Unit 4: Cell Communication and Cell Cycle
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Homeostasis
Steady state or internal balance

When do cells maintain homeostasis?
Maintain a relatively constant internal environment even when the external environment changes significantly
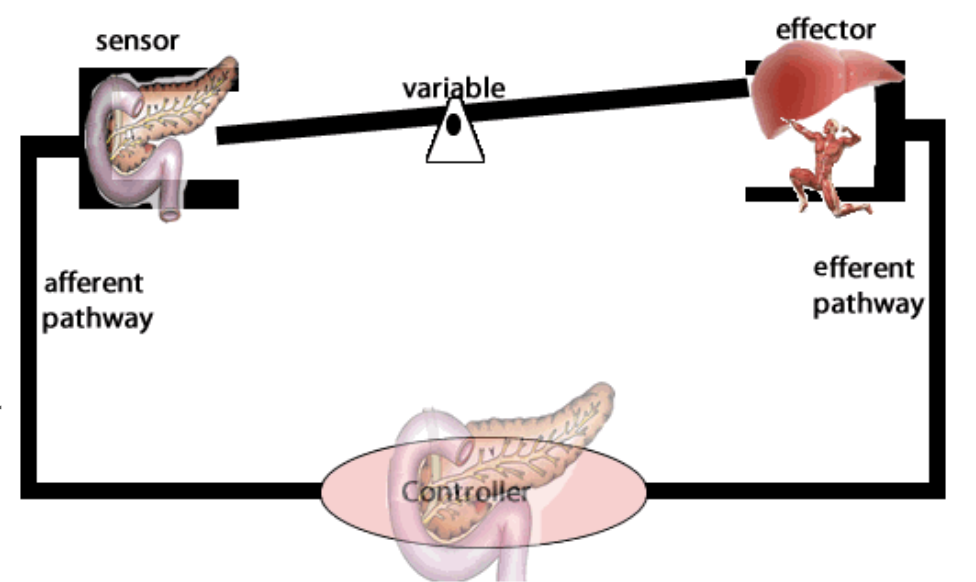
Set point
Internal conditions typical state
Stimulus
Fluctuations in that condition above or below the set point serve
Sensor
A receptor or sensor detects the stimulus and triggers a response
Response
Activity that returns the condition to the set point
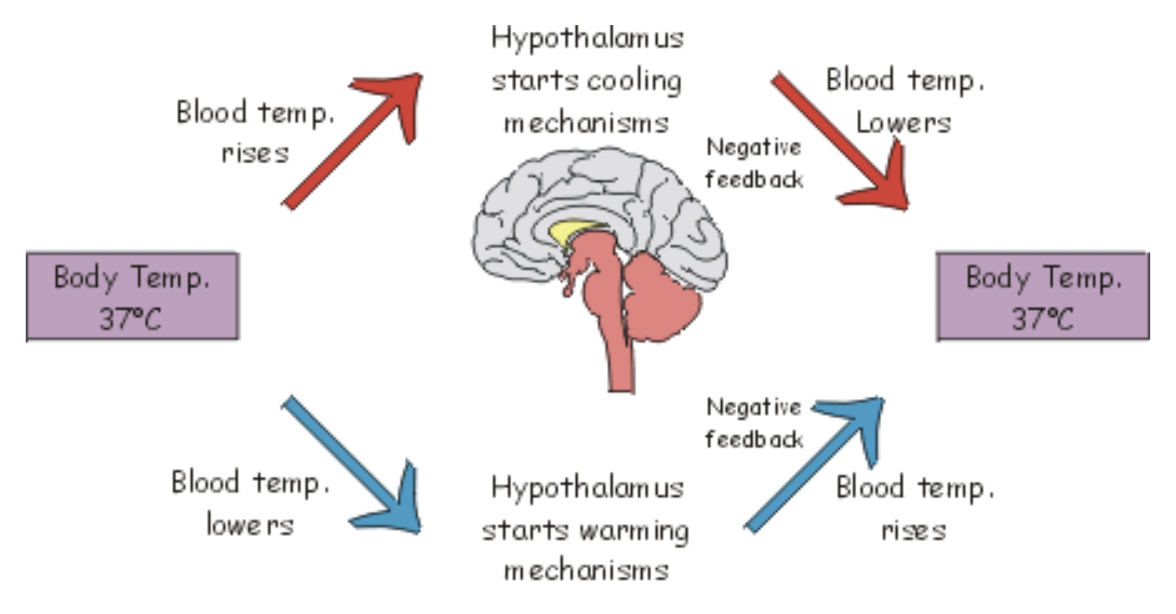
Negative Feedback
Response reduces the stimulus
Example of negative feedback
When you exercise, you produce heat, which increases your body temperature.
Your nervous system detects this increases and triggers sweating. As your sweat evaporates, your skin cools, returning your body to its set point.
Positive Feedback
Stimulus is amplified in order to complete a process; then the condition returns to the set point
Example of positive feedback
During childbirth, the pressure of the baby’s head against the uterus stimulates contractions.
The contractions result in greater pressure, thereby stimulating more contractions and then more pressure. This continues until the baby is born.
Methods Used by Cells to Communicate
Autocrine, Juxtacrine, Paracrine, Endocrine
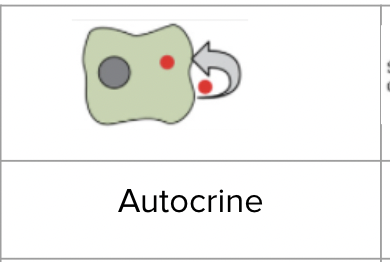
Autocrine signaling
A cell sends a signal to itself
Juxtacrine signaling
Cells communicate with adjacent cells through direct contact
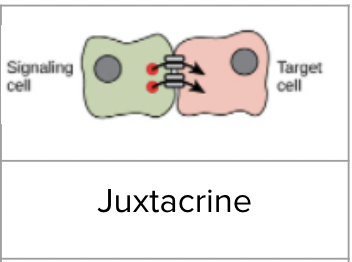
Two examples of juxtacrine signalling
Ex. plasmodesmata connect plant cells and gap junctions connect animal cells
Ex. glycoproteins on one cell interact with glycoproteins on another cell
Paracrine signalling
Cells communicate to nearby cells by releasing chemical messengers
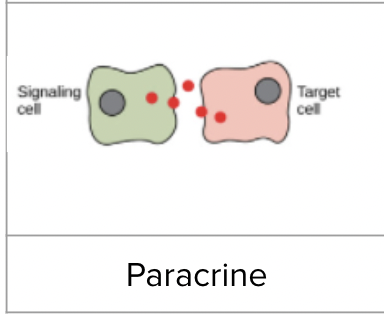
Paracrine signalling example
Ex. neurotransmitters released into a synapse
Endocrine signalling
Cells communicate to cells far away by releasing chemical messengers that are carried to the target cell
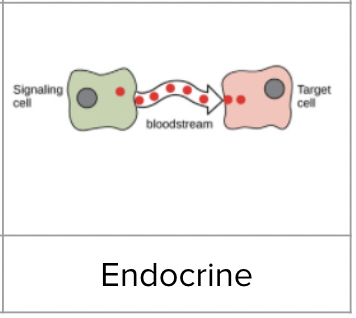
Endocrine signalling example
Adrenaline is produced by adrenal glands, released into the bloodstream, and carried to the heart and other muscles
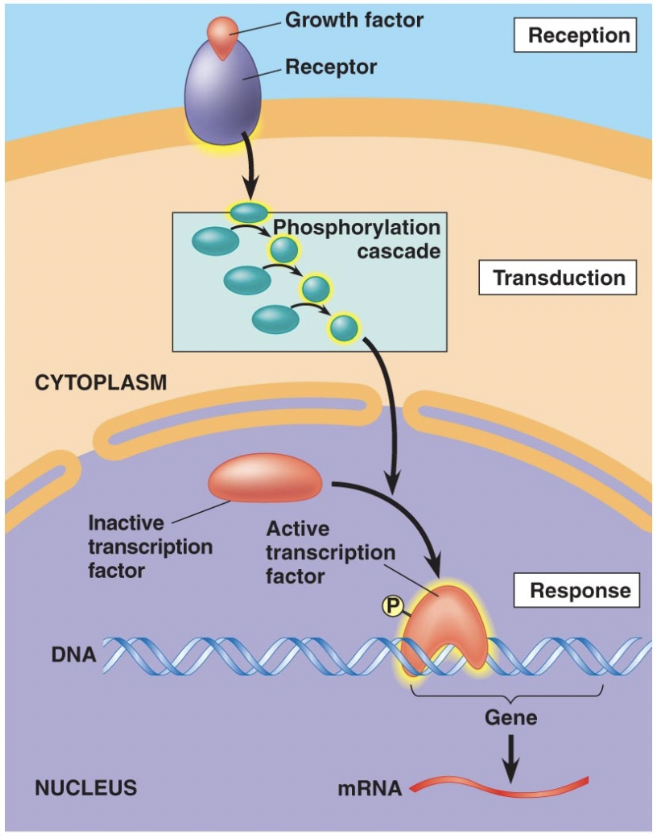
In all forms of cell signaling, a signal is converted to a cellular response in three steps:
Reception
Transduction
Response
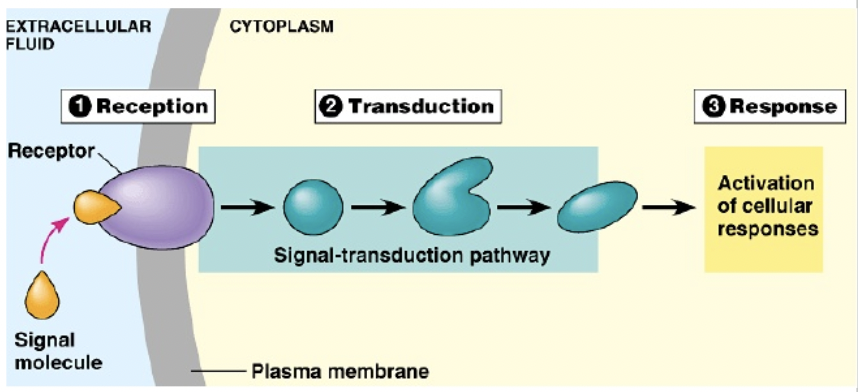
Reception
Signaling molecule binds to the receptor protein
Transduction
The signal is converted into a form that can produce a cellular response
Response
The transduced signal triggers a cellular response
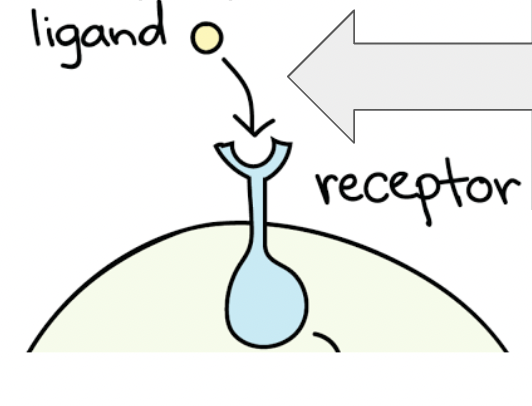
Reception process
A signal molecule, a ligand, binds to a receptor protein in a lock and key fashion, causing the receptor to change shape.
Where are receptor proteins found?
Most receptor proteins are in the cell membrane but some are inside the cell.
Locations of hydrophilic and hydrophobic ligands
Hydrophilic ligands bind to plasma membrane receptors
Small or hydrophobic ligands can pass through the membrane and attach to intracellular receptors (ex. steroid hormones like testosterone)
The three most common types of membrane receptor proteins:
G-protein coupled receptors
Receptor tyrosine kinases
Ion channel receptors
The binding of ligands is how specific?
Highly specific (must be the right shape).
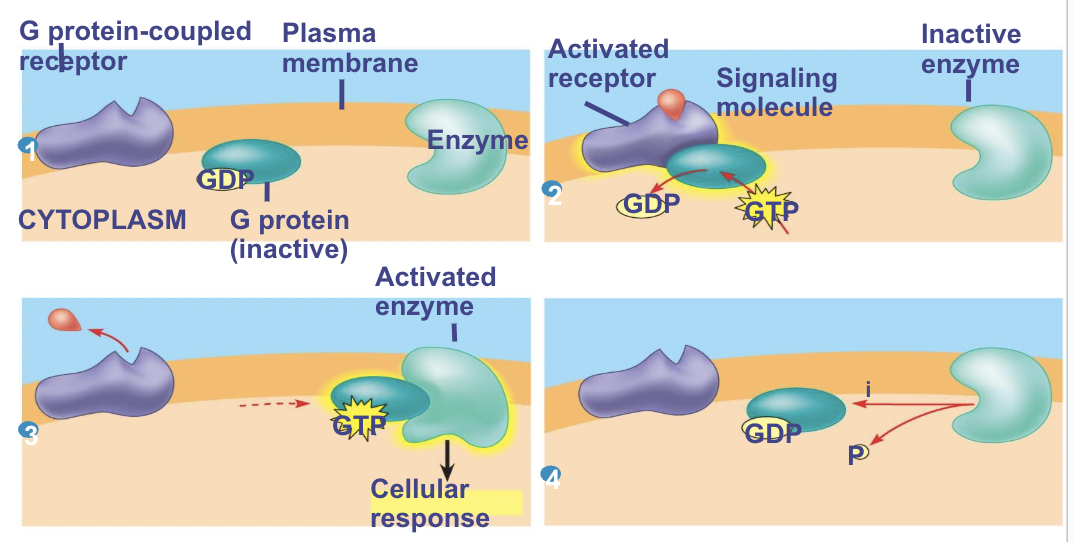
G-Protein Coupled Receptors
G proteins bind the energy-rich GTP (very similar to ATP- source of energy)
Do G-proteins vary in structure?
Are all very similar in structure
GPCR systems
Extremely widespread and diverse in their functions
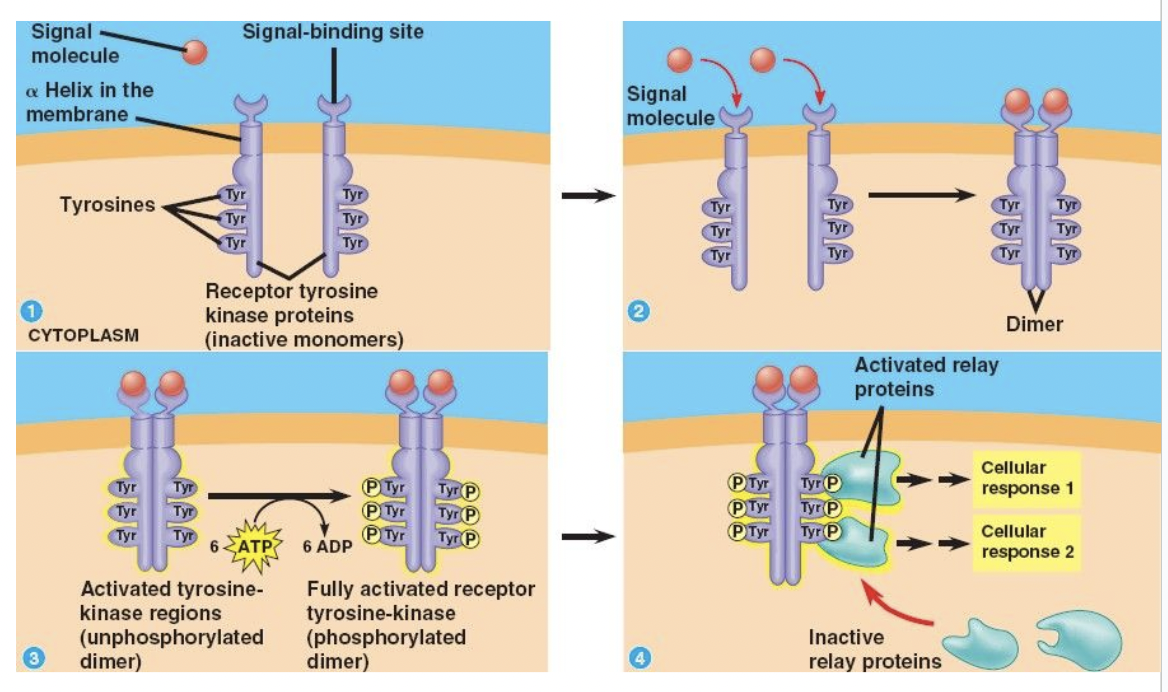
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)
Membrane receptors that transfer phosphate groups from ATP to another protein
How effective are RTKs?
Can trigger multiple signal transduction pathways at once
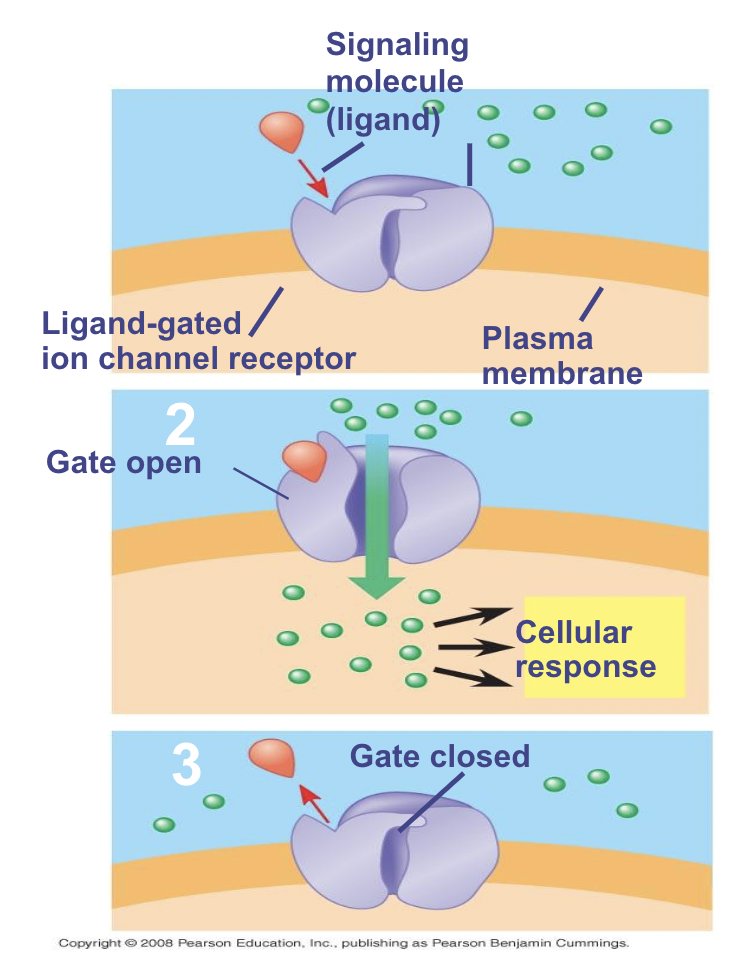
Ion Channel Receptors
Act as a gates that open and close when the receptor changes shape
What happens when a signal molecule (like a neurotransmitter in a synapse) binds as a ligand to the receptor?
The ate allows specific ions, such as Na+ or Ca2+, through a channel in the receptor
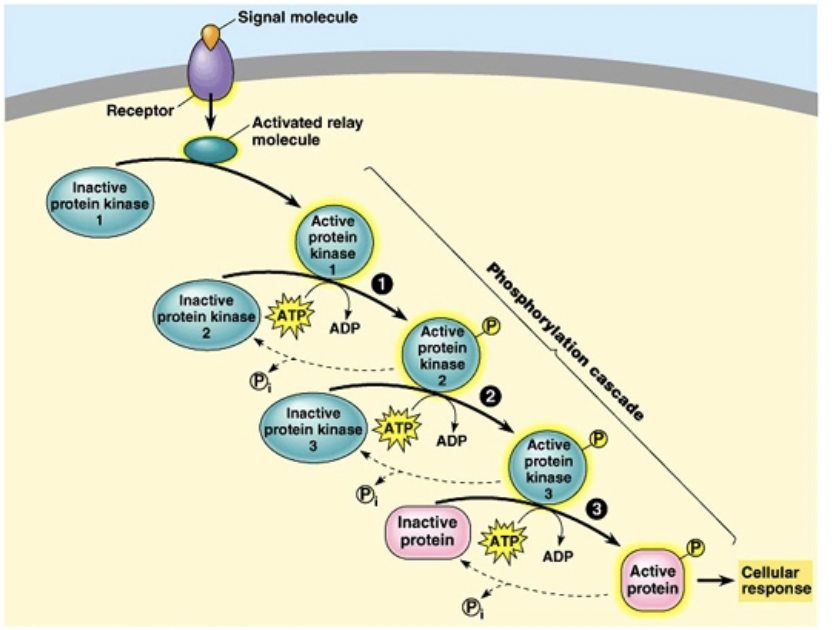
Transduction
Molecular interactions relay signals from receptors to target molecules in the cell
How does transduction have multistep pathways?
Can amplify a signal (by activating multiple copies of the next component in the pathway)
What is the benefit of having multistep pathways?
Provide more opportunities for coordination and regulation
Multistep pathways
At each step in a pathway, the signal is transduced into a different form, commonly a conformational change in a protein.
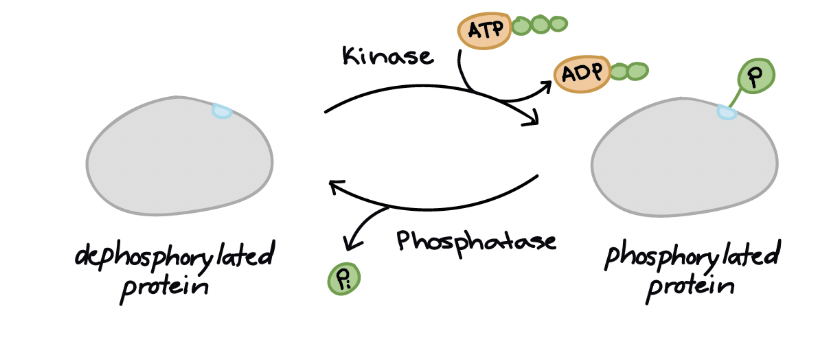
Transduction - Phosphorylation
In this process, a series of protein kinases add a phosphate to the next one in line, activating it
Phosphatase enzymes then remove the phosphates
Kinases
Enzymes (proteins) that add phosphate groups (PO43−) to other molecules (proteins) to change their shape and activate or inactivate them
Secondary messengers
Small molecules/ions that relay signals received by receptors to proteins.
Common secondary messengers -
cAMP (cyclic AMP)
Calcium
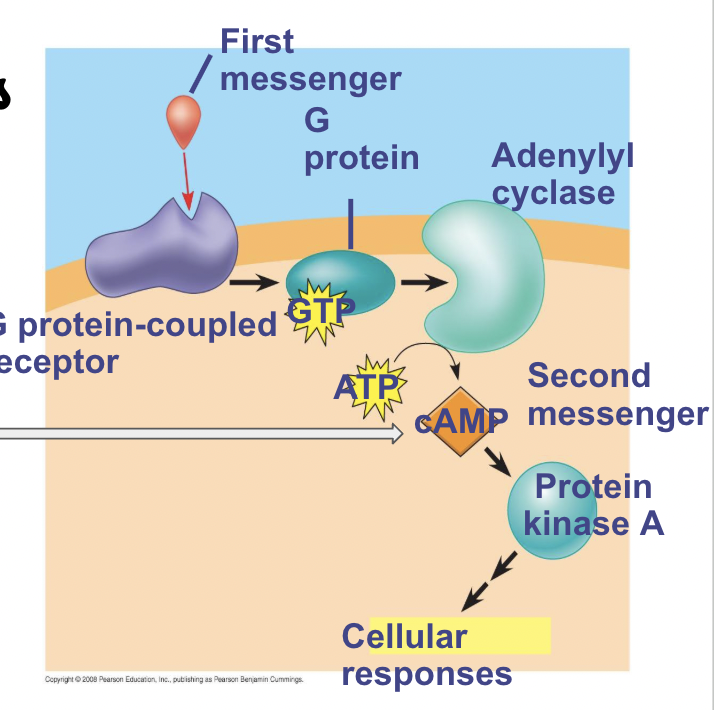
Calcium as a secondary messenger
Can function as a second messenger because its concentration in the cytosol is normally much lower than the concentration outside the cell; thus a small change in the number of calcium ions represents a relatively large percentage change in calcium concentration
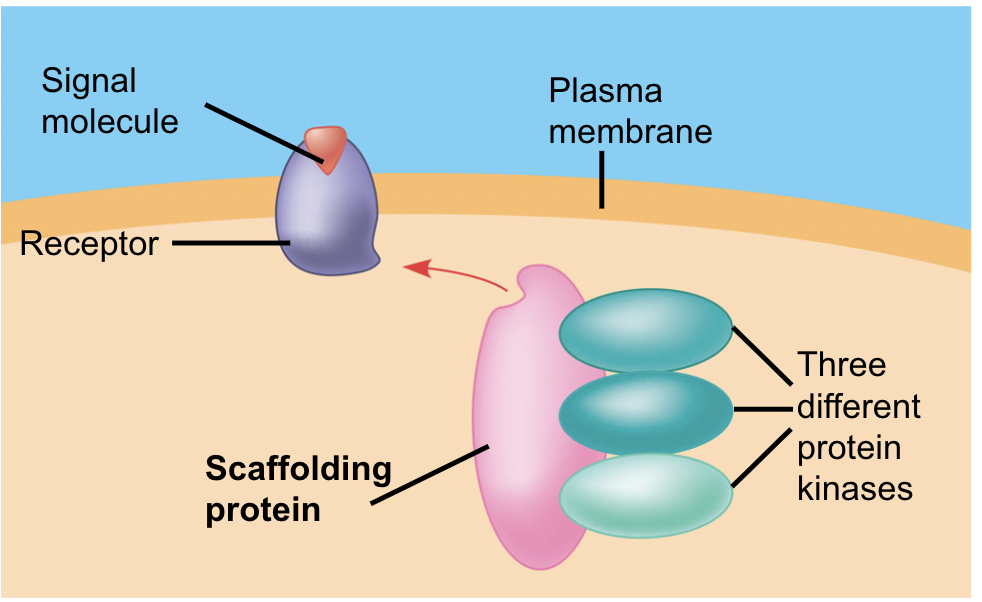
Scaffolding proteins
Can increase the signal transduction efficiency.
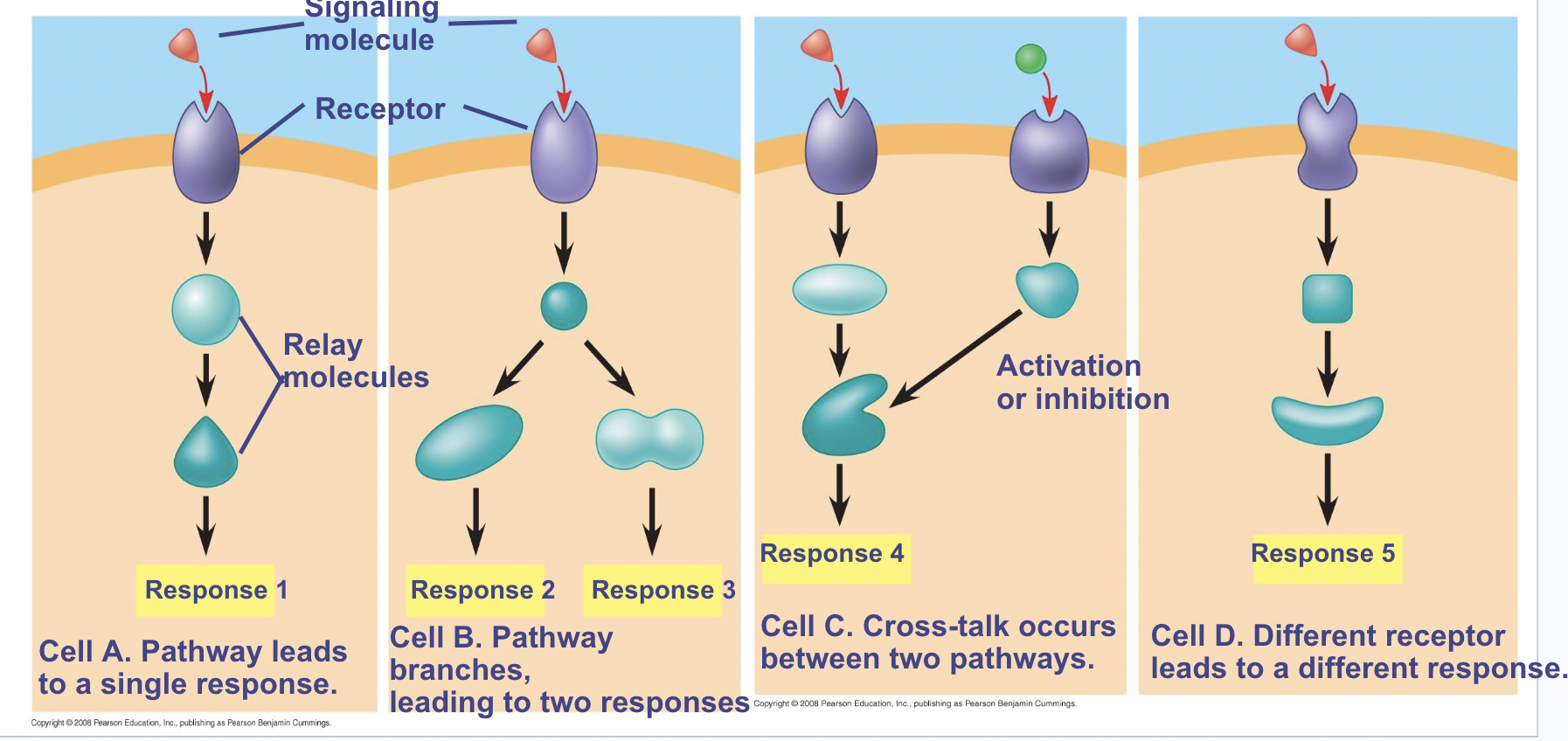
There can be many possible responses to a cell signal -
The same signal molecule can trigger different responses
Many response can come from one signal
The signal can also trigger an activator or inhibitor
The signal can also trigger multiple receptors and different responses
Example of responses
Turn transcription of DNA on/off or regulate activity of proteins in cytoplasm.
Stopping the Response
The signal response is terminated quickly when the ligand detaches from the receptor
Mitosis
Genetic material is divided as one cell divides, forming two identical cells
What is divided during cytokinesis?
Organelles and cytoplasm
Cell cycle in unicellular organisms
Used for reproduction
Called binary fission
Cell cycle in multicellular organisms
Used for growth and repair
Organelles Involved in the Cell Cycle
Nucleus
Protects the DNA
Cytoskeleton
Organizes structures in the cell
What is inlcuded in the cytoskeletan?
Centrioles
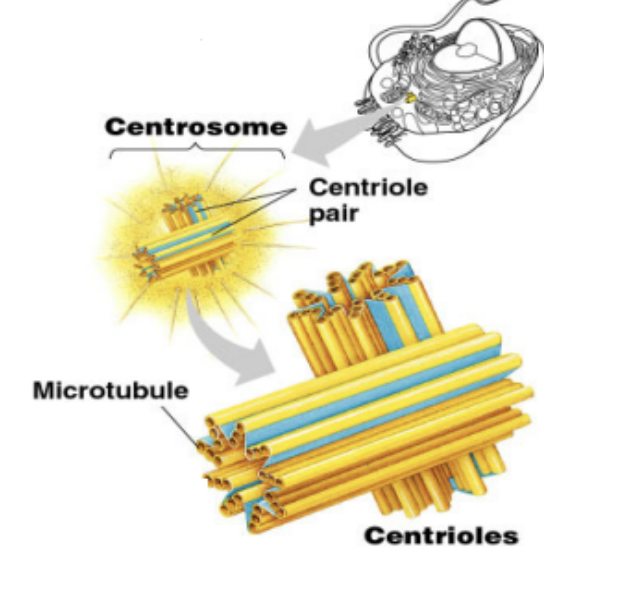
Centrioles
Responsible for the spindle fibers that guide the chromosomes during mitosis
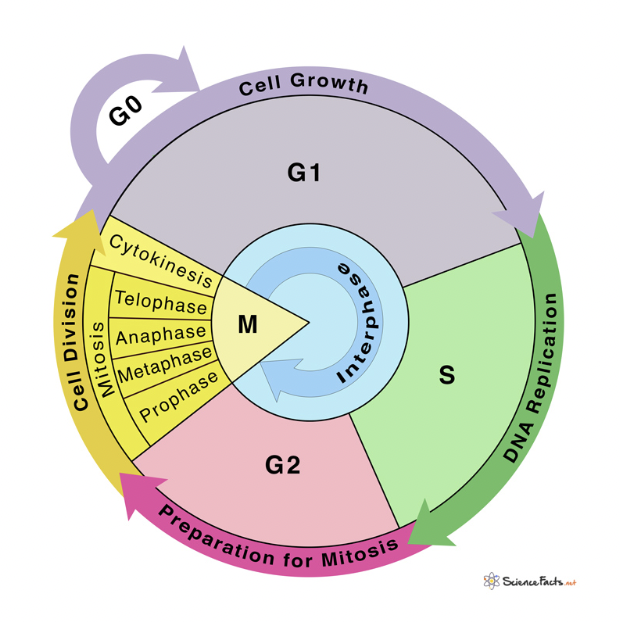
Overview of the Cell Cycle
:)
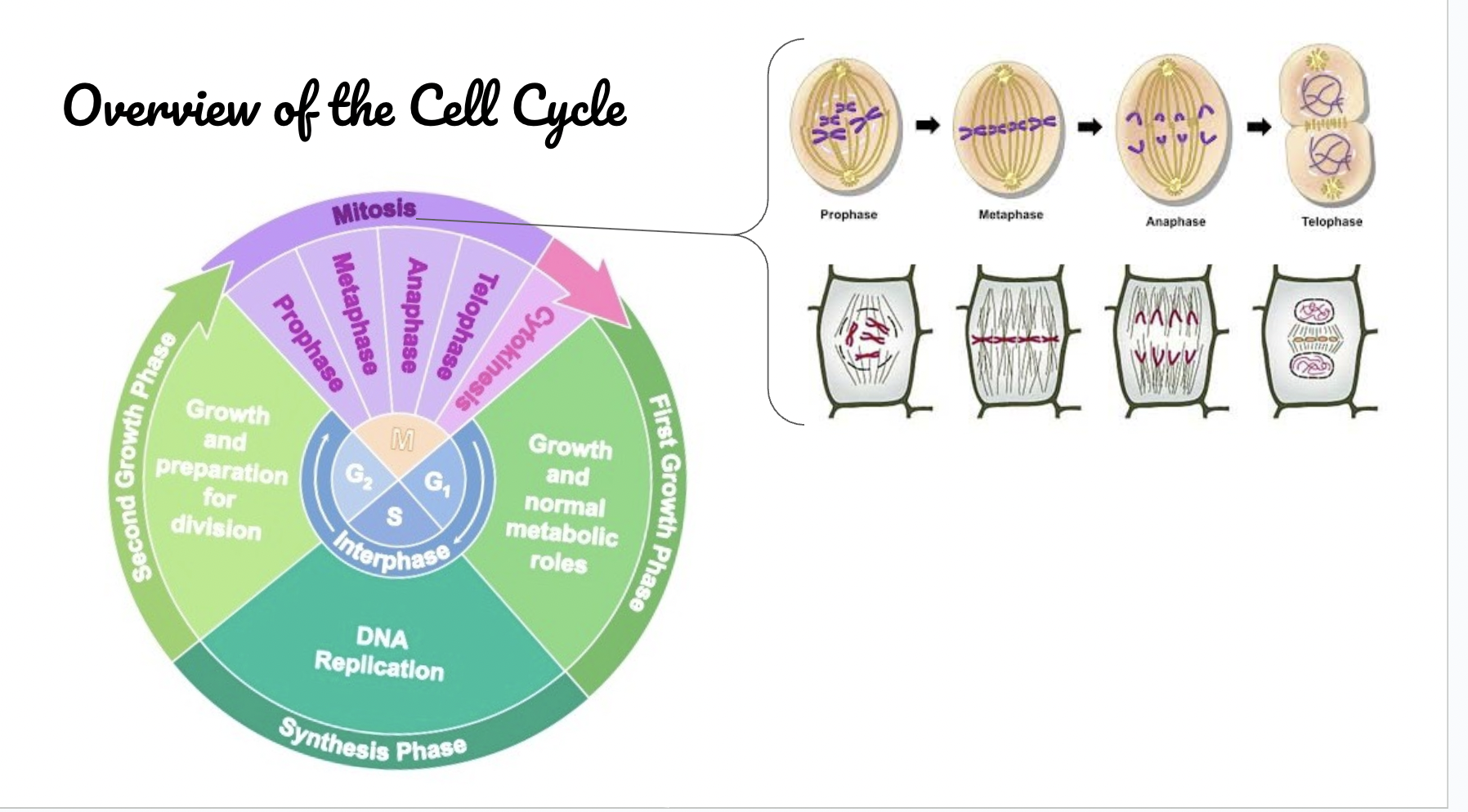
Cells spend 90% of their time in?
Interphase
G1
1st Gap
Everyday tasks such as making proteins
Cell grows
G0
Cell continues doing its job until it receives a signal to reenter G1 to get ready to divide
If the cell receives a signal to divide, it moves on to the next phases:
S and G2
S
DNA Synthesis
Copies genetics material (so each cell gets a copy)
G2
2nd Gap
Prepares for division
Cell grows more
Produces proteins, organelles, and membranes
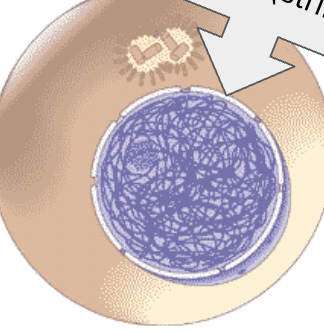
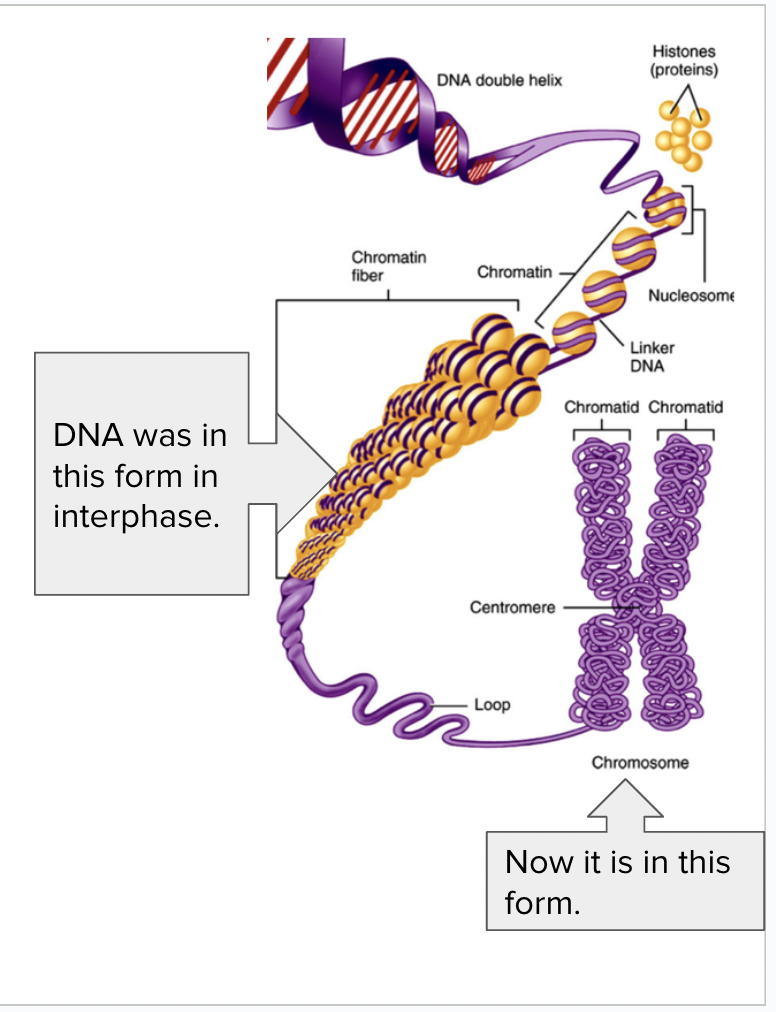
What is this?
DNA in the form of chromatin (stringy)
The DNA is divided between two daughter nuclei in four phases -
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
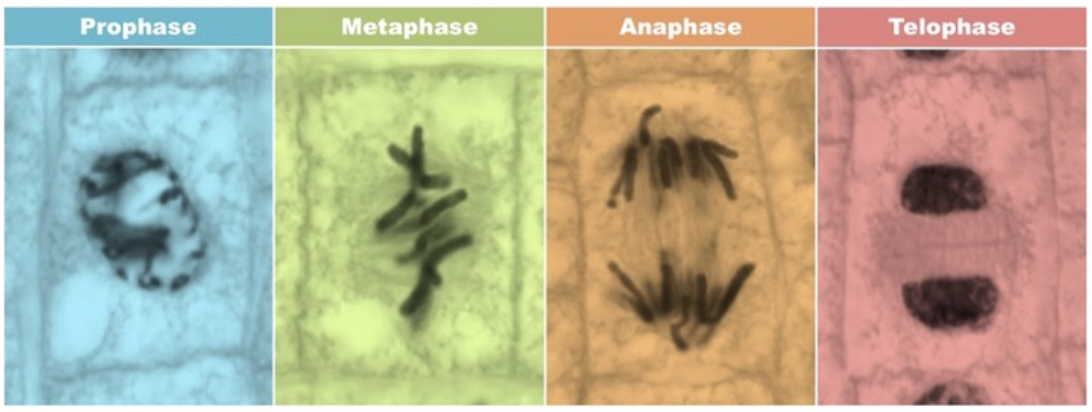
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
Centrioles (in animal cell) move to opposite ends of the cell
Protein fibers form across the cell
The nucleolus disappears
The nuclear membrane breaks down
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Spindle fibers (attached to kinetochores) coordinate movement
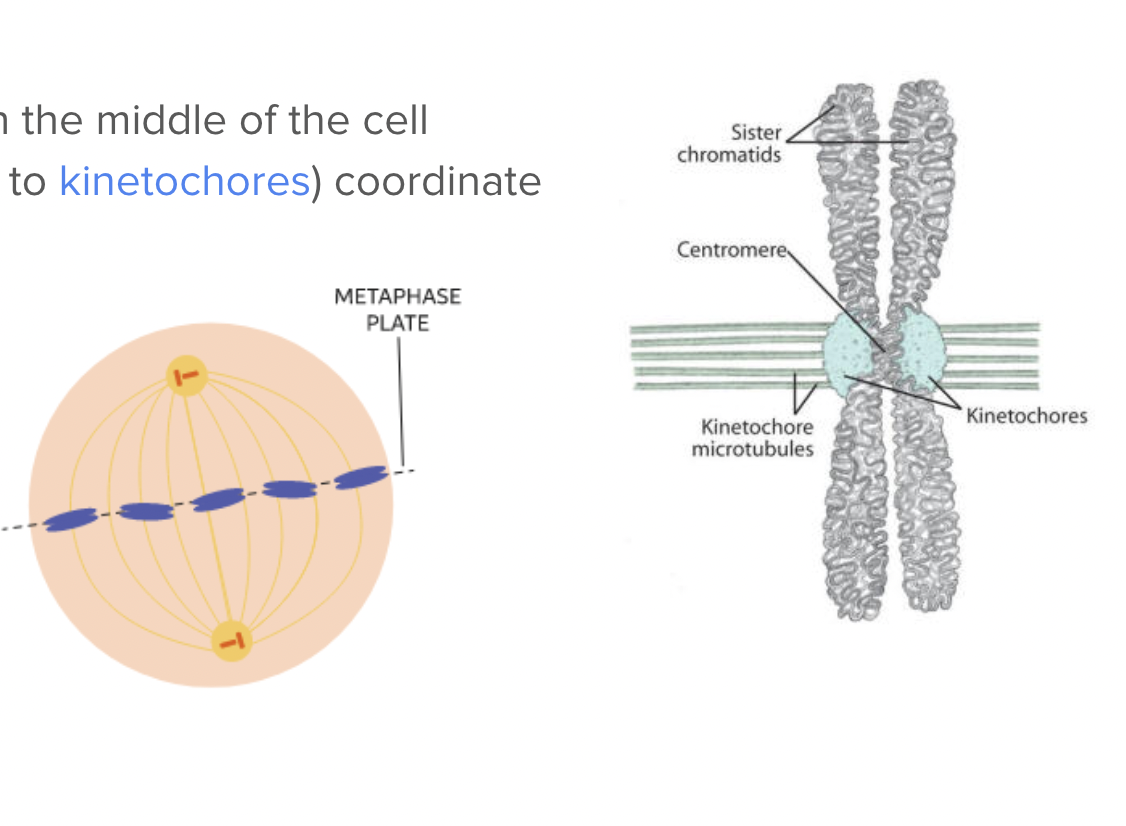
Kinetochores
Complex of proteins associated with the centromere of a chromosome during cell division, to which the microtubules of the spindle attach.
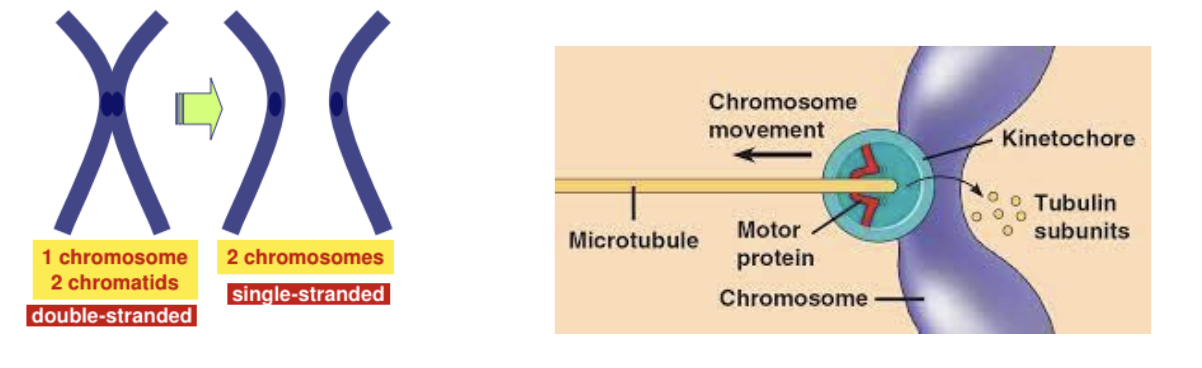
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate at kinetochores
Poles move farther apart
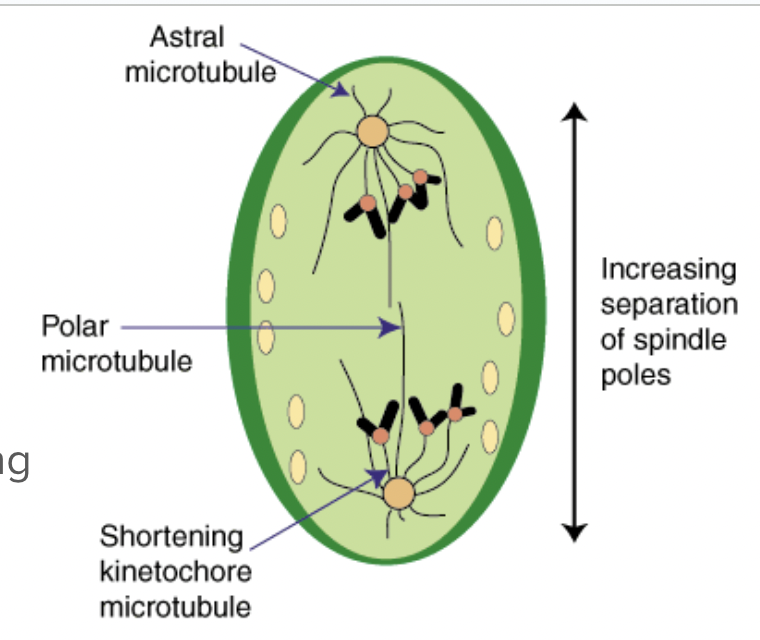
How are sister chromatids seperated?
Proteins holding the sister chromatids together are inactivated
Pulled by motor proteins “walking” along microtubules
Telophase
Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles
Daughter nuclei form
Chromosomes disperse
Spindle fibers disperse
Cytokinesis begins
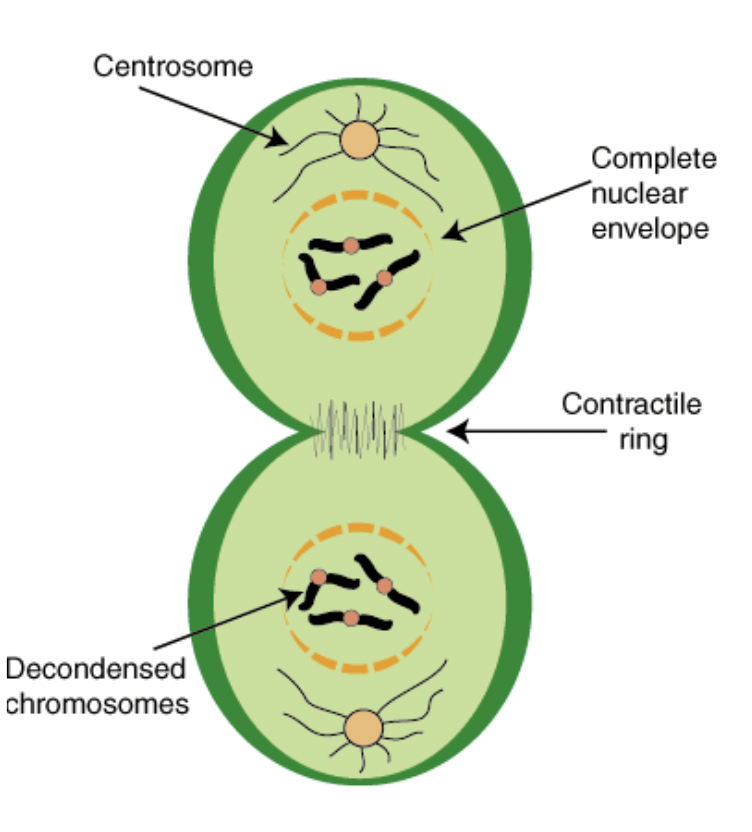
Cytokinesis for animal cells
Microfilaments contract, forming a cleavage furrow
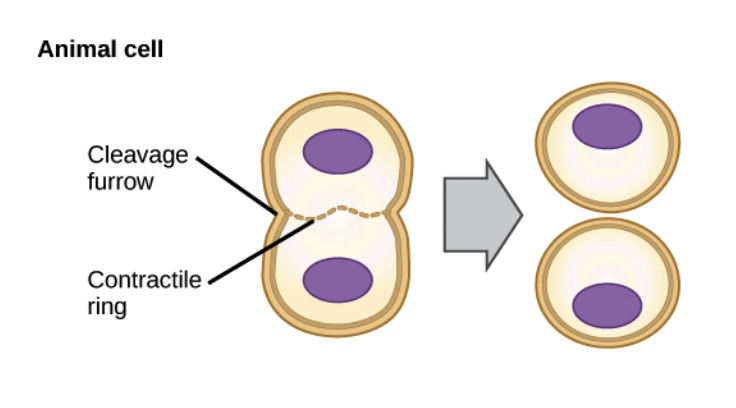
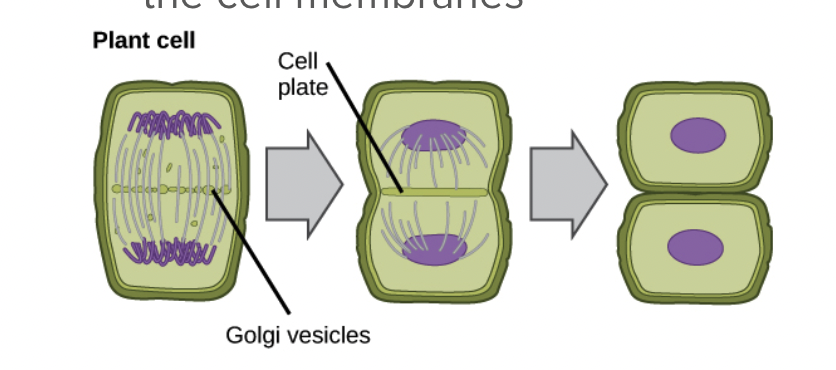
Cytokinesis for plant cells
Cell plate forms
Vesicles from the Golgi fuse to form two cell membranes
New cell wall laid down between the cell membranes
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Serve as control points where stop and go-ahead signals can regulate the cell cycle (controlled by signals inside and outside the cell).
G2 Checkpoint: Pass or fail?
Did the DNA copy correctly in the S phase?
Pass- Cell goes to mitosis
Fail - apoptosis
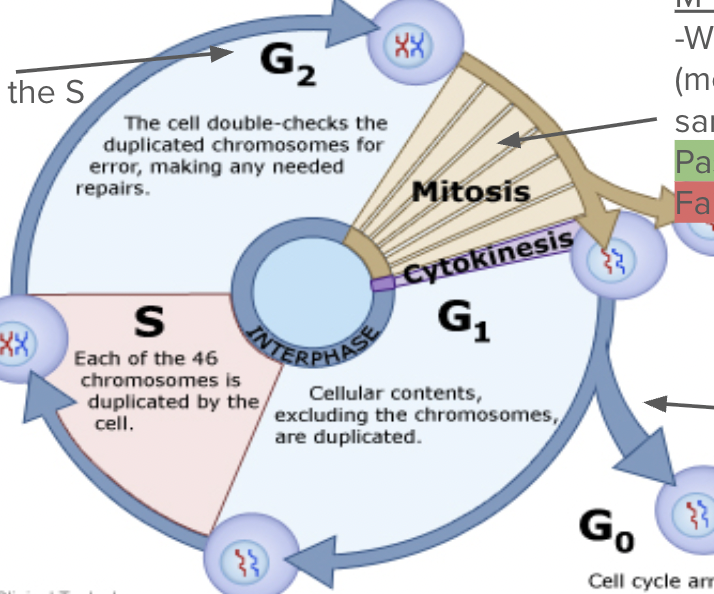
M Checkpoint- Pass or fail?
When the DNA lines up in the middle (metaphase), will each cell get the same amount of DNA?
Pass- cell divides
Fail - Apoptosis
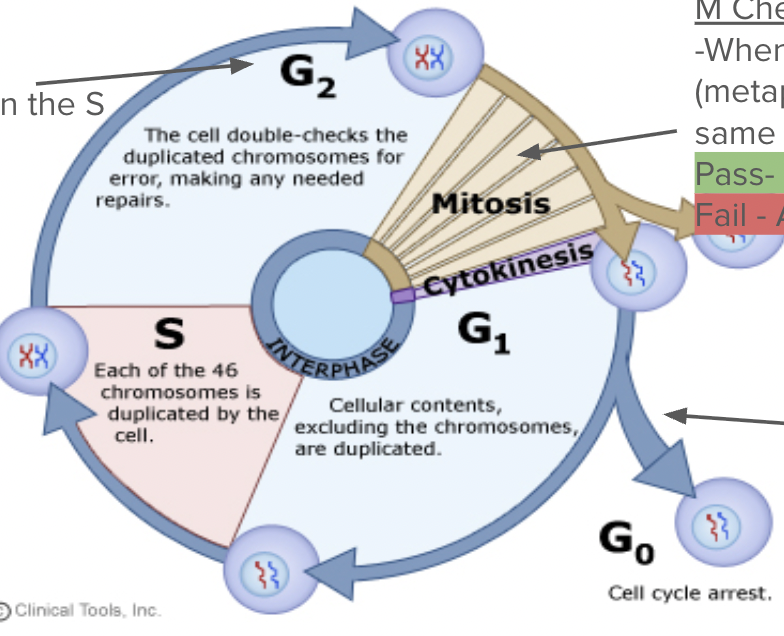
G1 checkpoint- Pass or fail?
-Do I need a new cell?
-Is this cell healthy?
-Are there enough nutrients to divide?
Pass - Cell enters S phase
Fail - Goes to G0
“Go” signals at checkpoints results in?
Changes in molecular signals in the cytoplasm
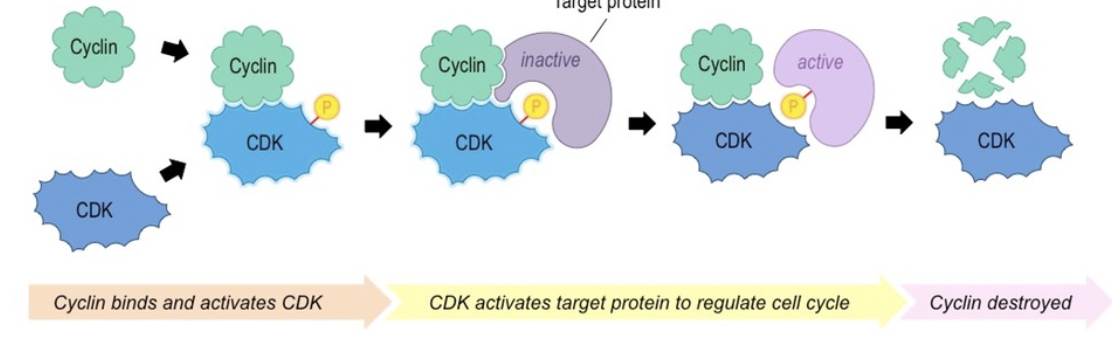
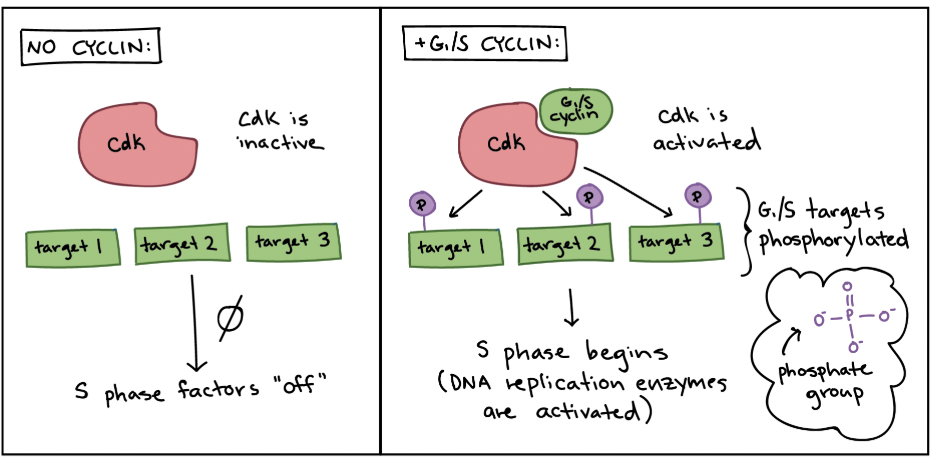
Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks)
Kinases that are only active when attached to a cyclin
Cyclin
A protein that fluctuates in concentration in the cell
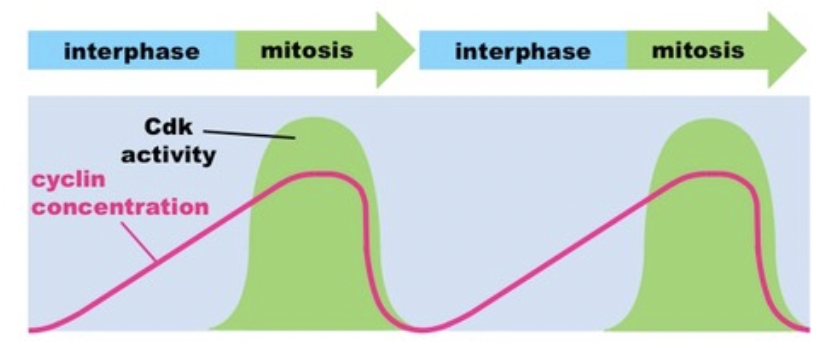
Cyclins and Cyclin-Dependent Kinases: What fluctuates and what doesn’t?
The concentration on Cdks does not fluctuate.
The concentration of cyclins does.
How are cyclins regulated?
Certain cyclins are made at certain times during the cell cycle, and their concentration will rise and fall. Cyclins are also destroyed after they are no longer needed by the cell.
What is the purpose of Cdkns activity?
Initiate the next step of the cell cycle
Cdks are only active when?
Attached to a cyclin.
Growth factors
Released by some cells and stimulate surrounding cells to divide
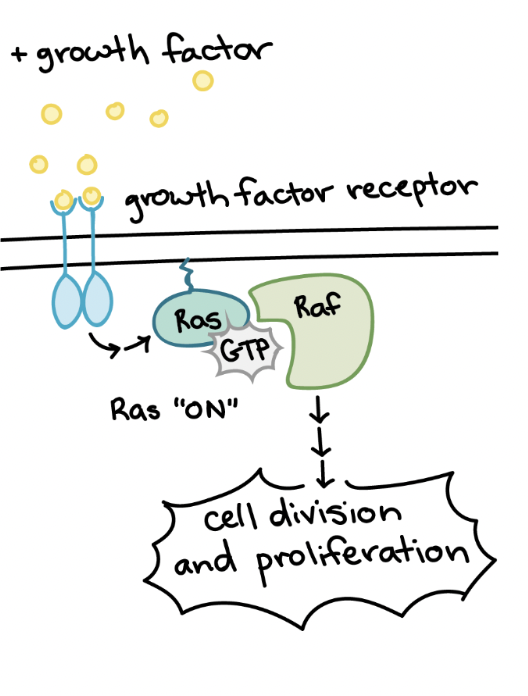
Examples of growth factors
Ex. Platelets release platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF). Fibroblasts (connective tissue) have receptors for PDGF. When PDGF binds to the receptors, a signal transduction pathway stimulates fibroblast division.
Density-dependent inhibition
Crowded cells stop dividing
Anchorage dependence
To divide, cell must be attached to something
Cancer cells bypass cell cycle controls by?
May make their own growth factor
May have an abnormal cell cycle control system
May convey a growth factor’s signal without the presence of the growth factor
How can your immune system react to cancer cells?
The immune system normally recognizes a cells conversion from a normal cell to a cancer cell and destroys it. If it is not destroyed, a tumor can form.
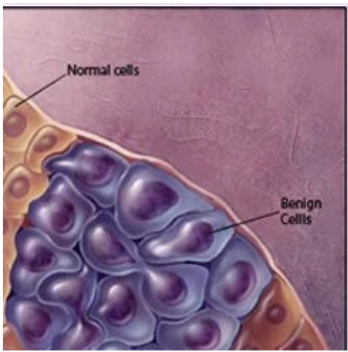
Benign
Stays in the same place
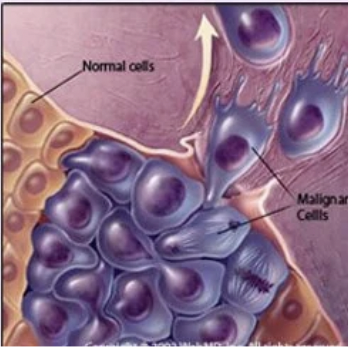
Malignant
Spreades to other parts in the body (metastaizes)
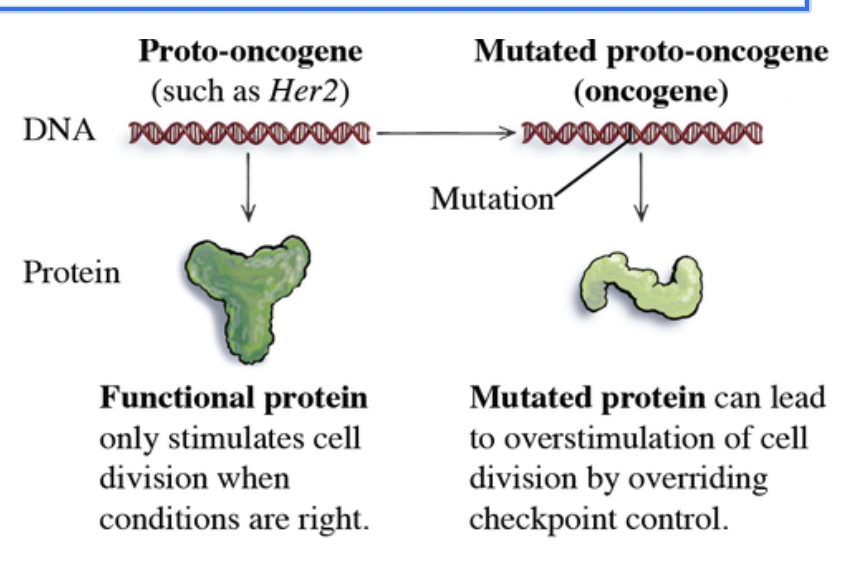
Proto-oncogens normal function
When activated, they signal for cell division to start (G1 checkpoint)
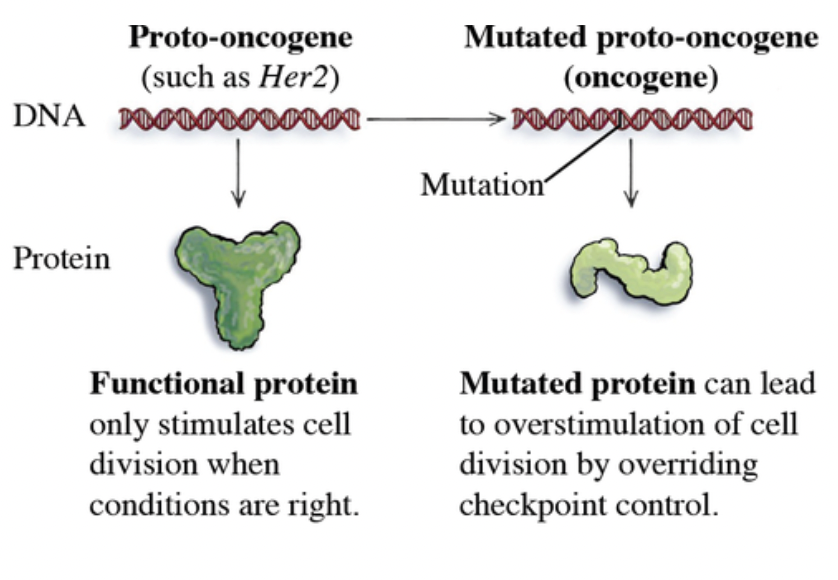
Proto-oncogens muatetd function
The gene is always activated, so it continues to divide (ignores the G1 checkpoint)
Once mutated, a proto-oncogene is called an?
Onocogene
Is the mutation for a proto-oncogen is dominant or recessive?
Dominant - only one copy of the defective gene is needed to impact the cell
Tumor Suppressor Genes normal function
Slow cell division, repair mistakes, or apoptosis
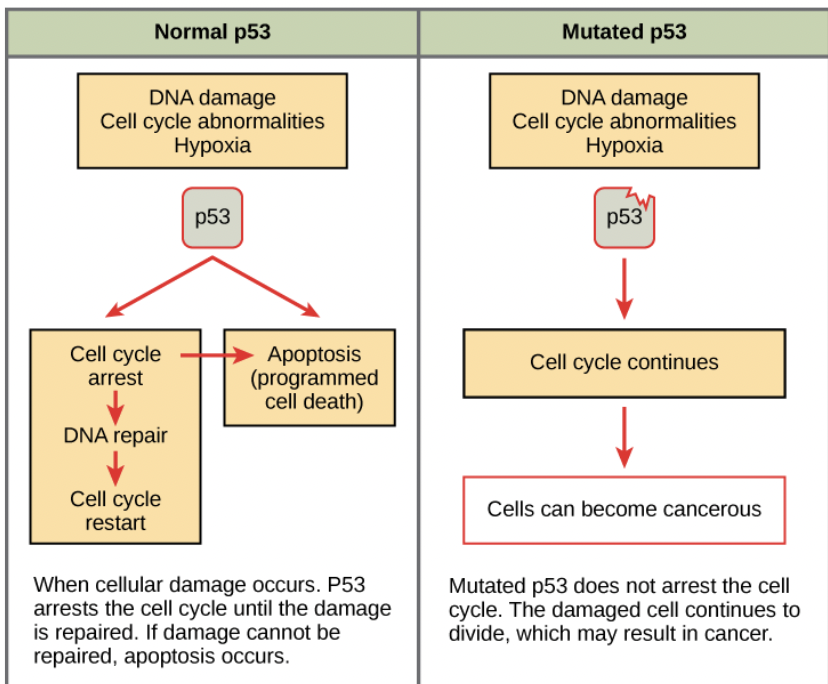
Tumor Suppressor Genes mutated function
Cell does not stop division if mistakes are found
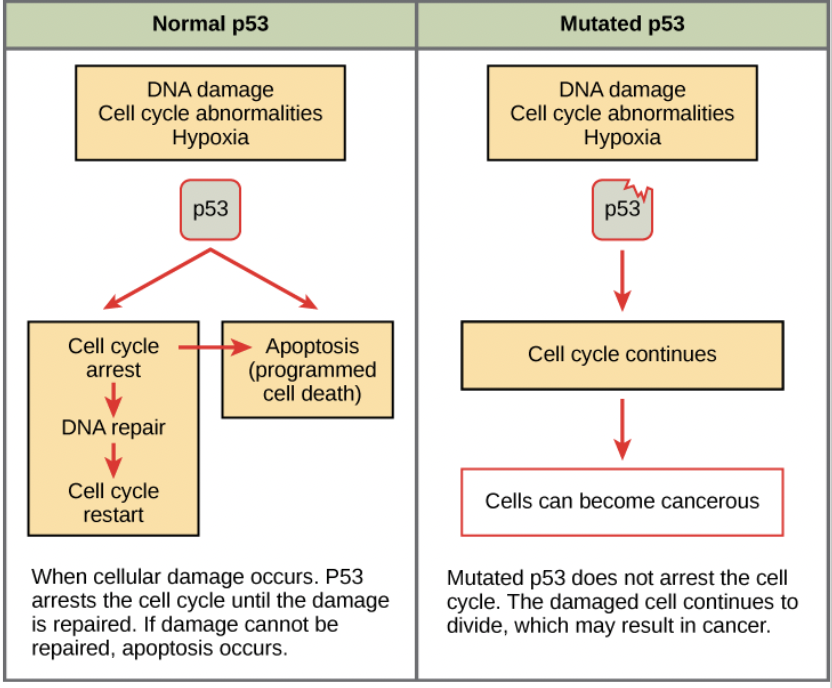
Is the mutation for tumor supressor genese dominant or recessive?
Recessive - both copies of the gene must be mutated to impact the cell
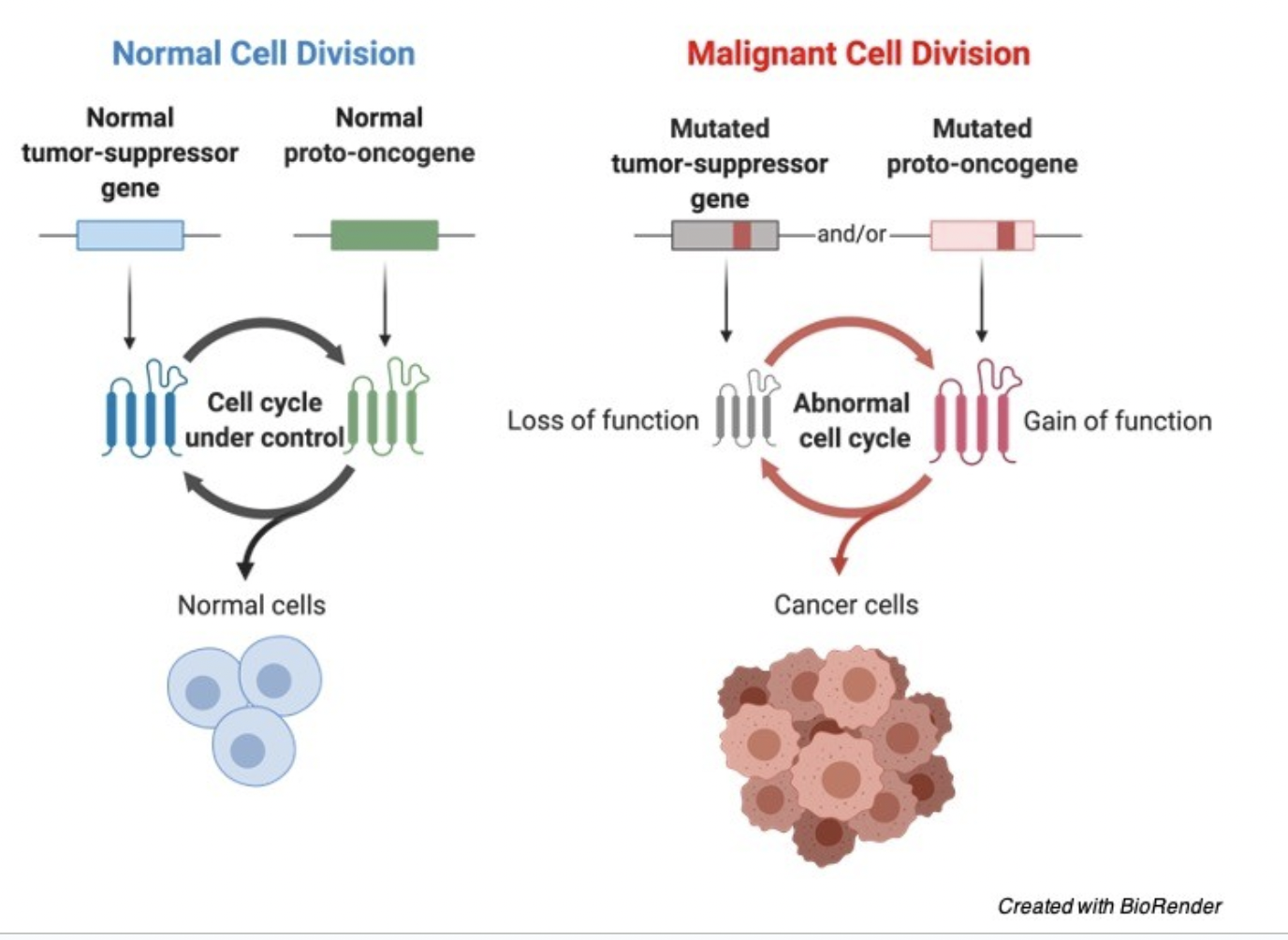
Chemotherapy
Drugs disrupt any cells going through mitosis; used in wide spread cancers
Radiation
High energy beams (mostly X rays) are emitted onto a cancerous body part, causing mutations in the DNA to the point where the cell cannot divide
Immunotherapy
Trains the immune system to recognize cancerous cells and kill them off