dermatomes myotomes and spinal cord levels.
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
A 45-year-old woman with Type 2 diabetes follows a strict exercise and meal plan. She tells her therapist, "I’ve really worked hard to keep my sugar under control — I know my discipline is why I’ve stayed out of the hospital."
What type of health locus of control does this patient demonstrate?
Internal locus of control
A 70-year-old stroke survivor states, "I’m only alive because my doctor knew exactly what to do. I trust him to keep me going."
Which best describes his health locus of control?
External locus of control
After surviving a heart attack, a patient says, "I was just lucky. It wasn’t my time yet. Nothing I did would’ve changed the outcome."
What health belief does this reflect?
Chance
A physical therapist asks a patient with chronic back pain how they’ve been managing their condition. The patient replies,
“I follow the stretches you gave me, but honestly, I think my recovery depends on whether God wants me to heal.”
What type of health locus of control does this most reflect?
Both external and chance
A young athlete recovering from ACL surgery says,
“If I hadn't worked so hard in physical therapy and pushed myself every day, I’d still be limping.”
Which health locus of control is most dominant?
Internal locus of control
A physical therapist prepares to lift a moderately heavy box from the floor. Which of the following best reflects proper lifting technique?
Keep the object close to the body and lift with the legs
During a patient transfer from wheelchair to bed, which of the following body mechanics principles is MOST important?
Maintain a wide base of support and neutral spine
A therapist assisting a heavy patient in standing reports back pain. Which error most likely contributed?
Twisting the trunk during the transfer
What position of the therapist’s center of gravity promotes the most efficient lifting?
Directly over and within the base of support
Which position is usually safe and recommended for pregnant women to reduce pressure on major blood vessels?
Left side-lying
_____ a chronic, autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the body’s own tissues.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
A 55-year-old woman presents with joint pain in both hands and wrists. She reports morning stiffness that lasts over an hour and swelling in her finger joints. On examination, the joints are warm and tender bilaterally. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Rheumatoid arthritis
A 25-year-old woman presents with fatigue, joint pain, and a red rash across her cheeks and nose. Laboratory tests show the presence of ANA (antinuclear antibodies) and mild proteinuria. Which of the following systems is least likely to be affected by this condition?
Articular cartilage only
A 60-year-old patient with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis presents with pain, swelling, and visible finger deformities. Which of the following deformities is most commonly associated with RA?
Swan-neck deformity
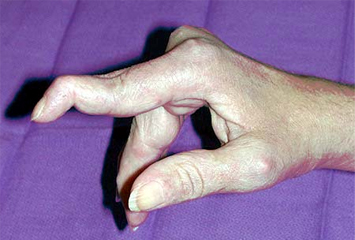
A patient with rheumatoid arthritis presents with hyperextension of the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints and flexion of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints in several fingers. What condition does this describe?
Swan-neck deformity
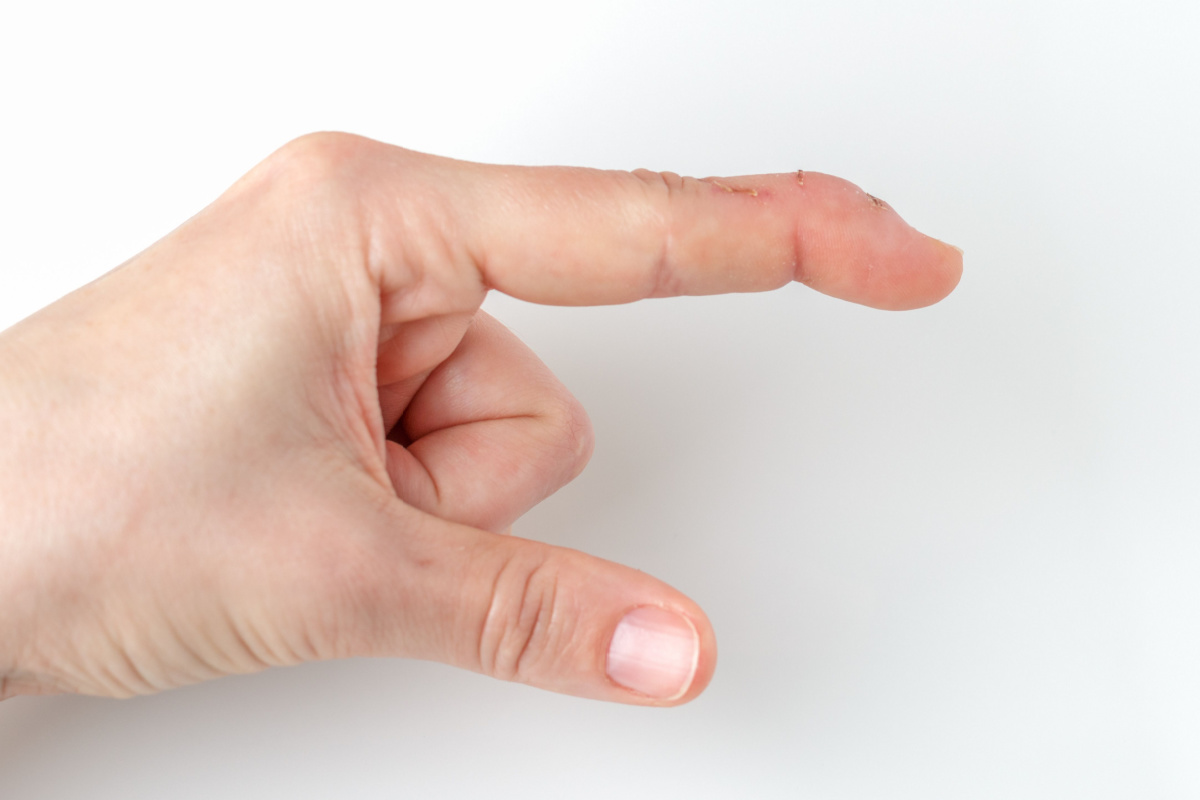

A basketball player presents with a finger that cannot actively extend at the DIP joint after jamming it on the ball. Passive extension is possible. What is the most likely diagnosis?
mallet finger
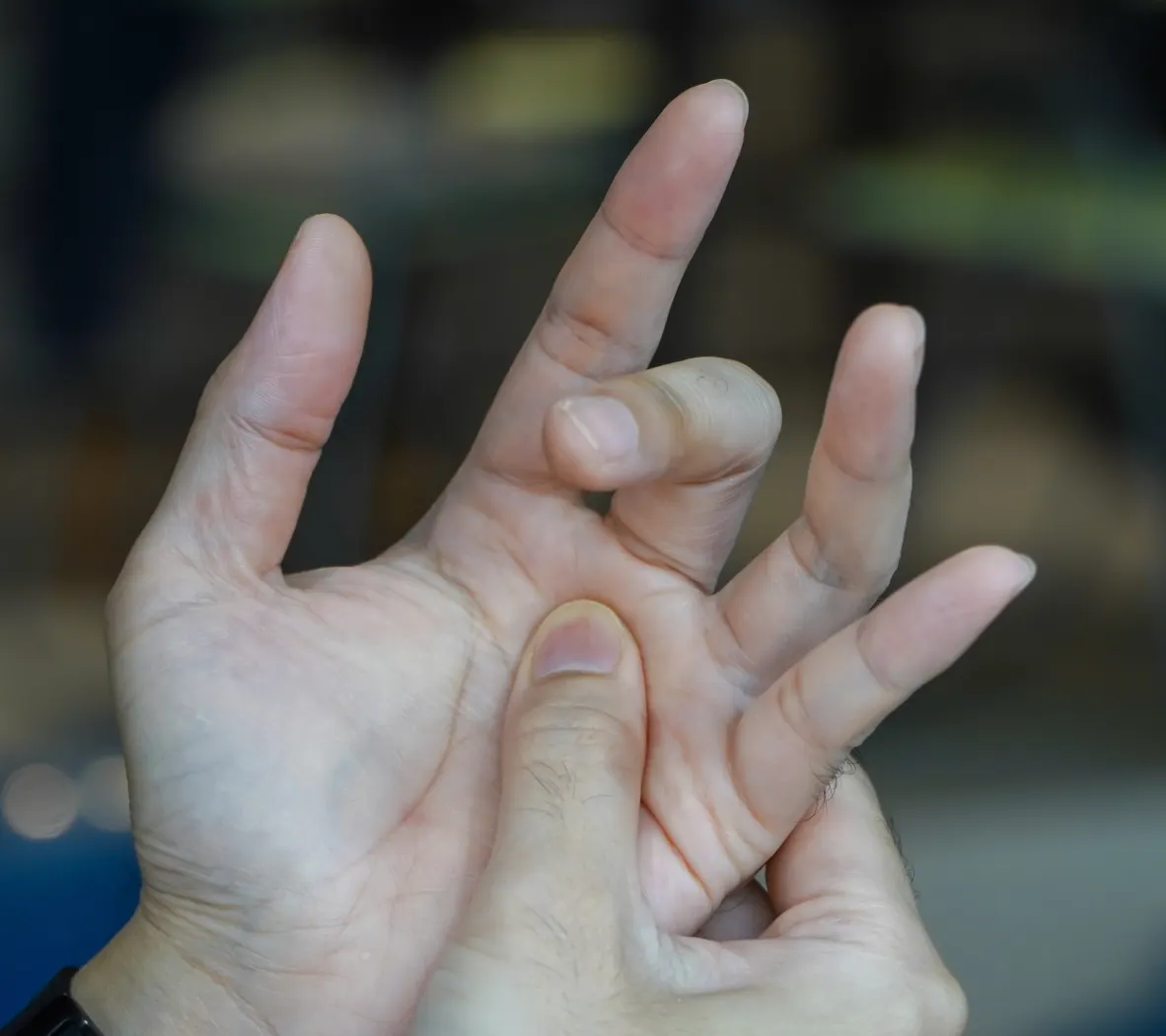

A patient reports painful catching and locking when flexing the ring finger. Sometimes they need to use their other hand to “pop” the finger into extension. Palpation reveals tenderness over the flexor tendon sheath. What is the diagnosis?
Trigger finger
Which of the following is true regarding the use of small electrodes in electrical stimulation?
They increase current density and may cause discomfort
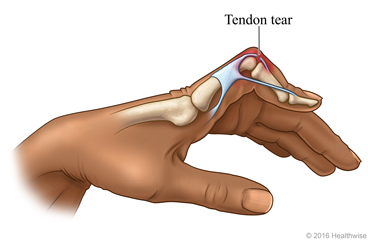
A patient with finger trauma shows flexion at the PIP joint and hyperextension at the DIP joint. What is this deformity called?
Boutonnière deformity
Which of the following statements is true about Interferential Current (IFC) electrode placement?
Four electrodes are used in a criss-cross pattern over the target area
What is the main difference between Premodulated current and IFC in terms of electrode setup?
Premod uses 2 electrodes with interference occurring in the machine
Which of the following electrical stimulation modalities is used primarily for pain management only, and not for edema reduction?
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Which of the following modalities can be used to treat both acute and chronic edema as well as pain?
Interferential and Premodulated current
A physical therapist applies two electrodes over a patient’s quadriceps muscle and instructs them to perform a quad set contraction during the stimulation cycle. The protocol includes a 10-second "on" time and a 50-second "off" time. Which form of electrical stimulation is being used?
Russian Stimulation
This type of e-stem uses direct current to help deliver medication into a wound
Iontophoresis
A patient reports numbness over the lateral shoulder (deltoid area). Which dermatome is most likely affected?
c5
A patient presents with tingling and burning sensation along the lateral forearm and thumb. Which spinal nerve root is likely involved?
c6
During a sensory screen, you note that the patient cannot feel pinprick on the tip of the middle finger. Which dermatome is impaired?
c7
A patient complains of numbness and tingling across the back of their head and upper neck. Which dermatome is affected?
c2
Sensory loss is noted over the medial upper arm near the elbow. Which dermatome is most consistent with this area?
t1
Numbness is noted across the ring and pinky fingers and the medial side of the forearm. What dermatome is most likely involved?
c8
A patient has altered sensation over the trapezius area and the top of the shoulder. Which dermatome is most likely involved?
c4
You suspect C3 nerve root compression. Where should you test sensation?
Neck and upper trapezius region
A patient has weakness with knee extension and numbness on the medial knee. Which nerve root is likely affected?
L3
A therapist notes decreased sensation over the top of the foot and difficulty extending the big toe. Which spinal nerve is likely involved?
L5
A patient presents with pain and numbness on the lateral aspect of the foot, along with difficulty in plantarflexion. What nerve root is most likely affected?
S1
A patient reports numbness in the groin and upper inner thigh with mild difficulty flexing at the hip. Which nerve root is most consistent with these findings?
L1
A runner presents with weakness in knee flexion and sensory loss in the posterior thigh. Which nerve root is most likely affected?
S2
Which of the following dermatomes includes the saddle area (genitals, perianal region)?
S3-S5
A patient has difficulty dorsiflexing the ankle and numbness on the medial shin. What is the most likely nerve root involved?
L4
A spinal cord lesion causes loss of bowel and bladder control. Which spinal levels are most likely involved?
S3–S5
A patient with a spinal cord injury retains light touch and pinprick sensation at the nipple line, but has impaired sensation below that level. What is the most likely intact spinal level?
T4
During a sensory exam, a patient demonstrates normal sensation at the level of the umbilicus, but decreased sensation below it. Which dermatome is most likely intact?
T10
A patient struggles to perform shoulder abduction. Which myotome is most likely affected?
c5
Weakness in cervical side bending would suggest involvement of which myotome?
c2
A therapist notes weak wrist extension during MMT. What spinal level is most likely involved?
C6
Elbow extension and wrist flexion are primarily associated with which spinal level?
C7
A patient is unable to elevate their shoulders against resistance. Which myotome is most responsible?
C4
Finger abduction is primarily controlled by which spinal root?
T1
A lesion to this myotome might impair thumb extension and ulnar deviation.
C8
Cervical flexion is mainly associated with which levels?
C1–C2
Weakness in hip flexion is most likely related to which myotome?
L1
A patient has trouble clearing their toes during swing phase due to weak dorsiflexion. What spinal level is most involved?
L4
Manual muscle testing shows decreased strength in knee extension. Which myotome is affected?
L3
Your patient can’t extend their great toe against resistance. Which spinal nerve root is responsible?
L5
Which myotome primarily controls ankle dorsiflexion?
L4
A patient has difficulty pushing off the ground during gait (toe-off phase). Which spinal level is most likely involved?
S1
Weakness in knee flexion would most likely be caused by damage to which myotome?
S2
A patient presents with urinary incontinence following a spinal cord injury. Which spinal levels are most likely affected?
S3-S5
Which myotome level is most responsible for voluntary control of the anal sphincter?
S4–S5
A patient presents with numbness along the lateral border of the foot and heel. Which nerve is most likely affected?
Sural
This type of spinal cord injury occurs from a gunshot wound or stab wound
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
A patient sustained a stab wound to the right side of the thoracic spinal cord. Upon examination, the therapist notes paralysis and loss of proprioception on the right leg, and loss of pain and temperature on the left leg.
Which condition does this most likely indicate?
Brown-Séquard syndrome
A patient presents with:
Motor weakness and loss of vibration sense in the left leg
Loss of pain and temperature sensation in the right leg
Which of the following best explains the side of spinal cord injury?
Left-sided Brown-Séquard lesion
This tract carries proprioception, vibration, and fine (discriminative) touch up the ipsilateral side of the spinal cord, then crosses over at the medulla before reaching the somatosensory cortex.
Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway
This tract carries pain, temperature, and crude touch. It crosses over within 1–2 spinal segments of entry and ascends on the contralateral side to the thalamus and somatosensory cortex.
Which tract is being described?
Spinothalamic tract
A 34-year-old male is brought to the emergency room after a motorcycle accident. He sustained a flexion injury to his cervical spine. On neurological exam, he has bilateral motor paralysis and loss of pain and temperature sensation below the level of the injury, but proprioception and vibration are preserved.
Which spinal cord syndrome is most consistent with these findings?
Anterior Cord Syndrome
A lesion in the right lateral corticospinal tract at the C5 level of the spinal cord would most likely cause which of the following?
Ipsilateral loss of motor function below C5
A lesion to the right lateral corticospinal tract at the T10 level of the spinal cord will most likely result in:
Ipsilateral loss of motor function below T10
Which spinal tract crosses at the spinal cord level (within 1–2 segments of entry) and carries pain and temperature information?
Spinothalamic tract
The anterior corticospinal tract primarily controls:
Postural and proximal trunk muscles
A spinal cord injury results in:
Ipsilateral motor loss
Contralateral loss of pain and temperature
Preserved proprioception and vibration
Which spinal cord syndrome is most consistent with this?
Brown-Séquard syndrome
A 56-year-old man presents with difficulty walking and frequent falls. On exam, he has a positive Romberg sign, loss of vibration and proprioception below the level of T8, but retains pain, temperature sensation, and motor function.
Posterior Cord Syndrome
This ascending sensory pathway travels ipsilaterally up the spinal cord, carrying information about proprioception, vibration, and fine/discriminative touch. It then crosses at the level of the medulla before projecting to the somatosensory cortex in the parietal lobe.
Which sensory tract is being described?
Dorsal column-medial lemniscal pathway
Which of the following is the most common type of incomplete spinal cord injury?
Central Cord Syndrome
A patient steps on a sharp object and reflexively pulls their foot away before they consciously feel pain. Which of the following best describes where the initial processing of this reflex occurs?
Spinal cord gray matter
Which of the following best describes the correct order of structures involved in a spinal withdrawal reflex, such as pulling your hand away from a hot surface?
Skin receptor → dorsal horn → interneuron → ventral horn motor neuron → muscle
Which of the following correctly distinguishes a spinal reflex arc from voluntary motor control?
Reflexes occur via spinal gray matter without brain involvement; voluntary movements use descending white matter tracts
A 68-year-old man presents with right leg weakness. On exam, you note:
Increased muscle tone (spasticity)
Hyperreflexia
Positive Babinski sign (toes extend upward)
No muscle atrophy or fasciculations
Which type of lesion is most likely present?
Upper motor neuron lesion
A 32-year-old woman presents after a minor motorcycle accident. On exam, you find:
Flaccid paralysis of the right arm
Decreased muscle tone
Hyporeflexia
Fasciculations (visible muscle twitches)
Ongoing muscle atrophy over several weeks
Babinski sign is absent
Which of the following best describes the location of the lesion?
Lower motor neuron lesion
A patient has right leg weakness. On exam, you find:
Increased tone
Hyperreflexia
No atrophy or fasciculations
Positive Babinski sign
What type of motor neuron lesion is most likely?
Upper motor neuron
A spinal cord injury at L1 results in:
Flaccid lower limb paralysis
Hyporeflexia
Muscle wasting
No Babinski sign
What’s the best explanation?
Lower motor neuron lesion
A 30-year-old woman presents with complaints of increasing difficulty keeping her eyes open by the end of the day. She also mentions recent trouble chewing and speaking clearly after prolonged conversation. On physical exam, she has bilateral ptosis that worsens with sustained upward gaze. Strength in her limbs is normal but fatigues with repeated testing. Reflexes and sensation are intact.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Myasthenia Gravis
A 28-year-old woman presents with several weeks of worsening double vision and drooping eyelids, especially in the evening. She also reports occasional difficulty chewing and swallowing. Neurologic exam reveals fatigable ptosis and weakness of facial muscles. Reflexes and sensation are intact.
Which of the following diagnostic tests would be most specific for confirming the suspected diagnosis?
Serum anti–acetylcholine receptor antibody test
A 45-year-old man presents to the emergency department with severe low back pain that started after lifting a heavy object. He reports numbness in his inner thighs and difficulty urinating. On exam, you find:
Decreased sensation in the saddle region
Weakness in both legs
Absent patellar and Achilles reflexes
Decreased anal sphincter tone on rectal exam
No Babinski sign
Cauda equina syndrome