Boody Semester Exam
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Define chemistry.
The study of matter and the changes it undergoes.
What is a particle?
Something really tiny--usually referring to an atom or molecule.
In chemistry, we use _____________ to collect ________________ about a system.
Observations, information
What is a model?
A representation of an object or system
Models, observations and measurements lead to a __________________.
Conclusion
Quantitative data
Data obtained using a measuring device.
Qualitative data
Anything that relates to the senses.
Define mass.
The amount of matter.
Define volume.
A measurement of the space the matter occupies.
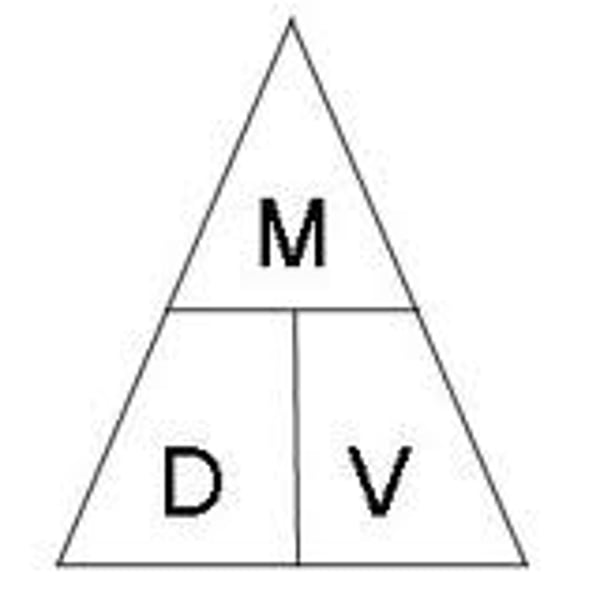
Define density.
The amount of mass in a given volume.
What does it mean for something to be high density?
A lot of mass in a small volume.
What does it mean for something to be low density?
A little mass in a large volume.
How do you find density? Mass? Volume?
Give examples of things that contain matter.
Batteries
Electricity
Dust
DNA
Helium
Bacteria
Atoms
Clouds
Car Exhaust
Give examples of things that do not contain matter.
Heat
Fear
Wind
Sound
Wisdom
Fire
What depends on gravitational force? Mass or weight?
Weight
"The length of a candle is 4.5 centimeters." Is this quantitative or qualitative data?
Quantitative
What would you use to remove chemicals from a reagant bottle?
Disposable pipette.
"The ball floats." Qualitative or quantitative?term-79
Qualitative.
What piece of lab equipment would you use to hold 50 mL of boiling water?
Beaker
What piece of lab equipment would you use to suspend glassware over a Bunsen Burner?
Ringstand
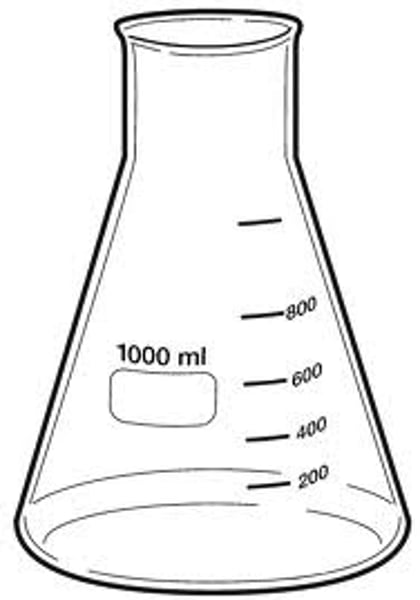
Identify this object.
Define accuracy.
How close the data is to the "true" or desired value.
Define precision.
How consistent the data is.
How do you calculate percent error?
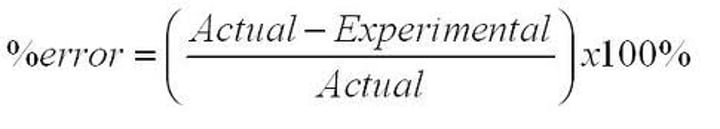
How do you determine if data is precise?
Range/2
The closer to ________, the more precise the data.
Zero
Convert 25 L to gallons using fenceposting.
1 gallon = 3.79 L
6.60 gal
Convert 4560 cm to miles using fenceposting.
100cm = 1m, 1609m = 1 mi
.0283 mi
Significant figures
The number of all known digits in a reported measurement, plus one estimated value.
Name the prefixes in order from largest to smallest.
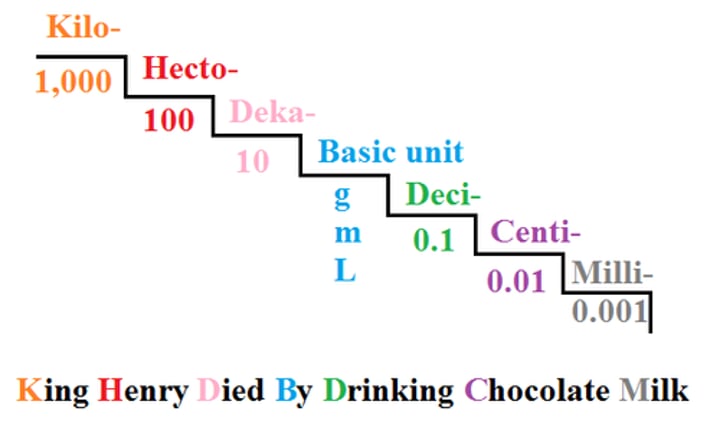
Convert 25g to dg using the prefix ladder.
250 dg
Convert .36 km to m using the prefix ladder.
360 m
Define atom.
The smallest unit of matter
What is an element?
A pure substance consisting of only one kind of atom.
What is a molecule?
Two or more atoms chemically bonded together.
What is the difference between pure substances and mixtures?
Pure substances contain a single type of particle. Mixtures contain more than one type of particle.
Define a compound.
Contains more than one element chemically bonded to form molecules.
Define a homogeneous mixture
A mixture with an even distribution of particles.
Define a heterogeneous mixture.
A mixture with an uneven distribution of particles.
Give an example of a homogeneous mixture
Solution (salt in water)
Give an example of a heterogeneous mixture
Suspension (oil in water)
List an example of a physical property.
Density, melting point, boiling point, etc.
Physical property can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance.
List an example of a chemical property.
Iron reacts with oxygen to form rust, metals react
with acid to produce a gas.
Chemical properties describe how a substance can chemically react with another.
State the Law of Conservation of Mass.
Matter cannot be created or destroyed.
Define neutron.
A neutral particle that is found in the nucleus of an atom.
Define proton.
A positively charged particle located in the nucleus.
Define electron.
A negatively charged particle located in the nucleus.
What does the atomic number represent?
Represents the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom.
What does the mass number represent?
The sum of protons and neutrons in the atom.
Define valence electrons.
Electrons in the outermost energy level of the atom.
Draw, describe and name Dalton's atomic model.
The atom is a solid sphere that cannot be divided up into smaller particles or pieces.
"Solid Sphere Model"

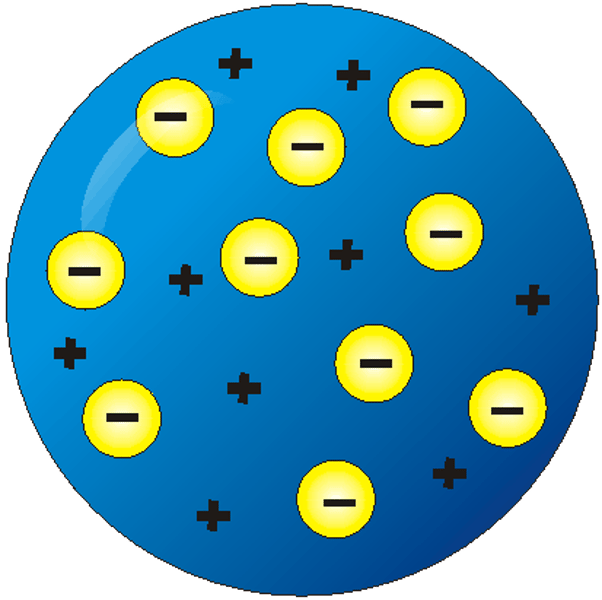
Draw, describe and name J.J. Thomson's atomic model.
The atom can be divided into a fluid and electrons, most of the atom is made of fluid.
"Plum Pudding Model"
Draw, describe and name Rutherford's atomic model.
The nucleus occupies a small amount of space in the center of the atom. The nucleus is dense and positively charged, and electrons circle around the nucleus. Most of the atom is an empty space.
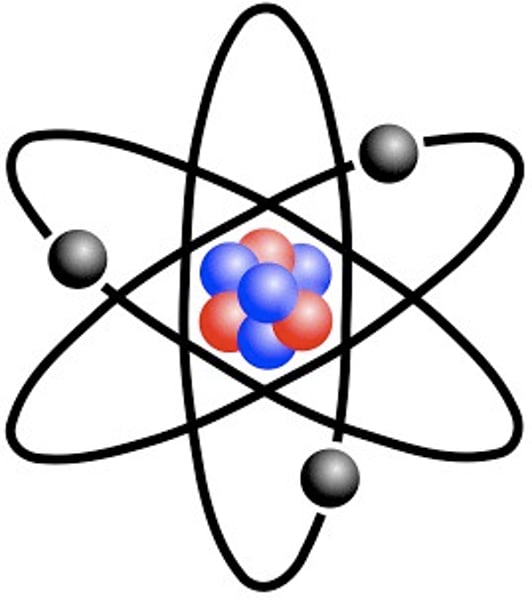
Who came up with the planetary model?
Bohr
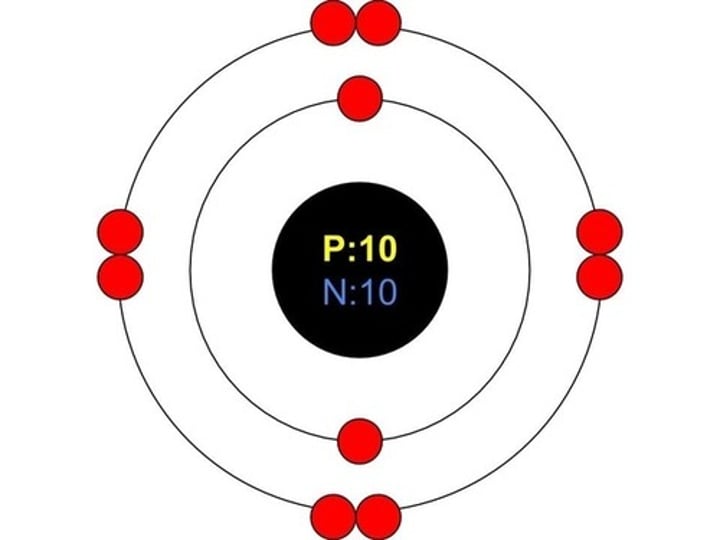
Draw a Bohr model for neon.
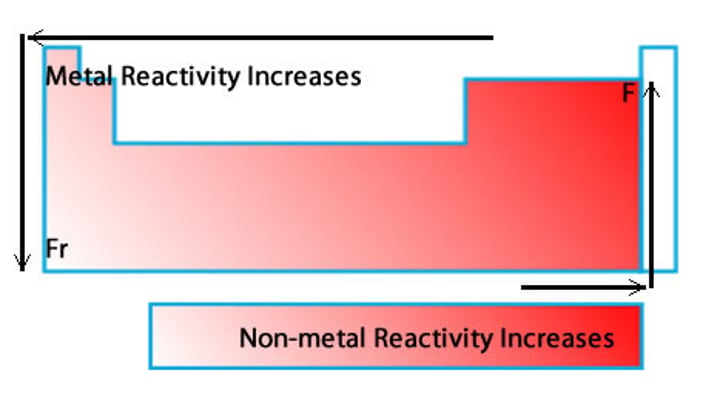
Define metal reactivity.
- The tendency of a substance to undergo a chemical change in a system.
Define atomic radius.
The distance from the nucleus of an atom to its valence shell.

Define ionization energy.
The energy required to remove a valence electron from an atom.
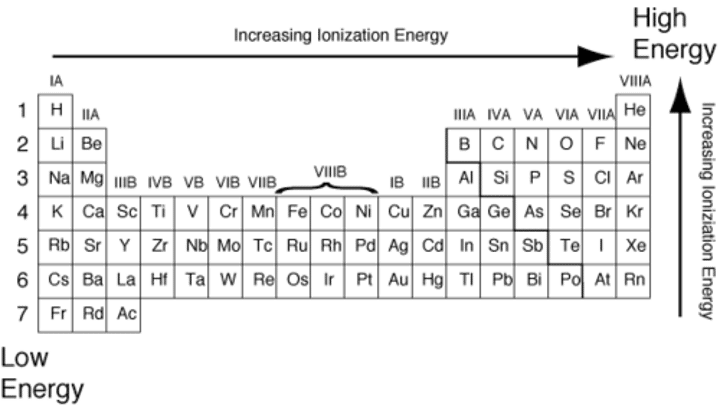
How did Dimitri Mendeleev arrange the periodic table?
By increasing atomic mass and similar properties.
How did Henry Moseley arrange the periodic table?
By increasing atomic number.
What is a family on the period table? What is a period?
Family - vertical column
Period- horizontal row
List some qualities of alkali metals and noble gases.
Alkali metals - all have one valence electron, mostly solids, lustrous, conduct electricity, malleable, very reactive.
Noble gases - most have eight valence electrons, all gases, colorless, do not conduct electricity, odorless, very nonreactive.
List properties of metals vs. nonmetals.
Metals - malleable, ductile, conducts heat
and electricity, reacts with acids,usually solids, tend to be lustrous.
Nonmetals - dull, brittle, do not conduct heat
and electricity well, do not react with acids.
What does it mean for something to be malleable?
The substance can be bent or shaped without breaking.
Explain why metals tend to be good conductors of electricity.
Metals do not "hold onto" their valence electrons with a lot of strength, these electrons are allowed to move through the metals crystal, which allows electricity to easily pass through metals.
Define chemical bond.
The force that holds two atoms together
Cation
A positively charged ion.
Anion
A negatively charged ion.
Ionic compound
The attractive force between positive and negative ions in an ionic compound.
Define monatomic ions
Ions made of a single atom.
Define polyatomic ions.
Ions made of a group of atoms chemically bonded.
Define ion.
An atom or group of atoms with a net charge
Write the chemical formula for calcium bromide.

List the base units.
Grams - mass
Liters - volume
Seconds - time
Meters - length
Name this piece of lab equipment.

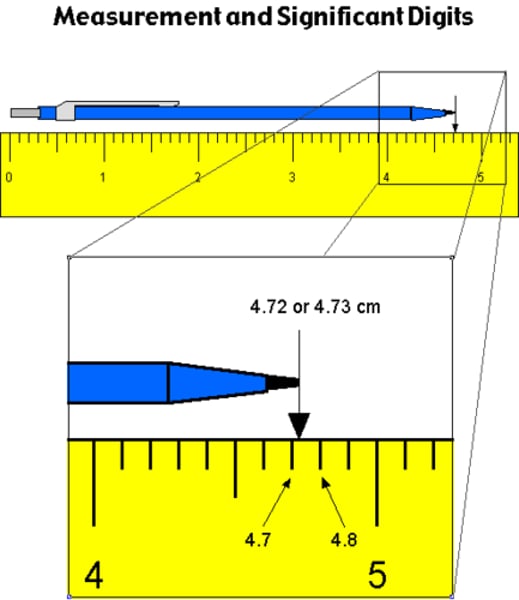
How would you measure significant figures using a ruler?
List and describe the three states of matter.
Solid, liquid, gas
Solid - definite shape and volume, high density
Liquid - Flows, constant volume, takes the shape of water container that it's in
Gas - Always fill the container, low density
List the four indicators of a chemical change.
Production of heat or light, production of gas, formation of a solid, color change.
What is the difference between a physical and chemical change?
In a chemical change, chemical bonds are broken and/or reformed. In a physical change, the identity of the particle does not change.
What types of impurities do filtration and distillation remove from a water sample?
Filtration - Undissolved particles
Distillation - dissolved particles
Explain the contribution of Democritus to our understanding of the atom.
Democritus believed that all matter was composed of atoms and the void. He felt that there was a smallest unit of matter.
Describe Rutherford's gold foil experiment.
Rutherford focused a beam of
positively charged alpha particles at a thin
sheet of gold foil. Rutherford believed that he
would observe a specific diffraction pattern in
the beam as it passed through the gold foil. He
monitored the path of the alpha particles using
a detection screen at many angles.
Define isotope.
Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons.
Define orbital.
A region of space in an atom in which you are likely to obtain an electron.
What is the emission spectrum?
A set of frequencies electromagnetic radiation that is emitted from an element when energy is introduced.
What is the ground state?
The lowest energy state of an atom
What is the excited state?
When electrons absorb energy, they jump to higher energy levels.
What is a photon?
A specific bundle of light emitted from an atom.
What is a metalloid?
A transition between metals and nonmetals, they have qualities of metals and nonmetals.
Define electronegativity.
The relative attraction an atoms has for a shared pair of
electrons.
Using electronegativity, how do you know if a pair of atoms will form an ionic or covalent bond?
If the difference is equal to or above 1.7, it will be ionic. If the difference is below 1.7, it will be covalent.
What is an oxidation number?
Charge on an ion in an ionic compound.
Describe the difference between the physical structure of an ionic compound and a metal.
Ionic compounds form a crystal lattice of
alternating positive and negative ions.
The valence electrons in the ions are
locked in place so electricity cannot flow
through the crystal.
Metal atoms sit in "an electron sea." Metal
atoms so not hold on to valence electrons
well so the electrons are free to flow and
move throughout the crystal. This allows
electrons to easily move throughout the
substance.
Describe Rutherford's observations and conclusions.
Observation - most of the Alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil, some were slightly defected, and some particles bounced back.
Conclusion - Most of the atom is made of empty space. There is a small, dense, positively charged center to the atom called a nucleus. Most of the atom is packed in the nucleus.