Transducers - Basic Ultrasound Physics (Chapter 8)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
A transducer is a device that converts
one form of energy into another
Ultrasound transducers perform two functions:
Electrical energy to sound energy (during transmission)
Sound energy to electrical energy (during reception)
Piezoelectric effect is the property of certain materials that create ____ when they are ____ ____ or ____ by some ____
voltage ; mechanically deformed ; applied ; pressure
Reverse piezoelectric effect is a process of ____
changing material’s shape when the voltage is applied to them
What’s a synonym with piezoelectric?
Ferroelectric
What are Piezoelectric materials?
Materials that are responsible for converting sound energy into electrical energy and vice versa.
What piezoelectric materials can be found in nature?
Quartz
Tourmaline
What is the name of the synthetic piezoelectric materials that are used in clinical settings?
Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT)
What are 3 synonyms for PZT?
Ceramic
Active element
Crystal
There are seven components of a basic transducer:
1. Case
2.Electrical shield
3.Acoustic insulator
4.PZT
5.Wire
6.Matching layer
7.Backing material
A case is a ____ tube made of ___ or ___.
Cylindrical ; metal ; plastic
What are 2 functions of the case?
Protects the internal components
Provides insulation from electrical shock
The electrical shield is a thin ___ ___
metallic barrier
What is the function of the electrical shield?
Prevents the electrical noise from entering the transducer
What is the acoustic insulator made of?
A thin barrier of cork or rubber
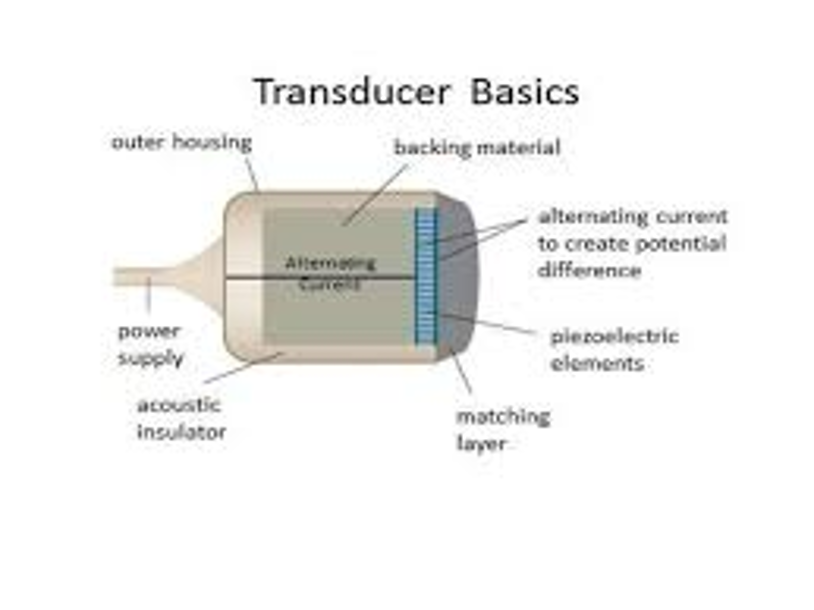
What are the two functions of the acoustic insulator?
Isolation of internal components
Prevention from vibration
How thick is the PZT element?
½ a wavelength thick
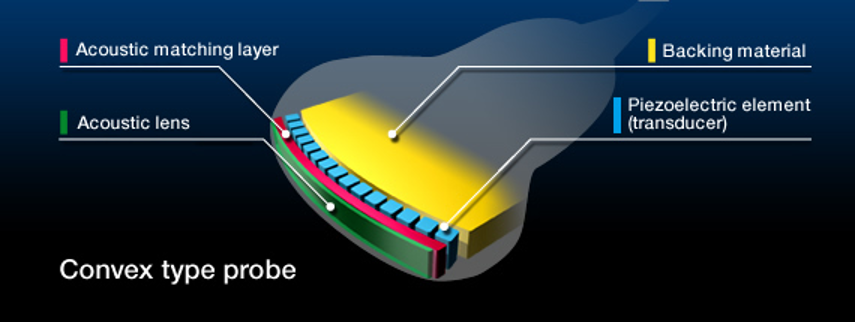
Where is the PZT located?
In between backing material and matching layer
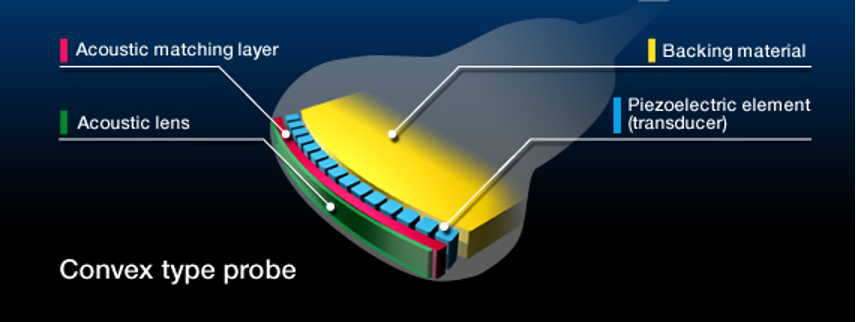
Characteristics of the sound beam are related to the dimensions of the ___ ____.
Active Element
What is the connection between the PZT and the ultrasound system?
Wire
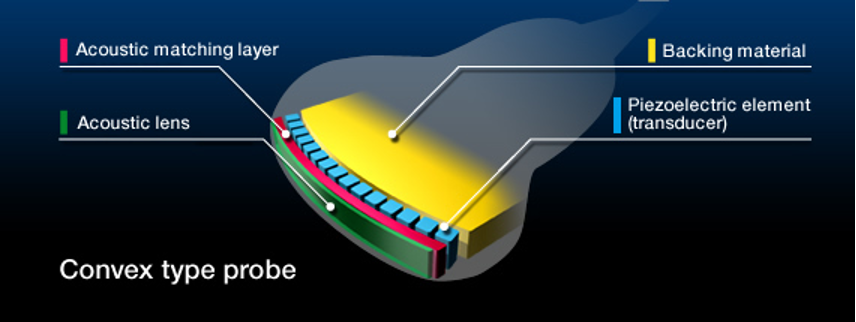
Where is the matching layer located?
In front of the PZT
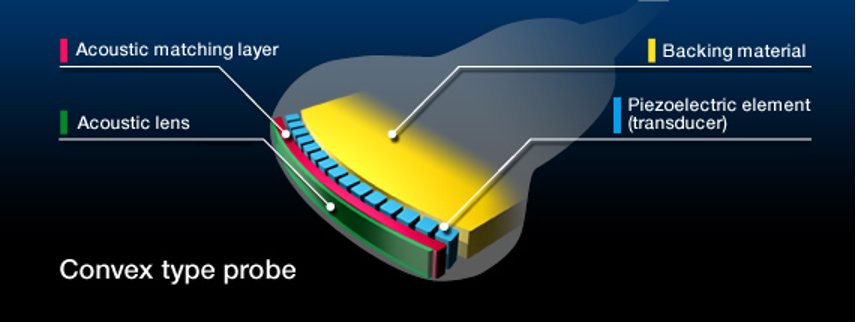
How thick is the matching layer?
¼ of a wavelength thick
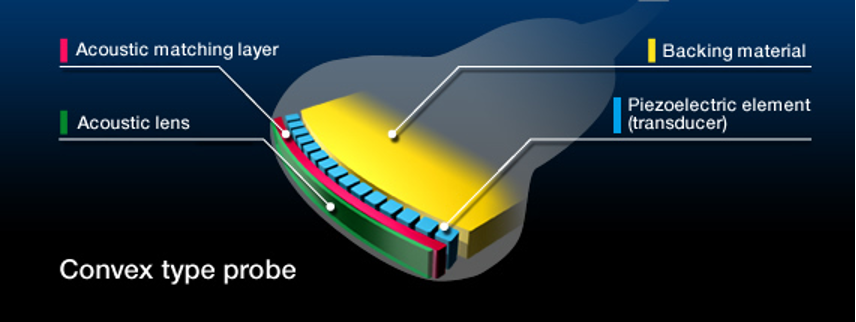
What are the 2 functions of the matching layer?
Increases the efficiency of the sound energy
Protects the active element
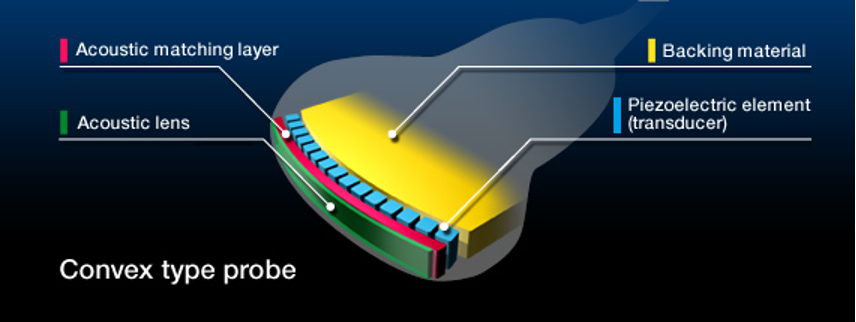
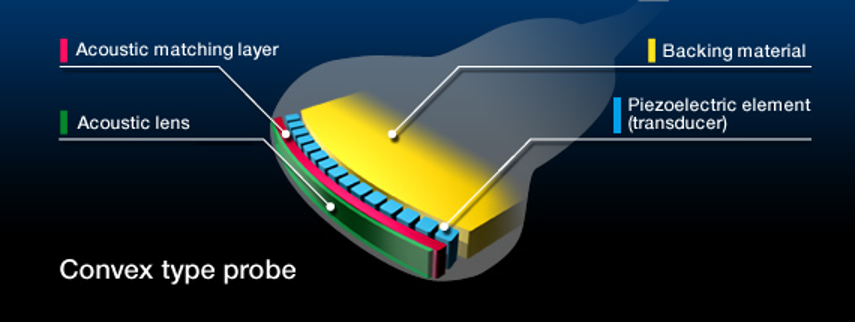
The backing material is also known as the ___ ___
damping element
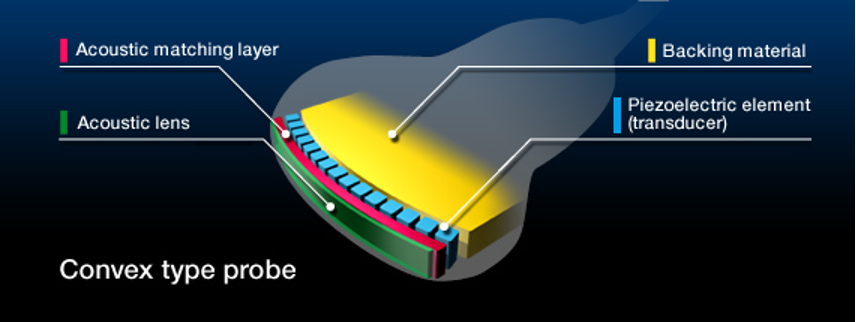
Where is the backing material located?
At the back of the active element
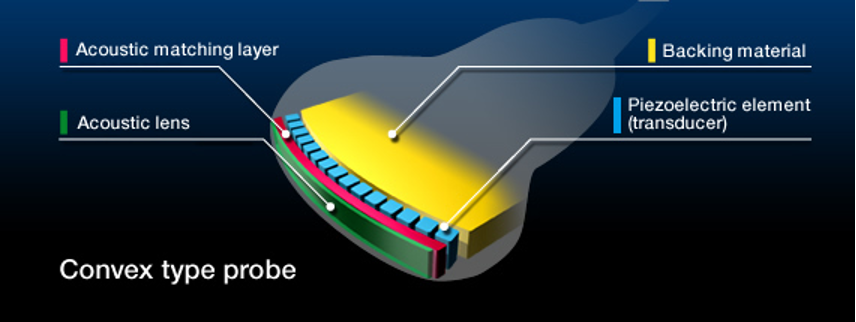
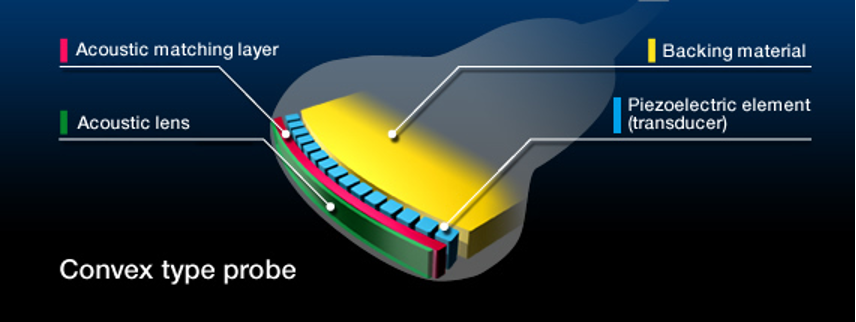
What is backing material made of?
Epoxy resin impregnated with tungsten filaments
What is the function of backing material? (3 relationships)
Reduces ringing of PZT
Restricts the PZT deformation
Enhances axial resolution
The matching layer is designed with an impedance between ____ ____ and ____.
Active element ; skin
What is the function of the matching layer?
Increases the percentage of transmission between matching layer and skin
Decreases reflection
The backing material is also known as ___
damping element
What is the function of the backing material?
ØReduces the ringing of PZT
ØRestricts the PZT deformation
ØEnhances axial resolution
Without backing material, PZT will ____
ring for a longer time
What are 2 characteristics of damping material?
High degree of sound absorption
Acoustic impedance similar to PZT
What are the consequences of backing material?
Decreased sensitivity
Wide bandwidth
Low Q Factor
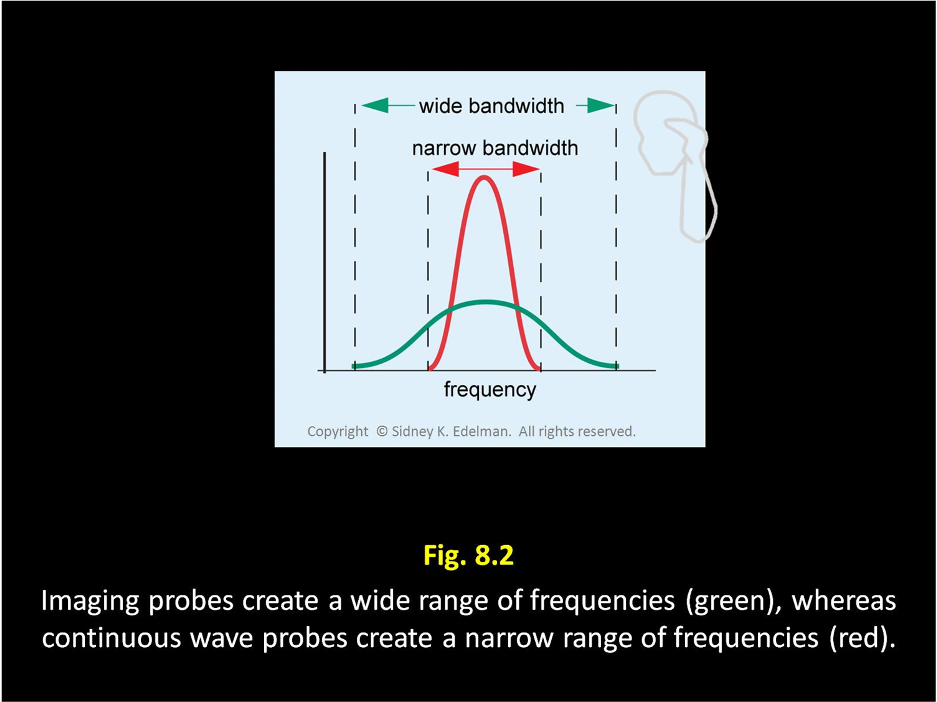
Define bandwidth
Range of frequencies in a pulse
Imaging probes have (wide/narrow) bandwidth and are also called ____.
wide broadband
Q-factor is a ____ number that is (directly/inversely) related to bandwidth.
unitless ; inversely
What is the equation for Q factor?
Q factor = (main frequency/bandwidth)
Continuous wave and therapeutic doppler do not contain ___ ____ and have a ___ bandwidth and ____ Q-factor.
backing material ; narrow ; high
Frequency of sound in pulsed wave is dependent on 2 characteristics of the PZT:
Speed of sound of the PZT
Thickness of the PZT
Arrange in decreasing order of impedance:
Gel
PZT
Skin
Matching Layer
PZT > matching layer > gel > skin
Define polarization
It is a process of creation of the PZT properties by exposing the active element to a strong electrical field while being heated to a substantial temperature.
Define Curie Point
The temperature at which the PZT is polarized
Define Curie Point:
The temperature at which the PZT is polarized.
Define Depolarization
When the polarized PZT is heated above the curie point, the PZT properties are destroyed. The loss of PZT properties is called depolarization.
Speed of sound in most piezoelectric materials range from ___ to ____ mm/us
4-6 mm/us