Fiscal policy - overview
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Fiscal policy: definition
The manipulation of govt. spending, taxation and borrowing to influence the level of economic activity
Macroeconomic functions of fiscal policy
Keep inflation on target (2%)
Stimulate economic growth and employment during times of recession
Maintain a stable economic cycle that minimises boom + bust.
What are the microeconomic functions of fiscal policy?
Can improve education, health and the redistribution of income.
What is expansionary fiscal policy?
If the government is trying to stimulate economic activity.
Methods of expansionary fiscal policy
1. Cutting taxes: Income tax - will give consumers more disposable income, raising consumption
Corporation tax - will increase available profits for firms, stimulating investment
2. Raising govt spending - may increase infrastructure spending or public sector pay
3. Increasing the budget deficit - an increase in borrowing, which must be repaid with interest
Contractionary fiscal policy - definition
To constrain aggregate demand, reduce debt or control inflation.
Methods of contractionary fiscal policy
1. Increasing taxes: will discourage spending
2. Cutting govt spending: if current levels are unaffordable or inflationary
3. Cutting the budget deficit: may stabilise economic growth as reduced debt repayments in future can be reinvested back into the economy.
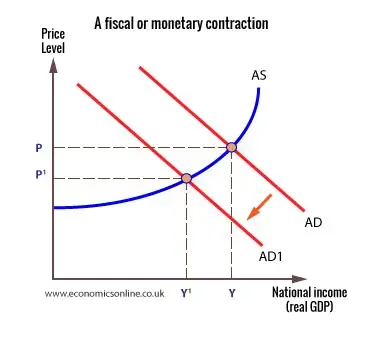
Expansionary fiscal policy - diagram
Assume the govt. would like to stimulate economic growth
May decide to cut taxes, which boosts AD to AD1 as consumption rises
RNO rises from Y to Y1
Creates employment
However, price level rises also, hampering inflation targets
If consumption is spent on imports, this will worsen balance of payments on current account
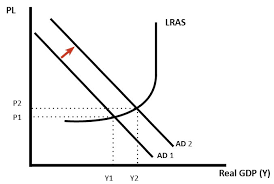
Expansionary fiscal policy - Aggregate Supply
Imagine the govt. would like to stimulate the supply side of the economy.
They may cut corporation tax in order to boost firms’ profits, which can then be reinvested into capital projects
LRAS will shift right to LRAS2
Productive capacity has increased and there’s been a fall in PL, softening inflationary pressure
However, if AD remains unchanged, spare capacity has also increase - a waste of economic resources.
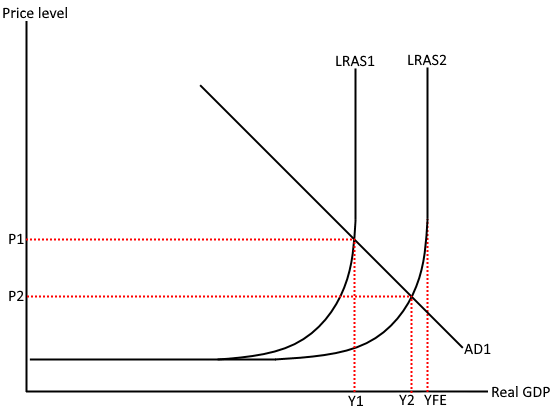
Contractionary fiscal policy diagram + chain of analysis
Assume the govt. would like to use fiscal policy to maintain its inflation target at 2%, as the economy is up against capacity constraints
It may decide to increase taxation, decreasing consumption, shifting AD to AD1
Reduces inflationary pressure, with price level falling to P1
Also improves balance of payments, as less income is spent on imports
But, this damages Real GDP as economic growth declines.
Also, falling consumption and lower Ad likely to increase cyclical unemployment