Fertilization
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Sperm cells undergo in the female reproductive tract to become capable
of fertilization. This involves changes in the acrosomal membrane, increased flagellar activity, and chemotactic activity guided by chemical signals from the egg
Capacitation
Fertilization events normally occur in
upper third of uterine tube
required for fertilization to occur
Releases enzymes from head to sperm (multiple sperm at different times)
Acrosome reaction
Sperm cells must penetrate the _________ and ________
corona radiata and zona pellucida.
enzyme allows sperm to break down extracellular matrix of corona radiata [granulosa cell layer]
Sperm head can now meet oocyte membrane
Hyaluronidase
The egg cell releases _____ ions to prevent polyspermy and undergoes a final
meiotic division to release the third polar body
calcium
Post-Fertilization Events
-The zygote travels down the uterine tube to the
uterus.
A solid ball of cells.
Morula
An inner cell mass develops within a fluid-filled sphere, which implants
into the uterine lining.
Blastocyst
Women pregnant with twins, first twin was delivered, went back and uterus was empty, where is the other twin?
In the uterus cavity
We hatched out of the
zona pellucida
_____ hatches out of zona pellucida
Allows:
Better access to uterine secretions (nutrients)
Increased growth
Blastocyst implants in specific orientation in uterus
blastocyst
____ hatches and implants with the embryonic disc facing the uterine wall.
The blastocyst
______ produce the chorion and chorionic villi, contributing to the fetal part of the placenta.
Trophoblasts
______ occurs to form the three germ layers (triploblastic nature of the embryo)
Gastrulation
(formation of the three primary layers, the bulk of our body is from mesoderm)
Gastrulation
Hormone Levels During Implantation:
- Estrogen levels ________l, while progesterone levels _____ to sustain the pregnancy and maintain the functionalis.
- The levels of estrogen and progesterone that is produced helps to (3)
-rise and then fall: increase
-maintain the functionalities, placenta and pregnancy in general.
Outermost cells of blastocyst [syncytiotrophoblast] secrete a hormone called
hCG
human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) (3)
Produced only during pregnancy [in urine and blood, basis of pregnancy tests]
Stimulates corpus luteum to secrete estrogen and progesterone
Promotes placental development
Progesterone suppresses menstruation and maintains uterine lining
Once placenta starts secreting estrogen and progesterone hCG level declines and
remains low
Blood supplies ______, however they connect through the sinus spaces in the functionalis, so that both mother and the fetus has blood support.
do not get mixed
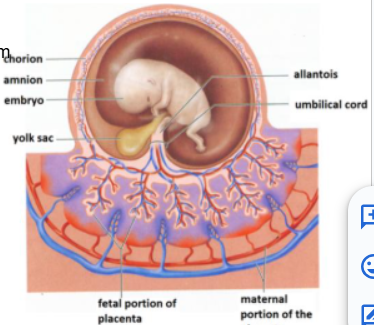
-The membranes lining: (4) are the membranes surrounding the fetus in development.
Amnion, Chorion, Elantois, and Yolk Sac
outermost embryonic membrane and arose from outer cell layer of blastocyst
Gives rise to fetal part of placenta
Chorion
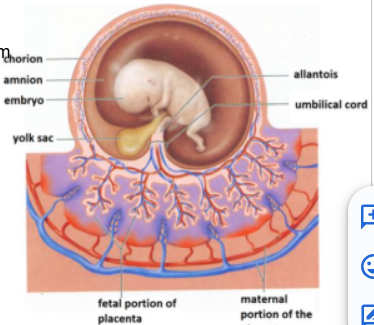
the innermost embryonic membrane
Cavity fills with amniotic fluid
Amnion
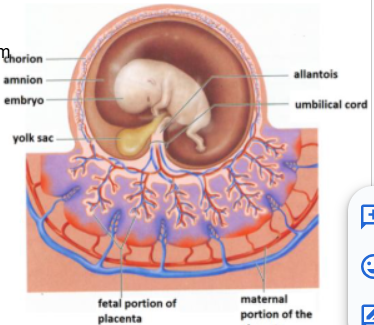
is nonfunctional
Contributes to umbilical vessels
Allantois
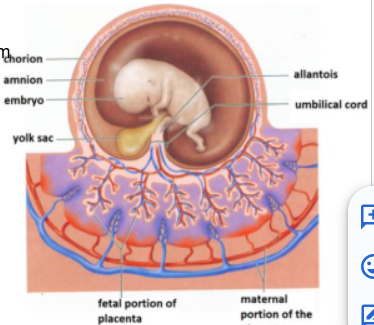
is nonnutritive
Blood cell production
Some cells migrate to gonads
Yolk sac
The amniotic fluid is protected inside the layers, or rather amniotic fluids and amnion is
what houses the water.
-Chorionic helps with circulation with the membrane mentioned above
Placenta
PLacenta: Fetal portion arises from
chorion
Placenta: Fetal side (____) and maternal side (____)
-smooth
-rough
Placental hormones (regulate cycles) (5)
-Human chorionic gonadotropin [hCG]
-Progesterone and estrogen
-Progesterone:
-Estrogen
-Corticotropin-releasing hormone
Pregnancy: The Mother
*Releasing hormone helps to signal: ____
-Pancreas: Insulin levels ___ because its donated to fetus, which increase sugar dependency in the mother herself as well.
-Thyroid _____ the circulation!
-CRH
-rise
- increase
produced by chorion so embryonic origin
Stimulates corpus luteum (progesterone)
Stimulates testosterone production fetal testes: surge that is measured
Human chorionic gonadotropin [hCG]
Stimulates development, maintenance of endometrium
Stimulates mammary development
Progesterone and estrogen
Inhibits uterine motility
Inhibits pituitary secretion of GnRH
Progesterone:
Stimulates mass increase myometrium
Estrogen
Likely involved in determine length of pregnancy and timing of childbirth
Corticotropin-releasing hormone
Hormone levels inside the pregnancy!:
_____ help maintain the function, as well as the thickness of the uterus itself, and the lining!
Pro and Estro
Maintenace of corpus luteum
Growth effects on fetus
Stimulate prostaglandin release
Decrease maternal use of glucose (could lead to gestational diabetes)
Increase maternal use of fatty acids
Human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS)
secreted by endometrium and corpus luteum
Transform pubic symphysis cartilage from rigid to more flexible
Relaxes myometrium (prevent expulsion)
Stimulates proliferation of blood vessels
Relaxin
Pancreas – insulin production _____
Response to decreased maternal sensitivity (glucose sparing)
-increases
Adrenal glands – maternal aldosterone level ___
Na+ retained
H2O retained (obligatory)
Fetal and maternal plasma volume increases
- rises
Thyroid hormones and metabolism level both _____ in mother
Resting pulse pressure increases
O2 delivery to fetus increases
increases
Amniocentesis and chorionic villi sampling