synaptic transmission
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
structure of synapse?
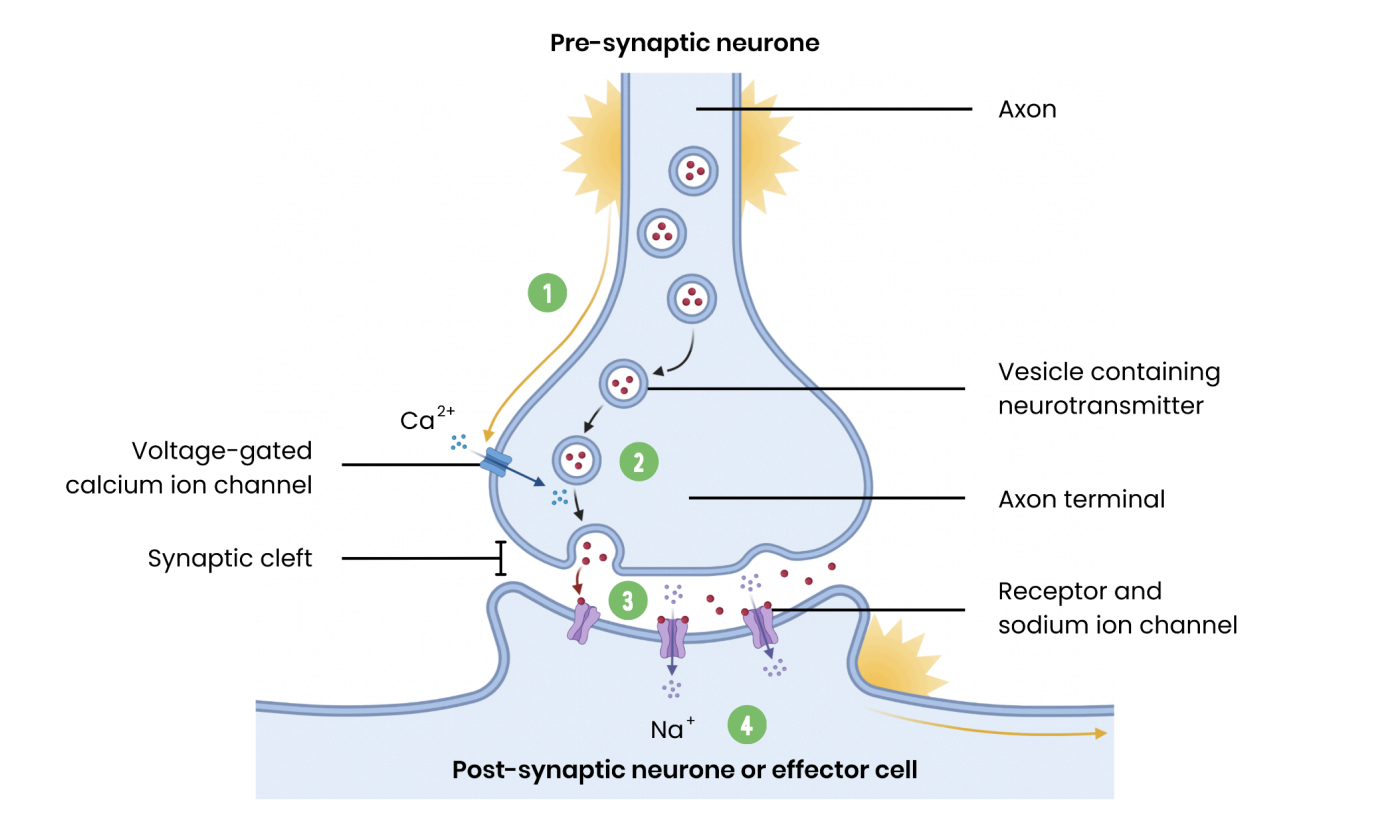
cholinergic synapses?
synapses that use the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh)
what happens at the pre-synaptic neurone during transmission across a cholinergic synapse?
depolarisation causes voltage-gated Ca2+ channels to open → Ca2+ diffuses in
causing vesicles w/ Ache to move + fuse w/ pre-synaptic membrane → releasing Ash into synaptic cleft by exocytosis
what happens at the post-synaptic neurone during transmission across a cholinergic synapse?
ACh diffuses across synaptic cleft to bind to specific receptors on post-synaptic membrane
causing Na+ channels to open
Na+ diffuses into post synaptic knob → depolarisation
if threshold met, action potential initiated
what happens to acetylcholine after synaptic transmission?
hydrolysed by acetylcholinesterase
products are reabsorbed by presynaptic neurone
to stop overstimulation - if not removed it would keep binding to receptors causing depolarisation
how do synapses result in unidirectional nerve impulses?
neurotransmitter only made in/released from pre-synaptic neurone
receptors only on post-synaptic membrane
summation by synapses?
addition of a number of impulses covering on a single post-synaptic neurone
causing rapid buildup of neurotransmitter
so threshold more likely to be reached to generate an action potential
why is synapse summation important?
low frequency action potentials release insufficient neurotransmitter to exceed threshold
spatial summation?
many pre-synaptic neurones share one synaptic cleft/post-synaptic neurone
collectively release sufficient neurotransmitter to reach threshold to trigger action potential
temporal summation?
one pre-synaptic neurone releases neurotransmitter many times over a short time
sufficient neurotransmitter to reach threshold to trigger an action potential
inhibition by inhibitory synapses?
inhibitory neurotransmitters hyperpolarise postsynaptic membrane as:
Cl- channels open → diffuses out
K+ channels open → K+ diffuse out
inside of axon has more negative change than outside/below resting potential
more Na+ req. to enter for depolarisation
reduced likelihood of threshold being met/action potential formation at post-synaptic membranes
importance of inhibitory synapses?
both excitatory + inhibitory neurones forming synapses w/ the same post-synaptic membrane gives control of whether it “fires” an action potential
structure of neuromuscular junction?
receptors are on muscle fibre sarcolemma instead of post synaptic membrane + there are more
muscle fibre forms cleft to story enzyme eg. acetylcholinesterase to break down neurotransmitter
transmission across cholinergic synapses vs neuromuscular junctions?
C:
neurone to neurone
neurotrans. can be excitatory or inhibitory
action potential may be initiated in postsynaptic neurone
N:
neurone to muscle
only excitatory
action potential propagates along sarcolemma down T tubules
effect of drugs on synapse?
stimulate nervous system → more action potentials:
similar shape to neurotransmitter
stimulate release of more neurotransmitter
inhibit enzyme that breaks neurotrans. down → Na+ continues to enter
inhibit nervous system → fewer action potentials:
inhibit NT release eg. prevent opening of Ca+ channels
block receptors by mimicking of neurotransmitter