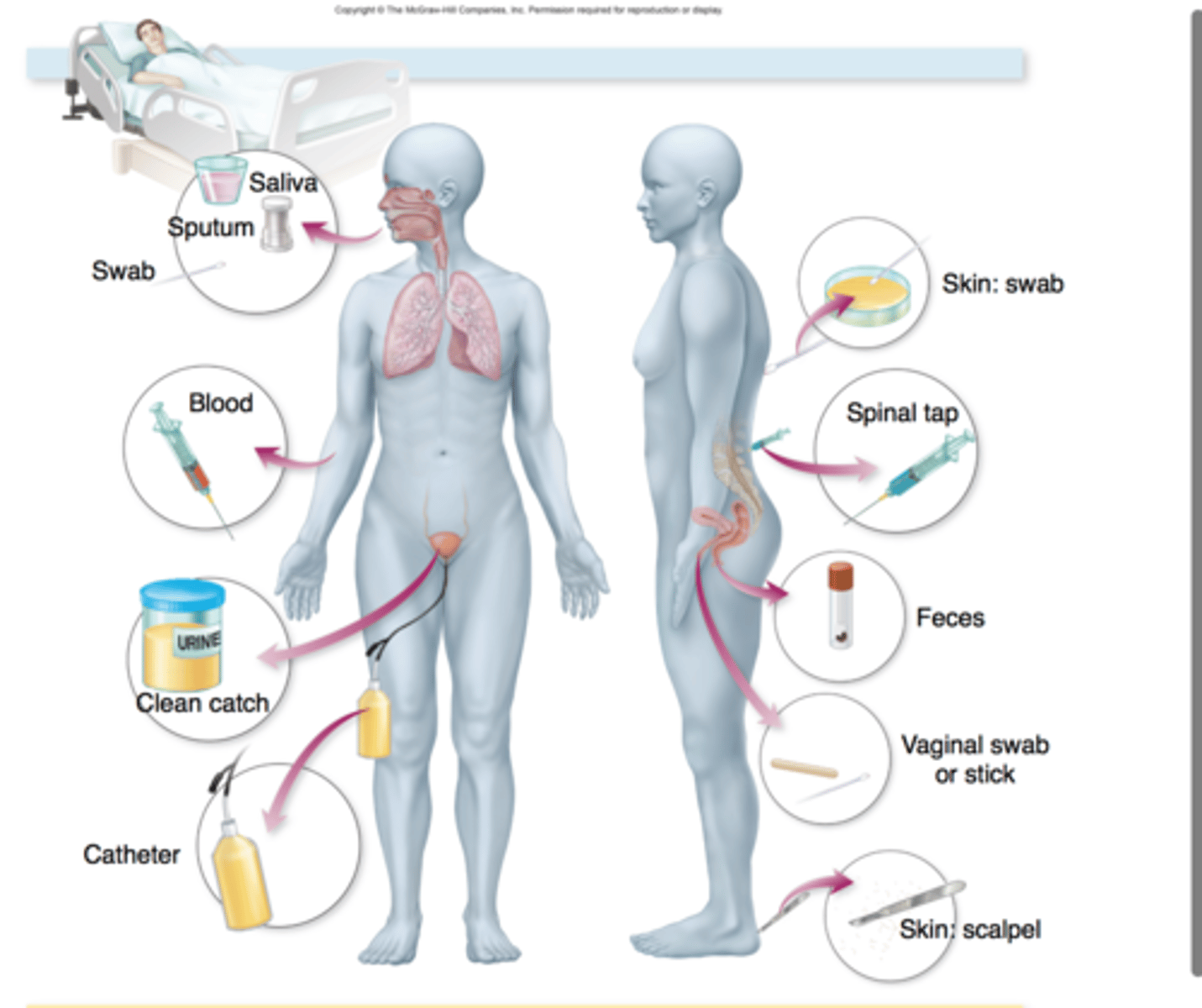
specimen collection
aseptic technique is imperative
sterile sample containers
prevent contamination
immunologic methods
molecular basis of immunologic testing is the binding of an antibody to a specific site or epitope of an antigen
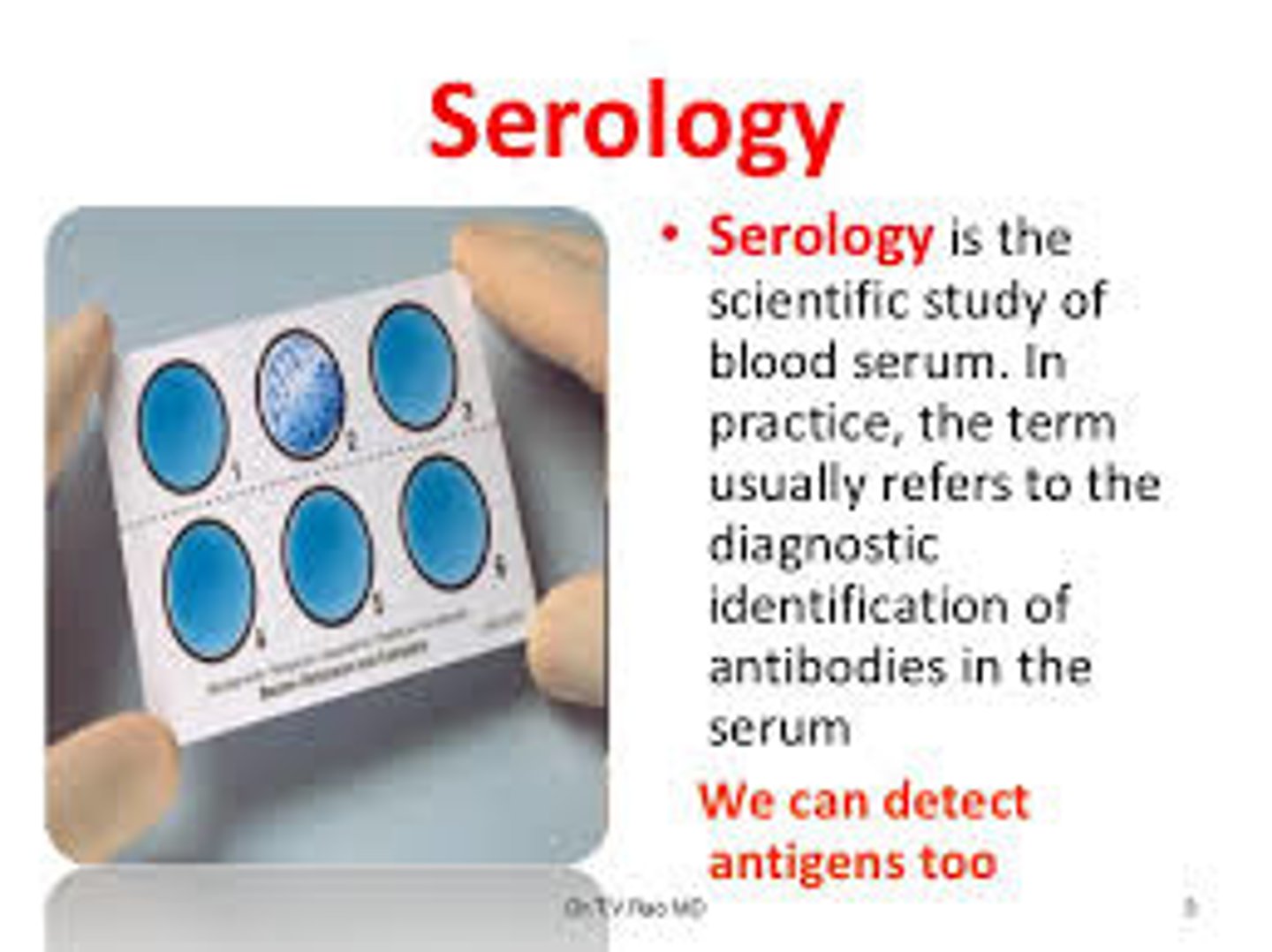
serology
involves in vitro testing of serum, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, whole tissues, and saliva for the presence of specific antibodies
based on the principle that antibodies have an extreme specificity for antigens
used to determine the immunologic status of patients, confirm a suspected diagnosis, and screen individuals for disease
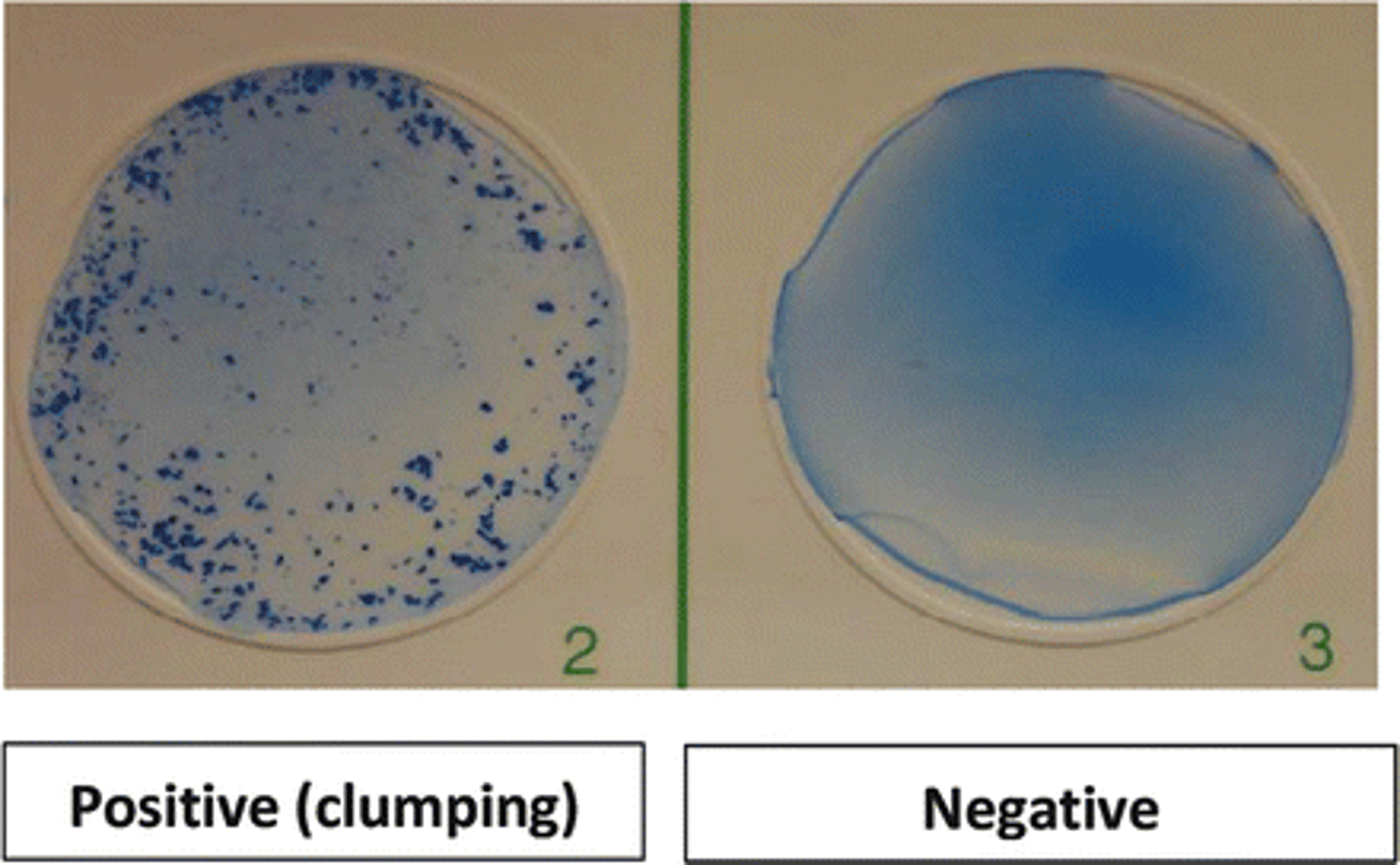
agglutination and precipitation
in both reactions, one antigen is interlinked by several antibodies to form insoluble aggregates that settle out in solution
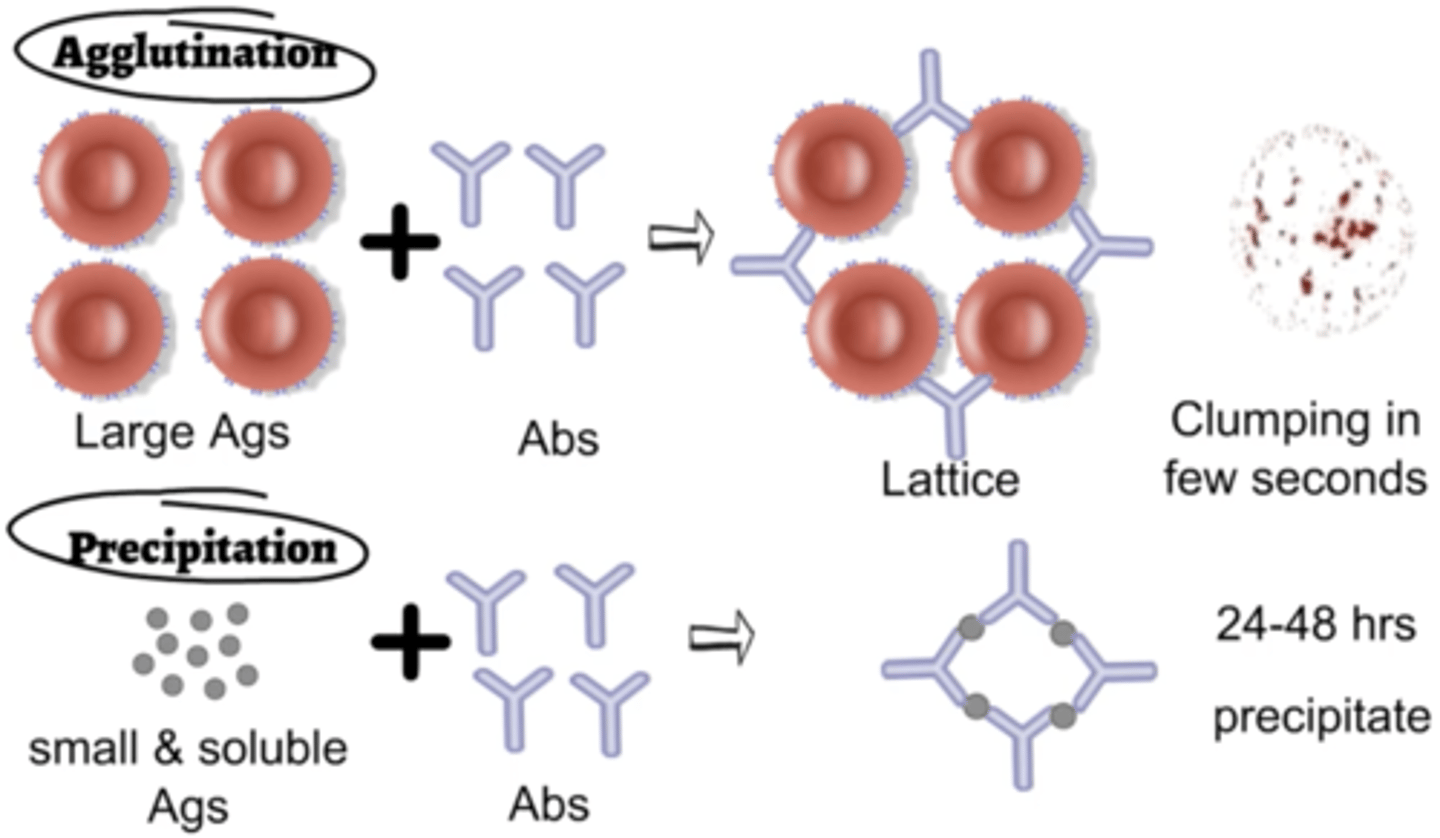
agglutination test
antigens are whole cells or organisms such as red blood cells, bacteria, or viruses displaying surface antigens
-forms visible clumps of cells
-used to determine blood compatibility
precipitation test
antigen examined is a small soluble molecule
more difficult to visualize because precipitates are easily disrupted in liquid media

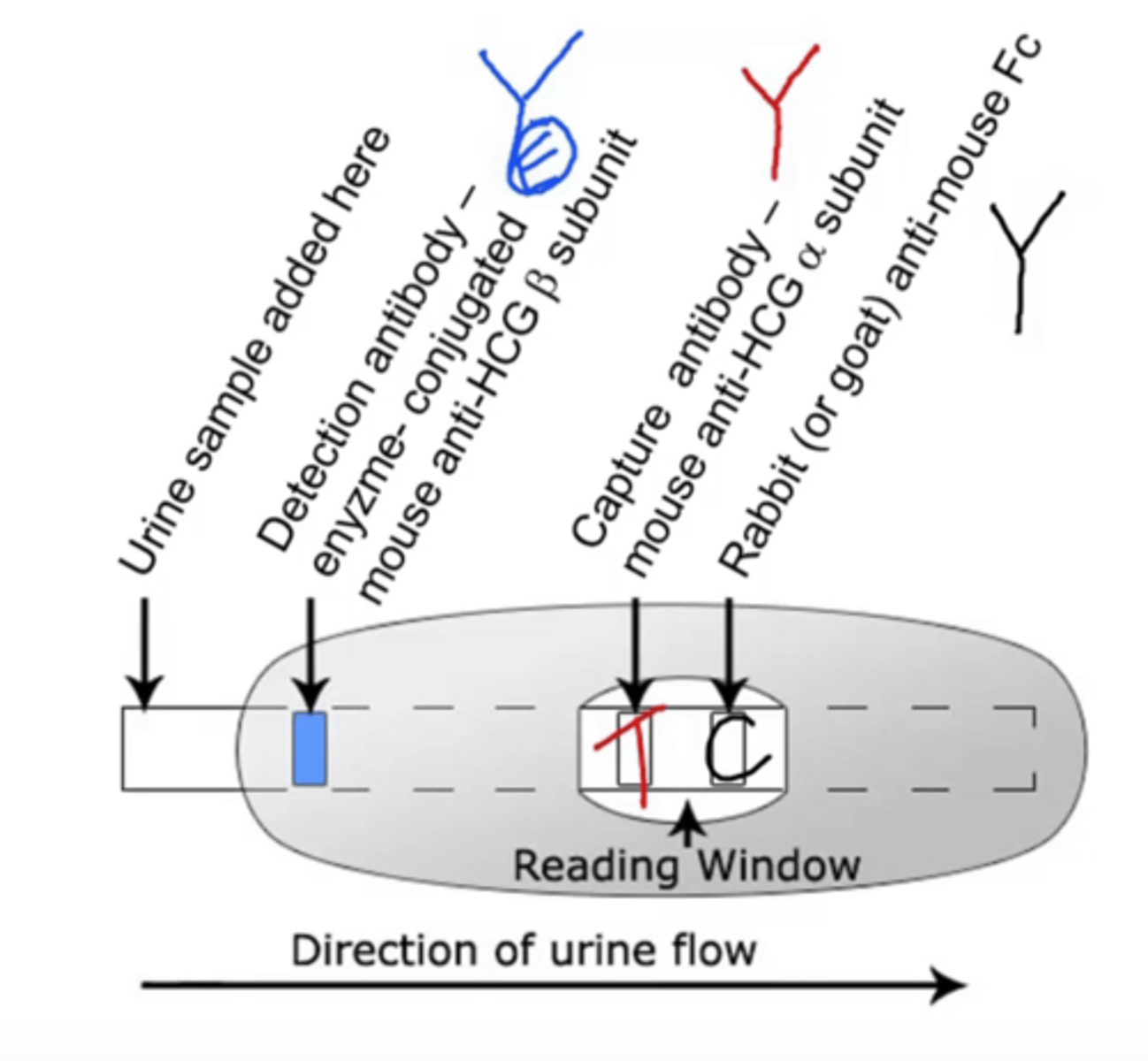
Immunochromatography (lateral flow test)
plastic cartridge contains porous material or polymer that directs fluid to flow in a particular direction
fluid will encounter antibodies along its route of flow
if the sample contains the correct antigen, it will bind to the antibodies and continue to the next station in the cartridge
next stage contains a third molecule that is impregnated on the paper in a stripe pattern
third molecule binds the complexes and eventually, this causes the stripe to change color
ex.) pregnancy test, rapid strep test, COVID-19 test
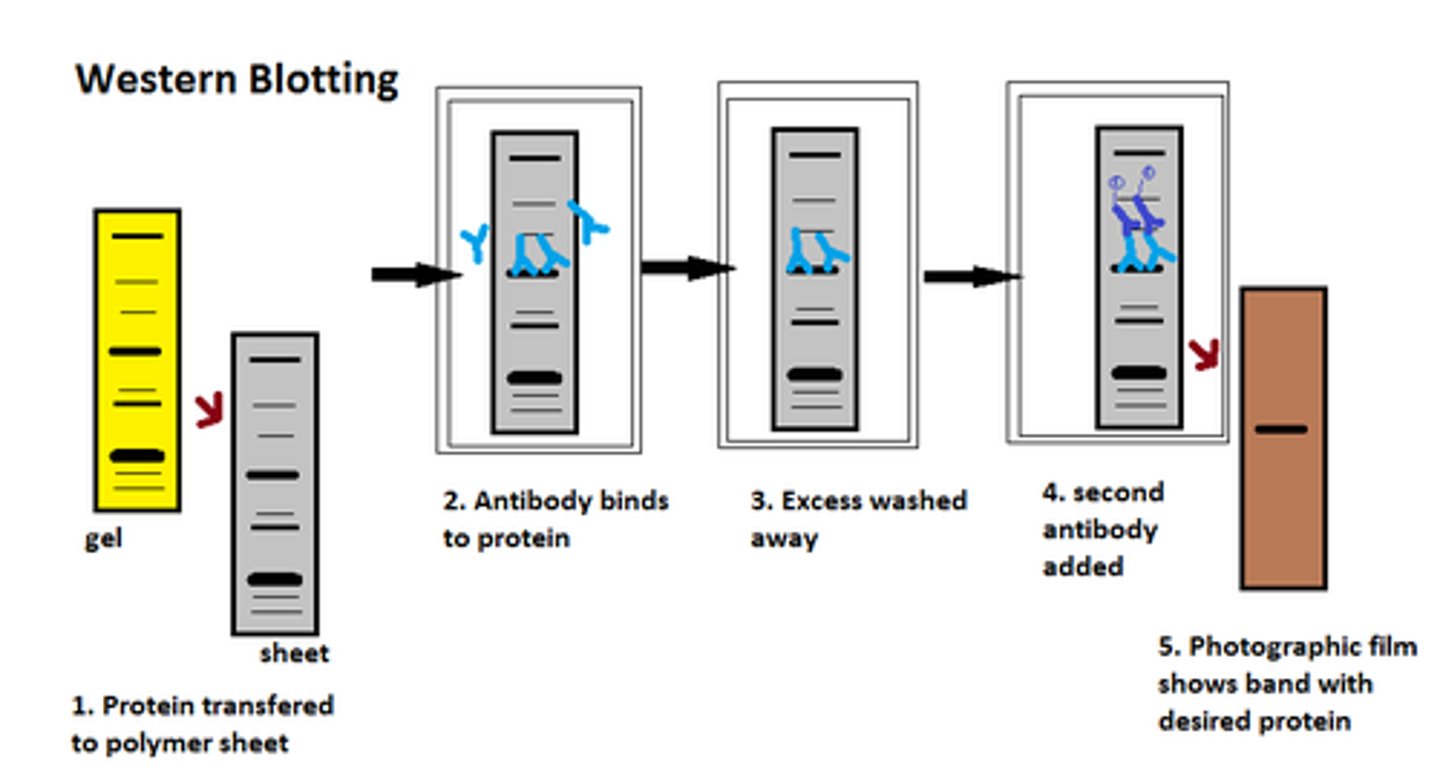
Western Blot test
antigens within microbial cell lysates are separated via electrical charge within a gel
proteins in the gel are transferred to a special filter
filter is incubated with patient fluid; antibodies are detected when a second, fluorescence-labeled antibody compatible fot the Fc portion of an antibody is added
sites of specific antigen-antibody binding will appear as a pattern of bands that can be compared to known positive and negative controls
verified microbial-specific antigens or antibodies in a patient sample
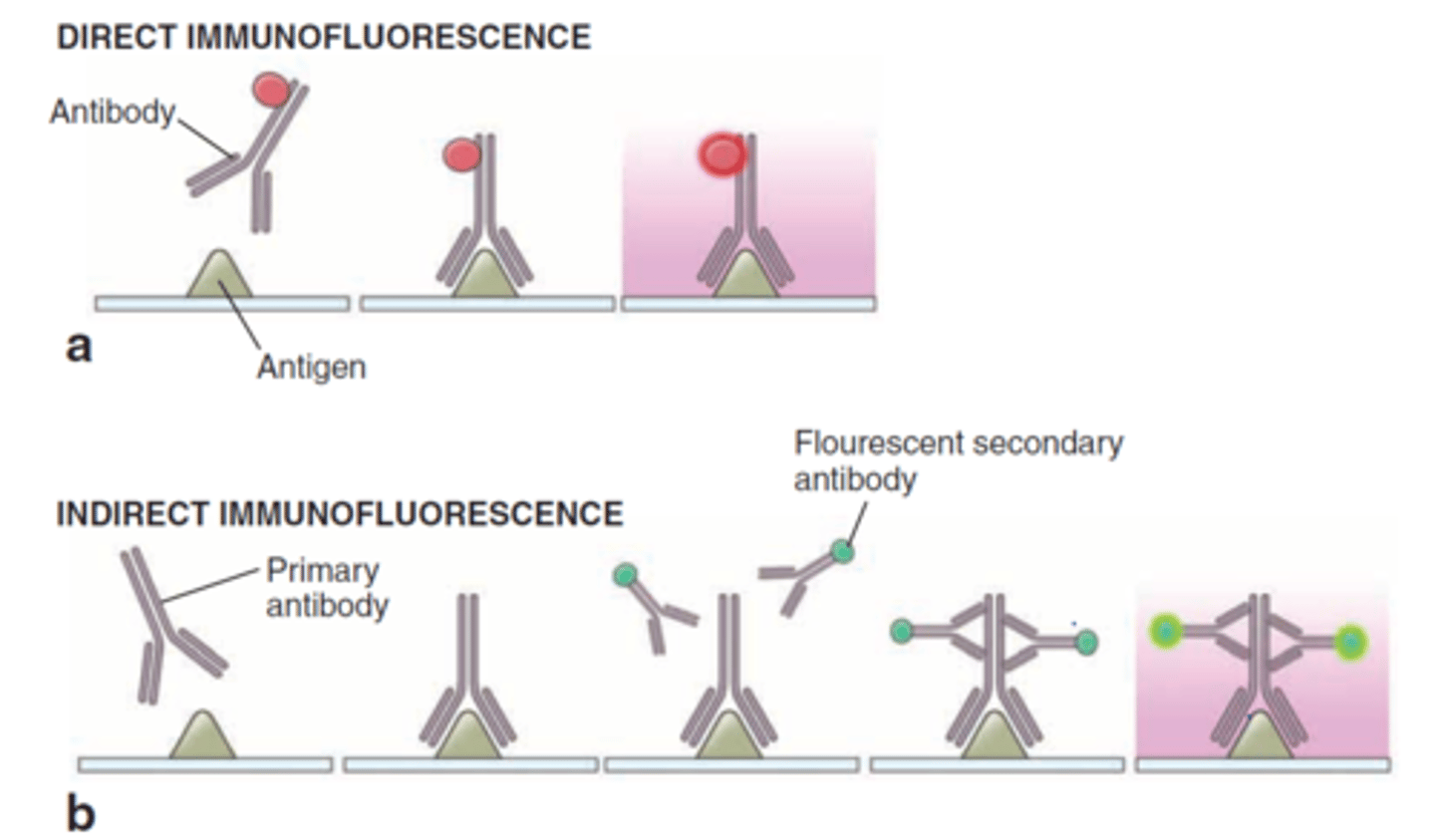
fluorescent antibodies
monoclonal antibodies labeled by a fluorescent dye

direct fluorescent antibody testing
if antigen-antibody complexes form, they will remain bound to the sample and will be visualized by fluorescence microscopy
valuable for identifying and locating microbial antigens on cell surfaces or tissues and in identifying the causative agents of syphilis, gonorrhea, and meningitis
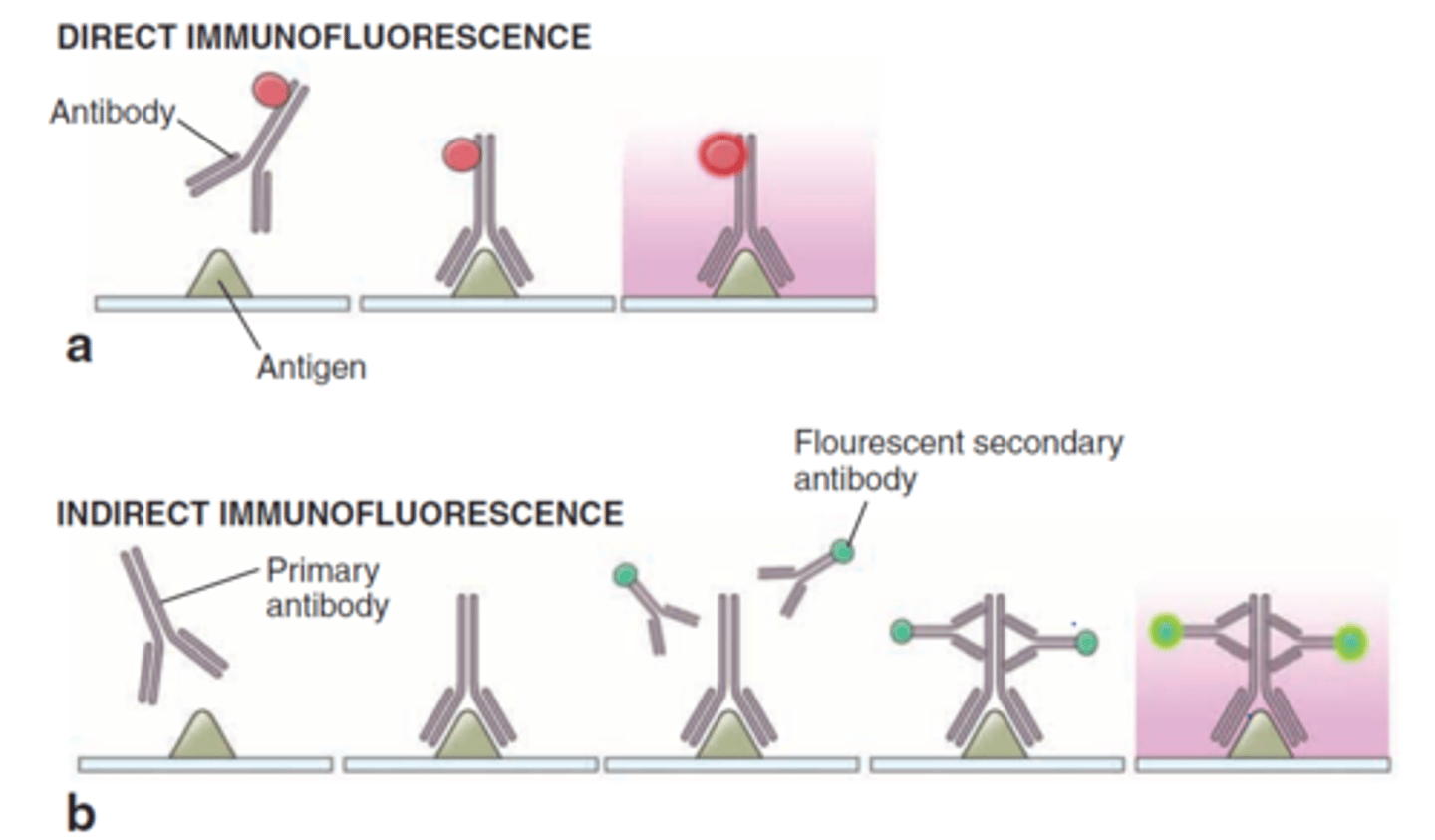
indirect fluorescent antibody testing
FAbs recognize the Fc region of antibodies in patient sera
known antigen is added to the test serum
binding of the fluorescent antibody is visualized through fluorescence microscopy
fluorescing aggregates or cells indicate the FAbs have complexed with microbe-specific antibodies
used to diagnose syphilis and various viral infections
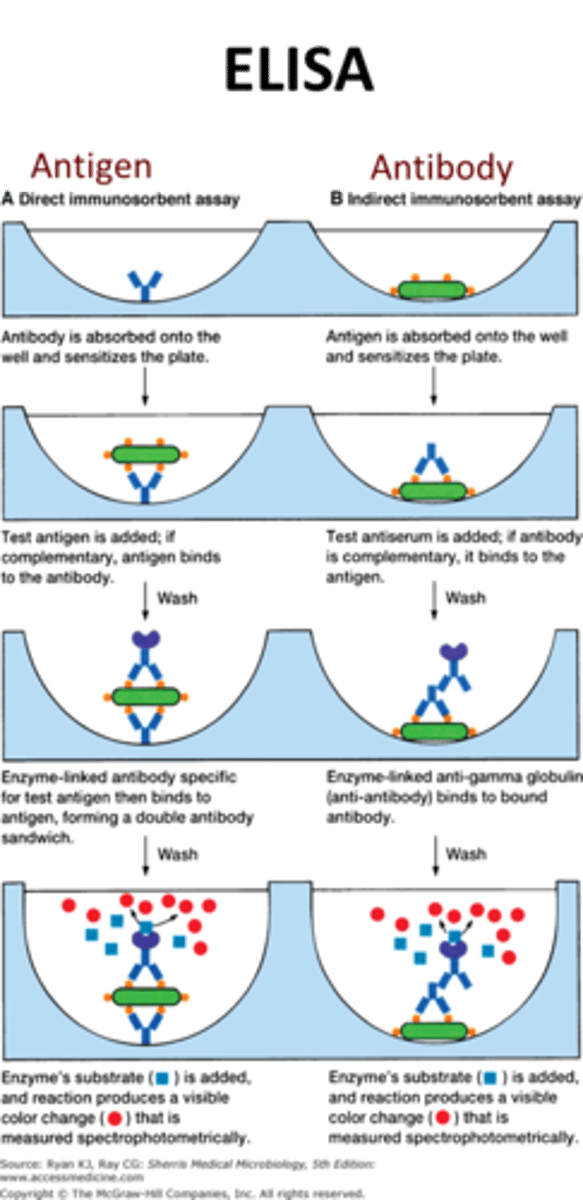
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent Assay)
uses an enzyme-linked indicator antibody to visualize antigen-antibody reactions