Patho GI System
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
GI system function
Chemical and physical breakdown of food to be absorbed and used by body cells
Digestion happens due to
Happens due to endocrine and exocrine glands
Beginning of digestion stuff
mouth
Teeth grind food
Tongue- taste- rolls food into for swallowing
Saliva- help swallows- moisten food
Aids in digestion
mechanical part of digestion
Mastication- chewing
Deglutition- swallowing
Churning in stomach mixes with HCL and enzyme- pepsin
Substance going into duodenum- chyme
Pancreas and liver secrete enzymes into duodenum for digestion
stomach enzymes
HCL and Pepsin
what does bile emulsify
Fats, A, D, E, K
Liver functions
Detoxify toxins in blood
Metabolism of proteins/fats/carbs
Maintain proteins for clotting- fibrinogen/prothrombin
Absorbs excess glucose
make bile
pancreas functions
digestion of proteins- (trypsin, chymotrypsin)
Fats (lipase)
Carbs (amylase)
Maintain glucose levels- secreting glucose and insulin
fats
lipase
carbs
amylase
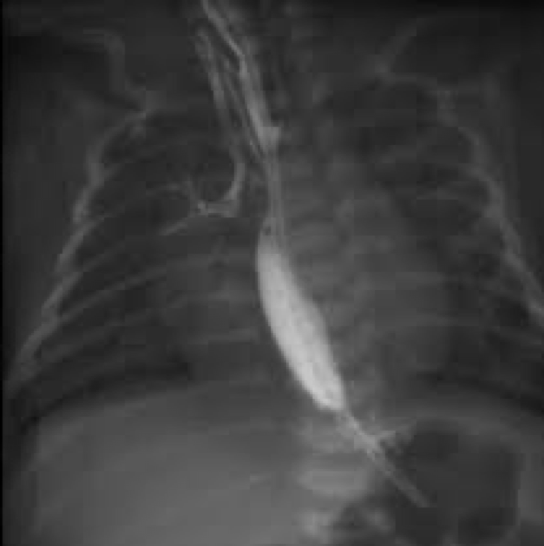
tracheoesophageal fistula
Abnormal or surgically made passage between structures
Trachea/esophagus
Common congenital abnormality
atresia
when esophagus does not fully develop
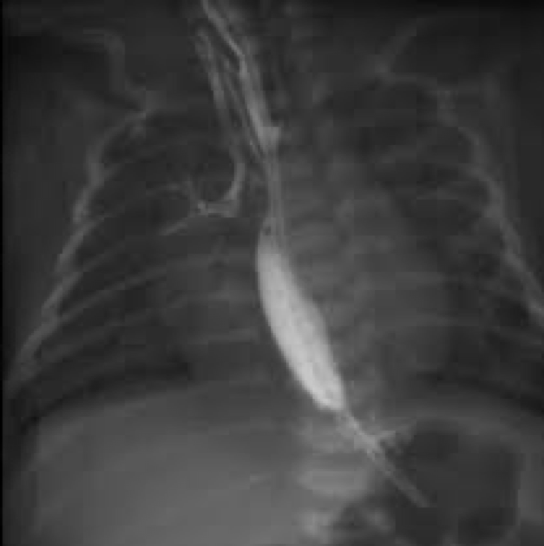
tracheosesophageal fistula
hiatal hernia
Reflux/GERD caused by
Esophagitis
Infection
Injury
Medication
Hiatal hernia
what decreases the pressure of the esophageal sphincter
Alcohol
Chocolate
Caffeine
Fatty foods
GERD
causes burning chest pain- mimic heart attack
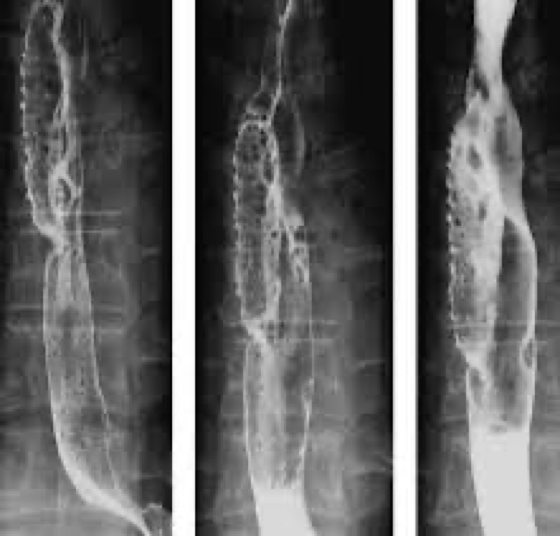
GERD/Reflux
Reflux can cause
Ulcers/erosion
Slow esophageal peristalsis
Dilation of esophagus
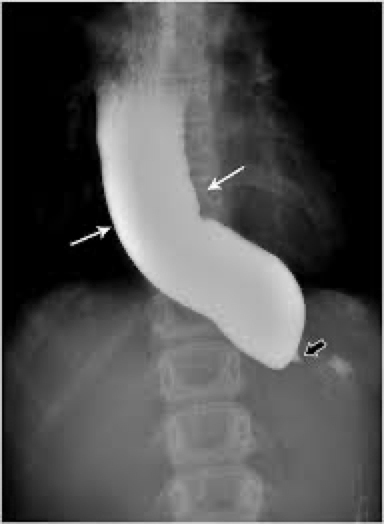
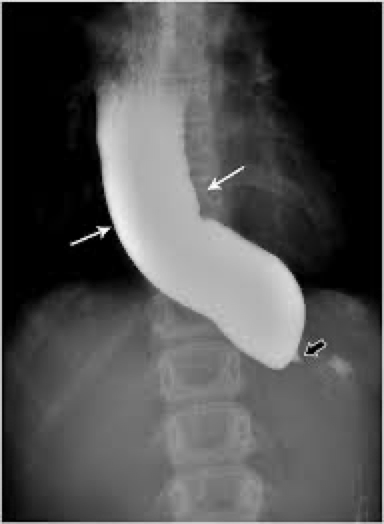
Reflux/Gerd
Barretts esophagus location and looks like
Usually middle to lower esophagus
Smooth- striated mucosa
Smooth tapered stricture
Barrett’s esophagus caused by
GERD
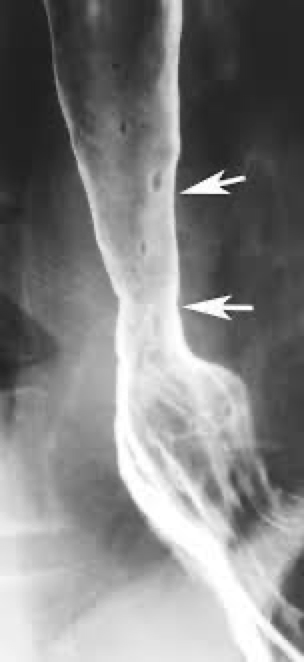
Barrett’s esophagus
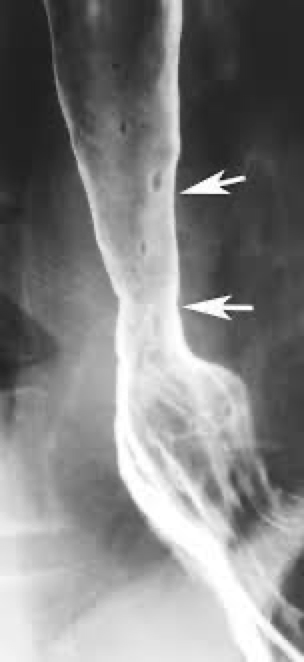
Schatzki ring
Narrowing- tissue forms a ring inside the esophagus
Close to cardiac sphincter
Usually associated with HH
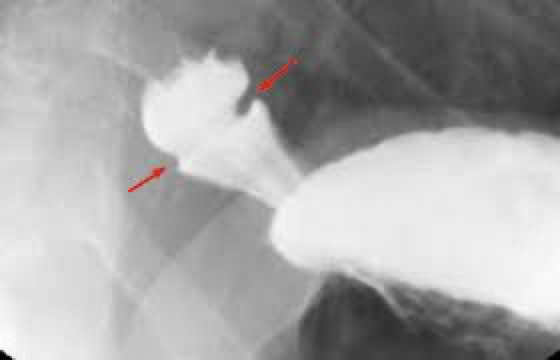
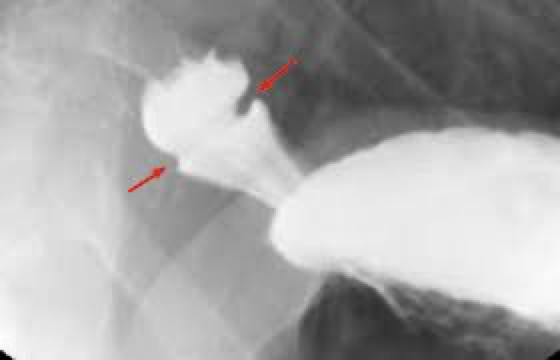
Schatzki ring
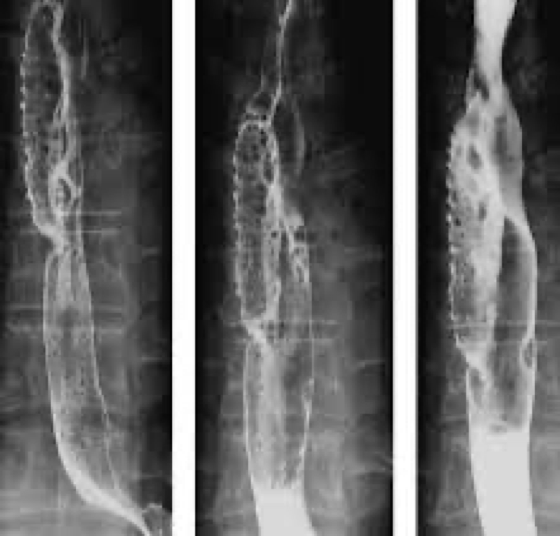
Esophageal diverticulitis
Outpouchings, are common lesions that herniate through the muscular layer of the esophagus
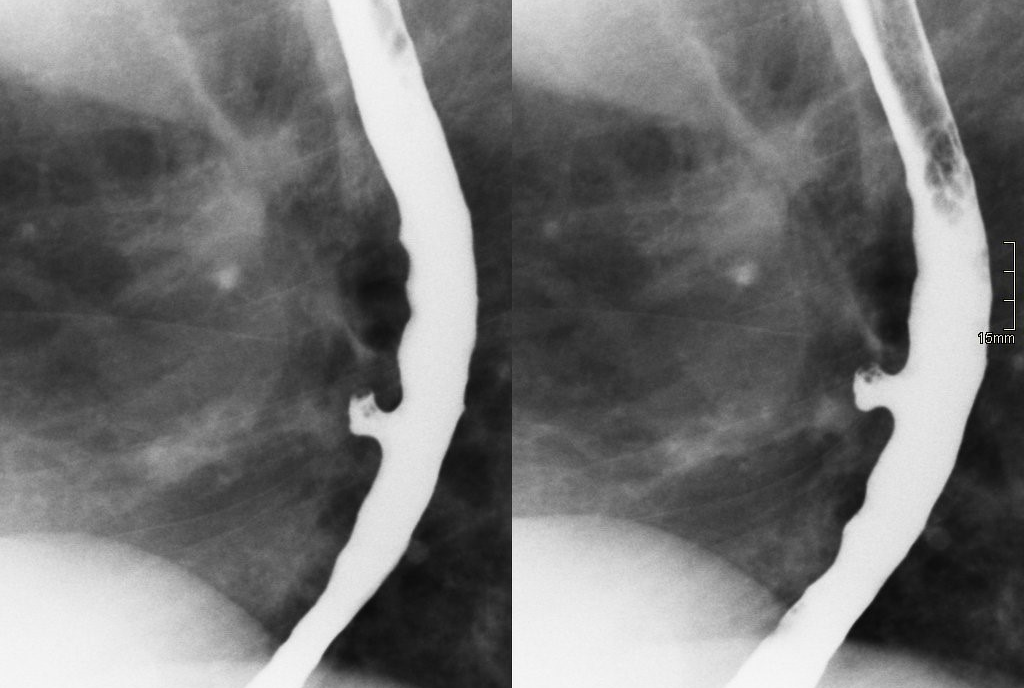
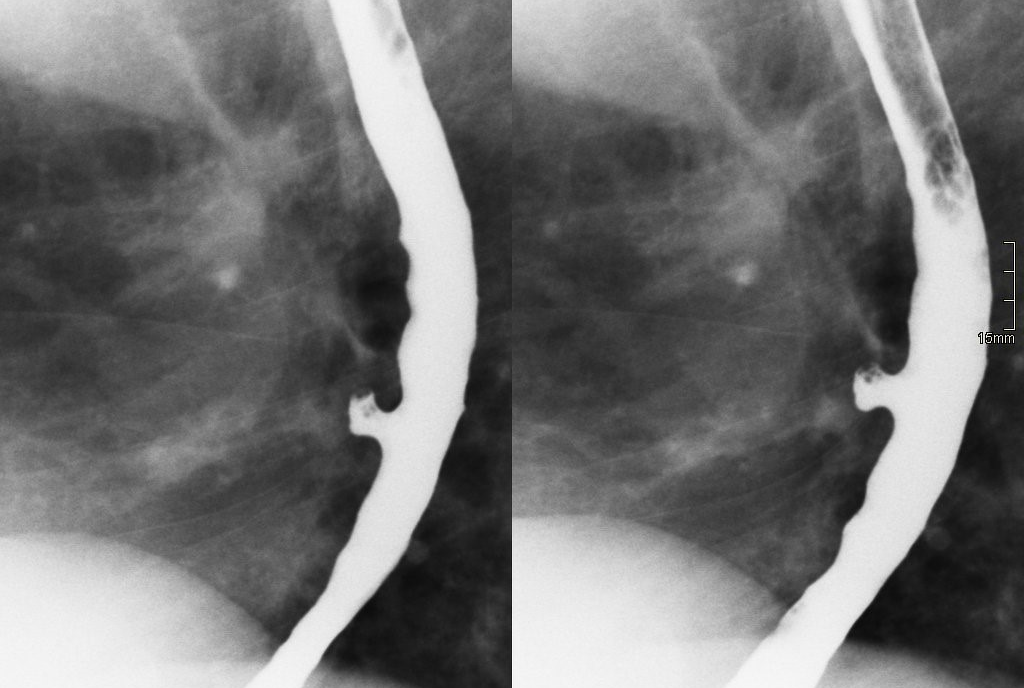
esophageal diverticulitis
zenker diverticula
upper esophagus
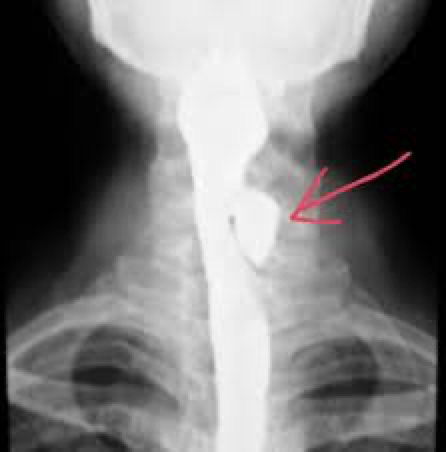
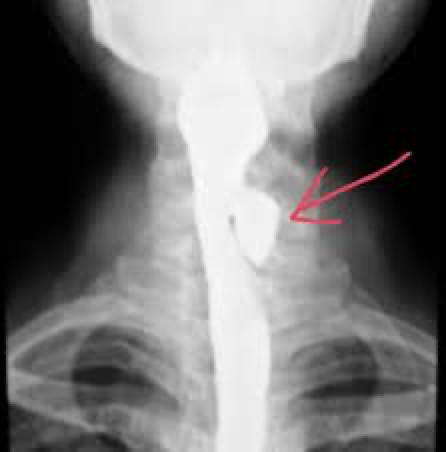
zenker diverticula
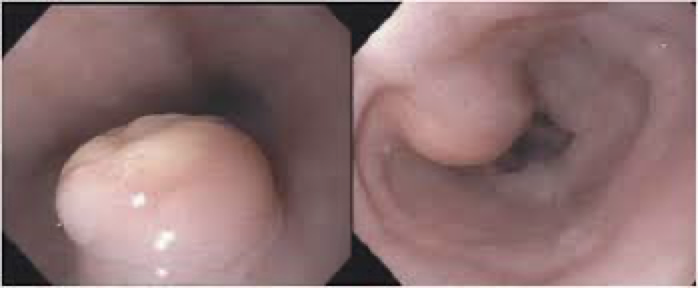
polyp
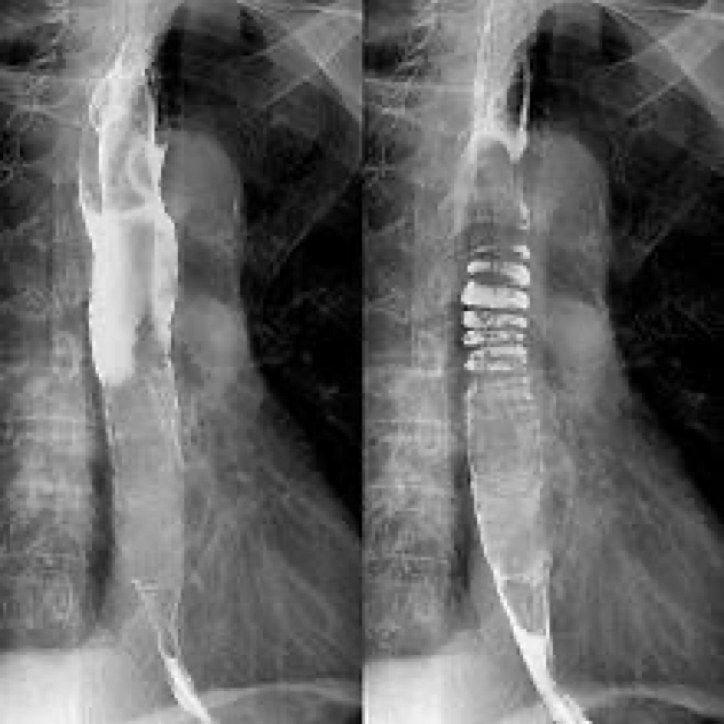
polyp
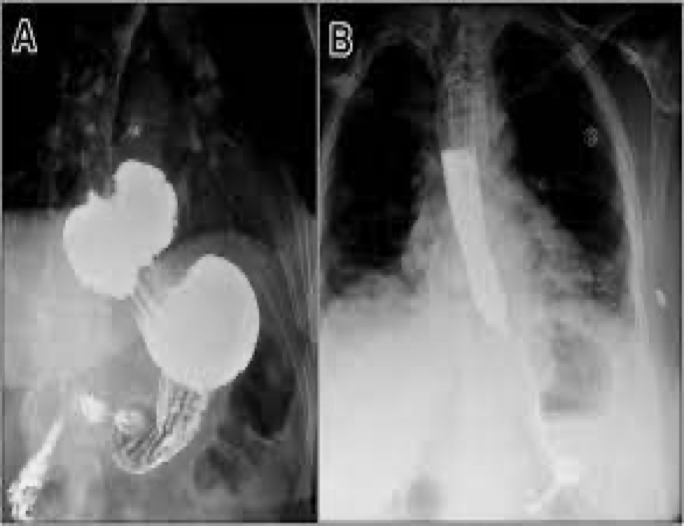
esophageal varices due to
what they look like on xray
Dilated veins in the wall of the esophagus can be a result of cirrhosis of the liver
Seen on xray- round or oval filling defects
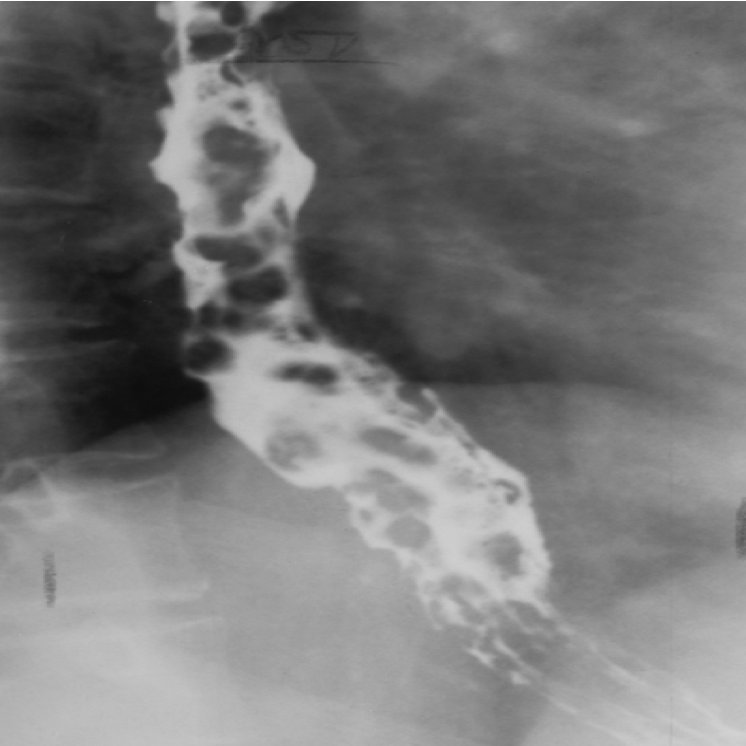
what causes esophageal varices
liver cirrhosis
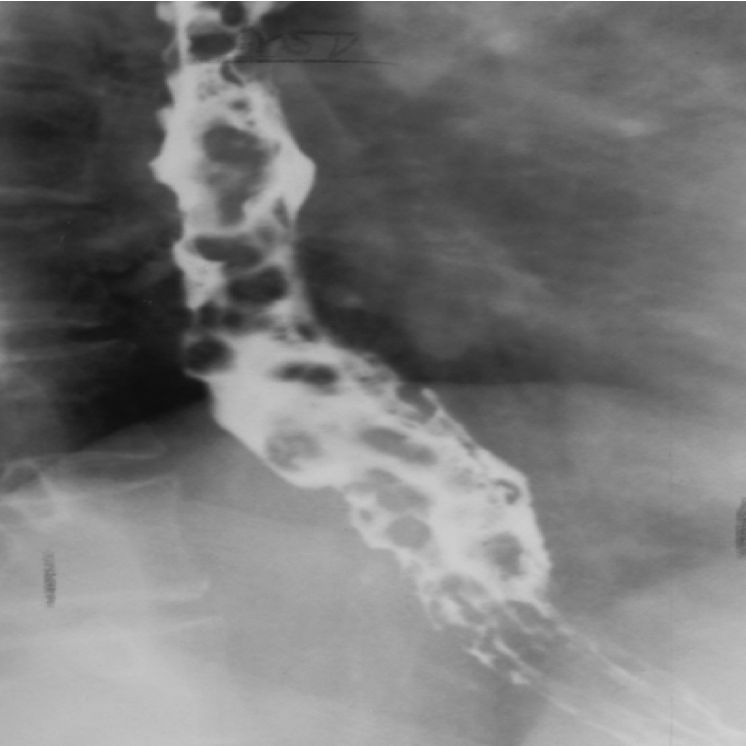
esophageal varices
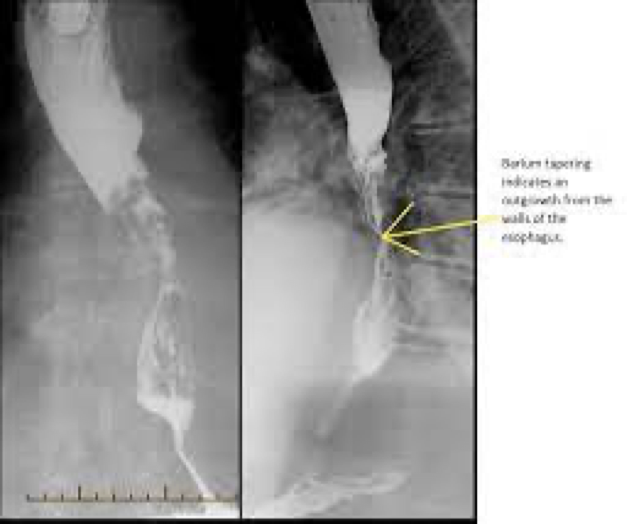
esophageal cancer
exams for esophagus
Endoscopy/ barium (single/double)
Exam and position
pathologies of esophagus
Ulcer
Hiatal hernia
Reflux
Diverticulum
Polyp
Stricture
Varices
Cancer
Barrett esophagus
Schatzki ring
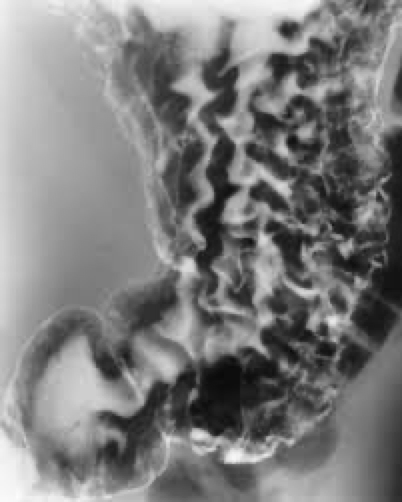
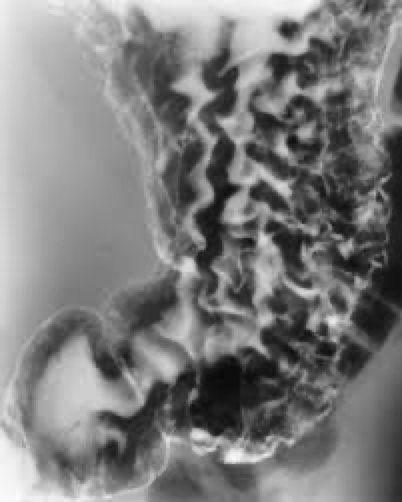
gastritis
Inflammation of lining
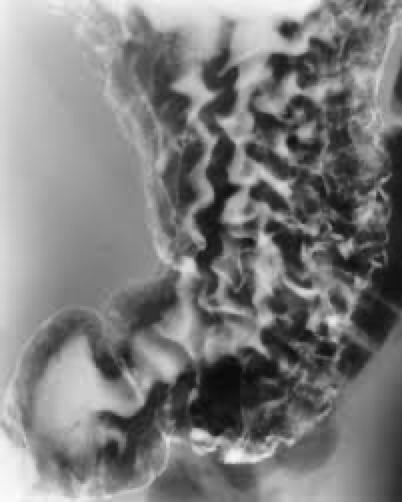
what causes gastritis
Alcohol
Corrosive agent
Infection- helicobacter pylori
Thickened mucosal folds
gastritis
pyloric stenosis and what its seen on
Infants
Best seen on US- thickened pyloric muscle
GI also- filling defect at antrum and delayed gastric emptying
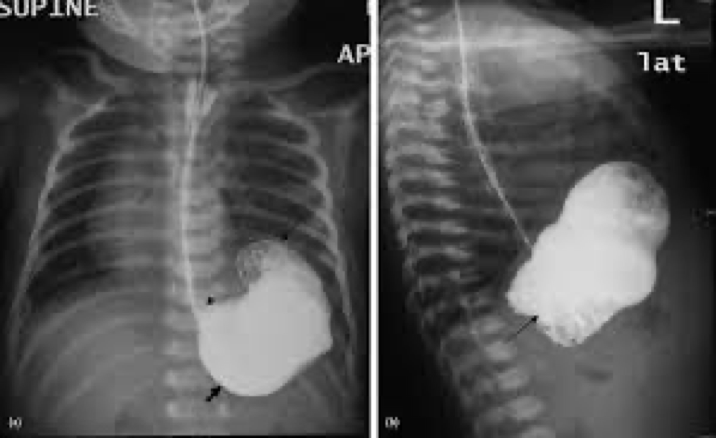
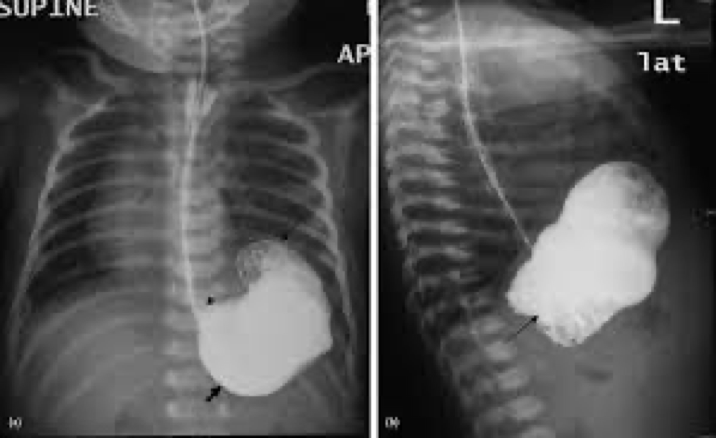
pyloric stenosis
peptic ulcer disease
location, cause
Stomach and duodenum
Usually seen on lesser curvature
Caused by acid and pepsin
Complications- bleeding
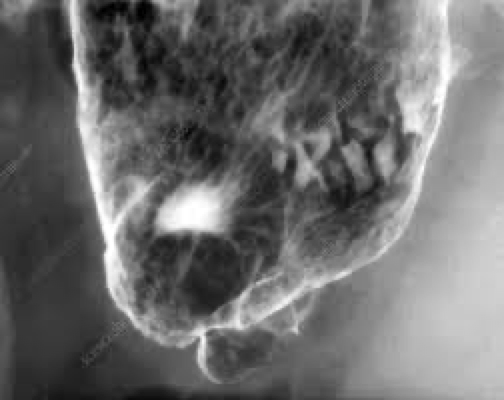
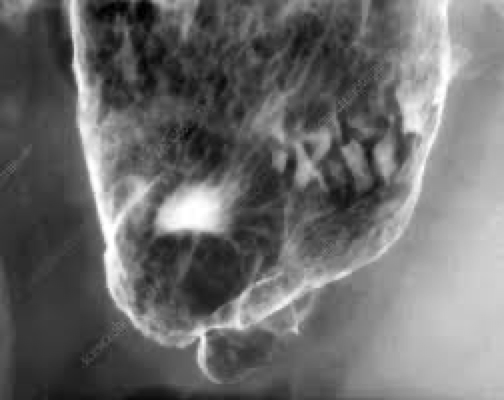
peptic ulcer disease
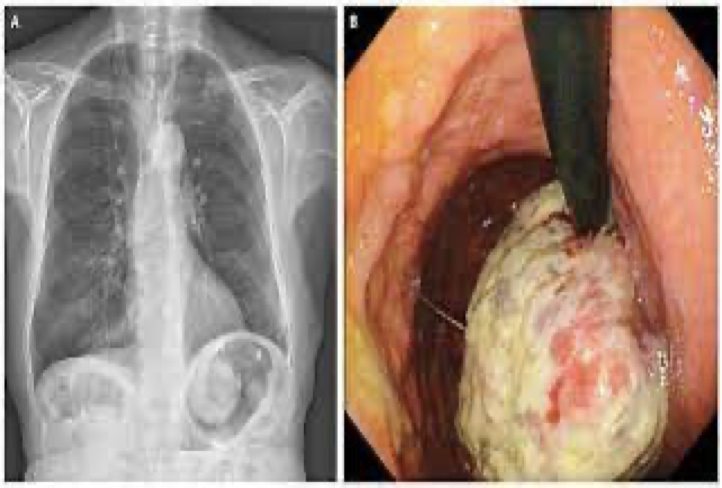
stomach cancer
chron’s disease and who its common in
Chronic Inflammatory- progressive- long term
A form of IBD
Unknown cause
Most common in young adults- 15-25
where is chrons disease found
Usually terminal ileum/proximal colon- can happen anywhere and more than one area
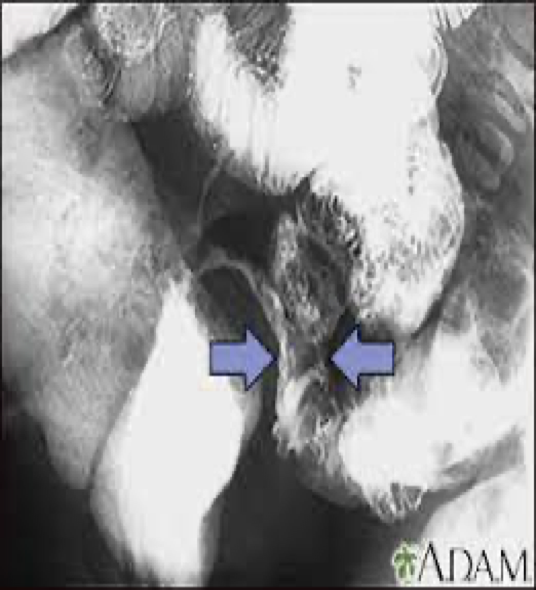
what does chrons disease cause
Can cause weight loss, anemia, bleeding
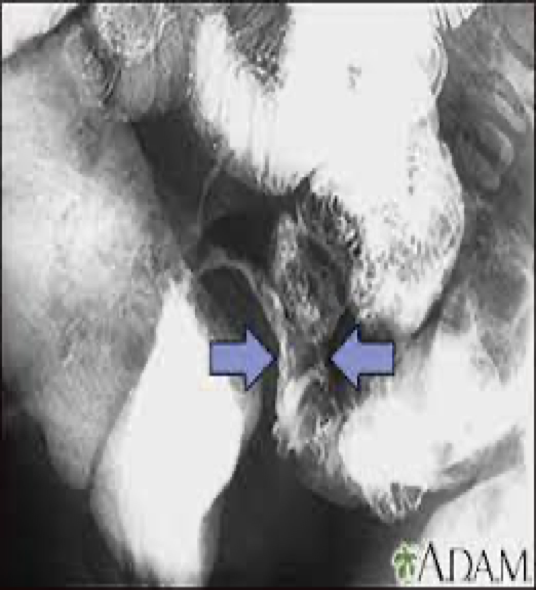
what does chrons disease look like on xray
Thickened mucosal folds
Sometimes separated by normal segments of bowel
inflammation-loss of haustral markings
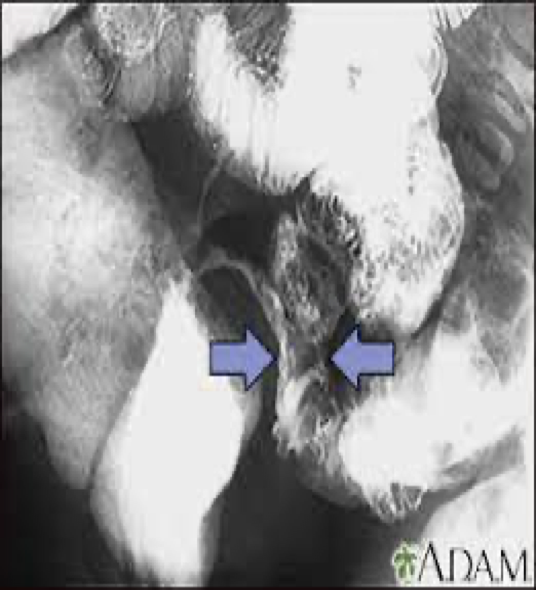
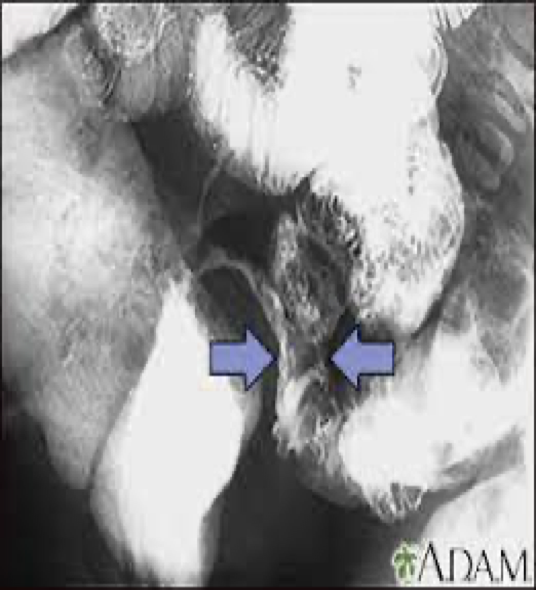
chrons disease
malrotation
congenital and can cause obstruction
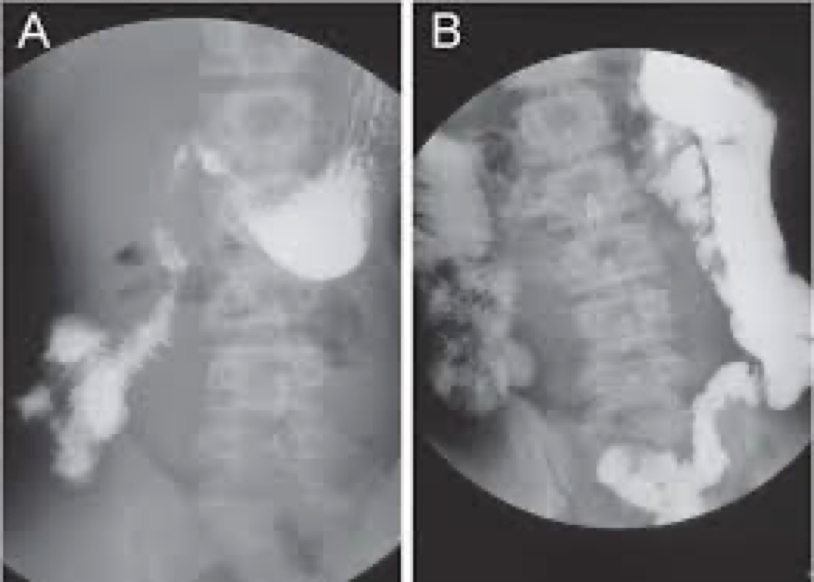
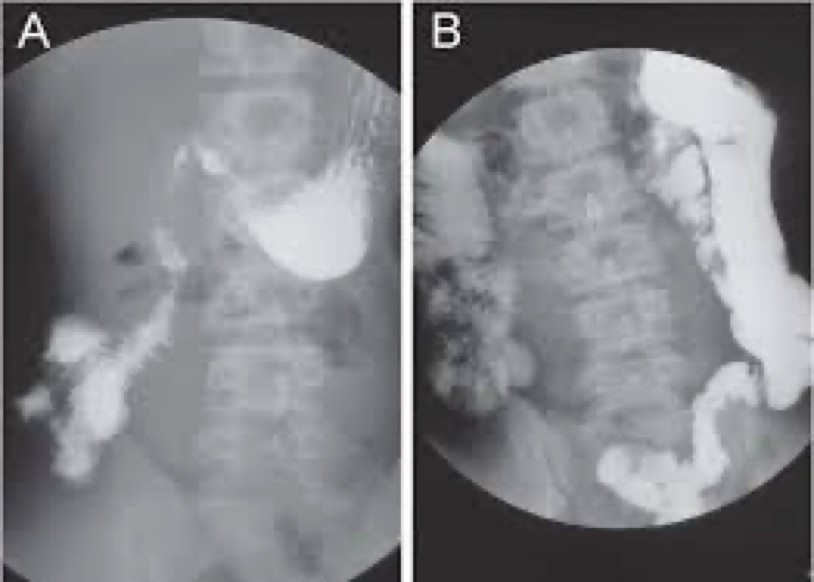
malrotation
ileus
intestinal obstruction
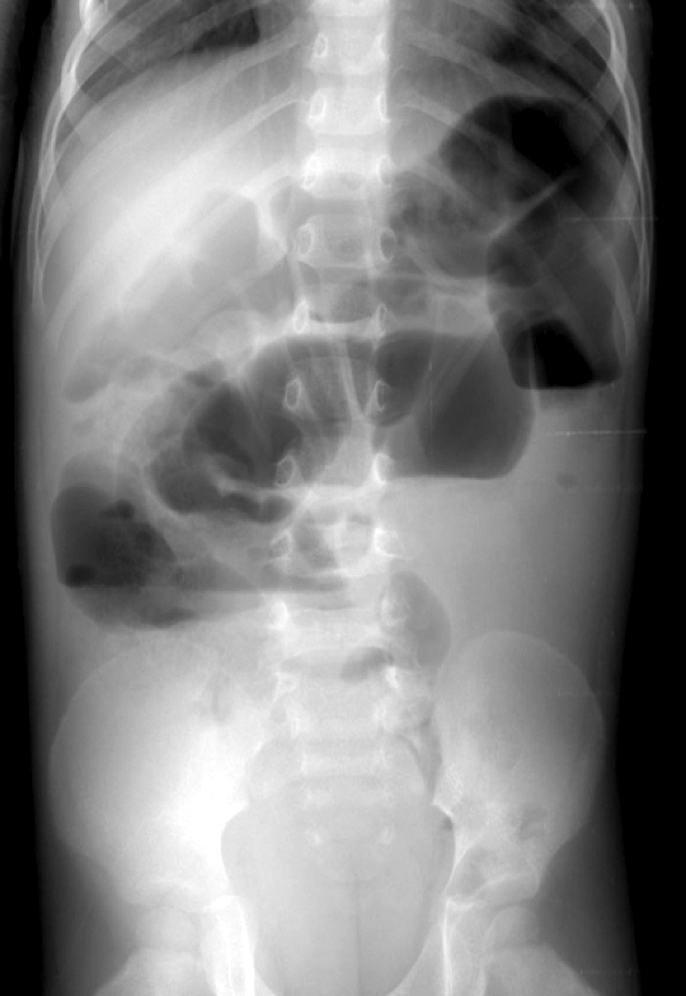
causes of ileus
Abdominal surgery
Electrolyte or metabolic disorders
Trauma
Some medications
adynamic/paralytic ileus
Lack of motility-peristalsis- no physical blockage
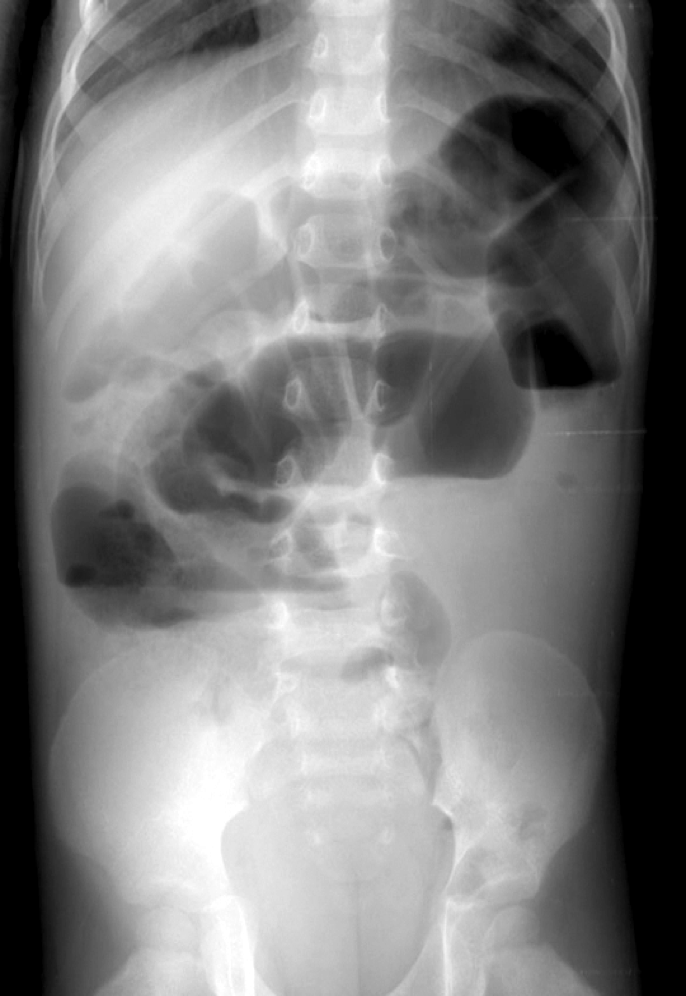
mechanical ileus
mechanical obstruction- definite blockage
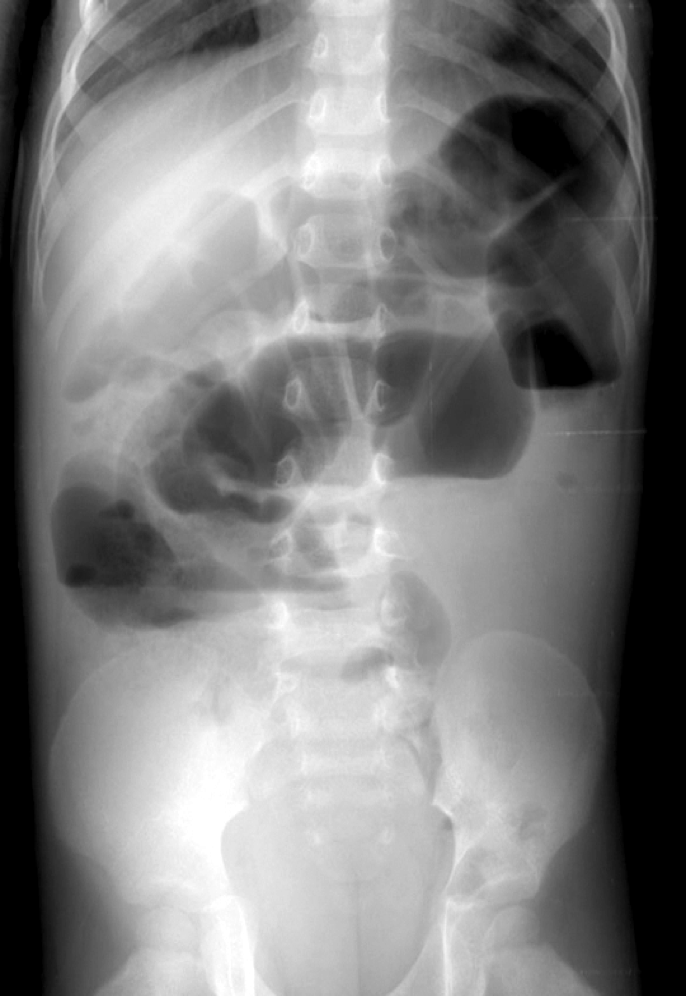
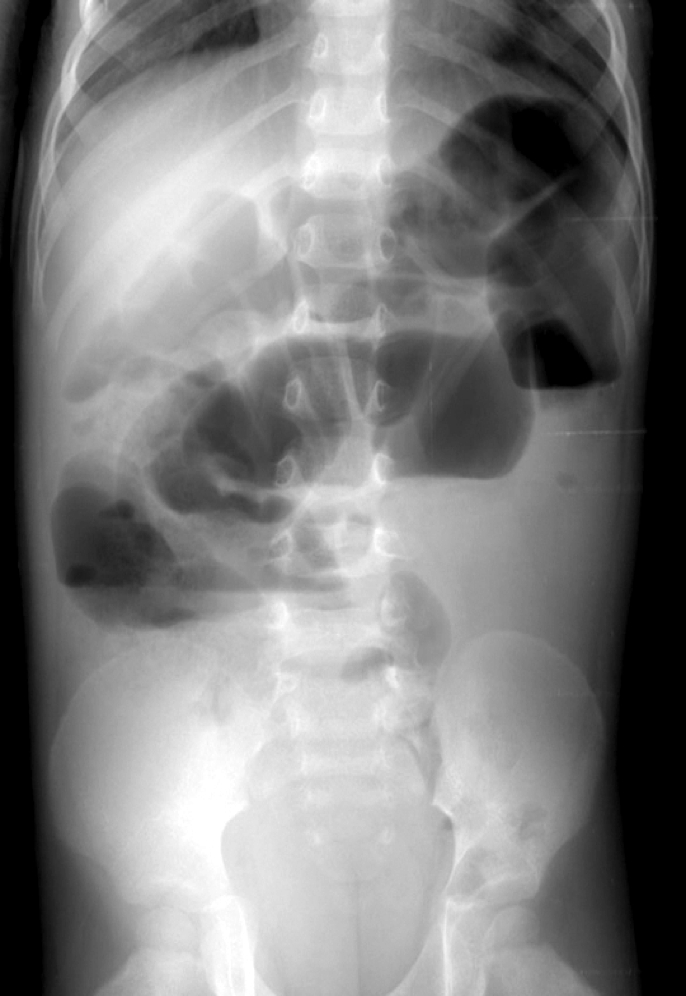
ileus
intussusception and its location
Major cause of bowel obstruction in children
Telescoping/prolapse of one part of the intestines into another
Can affect vascular supply or necrosis
Usually by ileocecal valve
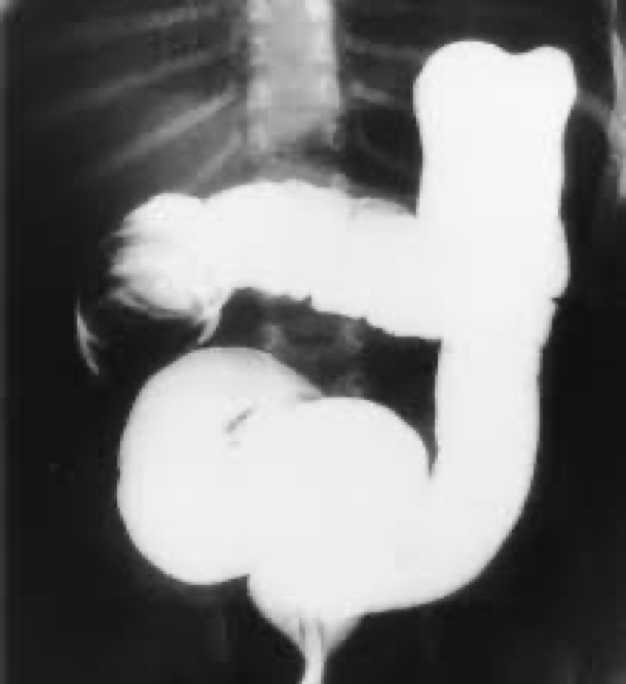
treatment of intussuception
BE can reduce
Too much pressure can lead to perforation
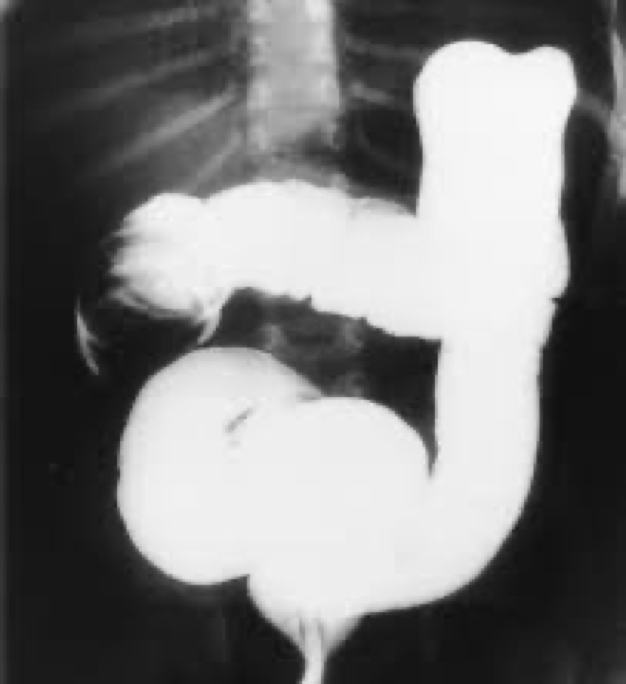
intussuception
malabsorption
Problems absorbing carbs, proteins, fats in small bowel
Results in steatorrhea- bulky, foul smelling, high fat containing stool
Caused by many diseases
steatorrhea
bulky, foul smelling, high fat containing stool
appendicitis
Neck of appendix gets blocked and feces/fluid can’t drain- breeds bacteria and develop abscess
On xray Round or oval calcified area
Acute- no barium enema- could perforate
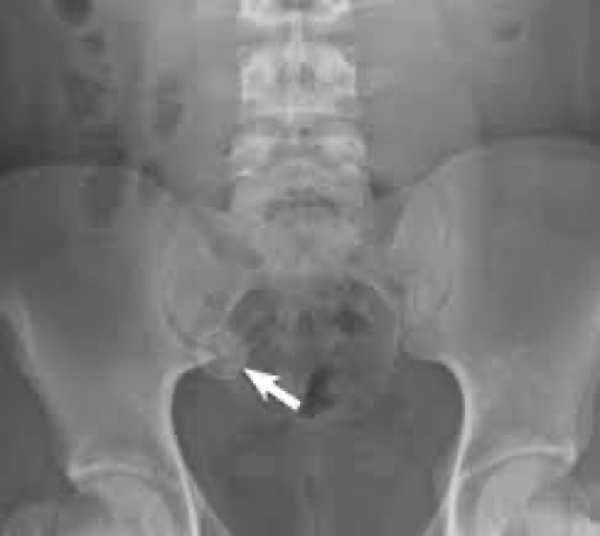
appendicitis
diverticulosis and its location
Condition of having one or more diverticula
Not inflamed
Mostly in sigmoid
Usually no symptoms
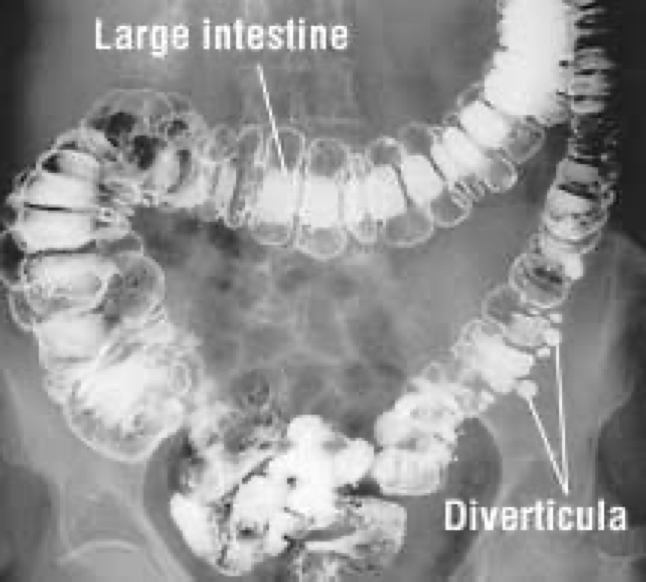
diverticulosis
diverticulitis
Inflamed diverticula
Usually diverticulosis leads into this
Could lead to perforation
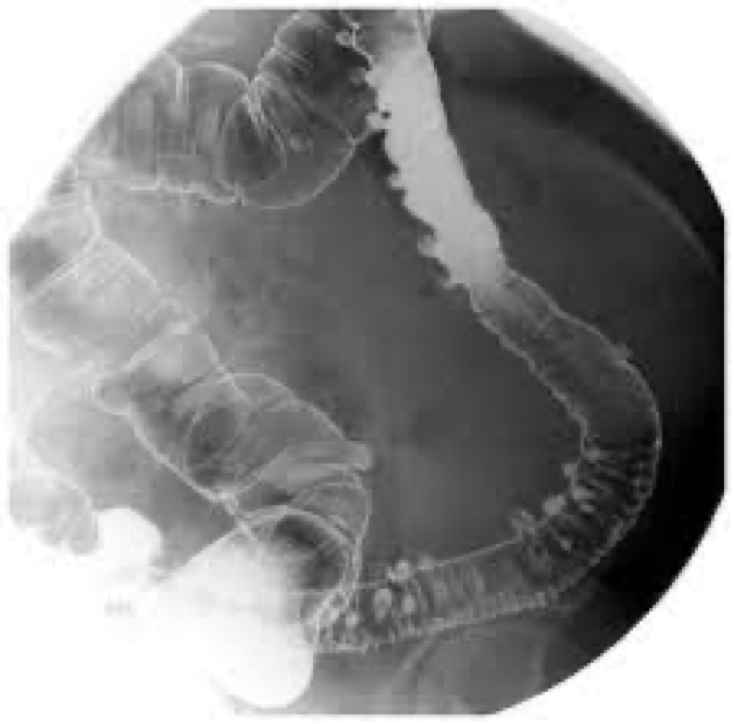
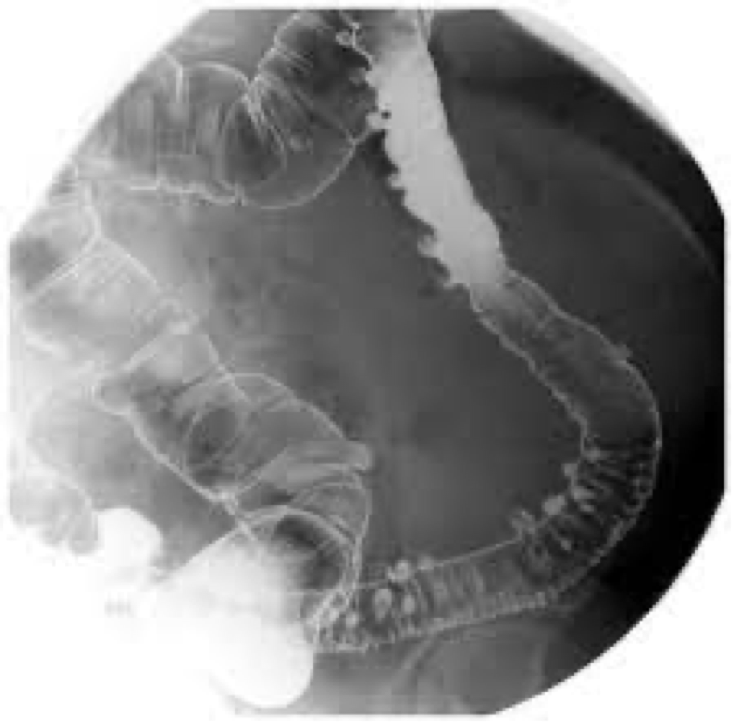
diverticulitis
ulcerative colitis
IBD
Young adults
Symptoms come and go
Extreme dilation of colon
Involves mucosal layer
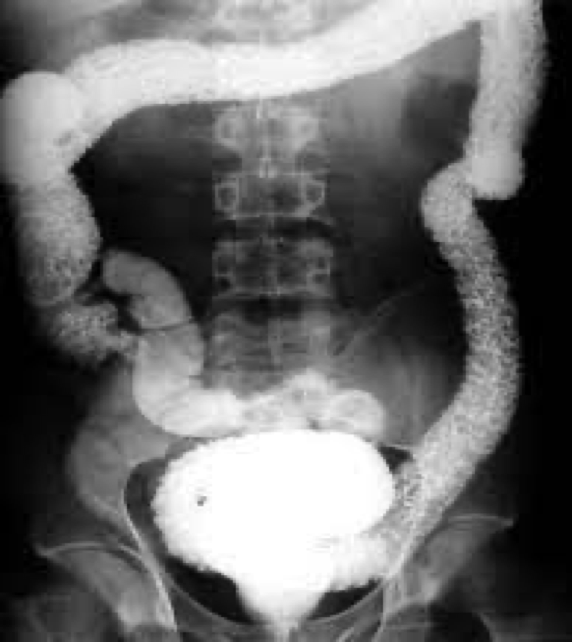
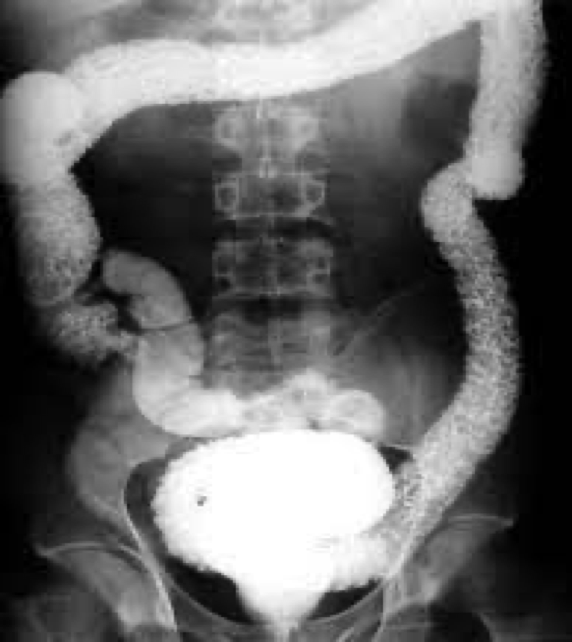
ulcerative colitis
ischemic colitis
sx and who its common in
Most older than 50
Prior cardiovascular disease
Sudden severe abdominal pain
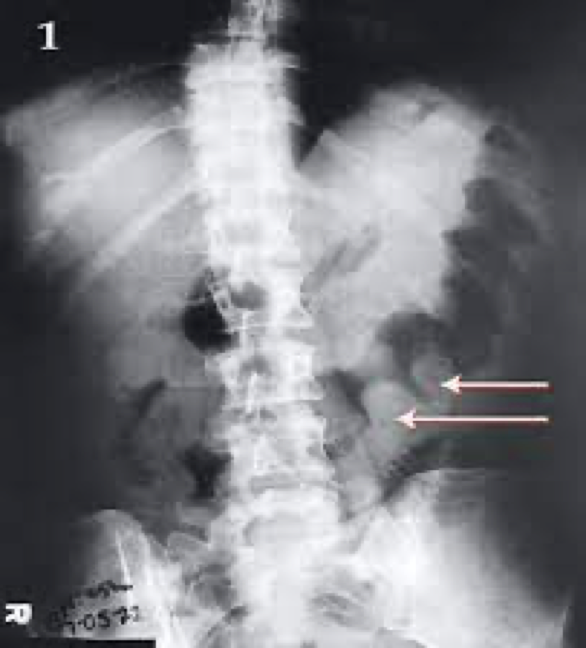
ischemic colitis on xray
On xray-deep ulcers, pseudopolyps, finger-like indentations along colon wall
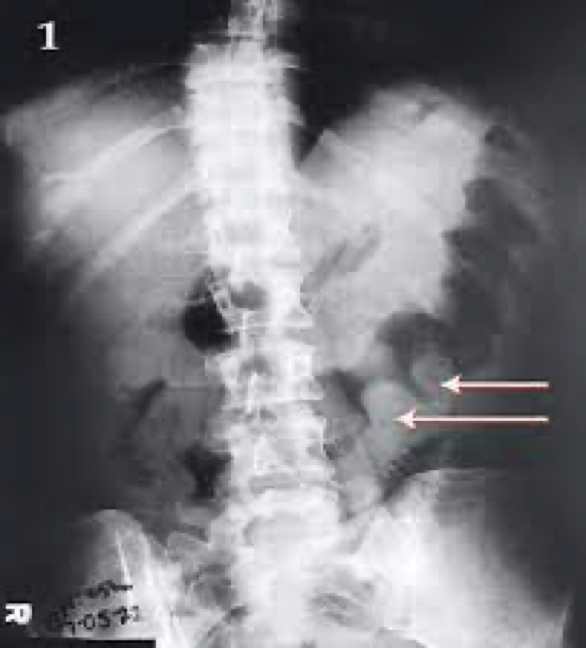
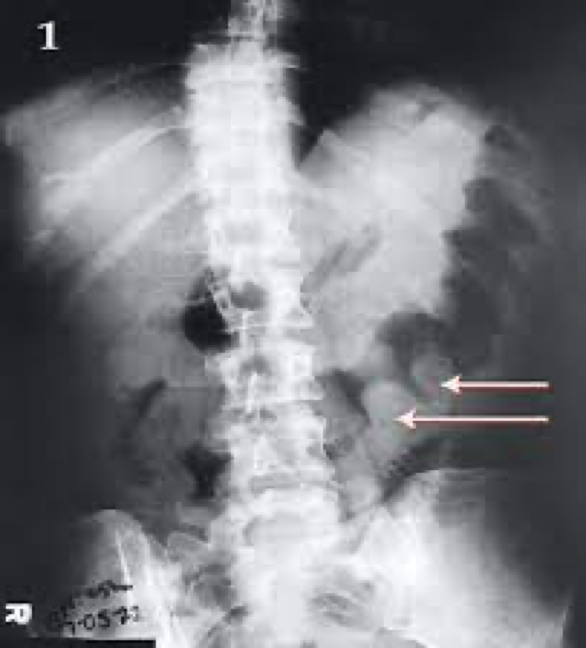
ischemic colitis
chrons seen in what group
15-25
IBS
Alteration in intestinal mobility from underlying condition
Chronic pain
Abnormal increase in small and large bowel motility
Not seen with radiology modalities
May have BE to rule out other conditions
colon/rectal cancer
Leading cause of death from cancer in the US
Most common annular carcinoma- in sigmoid and rectum
Btw ages 50-70 occur
Can develop from polyps and colitis
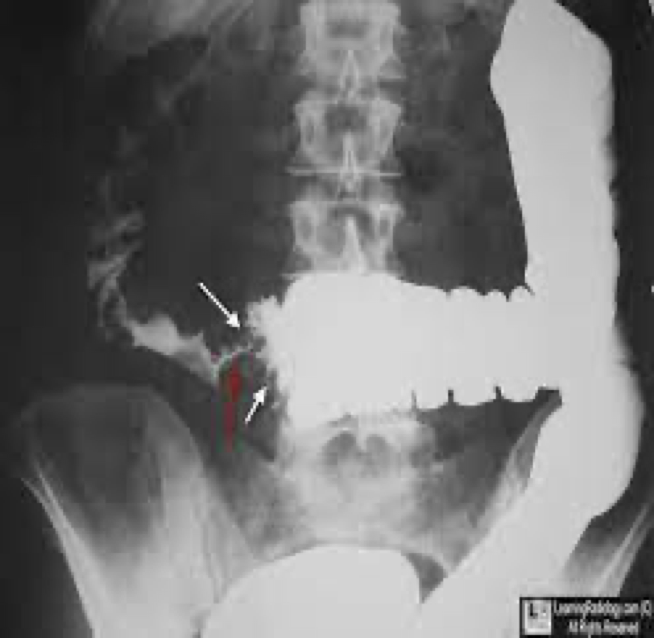
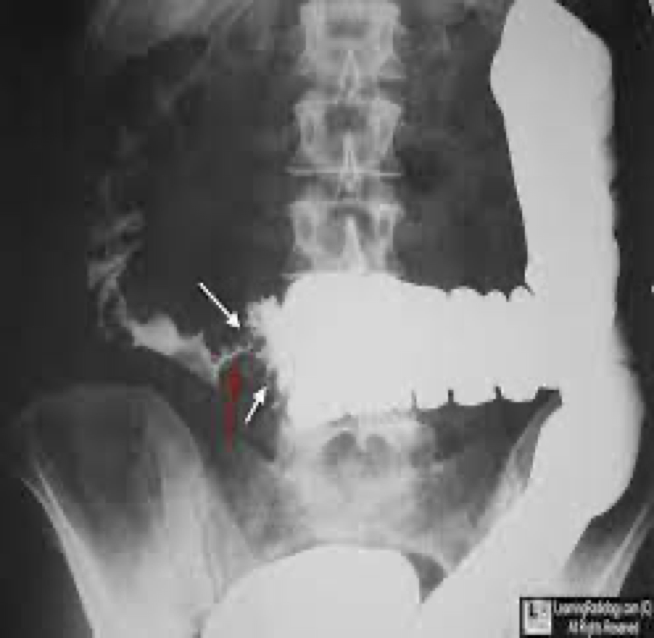
colon cancer
volvulus and its location
Twisting of the bowel on itself causing obstruction
Mostly cecum or sigmoid
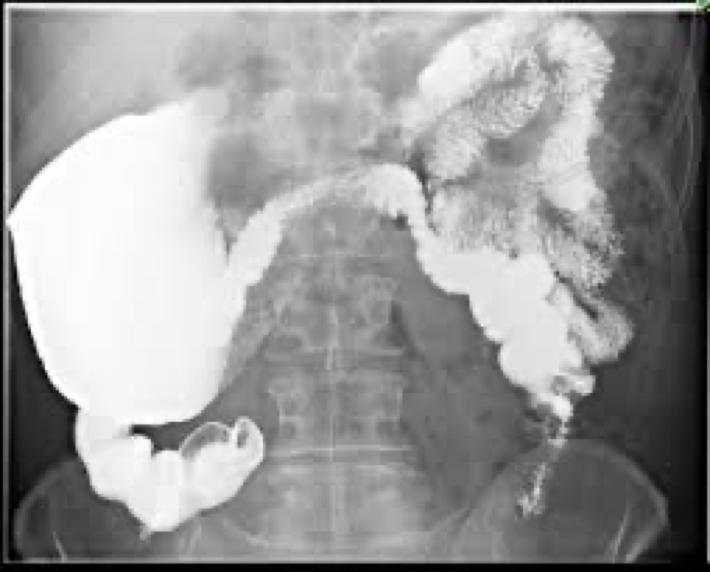
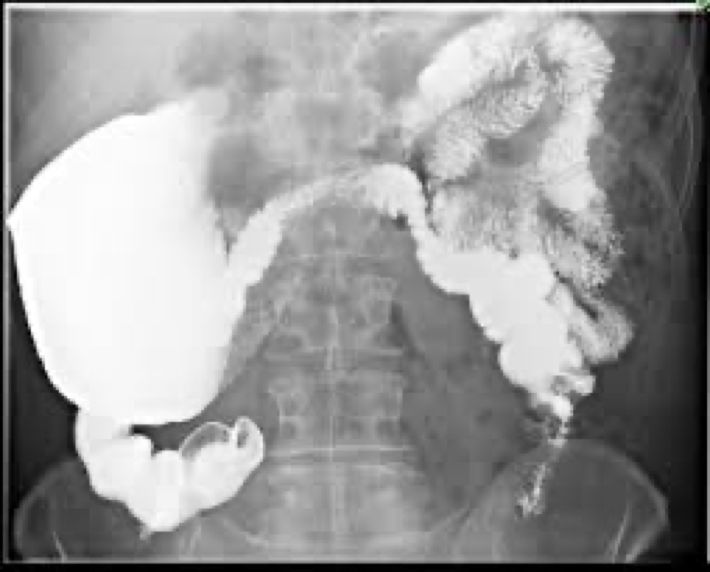
volvulus
small bowel obstruction
Distended loops filled with gas
Bowel proximal to obstruction may be filled with fluid
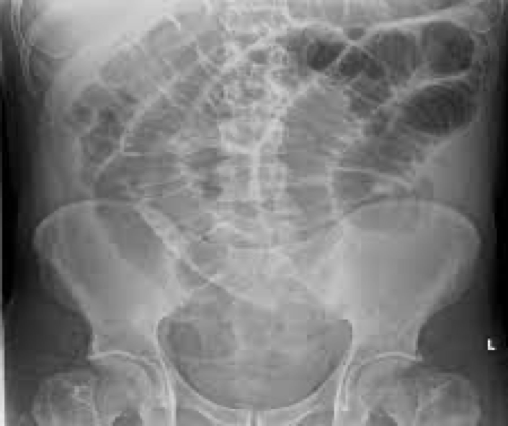
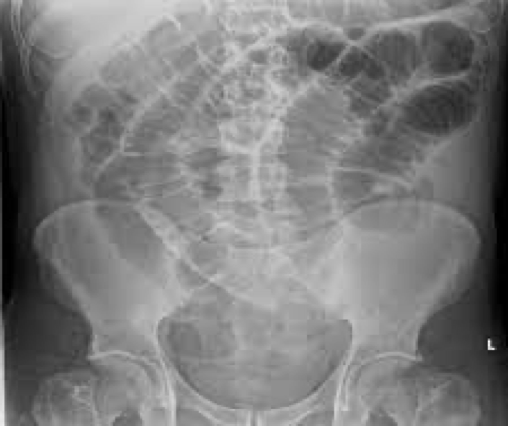
small bowel obstruction
large bowel obstruction
Massive accumulation of gas proximal to obstruction
Absence of gas distal to obstruction
High risk of bowel perforation
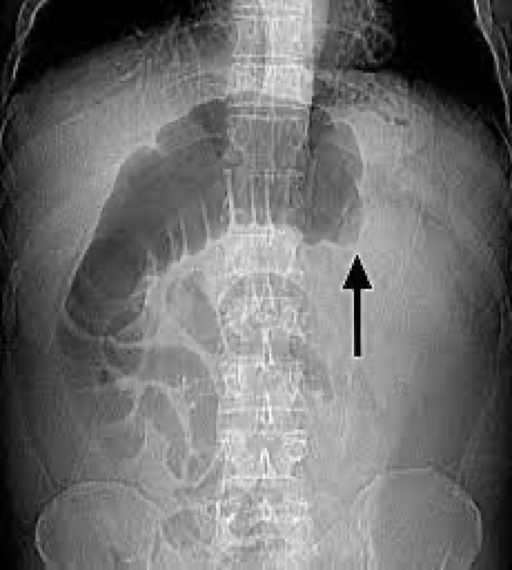
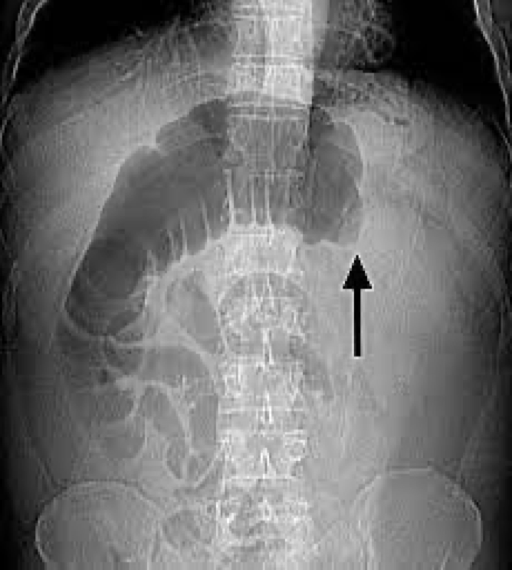
large bowel obstruction
hemorrhoids
Varicose veins of lower rectum- pain, itching, bleeding
Defect filling-look like polyps on distal rectum
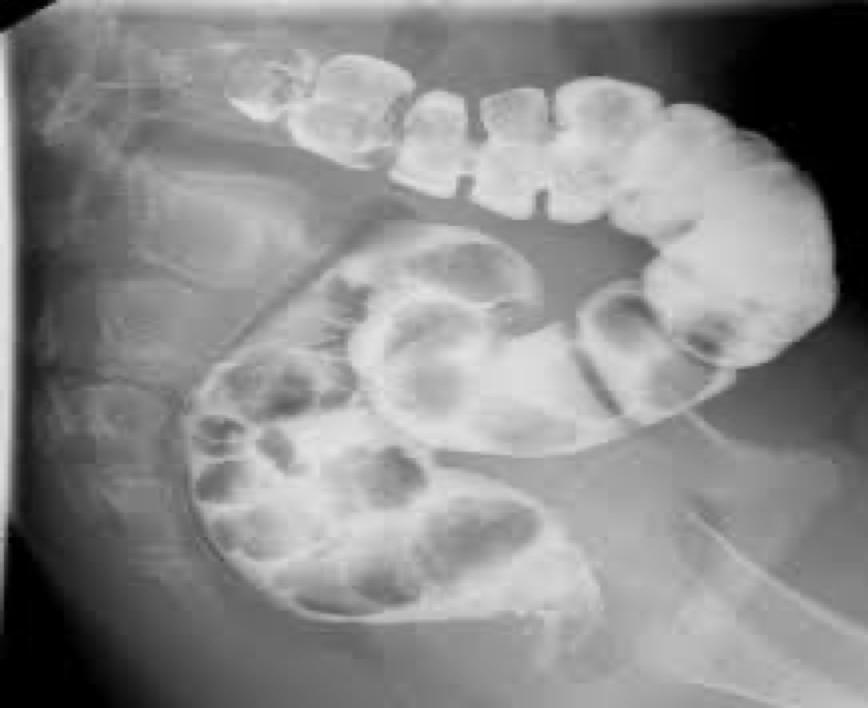
causes of hemorrhoids
increased pressure from constipation
Pelvic tumor
Pregnancy
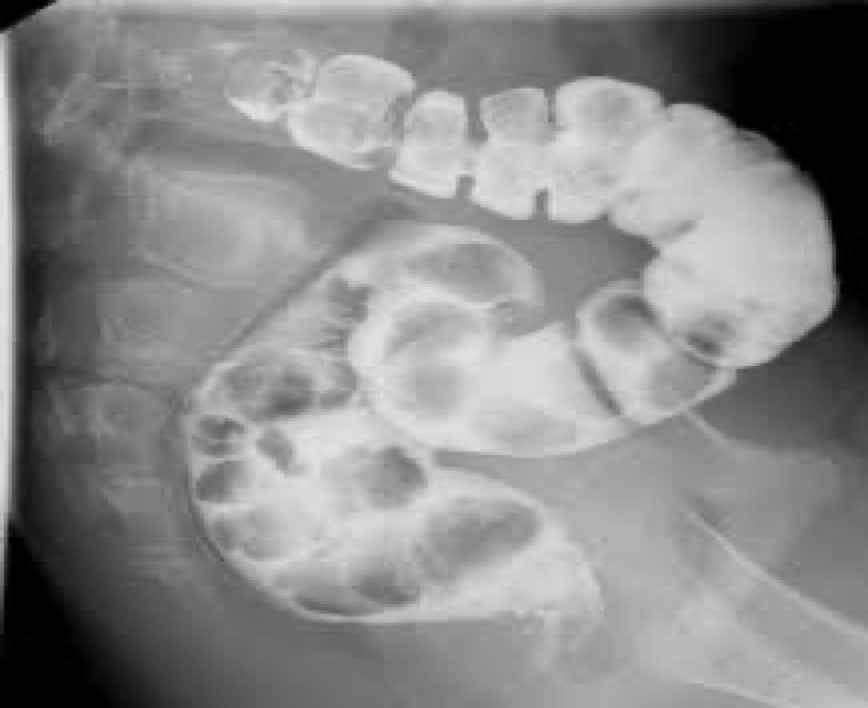
hemorrhoids
ascities
Fluid collects within abdominal spaces- between the 2 layers of peritoneum
Cause infection
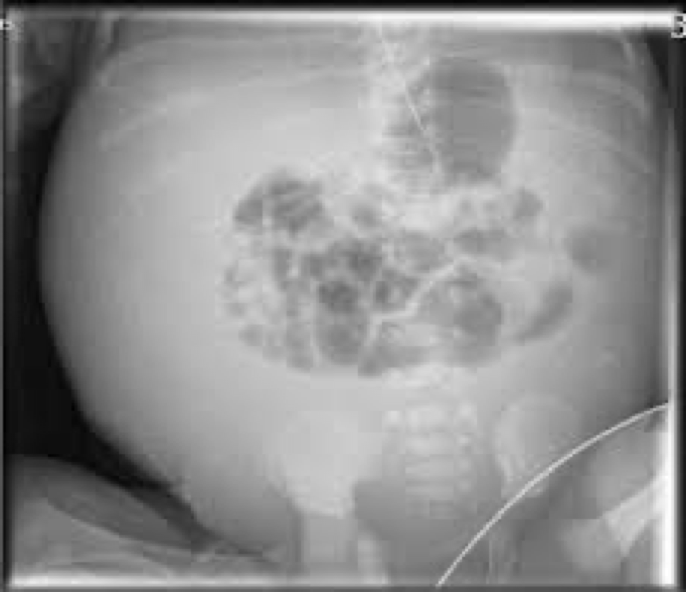
acites caused by
Usually caused by cirrhosis or other liver disease
High blood pressure can lead to leaking of fluid out of veins into abdomen
acites looks like on film
Diffusely increased density of the abdomen
Poor definition of soft tissue
Medial displacement of bowel
acites
pneumoperitoneum and what its caused by
Air trapped in the peritoneal cavity
Caused from tissue erosion, ischemia, infection, injury
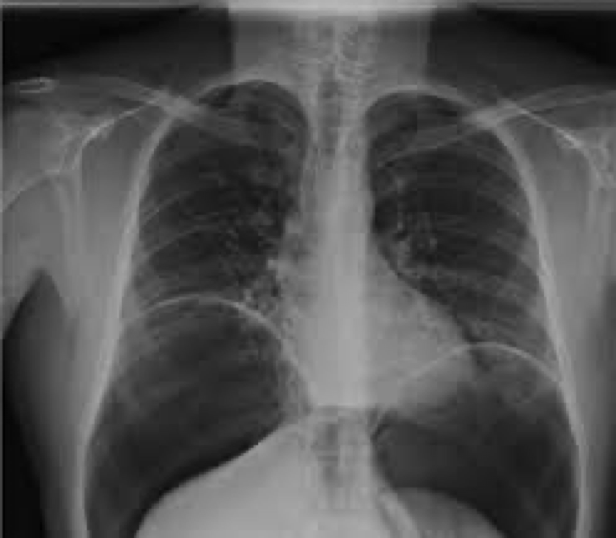
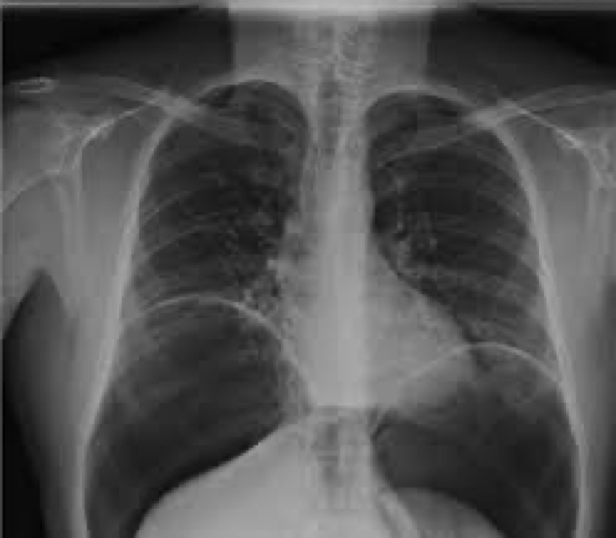
pneumoperitoneum
cholelithiasis
when it occurs
Occurs when bile doesn’t have enough bile salts and lecithin: cholesterol
Types:
Cholesterol stone- most common
Harder to penetrate
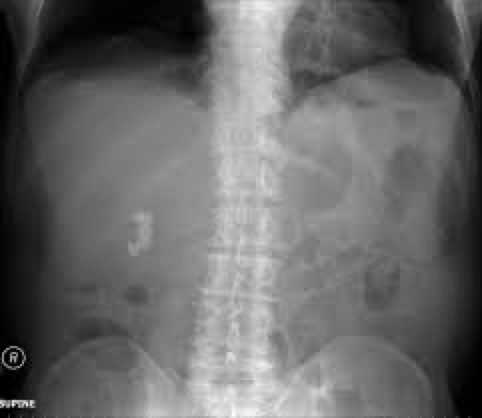
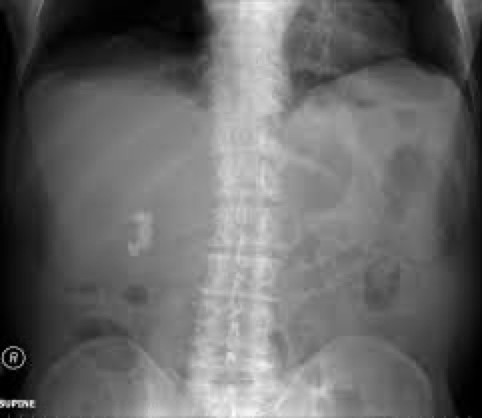
cholelithiaisis
cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder