Managerial Accounting Chapters 14, 15, 16
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Managerial Accounting
accounting used to provide information and analyses to managers inside the organization to assist them in decision making
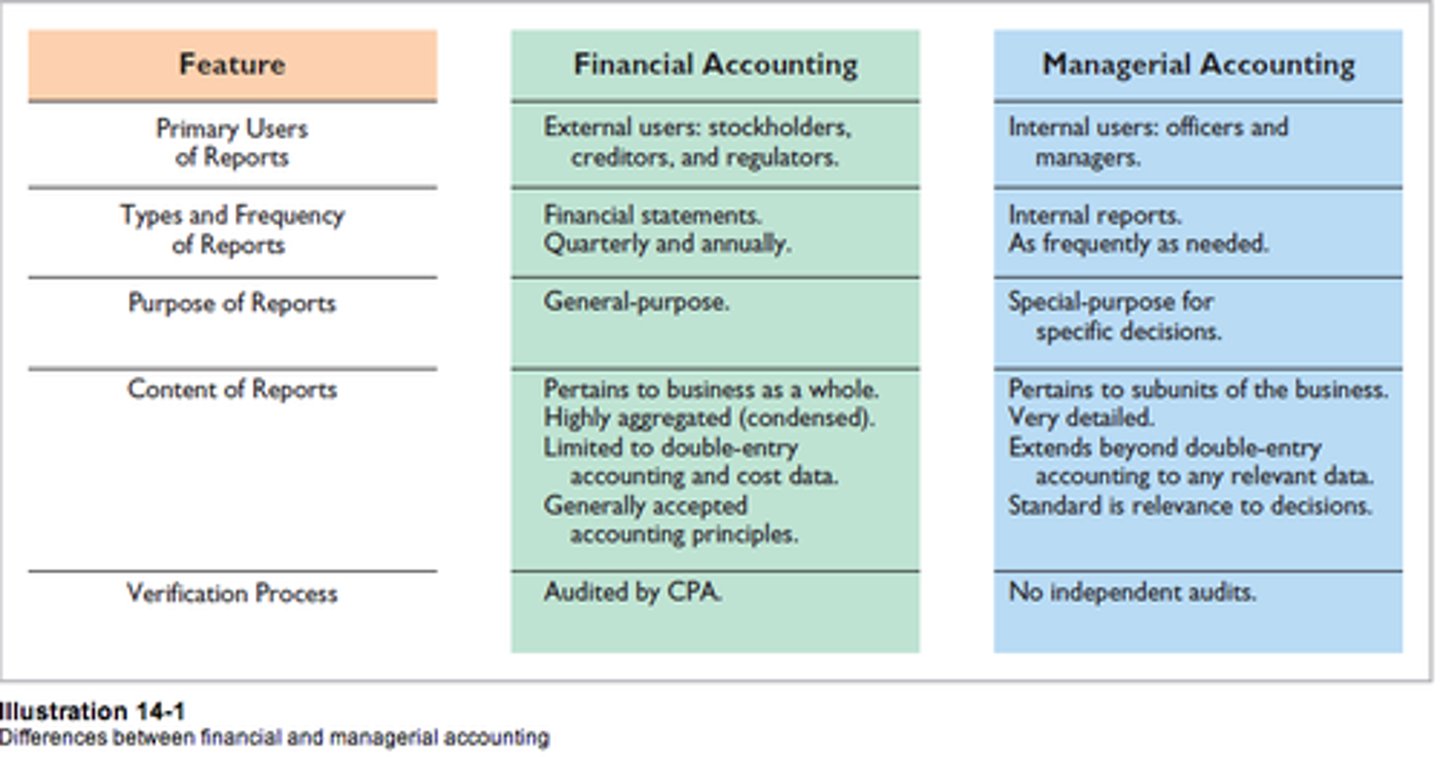
Differences between financial and managerial accounting
Financial Accounting:
- primary users are stockholders, creditors, and regulators.
- reports are in the form of financial statements and are made quarterly and annually
-Focuses on company performance
-Adheres to GAAP principles
-Audited by CPA
Managerial Accounting:
- Internal users:officers and managers
-internal reports are performed as frequently as needed
- Emphasis on relevant information
-Focuses on subunits of business
-No independent audits
Management Functions
1. Planning-requires managers to look ahead and establish objectives
2. Directing-involves coordinating a company's diverse activities and human resources to produce
3. Controlling- the process of keeping the company's activities on track.
chief executive officer
may serve as president or board chair; has a major role in planning and implementing the strategy

line positions
Jobs that are directly involved in a company's primary revenue-generating operating activities.
staff positions
Positions that are supportive in nature and have only indirect responsibility for an organization's basic objectives
Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
a high-level corporate executive who manages a firm's finances and reports directly to the company's chief executive officer or president
Responsibilities Include:
1. maintaining the accounting records
2. ensuring an adequate system of financial control
3. preparing financial statements, tax returns, and internal reports
Management cost concepts
1. what costs are involved in making a product or performing a service?
2. If we decrease production volume, will costs change?
3. What impact will automation have on total costs?
4. How can we best control costs?
raw materials
the basic material from which a product is made.

Direct Materials
Materials that become an integral part of a finished product and whose costs can be conveniently traced to it.
Indirect Materials
Small items of material such as glue and nails that may be an integral part of a finished product, but whose costs cannot be easily or conveniently traced to it.
Characteristics of indirect materials
1. they do not physically become apart of the finished product
2. they are impractical to trace the finished product because their physical association with the finished product is too small in terms of cost.
*Companies account for indirect materials as part of manufacturing overhead
Manufacturing Overhead
Manufacturing costs that are indirectly associated with the manufacture of the finished product.
*Also includes costs that cannot be classified as direct materials or direct labor.
*indirect materials, indirect labor, depreciation on factory equipment and buildings, machines and insurance, and maintenance on factory facilities.
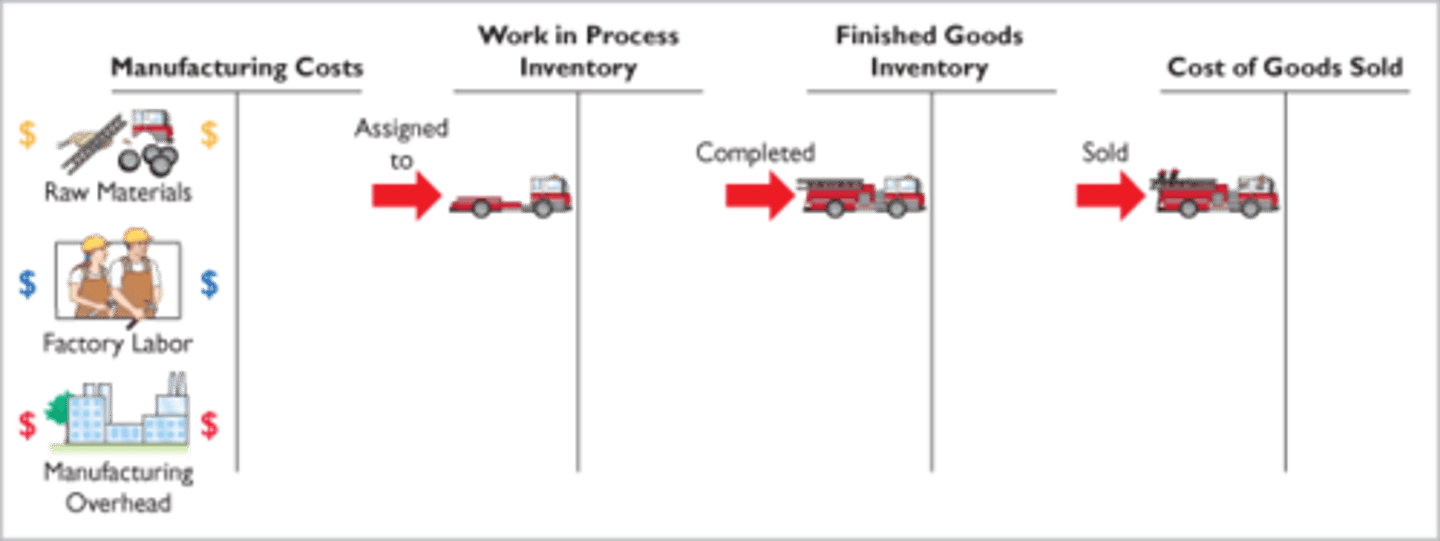
Product Costs (Manufacturing Costs)
costs that are a necessary and integral part of producing the finished product
Period Costs (Non-manufacturing Costs)
costs that are taken directly to the income statement as expenses in the period in which they are incurred or accrued
cost of goods sold is computed by....
adding the beginning inventory to the cost of goods purchased and subtracting the ending inventory.
Raw Materials Inventory
items acquired for the purpose of processing into finished goods
work in process inventory
goods that are partway through the manufacturing process but not yet complete
finished goods inventory
manufactured items that are completed and ready for sale
Value Chain
the series of internal departments that carry out value-creating activities to design, produce, market, deliver, and support a firm's products
Value Chain steps
1. Research and development and product design
2. Acquisition of Raw Materials
3. Production
4. Sales+Marketing
5. Delivery
6. Customer Relations+subsequent services
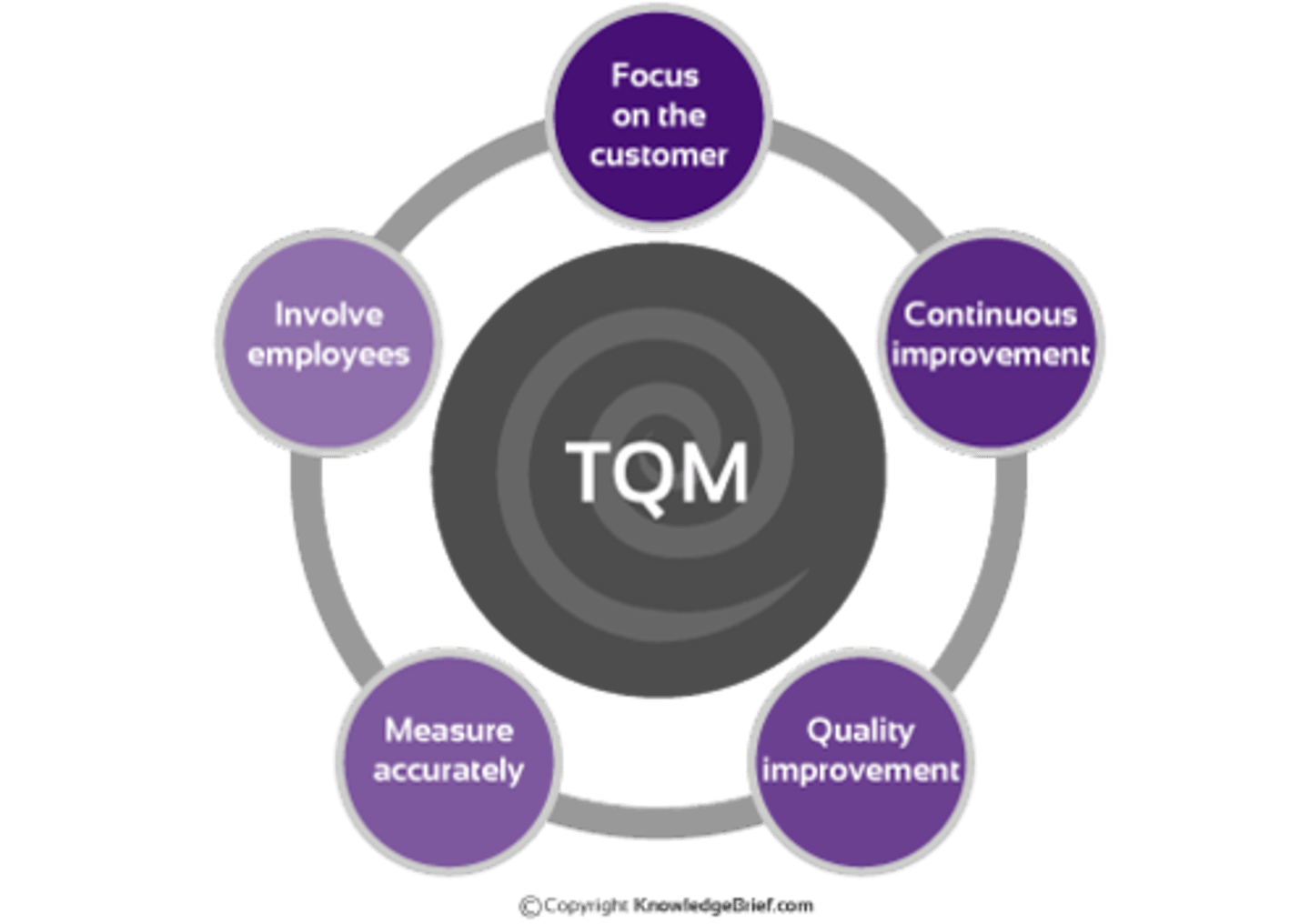
Total Quality Management
managing the entire organization so that it excels on all dimensions of products and services that are important to the customer
Theory of Constraints
A specific approach used to identify and manage constraints in order to achieve the company's goals.
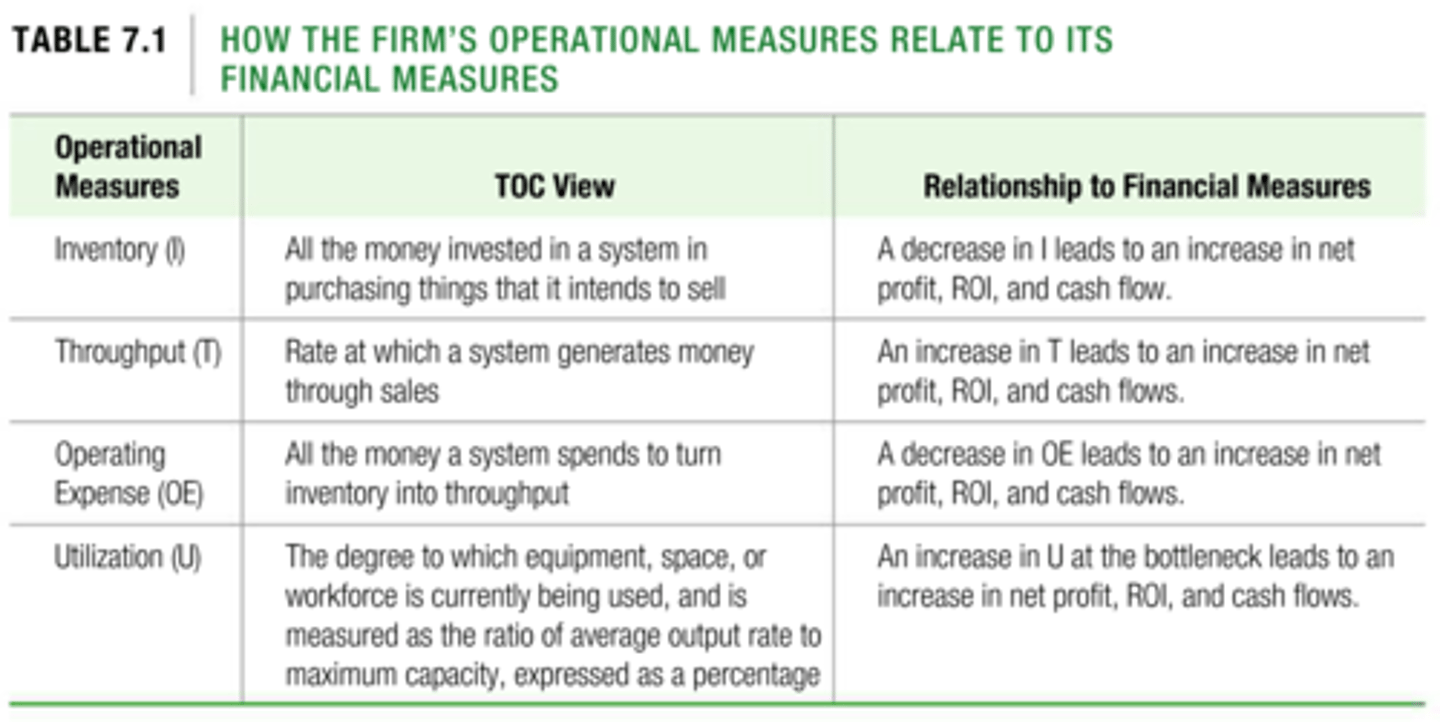
Activity-based costing (ABC)
A method of allocating overhead based on each product's use of activities in making the product.
Corporate Social Responsibility
considers a company's efforts to employ sustainable business practices with regard to its employees, society, and the environment.
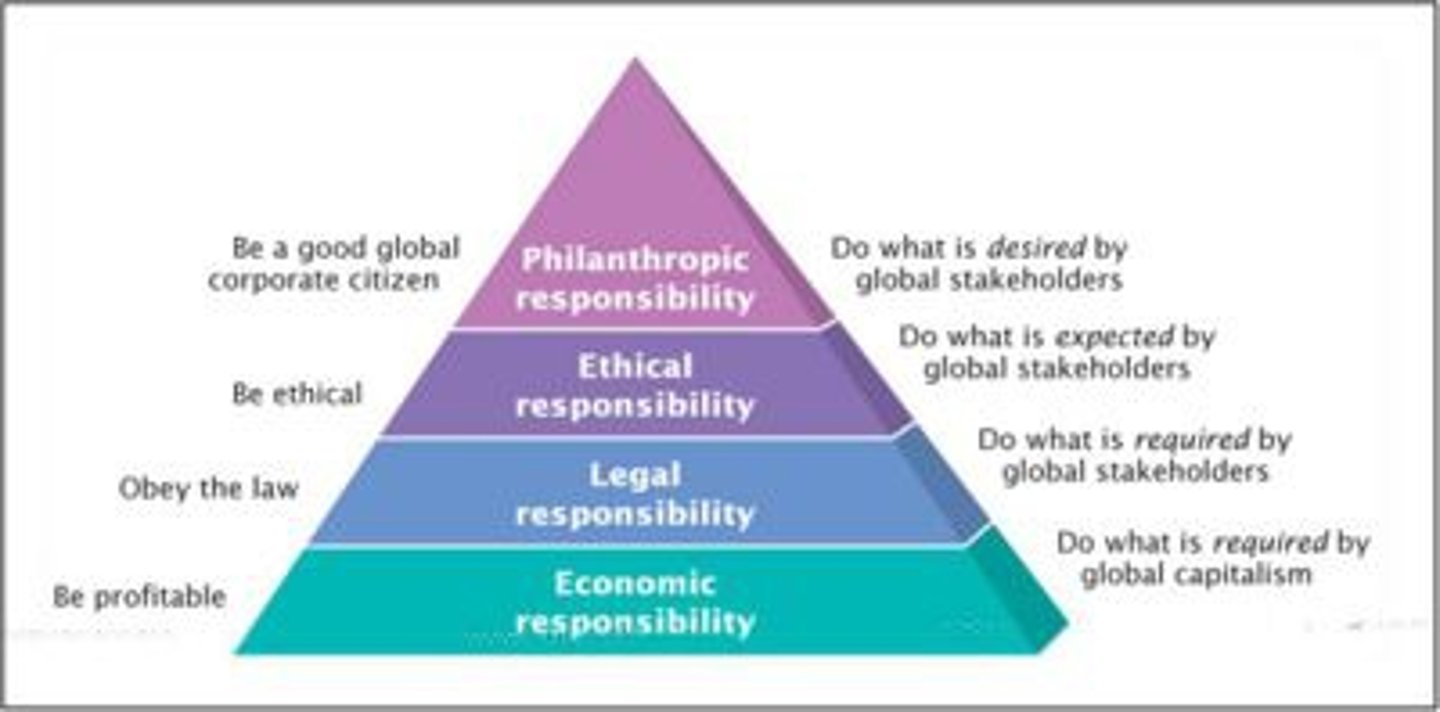
Triple Bottom Line
people, planet, profit

customer orientation
a company objective based on the premise that the firm should measure itself primarily according to whether it meets its customers' needs
Total Quality Management
managing the entire organization so that it excels on all dimensions of products and services that are important to the customer
Just-in-time manufacturing
(JIT) seeks to reduce inventories for the production process by purchasing inputs for arrival just in time to use and producing output just in time to sell. Rather than costly accumulation and storage of supplies, it requires frequent ordering of small lots of goods for precisely timed arrival and immediate deployment to the factory floor.
*Emphasis on quality and seeks to prevent defects.
continuous improvement
involves always searching for new ways to improve work quality and performance
Cost of Goods Manufactured
the manufacturing costs associated with the goods that were finished during the period
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
A law passed by Congress that requires the CEO and CFO to certify that their firm's financial statements are accurate.

cost accounting
An area of accounting that involves measuring, recording, and reporting product costs.
cost accounting system
Manufacturing and service cost accounts that are fully integrated into the general ledger of a company.
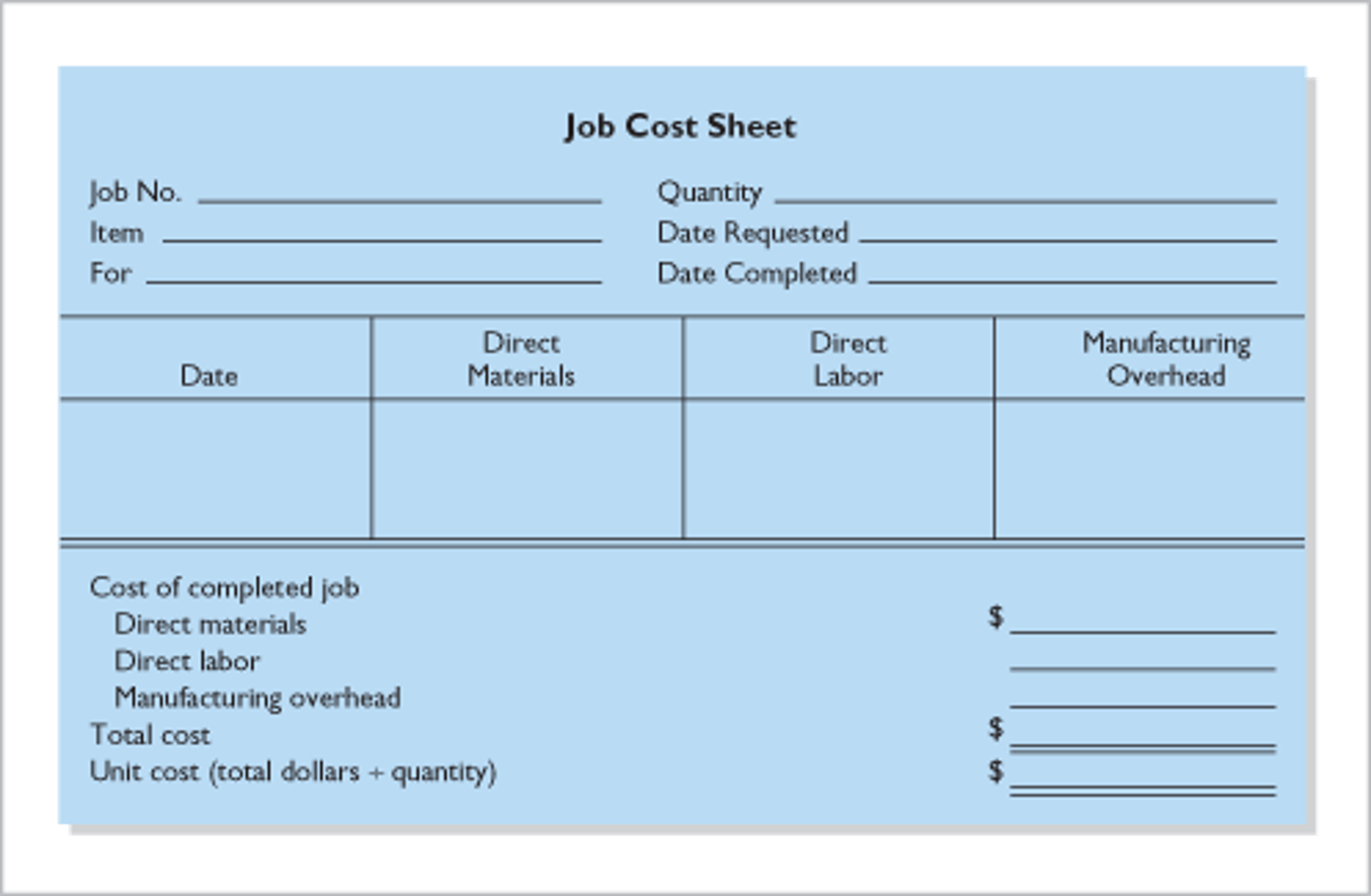
job cost sheet
A form used to record the costs chargeable to a specific job and to determine the total and unit costs of the completed job.
job order cost system
A cost accounting system in which costs are assigned to each job or batch.
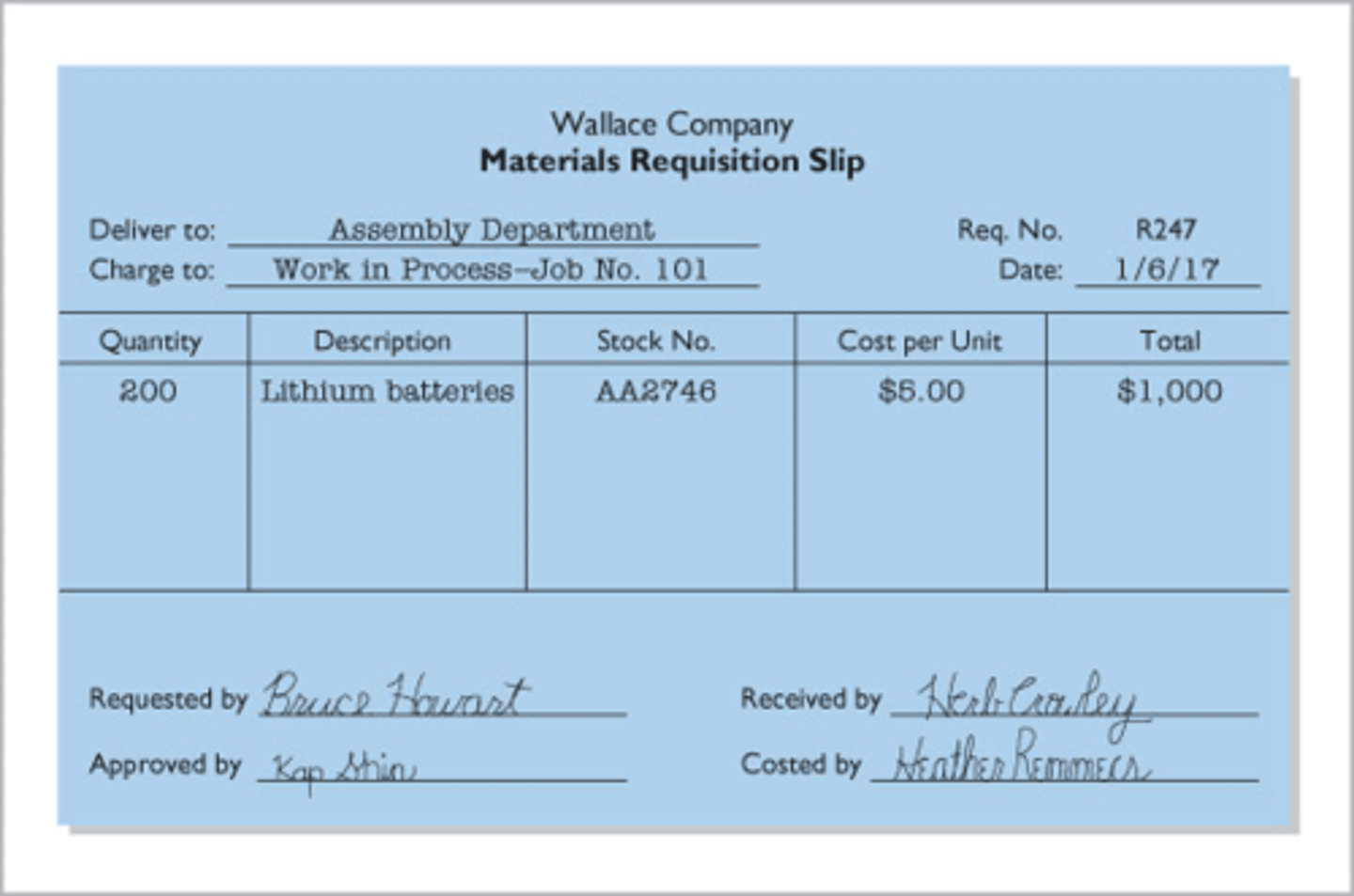
materials requisition slip
A document authorizing the issuance of raw materials from the storeroom to production.
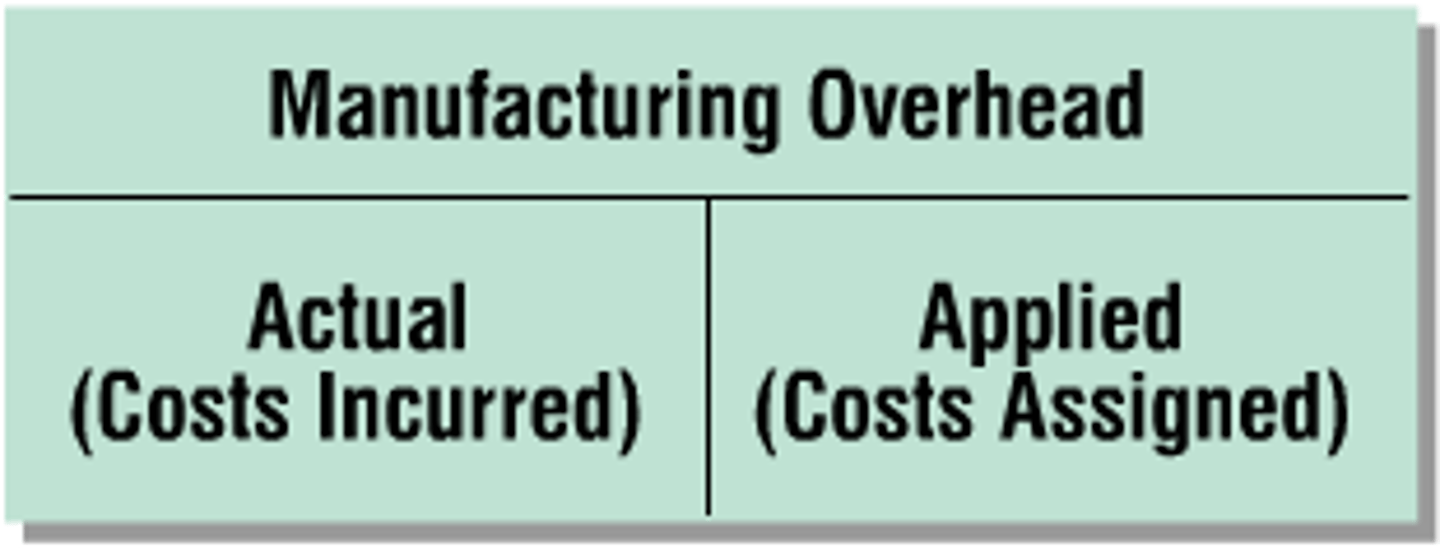
overapplied overhead
A situation in which overhead assigned to work in process is greater than the overhead incurred.
process cost system
A cost accounting system used when a company manufactures a large volume of similar products.
time ticket
A document that indicates the employee, the hours worked, the account and job to be charged, and the total labor cost.
underapplied overhead
A situation in which overhead assigned to work in process is less than the overhead incurred.
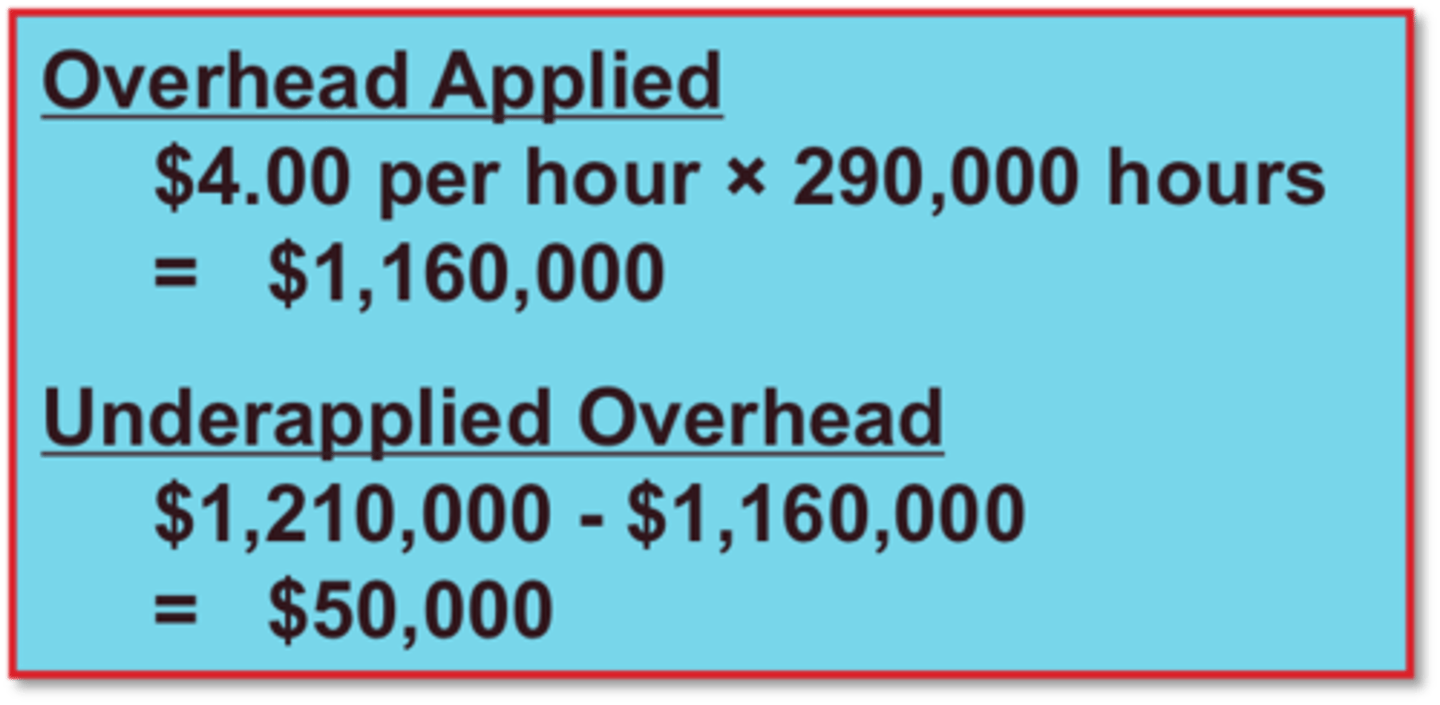
Predetermined Overhead Rate
A rate based on the relationship between estimated annual overhead costs and expected annual operating activity, expressed in terms of a common activity base.

Advantages and Disadvantages of job order costing
+ job order costing is more precise in the assignment of costs to projects than process costing
+If products are identical, then job costing is adequate for determining profit.
-If products are different, then it is not adequate
-requires a lot of data entry
-difficulty assigning overhead to the product.
Process Costing
a cost system that assigns costs to each process, or work center, in the production cycle, and then calculates the average cost for all units produced
Allocating Overhead
1. estimate total annual factory overhead
2. select a reasonable basis for allocation
3. divide estimated overhead cost by the allocation base to get an overhead rate
Activity
Any event, action, transaction, or work sequence that incurs costs when producing a product or performing a service.
activity cost pool
The overhead cost attributed to a distinct type of activity or related activities.
Activity Based Costing
A costing system that allocates overhead to multiple activity cost pools and assigns the activity cost pools to products or services by means of cost drivers.
activity based management
Extends ABC from product costing to a comprehensive management tool that focuses on reducing costs and improving processes and decision-making.
Batch-level activities
Activities performed for each batch of products rather than for each unit.
cost driver
Any factor or activity that has a direct cause-effect relationship with the resources consumed. In ABC, cost drivers are used to assign activity cost pools to products or services.
Facility-level activities
Activities required to support or sustain an entire production process.
just in time processing
A processing system dedicated to having the right amount of materials, parts, or products arrive as they are needed, thereby reducing the amount of inventory.
Non-Value-Added Activities
An activity that, if eliminated, would not reduce the perceived value of a company's product or service.
Product-level activities
Activities performed in support of an entire product line but not always performed every time a new unit or batch of products is produced.
Unit-level activities
activities performed for each unit of production
value-added activities
An activity that increases the perceived value of a product or service to a customer.
steps of activity based costing
1. Identify the cost driver that has a strong correlation to the costs accumulated in each cost pool and estimate total annual cost driver
2. Identify the cost driver that has a strong correlation to the costs accumulated in each cost pool and estimate total annual cost driver usage
3. compute the activity-based overhead rate for each cost pool (amounts in step 1 divided by amounts in step 2.)
4. Assign overhead costs to products using the overhead rates determined for each cost pool and each products use of each cost driver
ABC Benefits and Limitations
+ ABC employs more cost pools and therefore results in more accurate product costing
+ ABC leads to more enhanced control and overhead costs
+ ABC supports better management decisions
- ABC can be very expensive to use
- ABC systems are more complex than traditional systems
- some arbritrary allocations remain