PAGS - OCR Chemistry
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:44 AM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
PAG 1-Heating in a crucible - for oxidation and decomposition of crystals
Weigh empty crucible and lid, add mg ribbon , heat with bunsen burner, lift lid with tongs to allow oxygen to enter, cool , weigh crucible and contents again , reheat crucible and reweigh until you reach constant mass

2
New cards
why heat to constant mass
to ensure reaction is complete
3
New cards
why should small amounts of solid not be used
percentage uncertainties would be too high
4
New cards
why should too large amounts of solid not be used
decomposition is likely to be incomplete
5
New cards
PAG 1-Measuring gas volumes diagrams
ensure no gaps in diagram , gas syringe with measurement markings - could have an upturned measuring cylinder with trough of water instead
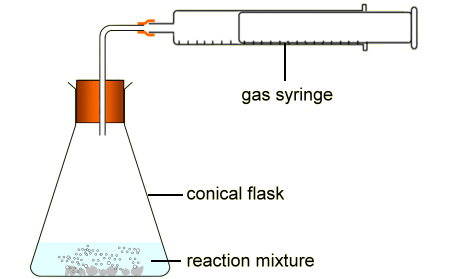
6
New cards
potential errors using a gas syringe
gas escaping before bung is inserted , co2 and so2 is insoluble in h20 so true gas amount is unknown
7
New cards
PAG 2- Making a standard solution
weigh sample bottle containing required mass of solid on a 2dp balance , transfer to beaker , reweigh empty sample bottle, record difference in mass , add 100cm3 of distilled H20 to beaker and stir with glass rod , pour solution into the 250cm3 graduated flask via a funnel , rinse beaker and funnel and add washings from beaker and glass rod to vol flask , make up mark with distilled H20 using a dropping pipette for the last few drops , invert flask several times to ensure uniform solution.

8
New cards
why should you not heat or add hot solutions to flask
the flask will expand therefore the volumes would not be accurate
9
New cards
PAG 2- Diluting a solution
pipette 25cm3 of original solution into 250cm3 volumetric flask , make up to mark with distilled water using a dropper pipette , invert flask several times to ensure uniform solution
10
New cards
why is using a volumetric pipette better than using a measuring cylinder
It has a smaller uncertainty
11
New cards
PAG 2 - acid-base titrations
rinse burette with alkali then fill burette with alkali , touch surface of solution with pipette to ensure correct amount of solution is added , add to acid solution in conical flask with indicator added , keep swirling conical flask until a colour change is reached , then stop the titration , repeat until concordant results are found
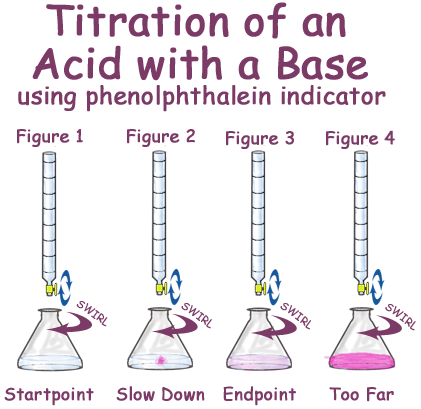
12
New cards
phenolphthalein
colorless in acid, pink in base

13
New cards
methyl orange
Red in acid, yellow in alkali

14
New cards
concordant results
within 0.10cm3 of each other
15
New cards
manganate redox titration
grind up tablets with little H2SO4 1M using a pestle and mortar , use a funnel to transfer paste to 100cm3 volumetric flask , add sufficient H2S04 to make up solution to 100cm3 , use stopper flask and shake to ensure contents are throughly mixed , titrate 10cm3 portions of solution with 0.005 potassium manganate , end point purple colour
16
New cards
manganate redox titration equation
MnO4- + 8H+ + 5Fe2+ ----> Mn2+ + 4H20 + 5Fe3+
17
New cards
MnO4-
purple

18
New cards
Mn2+
colourless
19
New cards
uncertainty- balance
+/- 0.001g
20
New cards
uncertainty-burette
+/- 0.1 cm3
21
New cards
uncertainty-volumetric flask
+/- 0.1cm3
22
New cards
uncertainty-25cm3 pipette
+/- 0.1 cm3
23
New cards
how to work out percentage uncertainty
uncertainty/measurement on apparatus x 100
24
New cards
how to work out percentage uncertainty of burette
0.10/average titre result x 100
25
New cards
how to reduce uncertainty in a burette
use a larger titre by increasing the volume and concentration of substance in conical flask or decreasing concentration of substance in burette
26
New cards
how to decrease apparatus uncertainty
using apparatus with finer scale divisions or increase size of measurements made
27
New cards
PAG 3-Measurement of an enthalpy change
used to measure enthalpy change of combustion
28
New cards
calorimetry
wash equipment, polystyrene cup , measure out desired volumes of solutions or powder , thermometer , measure initial temperature, add the substance and stir to even out the temperature , then record temperature change every 2-3 minutes
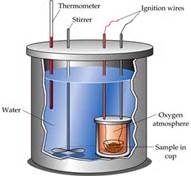
29
New cards
errors in calorimetry method
energy loss to surroundings , approximation of specific heat capacity , incomplete reaction , neglecting specific heat capacity of water
30
New cards
calorimetry graph
difference between both lines is enthalpy change
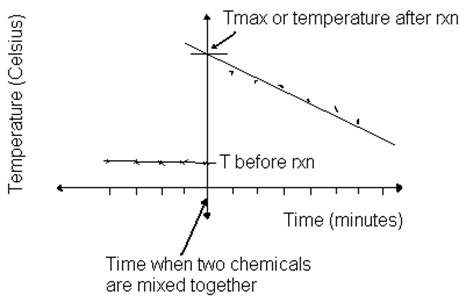
31
New cards
how to work out the enthalpy change
q=mc∆T then ∆H=q/n make sure q is in joules then answer in kj
32
New cards
what sign must go before enthalpy change of combustion
negative
33
New cards
flame calorimetry
measure mass of spirit burner before and after heating , volume of water and temperature change
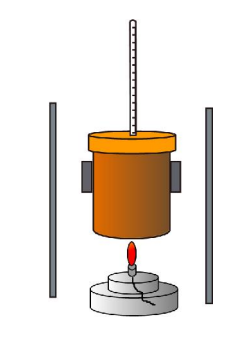
34
New cards
errors in flame calorimetry
heat loss to surroundings , incomplete combustion , non standard conditions
35
New cards
PAG 4-Testing for cations group 2
flame tests , adding NaOH
36
New cards
flame tests
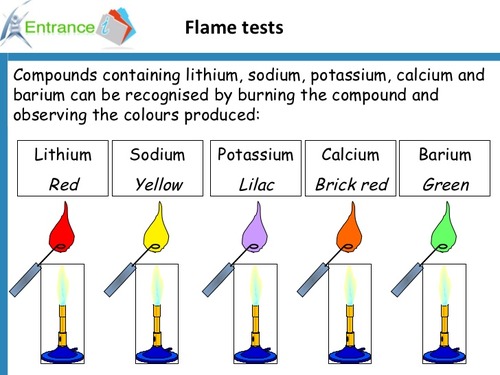
37
New cards
lithium
red

38
New cards
sodium
yellow orange

39
New cards
potassium
lilac

40
New cards
calcium
brick red

41
New cards
barium
apple green

42
New cards
copper
blue-green

43
New cards
Testing for NH4+
add 0.1 moldem-3 of ammonium chloride then add sodium hydroxide and shake the mixture , warm the mixture slightly with a water bath , test fumes using damp red litmus paper if present should turn blue

44
New cards
testing for anions
group 7
45
New cards
testing for sulfate ions
add BaCl2 with acidified HCL , if sulfate ions present a white precipitate of barium sulfate will form
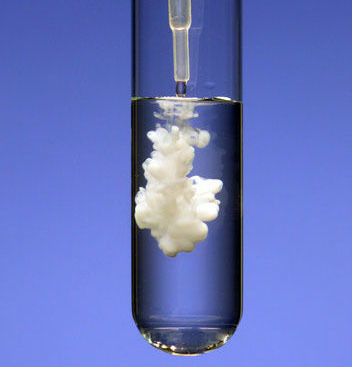
46
New cards
testing for halide ions
add silver nitrate solution
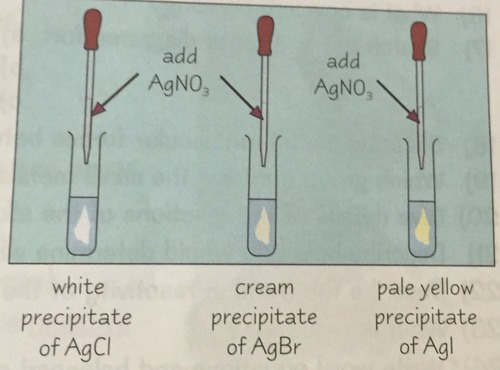
47
New cards
testing for carbonates
Add dilute acid to a solid carbonate and look for any effervescence and bubble through limewater if it goes cloudy , positive result
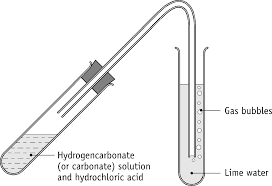
48
New cards
insoluble salts
- silver and lead chloride , bromides and iodides
- strontium , barium, and lead sulfate
- all carbonates and hydroxides except sodium, potassium, and ammonium
- strontium , barium, and lead sulfate
- all carbonates and hydroxides except sodium, potassium, and ammonium
49
New cards
filteration
A process that separates materials based on the size of their particles.
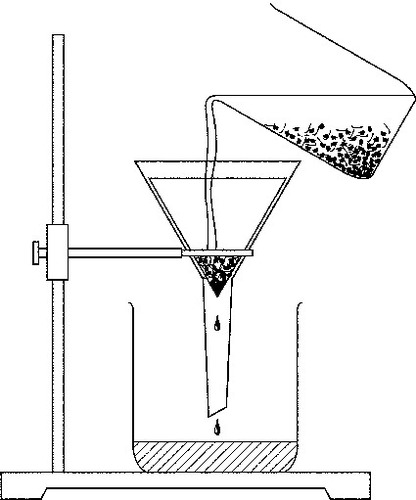
50
New cards
vacuum filteration
air outlet - water pump
Buchner flask - thicker glass walls to cope with vacuum
buchner funnel
Buchner flask - thicker glass walls to cope with vacuum
buchner funnel
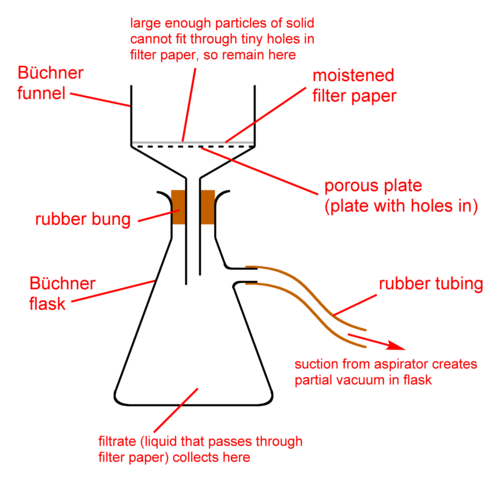
51
New cards
When is vacuum filtration used?
if large amounts of solid are used
52
New cards
how is the vacuum produced
apparatus is connected to a water pump
53
New cards
PAG 5- Preparation of a pure organic liquid
distillation , using a separating funnel , boiling point determination e.g purifying a haloalkane from an alcohol or cyclohexene from hexanol
54
New cards
distillation
used to separate an organic product from its reaction mixture
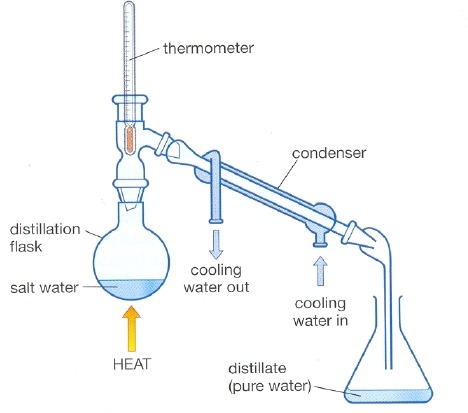
55
New cards
why does the water go in the bottom of the condenser in distillation
goes against gravity causing efficient cooling and prevents backflow of water
56
New cards
using a separating funnel
put impure product into a separating funnel , wash product using sodium hydrocarbonate or sodium chloride solution , allow layers to seperate in the funnel , run the organic layer into a clean conical flask and add a drying agent to and dry the organic liquid carefully decant the liquid into the distillation flask , distill to collect the pure product
57
New cards
drying agents
anhydrous sodium sulfate , calcium chloride

58
New cards
organic layer
layer with the lower density - upper layer
59
New cards
drying agent should be....
insoluble in the organic liquid , not reactive with the organic liquid
60
New cards
decant
pour off the organic liquid gently and leave the drying agent in the conical flask
61
New cards
what does NaHCO3 do
neutralises any remaining reactant acid
62
New cards
what does sodium chloride do
separates the organic layer from the aqueous layer
63
New cards
preparing and purifying an ester
propanol and propanoic acid then add c.H2S04 and keep the contents of the flask cooled and shaken in an ice water bath , reflux , distillation , distillate in a separating funnel , anhydrous calcuim chloride , filter into dry flask with a few anti bumping granules
64
New cards
why is anti bumping granules used
to prevent vigorous uneven boiling / to allow liquid to boil more gently
65
New cards
reflux
heating using a vertical condenser allowing continuous boiling and condensing of a liquid
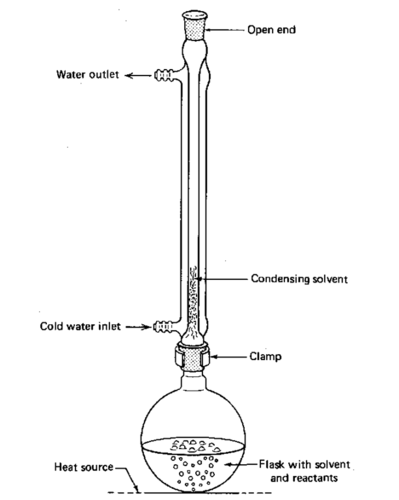
66
New cards
PAG 6- Recrystallisation
dissolve impure compound in minimum volume of hot solvent , filter the solution to remove any insoluble impurities and retain filterate. Allow the filterate to cool and crystallise. Wash the crystals with cold ethanol or cold water and then dry crystals in the open or using an oven
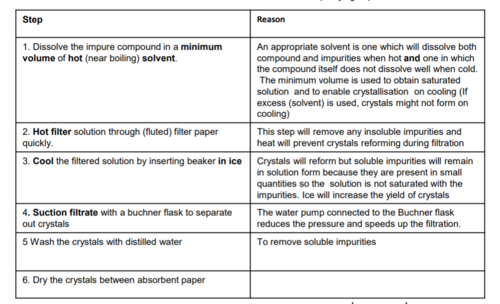
67
New cards
loss of yield during recrystallisation
loss of crystals during filteration and washing , some product stays in solution after recrystallisation and side reactions occurring
68
New cards
why should you never seal end of the condenser during reflux
build up gas pressure leading to apparatus exploding
69
New cards
Melting point determination
70
New cards
If there is impurities how would the melting point differ
the melting point would be lowered and sample would melt over a range of temperatures
71
New cards
thin layer chromatography
a separation technique that involves the separation of small molecules as they move through a silica gel
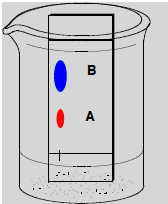
72
New cards
Process of TLC
pencil line 1cm above bottom of TLC plate , add solvent and ensure a lid is used , when solvent is about 1cm from the top of the plate mark solvent front with a pencil, allow plate to dry using a fume cupboard , use a locating agent
73
New cards
locating agent
ninhydrin - amino acids
UV or iodine crystals
used to make spots on chromatogram more visible
UV or iodine crystals
used to make spots on chromatogram more visible
74
New cards
why is a lid used in TLC
to prevent evaporation of solvent
75
New cards
Rf
distance moved by spot/distance moved by solvent
76
New cards
PAG 7- tests for alkenes
bromine water - orange to colourless
77
New cards
Test for aldehydes
Tollens reagent: silver mirror , Fehlings test - brick red precipitate

78
New cards
Test for carboxylic acids
carbonate ions - CO2 formed/effervescence

79
New cards
tests for alcohols
acidified dichromate orange to green
primary alcohols - aldehyde distillation , carboxylic acid reflux
secondary alcohol - ketone
primary alcohols - aldehyde distillation , carboxylic acid reflux
secondary alcohol - ketone
80
New cards
test for haloalkanes
warm with aqueous silver nitrate in ethanol - white precipitate
81
New cards
test for phenols
iron (111) chloride test
purple
purple

82
New cards
phenols and carbonates
don't react carbonates ions fizz with sodium but no reaction with carbonates
83
New cards
PAG 9- measuring rate of reaction by a continuous monitoring method
measuring change in volumes of gas , measuring changes in concentration via a continuous rate method
84
New cards
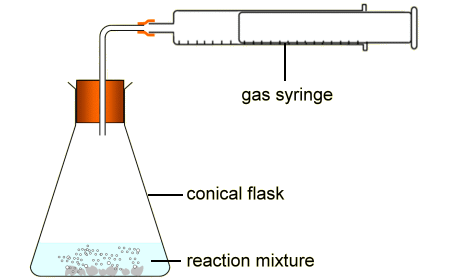
measuring change in gas volumes
use gas syringe to see volume of gas collected
85
New cards
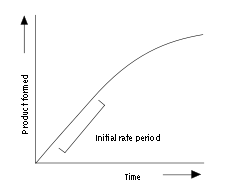
initial rate
instantaneous rate at t=0 of a concentration time graph , fastest rate
86
New cards
why is the measure of initial rate preferable
we know the concentrations at the start of the reaction
87
New cards
excess of a reactant doesn't...
affect rate , zero order
88
New cards
half life of a first order reaction
independent of the initial concentration
89
New cards
PAG 10- measuring the rate of reaction by an initial rate concentration
gradient of a continuous monitoring method or using a clock reaction
90
New cards
clock reactions
Measures the time from the start of reaction until there is a fixed concentration
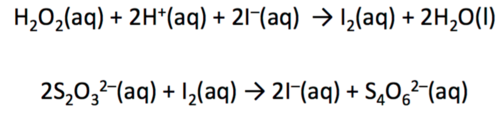
91
New cards
how is the end point of clock reactions determined
when one limiting reactant runs out leading to a sudden colour change
92
New cards
Example of clock reaction
hydrogen perioxide , sodium thiosulfate iodine titration
93
New cards
how to determine order of reaction of clock reactions
repeating experiment several times and varying concentration of a reactant several times by keeping concentrations of other reactants the same
94
New cards
how can initial rate of reaction be represented
1/t
95
New cards
describe the clock reaction method
put reactants into separate test burettes , measure out required volumes of potassium iodide , starch , and sodium thiosulfate and water a conical flask , measure hydrogen peroxide into a test tube and pour into the conical flask and immediately start timer , end point is when first blue/black colour appears
96
New cards
working out rate order graphically
log rate=log k + nlog conc
97
New cards
measuring rate of reaction changes with temperature
sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid
98
New cards
method for sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid.
place test tubes each with 2 reactants into a water bath to ensure they are are at the right temperature ,first place thiosulfate into a conical flask on top of a cross then pour in the hcl , start stopwatch and swirl , stop clock when cross disappears , repeat for other temperatures
99
New cards
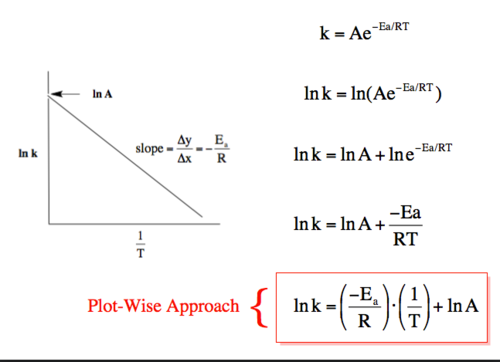
how to calculate Ea from a graph
lnk = -Ea/RT + lna
100
New cards
how to titrate samples of a reaction mixture with acid , alkali or sodium thiosulfate
take out small samples of the reaction mixture , quenching via dilution or cooling then titrate with a suitable reagent