Accounting practice exam questions multiple choice
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Which of the following statements is true?
A. The break-even point is that level of activity where sales revenue equals total variable cost.
B. Total contribution margin is defined as total sales revenue plus total variable cost.
C. The break-even point in unit sales is found by dividing total fixed cost by the contribution
margin per unit.
D. The difference between budgeted sales revenue and break-even sales revenue is the operating
leverage.
E. The safety margin is another name for the break-even point.
C. The break-even point in unit sales is found by dividing total fixed cost by the contribution margin per unit
Which of the following occurs if a company increases its variable cost per unit? (Assume that
selling price per unit, sales volume, and total fixed cost remain constant.)
A. The contribution margin would increase.
B. The break-even point would decrease.
C. The break-even point would increase.
D. Net income would increase.
E. More than one of the answers would occur.
C. The break-even point would increase.
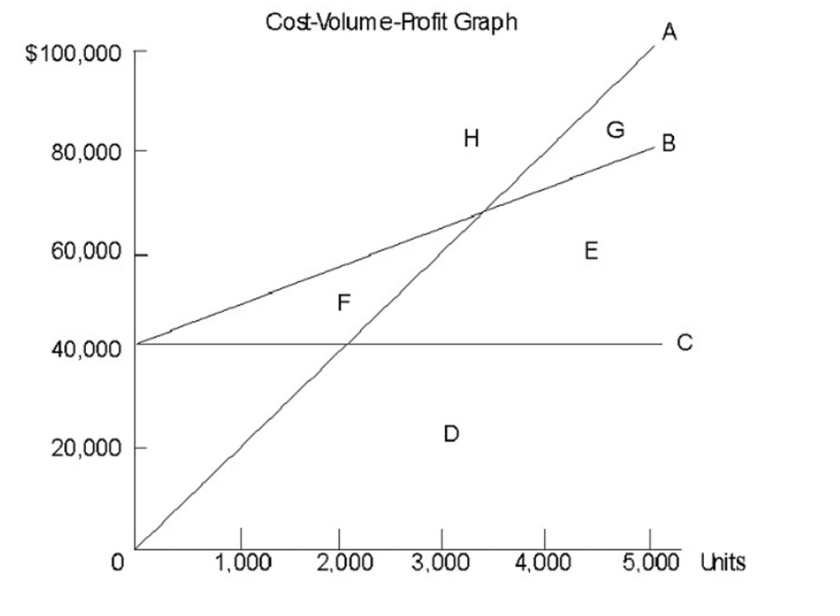
Refer to the figure below. The vertical distance between the total cost line (Line B) and the
total revenue line (Line A) represents:
A. fixed cost.
B. variable cost.
C. profit or loss at that volume.
D. semivariable cost.
E. the safety margin
C. profit or loss at that volume.
Dachshund Company has a break-even point of 20,000 units. If the company’s sole product
sells for $38 and fixed costs total $260,000, the variable cost per unit must be:
A. $13.
B. $25.
C. $12.
D. $51.
E. None of these.
B. $25
The following monthly data are available for Coco Chips Company and its only product:
Unit Sales Price $85
Unit Variable Expenses $51
Total Fixed Expenses $37,400
Actual sales in August 1,230 units
The company’s safety margin in August was:
A. $10,400
B. $11,050
C. $15,300
D. $93,500
E. None of these
B. $11,050
Cost-volume-profit analysis assumes that:
A. total costs are constant as activity changes.
B. the average fixed cost per unit is constant as activity changes.
C. the average variable cost per unit is constant as activity changes.
D. variable costs are nonlinear.
E. the efficiency and productivity of production process and workers will change to reflect
manufacturing advances.
C. the average variable cost per unit is constant as activity changes.
A contribution format income statement of Yang Company reported the following data for
February:
Sales revenue $2,500,000
Variable costs $1,500,000
Fixed costs $800,000
If the company’s sales increase by 10%, its net operating income should increase by:
A. 2%
B. 10%
C. 25%
D. 50%
E. None of these
D. 50%
Saturn Company sells a single product, organic almond butter, for $10 per jar. Variable costs are $6 per jar and fixed costs total $54,000 per month. What dollar sales level would the
company have to achieve to earn a monthly target profit of $16,000?
ANS:
ANS: $175,000
Thai Two sells hot pots for $40 each. The company incurs monthly fixed costs of $5,000. The contribution margin ratio is 20%. Based on this information, what is the variable cost per hot pot?
ANS:
ANS: $32
A company’s plan for the acquisition of long-lived assets, such as buildings and equipment,
is commonly called a:
A. pro-forma budget.
B. master budget.
C. financial budget.
D. capital budget.
E. rolling budget.
D. capital budget.
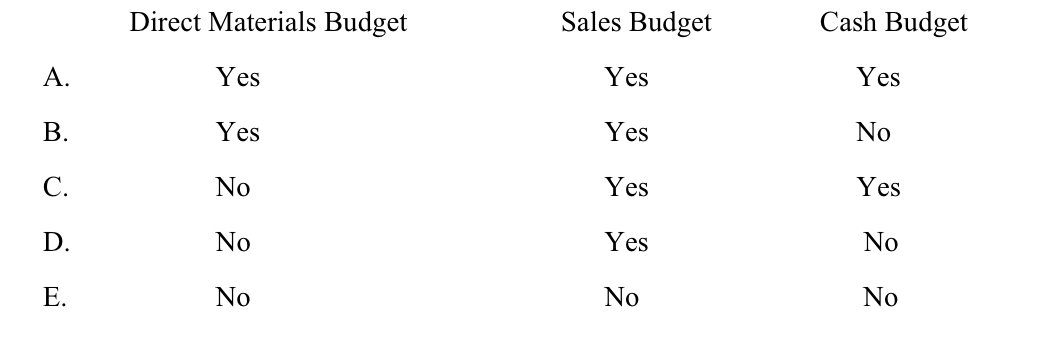
Which of the following budgets are prepared before the production budget?
D. No, yes, no
Consider the following statements about the budgetary slack:
I. Managers build slack into a budget so that they stand a greater chance of receiving favorable performance evaluations.
II. Managers can build slack into a budget by underestimating revenues.
III. Managers can build slack into a budget by overestimating expenses.
Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true?
A. I
B. I and II
C. II and III
D. I, II, and III
E. none
D. I, II, and III
When an organization involves its many employees in the budgeting process in a meaningful
way, the organization is said to be using an approach most commonly known as:
A. employee-based budgeting.
B. budget padding.
C. imposed budgeting.
D. budgetary slack.
E. participative budgeting.
E. participative budgeting.
Virginia Enterprises makes all purchases on account, subject to the following payment
pattern:
Paid in the month of purchase: 30%
Paid in the first month following purchase: 60%
Paid in the second month following purchase: 10%
If budgeted purchases for January, February, and March are $200,000, $180,000, and $230,000,
respectively, what are the firm's budgeted payments in March?
A. $69,000
B. $138,000
C. $177,000
D. $197,000
E. None of these
D. $197,000
The company had 3,000 units in finished-goods inventory on December 31. The following
data are available for the upcoming year:
January February
Units to be produced 9,400 10,200
Desired ending finished-goods inventory 2,500 2,100
Budgeted sales for January would be:
A. 6,900 units.
B. 8,900 units.
C. 9,400 units.
D. 9,900 units.
E. 11,900 units
D. 9,900 units.
Fortune, Inc. has budgeted sales for January and February at $680,000 and $720,000,
respectively. Sales are 80% credit. The collection pattern of credit sales is as follows:
70% in the month of sale,
20% in the month following sale,
10% in second month following sale.
What is the budgeted accounts receivable balance at the end of February?
ANS:
ANS: $227,200
Greenwich Corporation manufactures a product requiring 0.5 ounces of platinum per unit.
The cost of platinum is approximately $360 per ounce. The company maintains an ending
platinum inventory equal to 10% of the following month’s production usage. The following data
were taken from the most recent quarterly production budget:
July August September
Planned production in units 1,000 1,100 980
The cost of platinum to be purchased to support August production is:
ANS:
ANS: $195,840
A favorable labor rate variance is created when:
A. actual labor hours worked exceed standard hours allowed.
B. actual hours worked are less than standard hours allowed.
C. actual wages paid are less than amounts that should have been paid for the number of hours
worked.
D. actual units produced exceed budgeted production levels.
E. actual units produced exceed standard hours allowed.
C. actual wages paid are less than amounts that should have been paid for the number of hours worked.
Consider the following statements:
I. Behavioral scientists find that perfection standards often discourage employees and result in
low worker morale.
II. Practical standards are also known as attainable standards.
III. Practical standards incorporate a certain amount of inefficiency such as that caused by an
occasional machine breakdown.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A. I only.
B. II only.
C. III only.
D. II and III.
E. I, II, and III
E. I, II, and III.
Consider the following statements about variance investigation:
I. The absolute size of a variance is more important than the relative size when trying to decide
what variances to investigate.
II. A manager is more likely to investigate the variance of a cost that is controllable by someone
in the organization than one that is not.
III. A statistical control chart can be used for determining whether a particular variance should be
investigated.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A. I only.
B. II only.
C. III only.
D. II and III.
E. I, III, and III.
D. II and III.
Which department would normally begin an investigation regarding an unfavorable materials
quantity variance?
A. Quality control.
B. Purchasing.
C. Engineering.
D. Production.
E. Receiving
D. Production.
Boba Company produces cashmere sweaters. According to the production standard, each
sweater is expected to consume 2 pounds of cashmere. The standard price of cashmere is $3 per
pound. Last week 2,460 pounds of cashmere were purchased at a total of $7,872, and 2,580
pounds were used to make 1,100 sweaters. Determine direct-material quantity variance.
A. $1,140 F
B. $1,140 U
C. $780 F
D. $780 U
E. None of these
B. $1,140 U
Consider the following information:
Direct labor standard: 5 hours at $14 per hour
Total actual direct labor cost: $639,000
Direct-labor rate variance: $9,000U
Actual production: 8,900 units
The direct-labor efficiency variance is:
A. $7,000 F.
B. $7,000 U.
C. $25,000 F.
D. $25,000 U.
E. None of these
B. $7,000 U.
Consider the following information:
Standard price of direct material $3 per gallon
Standard direct material quantity 2.5 gallons per unit
Actual production 200 units
Direct-material price variance $300 U
Direct-material quantity variance $420 F
How many gallons of direct material were purchased and used?
ANS:
ANS: 360 gallons
St. John Company manufactures a single product with the following unit standard related to
direct labor:
Standard hours 2 hours per unit
Partial production data for the most recent month are shown below:
Budget Actual
Production (units) 500 450
Direct labor hours 1,000 ?
An analysis of results for the month included the following variances:
Direct labor rate variance $1,920 Unfavorable
Direct labor efficiency variance $600 Unfavorable
If the company incurred $11,520 on direct labor costs, how many hours did the company work
during the month?
ANS:
ANS: 960 hours
The break-even point is that level of activity where:
A. total contribution margin equals the sum of variable cost and fixed cost.
B. variable cost equals fixed cost.
C. profit is greater than zero.
D. total revenue equals total cost.
E. sales revenue equals total variable cost
D. total revenue equals total cost.
Which of the following occurs if a company experiences an increase in its fixed cost?
(Assume that selling price per unit, sales volume, and variable cost per unit remain constant.)
A. The contribution margin would increase.
B. The contribution margin would decrease.
C. The break-even point would increase.
D. Net income would increase.
E. More than one of the answers would occur.
C. The break-even point would increase.
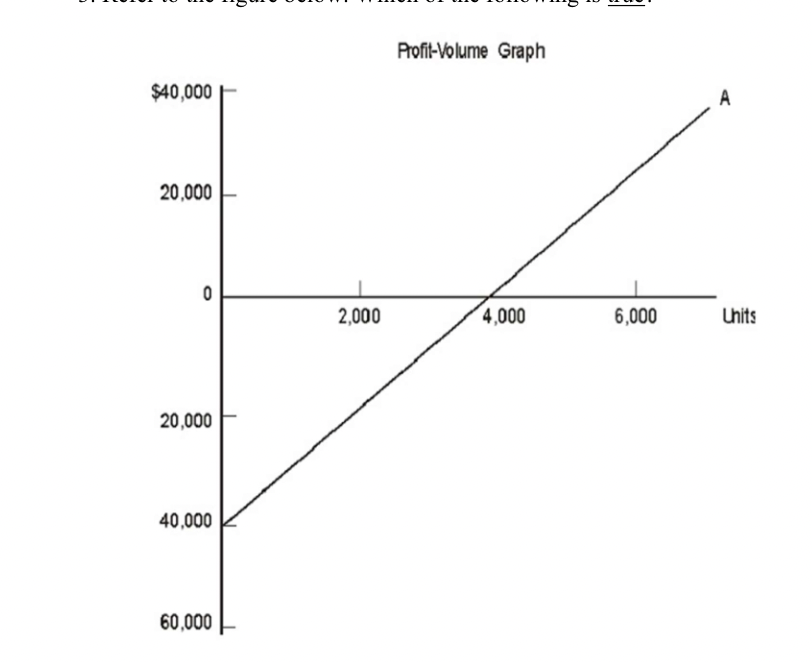
Refer to the figure below. Which of the following is true?
A. Total fixed cost is $20,000.
B. Unit contribution margin is $1.
C. The break-even point is 4,000 units.
D. The triangular area between the horizontal axis and Line A, to the left of 4,000, represents
profit.
E. None of these
C. The break-even point is 4,000 units.
Last year Max Corporation reported sales of $720,000, a contribution margin ratio of 30% and
a net loss of $24,000. Based on this information, the break-even point was:
A. $640,000
B. $744,000
C. $800,000
D. $880,000
E. None of these
C. $800,000
Coco Chips Company produces a single product that sells for $100 per unit. Fixed expenses
total $12,000 per month, and variable expenses are $60 per unit. The company sold 500 units
during the month. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. The company’s break-even point is $12,000 per month.
B. The company’s contribution margin ratio is 60%.
C. The company’s safety margin is $20,000.
D. The company’s profit is $10,000.
E. The company’s operating leverage factor is 2.
C. The company’s safety margin is $20,000.
Cost-volume-profit analysis is based on certain general assumptions. Which of the following
is not one of these assumptions?
A. Costs can be categorized as fixed, variable, or semivariable.
B. Total fixed costs remain constant as activity changes.
C. Product prices remain constant as activity changes.
D. The efficiency and productivity of production process and workers will change to reflect
manufacturing advances.
E. Unit variable cost remains constant as activity change
D. The efficiency and productivity of production process and workers will change to reflect
Gandee Company has an operating leverage factor of 4. Which of the following statements is
true?
A. A 9% change in income should result in a 36% change in sales revenue.
B. A 9% change in sales revenue should result in a 36% change in income.
C. A 9% change in variable costs should result in a 36% change in break-even sales.
D. A 9% change in variable costs should result in a 36% change in contribution margin.
E. A 9% change in fixed costs should result in a 36% change in income.
B. A 9% change in sales revenue should result in a 36% change in income.
Jupitor company sells a single product for $150 per unit and its variable cost is $116 per unit.
The company’s monthly fixed cost is $26,920 per month. How many units must be sold to attain
the company’s month target profit of $20,000?
ANS:
ANS: 1,380
The following information comes from the company’s accounting records at a sales level of
50,000 units.
Sales price per unit $60
Variable cost per unit $20
Fixed cost per unit $4
What is the contribution margin ratio? (Express the answer as a percentage. For example, if
contribution margin ratio is 0.435, key in 43.5%).
ANS:
ANS: 66.67%
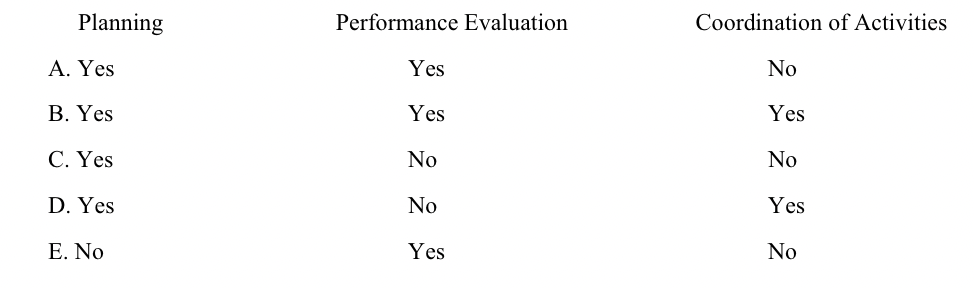
Which of the following choices correctly denotes managerial functions that are commonly
associated with budgeting?
B. yes, yes, yes
Which of the following would depict the logical order for preparing (1) a production budget,
(2) a cash budget, (3) a sales budget, and (4) a direct-labor budget?
A. 1-3-4-2
B. 2-3-1-4
C. 2-1-3-4
D. 3-1-4-2
E. 3-1-2-4
D. 3-1-4-2
If a manager builds slack into a budget, how would that manager handle estimates of
revenues and expenses?
Revenues Expenses
A. Underestimate Underestimate
B. Underestimate Overestimate
C. Overestimate Underestimate
D. Overestimate Overestimate
E. Estimate correctly Estimate correctly
B. Underestimate Overestimate
Company A uses a heavily participative budgeting approach whereas at Company B, top management develops all budgets and imposes them on lower-level personnel. Which of the following statement is false?
A. A’s employees will likely be more motivated to achieve budgetary goals than the employees
of Company B.
B. B’s employees maybe somewhat disenchanted because although they will be evaluated
against a budget, they really had little say in budget development.
C. Budget padding will likely be a greater problem at Company B.
D. Budget preparation time will likely be longer at Company A.
E. Ethical issues are more likely to arise at Company A, especially when the budget is used as a basis for performance appraisal
C. Budget padding will likely be a greater problem at Company B.
Fortune, Inc. has the following budgeted sales:
April May June
Cash sales $5,000 $4,000 $1,000
Credit sales $8,000 $3,000 $2,000
The collection pattern of credit sales is as follows: 60% in the month of sale, 30% in the month following sale, and 10% uncollectible.
What are June’s budgeted cash collections from sales?
ANS:
ANS: 3,100
The following data were taken from our company’s most recent quarterly sales forecast:
Expected Sales
July 1,400 units
August 1,850 units
September 1,660 units
Our company requires that 30% of the next month’s sales be on hand at the end of each month.
Based on the information above, how many units should the company produce in August?
ANS
ANS: 1,793
Wilmar Corporation is in the process of preparing its annual budget. The following beginning and ending inventory levels are planned for the year. Sales are projected to be 670,000 units for the year.
Beginning inventory Ending inventory
Finished goods (units) 20,000 70,000
Raw material (grams) 50,000 40,000
Each unit of finished goods require 2 grams of raw material. How many grams of the raw
material should the company purchase during the year?
ANS:
ANS: 1,430,000
Moomin Company is preparing a cash budget for June. The budgeted beginning cash balance is $500. Budgeted cash receipts total $1,000, and budgeted cash disbursements total $600. The
desired ending cash balance is $1,200.
How much is the excess (deficiency) of cash available over disbursements for June?
ANS
ANS: 900
Consider the following statements:
I. The standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials price variance.
II. The standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials quantity variance.
III. The standard cost per unit of materials cannot be determined until the end of the period.
Which of the following statements is (are) true?
A. I only.
B. II only.
C. III only.
D. I and II.
E. I, II, and III.
D. I and II.
A direct-material quantity variance can be caused by all of the following except:
A. improper employee training.
B. changes in sales volume.
C. acquisition of materials that are below standard quality.
D. adjustment problems with machines.
E. disgruntled workers.
B. changes in sales volume.
When considering whether to investigate a variance, managers should consider all of the
following except the variance’s:
A. size.
B. pattern of recurrence.
C. trends over time.
D. nature, namely, whether it is favorable or unfavorable.
E. controllability
D. nature, namely, whether it is favorable or unfavorable.
The individual generally responsible for the direct-material price variance is the:
A. sales manager.
B. production supervisor.
C. purchasing manager.
D. finance manager.
E. head of the human resources department
C. purchasing manager.
To make giant cookies, Elmo Company established the following unit standards:
Standard Price Standard Quantity
Direct material (flour) $10 per bag 0.5 bag per cookie In July, the company purchased 4,200 bags of flour at $9 per bag from suppliers. It made a total of 9,300 cookies and used 5,200 bags of flour in production.
The direct-material quantity variance is:
A. $5,500 F.
B. $5,500 U.
C. $4,500 U.
D. $4,500 F.
E. None of these.
B. $5,500 U.
Big Bird Company recently completed 2,400 units of its single product, consuming 4,650
labor hours that cost the firm $88,350. According to manufacturing specifications, each unit
should have required 2 hours of labor time at $18 per hour.
The company’s labor rate variance is:
A. $2,700 F.
B. $2,700 U.
C. $4,650 F.
D. $4,650 U.
E. None of these
D. $4,650 U.
Consider the following information:
Actual cost of direct material purchased and used: $72,000
Standard direct material quantity: 96,000 gallons
Direct-material price variance: $9,000 U
Direct-material quantity variance: $4,200 F
What is the standard price per gallon of direct material?
ANS:
ANS: .7
Ricket Company had a favorable labor efficiency variance of $6,300 for the period just
ended. The actual wage rate was $0.60 more than the standard rate of $12. If the company’s
standard hours allowed for actual production totaled 9,400, how many hours did the company
actually work?
ANS:
ANS: 8875