MICB 3301 Exam 4
1/292
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
293 Terms
Antibodies
-Glycoproteins produced by B cells
-Found in blood, mucosal surfaces, and tissues
-Bind antigens (neutralize or opsonize)
-5 classes or isotypes
Immunoglobulin
Another name for antibody
Antibody affinity
Strength with which antibody binds to its antigen at a given antigen-binding site
Epitope
The part of an antigen molecule to which an antibody attaches itself (there can be multiple of these on antigens)
IgM
First Ig produced after antigen exposure, cells that produce this immunoglobulin can switch and produce another Ig classes
IgG
-Major Ig in blood
-Can cross placenta
-Activate complement system
IgA
Major Ig in secretions (saliva, breast milk, tears)
IgE
Major Ig in allergic reactions
IgD
Ig found on B cell surfaces that participate in signaling
Half life of Ig
days
Half life of IgG
~20 days
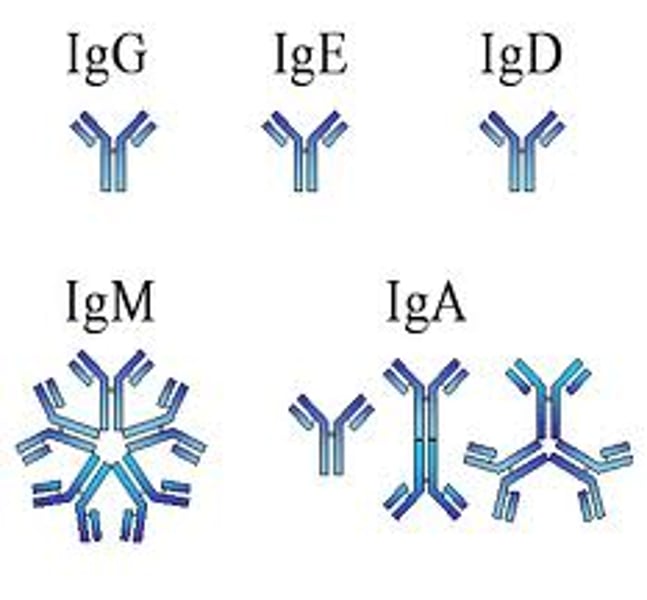
Monomer
IgD, IgE, IgG
Dimer
IgA
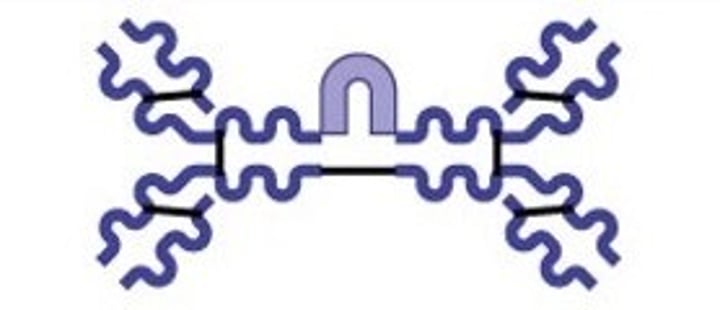
Pentamer
IgM
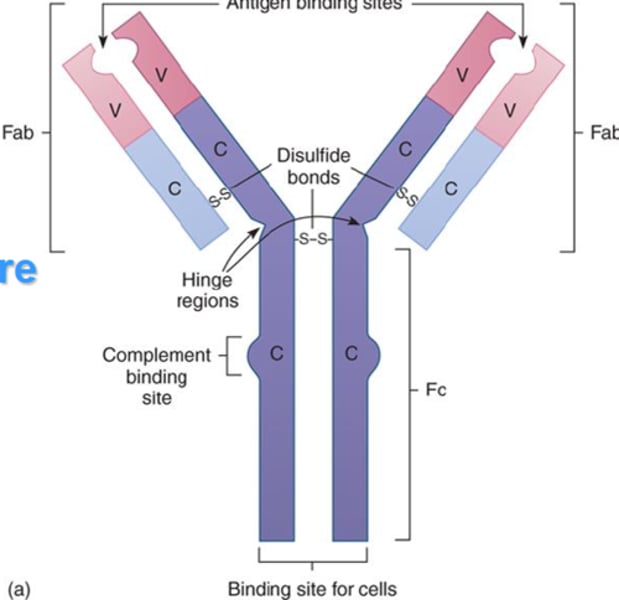
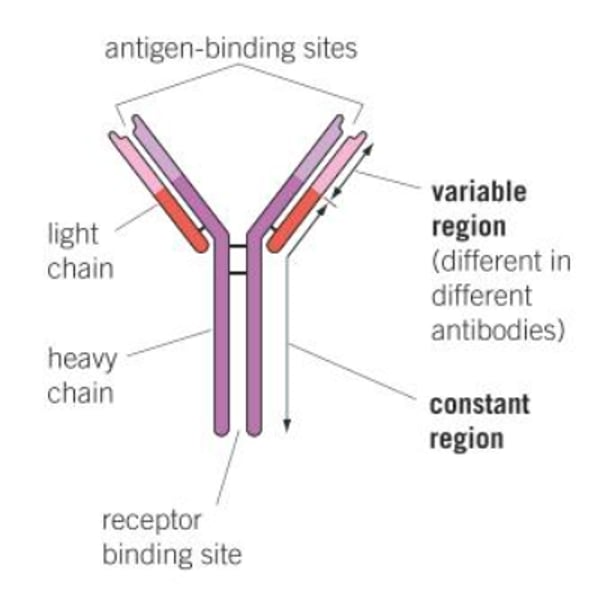
Structure of antibody
2 heavy chains and 2 light chains
Heavy chain
2. the larger chain
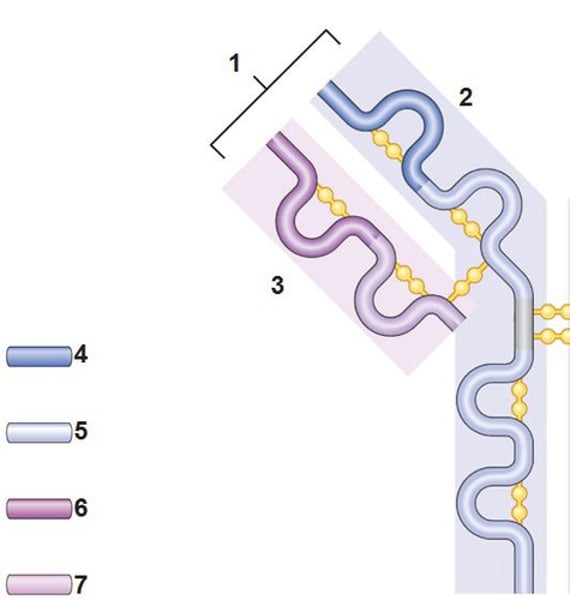
Light chain
3. the shorter chain
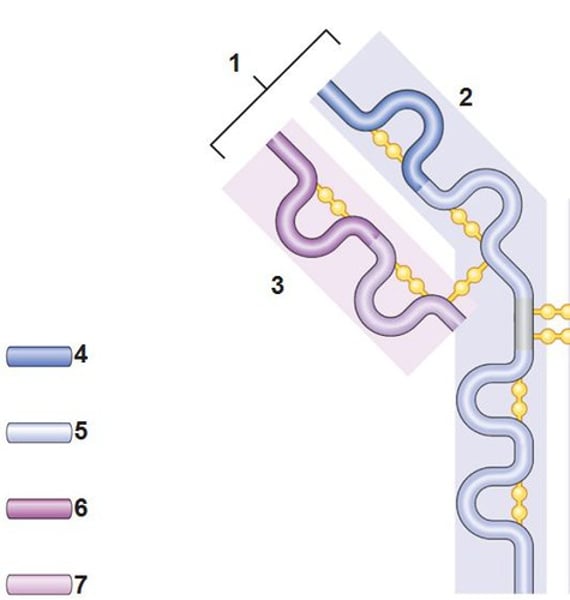
Variable region (antigen binding site)
A
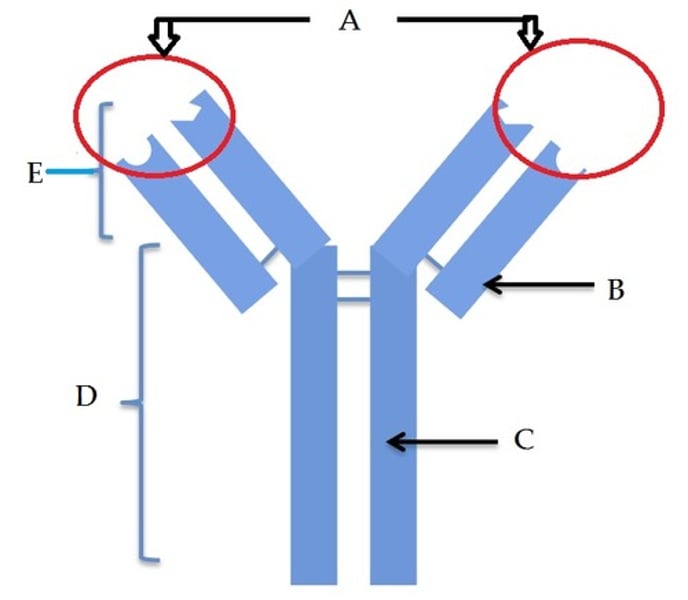
Constant region
D
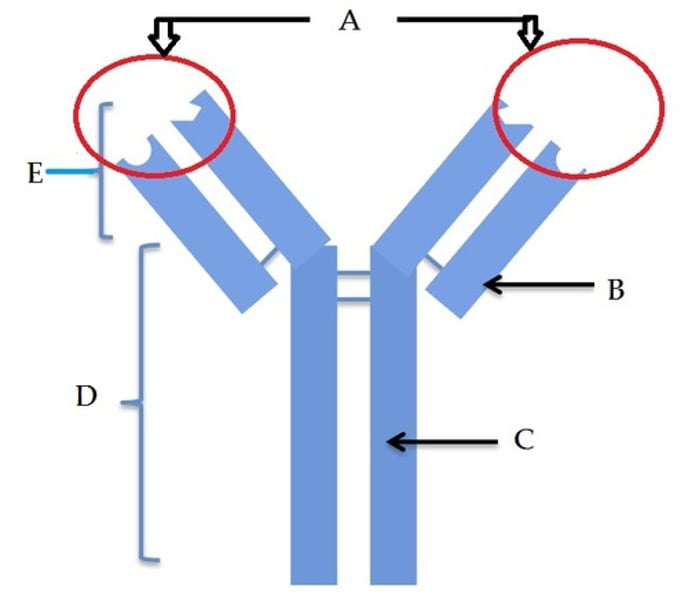
Fc fragment
E
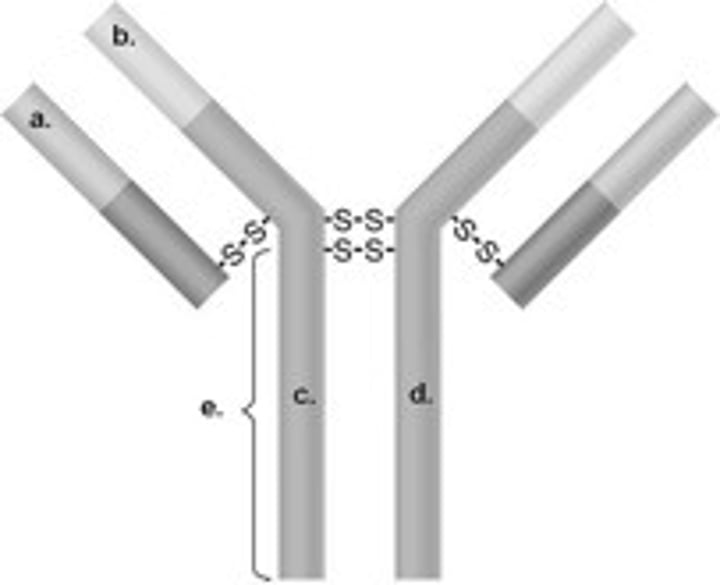
Disulfide bonds
Chemical bonds that link the heavy and light chains
Receptor binding site
Region that can bind Fc receptor on other cells
VDJ recombination
Mechanism of somatic recombination that occurs in developing lymphocytes during the early stages of T and B cell maturation
Clonal selection
1. Random rearrangement of antibody gene segments occurs as B cells develop in bone marrow early in embryonic life, before infection
2. Generates vast array of B cells, each preprogrammed to bind a specific antigen
3. Tolerance - removal of self-reactive B cells
4. Remaining B cells travel to lymphoid organs and tissues
5. Upon infection, antigen "selects" B cell with antibody that matches it
6. B cell proliferates, forming clone of identical cells, each with antibody for the antigen
Tolerance
-Removal of B cells recognizing self antigens
-Largely occurs in bone marrow
-Breakdown is one basis of autoimmunity
Helper T cells
Make cytokines that activate B cells, macrophages, and other T cells
Cytotoxic T cells
T cells that kill cells expressing foreign antigen using perforin and granzymes
Perforin
One of the proteins released by cytotoxic T cells on contact with their target cells. It forms pores in the target cell membrane that contribute to cell killing.
Granzymes
Cytotoxic enzymes that initiate apoptosis
Cluster of differentiation (CD)
Membrane proteins that function as co-receptors and can be used to determine a cell's identity
CD4
Helper T cells that interact with MHC class II molecules
CD8
Cytotoxic T cells that interact with MHC class I molecules
T Cell receptors (TCRs)
-Bind antigens (usually peptides) presented to them by other cells
-Only when presented by MHC molecule
-Expressed from gene segments rearranged in the thymus
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
Collection of genes encoding cell surface proteins for self/nonself recognition
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex
MHC genes in humans
HLA typing
a process used to identify and compare HLA
Human chromosome 6
Where HLA is located
MHC Class I
-Presents peptides that originate in the cytoplasm from intracellular pathogens
-Expressed on surfaces of nucleated cells
-Presents peptides to CD8 cytotoxic T cells
MHC Class II
-Presents peptides from extracellular pathogens taken up by phagocytosis
-Expressed on surfaces of APCs
-Presents peptides to CD4 helper T cells
Antigen processing
1. Dendritic cell takes up pathogen for degradation
2. Pathogen is taken apart inside the dendritic cell
3. Pathogen proteins are unfolded and cut into small pieces
4. Peptides bind to MHC molecules and the complexes go to the cell surface
5. T-cell receptors bind to peptide: MHC complexes on dendritic cell surfaces
How big are antigen processed peptides?
8-25 amino acids
Pathogen
An organism that causes disease
Opportunistic pathogen
A microbe that normally doesn't cause disease in healthy people, but can become virulent in immunocompromised individuals
Carrier
An infected individual that may be a potential source of infection with no observable symptoms
Zoonoses
Diseases transmitted from animals to humans
Vectors
An organism (typically insects) that transmit disease to humans (e.g. mosquitoes, ticks, fleas)
Pathogenicity
Ability to cause disease
Virulence
Degree of pathogenicity
Virulence factors
Genetic, biochemical, or structural features that contribute to virulence
Latency
Pathogen stops reproducing, dormant, can become active again
Infectious dose 50
Number of microbes required to cause clinical disease in 50% of inoculated hosts
Model systems
Animal models or cell cultures to study disease
Human studies
Clinical trials, case studies
Epidemiology
The branch of medicine that deals with the incidence, distribution, and possible control of diseases and other factors relating to health.
Viral attachment
Capsid and envelope spike proteins mediate attachment
How does influenza infect cells?
Hemagglutinin spikes bind to receptors containing sialic acid
How does HIV infect cells?
GP120 spike binds to CD4 and CCR5
How does SARS-CoV-2 infect cells?
Spike proteins bind to ACE2 receptors
How do viruses spread in the body?
Lymph, blood, neurons
Syncytia
Virus-induced cell-cell fusion, forming multinucleated cells
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
A virus that causes an infection of the lungs and breathing passages that forms syncytia
Antigenic variation
Amino acid changes in virion spikes (common in RNA viruses)
Bacterial attachment
Pili and capsules
Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis
Bacterial capsules targetable by vaccines
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
-Opportunistic pathogen that forms biofilms in burn and cystic fibrosis patients
-Some strains called mucoid strains make capsules
Uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC)
Most common cause of UTIs
Bacterial virulence factors
Coagulase, streptokinase, IgA proteases, hemolysins, siderophores, DNase
Coagulase
Clots fibrinogen in plasma that protects pathogen
Streptokinase
Activates plasmin, digests fibrin clots- pathogen moves from clotted area
IgA proteases
Destroy IgA antibodies
Hemolysins
Lyse red blood cells to degrade hemoglobin and release iron
Siderophores
Bacterial iron-binding proteins
DNase
Degrades DNA, lowers viscosity of secretions, spread
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs)
Extracellular fibrillar networks produced by neutrophils in response to bacteria and fungi that are made up of DNA and antimicrobial proteins and enzymes
What bacterial virulence factor would help bacteria escape NETs?
DNase because DNA is part of NET backbone
How do bacteria evade innate immunity?
-Capsules block complement opsonization and membrane attack complex formation
-Proteases degrade complement C3b or C5a
How do bacteria evade adaptive immunity?
Capsules prevent antibody binding and some pathogens can degrade IgA antibodies
Chlamydia, Rickettsia, Mycobacterium, Salmonella, Listeria
Examples of intracellular bacterial pathogens (5)
Listeria monocytogenes
-Gram-positive, foodborne pathogen
-Found in produce, raw unpasteurized milk, cheese, and deli meat
-Psychrophile
-Can cross placenta
-Polymerizes host actin to move inside and between host cells (Actin rockets)
How does Listeria move?
Listeria propels itself by hijacking the actin cytoskeleton and can travel between different cells in a vacuole
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Bacteria that forms biofilms in the middle ear that causes otitis media (middle ear infections) and can also cause pneumonia
Staphylococcus and Enterococcus
Two bacteria that form biofilms on heart valves that cause endocarditis
Streptococcus mutans
Bacteria that causes dental plaque
Types of exotoxins
Membrane disrupting, superantigens, AB
Membrane-disrupting exotoxin
A type of exotoxin that lyses host cell by disrupting the integrity of the plasma membrane (e.g. hemolysin)
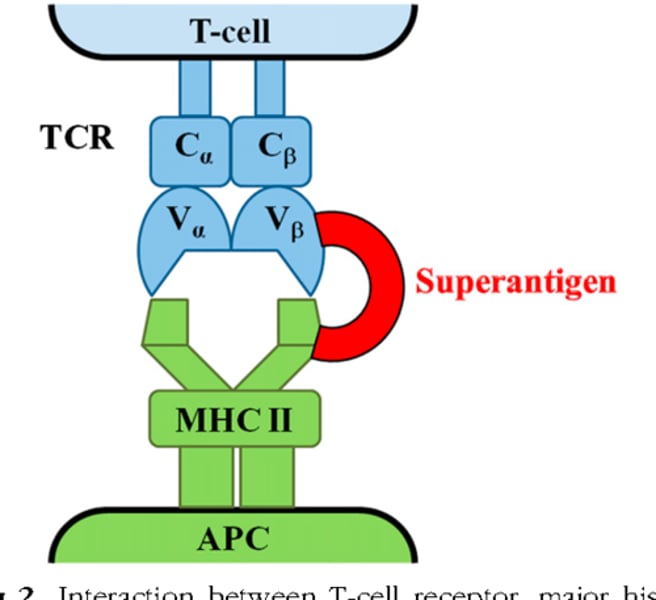
Superantigens
Cause T cells (>30%) to overexpress and release too many cytokines that can lead to multiple organ failure and Toxic Shock Syndrome
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Life-threatening condition caused by S. aureus superantigen
Where do superantigens bind?
TCR and MHC
AB exotoxins
-Composed of A and B subunits
-Many are ADP-ribosyl transferases
-Remove ADP-ribose group from NAD, attach it to host cell protein - protein inactivated or functions abnormally
A subunit
Causes a toxic effect
B subunit
Binds to target cell receptor
Diphtheria, Cholera, Botulinum
Bacteria with AB exotoxins (3)
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
Bacteria that produces diphtheria toxin
Diphtheria toxin
-Binds growth factor receptor
-Enters via endocytosis
-ADP-ribosyl transferase attaches ADP ribose from NAD onto EF-2
-Inhibits protein synthesis
-Inhibition of protein synthesis causes destruction of cardiac, kidney, and nervous tissues
Vibrio cholerae
Bacteria that produces cholera toxin
Cholera toxin
-Enterotoxin produced by Vibrio cholerae
-ADP-ribosylation of host G protein controlling cAMP production
-Increased cAMP causes water secretion from cells, leading to severe diarrhea
Clostridium botulinum
Bacteria that produces botulinum toxin
Botulinum toxin
-Neurotoxin produced by C. botulinum
-Blocks release of acetylcholine at neuromuscular junctions
-Muscles can't contract, causes flaccid paralysis
Antitoxin
Antibody that can neutralize exotoxins
Toxoid
Inactivated toxin that can still elicit an immune response