6.1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Last updated 3:37 PM on 5/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
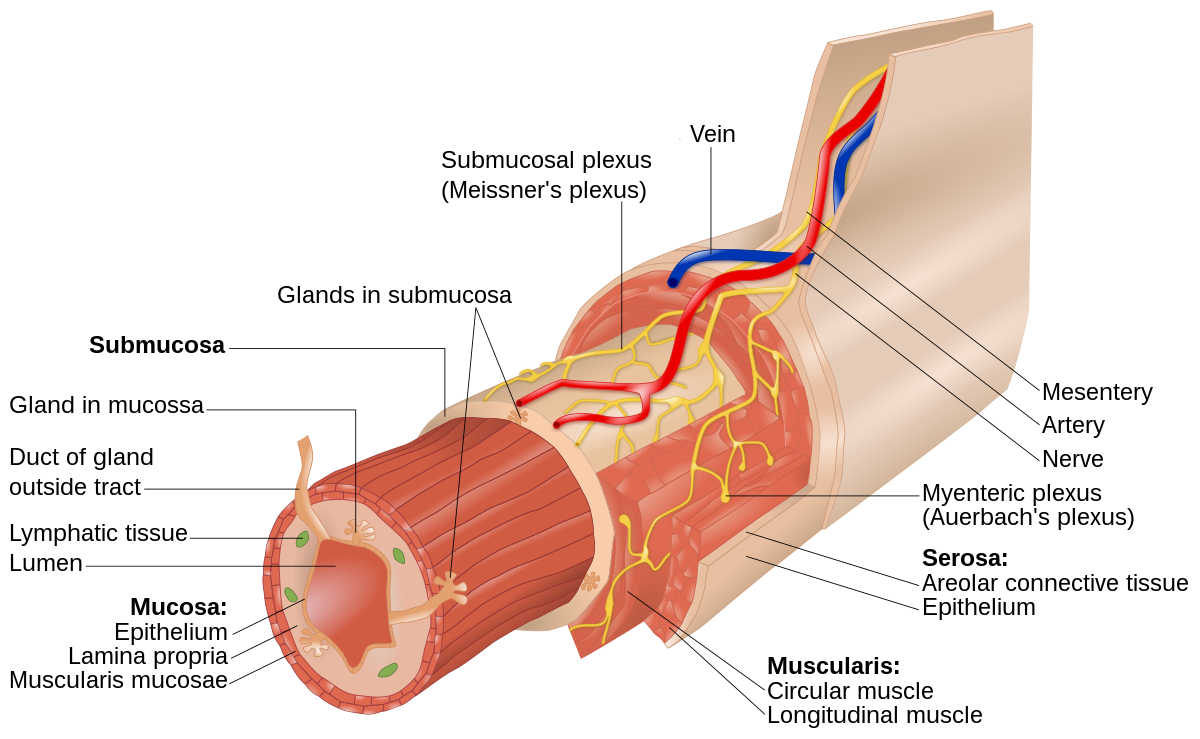
Serosa
the outermost layer of the small intestine, reinforced by fibrous connective tissue
2
New cards
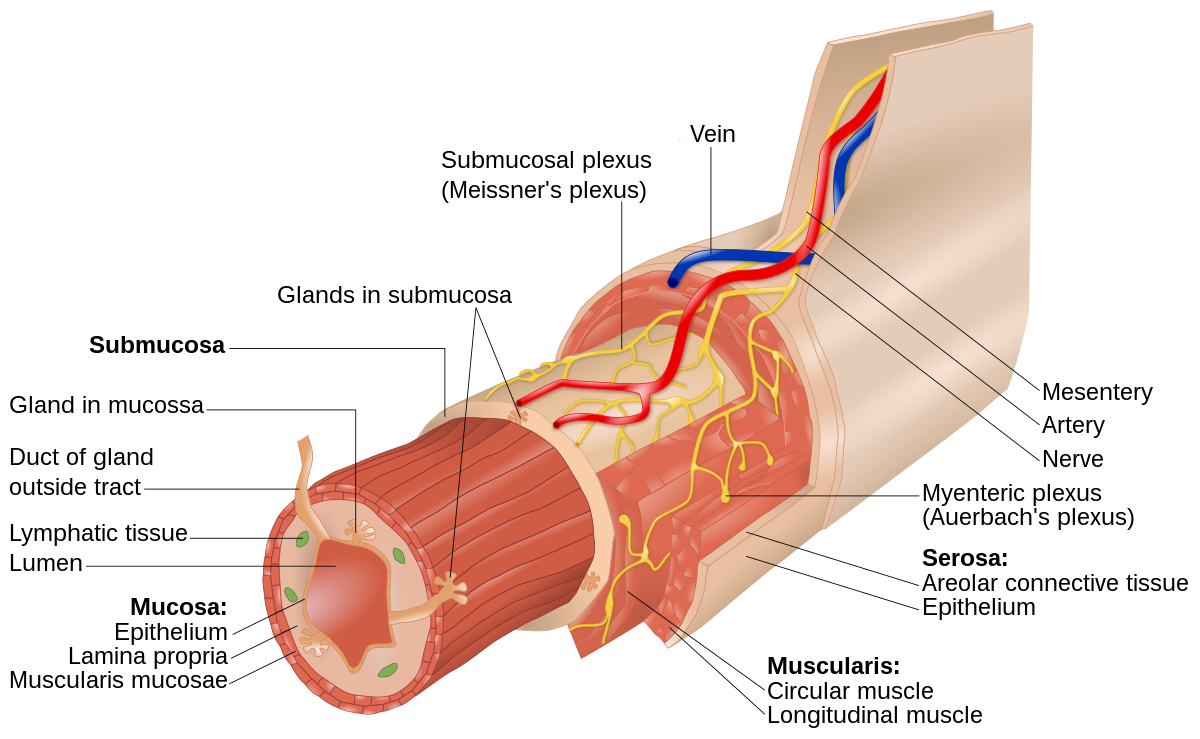
Muscle Layers of the Small Intestine
Outer layer→ Longitudinal- Peristalsis
Inner layer→ Circular- Segmentation
Inner layer→ Circular- Segmentation
3
New cards
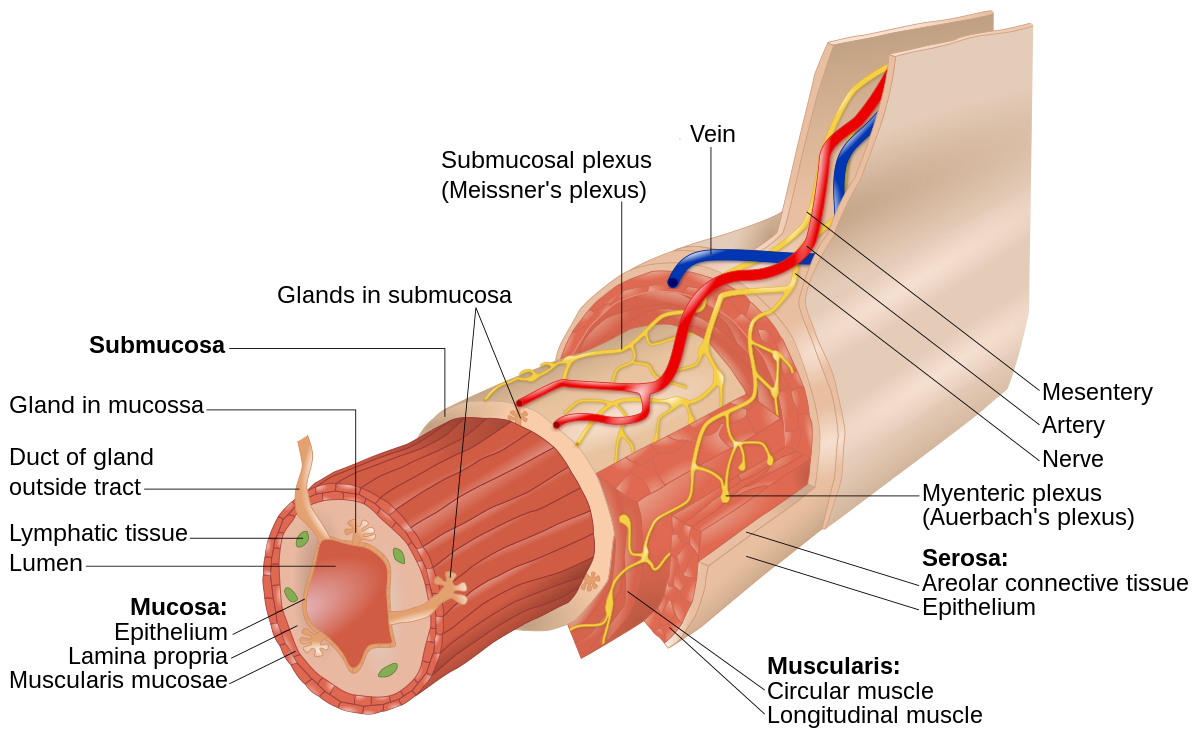
Submucosa
Layer separating the muscle from the inner lining of the small intestine
4
New cards
Mucosa
Inner layer of the small intestine that absorbs material through its surface epithelium
5
New cards
Features of Villi
\-Microvilli→ ruffling of epithelial membrane
\-Rich blood supply
\-Single layer epithelium
\-Intestinal glands→ release digestive juices
\-Membrane protens→ facilitates transport
\-Rich blood supply
\-Single layer epithelium
\-Intestinal glands→ release digestive juices
\-Membrane protens→ facilitates transport
6
New cards
Epiglottis
Prevents the bolus from entering the trachea
7
New cards
Uvula
prevents the bolus from entering the nasal cavity
8
New cards
Chyme
The digestion of bolus within the stomach for several hours which turns it into a creamy paste
9
New cards
Peristalsis
when ***longitudinal*** smooth muscle rhythmically contracts and relaxes, causes the food to be moved
10
New cards
Segmentation
\-contraction and relaxation of non-adjacent segments of ***circular*** smooth muscle in the intestines
\-bidirectional
\-bidirectional
11
New cards
What is the protective layer in the stomach called?
The stomach epithelium contains a **mucous membrane** which prevents the acids from damaging the gastric lining
12
New cards
Bile function
Bile contains bile salts which interact with fat globules and divide them into smaller droplets EMULSIFICATION
13
New cards
Carbohydrate digestion in the small intestine
Enzymes for **disaccharide hydrolysis** are often immobilised on the epithelial lining of the small intestine, **near channel proteins**
14
New cards
Protein digestion in the small intestine
Smaller polypeptide chains enter the small intestine where they are broken down by *endopeptidases* released by the pancreas (neutral pH)
15
New cards
Alimentary canal
consists of organs through which food actually passes through
16
New cards
accessory organs
aid in digestion but do not actually transfer food
17
New cards
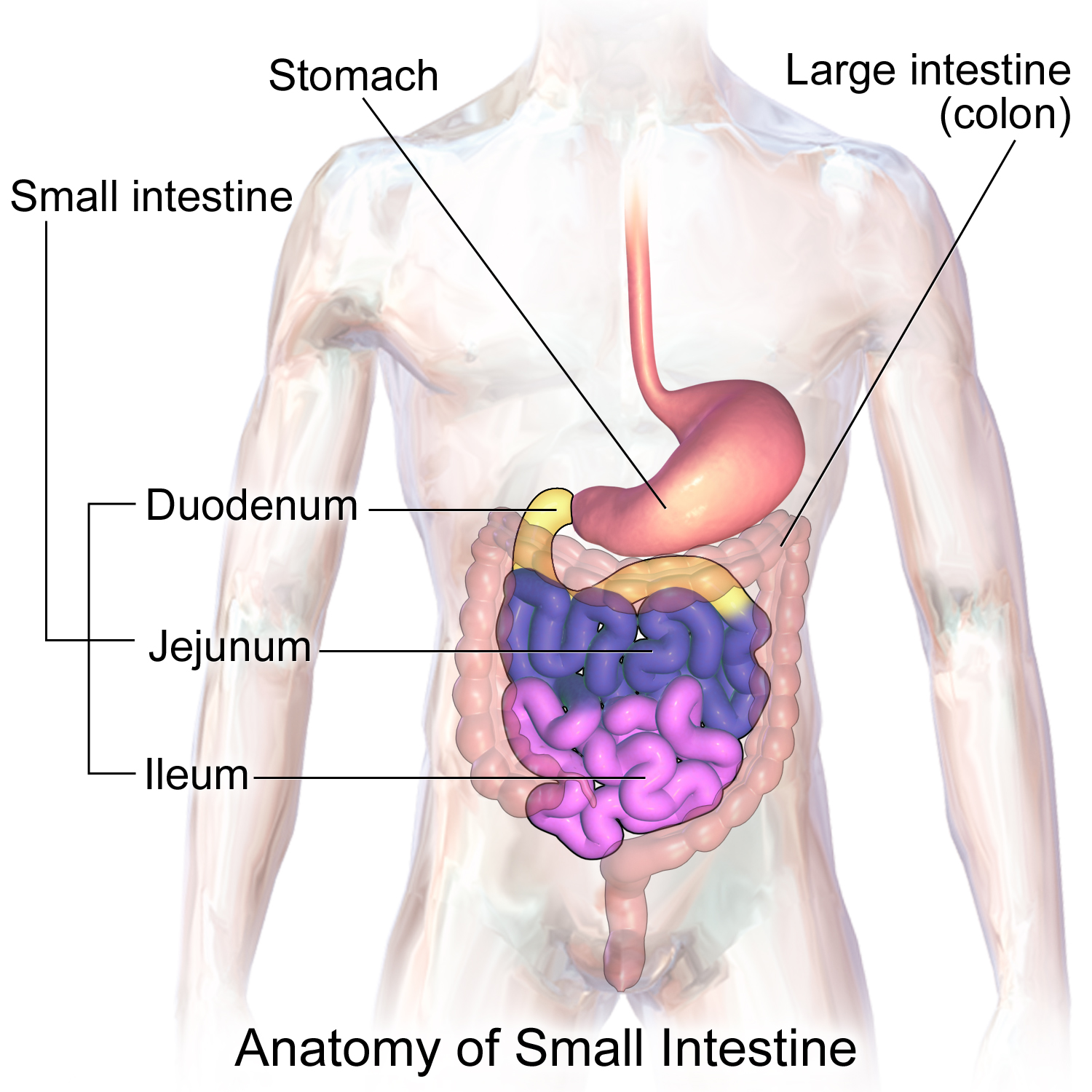
Sections of the small intestine
duodenum
jejunum
ileum
jejunum
ileum
18
New cards
Active transport in the small intestine- molecules
glucose, amino acids
19
New cards
Facilitated diffusion in the small intestine- molecules
monosaccharides
20
New cards
Osmosis in the small intestine- molecules
Water
21
New cards
Simple diffusion in the small intestine- molecules
triglycerides
22
New cards
Amylase
\-Breaks amylose into maltose subunits in the mouth and the small intestine (pH\~7)
\-Breaks amylopectin into branched chains called **DEXTRINS**
\-Breaks amylopectin into branched chains called **DEXTRINS**
23
New cards
Breaking down of maltose and dextrin
\-They are digested by the enzymes **maltase** which is fixed to the epithelial lining of the small intestine
\-The hydrolysis of maltose/dextrin results in **glucose monomers**
\-The hydrolysis of maltose/dextrin results in **glucose monomers**
24
New cards
Breakdown of starch- fuctions of the pancreas
\-releases amylase which is released from exocrine glands
\-produces insulin and glucagon from endocrine glands
\-produces insulin and glucagon from endocrine glands
25
New cards
Exocrine vs Endocrine
Exocrine glands→secrete their substances onto your body's surfaces
Endocrine glands→ secrete their substances directly into the bloodstream
Endocrine glands→ secrete their substances directly into the bloodstream
26
New cards
Key functions of digestion
\-Breaks down insoluble molecules into smaller subunits which can be readily absorbed into body tissues
\-Breaks down inert molecules into usable subunits which can be used by cells and reassembled into new products
\-Breaks down inert molecules into usable subunits which can be used by cells and reassembled into new products