Epidemiology week 1: study design
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
case series
cross-sectional
case control
cohort
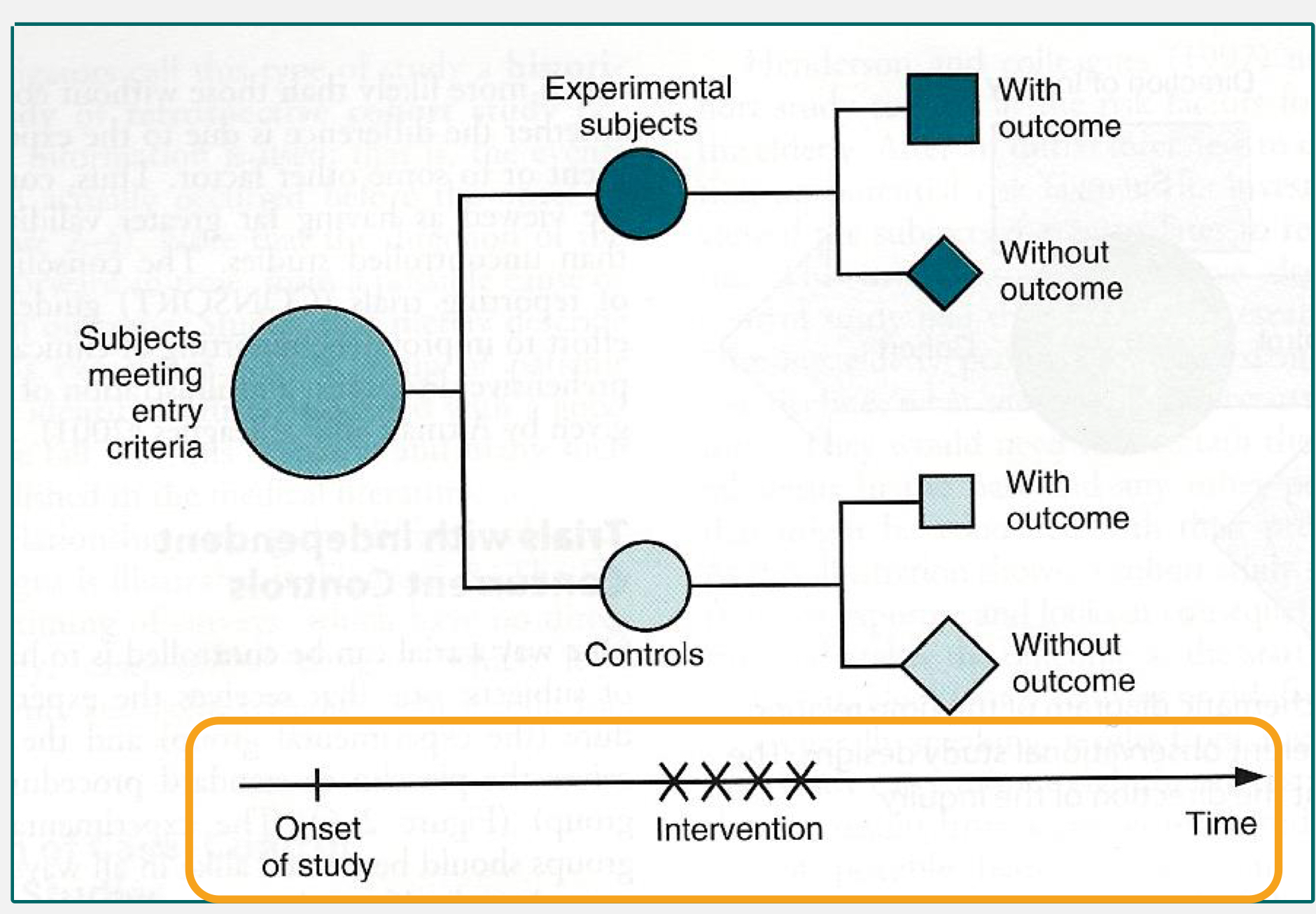
RCT classic design
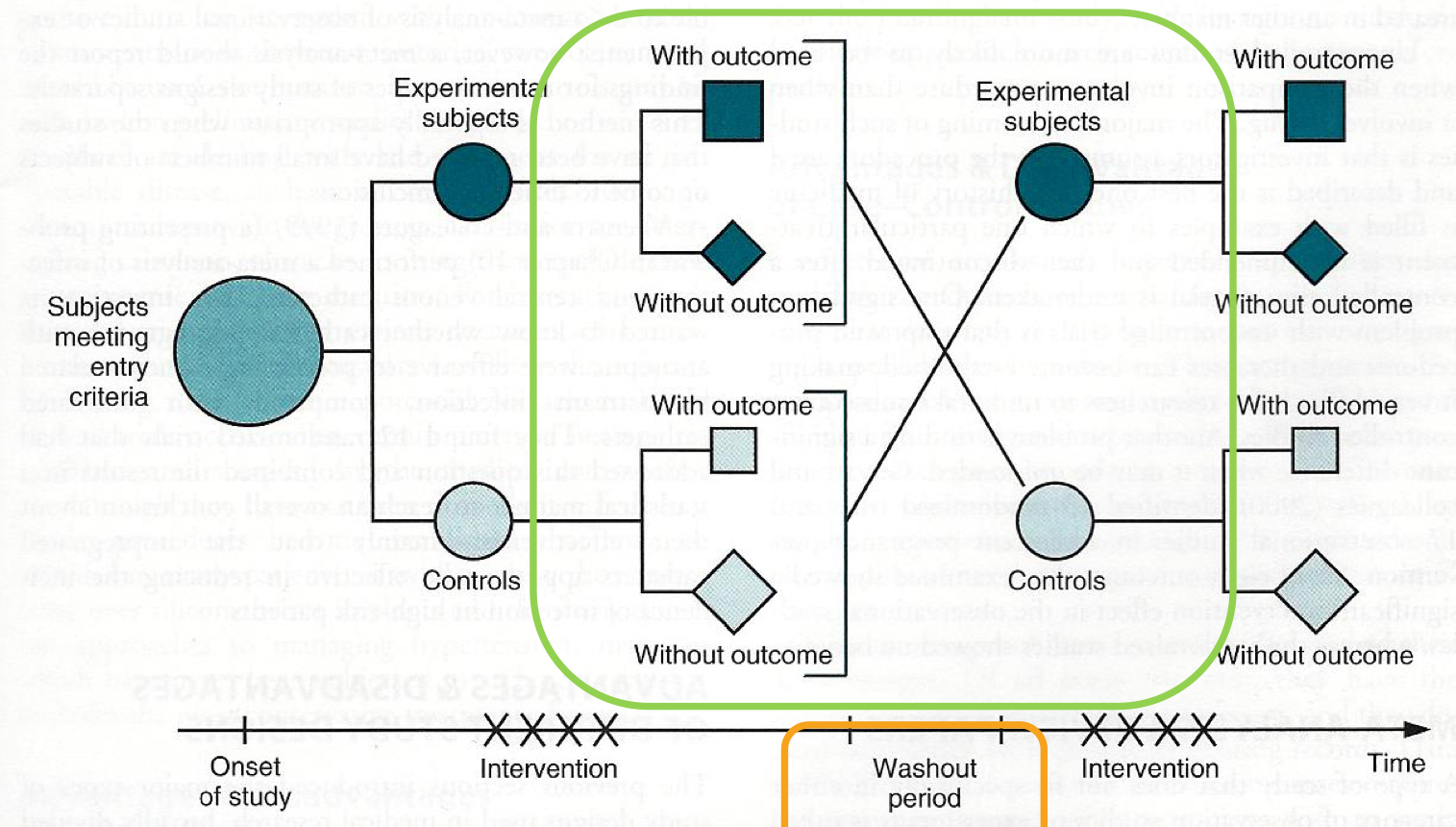
case-crossover RCT
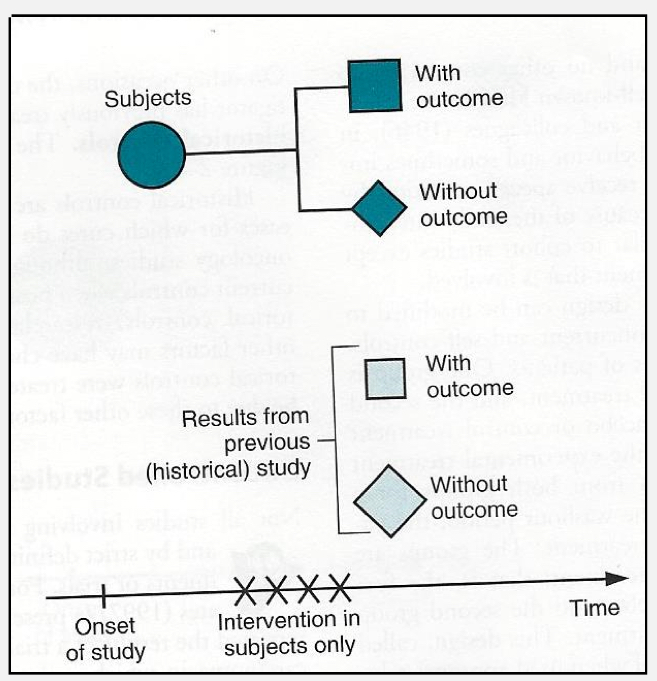
trials w external controls
which two study designs take from past, present, and future?
case study and case series
which study design take from past and present?
cross-sectional
which study design is retrospective?
case-control
which designs allow for future application/understanding?
prospective cohort and RCT
what are the three descriptive studies?
case study/report
case-series
cross-sectional
what are the three analytical studies?
cross-sectional
case-control (retrospective)
cohort (prospective/longitudinal)
what are the two experimental/interventional studies?
controlled trials
trials w no controls or external contorls
describe the eight rankings for hierarchy of evidence best to worst
systematic review & meta-analyses
RCT
cohort
case-control
cross-sectional
case repor/series
expert opinion
anecdotal
definition:
Characteristic of the individual (age, gender, weight)
variable related to environment (air pollution)
lifestyle (smoking, exercise)
social status (poverty or income level)
participant’s background (education level, race/ethnicity)
exposure aka risk factor
definition: result of effect of interest
outcome
T or F: there is only 1 exposure and 1 outcome per study
true
which descriptive study?
no control used
precursor to future studies (hypothesis generating)
characteristics of pt recorded and published
short duration
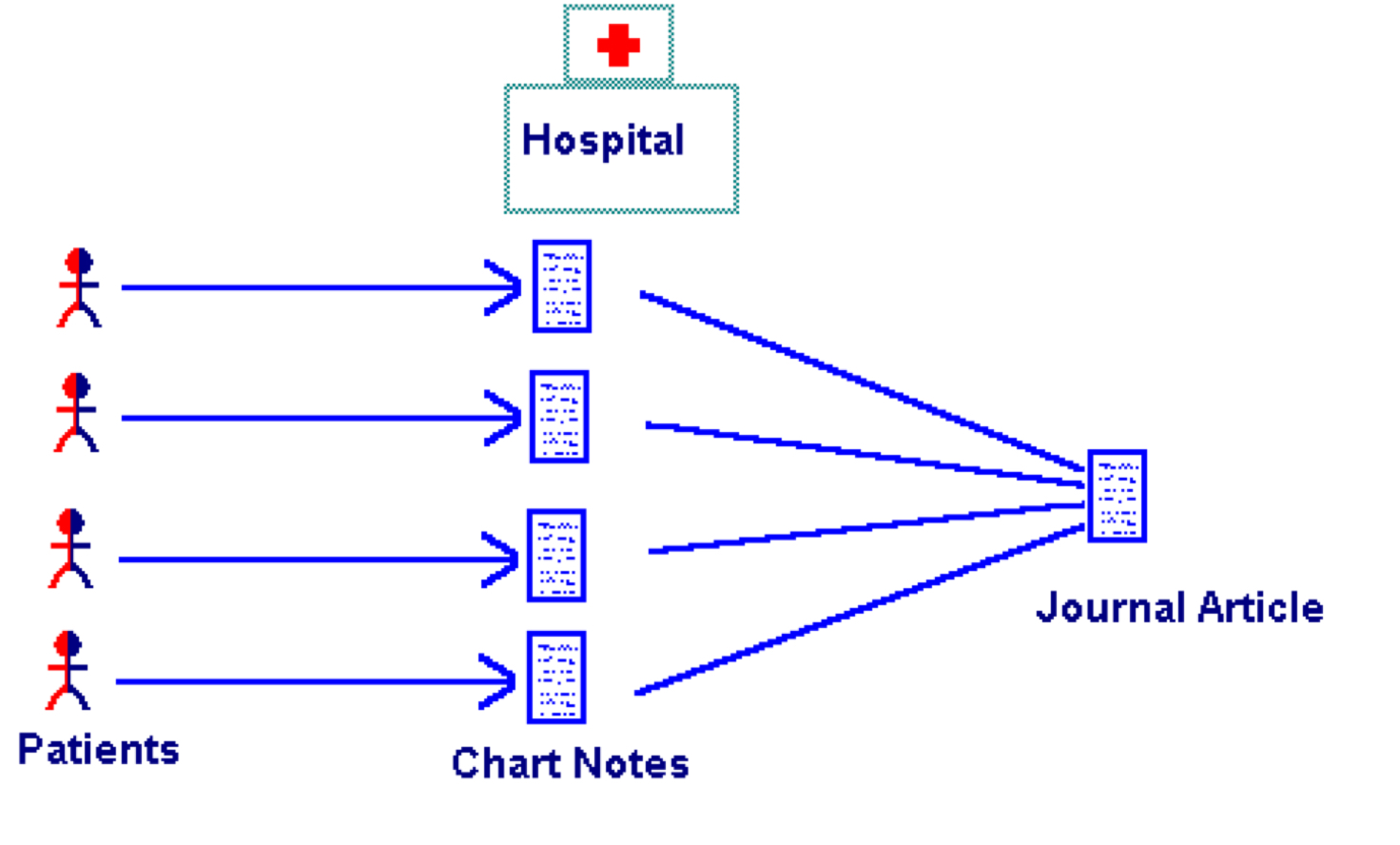
case study
which descriptive study:
no control used
precursor to future studies (hypothesis generating)
series of pt recorded and published o observe trends or patterns for same condition or Tx
short duration
case series
advantages:
useful for generating hypothesis for larger studies
disadvantages:
cannot evaluate association generalizability is an issue
case report and case series
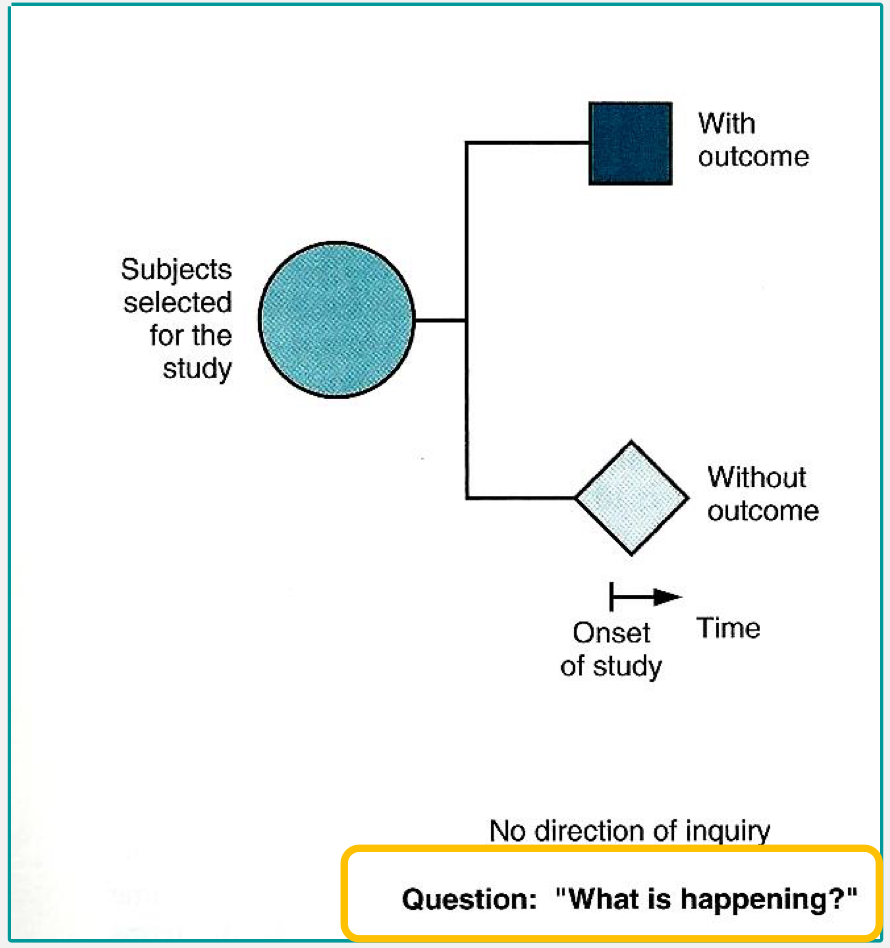
definition: descriptive studies population at one point in time
descriptive cross-sectional
which descriptive study:
referred to as prevalence study
examine prevalence of disease or condition
short or long duration
precursor to cohort and case control studies
cross-sectional study
surveys, epidemiologic studies, incidence or mortality studies are example of
cross-sectional studies
which descriptive study is precursor to cohort and case-control studies?
cross-sectional studies
advantages:
less time consuming
large samples
can be done w limited resources
disadvantages:
Cannot evaluate causal associations as we cannot
determine direction of association
Participation bias
Interview or reporting bias
slice of time = may not be representative of the full picture
descriptive cross-sectional
definition: studies that test the research hypothesis about exposure-outcome relationship
analytical studies
studies that can measure the association and magnitude of association btwn exposure and outcome
analytical studies
definition: association btwn exposure and outcome at one point in time is evaluated, magnitude of relationship estimated but not direction
analytical cross-sectional
in descriptive or analytical cross-sectional can research hypothesis/research question can be evaluated statistically?
analytical
in descriptive or analytical cross-sectional can odds ratios for relationship btwn exposure and outcome can be estimated?
analytical
advantages:
commonly used to describe burden of disease, disease trends, behavioral patterns
correlation btwn variables can be determined and (blank) relationships can be analyzed
disadvantages:
requires large sample size
cannot establish causal association
cannot establish time sequence or temporality
cross-sectional analytical
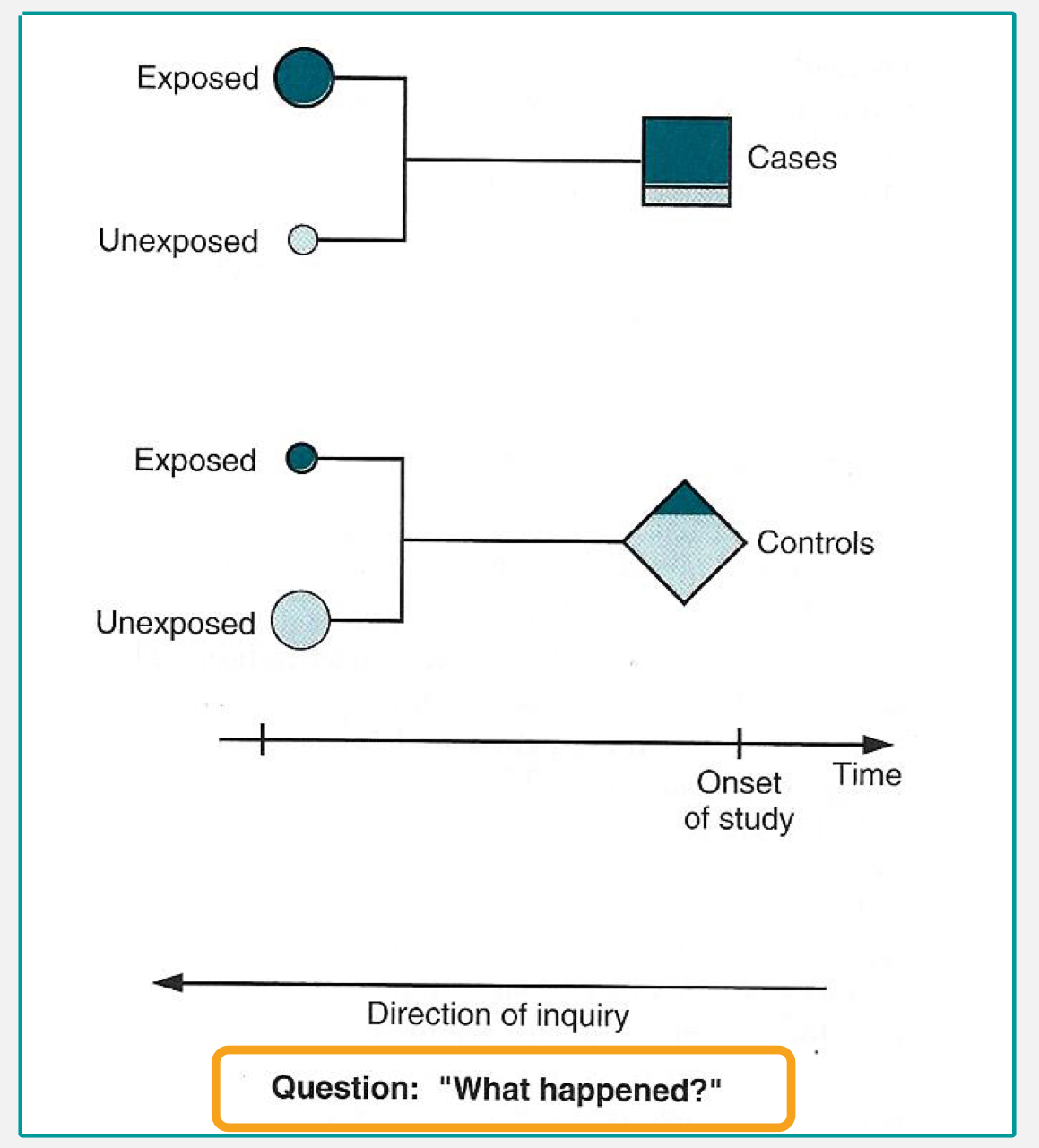
which analytical study:
compares diseased indiv to non-diseased in relation to exposure status
retrospective
analyze factors/exposures related to outcome in cases and controls
case-control
which analytical study:
the disease or outcome has already occurred
cases and controls are grouped based on the outcome/diseased status
case-control
define odds ratio:
they can be used to evaluate the association btwn exposure-outcome
estimated based on prob of disease among the exposed indiv relative to prob of diseased among unexposed indiv
advantages:
efficient, short, less expensive
convenient for studying many exposures
efficient for rare diseases and for diseases w long latency
measures of association can be calculated to evaluate exposure-outcome relationship (odds ratio)
disadvantages:
retrospective nature makes it difficult to establish time sequence of exposure-outcome
retrospective nature leads to potential biases
case-control
what are the four relevant biases that can affect case-control study outcomes?
review bias
interview bias
reporting bias
misclassification bias
which bias:
cases remember/recall & report their previous exposure experience diff from controls
can occur in cross-sectional
most common type of bias in case-control
recall
case-control is most prone to which bias?
recall bias
which bias:
differences that occur in recording or interpreting info from participants
subject status may lead to increased questioning
present in cross-sectional, case-control, cohort
interview
which bias:
under-reporting of socially undesirable
subjects may refuse to answer
over-reporting of exposures, etc
reporting
which bias:
participants are incorrectly assigned/categorized into wrong exposure or outcome
inaccurate case definitions or inclusion/exclusion criteria
lead to diluted or exaggerated effects
most common in case-control studies
misclassification
which bias is the most common in case-control studies
misclassification
can temporality be established in cross-sectional studies?
NO!
can temporality be established in case-control studies?
no but technically YES! if info about exact time period of exposure and date of diagnosis is available
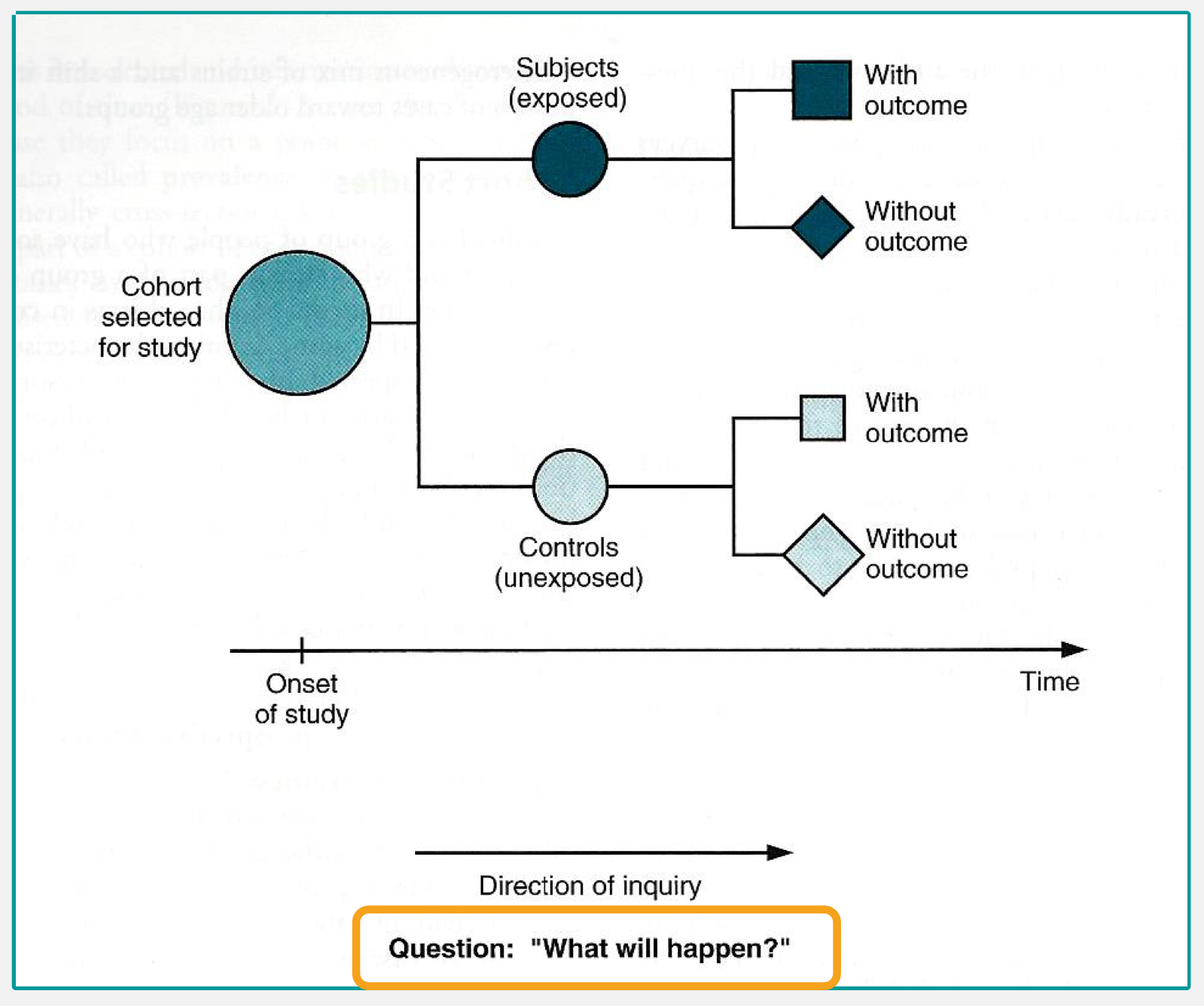
which analytical study design?
prospective or longitudinal studies
identify exposure right off
compare disease rates exposed vs non-exposed
can calculate incidence (proportions) and incidence rates
cohort study
can time sequence of events be established for cohort studies?
yes temporality and causality can be determined
advantages:
can be more ethical
good for rare exposure
can look at multiple outcomes for single exposure
can estimate incidence rates over time as we have info
can be used to establish temporality and causality
disadvantages:
not efficient for rare disease
long duration = t and money
exposure status may change overtime
prone to loss of follow-up bias
cohort
cohort or case control:
participants grouped by disease status
less t and money
can be used for rare disease
multiple exposures can be studied
does not work well for rare exposures
prone to recall bias/info
case-control
cohort or case control:
participants grouped by exposure status
long duration = ↑t and money
can be used for rare exposure
may not work for rare disease
multiple outcomes evaluated
prone to loss to follow-up bias due to dropouts
cohort
advantages:
efficient way to summarize
results can be broadly generalized
most reliable bc summary of info
highest quality of info
disadvantages:
laborious
time consuming
may be difficult to combine info when methods and measures vary across studies
systematic reviews
which study:
statistical combo of results from two or more studies
quantitative formal epidemiological study design used to systematically assess previous research studies to derive conclusions about that body of research
summarized data is used to make interpretations or causal inferences
meta analysis
advantages:
most ideal, efficient, highest quality
most most ideal is quantitative combo or RCT
highest statistical power
disadvantages:
(blank) is not possible in all systematic reviews
for new research few studies available
diffs in reporting, indiv bias, variability in research methods and/or clinical approach
requires advanced stat methods and software
meta-analysis
what category of studies:
longitudinal or prospective studies that examine the effect of an intervention on outcome of interest, investigator assigns and intervenes (aka intervention studies)
experimental studies
what are the two types of experimental studies?
controlled vs trials w no controls
controlled trials: random vs non-randomized
parallel, cross-over, split-mouth
what are the three types of controlled trials
parallel
cross-over
split-mouth
what is the gold standard of experimental studies?
RCT
what are the three types of randomization?
simple
stratified (categories)
block (restricted randomization to ensure equal number in each group)
these are advantages of what?
covariates are equally distributed
minimizes bias in treatment allocation
minimizes bias in outcome assessment
randomization in RCT
what is blinding and what are the three types?
concealing info about Tx assignment from key participants in the trial
single: patients only
double: patients and investigation
triple: patients, investigation, data analysis
what do placebos contain?
sugar or non-essential ingredients
advantages:
ability to make causal inferences
provides strongest empirical evidence of a Tx efficacy
tailor-made to answer a specific research
randomization of participations to the test and control arms minimize bias and confounding of unknown variables
disadvantages:
expensive and complicated
dropout rates may be high if intervention unpleasant\
interventions must be beneficial
prior knowledge required about level of improvement
large sample size required
experimental studies
which RCT?
comparisons btwn two intervention groups
participants remain in same group during the study
parallel
which RCT?
each subject can serve as his/her own control
same subject will receive exposure/intervention
cross over
which RCT?
participants receive intervention in one quadrant of mouth and comparison intervention in another quadrant
split-mouth
which RCT:
Study subjects meeting inclusion criteria are enrolled
Treatment versus placebo randomly assigned
Switch the groups to receive treatment versus placebo
Groups who received treatment will switch to placebo group and vice versa (cases act as their own control so no need for separate control group)
case-crossover
definition: To remove bias from contamination of effect of one treatment on the other it is important to wait for the effects of the first treatment to disappear
washout period
what is it called when effects linger even after Tx termination?
carryover effect
what aids in minimizing carryover effect?
washout period
which RCT?
Common in dental clinical research
RCT trials where interventions are randomly allocated to different areas in the oral cavity
Experimental and control interventions can be allocated by teeth, surfaces of teeth, arches an / quadrants
Higher statistical power
Each patient serves as his/her own control
Difficulty in obtaining patients with symmetrical disorders
split-mouth
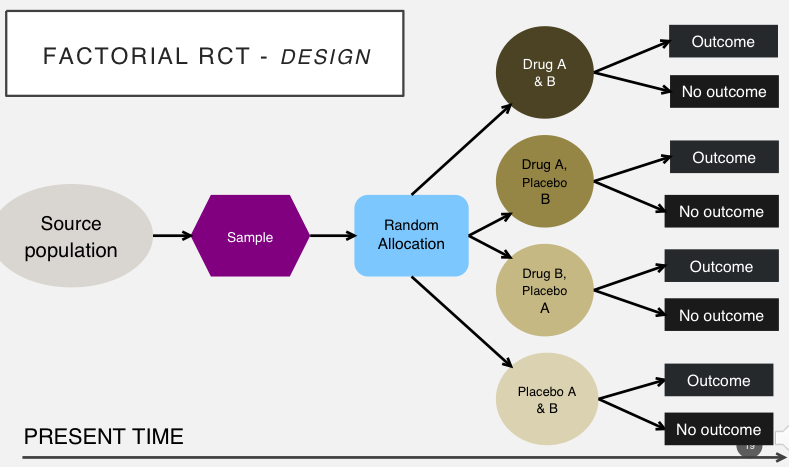
explain process of factorial RCT
which other types of trials:
Cases selected from hospital or clinic setting
Controls from a previous study or existing large cohort study
Information readily available
Less expensive
Saves time and resources
trials with external controls
which other type of trial:
Goal is usually to study primary prevention of a disease
Example: Experiments of new vaccines
(Salk vaccine trial 1954)
field trials
which other type of trials:
Exposure is assigned to groups pf people in the community
Here exposure could be comparing regions with fluoride in water to regions without fluoride in water
community intervention trials