Motor Learning & Control
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the reflex theory?
Motor skills are learned through the development and refinement of specific reflex actions
What is the hierarchal theory?
Motor control is organized in a hierarchal structure.
High level (cognitive processes) and low-level (spinal reflexes)
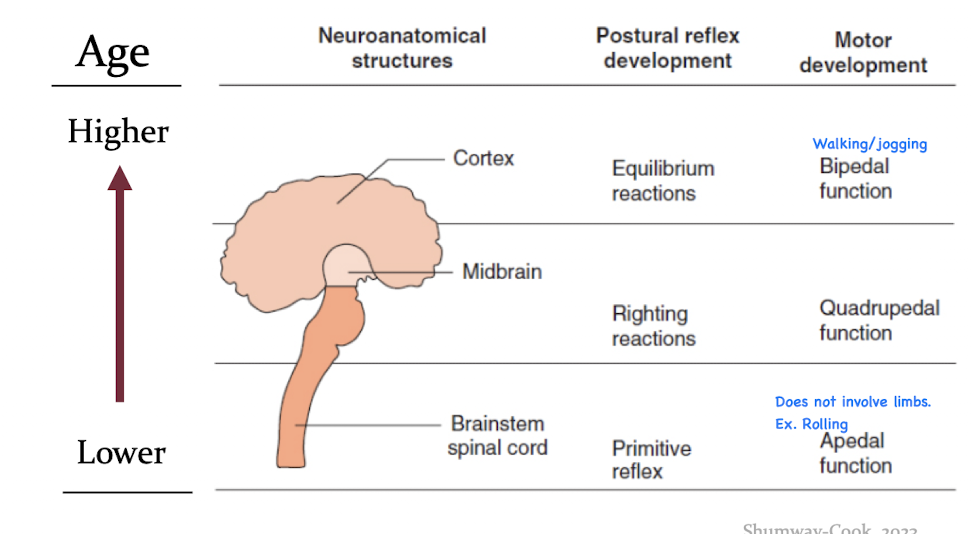
What is the neuro-maturational theory?
Motor skills develop in a predictable sequence and is influenced by the maturation of the CNS.
What is the motor programming theory?
Representation of movement that centrally organizes the many DF involved in performing an action.
Movements can occur in the absence of sensation or limited speed of processing feedback.
Frees the NS from conscious decisions about movement, decreases the issue of multiple DFs
Explain Adam’s theory
Based on closed-loop control
Sensory feedback from ongoing movement is compared with stored memory of the intended movement (perceptual trace) to provide the CNS with a reference of correctness and error detection.
The stronger the perceptual trace developed through practice, the greater the capability of the learner to use closed-loop processes for learning movements.
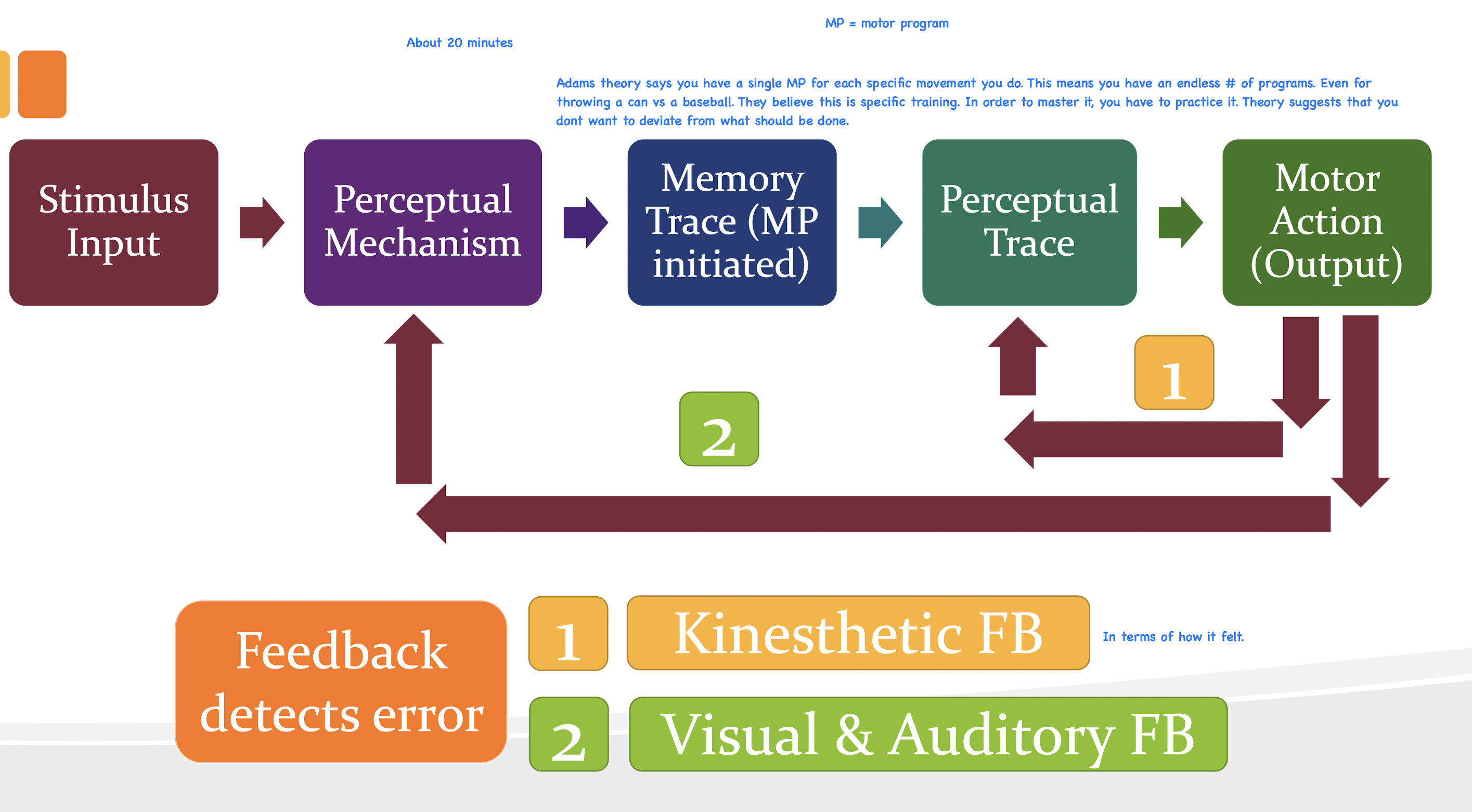
What does Adam’s theory not explain?
Learning under conditions of rapid movements or in the absence of sensory feedback
Explain schema theory.
Sensory feedback is not necessary for learned movements (open loop)
Viewed as generalized motor program.
What are the two parts to the schema theory?
Recall Schema: used to select a motor response. Before or during the movement.
Recognition schema: used to evaluate movement responses. During or after the movement.
What ist he ecological theory of direct perception?
Learning motor skills heavily relies on the environmental context.
Perception of environment is key.
What is Newell’s Theory of Constraints?
The interaction of the individual, environment, and the task shapes human motor behavior.
Altering the environment, the task, or both will result in a change of motor behavior.
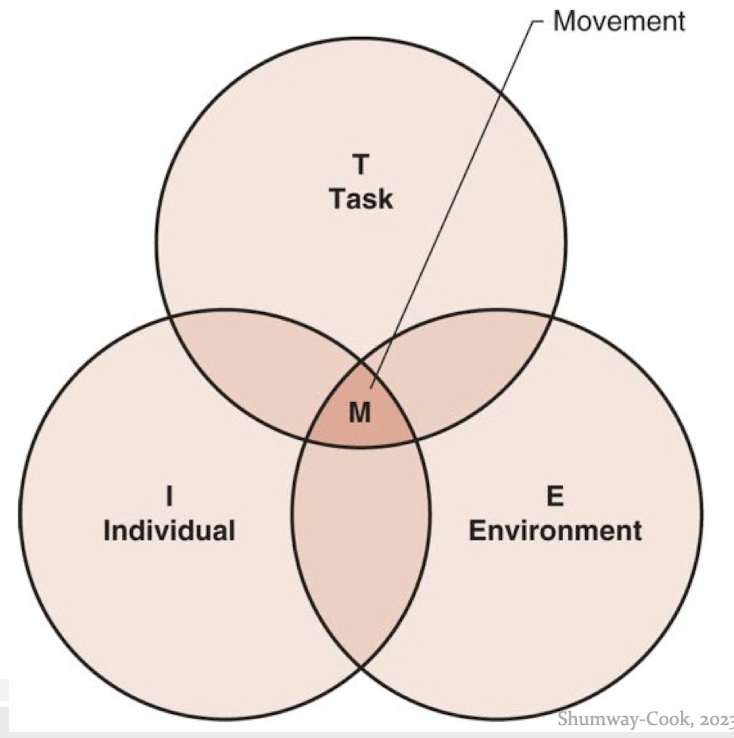
What does constraint mean in the Newell’s theory of constraints?
Any aspect that limits or restricts movement choices. Individual, environment, or task.
What are the 3 stages of motor learning?
Cognitive stage
Associated state (refines motor program)
Autonomous stage
What is compensation in terms of recovery of motor function?
The appearance of new motor patterns resulting from the adaptation of remaining motor elements or substitution of alternative motor strategies and body segments
Using same body segment but in a different way.
What is substitution in terms of recovery of motor function?
Functions are assumed or substituted by different areas of the brain and engaging different effectors or body segments.
Same function but totally different set up and using new body segments.
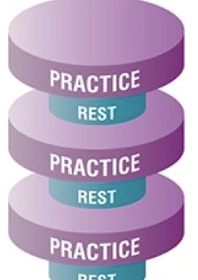
What is massed practice?
Rest time is much less than practice time
Best when motivation and skill levels are high and pt has adequate endurance, attention, and concentration.
What is distributed practice?
Practice time is equal to or less than time at rest.
Preferred for pt w/ limited performance capabilities and endurance
Considered if the task is complex, long, or has a high-energy cost
Most learning per training time
Distributed practice: training time 2 hours, but actually training for 30 minutes. Massed: training time 45 mins, but actually training for 30 minutes. Most learning occurred with distributed.
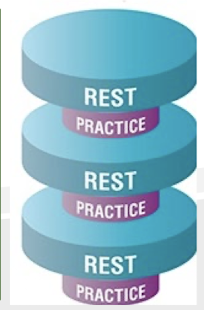
Which practice (massed or distributed) is best for acute conditions?
Distributed
What is blocked (constant) practice?
All trials on one task are done together, uninterrupted by practice on any of the other tasks.
What is random (variable) practice?
Practice the same skill differently (STS from toilet, bed, car, bench, etc.)
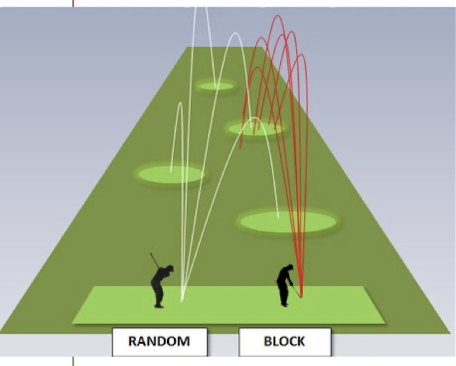
Which type of practice (blocked or random) is best if you want better success initially?
Blocked (superior initial performance, low contextual interference)
Which type of practice (blocked or random) is best if you want more long-term benefits?
Random (superior long-term retention effects) Skilled performance is delayed initially.
What is the difference between intrinsic (inherent) and extrinsic (augmented) feedback?
Intrinsic: Occurring as a natural result of the movement.
Proprioceptive, visual, vestibular, ect.
Extrinsic: sensory cues that are no normally received during movement
Verbal/manual cues, biofeedback, pressure sensing (force plates)
What is knowledge of results (KR)?
The nature of the end result produced in relation to the goal. Outcome of the action (did it work or not?)
What is knowledge of performance?
The quality of the movement pattern produced. How the movement felt (did it feel correct?)