AP Chemistry Summer Homework Review
1/253
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
254 Terms
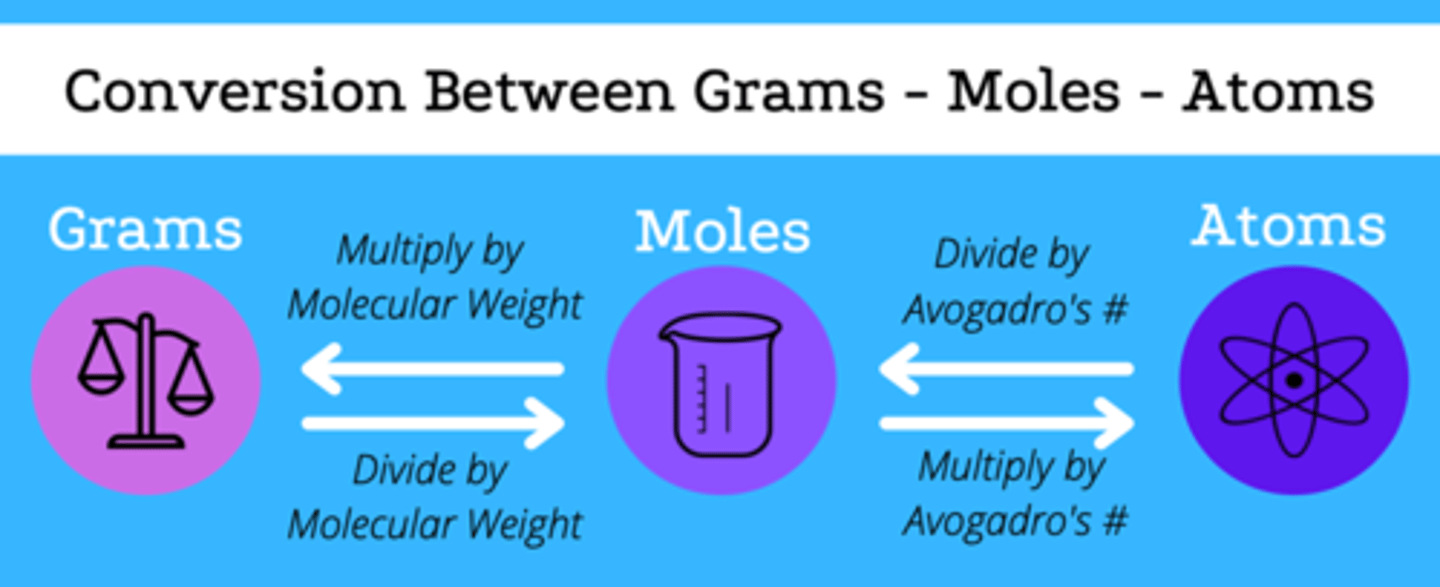
Conversion grams to atoms
1. Grams substance/grams per mol = moles of substance
2. Moles substance * (Avogadro's number/mol) = atoms
What are the units for molar mass
grams/mole
John Dalton
Solid sphere model, elements exist in small "packets" of matter.

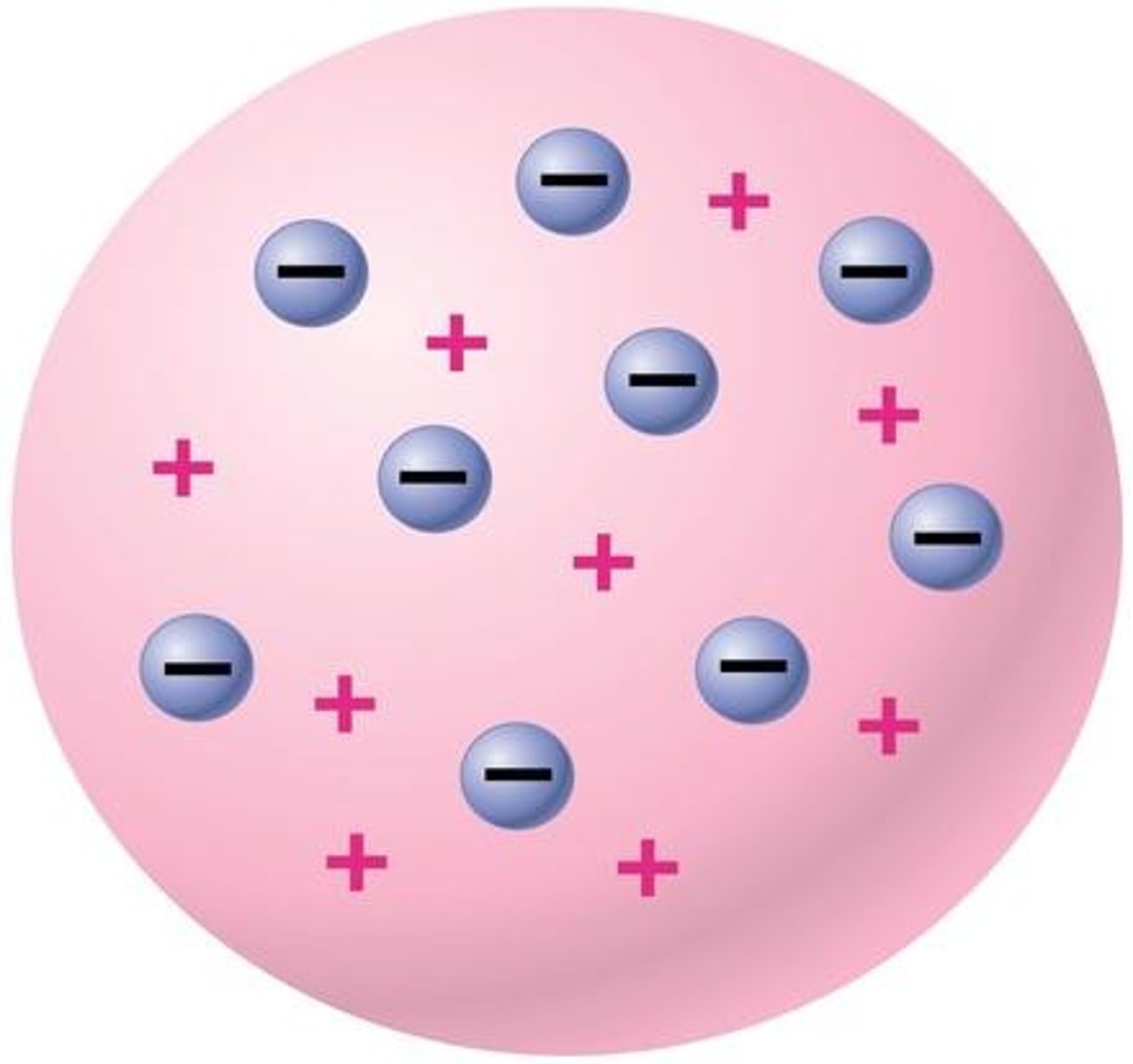
JJ Thomson
discovered the electron, plum pudding model
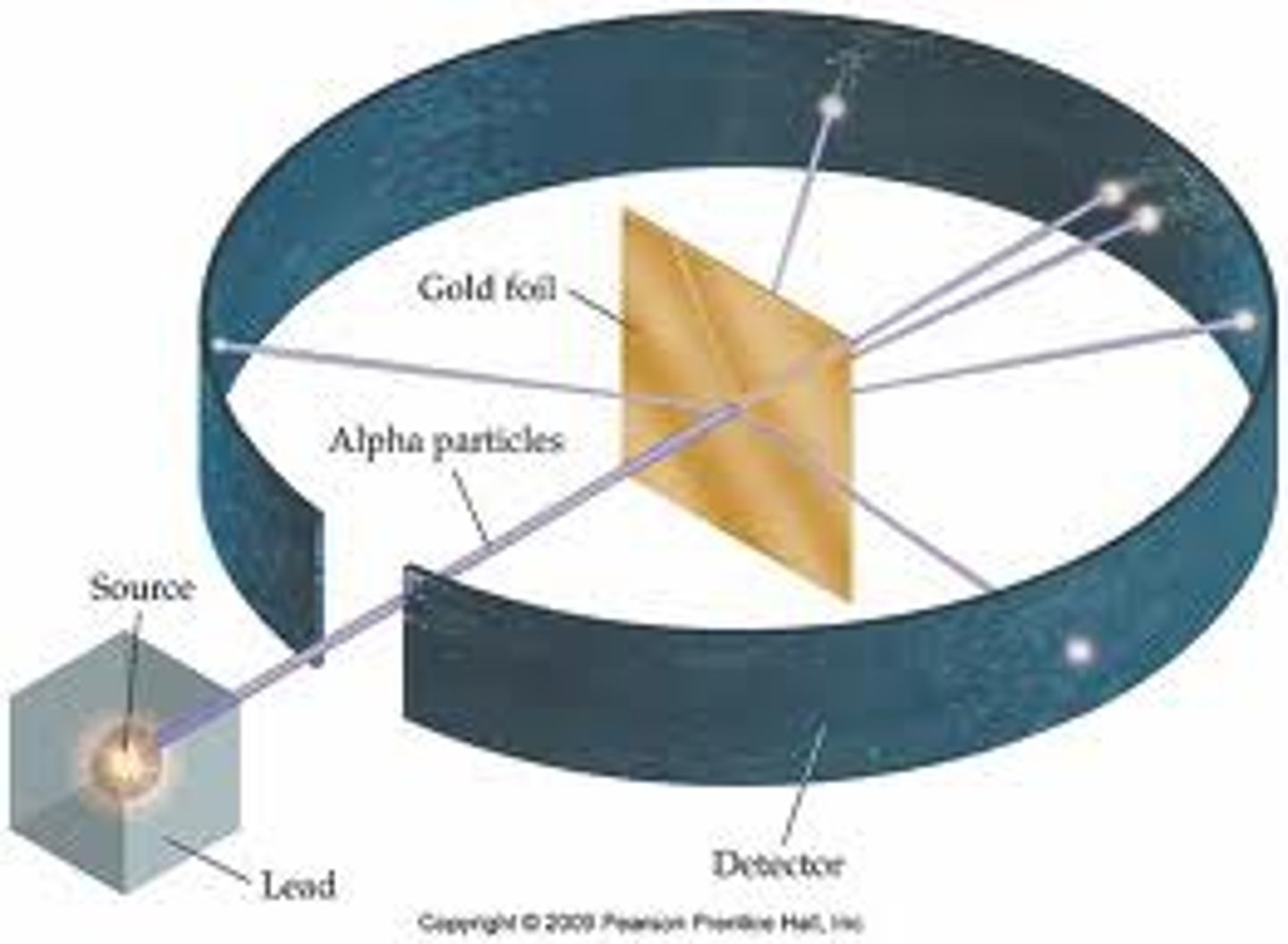
Ernest Rutherford
Solar system model of the atom, gold foil experiment- fired negative ions at thin sheet of gold foil, discovered the atomic nucleus and proposed a nuclear model of the atom. Discovered nucleus and protons.
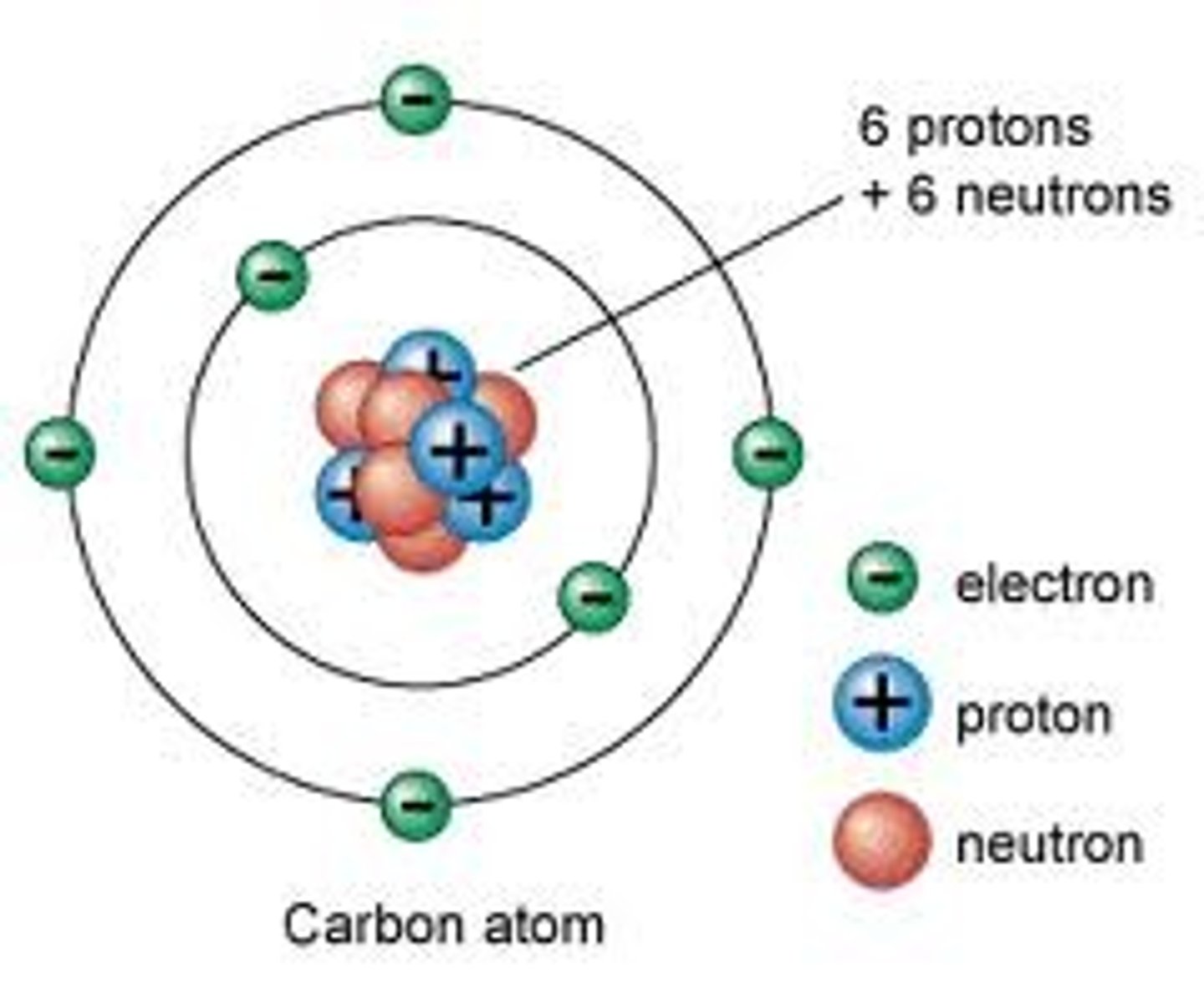
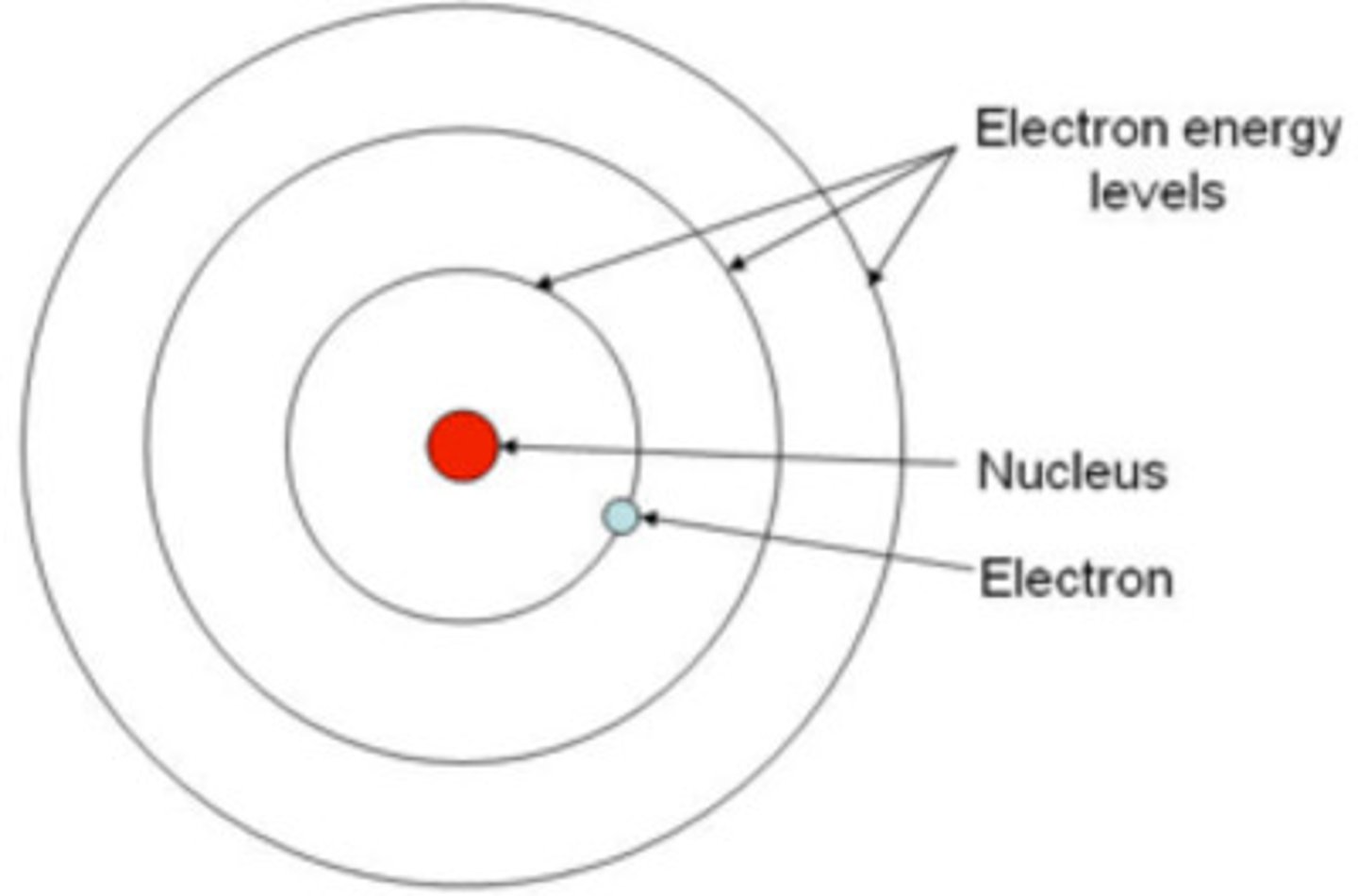
Bohr
Planetary model
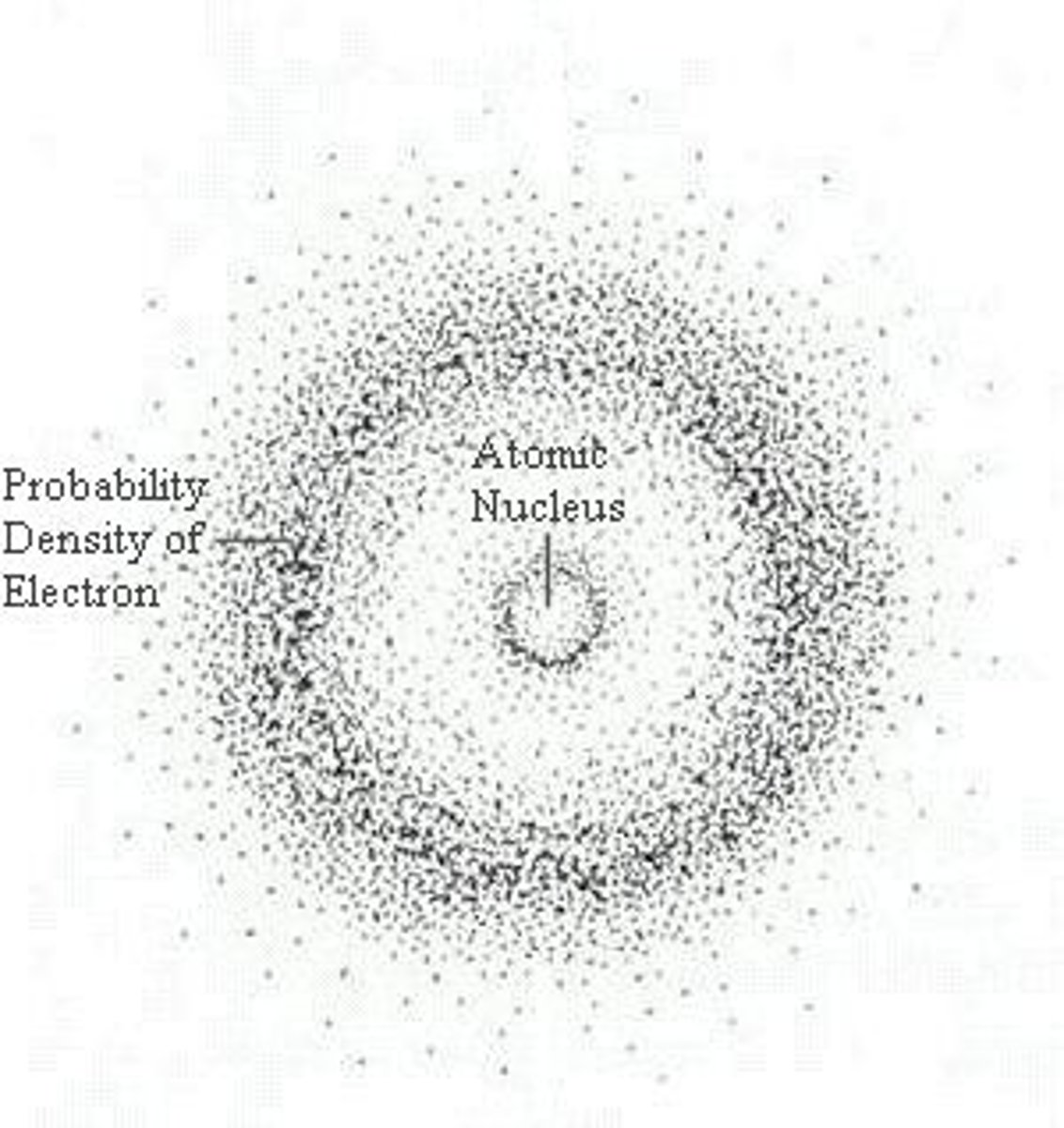
Schodinger
quantum model, discovered Orbitals
Conversion of atoms to moles
1 Mol/6.02x10^23 atoms
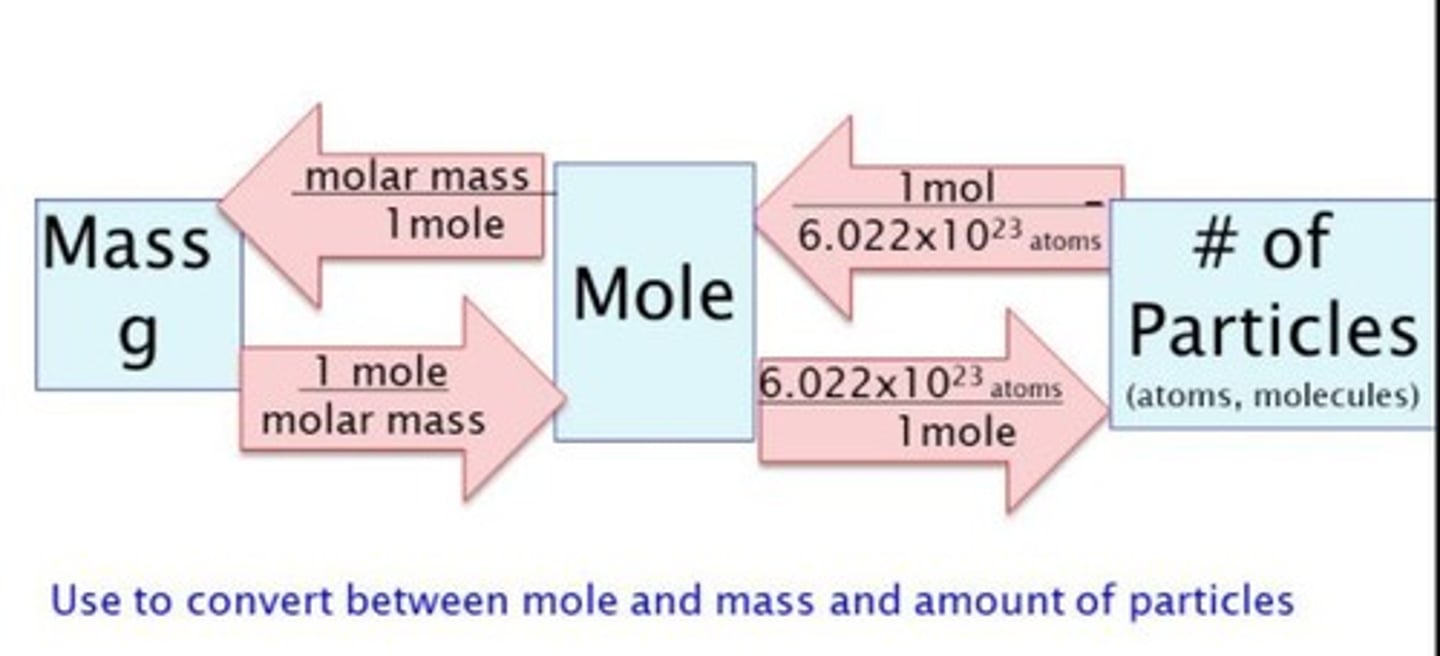
Conversion of moles to grams
Molar mass/ 1 mol

What is molar mass?
the mass in grams of one mole of a substance

What are the units for mass
grams

Dalton's law or partial pressures
the total pressure of a gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the component gases
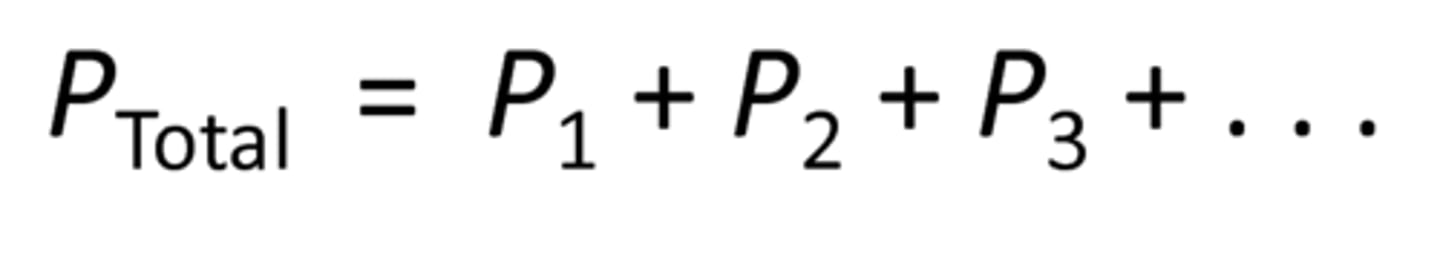
absolute zero
The coldest temperature, 0 Kelvin, that can be reached. It is the hypothetical temperature at which all molecular motion stops.

pressure
the force per unit area exerted on an object
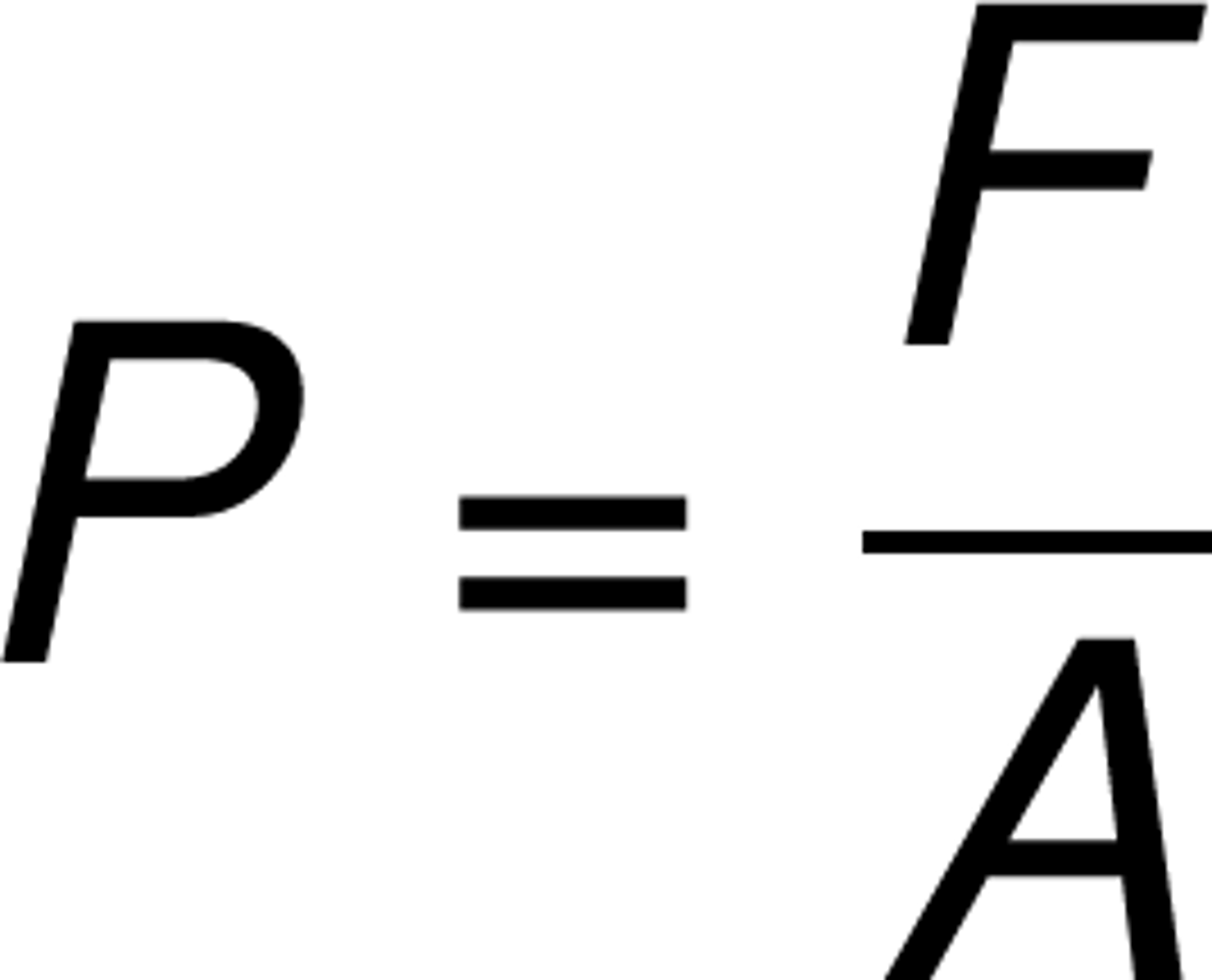
Newton
A unit of measure that equals the force required to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at 1 meter per second per second
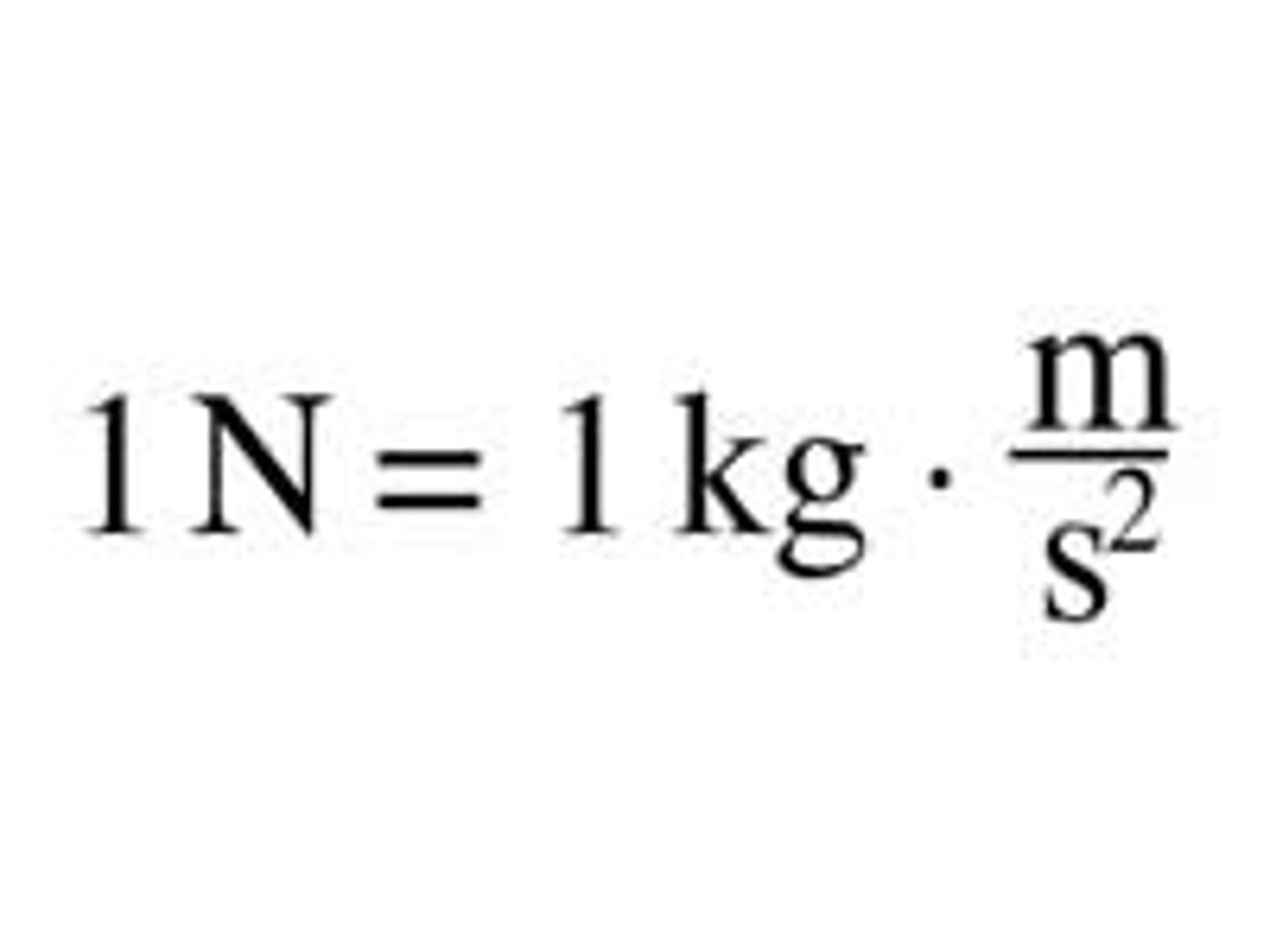
What is Atomspheric pressure at sea level?
10.1 N/cm^2
What are some common units of pressure?
- Pascal/ Pa (1 Pa=1N/m^2)
-Millimeter of mercury/ mm Hg
- Torr (1 torr=1mm Hg)
-Atmosphere/ atm

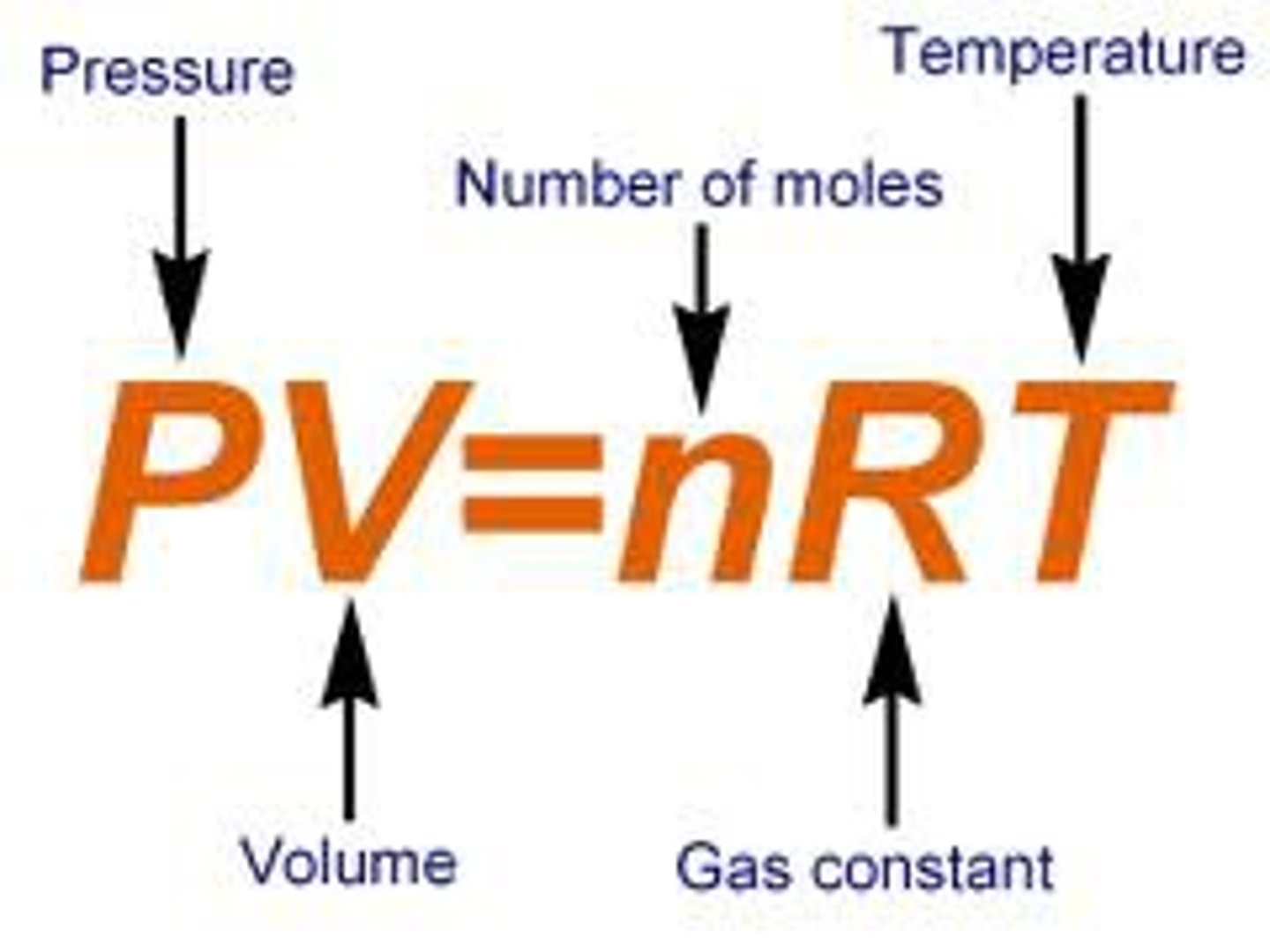
Ideal Gas Law
the relationship PV=nRT, which describes the behavior of an ideal gas
Kinetic Molecular Theory
1) Small sized particles in large amounts
2) Elastic collisions
3) Constant Motion
4) No force of attraction
5) Temp of a gas depends on Kinetic energy
real gas
a gas that does not behave completely according to the assumptions of the kinetic-molecular theory

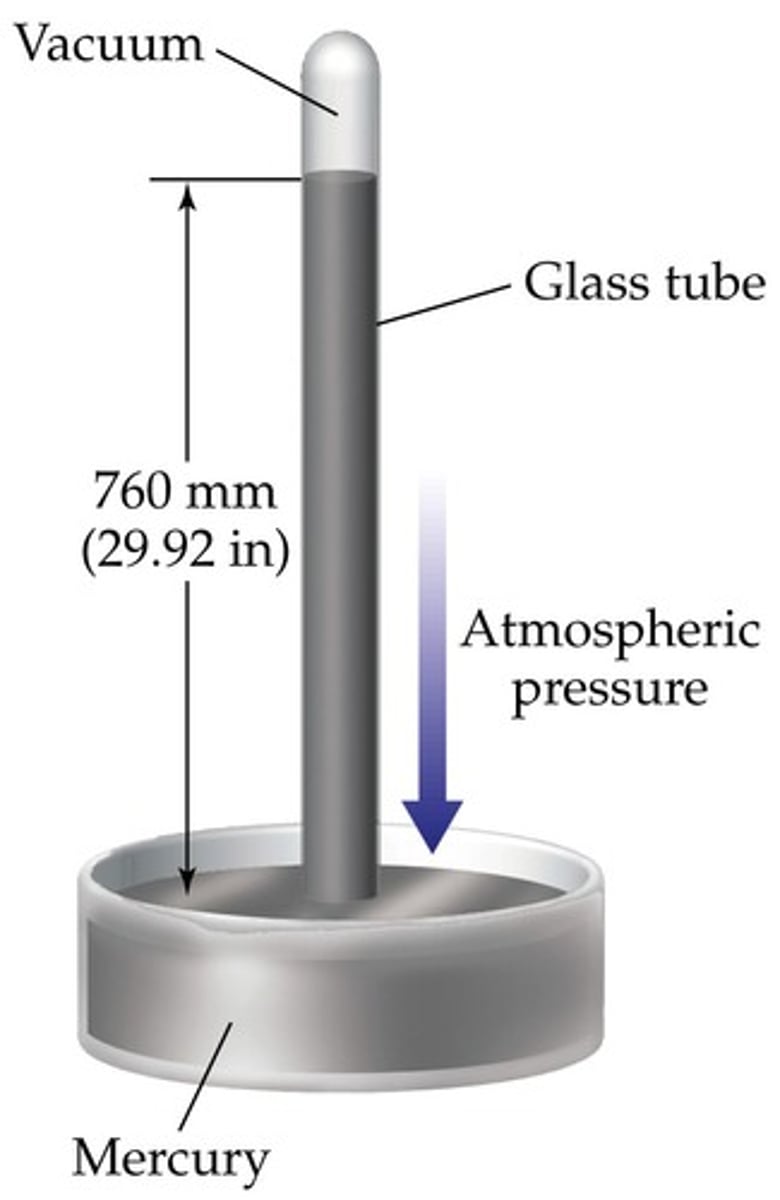
A barometer measures
atmospheric pressure
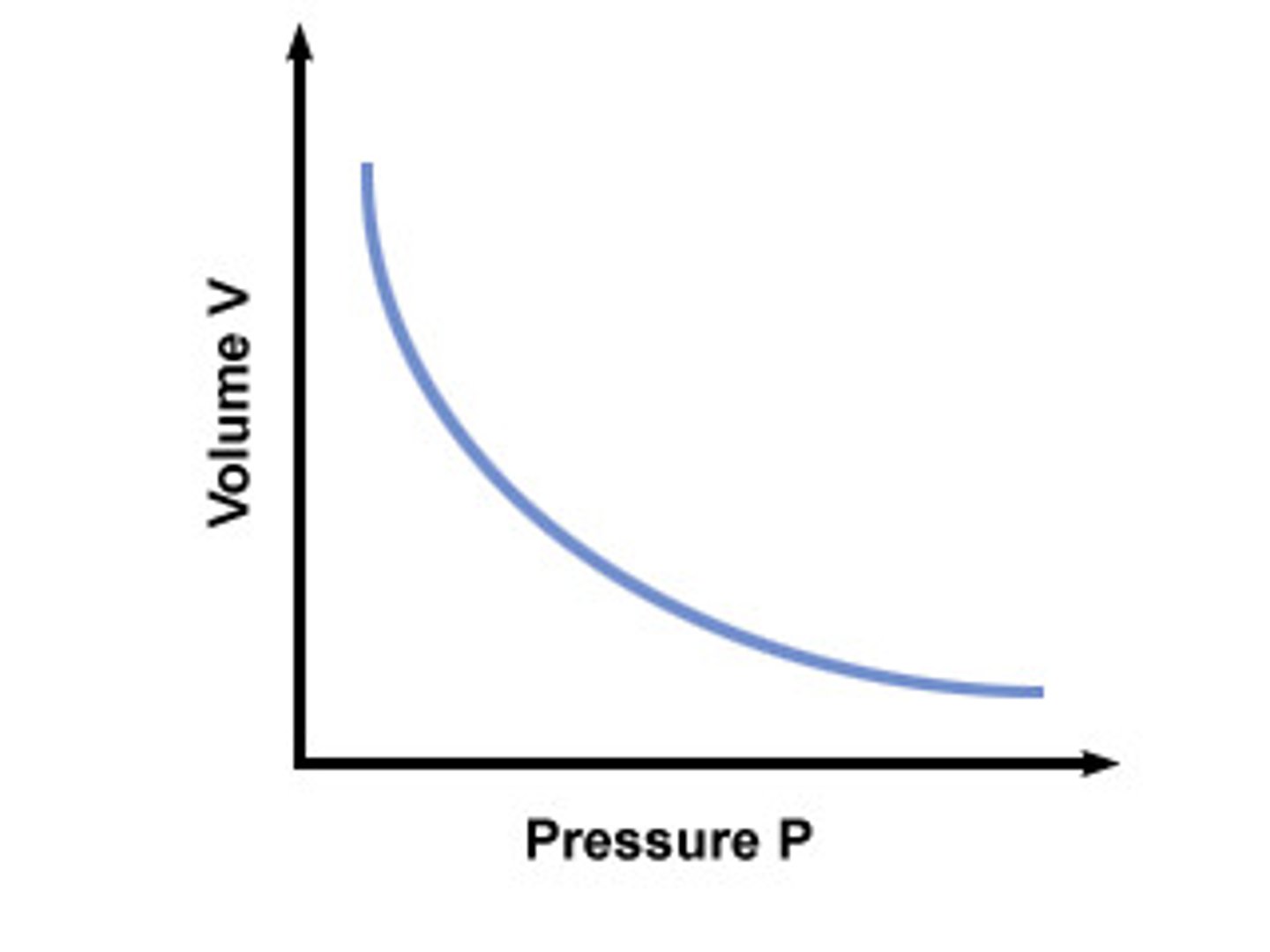
Boyle's Law
A principle that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature
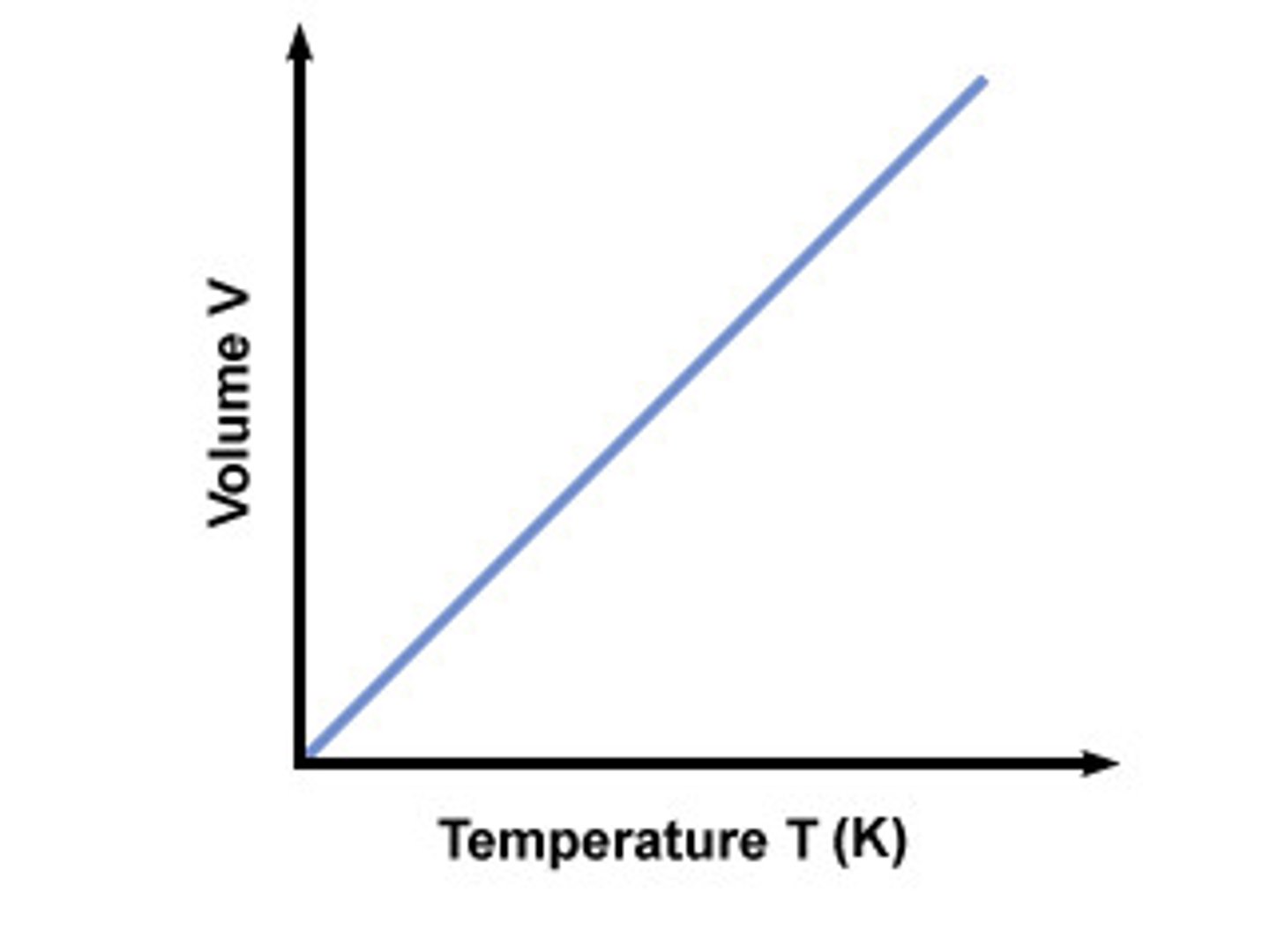
Charles' Law
the law that states that for a fixed amount of gas at a constant pressure, the volume of the gas increases as the temperature of the gas increases and the volume of the gas decreases as the temperature of the gas decreases
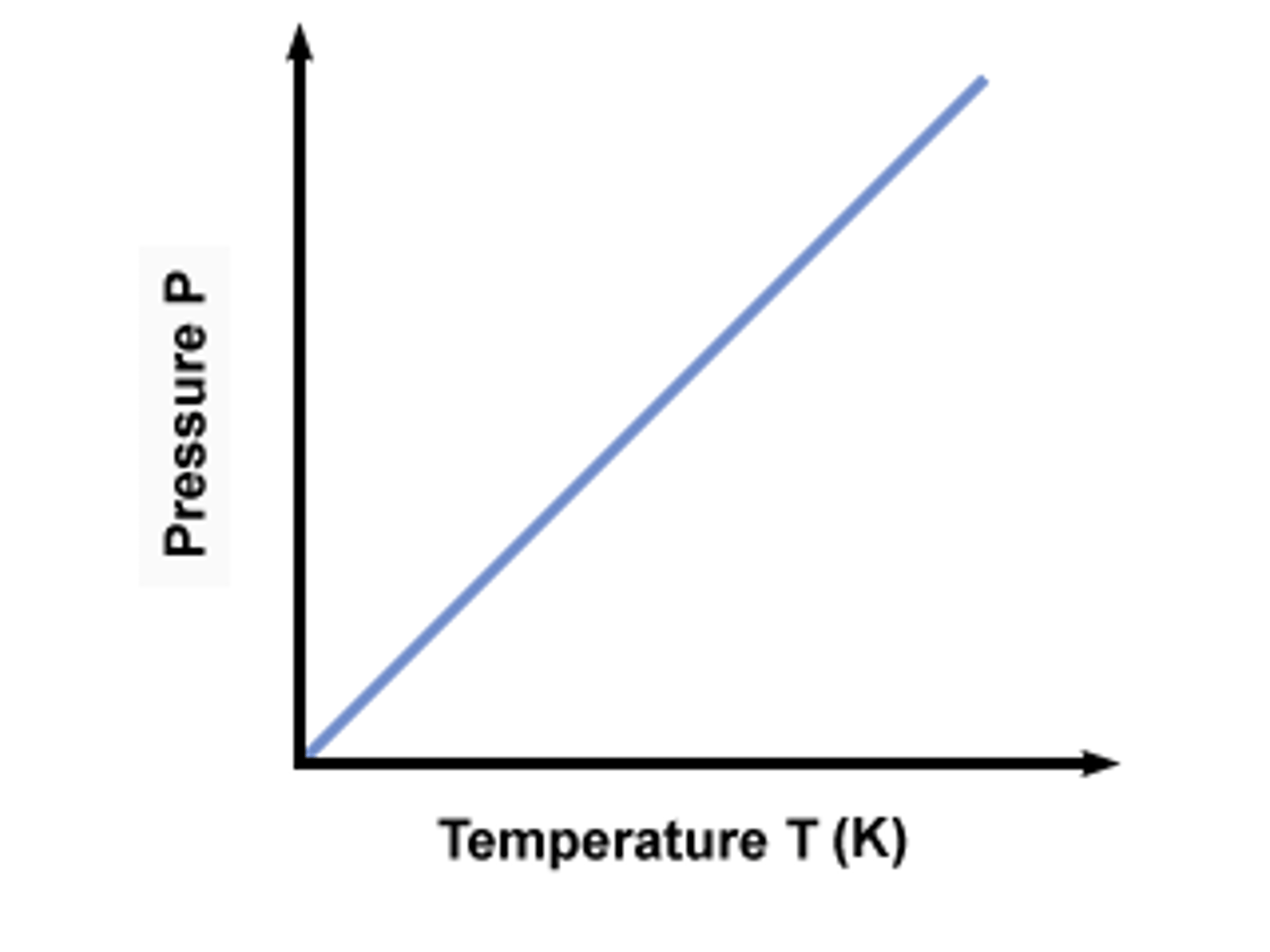
Gay-Lussac's Law
the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the Kelvin temperature if the volume is constant
Combined Gas Law
the relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature of a fixed amount of gas
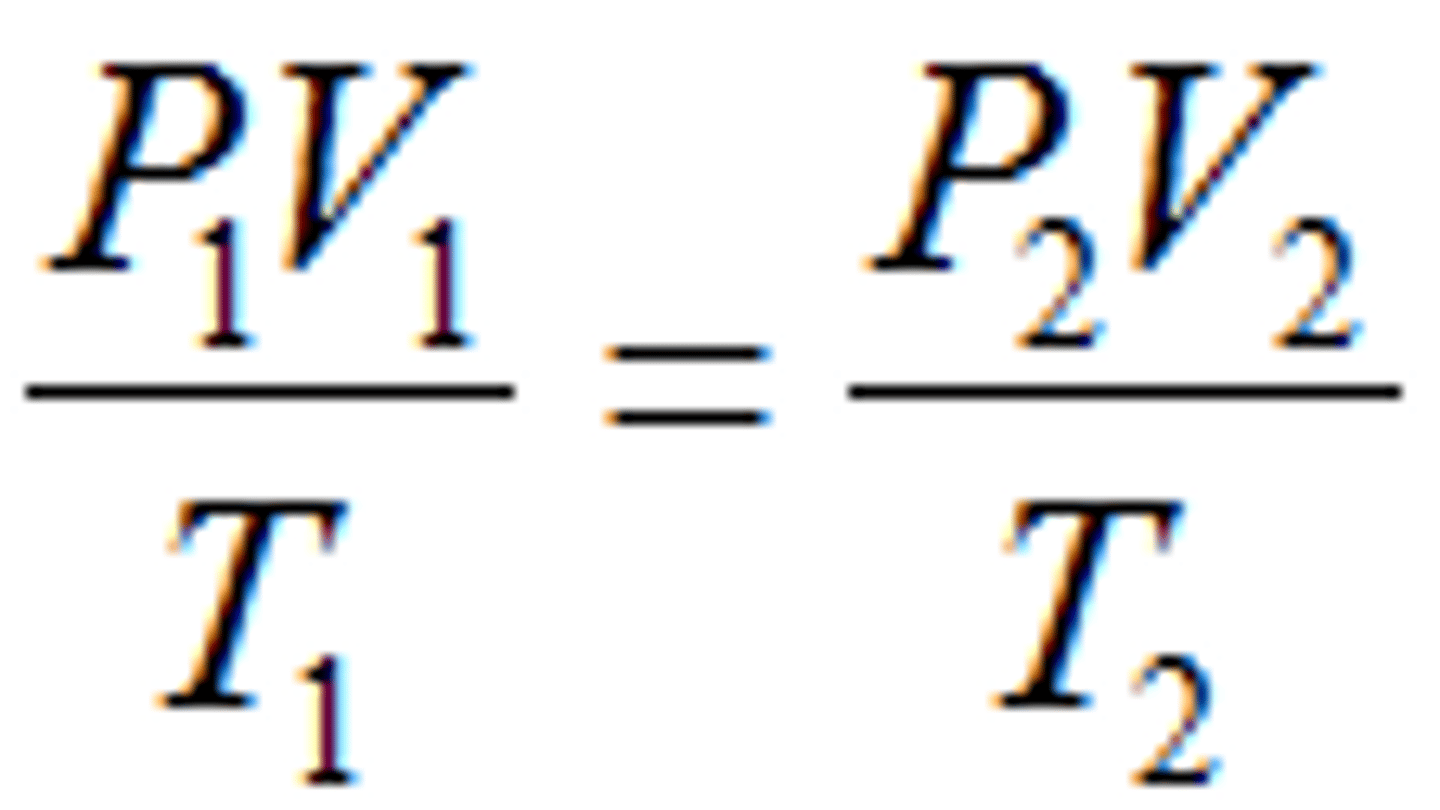
Avogadro's number
6.02 x 10^23
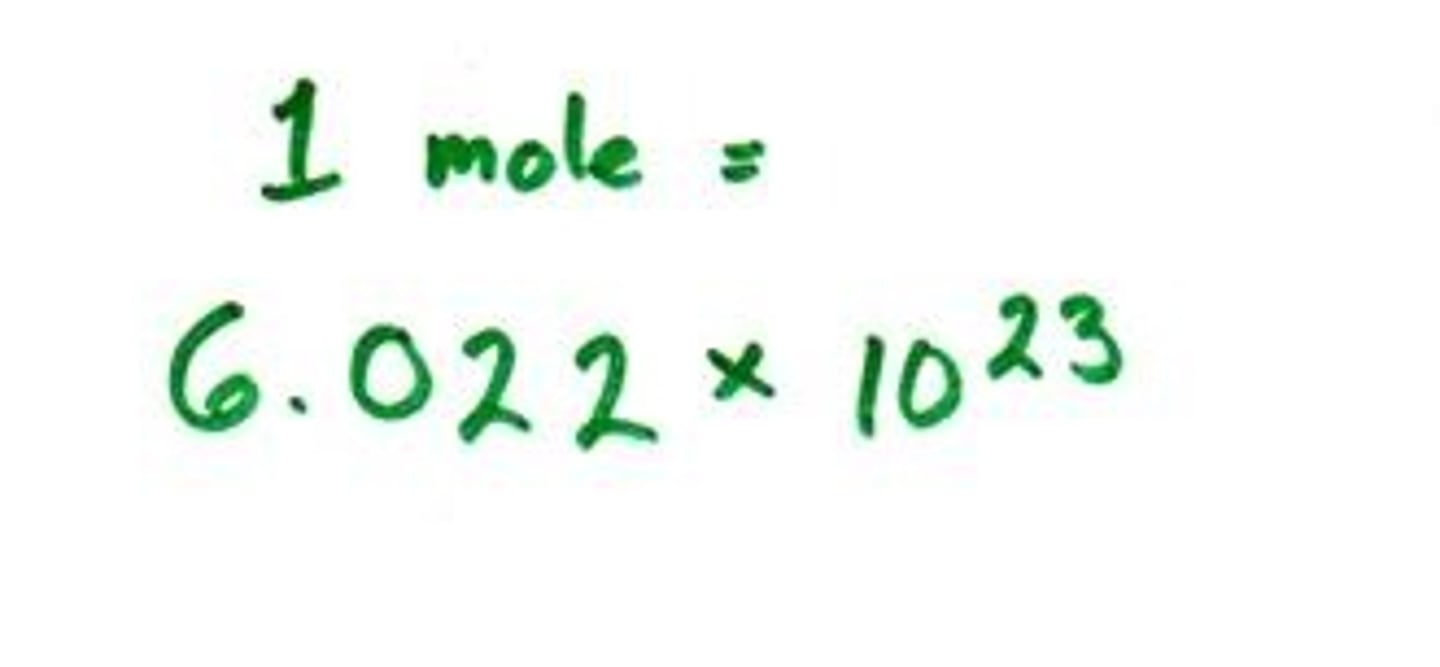
Why does it take longer to cook at higher altitudes
There are less particles in the atmosphere. Once the molecules are high in energy, they will just bounce out, instead of increasing the pressure. Without this pressure the boiling point will be lower than favored.
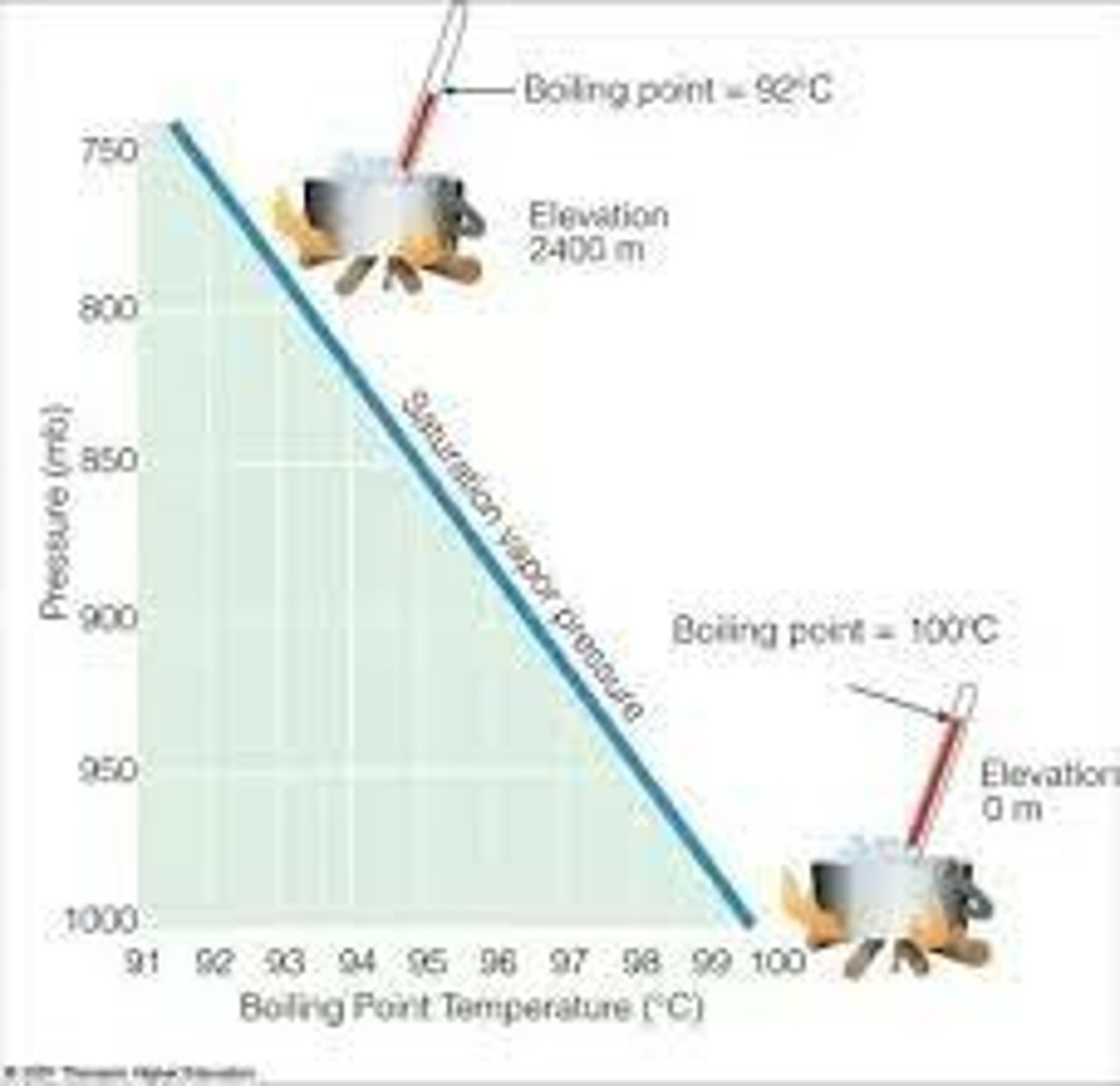
How can you convert Celsius to kelvin
Kelvin= Celsius + 273.15

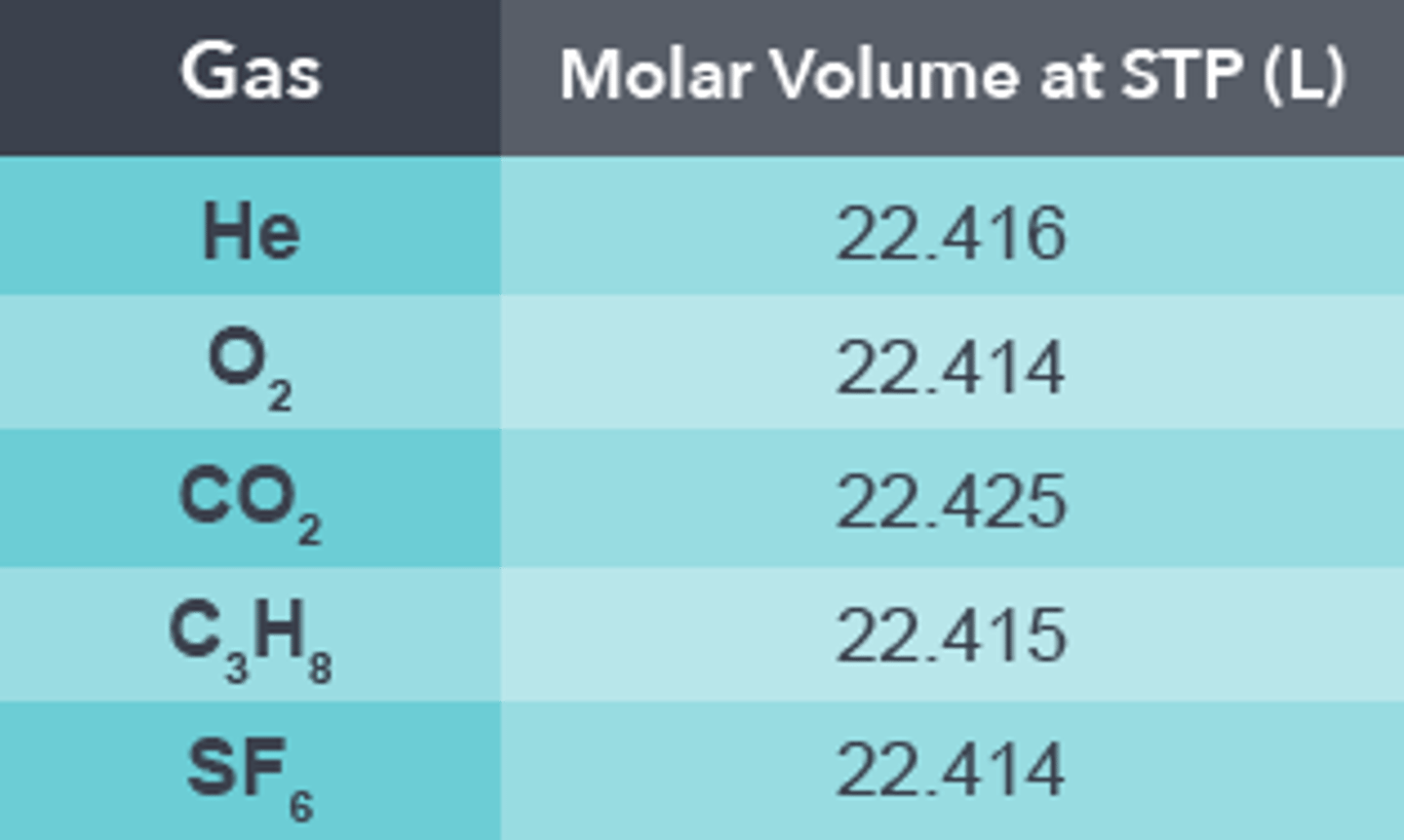
What is the volume taken up by 1mole (STP)
Its the standard molar volume of a gas. Its about 22.414L
What is the first thing you do in an emergency or when something breaks or goes wrong?
Tell Sister Mary Albert
What is a C fire?
Electrical
When do you use goggles and when do you use aprons?
Goggles: always
Aprons: hazardous lab experiments
How do you deal with contact lenses?
Wear glasses to class that day or tell Sister before the lab
What do you do with chemical waste?
put it in the trash can, the sink, or the labeled bin, depending on what the chemical waste is
What do you need to know about hot glassware and heating in test tubes?
You can't see if it is hot or not with your eyes
What is located in the prep room that you need to know about?
Different kinds of chemicals and supplies for labs
What should you do to safely prepare for an experiment, do an experiment, and end an experiment?
Read the directions, be knowledgeable, and clean up
How do you work safely with others in your group?
Maintain a business-like attitude, and communicate with them
What if you have long hair?
Put it up
What do you know about types of fires and how to put them out?
A, B, C, and K fires can (usually) be put out with a fire extinguisher, and D fires have to be put out with sand
What is an A fire?
Normal combustible
What is a B fire?
Flammable liquids
What is a D fire?
Flammable metals
What is a K fire?
Kitchen
How do you use a fire extinguisher?
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
What is the fume hood?
A safety device that can expel noxious fumes from the room
Ground state
The lowest energy state of an atom
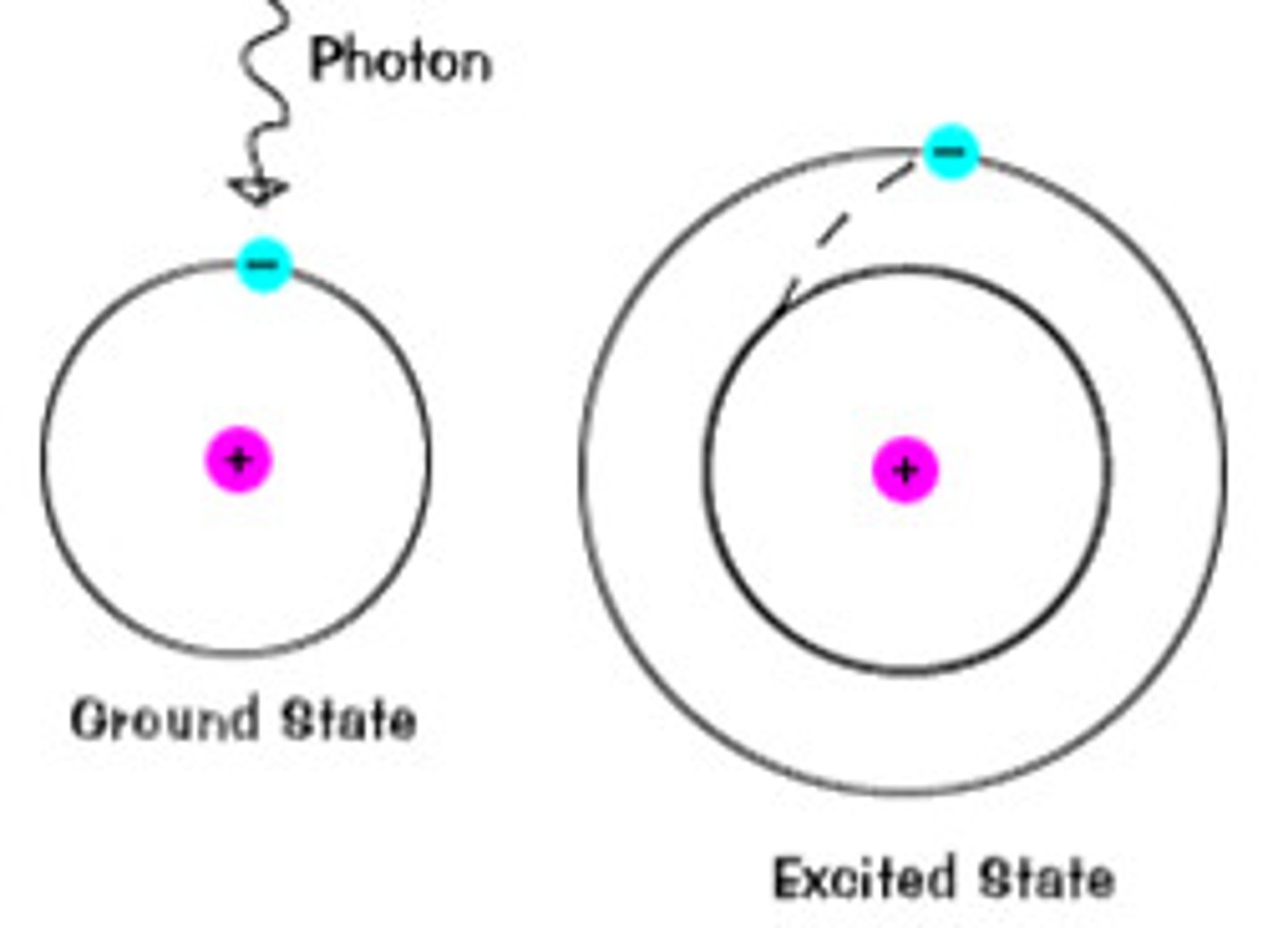
Excited state
a state in which an atom has more energy than it does at its ground state
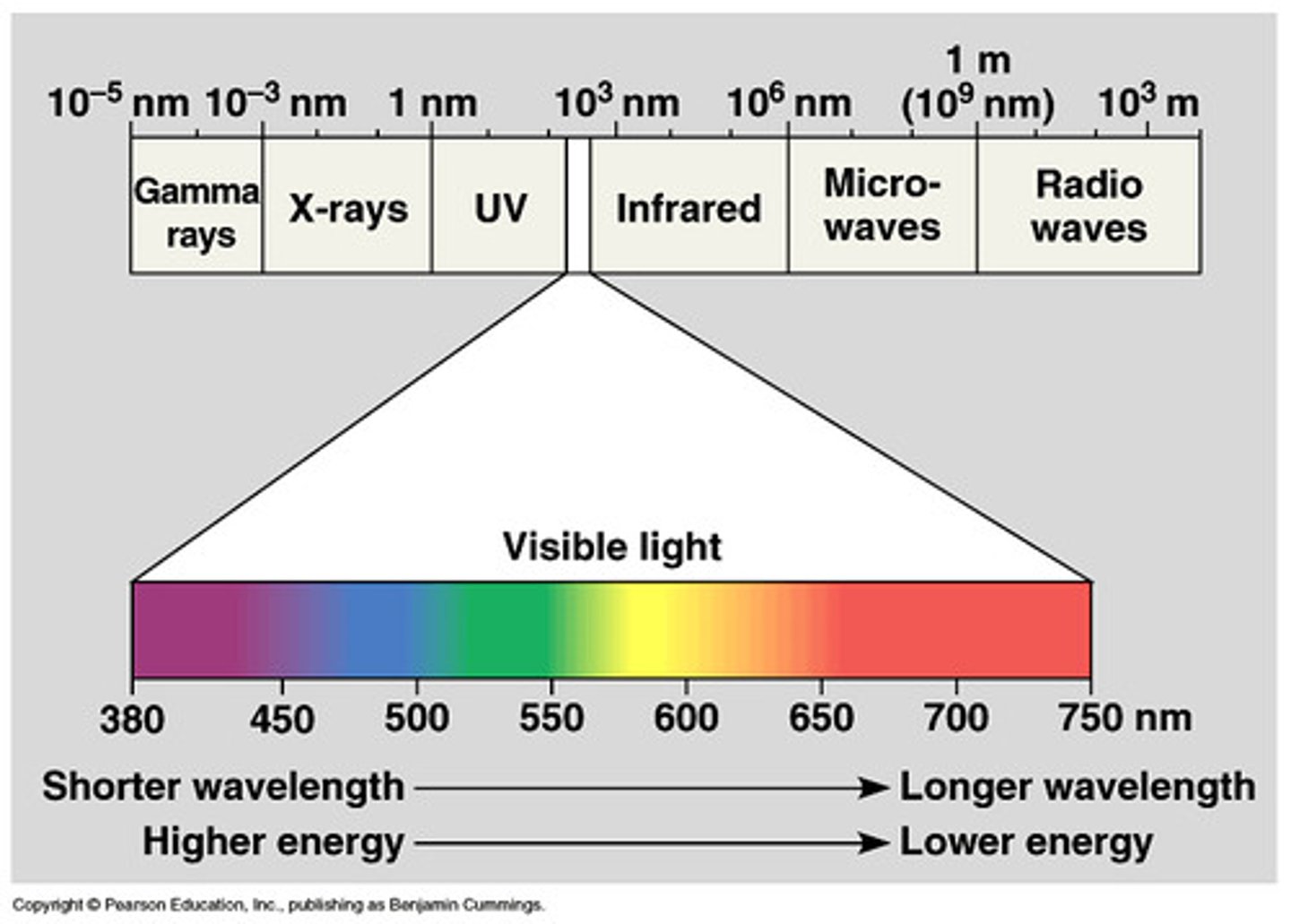
electromagnetic radiation
a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space
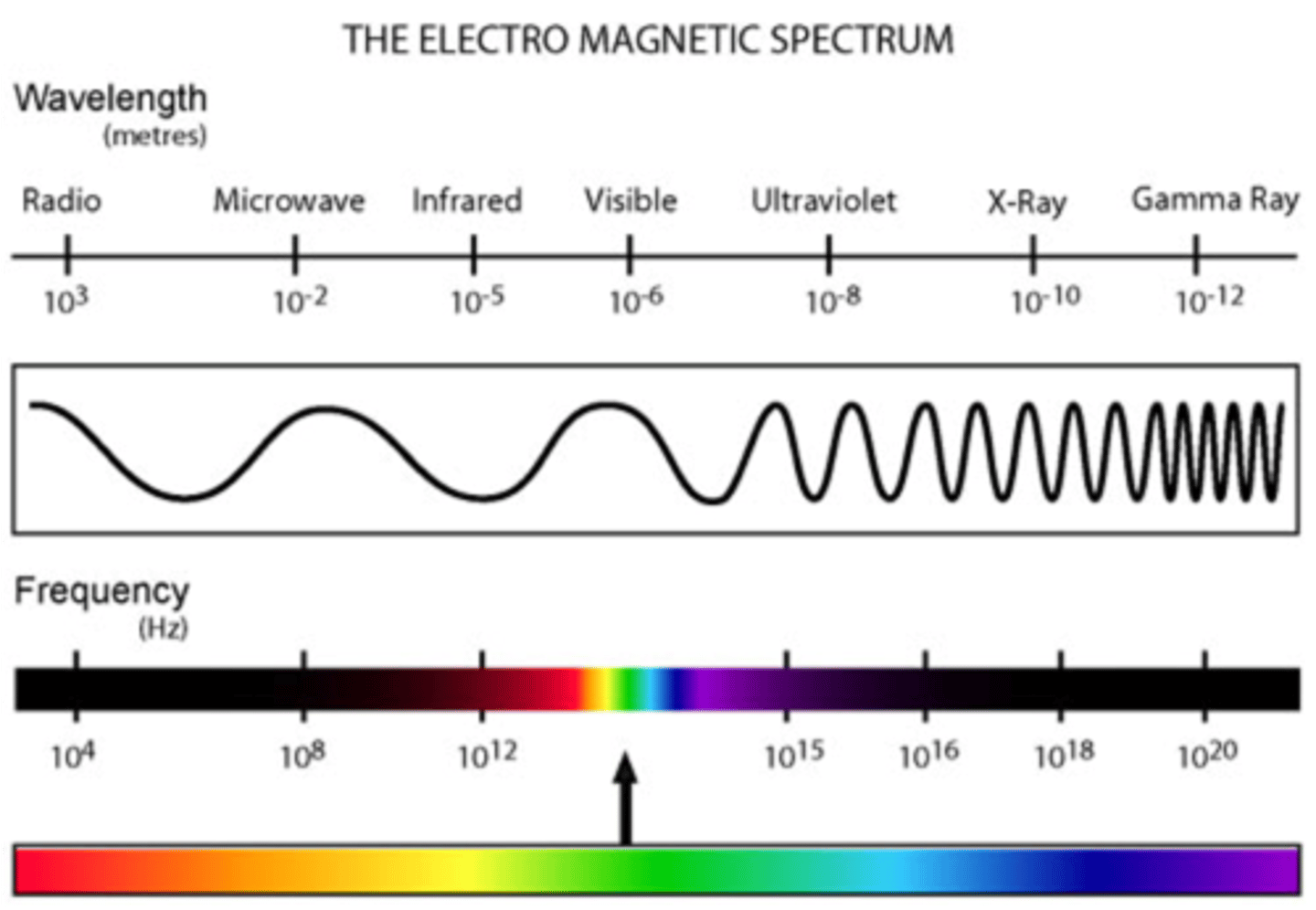
electromagnetic spectrum
the range of wavelengths or frequencies over which electromagnetic radiation extends.
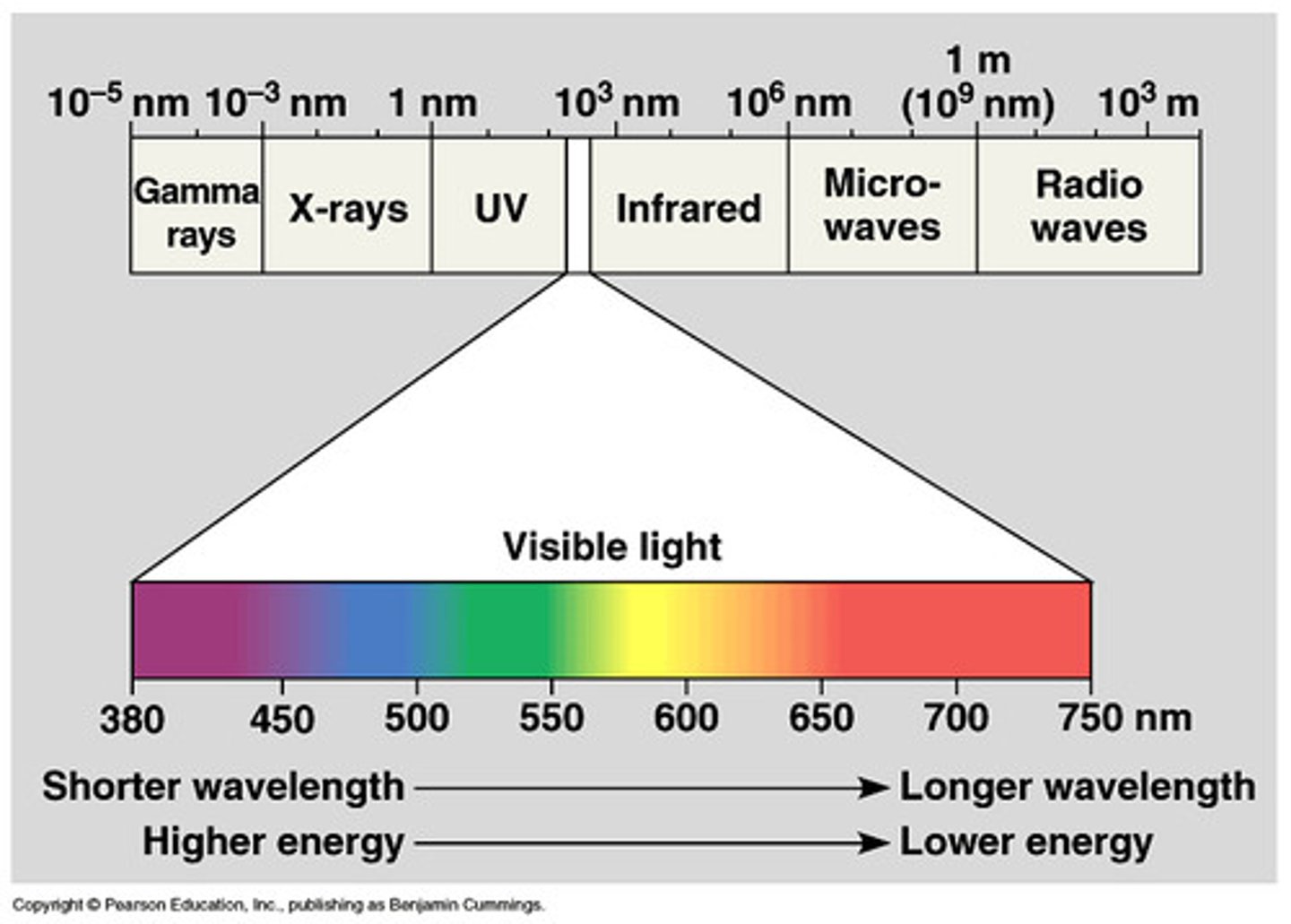
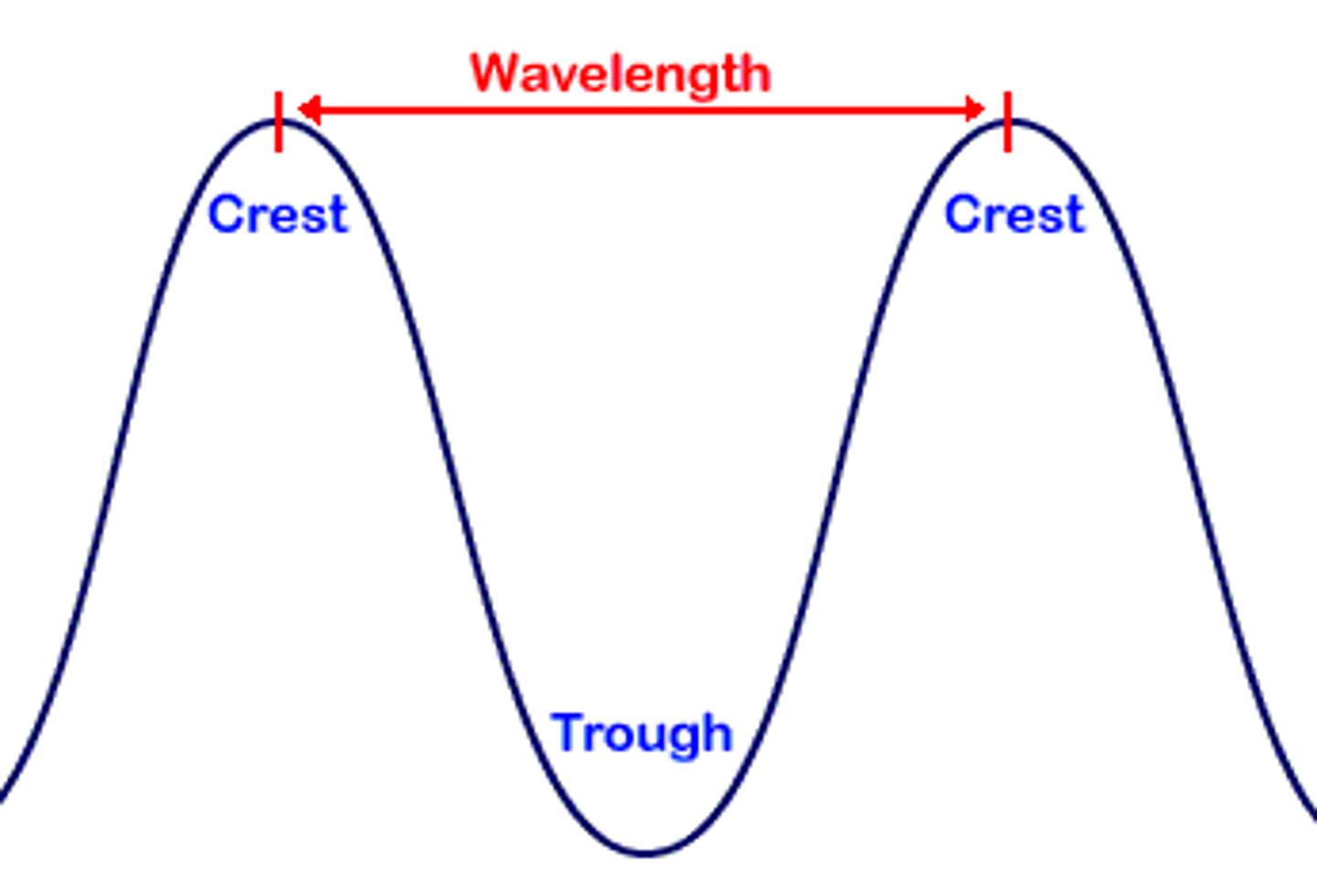
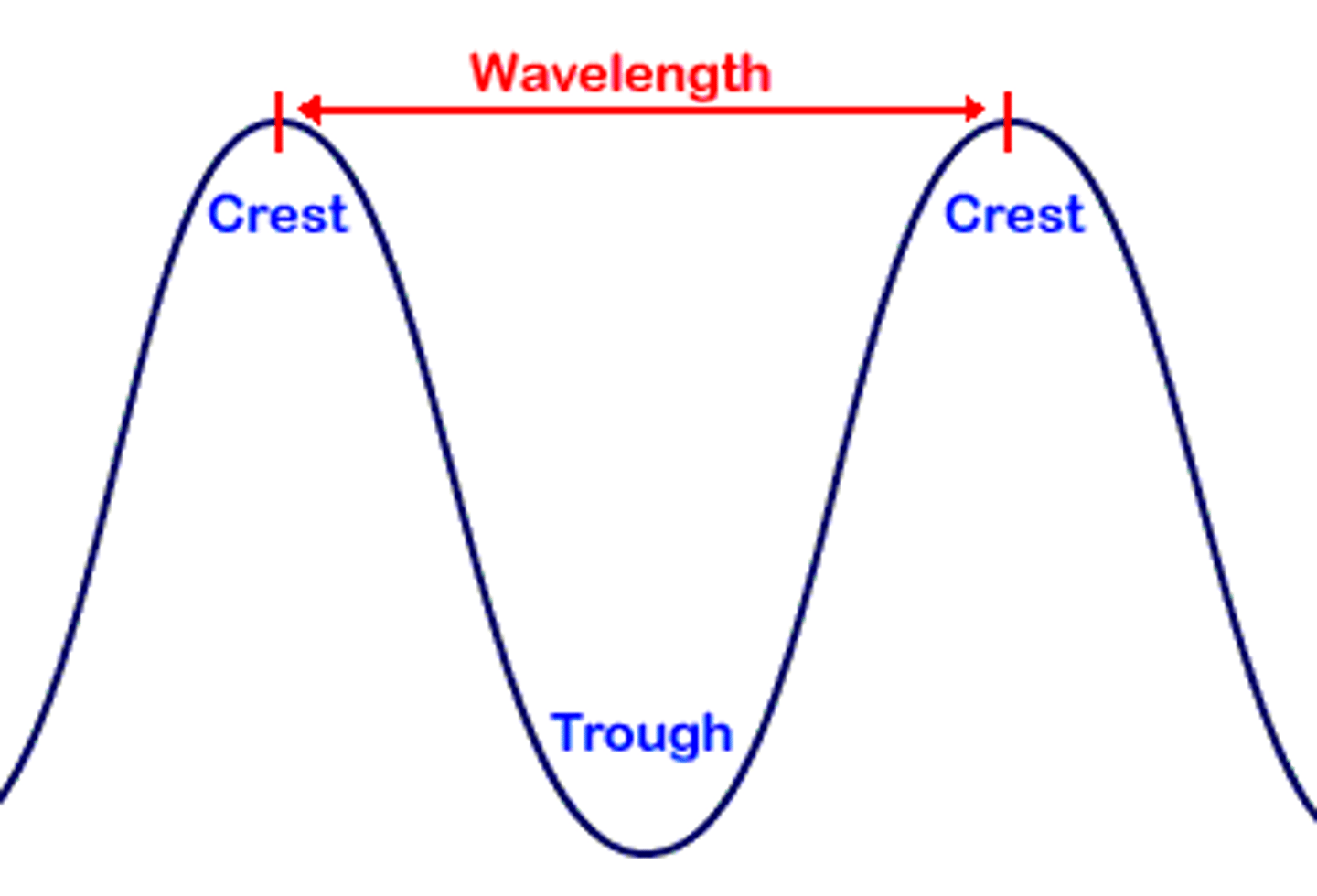
Wavelength ( ⁁ ) (cm, m, nm)
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
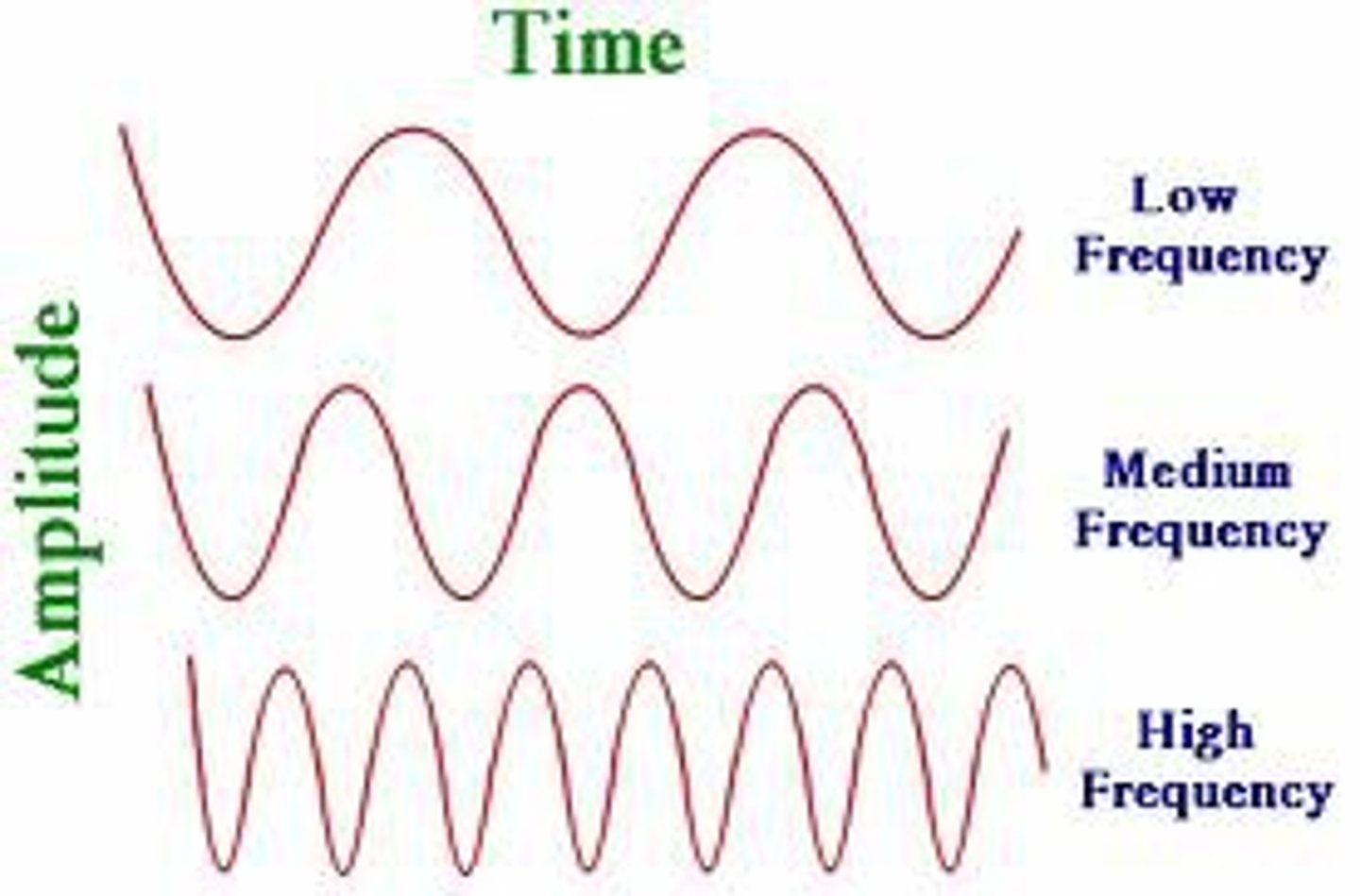
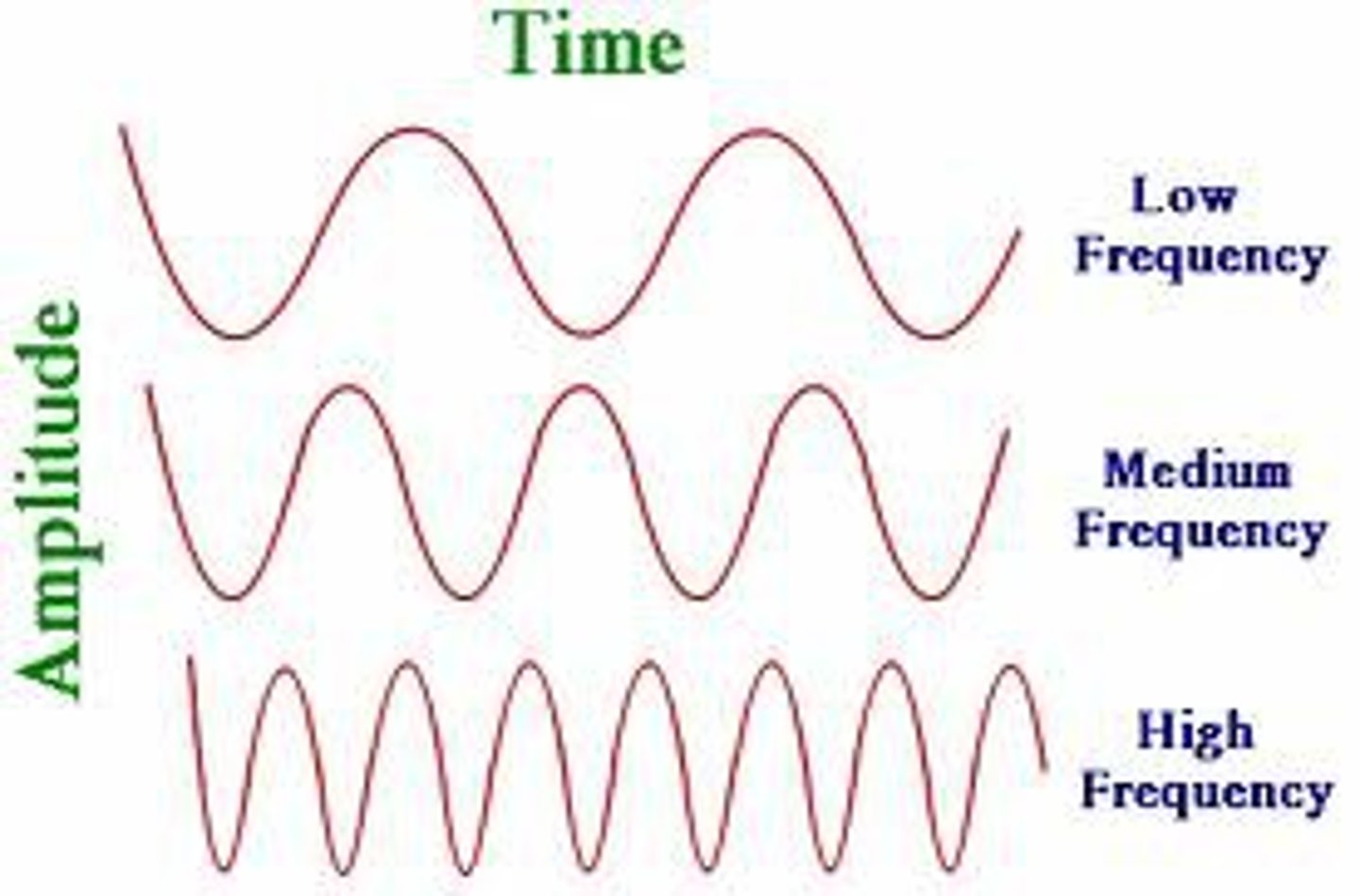
Frequency (v) (HZ=waves/s)
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
What's the formula for frequency and wave length
c=⁁v
Speed of light?
3.00 x 10^8 m/s

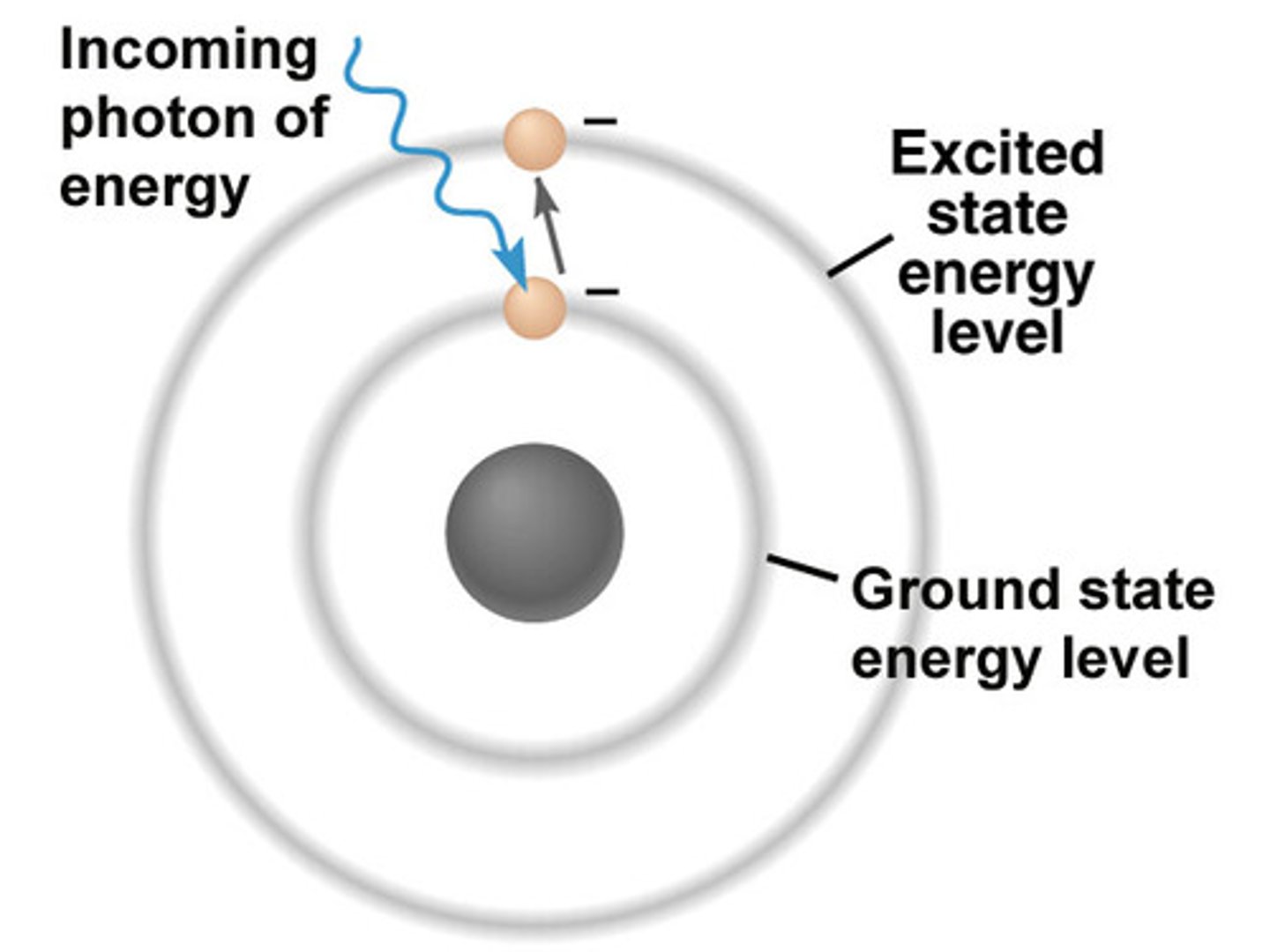
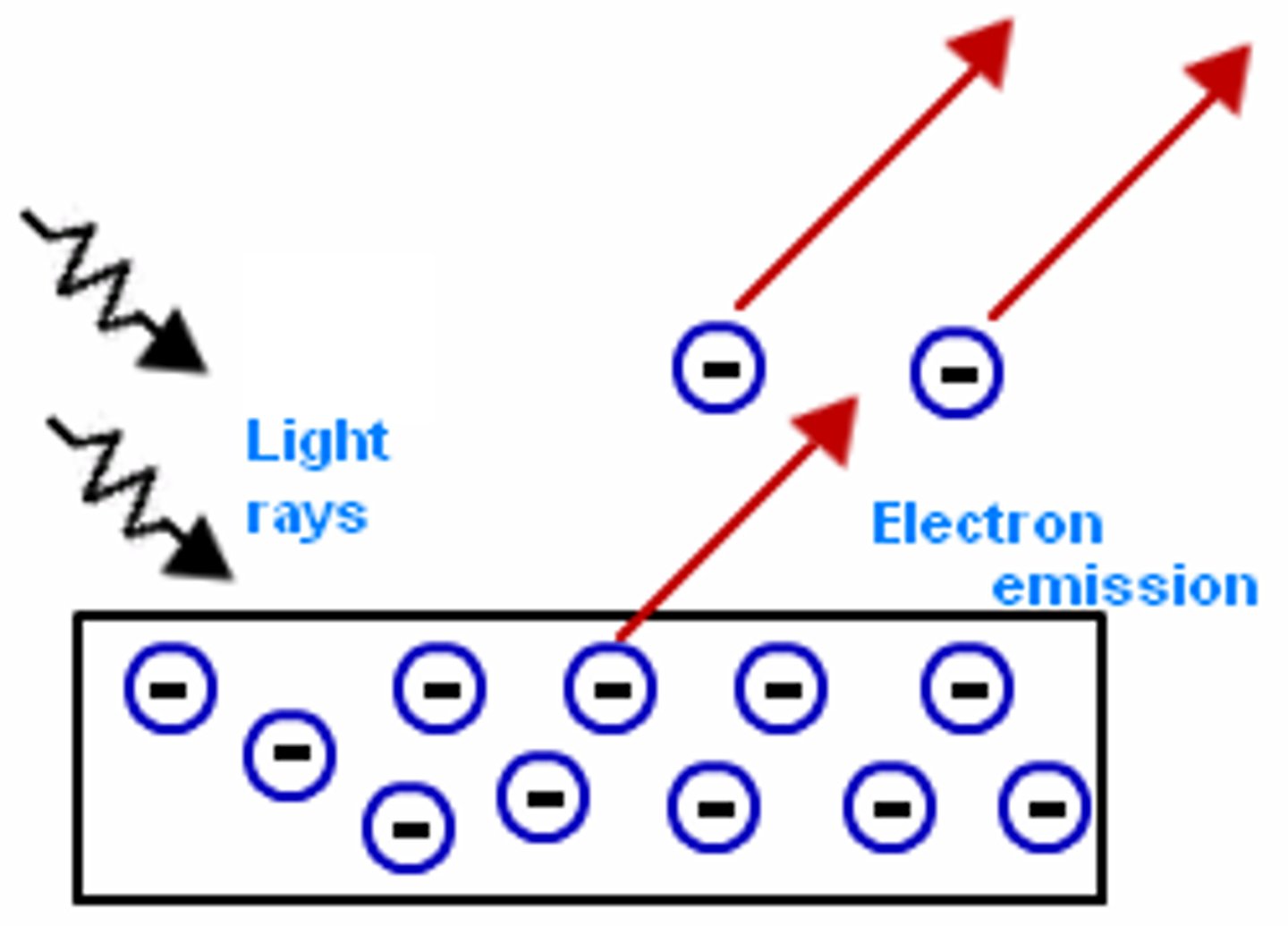
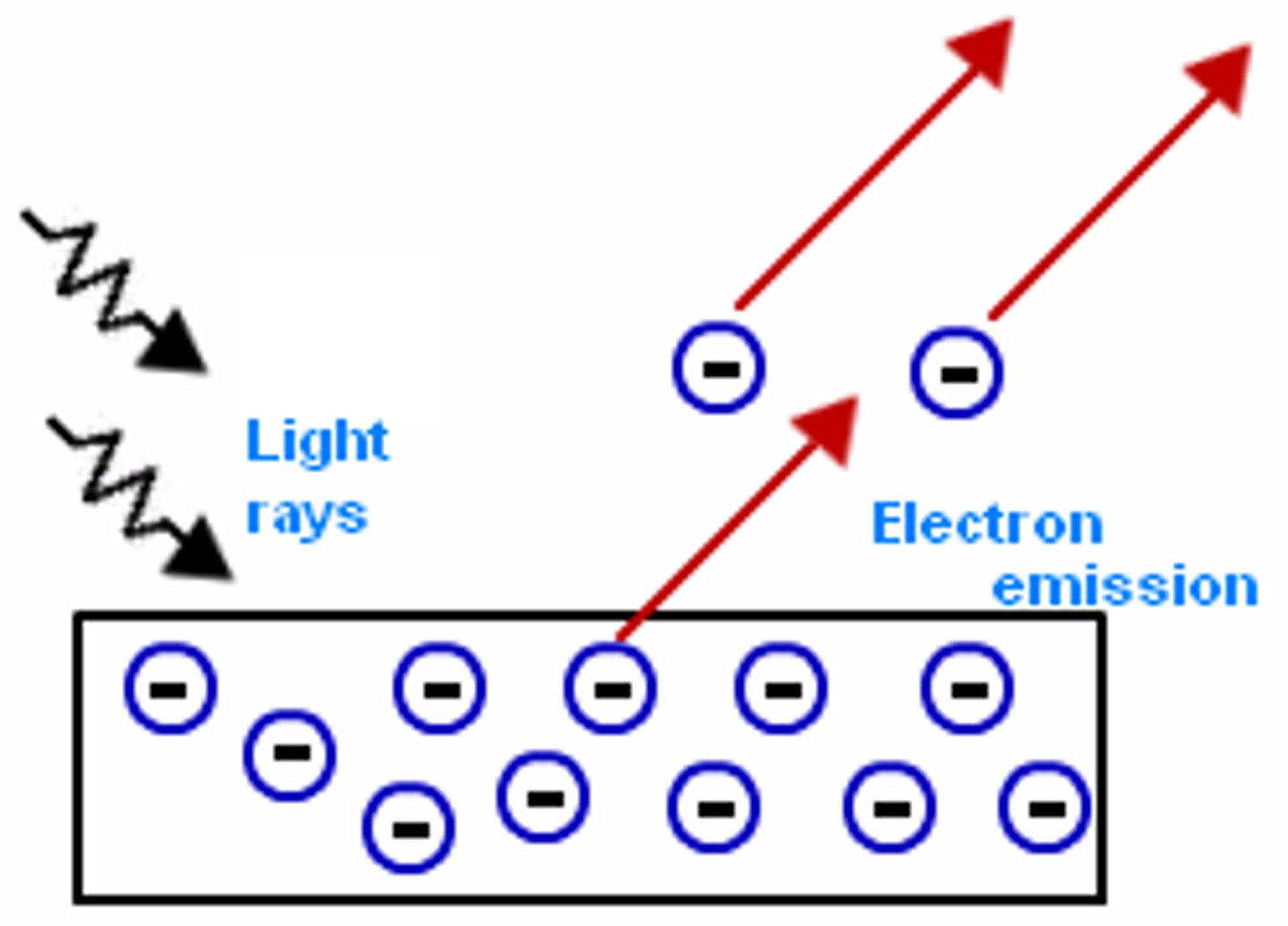
photoelectric effect
The emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
quantum
the minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
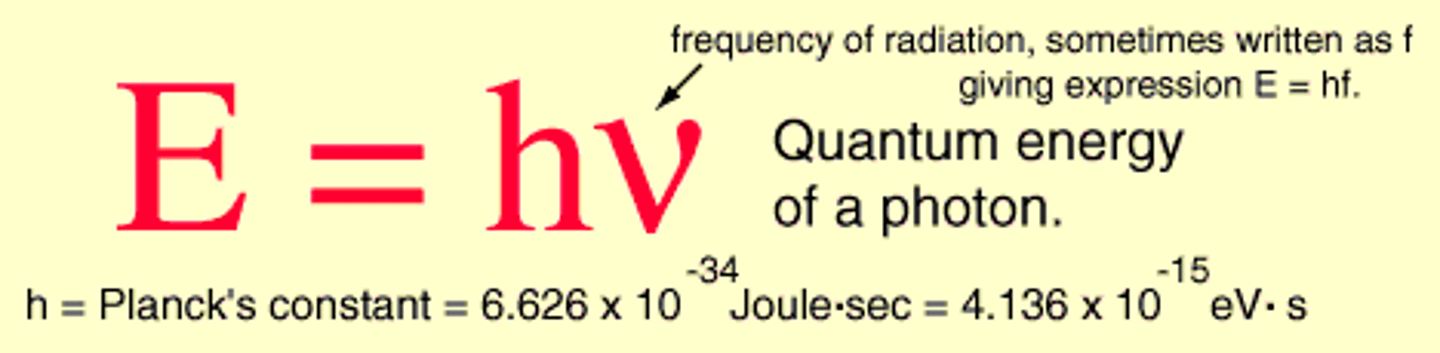
Photon
A particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy
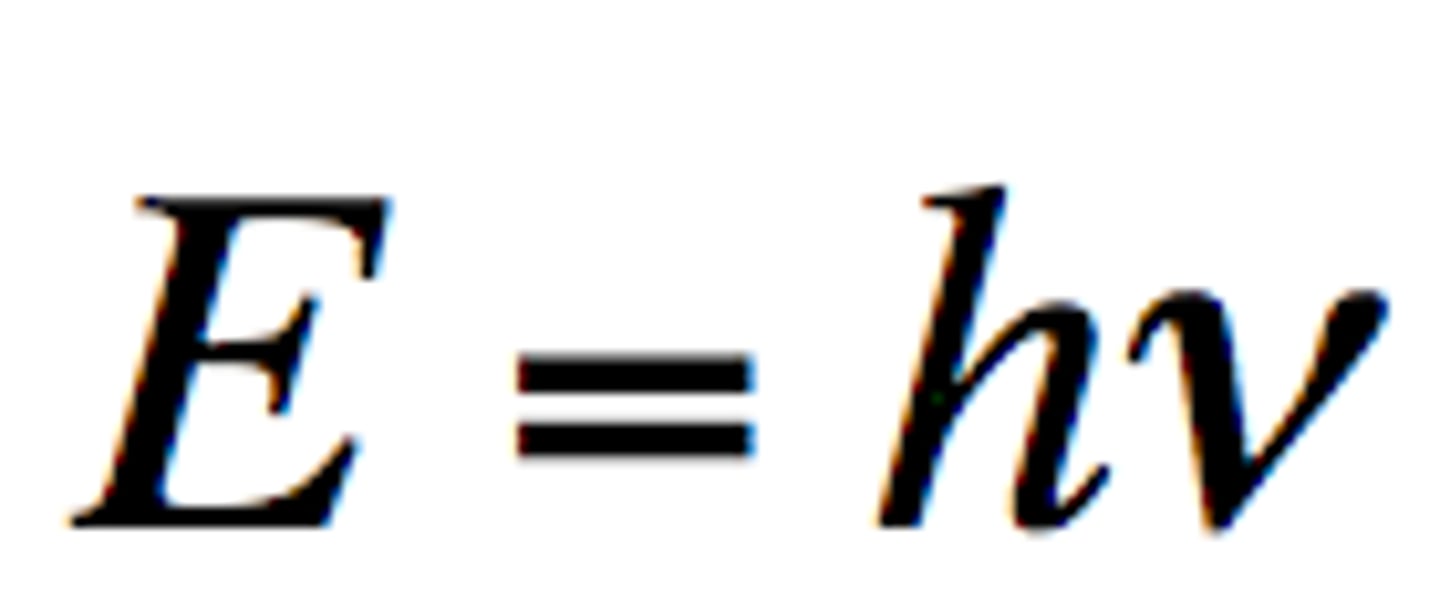
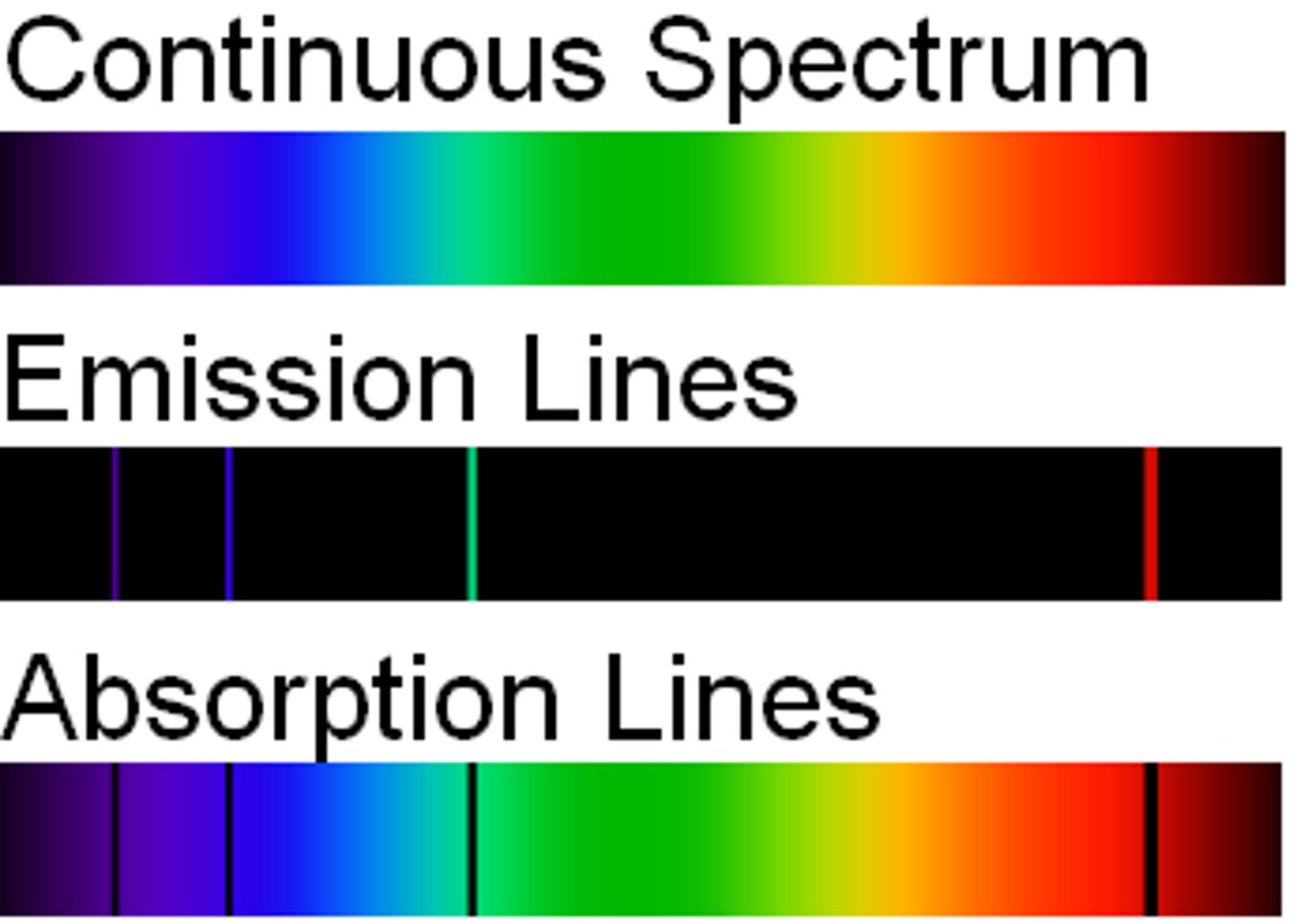
emission line spectrum
when a narrow beam of the emitted light was shined through a prism, it was separated into four specific colors of the visible spectrum
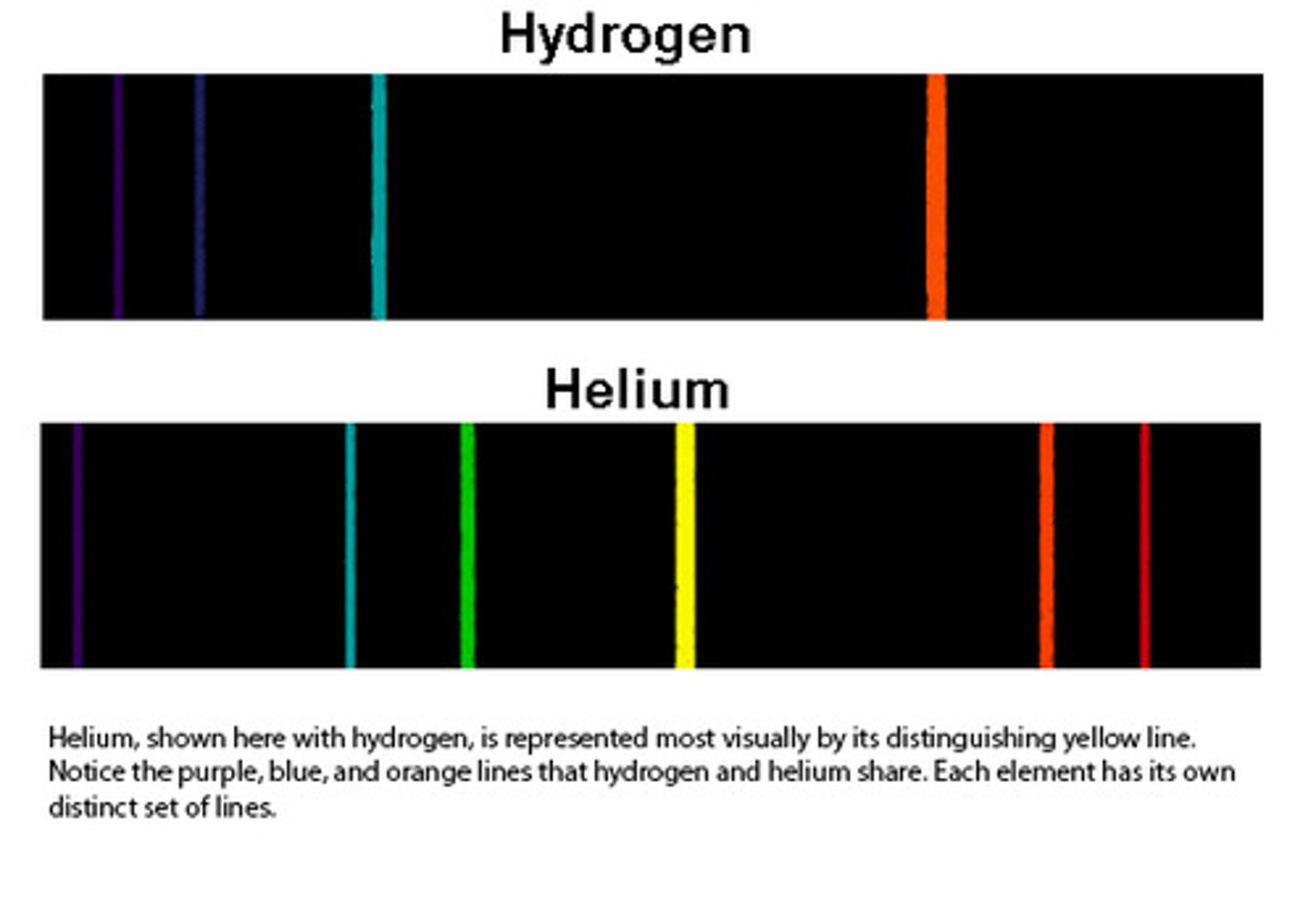
continuous line spectrum
the emission of a continuous range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation
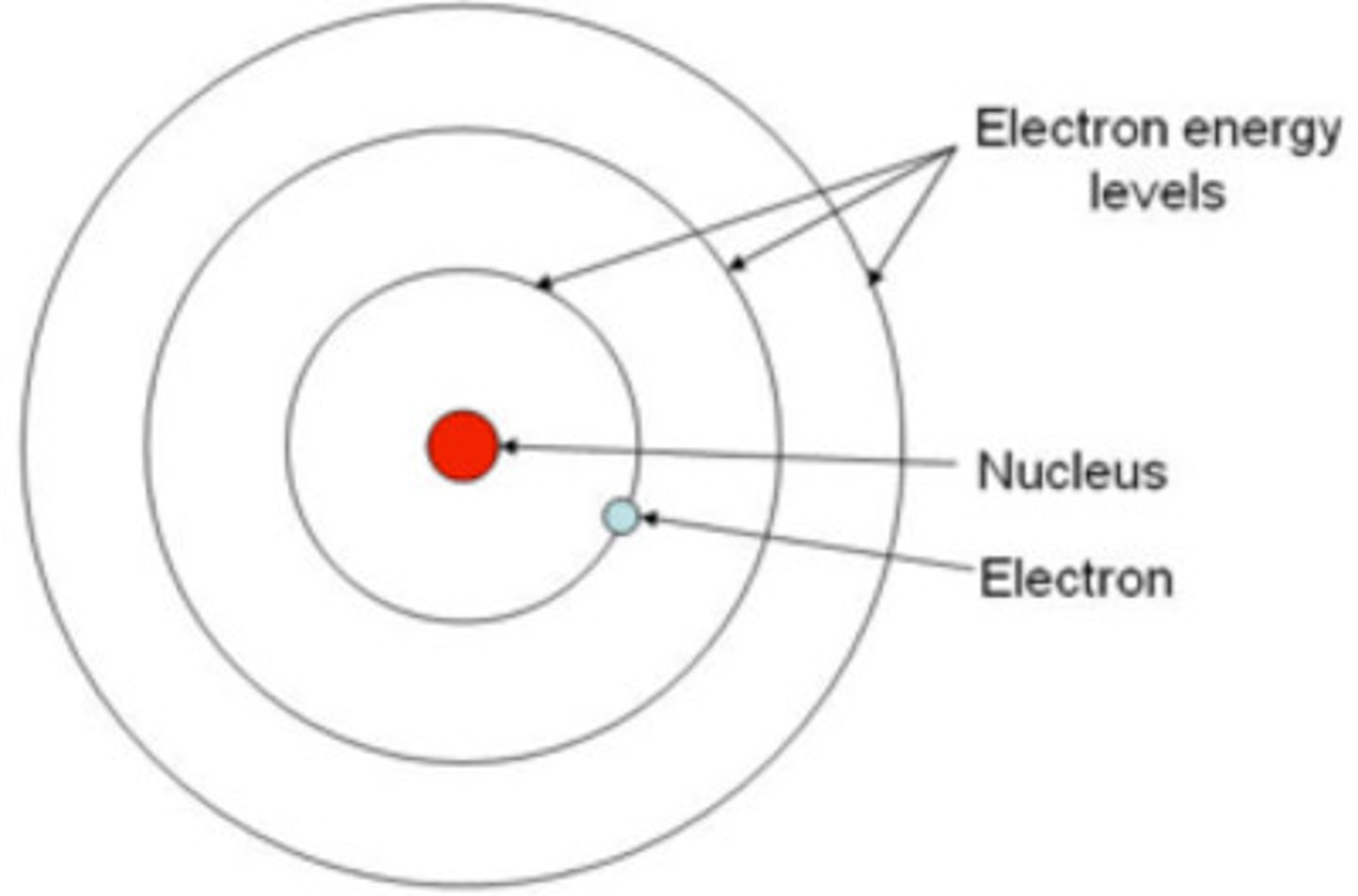
What can Bohr's model be compared to?
A ladder
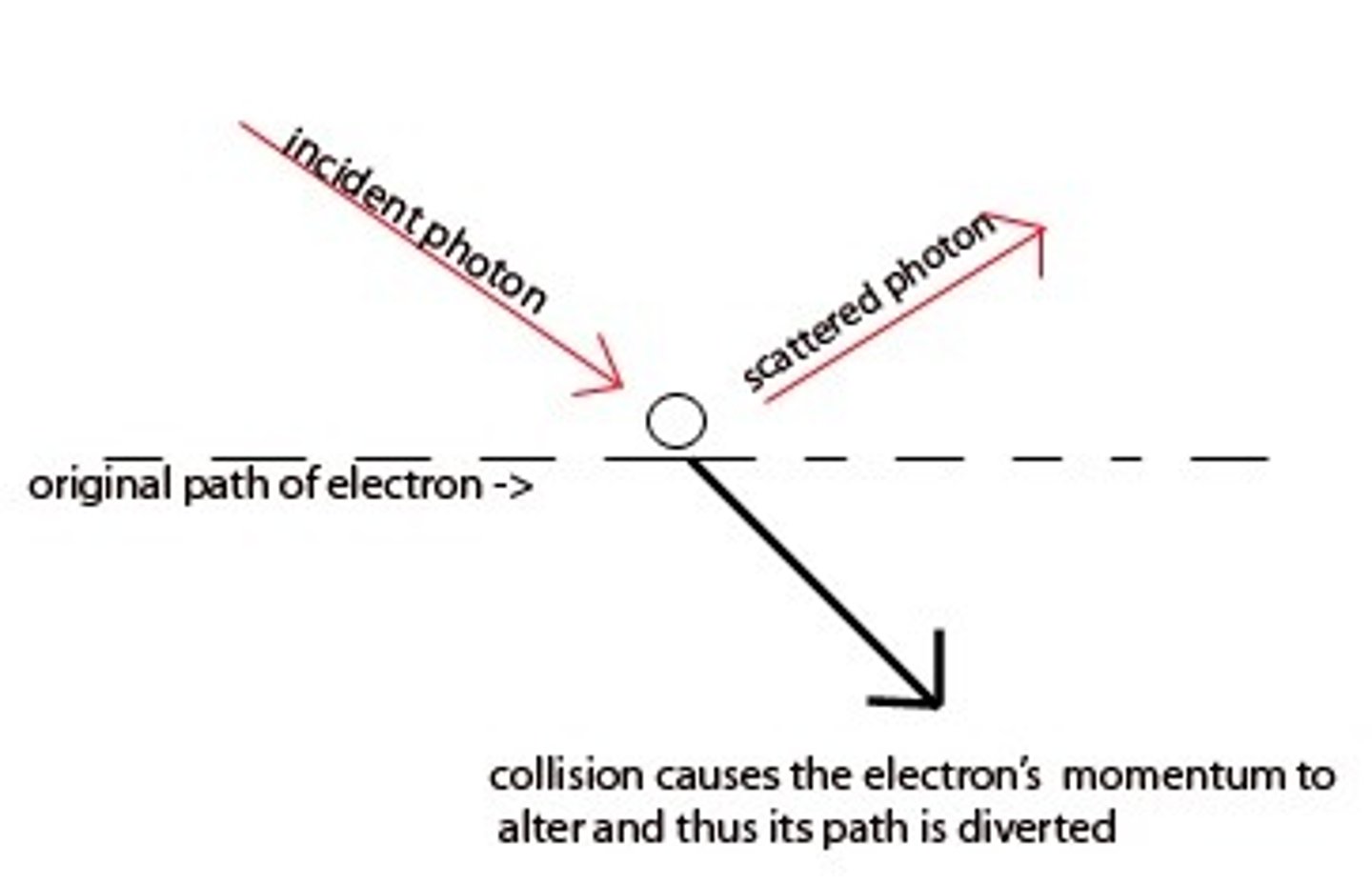
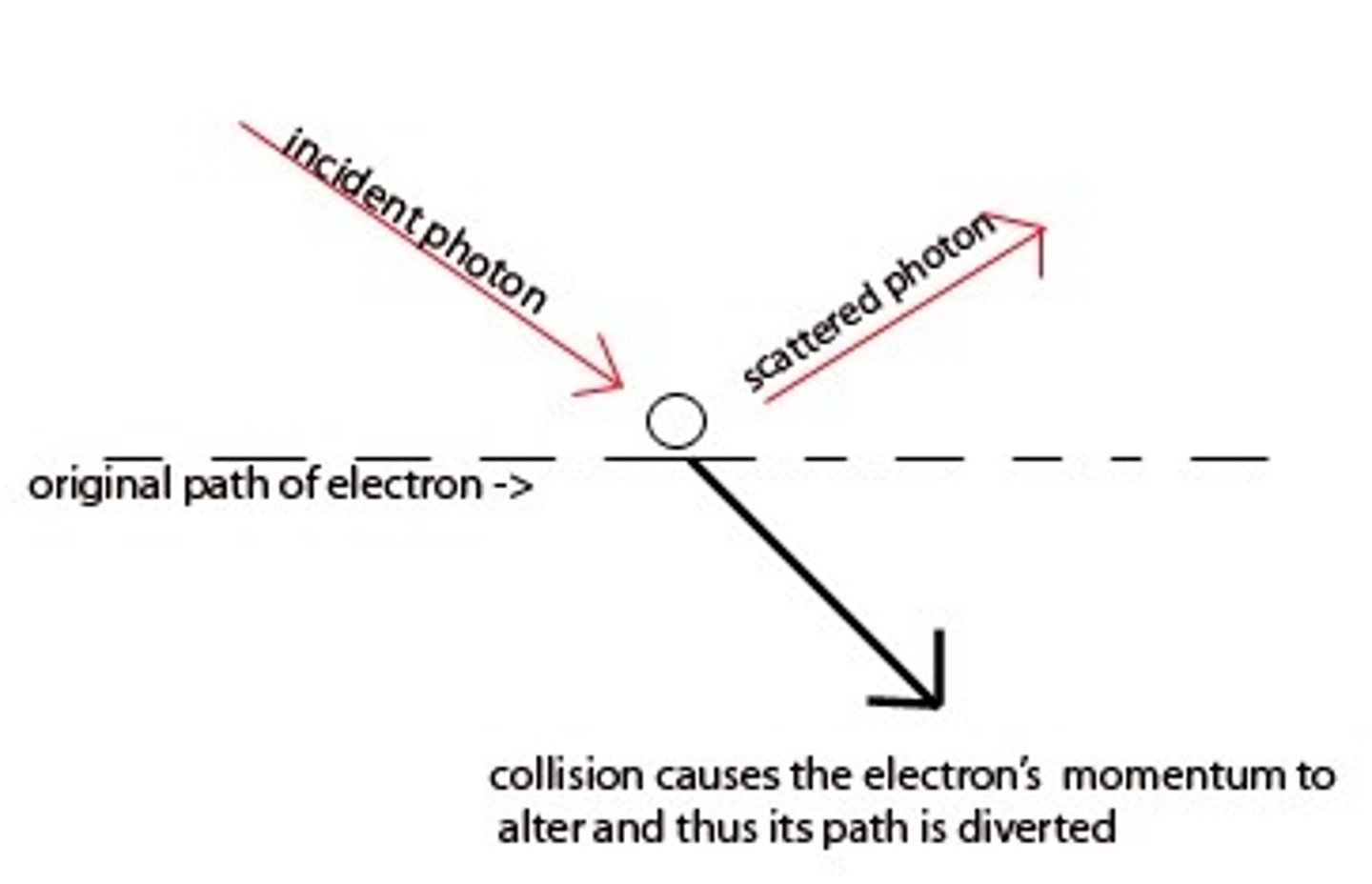
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to know exactly both the velocity and the position of a particle at the same time
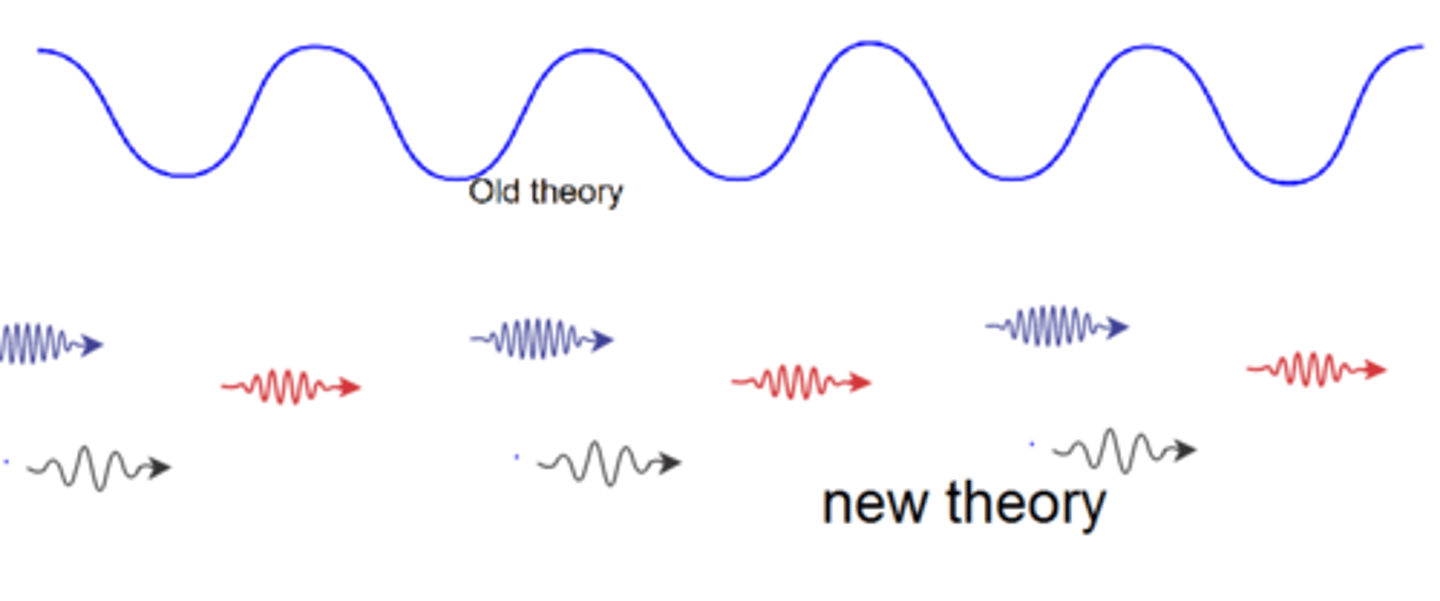
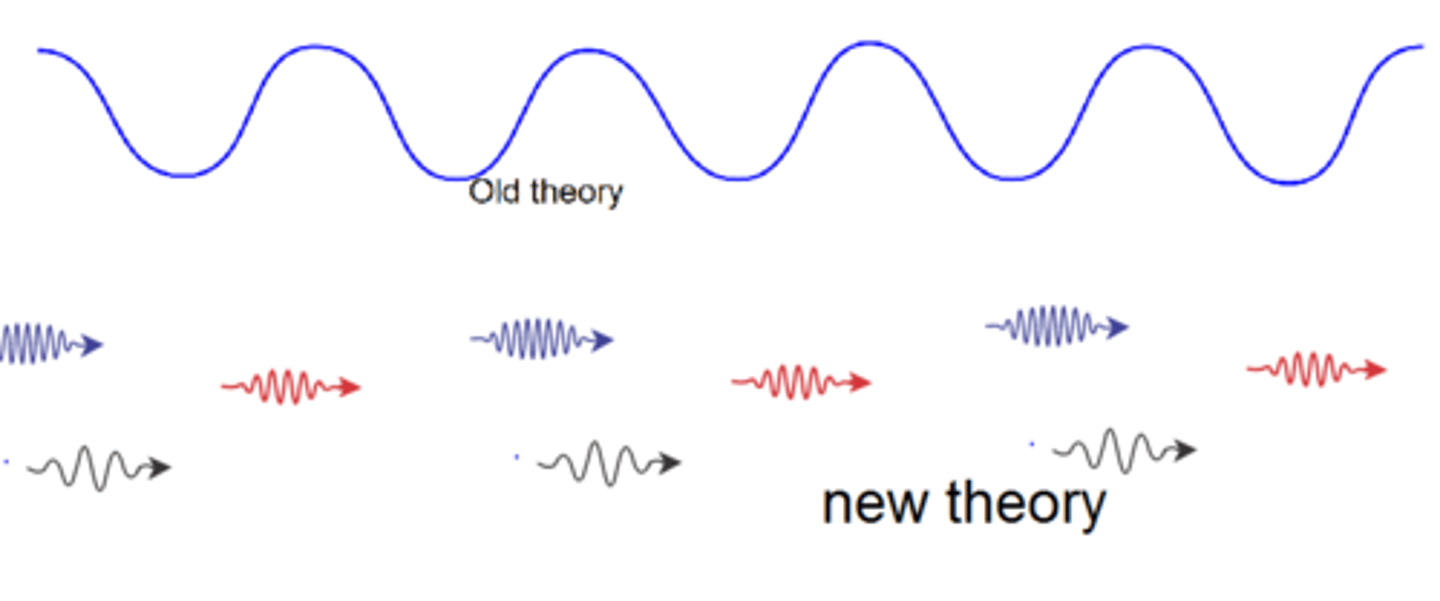
quantum theory
describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons and other very small particles
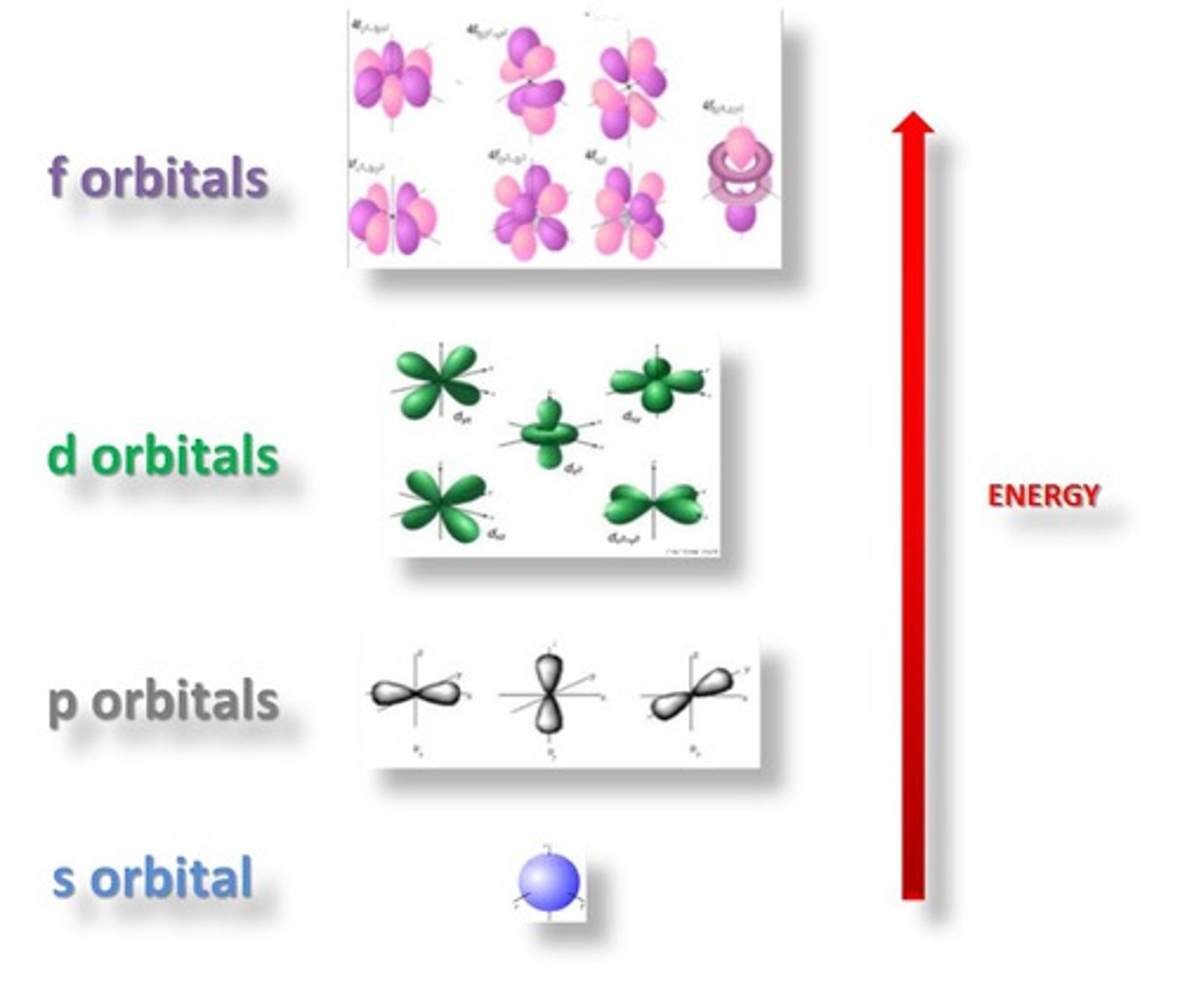
Orbital
A three-dimensional region around the nucleus that indicates the probable location of an electron
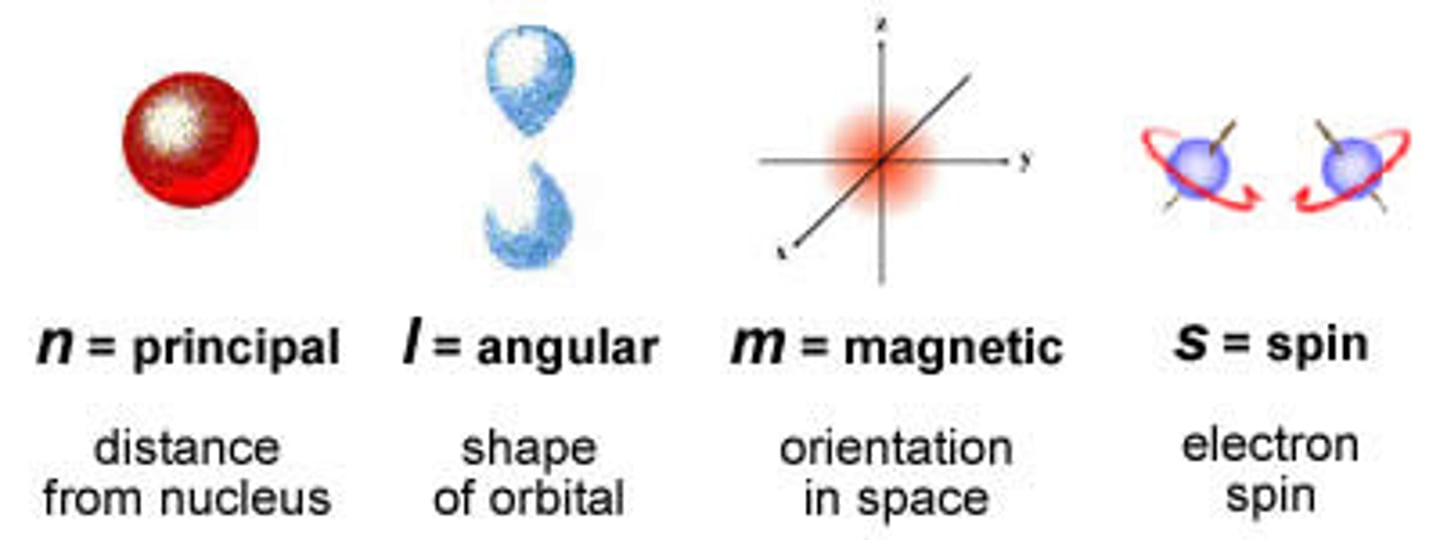
quantum numbers
specify the properties of atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in orbitals
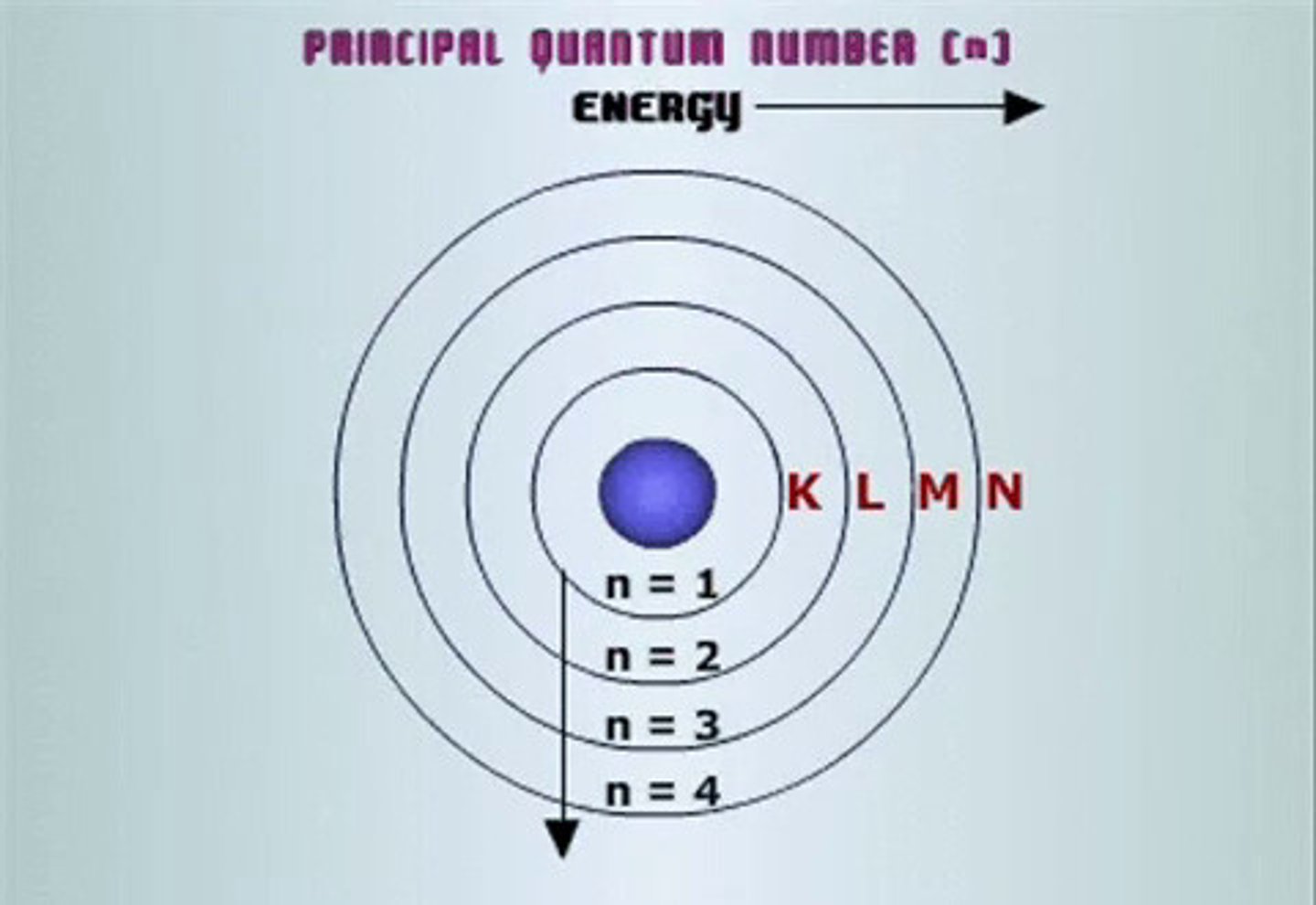
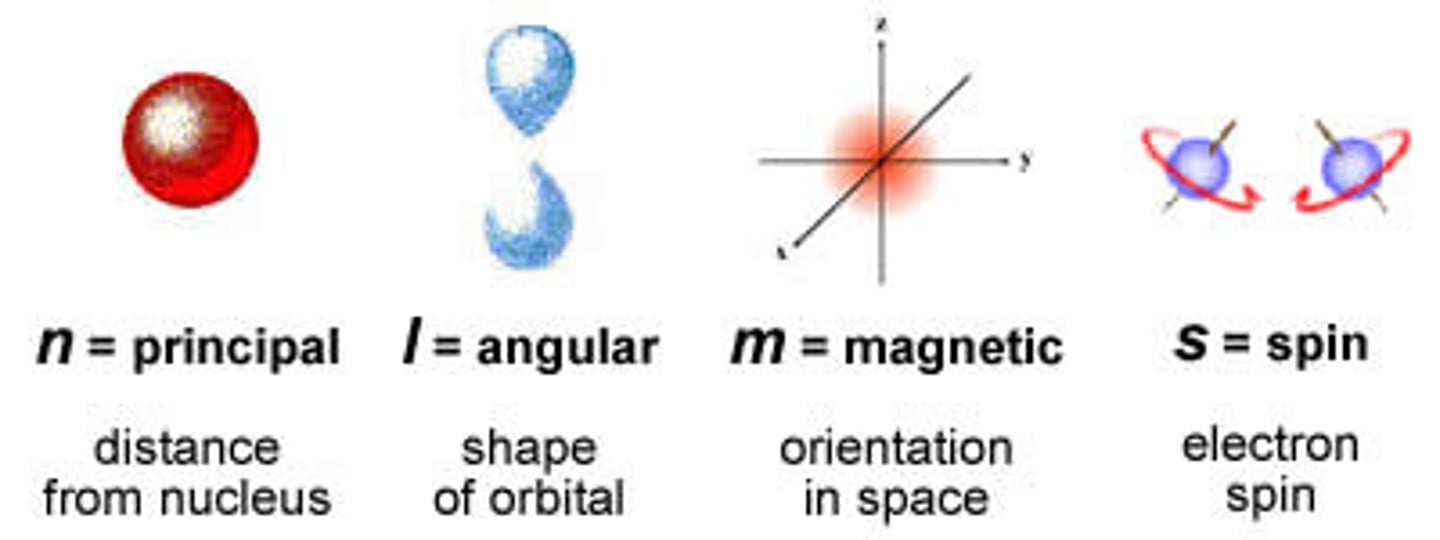
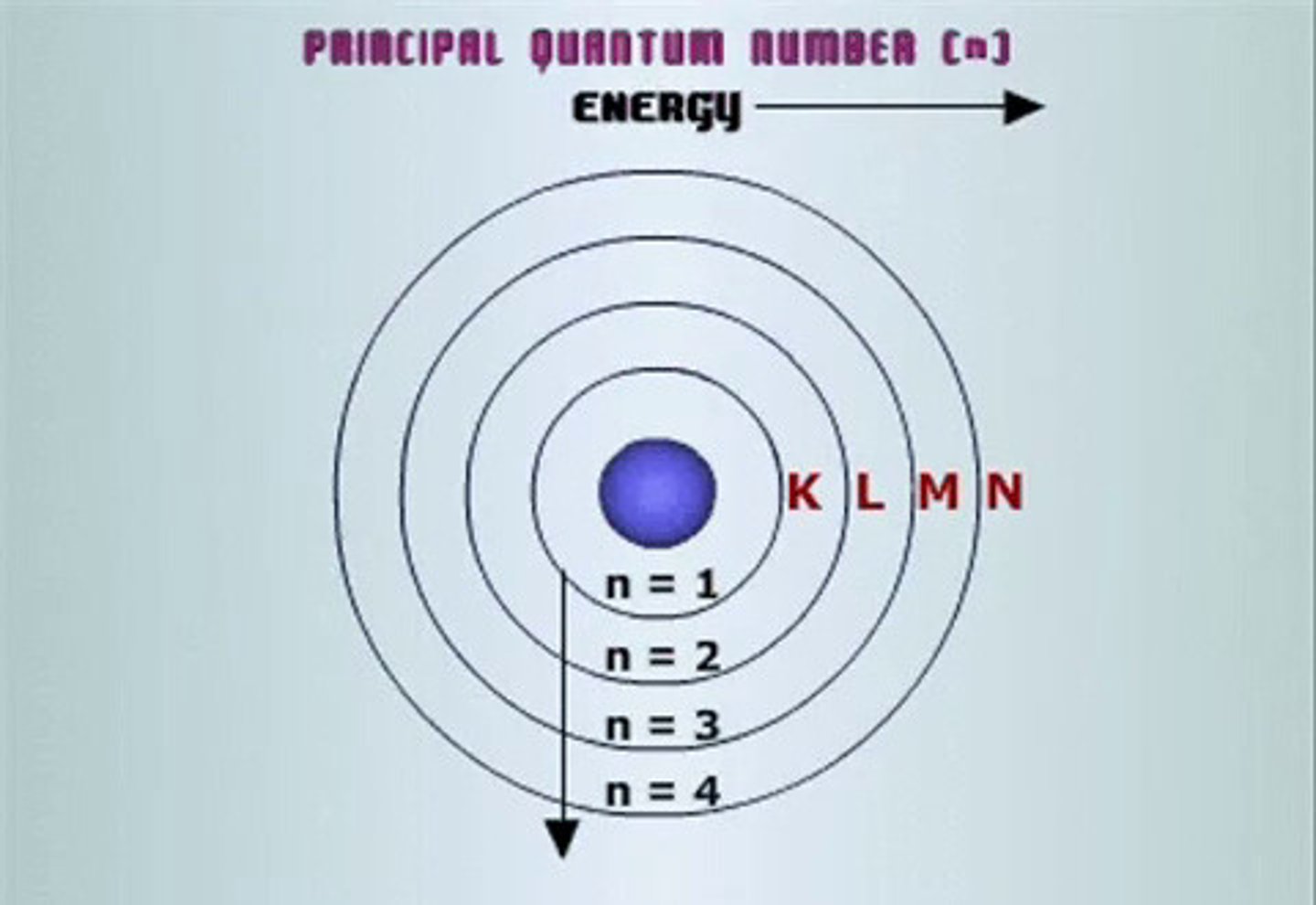
principle quantum number
symbolized by n, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron
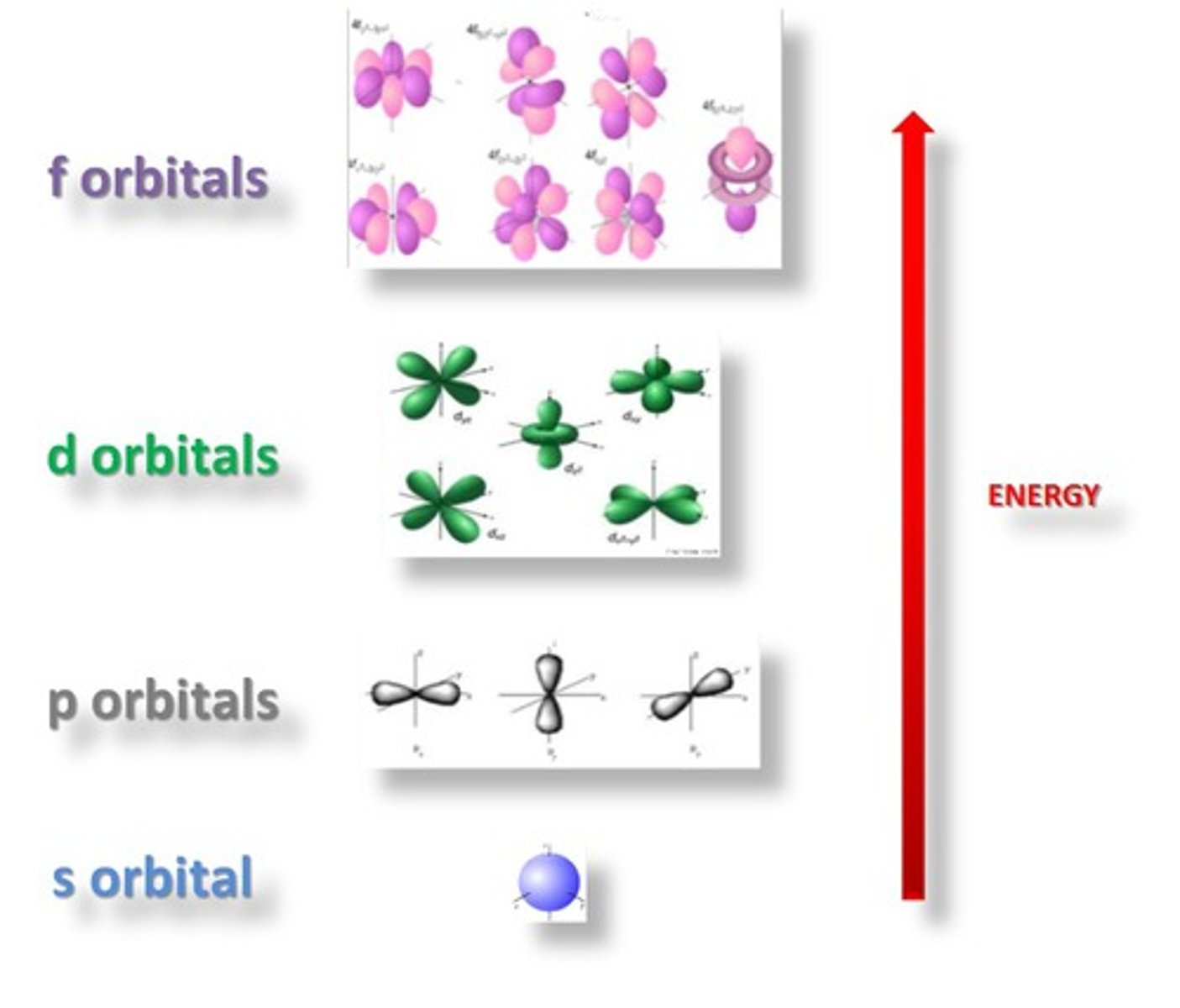
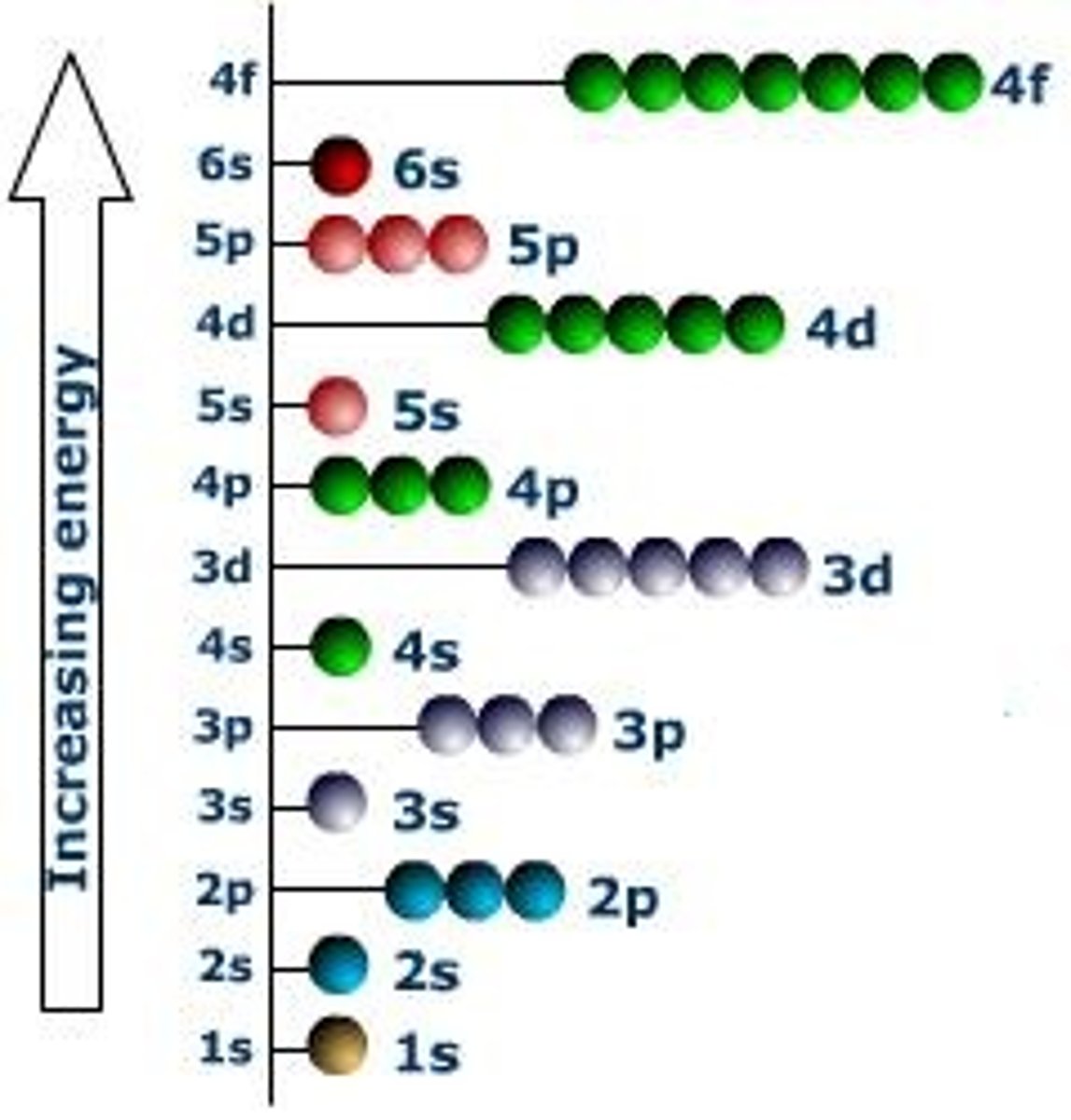
sublevel
An atomic orbital, or collection of atomic orbitals, that occupy a principal energy level and are called s, p, d, and f.
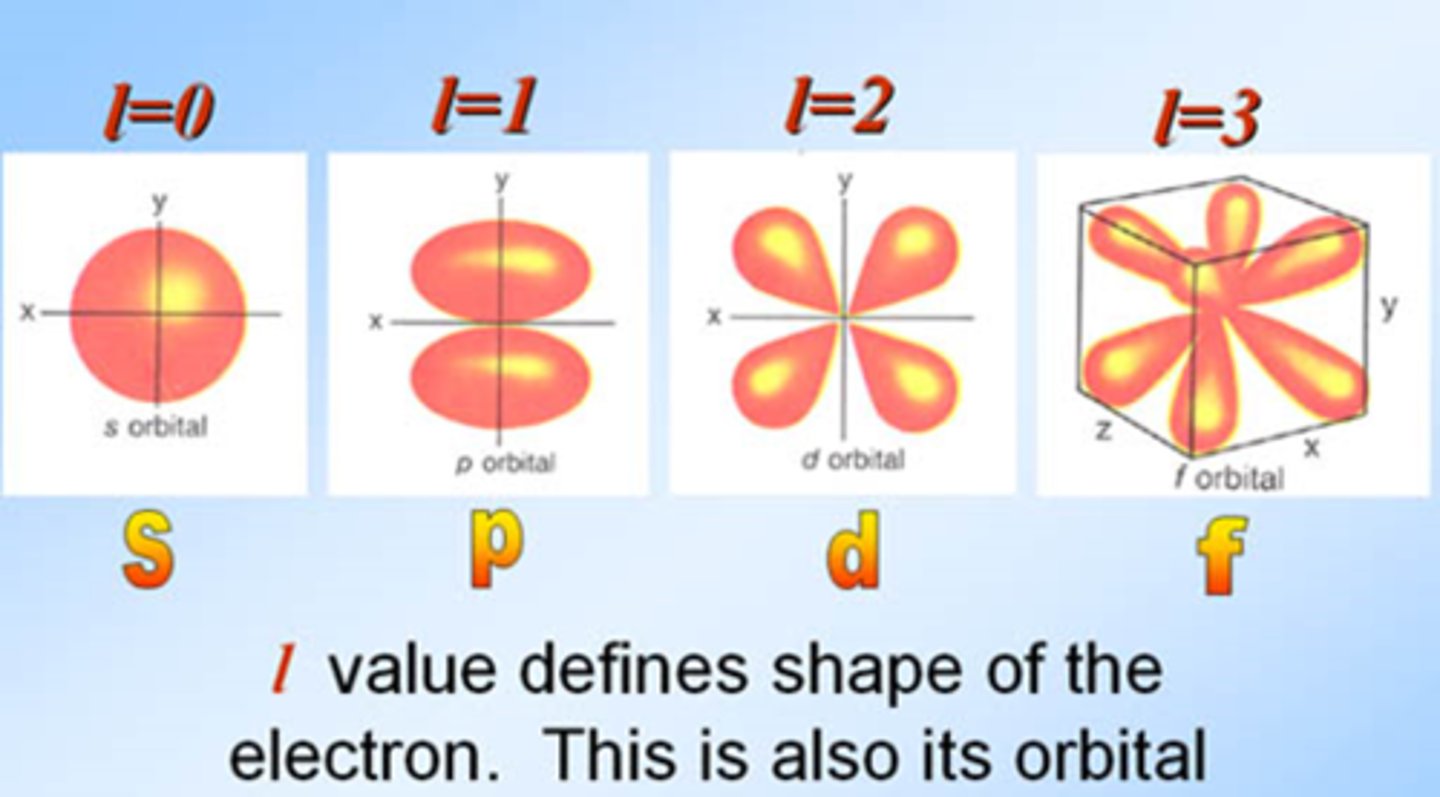
angular quantum number
symbolized by l, indicates the shape of the orbital
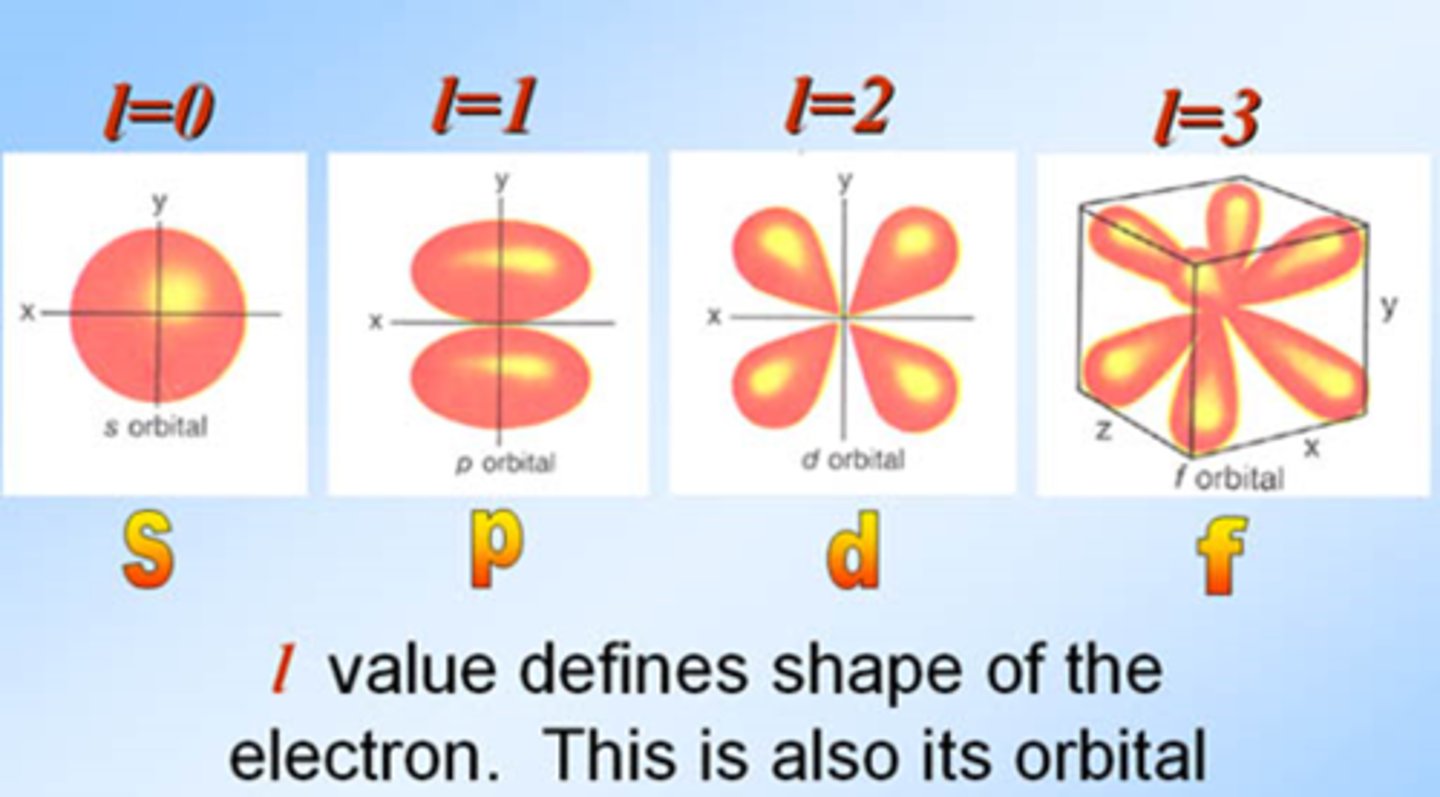
magnetic quantum number
symbolized by m, indicates the orientation of an orbital around the nucleus
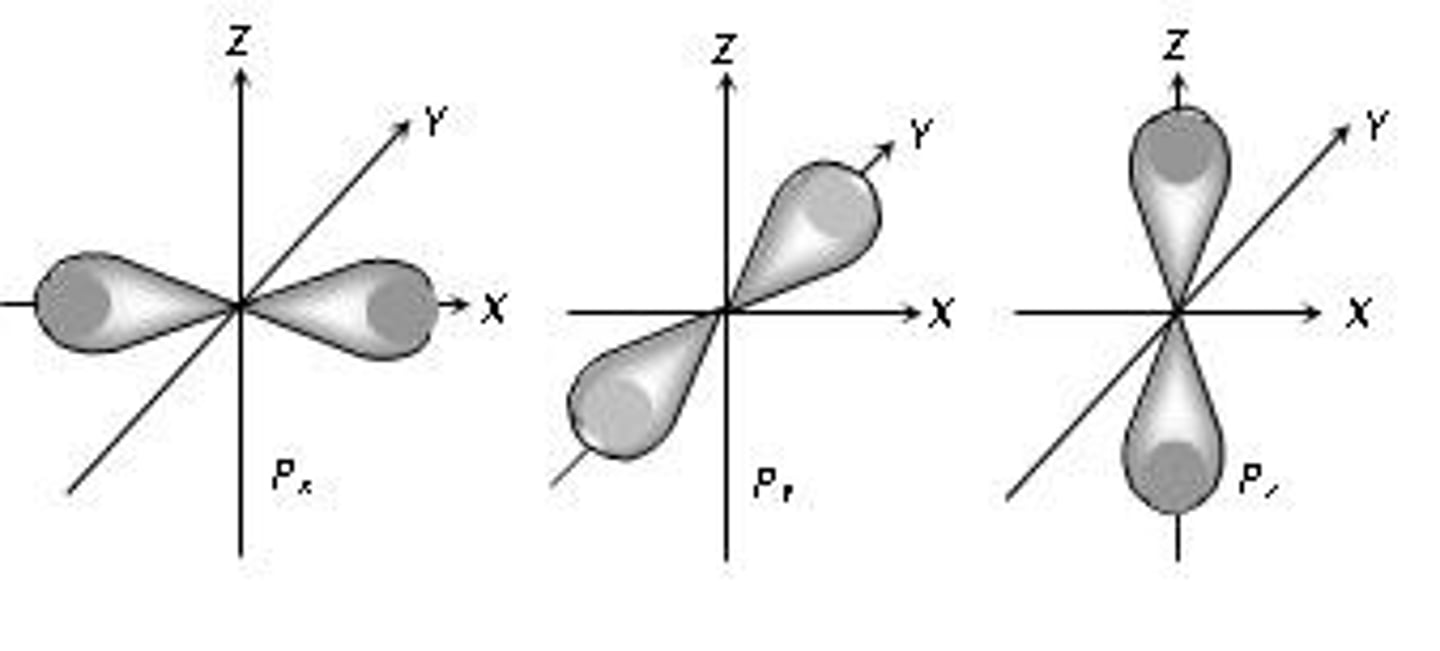
How do you know how may orientations are in a orbital
Add 2
s=1
p=3
d=5
f=7
spin quantum number
The quantum number that has only two possible values, +1/2 and -1/2, which indicate the two fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital
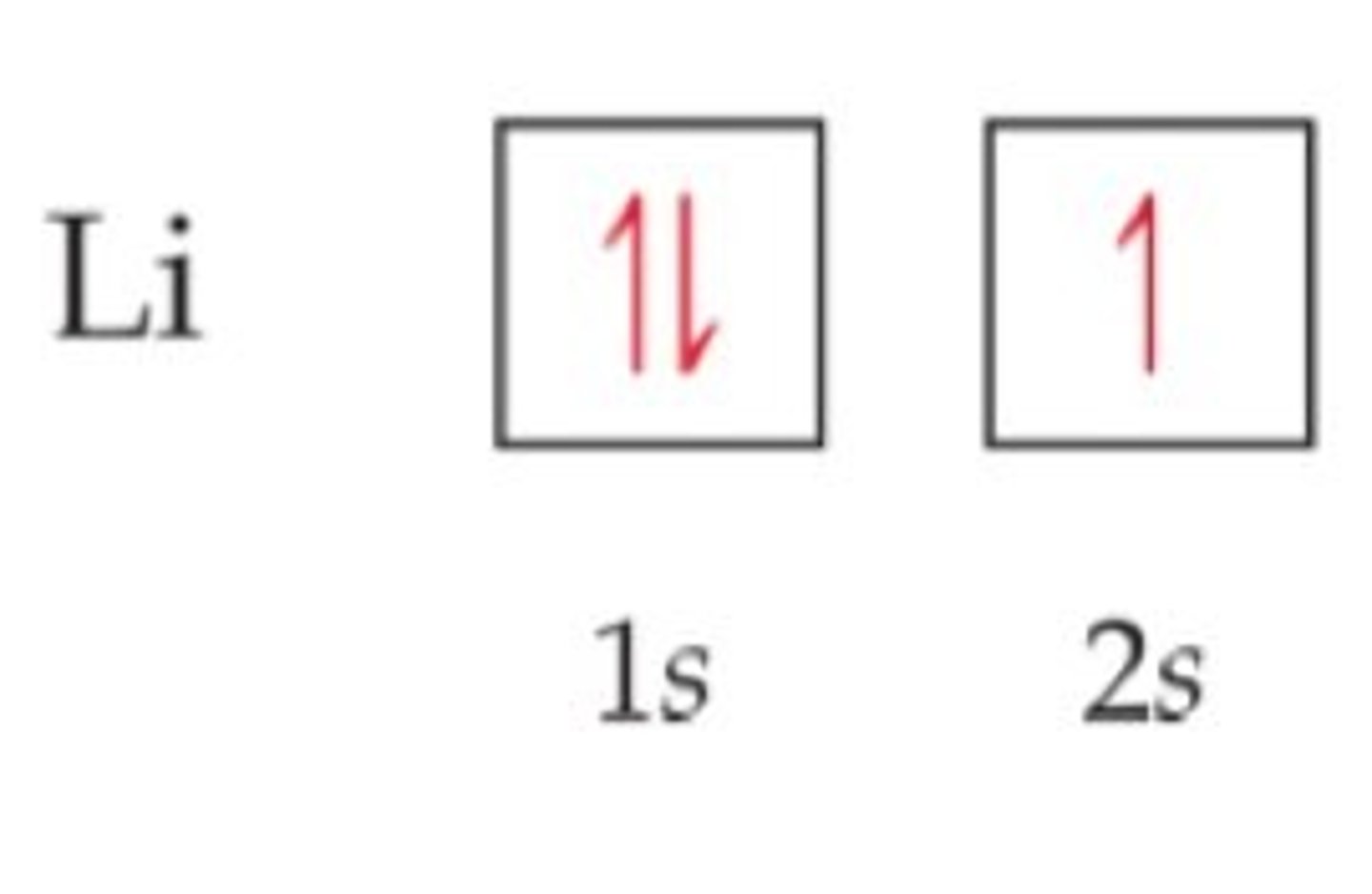
electron configuration
the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom
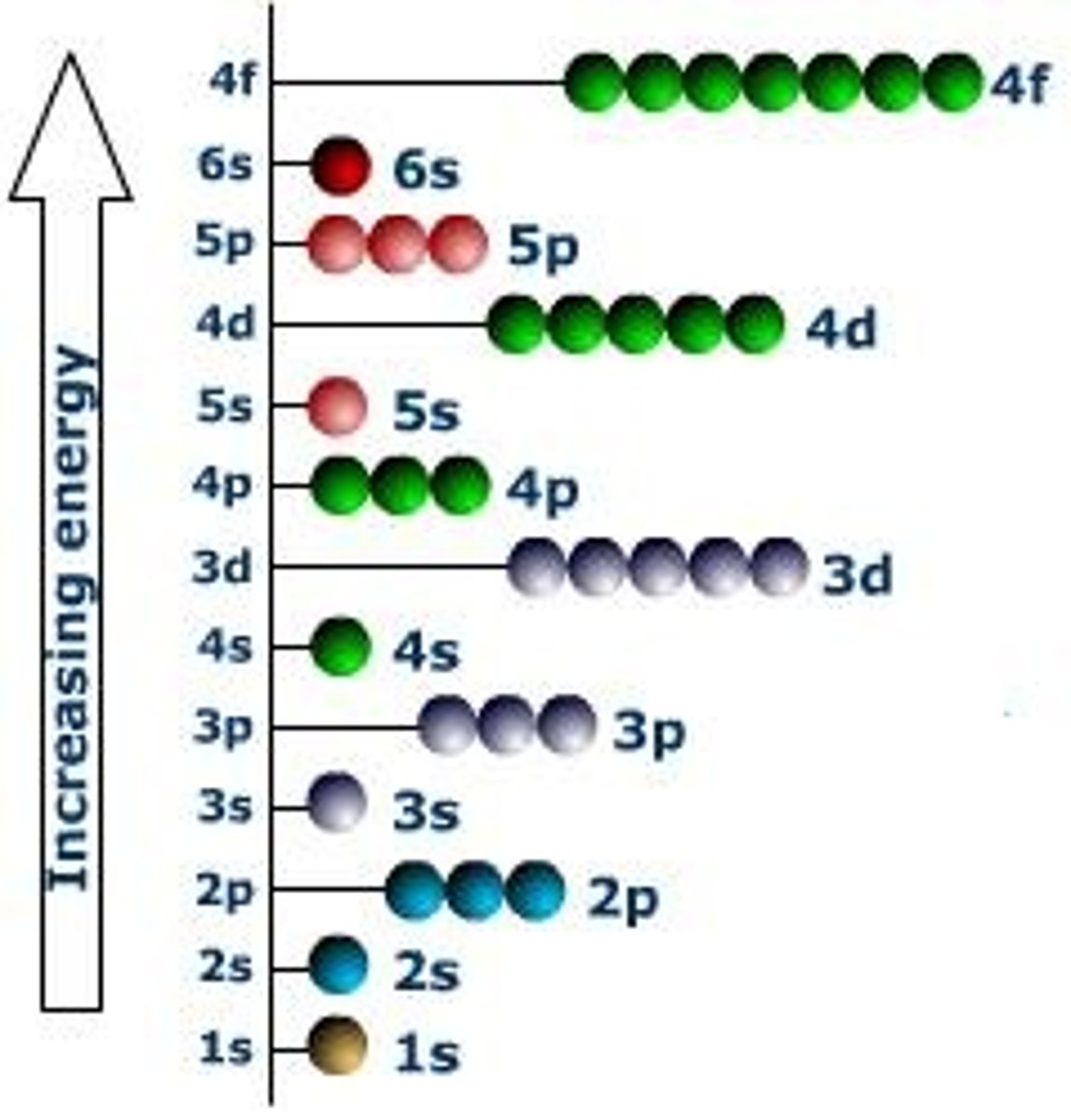
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it
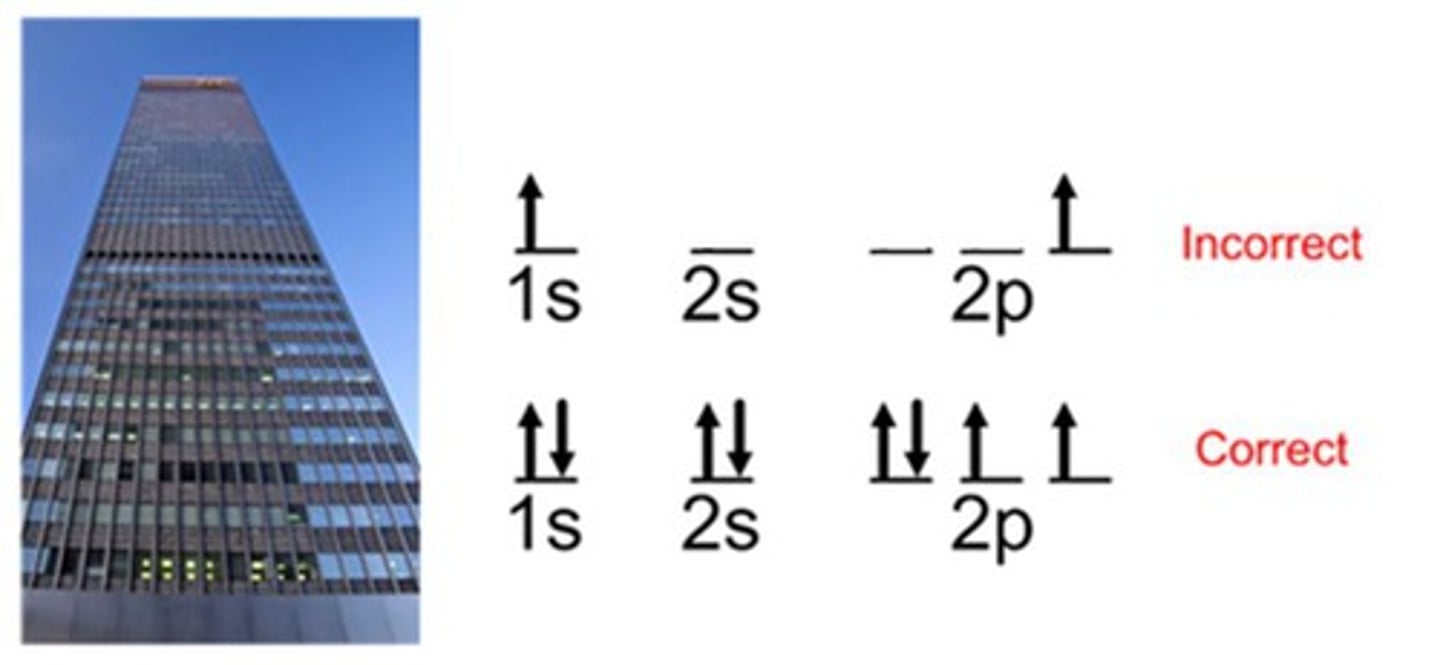
Pauli Exclusion Principle
no two electrons can have the same quantum numbers
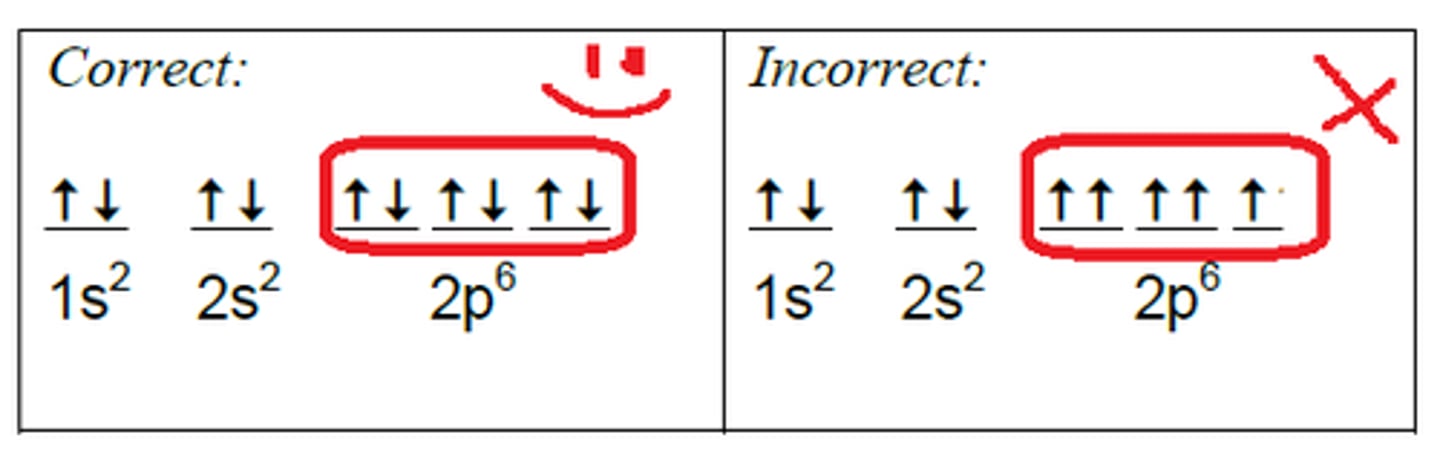
Hund's Rule
electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as large as possible
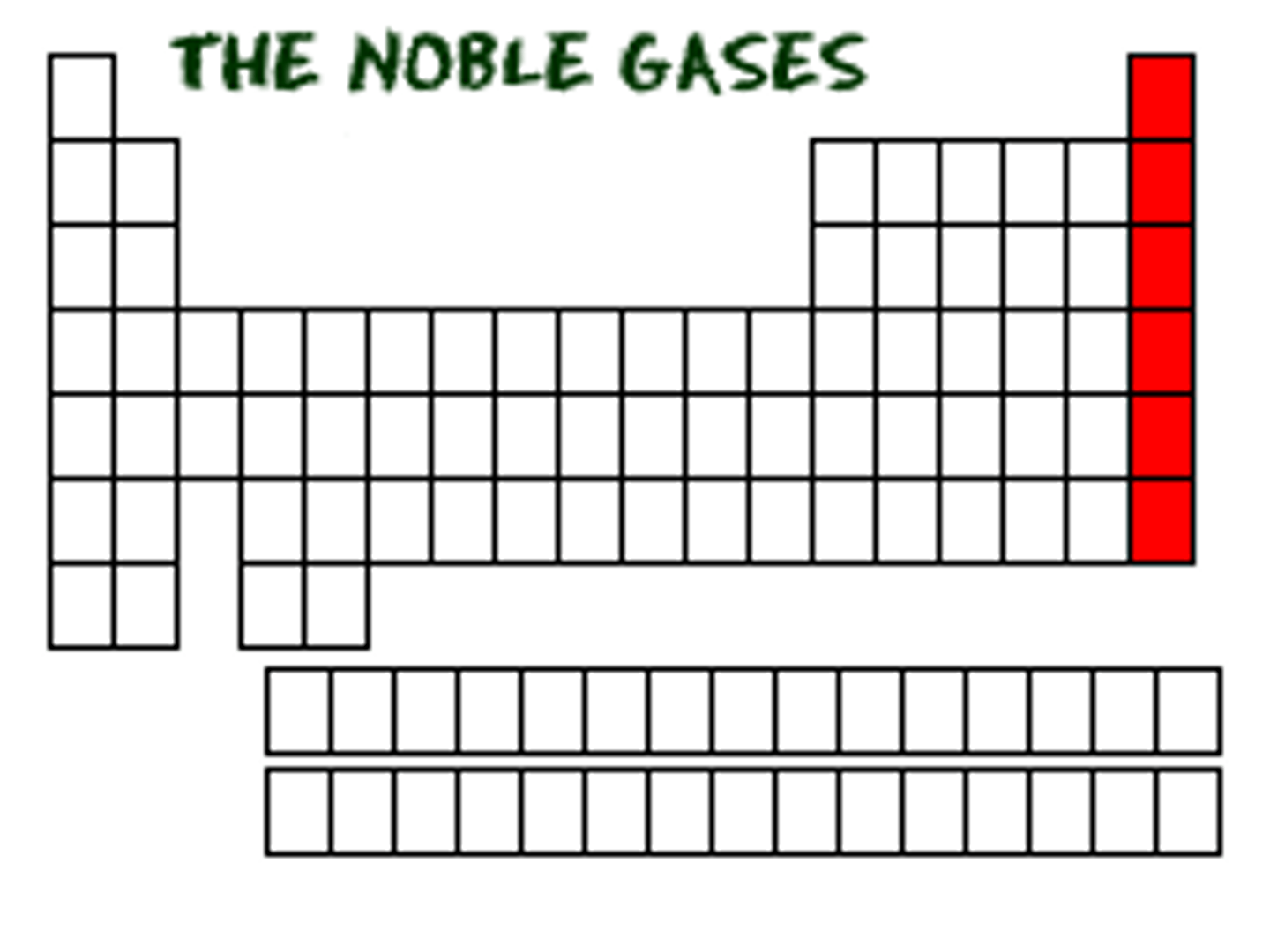
Noble gases
Group 18, A.K.A the group that has all of their respective s and p orbitals filled
noble gas configuration
an outer main energy level fully occupied, in most cases, by eight electrons
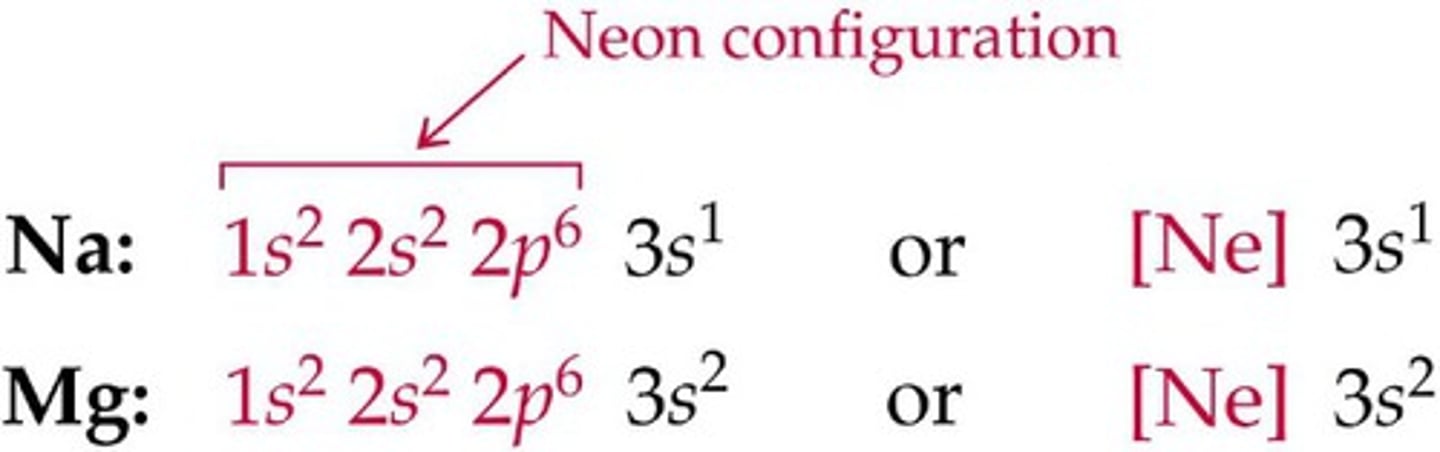
How many electrons can the 4p orbital hold?
6
Who said electrons can act as waves or particles?
De Broglie
Who said Light can act as waves or particles?
Einstein
Ground state
The lowest energy state of an atom
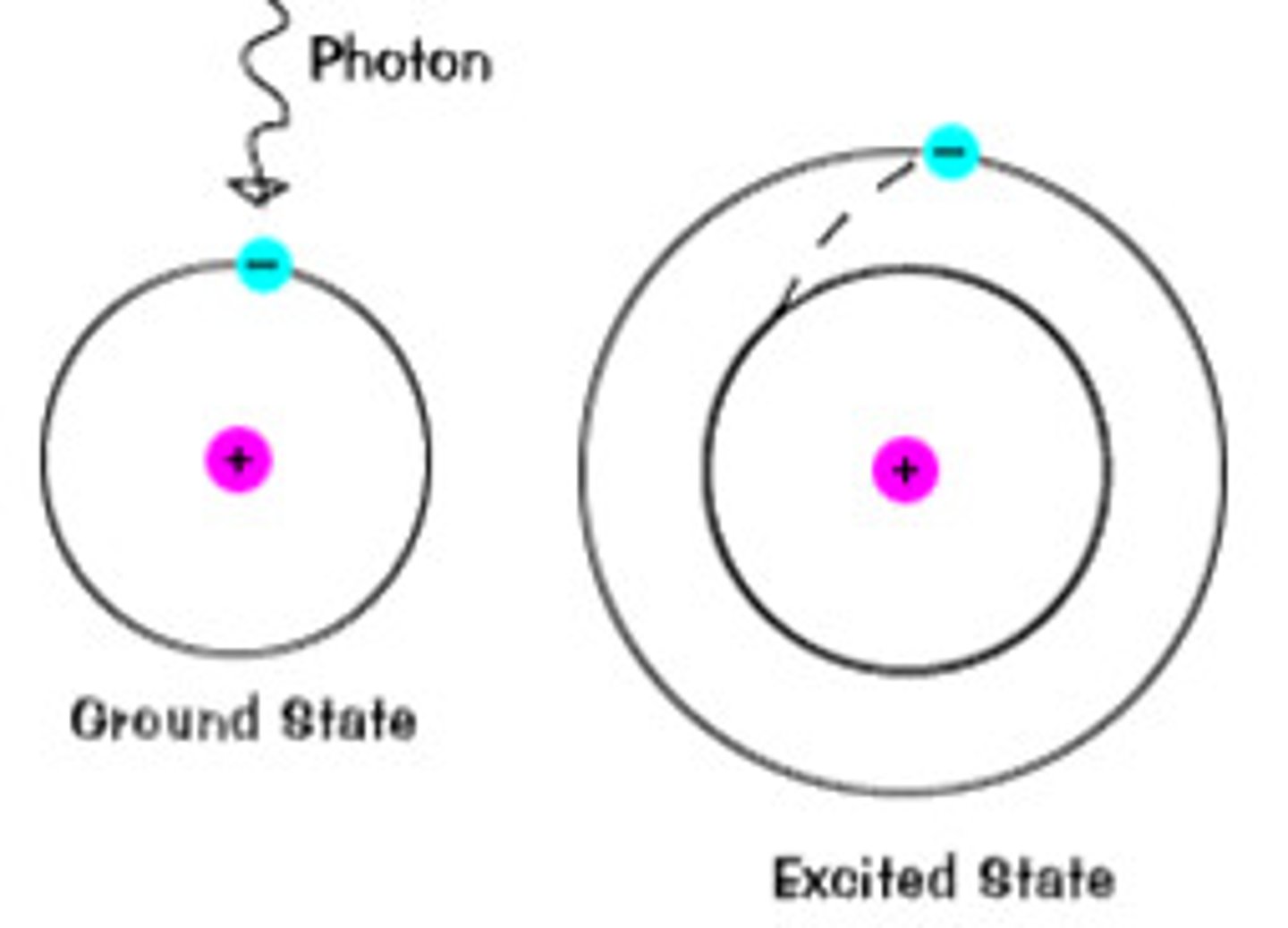
Excited state
a state in which an atom has more energy than it does at its ground state
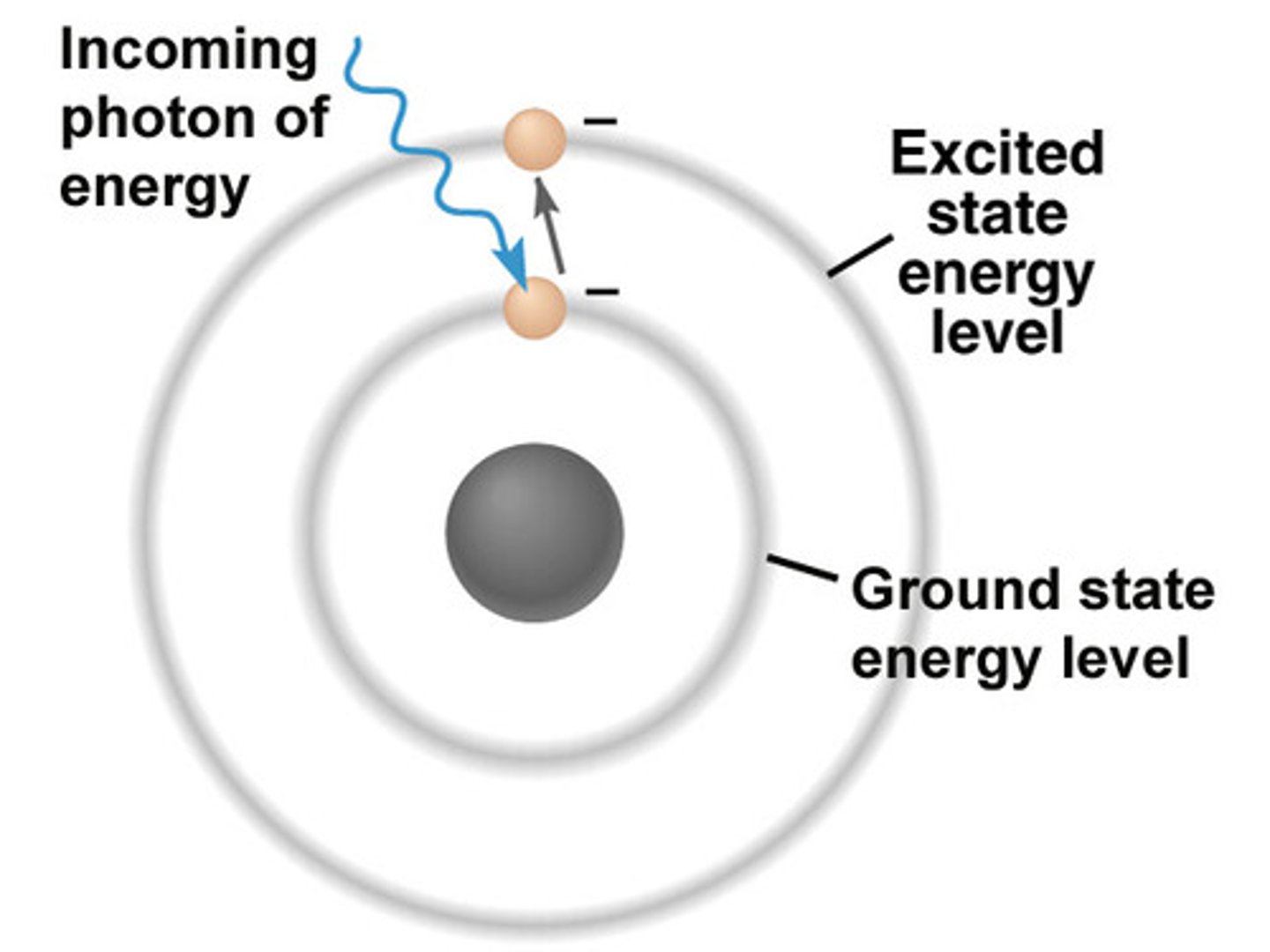
electromagnetic radiation
a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space
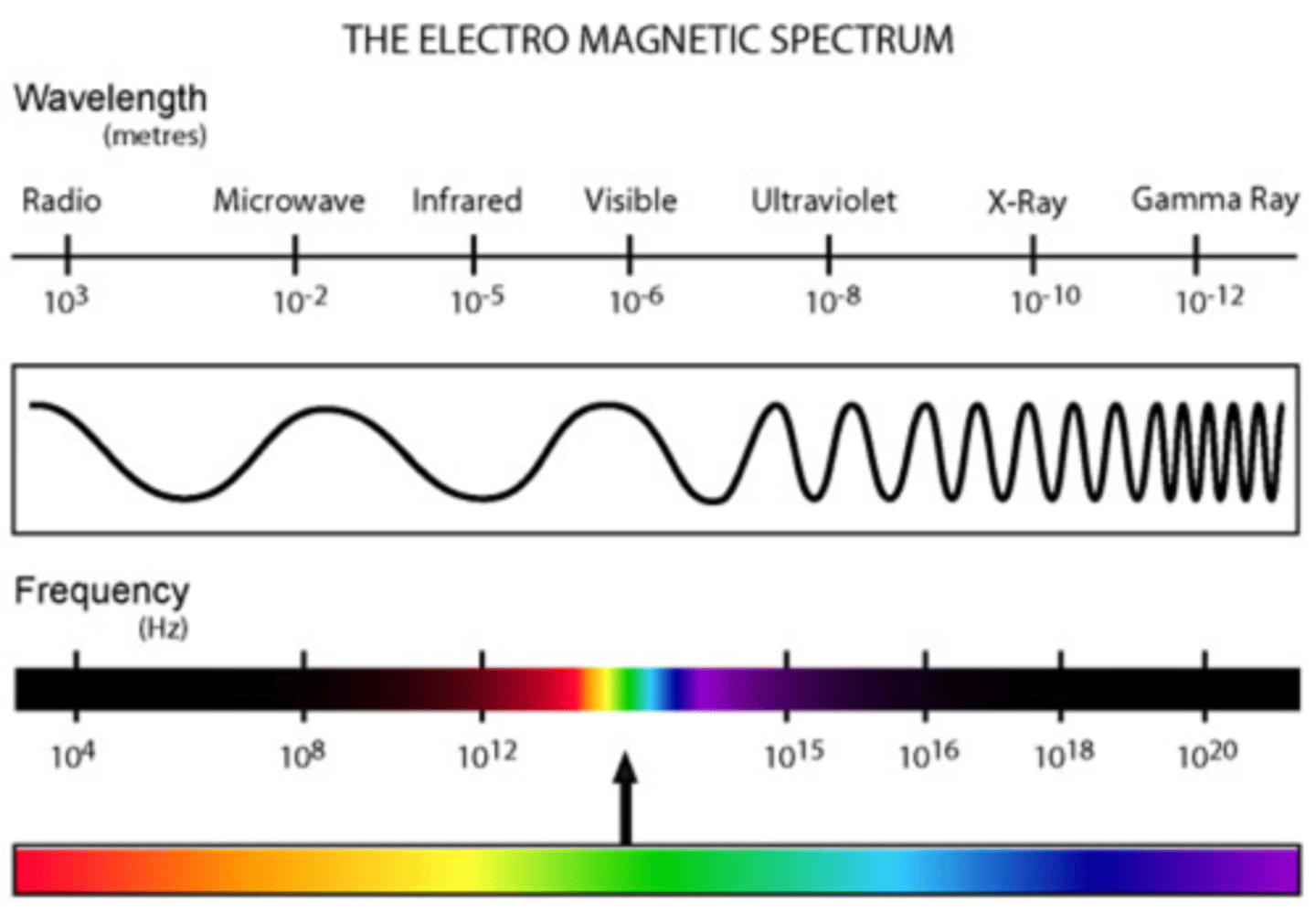
electromagnetic spectrum
the range of wavelengths or frequencies over which electromagnetic radiation extends.
Wavelength ( ⁁ ) (cm, m, nm)
The distance between two corresponding parts of a wave
Frequency (v) (HZ=waves/s)
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
What's the formula for frequency and wave length
c=⁁v
Speed of light?
3.00 x 10^8 m/s

photoelectric effect
The emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
quantum
the minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
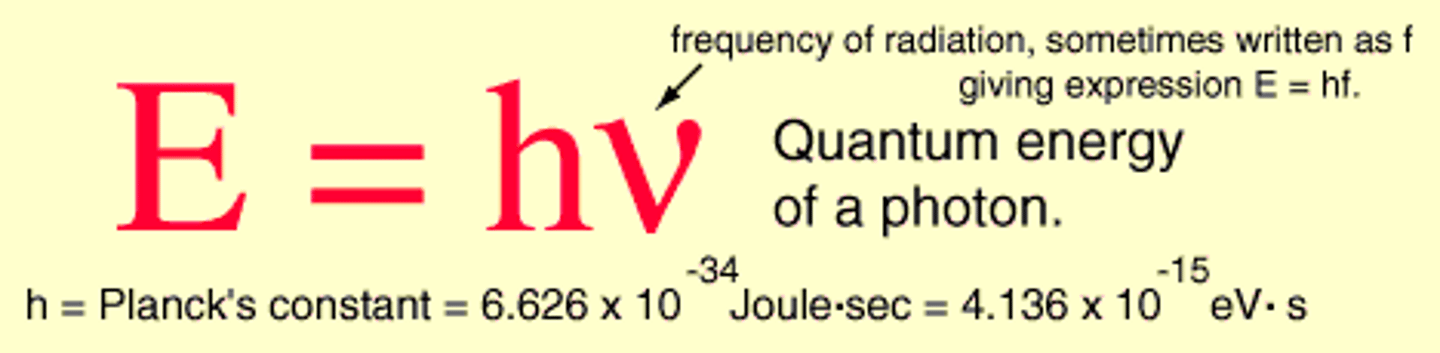
Photon
A particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy
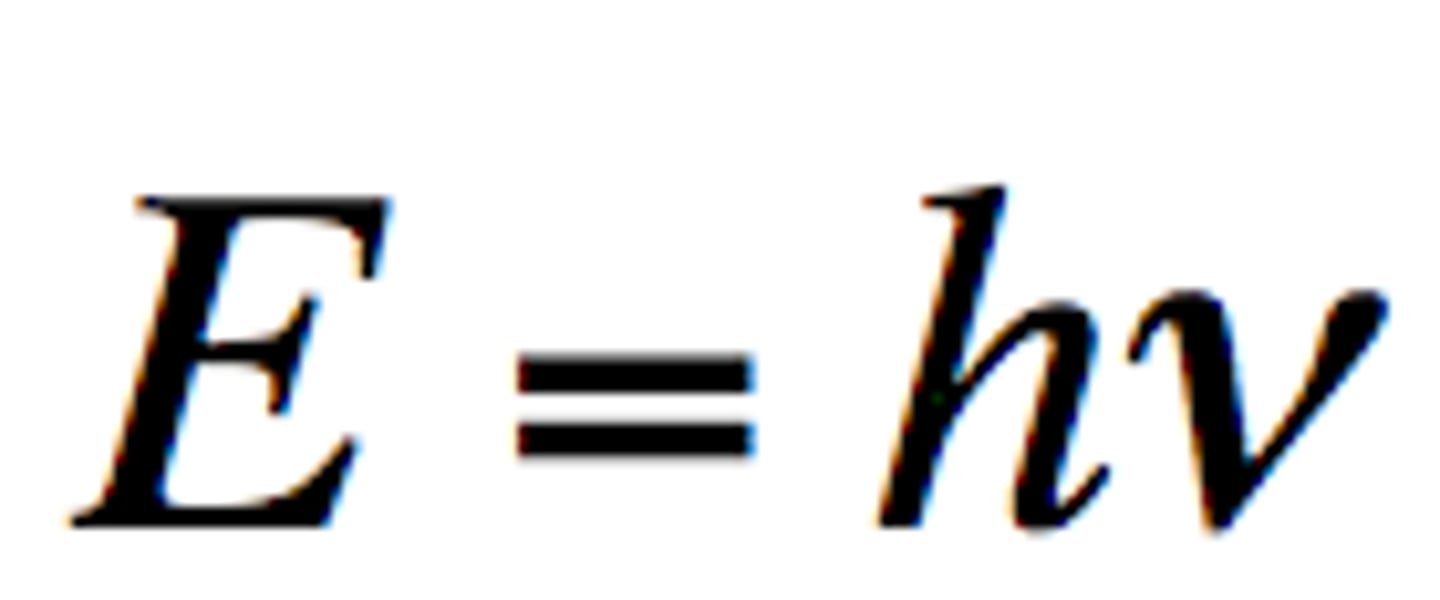
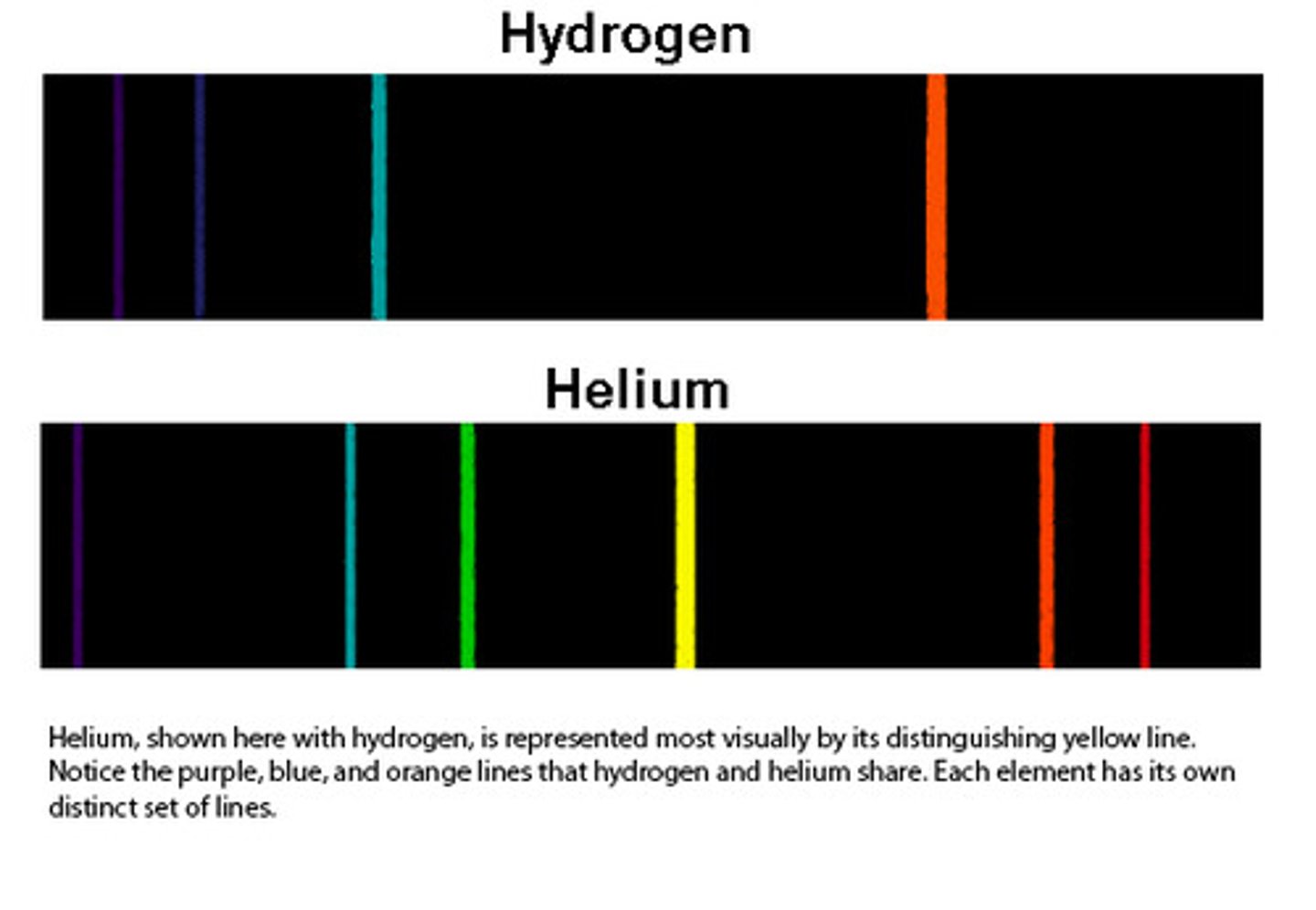
emission line spectrum
when a narrow beam of the emitted light was shined through a prism, it was separated into four specific colors of the visible spectrum
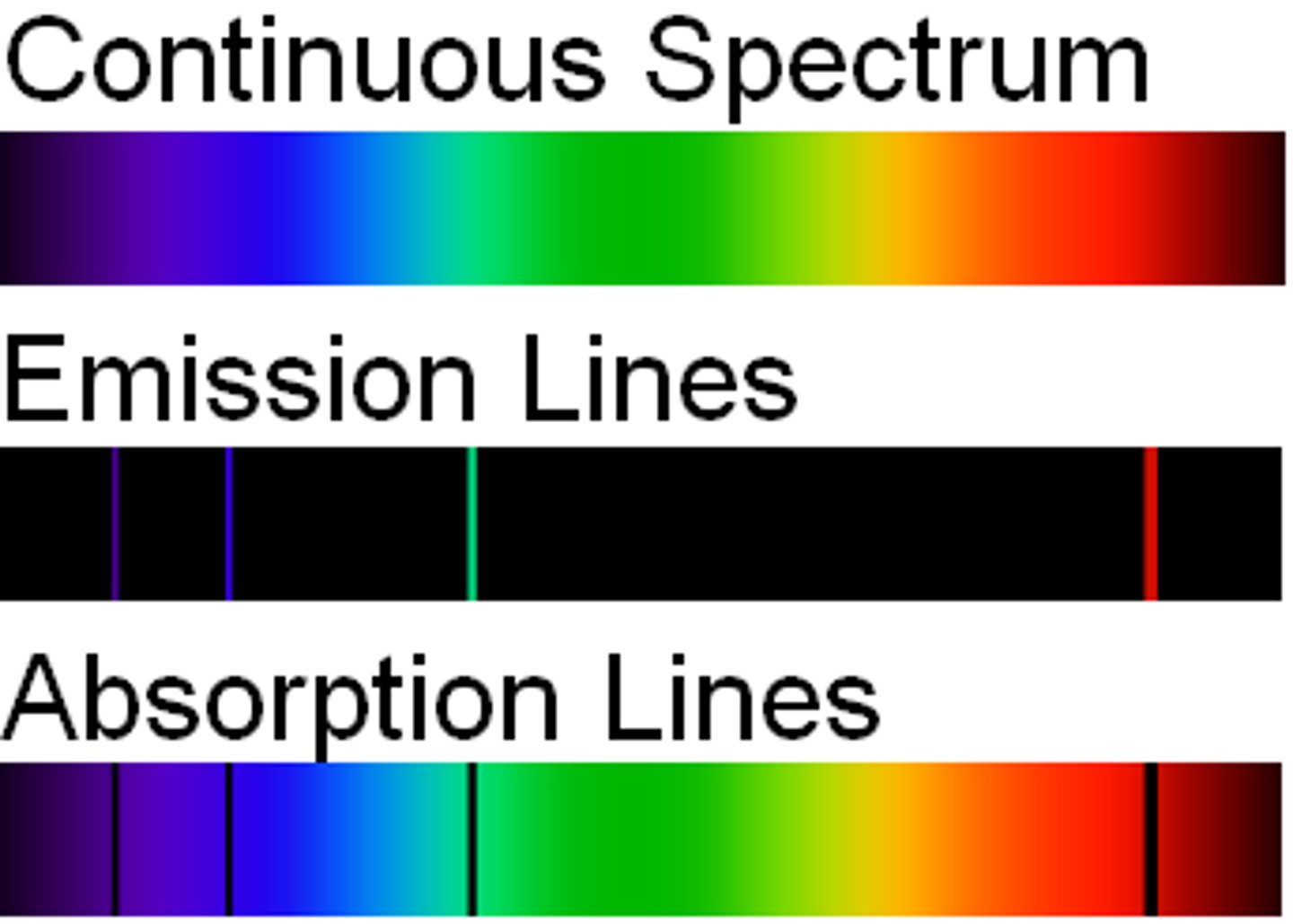
continuous line spectrum
the emission of a continuous range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation
What can Bohr's model be compared to?
A ladder
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to know exactly both the velocity and the position of a particle at the same time
quantum theory
describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons and other very small particles
Orbital
A three-dimensional region around the nucleus that indicates the probable location of an electron
quantum numbers
specify the properties of atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in orbitals
principle quantum number
symbolized by n, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron
sublevel
An atomic orbital, or collection of atomic orbitals, that occupy a principal energy level and are called s, p, d, and f.
angular quantum number
symbolized by l, indicates the shape of the orbital