🧠 Flashcards for Quiz 11
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What drives surface ocean currents?
Wind, Coriolis Effect, and deflection by continents.
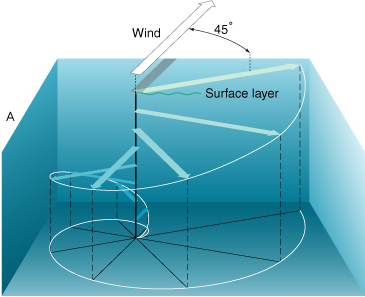
What is the Ekman Spiral?
A spiraling motion of water due to wind, Coriolis, and friction, causing surface flow ~90° from wind direction.
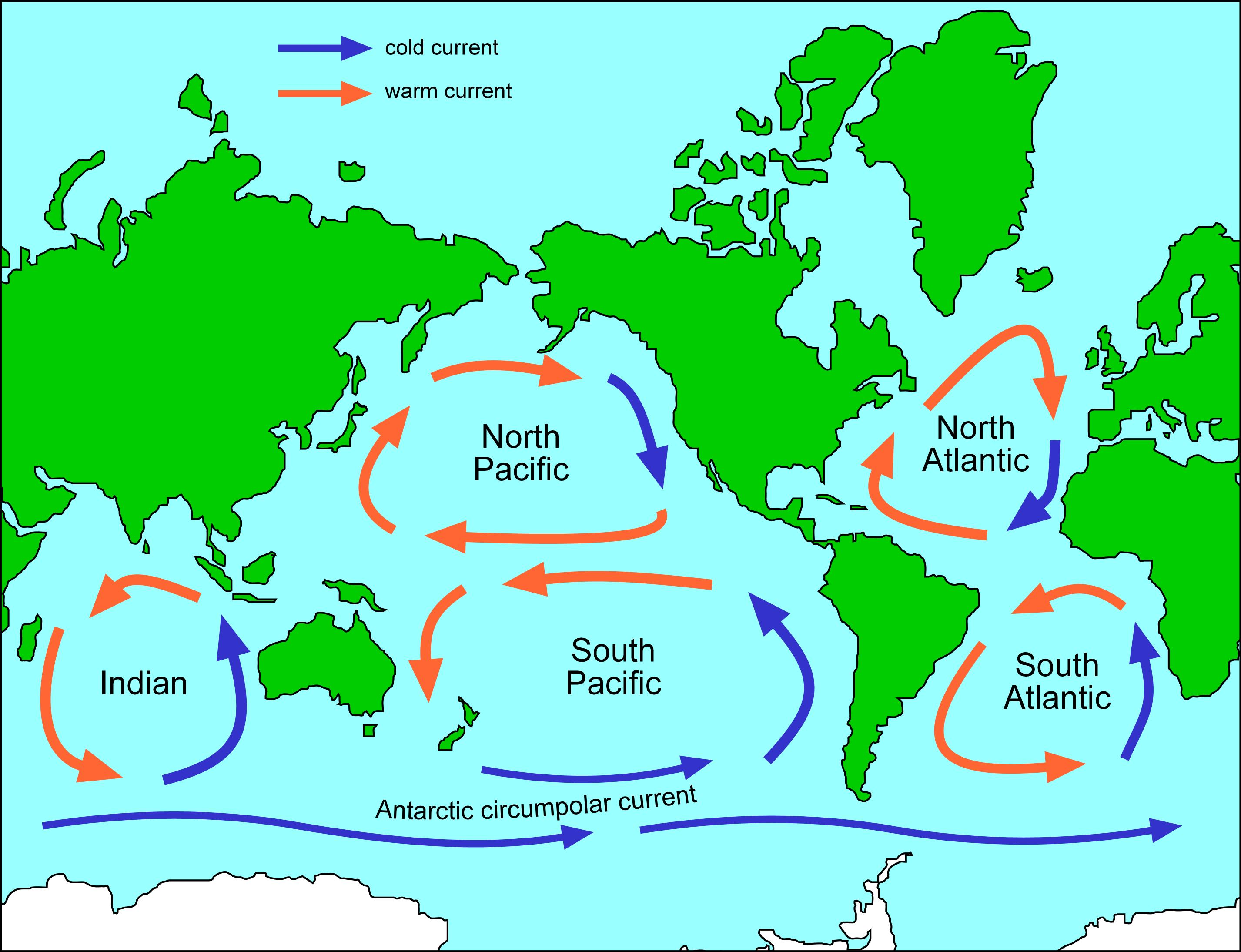
What are ocean gyres?
Wind-driven circular currents that help regulate global climate.
What is wave refraction?
Bending of waves around headlands, concentrating energy and causing erosion.
What does longshore drift do?
Moves sediment along the shore, forming spits and barrier islands.
What's the difference between submergent and emergent coastlines?
Submergent = rising sea level (barrier islands); emergent = land uplift (terraces).
What are tides mainly caused by?
The Moon’s gravitational pull.
Where is the ozone layer located?
In the stratosphere.
What does the ozone layer block?
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
What is the lapse rate?
6.5°C drop per 1000 meters in elevation.
What season starts when the Sun is over the Tropic of Cancer?
Summer in the Northern Hemisphere.
What type of heat transfer moves warm fluids?
Convection.
What does increased albedo mean?
More sunlight is reflected by the Earth.
What gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?
CO₂, H₂O vapor, CH₄.
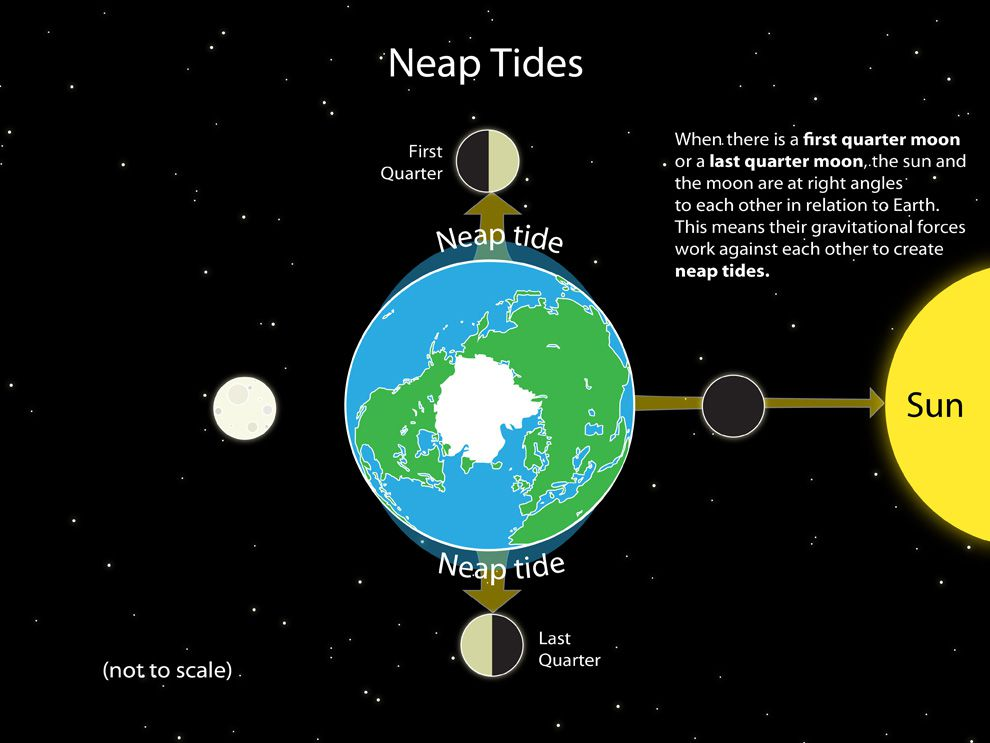
What happens during a neap tide?
The smallest tidal range occurs.
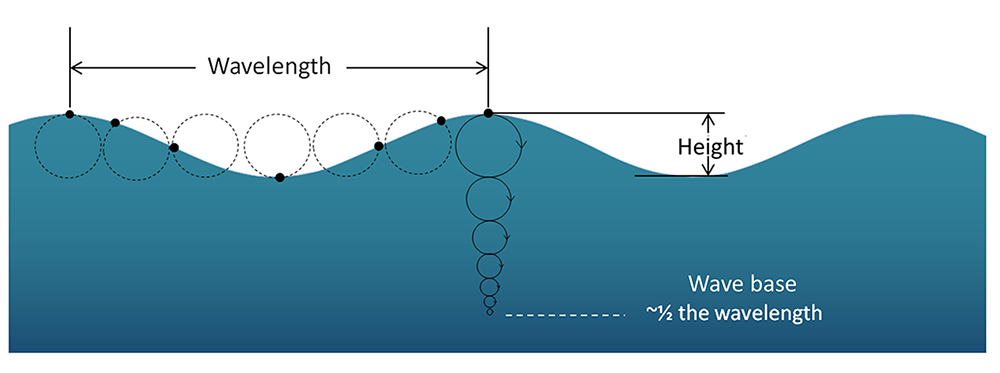
What is wave height?
The vertical distance between the crest and the trough of a wave.
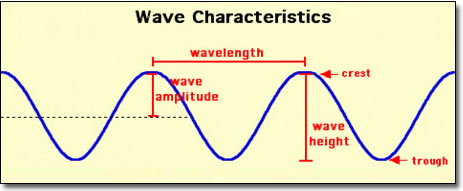
What is wave base?
The depth at which wave motion stops—typically half the wavelength.
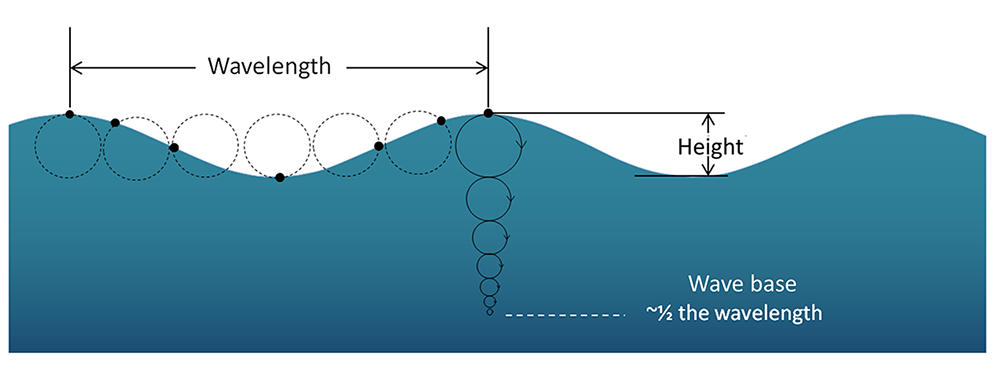
What is wavelength?
The horizontal distance between two consecutive wave crests.
What causes a breaker to form?
The wave base touches the ocean floor, slowing the wave and increasing its height until it collapses.
What is a seawall?
A human-built wall to protect the coast from wave erosion.
What is a groin?
A structure built perpendicular to the shoreline to trap sand and reduce longshore drift.
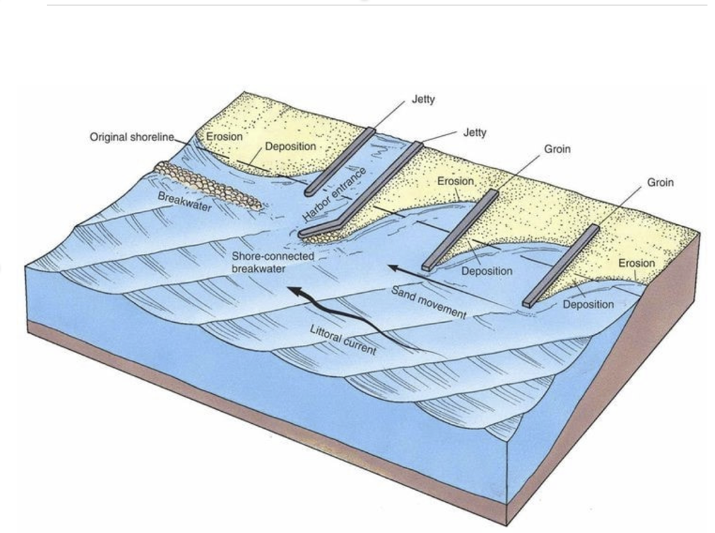
What is a jetty?
A barrier at a harbor or river mouth to control water flow and sediment buildup.
What is a breakwater?
An offshore wall that breaks wave energy before it hits the shore.
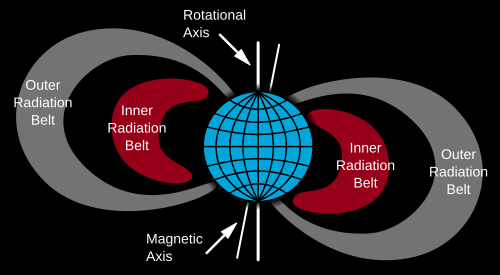
What is the magnetosphere?
The Earth's magnetic field zone that contains the Van Allen radiation belts.
What are the Van Allen belts?
Zones of charged particles trapped by Earth’s magnetic field in the magnetosphere.
What’s the difference between weather and climate?
Weather = short-term atmospheric conditions (days); Climate = long-term average conditions (decades+).
Do cold objects do not emit radiation.
all objects emit radiation, even cold ones.
True or False: The hotter the object, the shorter the wavelength it emits.
T or F — hotter objects emit shorter wavelengths.
What is planetary albedo?
The percentage of solar radiation reflected by Earth's surface and atmosphere.
What happens if albedo increases?
More solar radiation is reflected, which can lead to cooling.
What’s the key cause of the greenhouse effect?
Trapping of longwave (infrared) radiation by gases like CO₂ and water vapo