SL Economics - Unit 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
1
New cards
Competitive Market
Where buyers and sellers carry out an independent exchange where no one individual has market power
2
New cards
Good vs Service
Goods are tangible. Services are not tangible
3
New cards
Demand
Quantities consumer is willing/able to buy at different prices
4
New cards
Law of Demand
higher price = lower demand (etc)
5
New cards
Increase Demand Graph
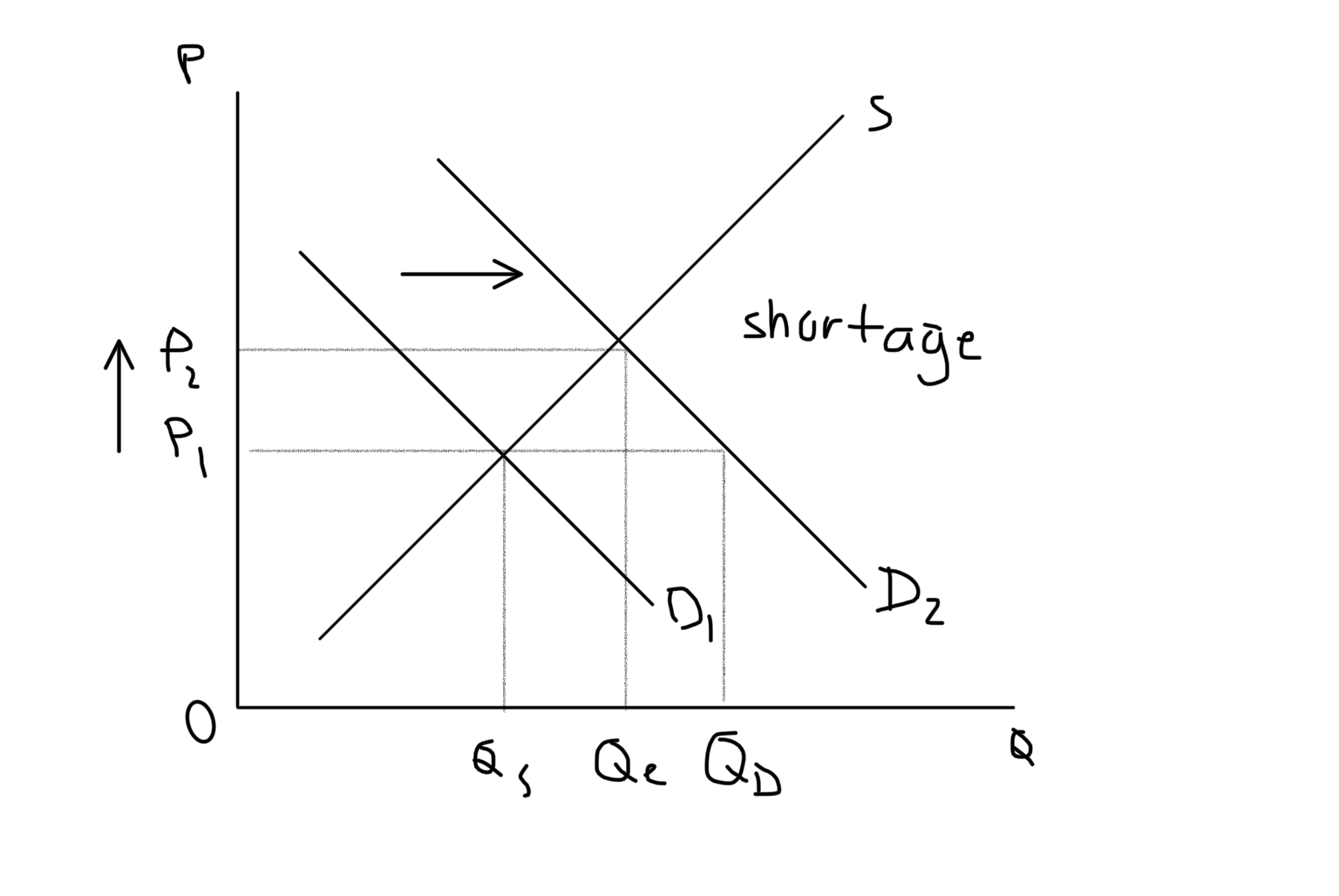
6
New cards
Decrease Demand Graph
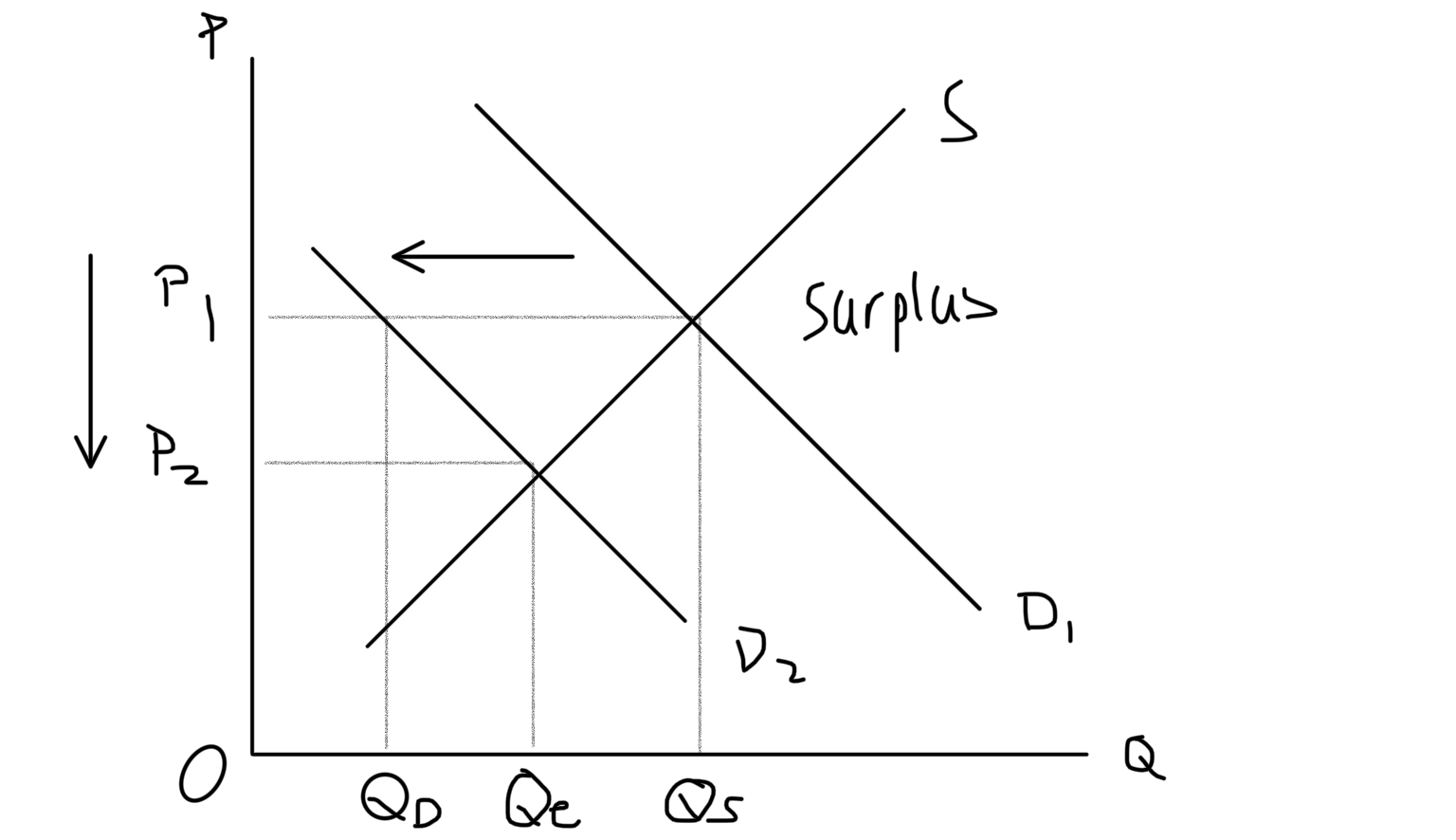
7
New cards
Aggregate vs Market
Aggregate = whole economy. Market = 1 industry
8
New cards
Non-Price Determinants of Demand
Income (normal goods↑↑/inferior goods↑↓), preferences and tastes↑↑, price of substitute goods↑↑, price of complementary goods↑↓, population↑↑
9
New cards
Increase Quantity Demand vs Increase Demand
Increase quantity demand is a movement along demand curve (has to do with price). Increase demand is a shift.
10
New cards
Supply
Quantity producer willing/able to supply at different prices
11
New cards
Law of Supply
Increase price = increase supply
12
New cards
Increase Supply Graph
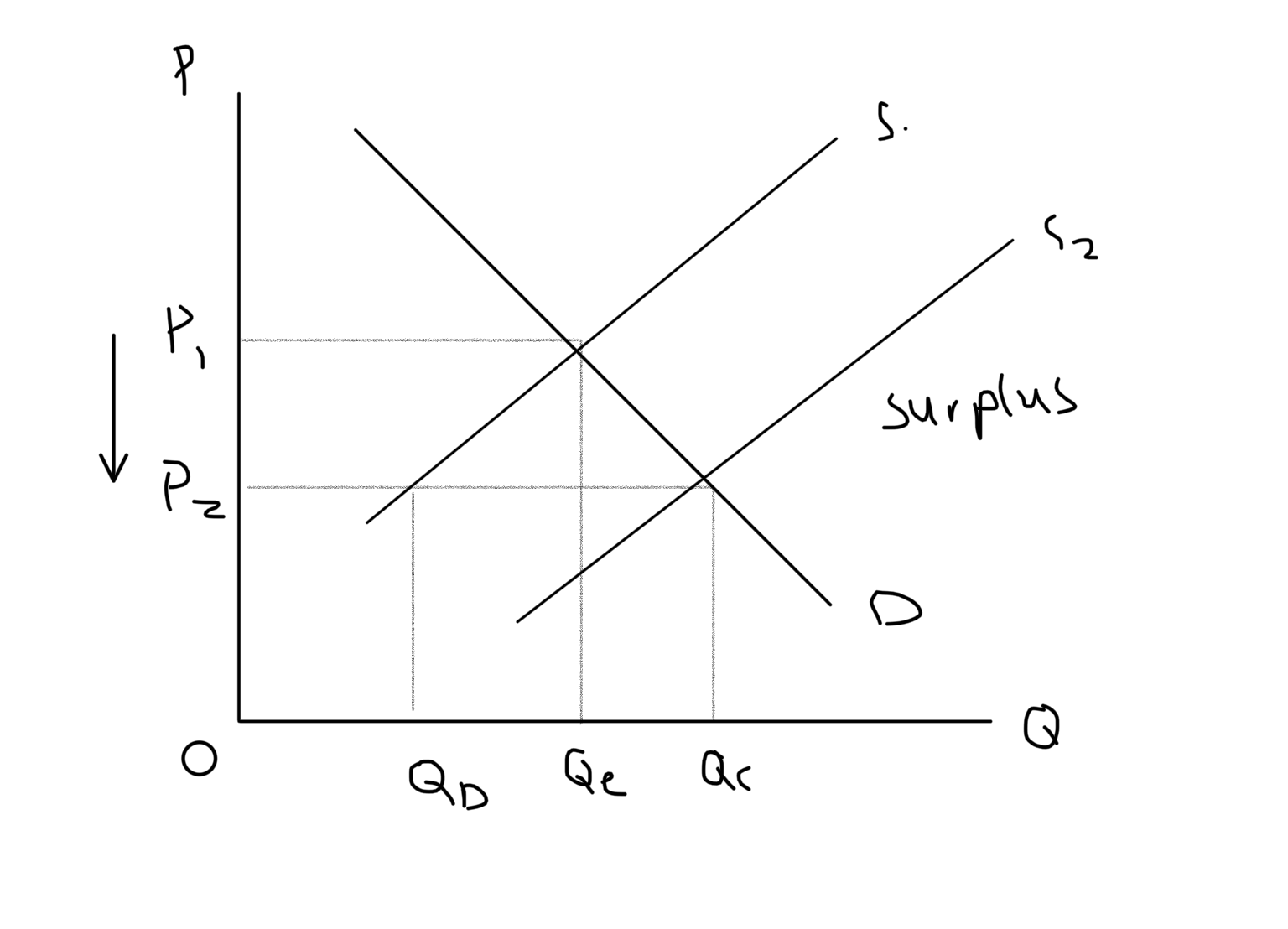
13
New cards
Decrease Supply Graph
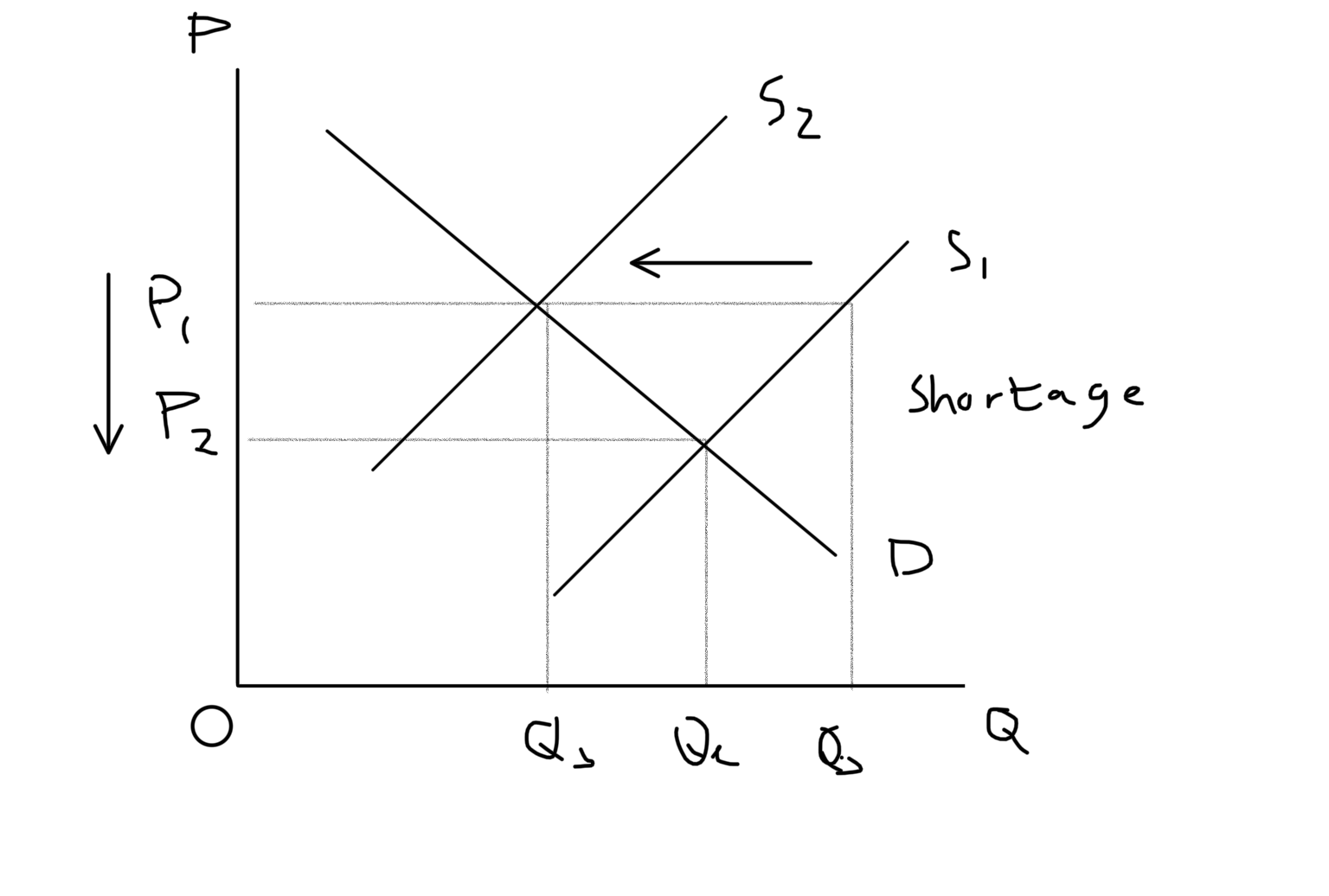
14
New cards
Non-Price Determinants of Supply
Prices of related goods (joint supply↑↑/competitive supply↑↓), government intervention (tax↑↓/subsidy↑↑), cost of resource prices ↑↓, changes in technology↑↑, price of complementary goods↑↑, producer price expectations↑↓, number of suppliers↑↑, unpredictable events↑↓
15
New cards
Market equilibrium
The intersection between demand and supply
16
New cards
Surplus
QD > QS. P > Pe. Price often drops with surplus
17
New cards
Shortage
QD < QS. P < Pe. Price often increase with shortage
18
New cards
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
Measures how much QD responds to change in price
19
New cards
Price Elastic (Demand)
Demand is highly responsive to change in price (PED > 1)
20
New cards
Price Inelastic (Demand)
Demand not very responsive to change in price (PED < 1)
21
New cards
PED Formula
| (Qf-Qi / Qi) / (Pf-Pi / Pi) | or | %ΔQD / %ΔP|
22
New cards
Price Elastic Demand Graph
\
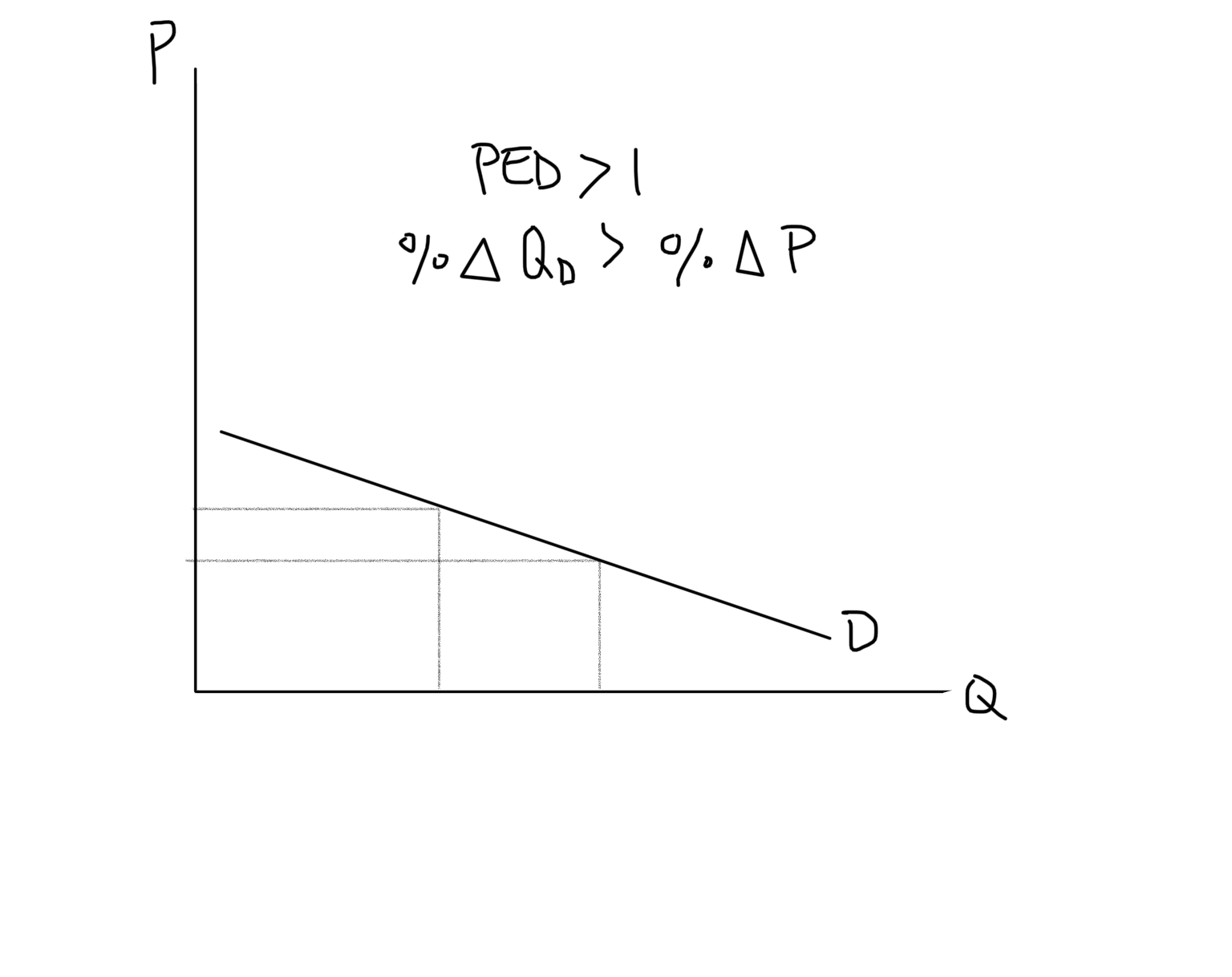
23
New cards
Price Inelastic Demand Graph
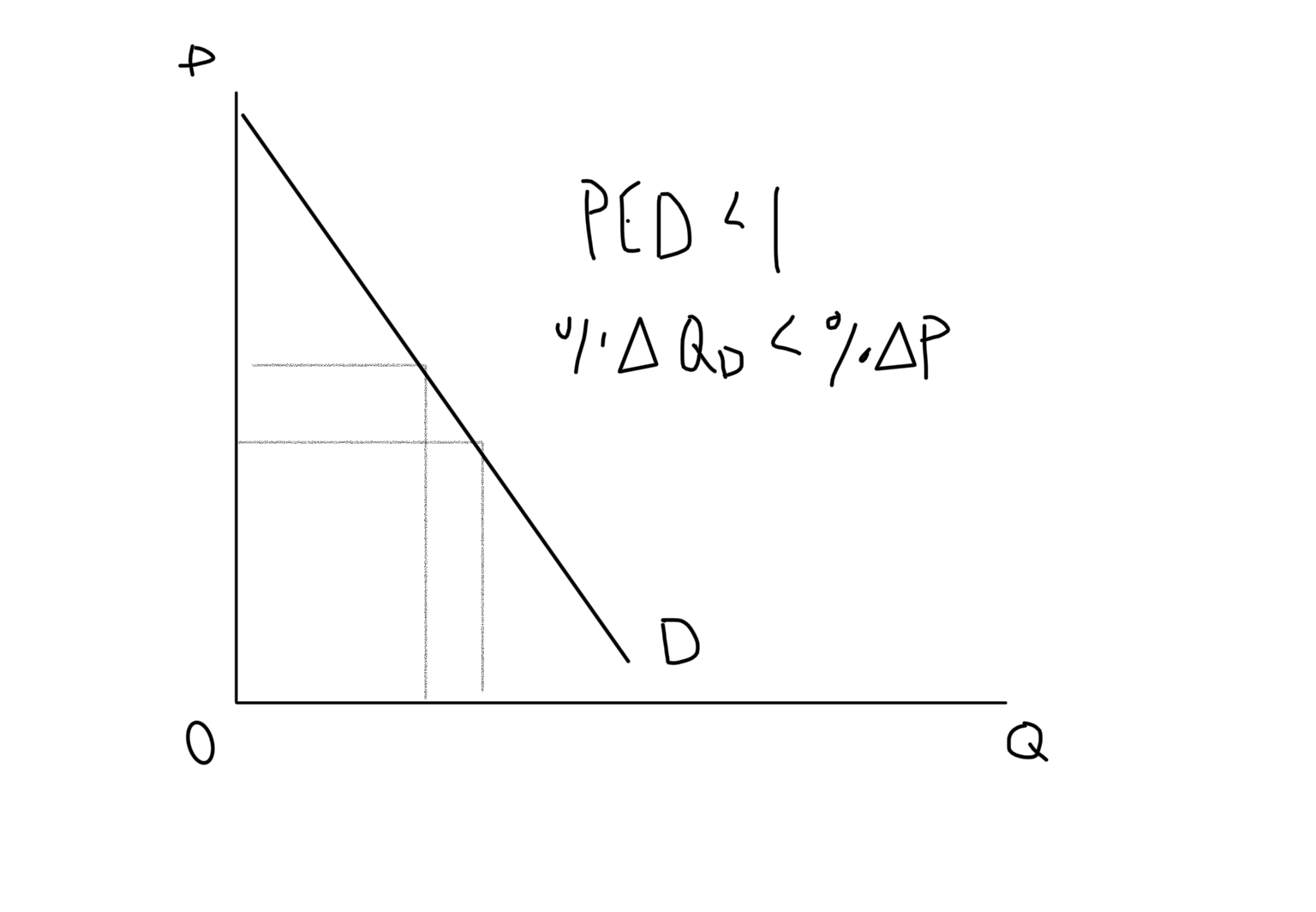
24
New cards
Unit Elastic Demand Graph
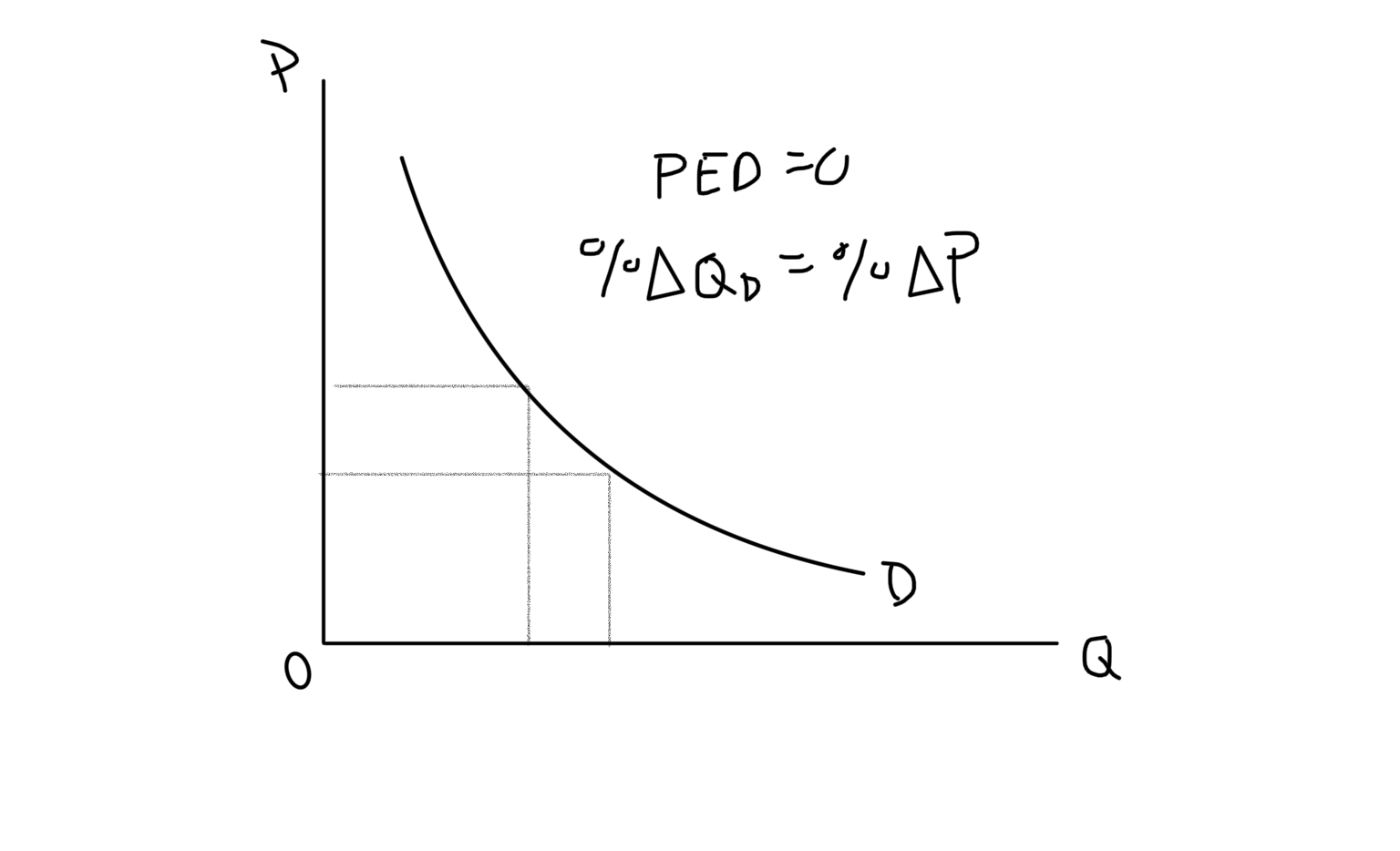
25
New cards
Perfectly Elastic Demand Graph
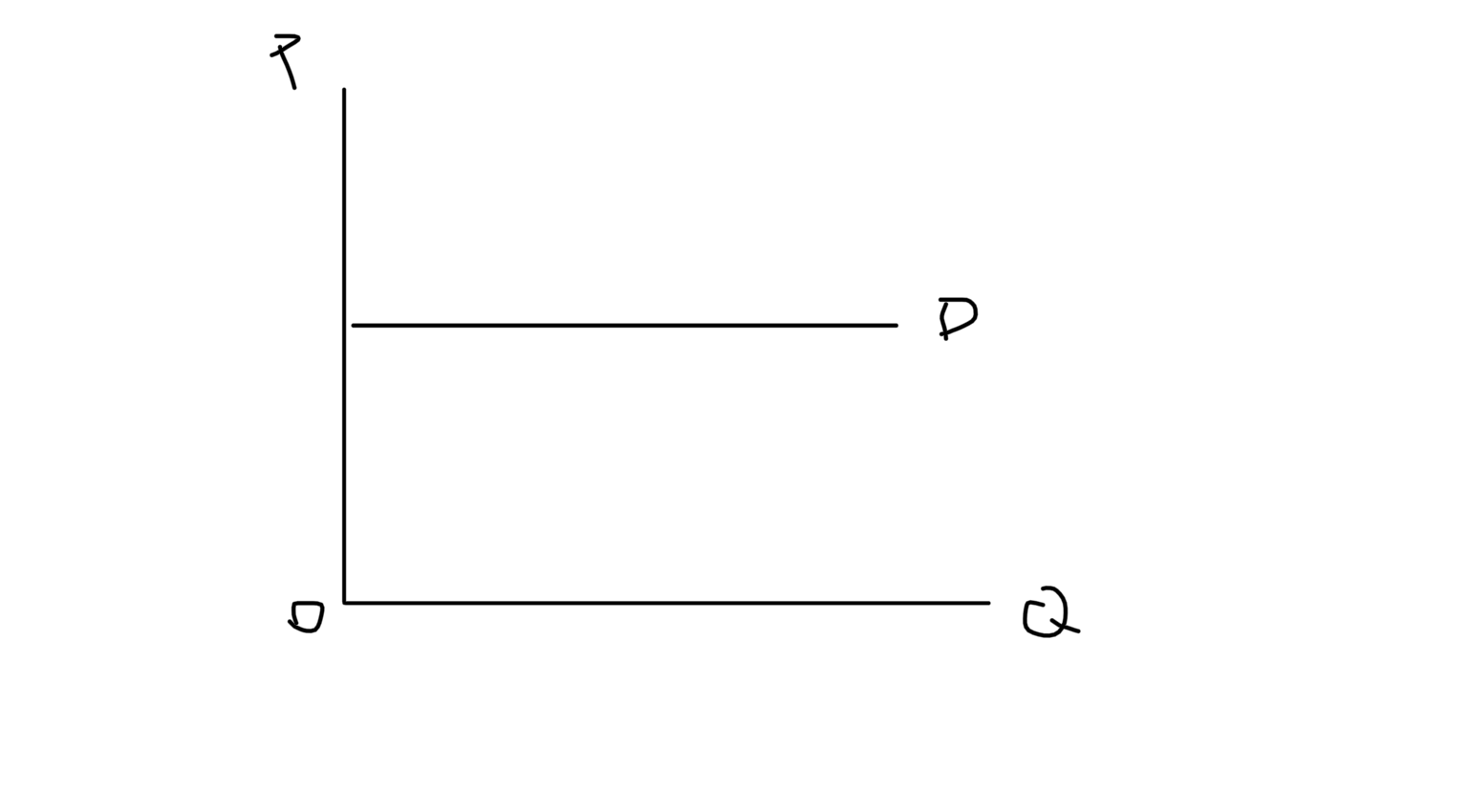
26
New cards
Perfectly Inelastic Demand Graph
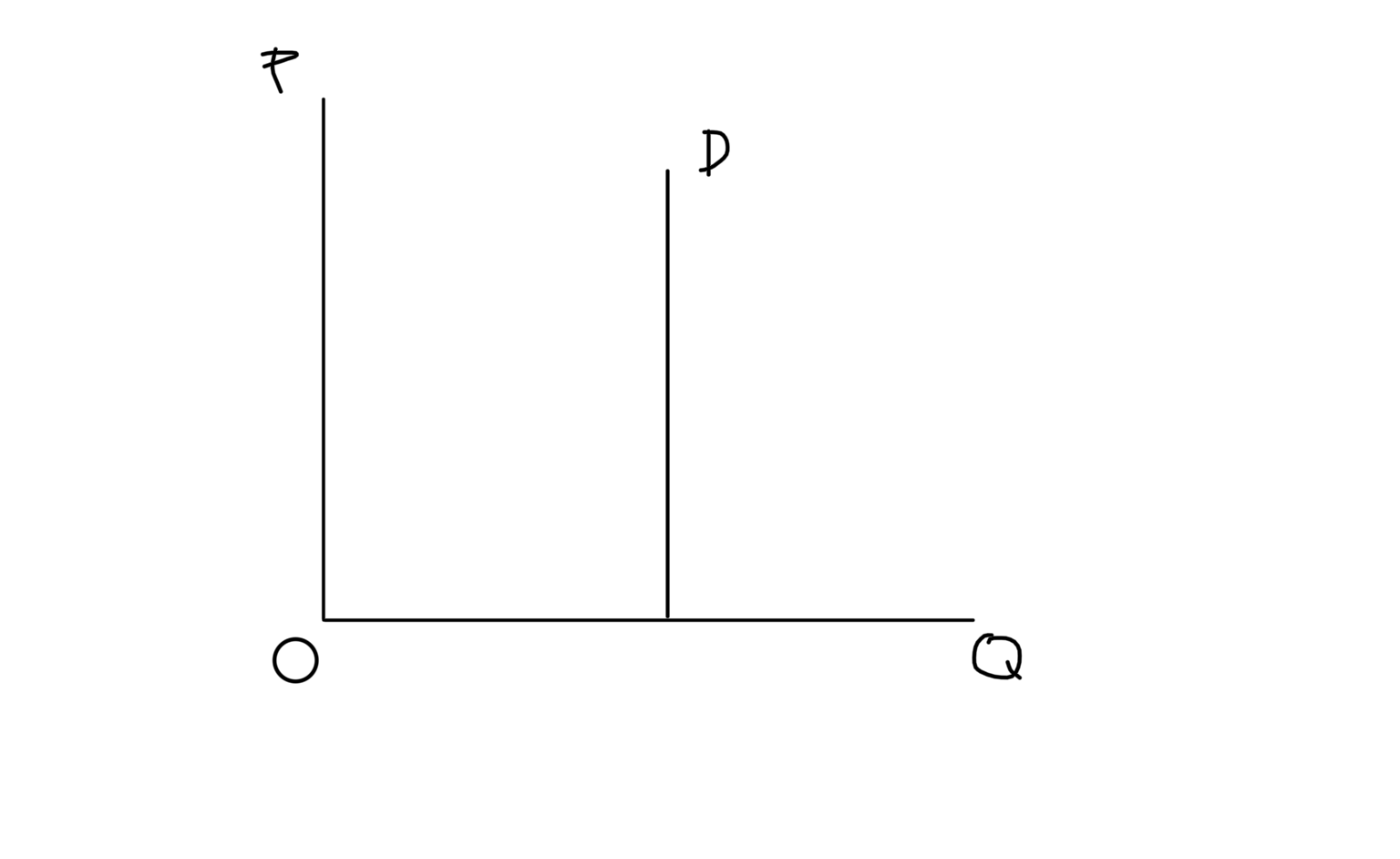
27
New cards
Determinants of PED
Number of substitutes, closeness of substitutes, necessities vs luxuries, length of time, proportion of income spent
28
New cards
Calculate total revenue
TR = QS x QD
29
New cards
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)
How much demand responds to change in income
30
New cards
YED Formula
(Df-Di / Di) / (Yf-Yi / Yi) or | %ΔQD / %ΔY|
31
New cards
YED > 0 (positivie)
Demand for normal good
32
New cards
YED < 0 (negative)
Demand for inferior good
33
New cards
0 < YED
Income elastic demand (necessities)
34
New cards
YED > 1
income inelastic demand (luxuries)
35
New cards
YED Shifts in Demand Graph
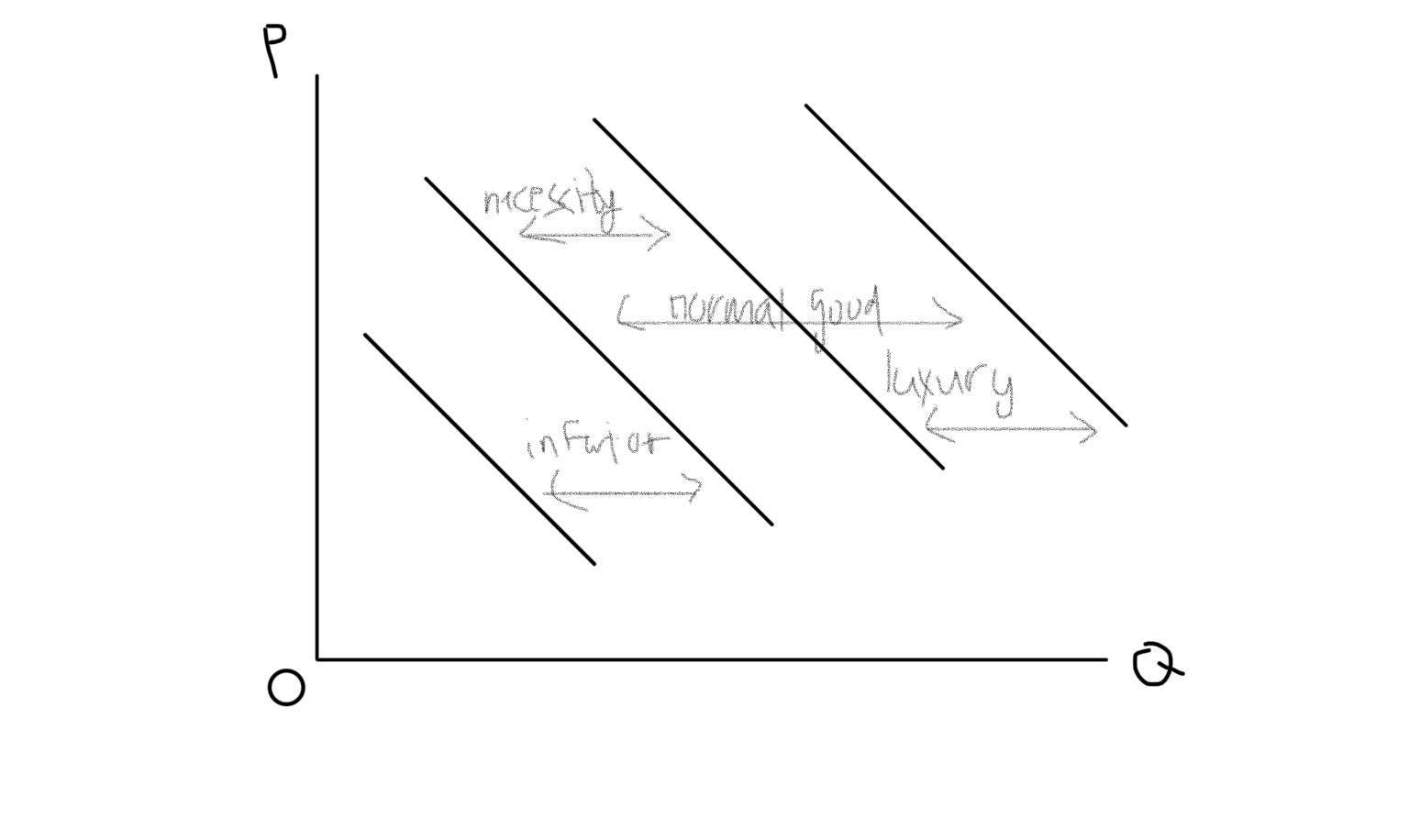
36
New cards
Engel Curve
As you get rich, changes in income don’t affect you as much. Graph looks like a spiral
37
New cards
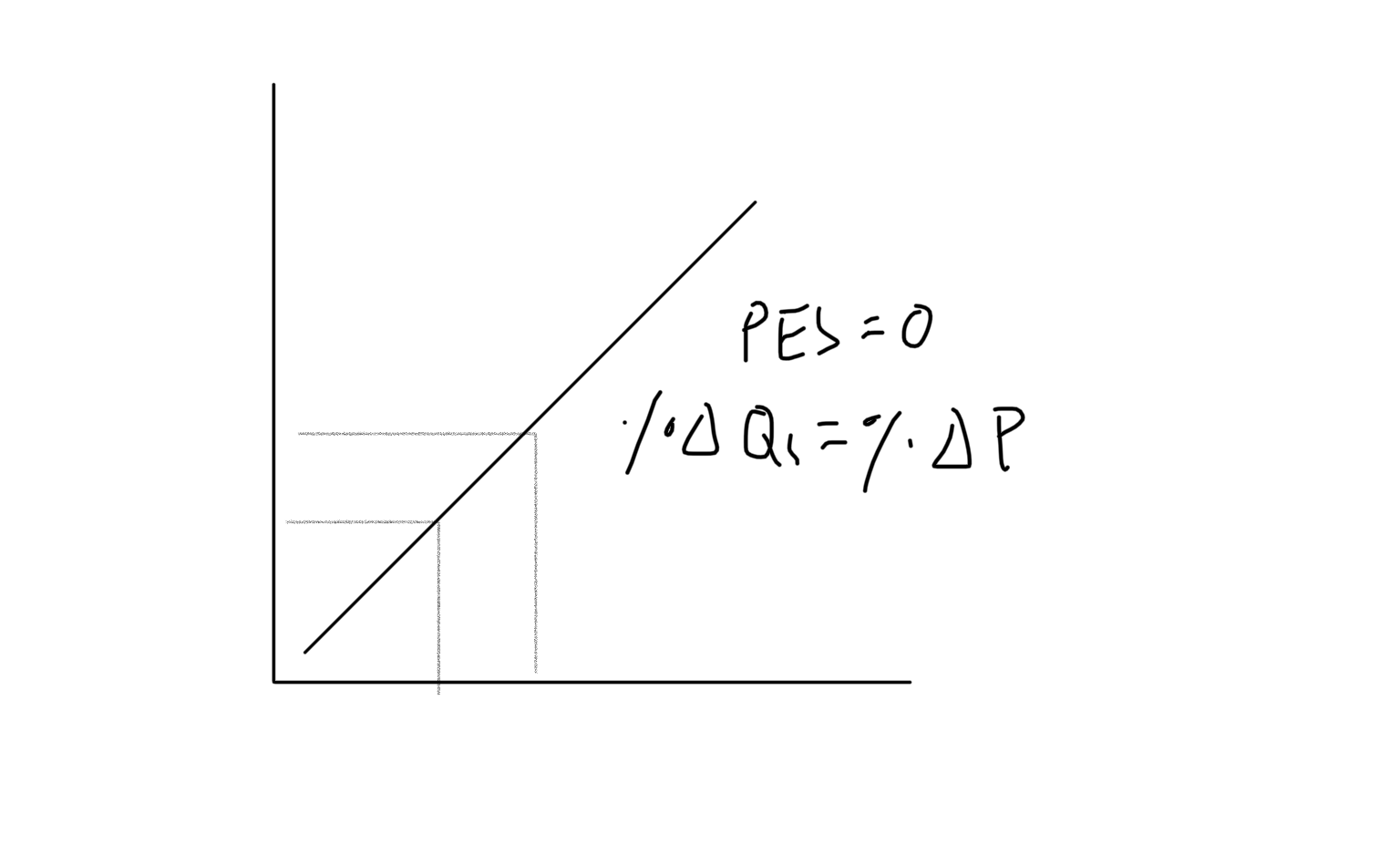
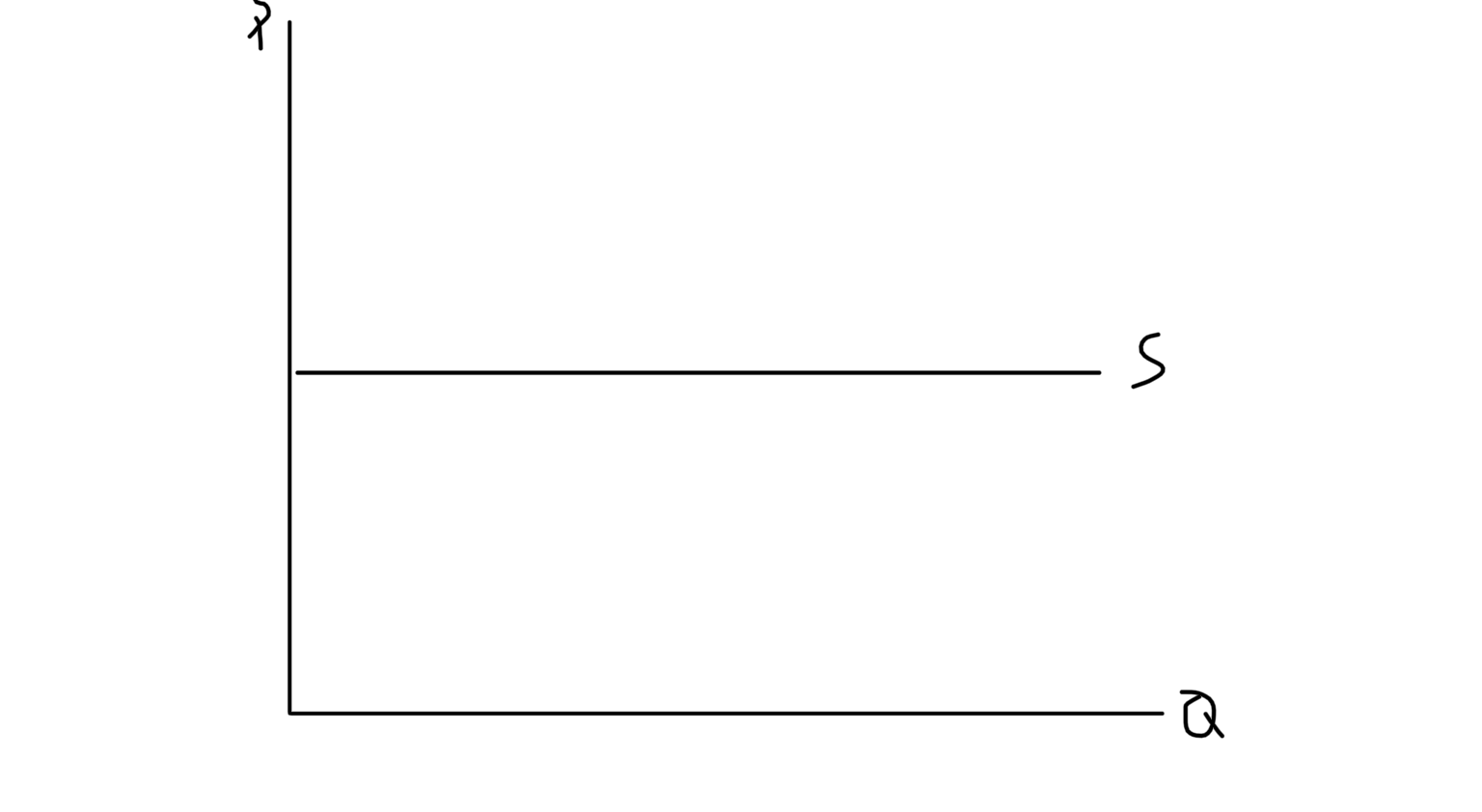
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES)
How much quantity supplied responds to change in price
38
New cards
Price Elastic (Supply)
Supply is highly responsive to change in price (PES > 1)
39
New cards
Price Inelastic
Supply is not very responsive to change in price (PES < 1)
40
New cards
PES Formula
(Qf-Qi / Qi) / (Pf-Pi / Pi) or or %ΔQD / %ΔP
41
New cards
Price Inelastic Supply Graph
\
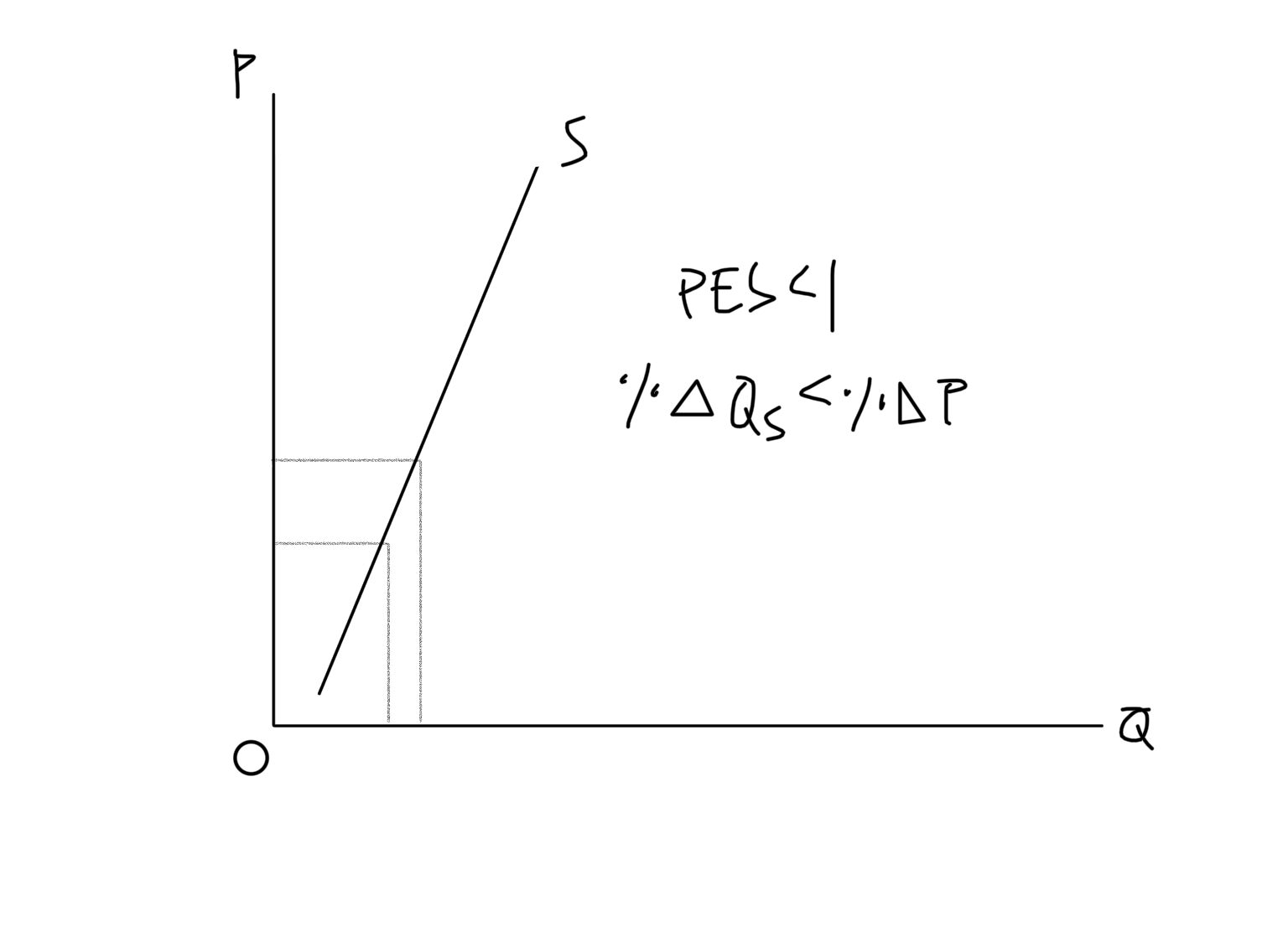
42
New cards
Price Elastic Supply Graph
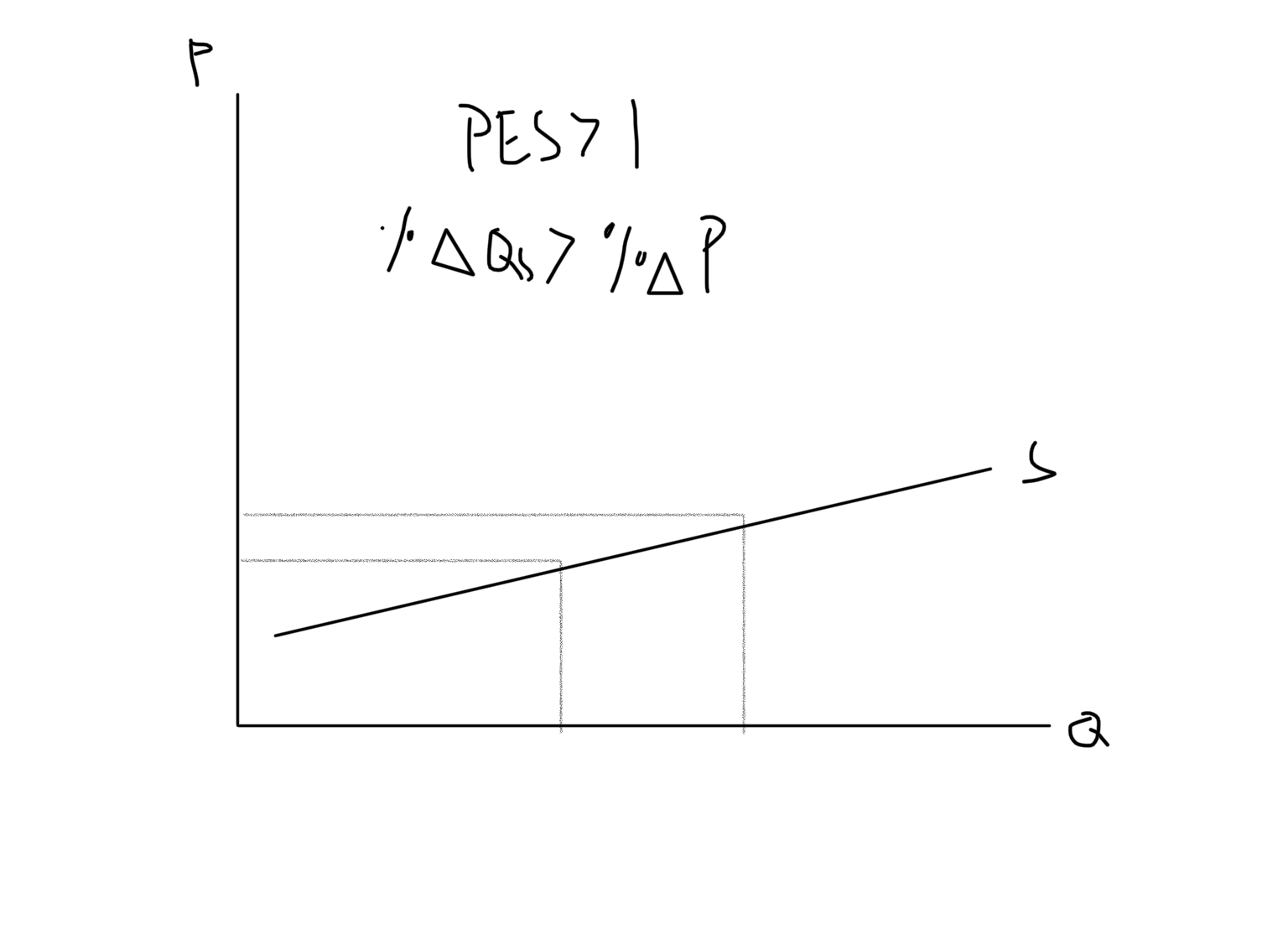
43
New cards
Unit Elastic Supply Graph
44
New cards
Perfectly Elastic Supply
45
New cards
Perfectly Inelastic
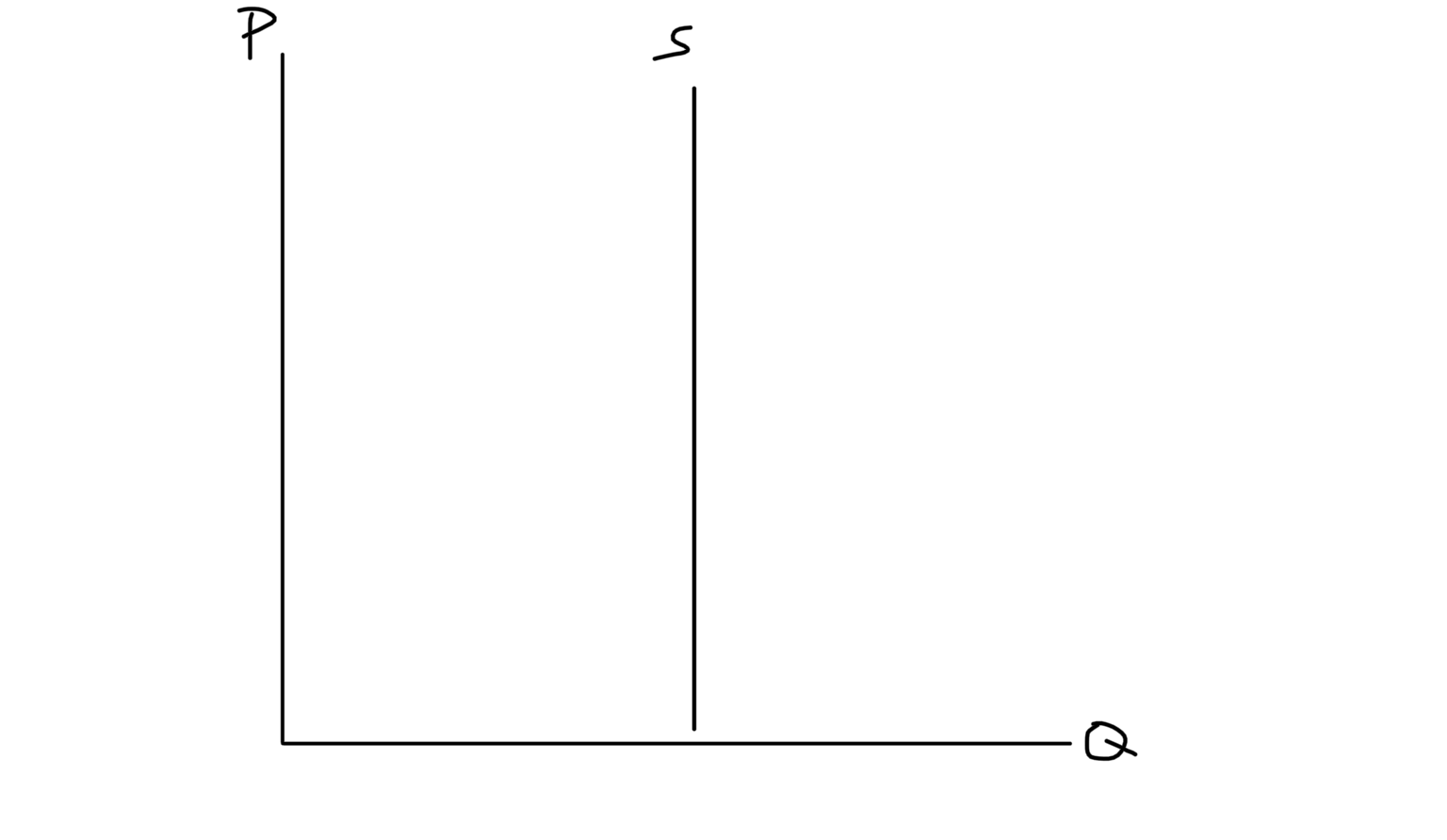
46
New cards
Determinants of PES
Length of time↑↑, mobility of factors of production ↑↑, spare capacity of firms↑↑, Access to inventory ↑↑, rate at which costs increase, ↑↓
47
New cards
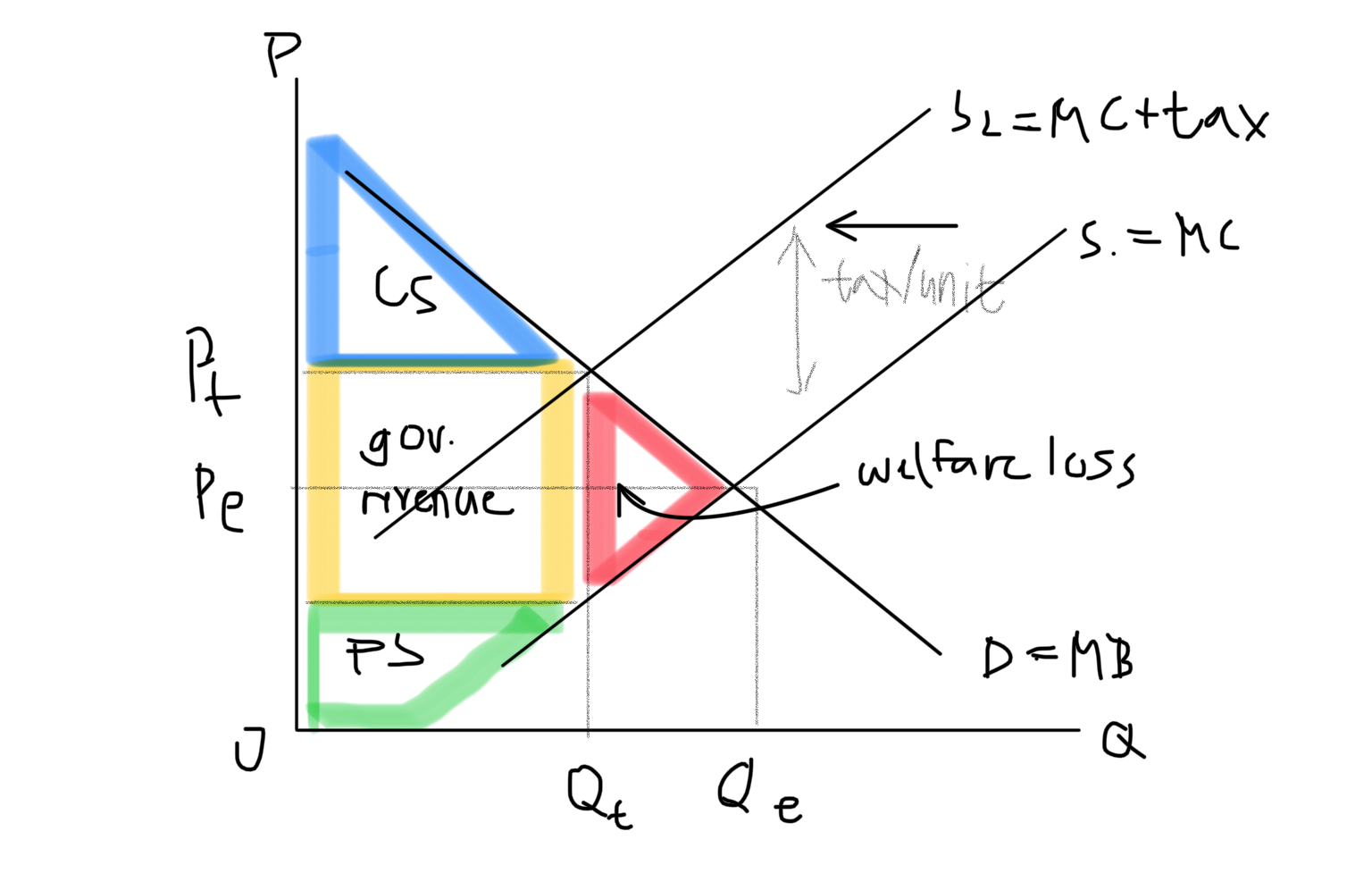
Indirect Tax Graph
48
New cards
Government Legislation Graph
Same as indirect tax
49
New cards
Price Floor Graph
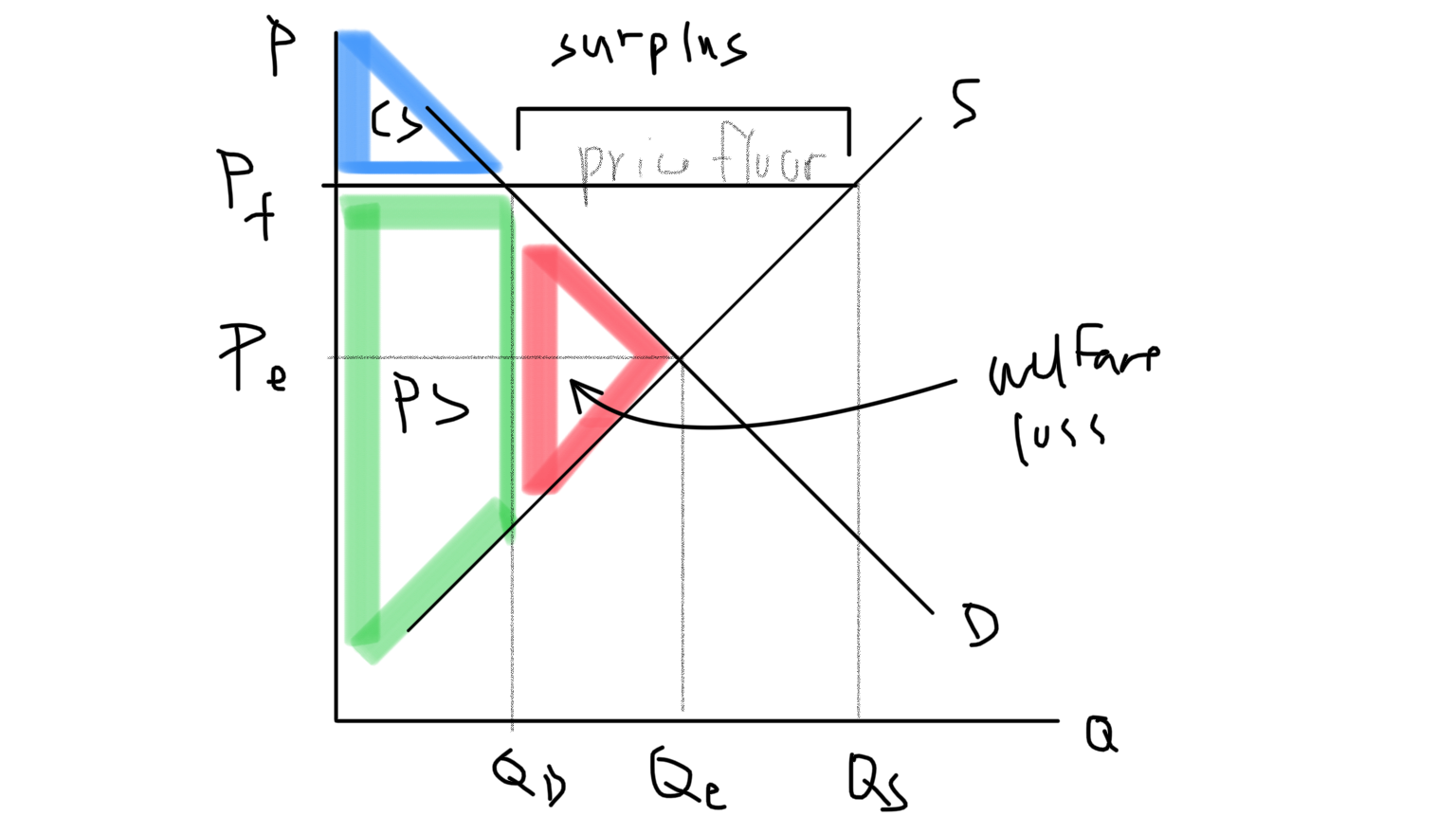
50
New cards
Price Ceiling Graph
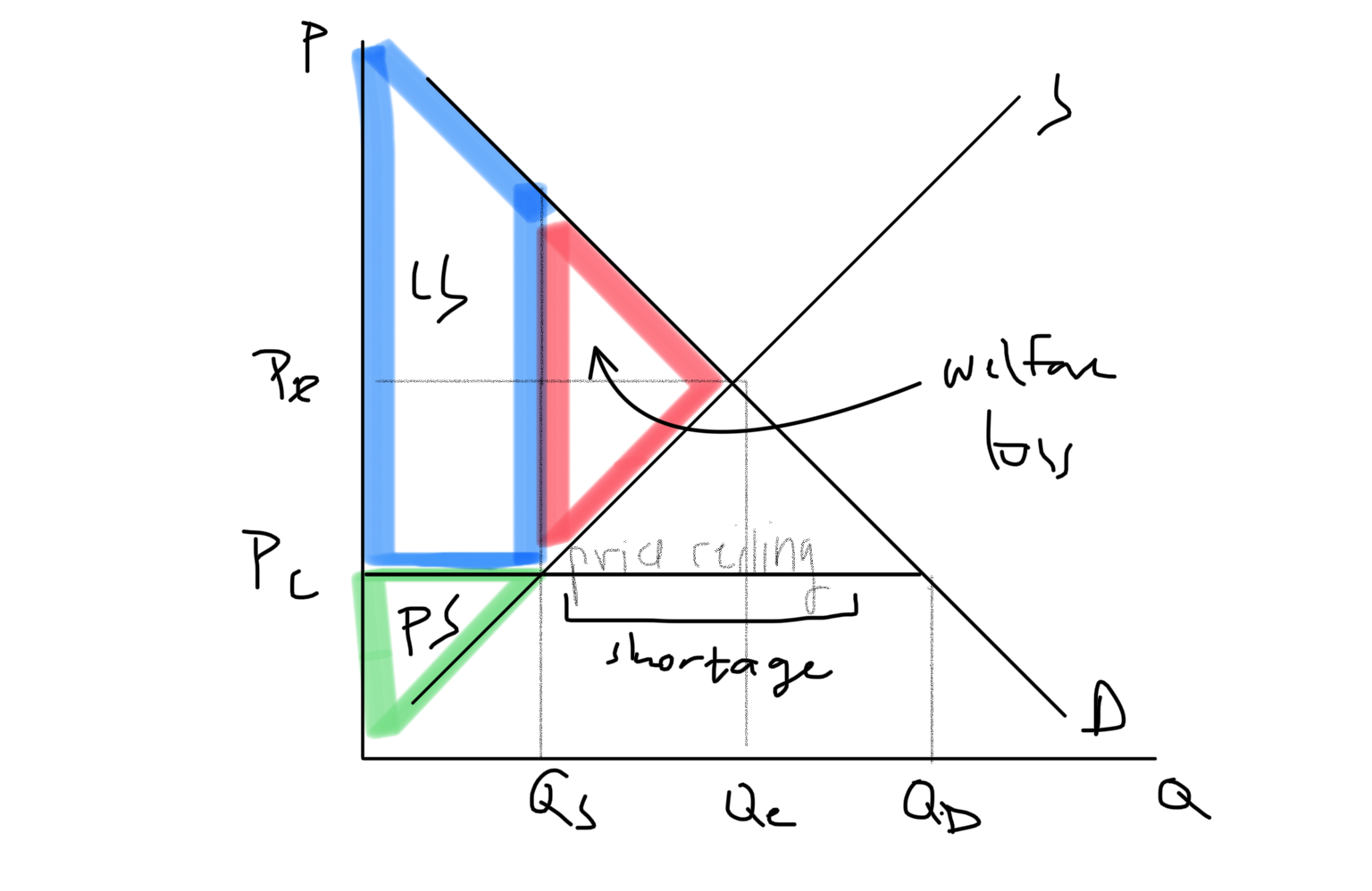
51
New cards
Subsidies Graph

52
New cards
Negative Production Externality Graph
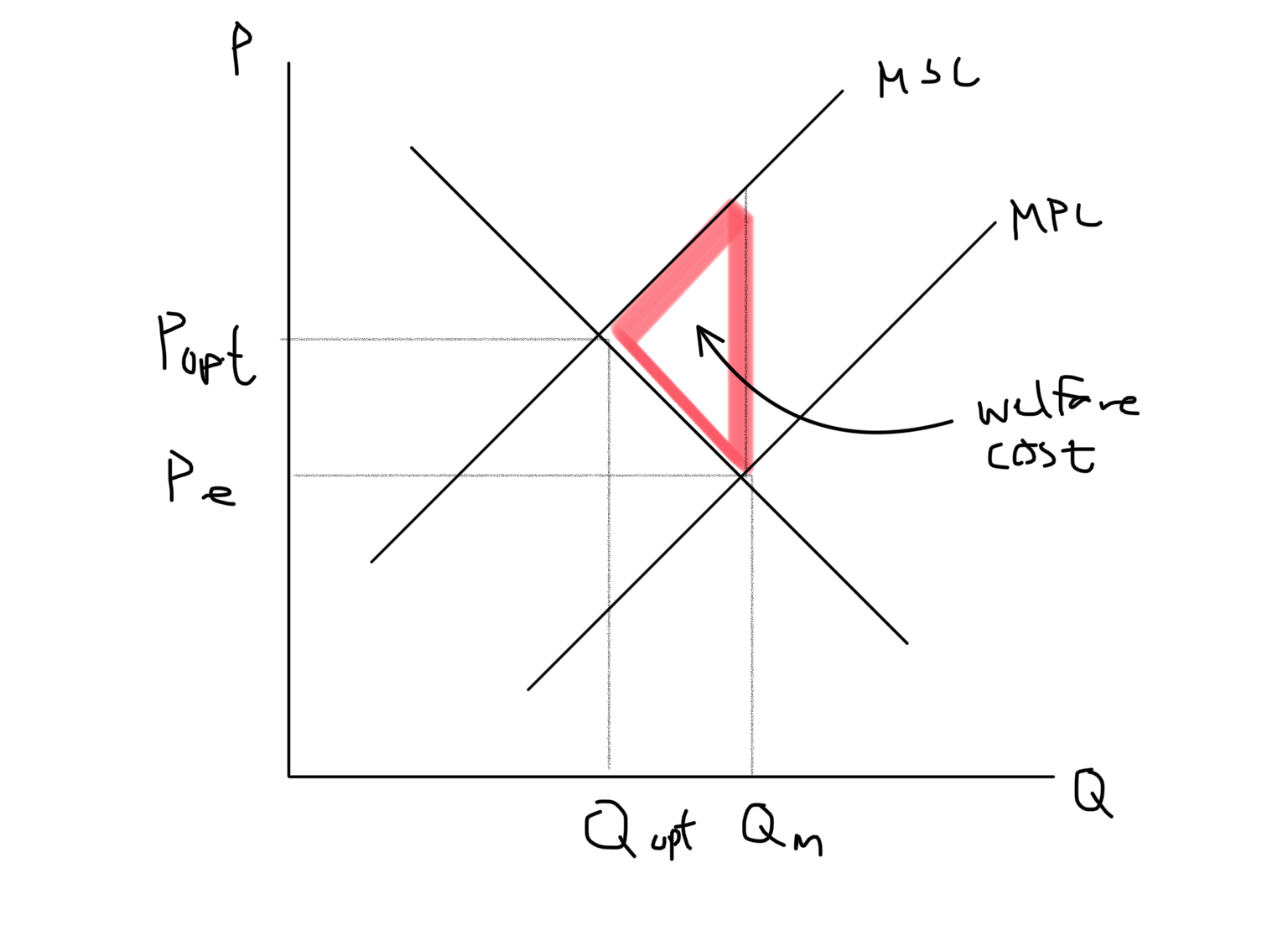
53
New cards
Indirect Tax Externality Graph

54
New cards
Carbon Tax Graph
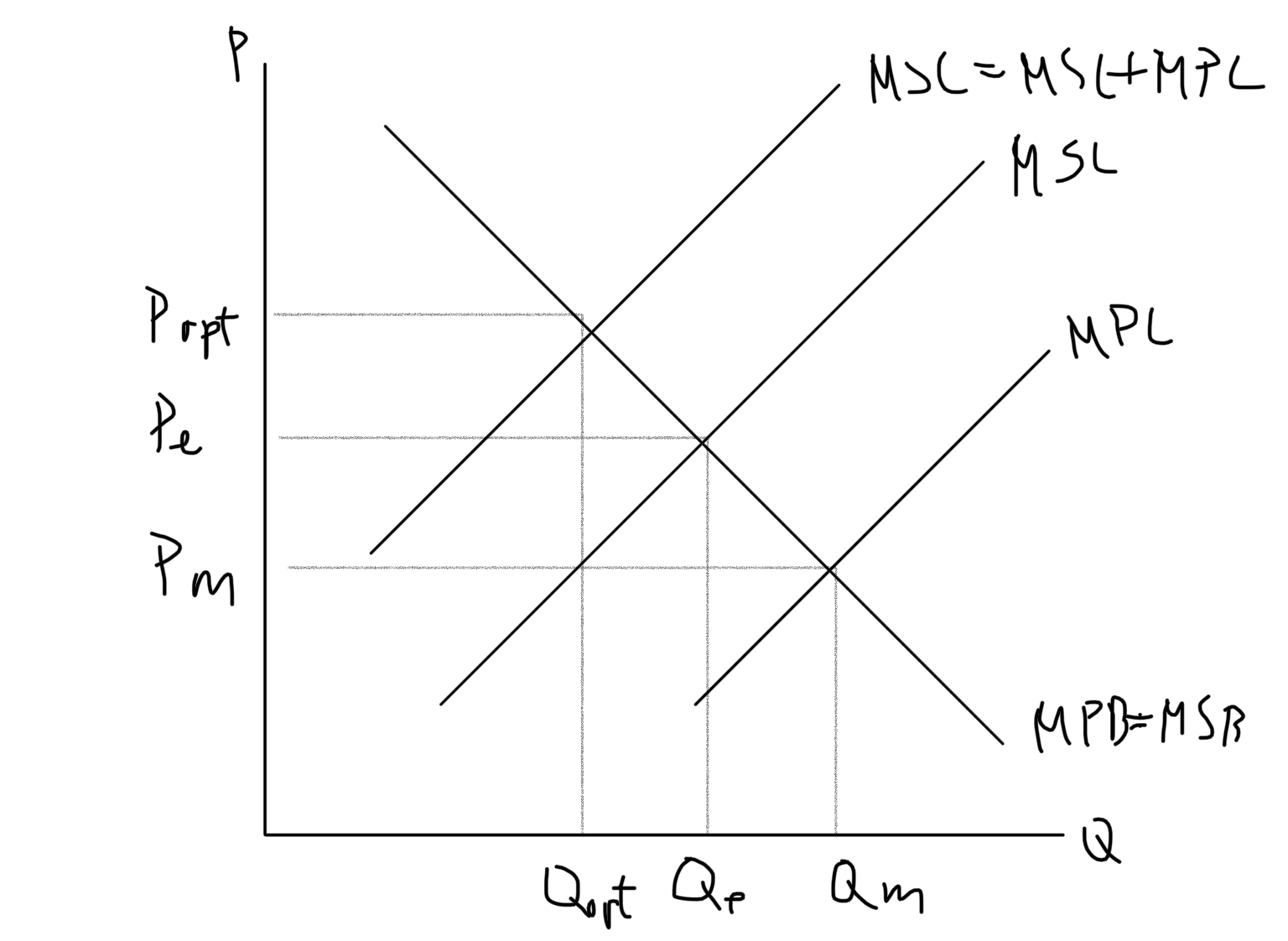
55
New cards
Traceable Permits Graph
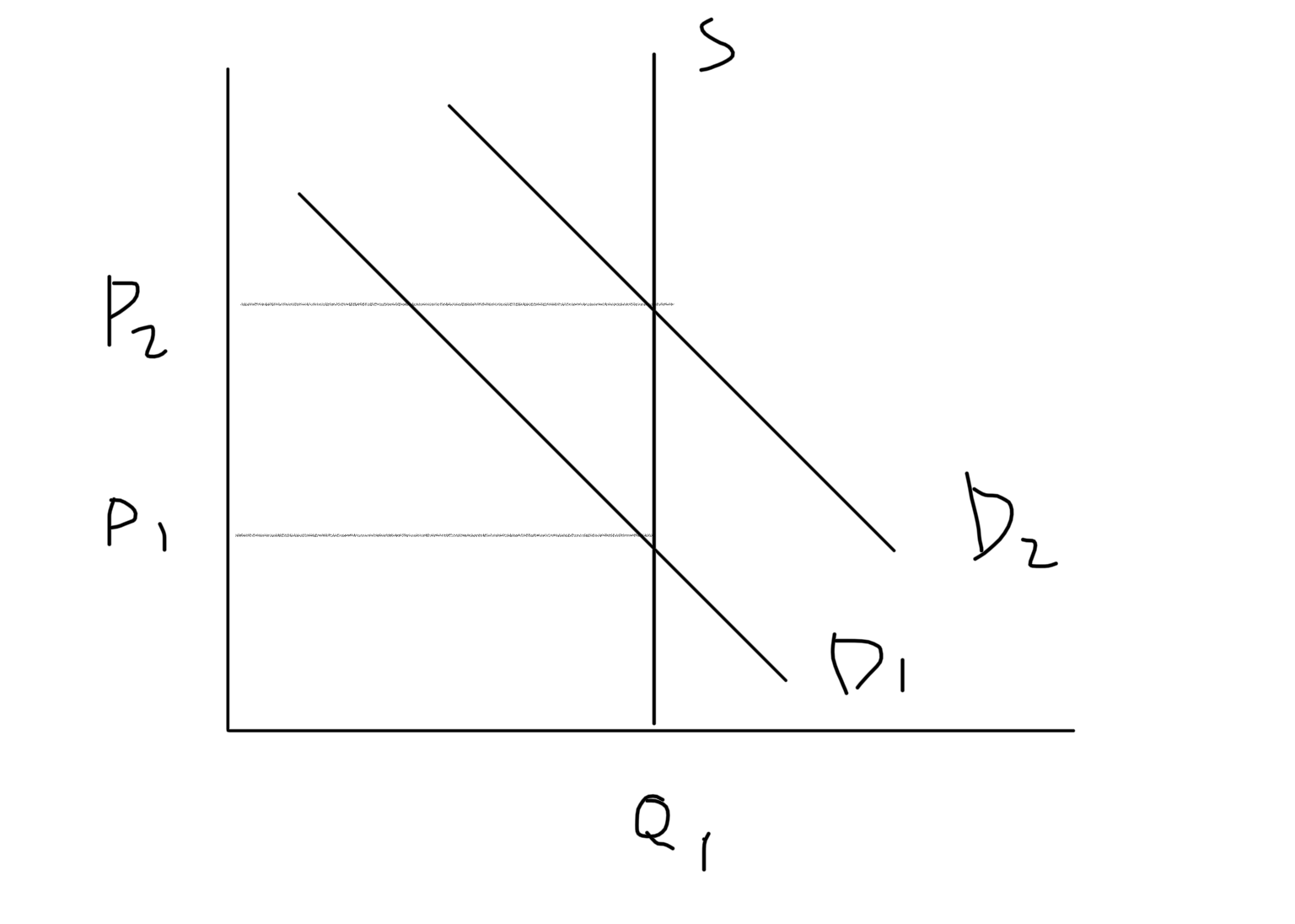
56
New cards
Common pool resource
Resources not owned by anyone. Rivalrous (If I take some, less for you) and non-excludable. Examples: air, river, forest
57
New cards
Tragedy of the commons
Herders share field for cattle. As herd grows, grass decreases. Eventually there is no more grass.
58
New cards
Marginal cost (MC)
Cost to producers of producing goods.
59
New cards
2 Types of marginal cost
Marginal private cost (MPC): cost to private firm/producers
Marginal social cost (MSC): cost to society
Marginal social cost (MSC): cost to society
60
New cards
Marginal benefit (MB)
Benefit to consumers for consuming goods
61
New cards
2 Types of marginal benefit
Marginal private benefit (MPB): benefits go to private individuals
Marginal societal benefit (MSB): benefits for society
Marginal societal benefit (MSB): benefits for society
62
New cards
Social surplus
Sum of consumer and consumer surplus
63
New cards
Externality
When actions of consumers/producers causes positive/negative side effects to third parties
64
New cards
2 types of positive externalities
Positive production externality: external benefit created by producers (research, new tech)
Positive consumption externality: external benefits created by consumers (education)
Positive consumption externality: external benefits created by consumers (education)
65
New cards
2 types of negative externalities
Negative production externality: external costs created by producers (pollution)
Negative consumption externality: external costs created by consumers (smoking)
Negative consumption externality: external costs created by consumers (smoking)
66
New cards
Carbon tax
Tax per unit of carbon emissions of fossil fuels
67
New cards
Tradable permits
Permits to pollute issued by gov. which can be bought and traded
68
New cards
Collective self-governance
Solution to common pool resources where consumers choose to use sustainably
69
New cards
Market failure
Overallocation/provision: QS > QD
Under-allocation/provision: QS > QD
Not always bad as it signals areas to be corrected
Under-allocation/provision: QS > QD
Not always bad as it signals areas to be corrected
70
New cards
Policies to correct negative production externality
Indirect taxes, carbon taxes, tradable permits, gov. legislation/regulation, education and awareness creation, collective self-governance
71
New cards
Advantages of market-based policies
* Can internalize externalities where costs are covered by producers and consumers
* Taxation on emission = less pollution/cost
* Taxation on emission = less pollution/cost
72
New cards
Disadvantages of market-based policies
* May be impractical (calculating amount of emission is hard)
* Technical limitations
* Technical limitations
73
New cards
Advantages of government legislation and regulations
* Easier to implement
* Can avoid technical difficulties
* Highly effective
* Can avoid technical difficulties
* Highly effective
74
New cards
Disadvantages of government legislation and regulations
* More costly as no gov. revenue
* Can still face technical difficulties
* Cost involving monitoring regulations
* Can still face technical difficulties
* Cost involving monitoring regulations
75
New cards
Advantages of self-governance
* Sustainability without private or government ownership
76
New cards
Disadvantages of self-governance
* Unlikely
* Much communication needed
* Much communication needed
77
New cards
Education and awareness creation advantages
* Part of “natural” free market system
78
New cards
Education and awareness creation disadvantages
* May not be effective
* Difficult to measure
* Difficult to measure
79
New cards
Positive production externality and graph
* External benefits created by producers
* MSC < MPC
* MPC – MSC = external benefit
* MSC < MPC
* MPC – MSC = external benefit

80
New cards
Direct government provision externality
* Positive production externality
* Direct government provision to producers to continue to continue to produce goods/services
* Can be capital or resources
* Direct government provision to producers to continue to continue to produce goods/services
* Can be capital or resources
81
New cards
Direct government provision externality graph?????
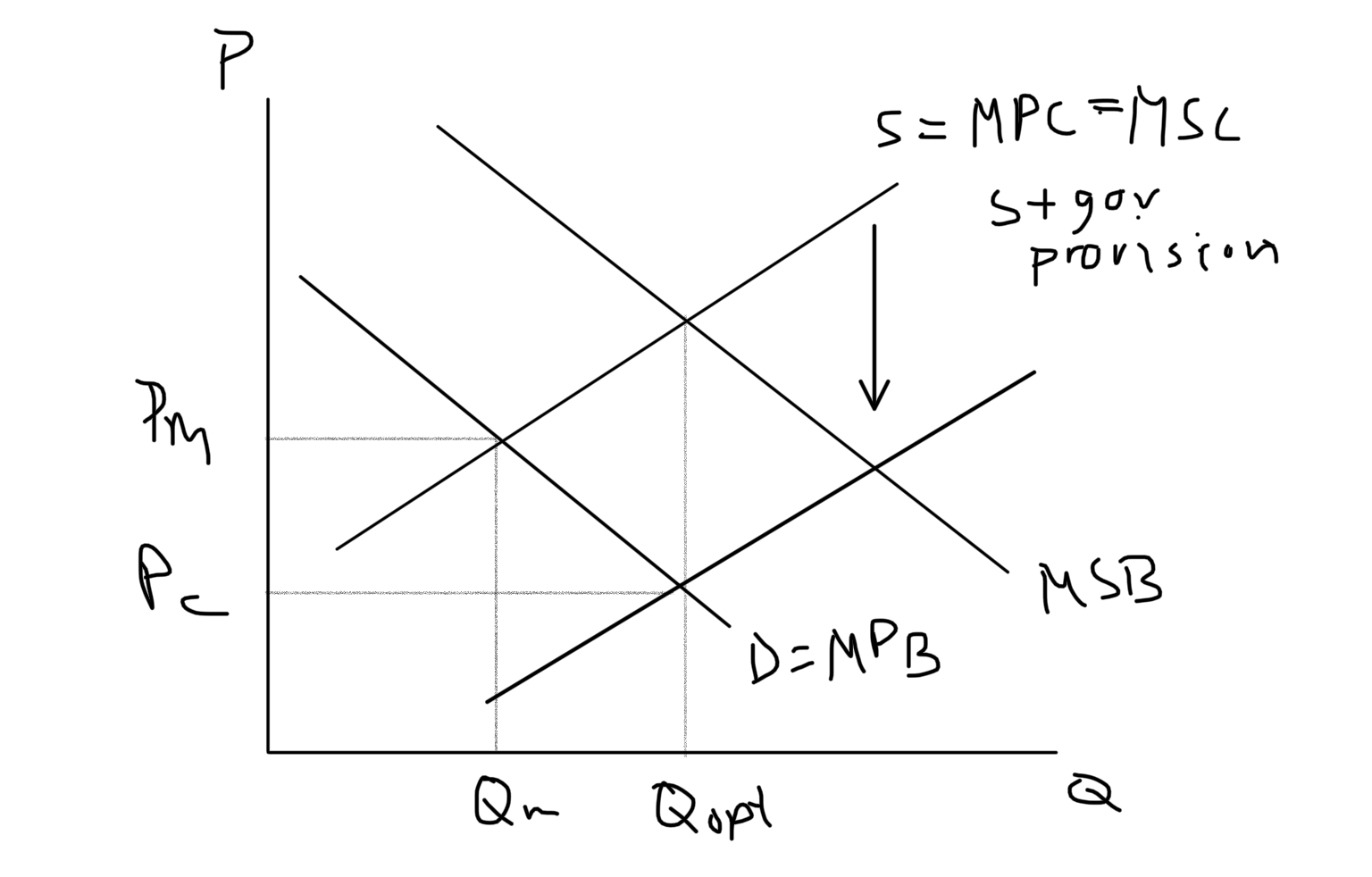
82
New cards
Subsides external benefit
* Positive production externality
* Subsidy to a firm per unit of the good provided = external benefit
* Subsidy to a firm per unit of the good provided = external benefit
83
New cards
Subsides external benefit graph??????
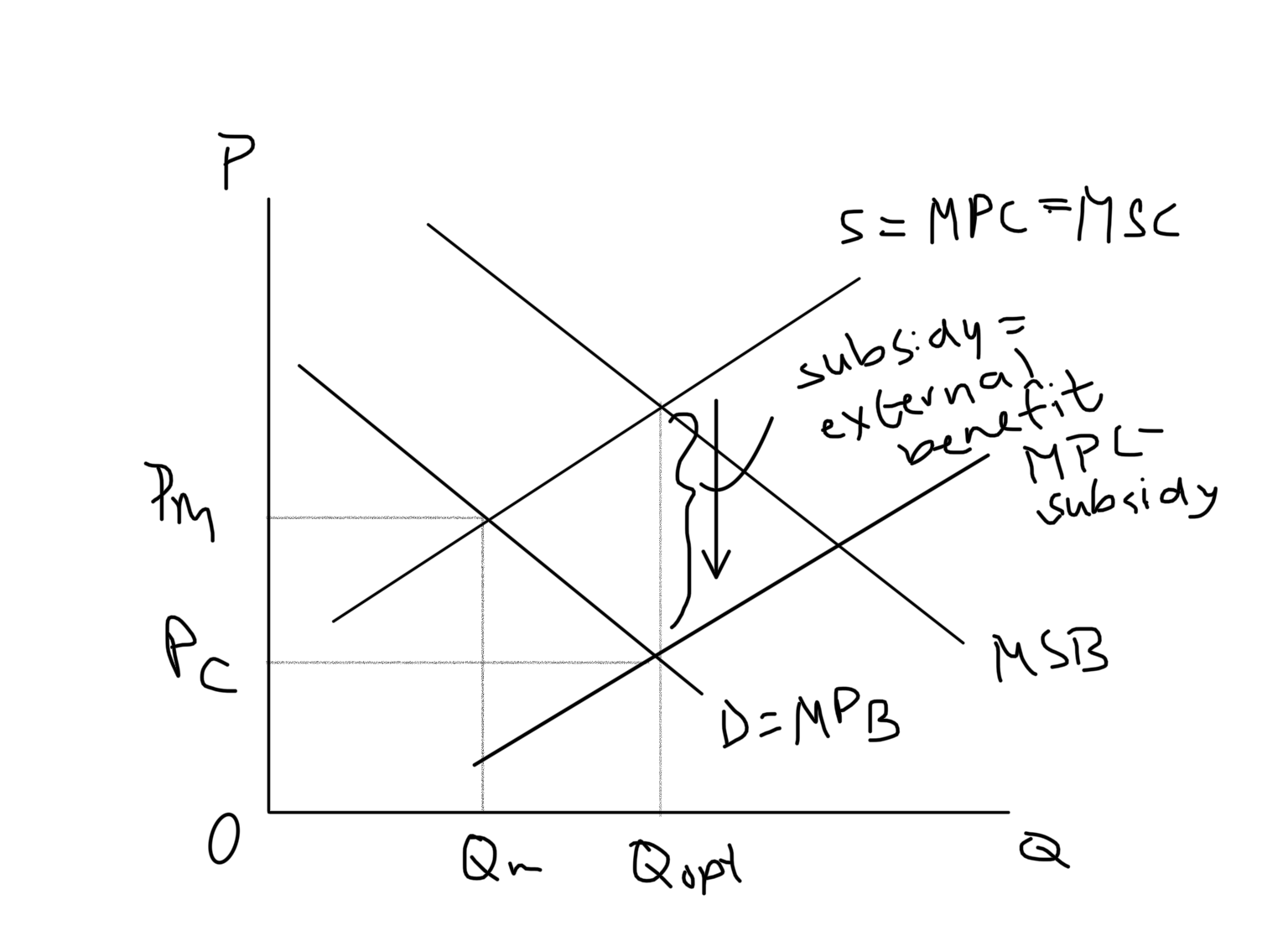
84
New cards
Positive consumption externality and graph
* External benefits created by consumers
* Often caused by consumption of merit goods
* MSB > MPB
* MSB –MPB = external benefit
* Often caused by consumption of merit goods
* MSB > MPB
* MSB –MPB = external benefit
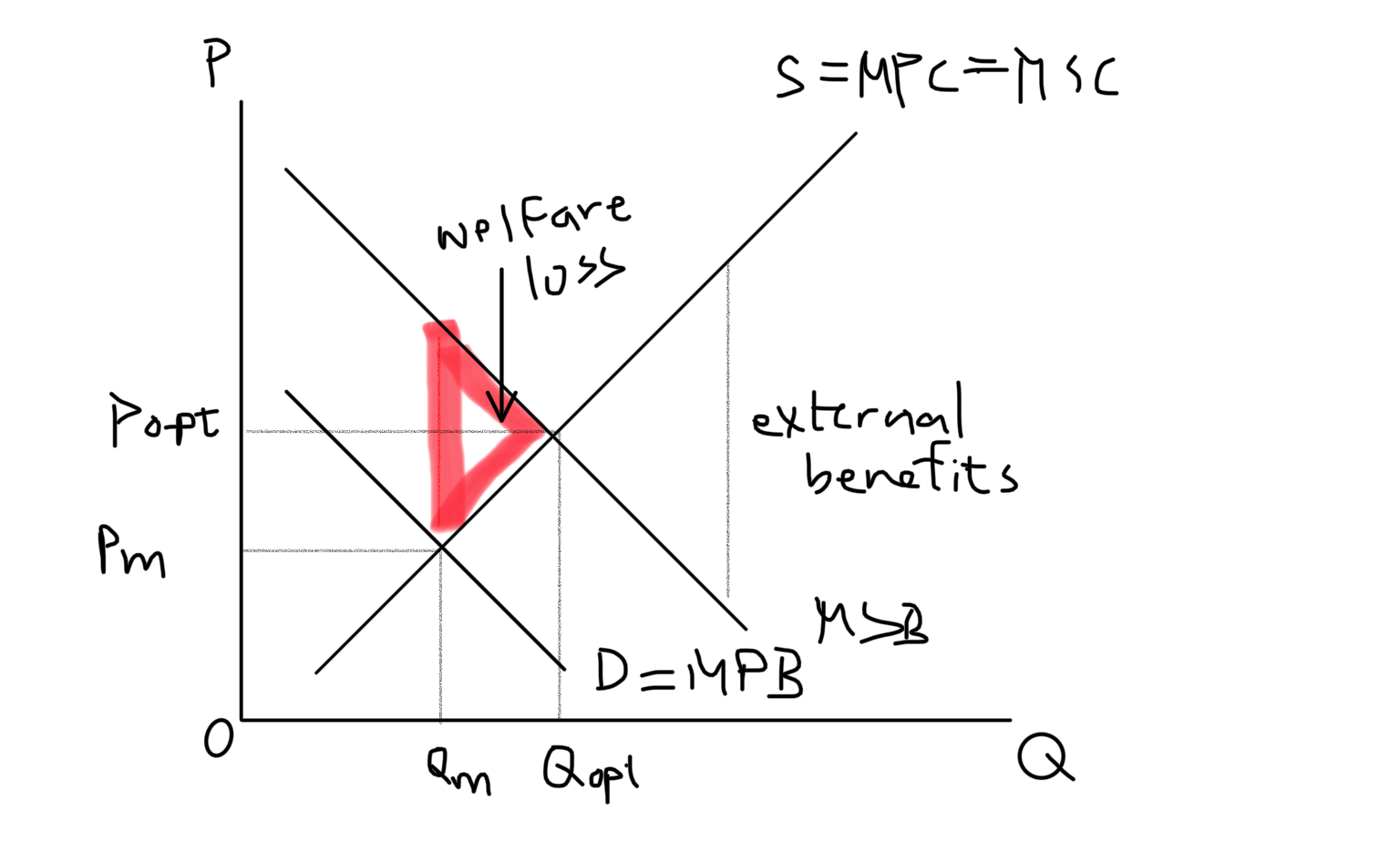
85
New cards
Government legislation and regulation
* Positive consumption externality
* Regulations to promote greater consumption of goods with positive externalities
* Regulations to promote greater consumption of goods with positive externalities
86
New cards
Education and awareness creation
* Influencing consumer taste and preference to directly influence consumption choices (increase the demand)
87
New cards
Indirect tax
Is imposed on one person or group (like manufacturers), then shifted to a different payer, usually the consumer. (Taxes are put on goods, not consumers)
88
New cards
4 types of indirect taxes
Excise taxes, Specific taxes, Ad Valorem taxes, General sales taxes
89
New cards
Excise taxes
Are imposed on a particular goods and services
90
New cards
Specific taxes
A fixed amount of tax per unit of goods/service sold
91
New cards
Ad Valorem taxes
A fixed % of the price of the good/service (price up → tax up)
92
New cards
Direct tax
(Paid to the government by taxpayers. Suppliers →gov) income tax, business tax, property tax
93
New cards
Effects of indirect taxes (increase the price)
reduces consumer spending on taxed goods (QD decreases), signal producers to produce less (QS decreases)
94
New cards
Effects of indirect taxes (changes allocative efficiency)
Economy with a high degree of allocative efficiency → allocative efficiency goes down, welfare loss goes up. Economy with a low degree of allocative efficiency → allocative efficiency goes up (potentially)
95
New cards
Reasons for imposing indirect taxes
Indirect taxes → source of gov revenue. Indirect taxes are a method to discourage consumption of demerit goods. Indirect taxes can be used to redistribute income (by taking luxury goods) Indirect taxes are a method to improve the allocation of resources
96
New cards
Price ceiling
A gov setting a legal maximum price for a good. These are usually set to make certain goods more affordable to people on low incomes. Price ceiling must be below equilibrium price. AFFORDABILITY IS IMPORTANT. Creates a shortage.
97
New cards
Possible consequences of price ceilings
Non-price rationing (distribution of goods determined not solely by price). Underground (parallel) markets (black market) (unrecorded transaction involving markup on goods with price ceiling). Under-allocation of resources (allocative inefficiency), creates shortage. Negative welfare impacts (due to disequilibrium, max social surplus not reached; there is welfare loss)
98
New cards
A legal minimum price; sellers can’t charge less than this price. Must be above market equilibrium price. It creates a surplus
price floor
99
New cards
Creates surplus (QD
Possible consequences of price floor
100
New cards
Subsidies
A payment made to the firm by the gov (opposite of tax), to lower production cost. Right supply shift.