BIO-249 Lecture Exam 2: Chemistry & Biomolecules
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What are the three subatomic particles that make up an atom?
How are protons, neutrons, and electrons arranged in an atom?
What subatomic particles make up the nucleus of an atom?
What does it mean for an atom or molecule to be ‘electroneutral’?
Subatomic Particles
Neutron: neutral charge
Proton: positive charge
Electron: negative charge
Arrangment
Nucleus: Neutron & proton
Electron cloud: electrons orbit the nucleus in orbitals
Electroneutral
Net charge of zero
In a sentence, define what a chemical element is. Name the four major elements that comprise the human body.
Element: has a unique atomic number
4 Major Elements
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
In a sentence or two, describe the octet rule for electrons
The tendency of atoms to prefer to have eight electrons in the valence shell
When atoms have fewer than eight electrons, they tend to react and form more stable compounds
Atoms can lose or gain electron to acheive the octet rule
What is an ion, cation, and anion? Are these atoms electroneutral?
Ion: charged atom
Cation: positively charged ion
Anion: negatively charged ion
NONE of them are electroneutral
In a sentence or two, describe what a molecule is and what a chemical bond is.
Molecule: two or more atoms bonded together by attractive forces
Chemical bond: connects two or more atoms and formed when atoms donate OR share their electrons
Ionic bond definition
Covalent bond definition
Ionic Bond: when electrons are DONATED or STOLEN hehehe
Metal and nonmetal atoms
Covalent Bond: when electrons are SHARED between atoms
nonmetal atoms
Polar molecule definition
Nonpolar molecule definition
Classify water’s polarity
Polar Molecule: uneven share of electrons
Nonpolar: even distribution of electrons
Water is polar
electrons are MORE attracted to oxygen
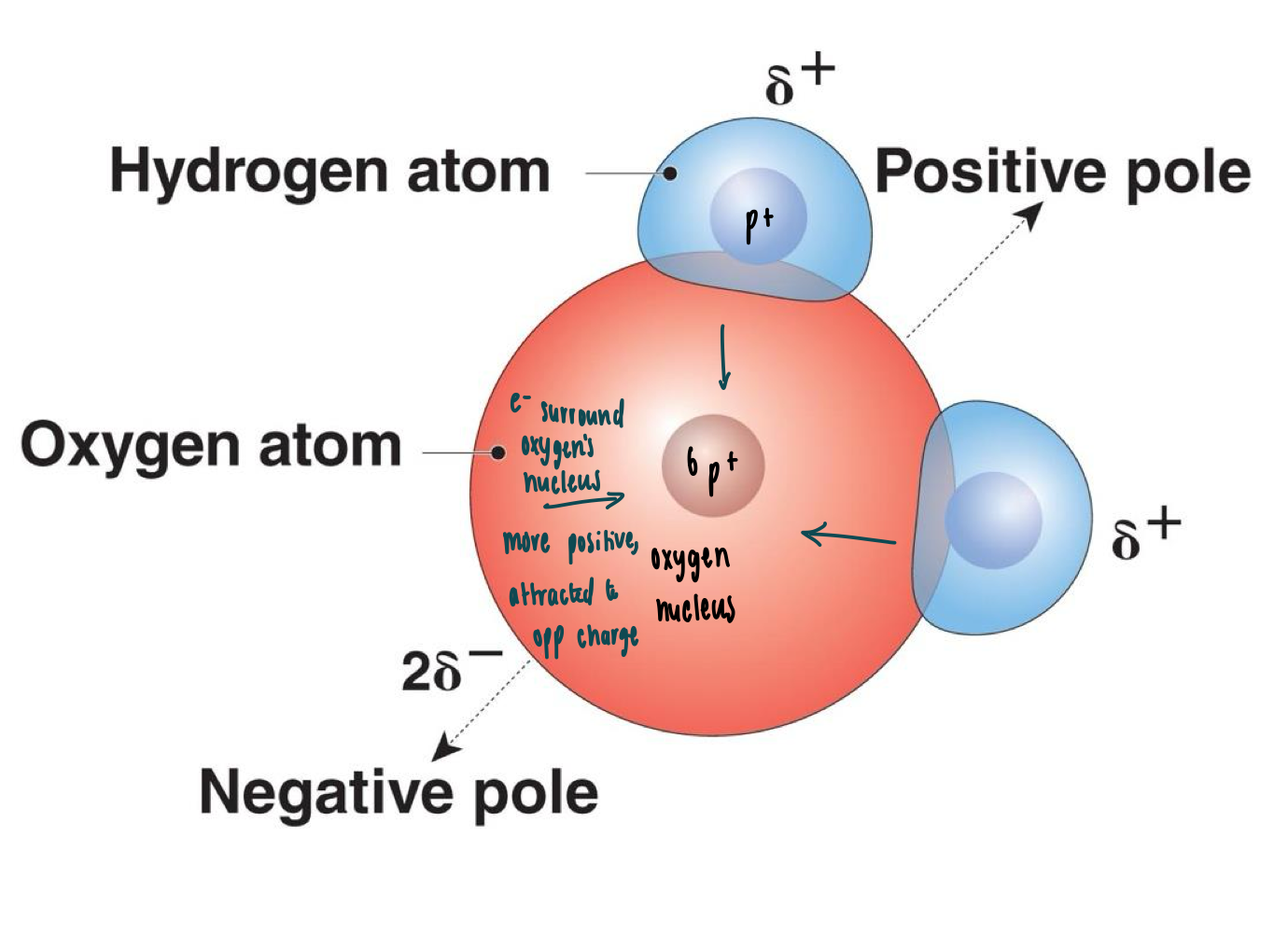
Hydrogen bond definition
Hydrogen Bonding: temporary bonds between polar MOLECULES
Covalent & ionic bonds connect ATOMS, whereas hydrogen bonds connect MOLECULES
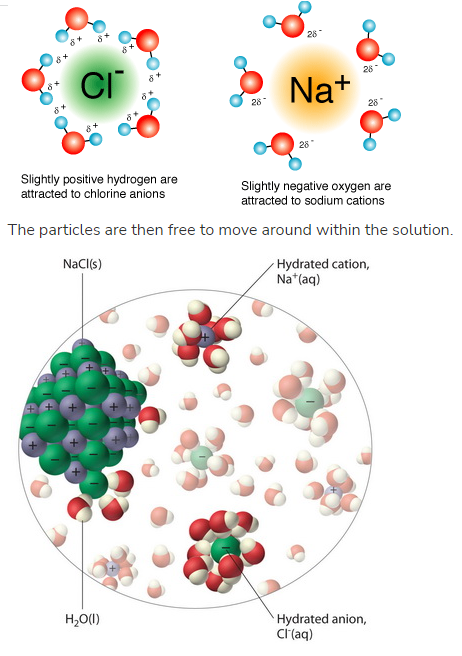
What happens to ionic compounds (e.g., Sodium Chloride) when mixed in water? What happens to polar molecules when mixed in water?
Ionic compounds break up into individual ions
the hydrogen bonds are stronger than the ionic bonds, thus they break them apart
Lots of H2O molecules surround the ions
Polar molecules DISSOLVE in water/polar solvent
the covalent bonds are stronger than the hydrogen bonds, so the polar molecules will still stay in tact
The molecule WILL NOT be broken down into its individual atoms
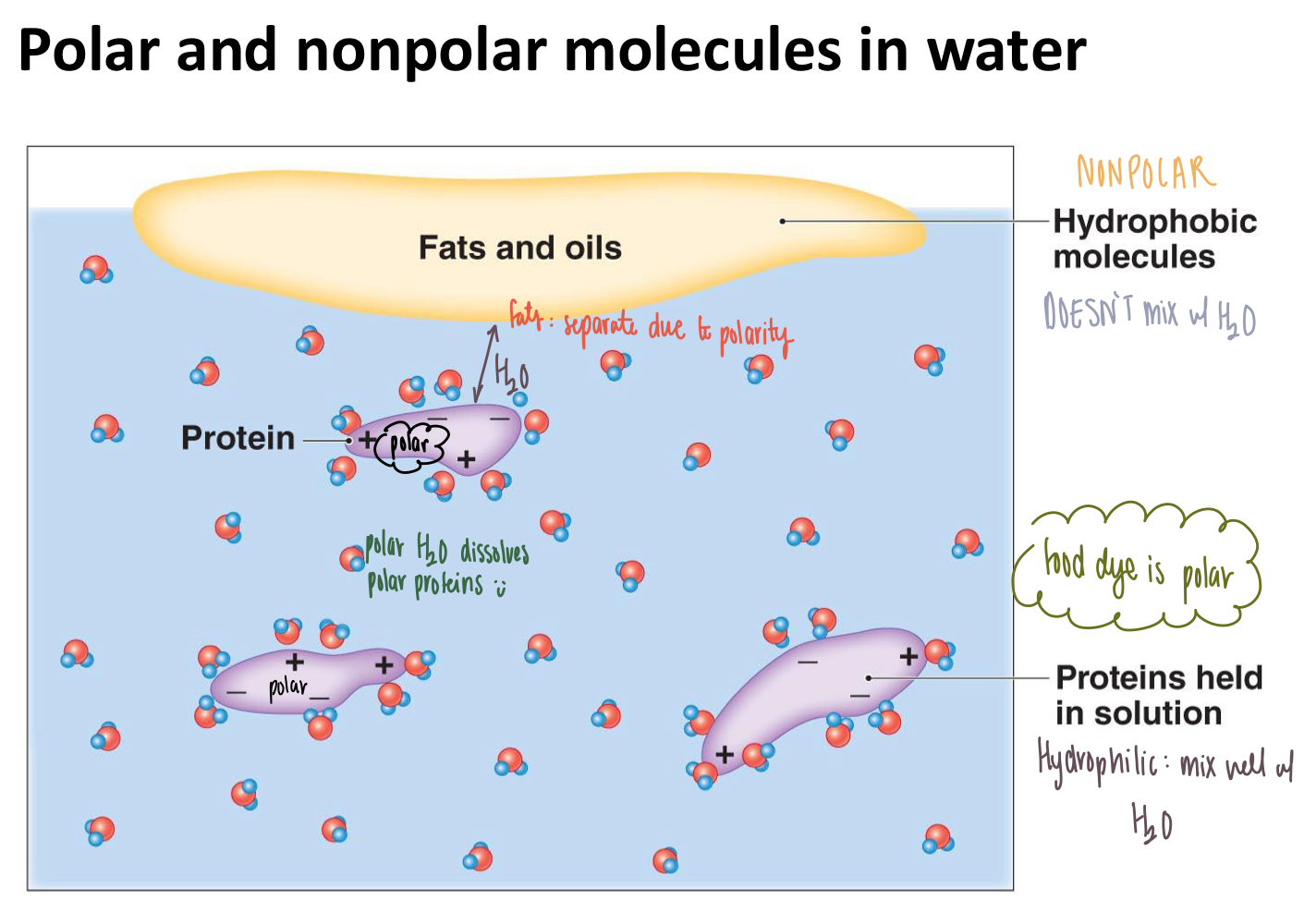
If a molecule is polar, is it hydrophillic or hydrophobic?
Hydrophilic
Do polar and nonpolar molecules “mix well” in a water solution?
No, they separate into distinct layers due to their polarity
What is a chemical reaction, and what are the reactants and products of a chemical reaction?
Chemical Reaction:
Interactions between different molecules or atoms
Creating OR destroying bonds
Reactants: Molecules before a chemical reaction
Products: molecules after a chemical reaction
What are the three basic types of chemical reactions (each described in a sentence)? Note: See lecture.
Decomposition: breaking a compound and its bond into individual atoms
Digestive processes (fats & proteins)
Synthesis: creating compound and forming new bonds
Building fuel sources (fat, muscle proteins, etc)
Displacement/exchange: redox reactions and acid/base reactions
What are 2-3 factors that can change the rate of chemical reactions in the human body?
Which of these two is more likely to change within the human body?
Chemical Rate Factors
ALL are directly proportional to the rate
Temperature
Fluxtuates
Pressure
stays consistent
Concentration
Constant changes in the body
What is a solution?
What is the solute and solvent of a solution?
Solution
Contains a solvent and a solute
Solute: the thing being dissolved
Solvent: the dissolving agent
In the lecture, what are the two ways we can describe the concentration of a solution?
What is a mole?
How do we define molarity?
How is molarity expressed in units?
Concentration
Mass/volume
g/L OR mg/mL
Molarity
moles/L or M
Mole: an atomic mass in grams of a certain substance
180 g of glucose = 1 mole of glucose
Molarity: number of moles of solute per liter of solution
moles/L or M
What are the basic definitions (1 sentence) of an acid and a base?
When an acid dissolves in water, what does it release typically?
When a base dissolves in water, what does it typically release?
Acids: give off hydrogen ions
Bases: remove hydrogen ions
produces hydroxide as well
What is pH?
What does it mean for a solution to have a low or high pH?
pH: measure of how much hydrogen ions are in a solution
Low pH
HIGH concentration of [H+]
acidic
High pH
LOW concentration of [H+]
basic
What is the range of a pH scale?
What is considered a neutral pH?
pH Range
0-14
Neutral pH: 7
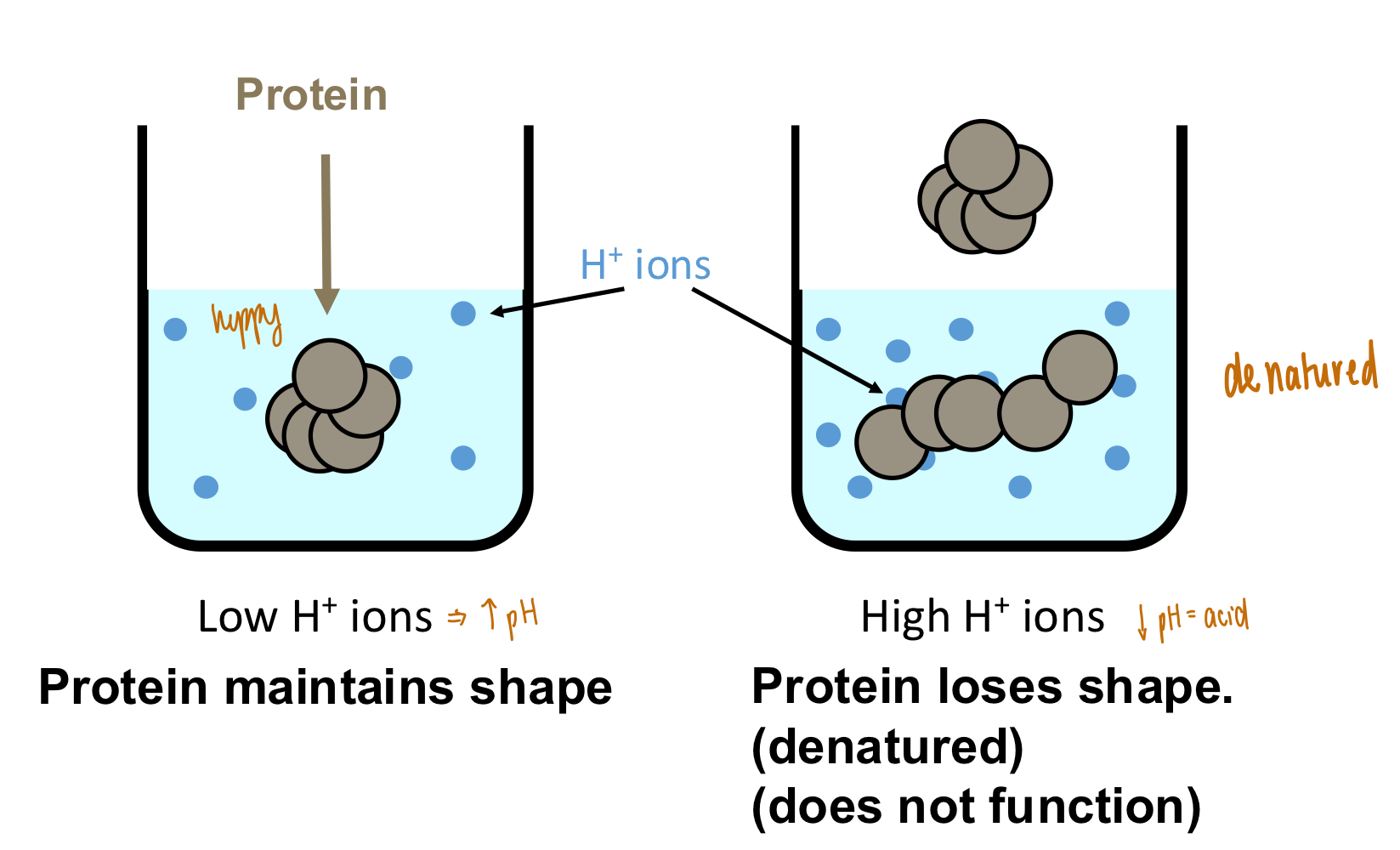
Why does pH have to be kept constant within the human body?
What happens to proteins and cells when pH changes?
Constant pH
Proteins will be denatured if the pH deviates from their normal range
pH changes lead to protein denaturation
Protein loses shape & cannot function
Describe what carbohydrates are in a sentence or two.
What elements are they typically composed of?
Are carbohydrates polar or nonpolar?
In a sentence or two, describe the general function of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates: energy source for humans
formed from monosaccharides (simple sugars)
Elements
Carbon, hydrogen, & oxygen
ALL carbohydrates are POLAR → hydrophilic
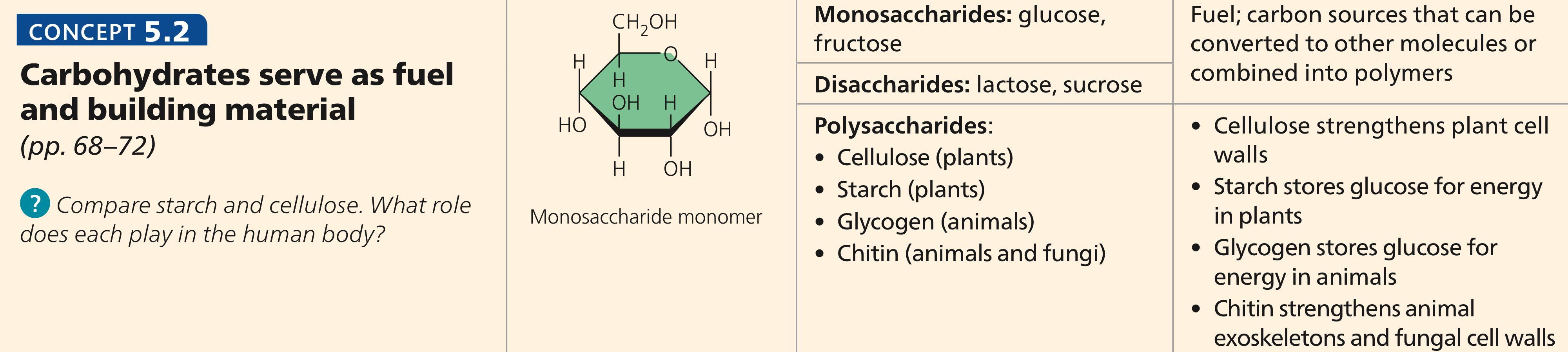
What is a monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide? Give example molecules for each type of carbohydrate.
Monosaccharide: simplest unit of sugar
Fructose
Glucose
Galactose
Disaccharide: two sugar molecules bonded by covalent bonds
Sucrose: glucose + fructose
Maltose: glucose + glucose
Lactose: galactose + glucose
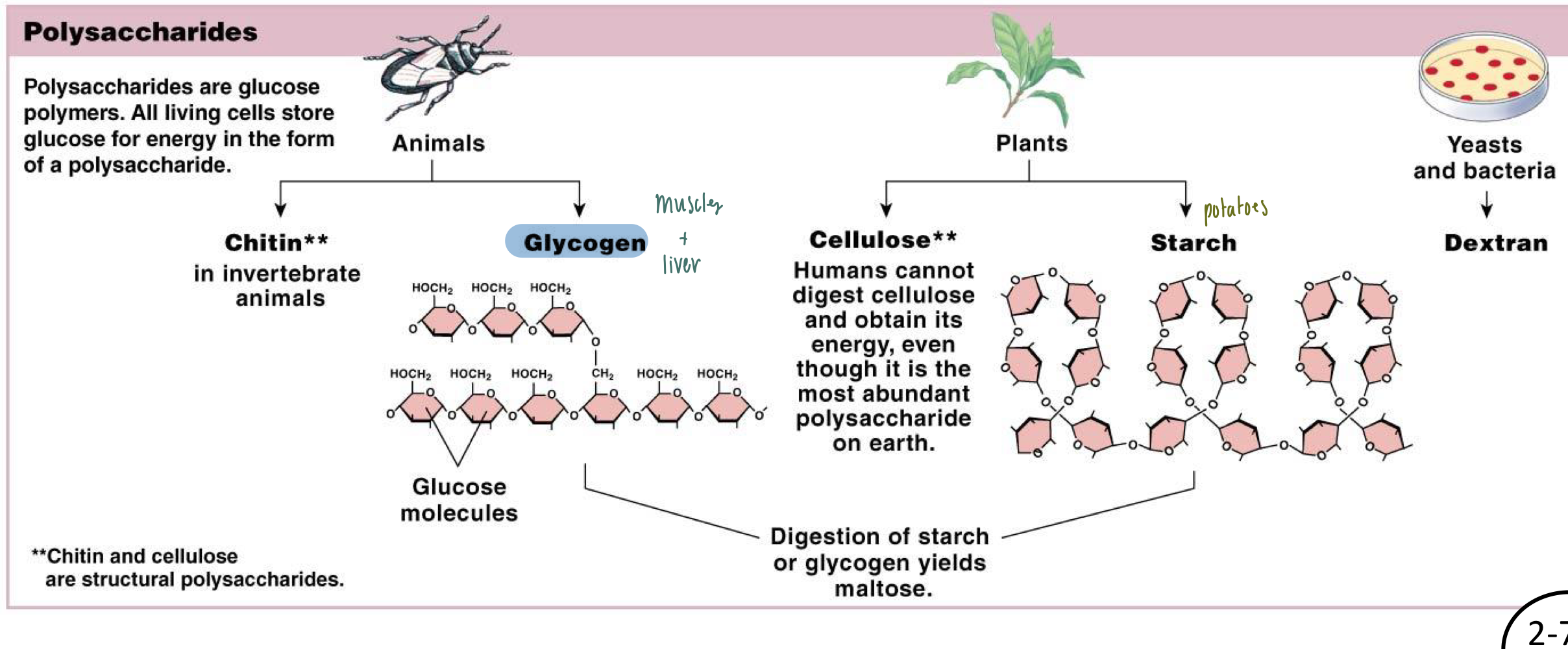
Polysaccharide: multiple monosaccharides bonded together
Chitin: in invertebrate animals
Glycogen: stored glucose molecule, found in the muscles & liver
Cellulose: plant cell walls
Starch: stored energy for plants
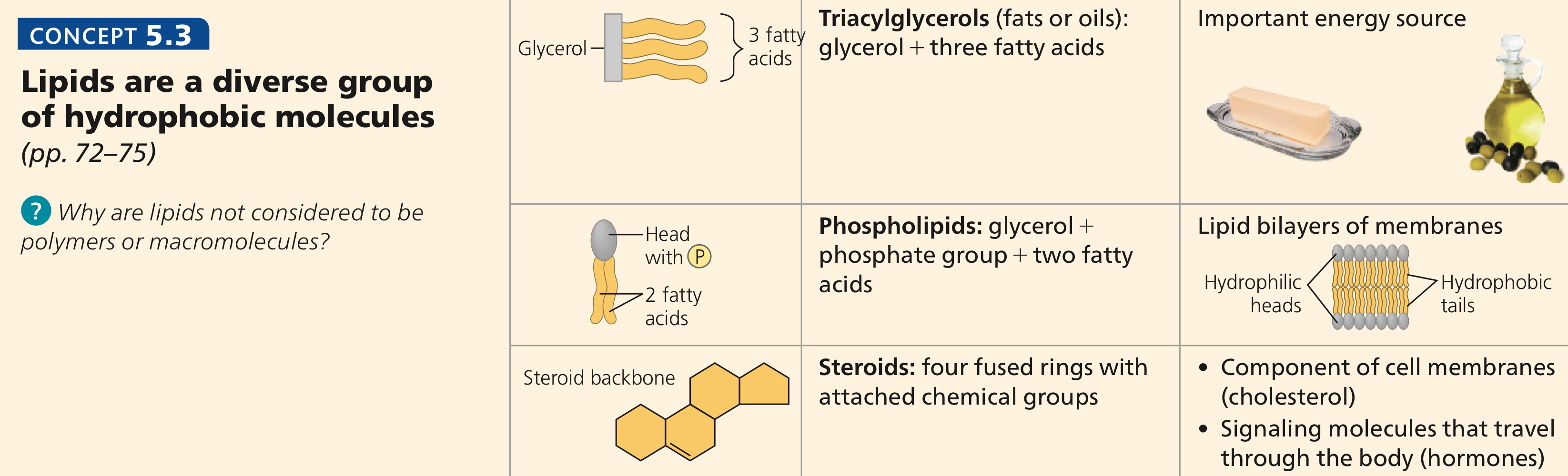
Describe what lipids are in a sentence or two.
Are lipids polar or nonpolar?
Based on its atomic composition, how is it similar and different from carbohydrates?
Lipids: fatty nonpolar, & hydrophobic compounds that serve as an energy source
Lipids vs Carbohydrates
Similarities
Chemical composition
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Energy source
Differences
Lipids = nonpolar
Lipids can be saturated or unsaturated (double bond)
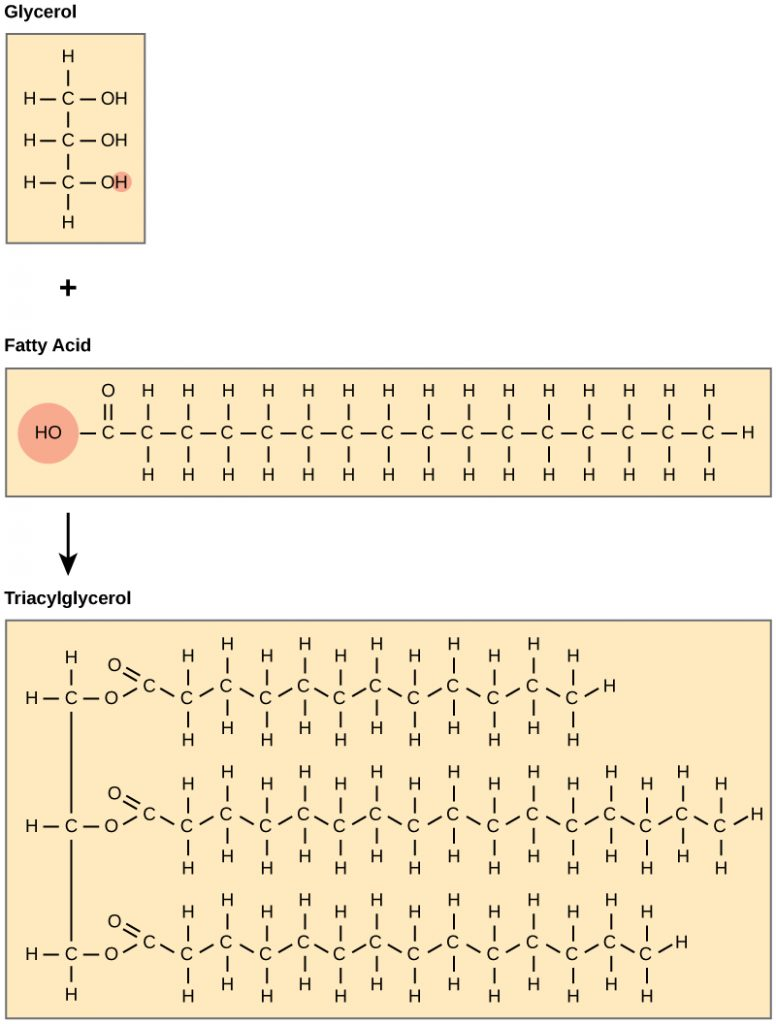
For triglyceride, identify the glycerol part and what part is the fatty acid chain
Triglyceride Function
Most common lipid form → used as a slow source of energy
Glycerol
alcohol group acts as the backbone of triglycerides
Fatty Acid Chain
long carbon skeleton with a carboxyl group at the end
Describe three representative lipids found in the body and their respective function
Triglycerides: slow source of energy
insulates the body & protects internal organs
Phospholipids: animal cell membrane that protects the cell from the external environment
Steroids: cell signaling
Ex: Cholesterol: fluidity in the animal cell membrane & precursor to hormones
Describe what proteins are in a sentence or two
What is the basic, repeating molecule that makes up proteins?
What makes one amino acid unique from another amino acid?
Protein Function
Defense, catalysts, transport, cellular communication, structural support, etc
Amino Acids: building blocks of proteins
R group
differs with each amino acid
Determines the unique characteristics of a particular amino acid → determines function
What is a peptide bond?
What is a chain of amino acids called?
What is the specific name of the reaction that forms the peptide bond, and its chemical reaction (synthesis, decomposition, or exchange)?
Peptide Bond
Amino group joins the carboxyl group via a dehydration rxn
Covalent bond that joins amino acids → forms a polypeptide
Polypeptide: a chain of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds
Synthesis/Dehydration Reaction
forms the peptide bond
Protein Structure Levels
Primary Structure: chain of amino acids
linear chain
Secondary Structure: pleated sheet/helix structure
amino acids folds onto itself
intermolecular forces (hydrogen bonds)
Tertiary Structure: specialized structure & shape → niche function
intermolecular interactions between R chains of the amino acids
hydrophobic interactions
hydrogen bonding b/w polar sides
disulfide bridges (covalent bonding)
Quaternary Structure: multiple polypeptide chains
megaproteins (hemoglobin and collagen)
When a protein loses its shape, we say the protein has been _______.
What two properties of water can change the shape of protein
Denatured
Water denaturing properties
Temperature
pH
What are active/binding sites on proteins?
What is a ligand for a protein?
Ligand Binding Steps
Active Sites: location where the protein accepts the ligand
Ligand: signal molecule that initiates a cellular process by binding to the protein’s active site
Ligand Process
Ligand binds to the protein’s active site
Protein changes its shape & transforms the ligand
Protein reverts back to its normal shape & ligand unbinds & leaves
If the shape of the protein changes, how does it affect the function of the protein?
Location of protein shape change determines the protein’s functionality
Active site: changes protein function
non-active site: no effect
Enzyme Function
Selective accerlation of chemical reactions
digestive enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of bonds in food molecules
Protein Functions
Catalyst: accelerates a chemical reaction
substrate binds to the protein’s active site → transforms into products
Membrane Transporters & Receptors
Transporters
Channel proteins for water
Gated channels open/close in response to signals
Receptors
signal attaches to the protein → creates an internal signal for the cell to respond with
Signal Molecules: cellular response/communication
Cell to cell
Bloodstream
Binding Proteins: binds to nonpolar & hydrophobic substances (can’t be dissolved in water)
lipids
O2 (Fe in red blood cells)
Lipoprotein: holds onto lots of fat
uses LDL to bind to fat
Defensive Proteins: immune system produces immunoglobulins/antibodies
immunoglobulins: glycoproteins produced by the plasma cells that detect pathogens
Regulatory Proteins: regulate gene expression
proteins inside the nucleus that bind to DNA to initiate or stop gene expression
Structural proteins: support (resilience & strength)
active sites aren’t used
microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules, etc
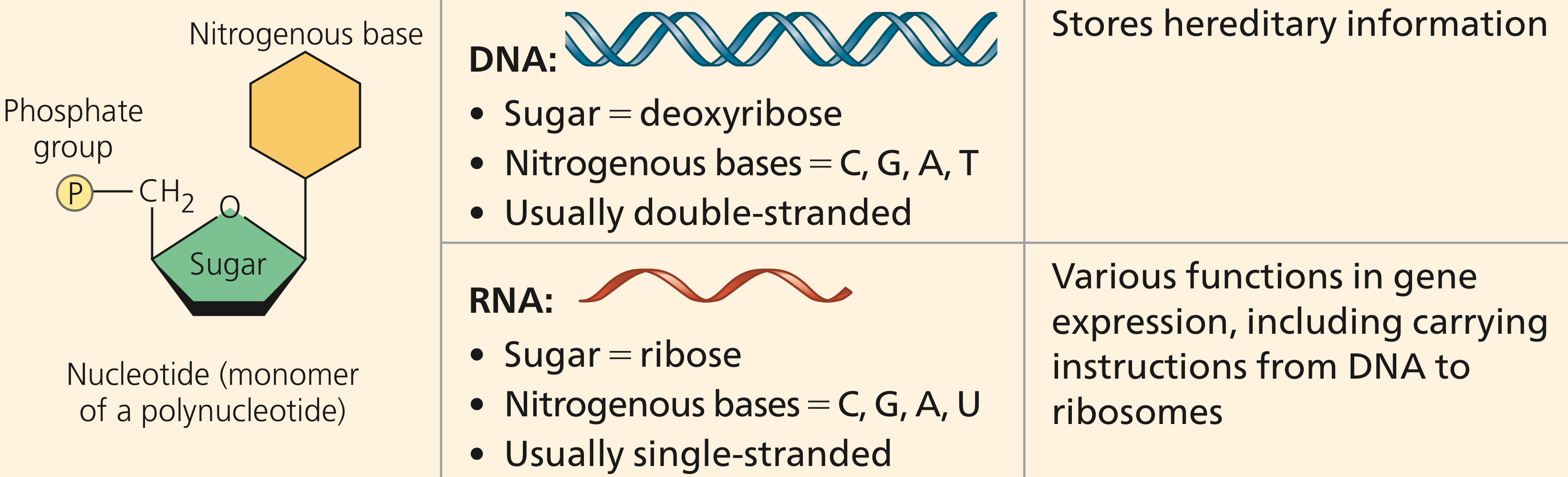
What are DNA and RNA and their function?
What is the basic repeating molecule that makes up DNA and RNA?
What are the four different nucleotides that make up DNA, and what are the four different nucleotides that make up RNA?
DNA & RNA Function
Hold genetic information for our cells
RNA: single-stranded & contains uracil
Nucleic Acids
monomer for DNA & DNA
Sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), phosphate group, & nitrogen base
Nucleotides
DNA: G, C, T, A
RNA: G, C, U, A
What is ATP, and how is it different than ADP?
ATP Function
Cellular energy currency
Remove a phosphate group to release energy
ATP vs ADP
ATP → ADP: releasing/creating energy
ADP → ATP: spending energy