Physics - Circuits, Current, Voltage
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Circuit
A complete pathway that current can flow through
what components can circuits contain and how do u draw them
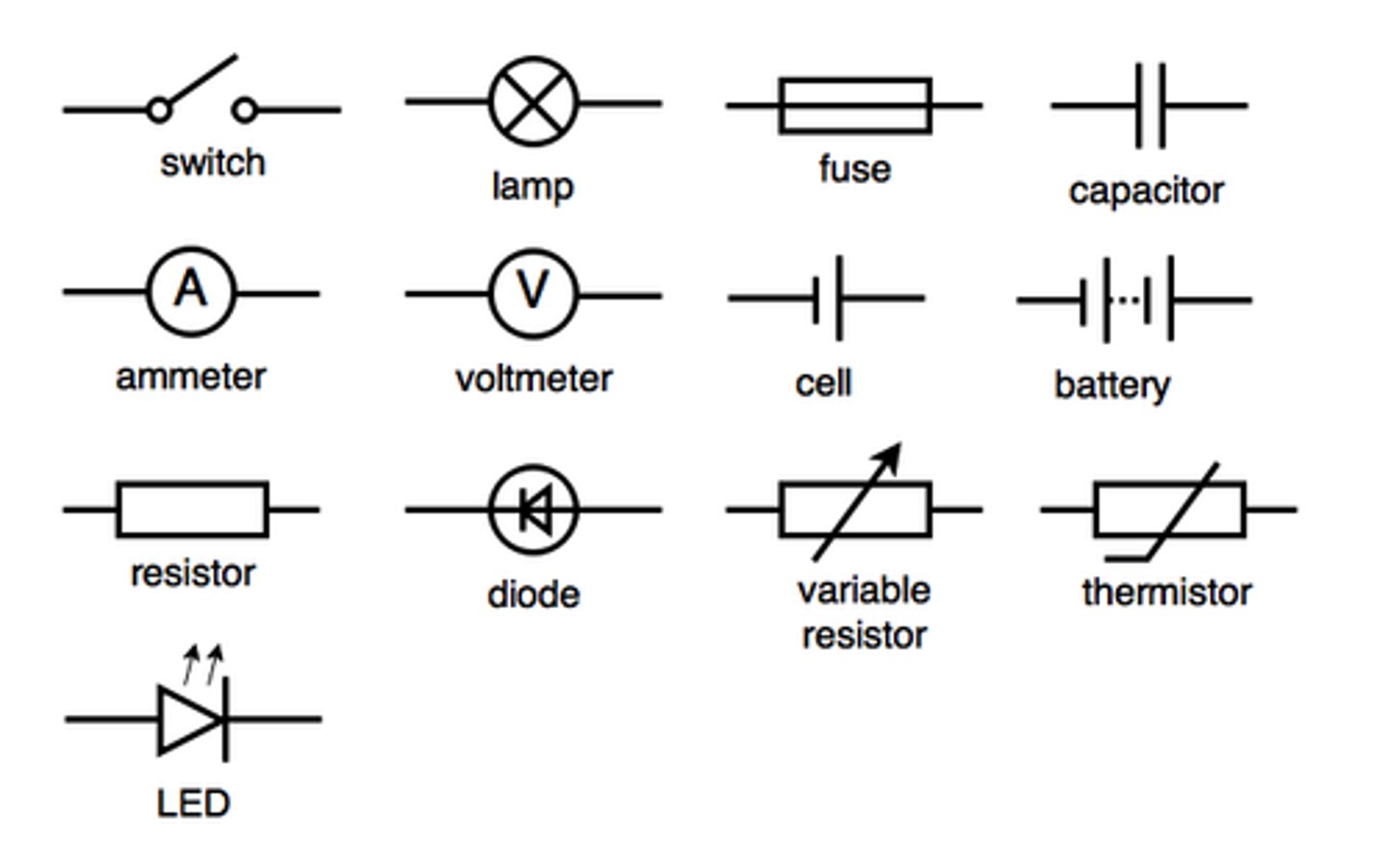
What is a series circuit
A circuit that has only one path for the elecric current to flow.
What is a parallel circuit
A circuit that has more than one pathways for current to flow through.
Voltage
the energy transformed per unit of charge
Current
flow of charge
Resistance
A measure of how hard it is for the current to flow through in a circuit
Power
the rate at which energy is transformed
Electrical conductor
Something an electrical circuit can flow through
Electrical insulator
a material an electrical current cannot flow through
What symbol and unit is used for current
Symbol = I
Unit = Amperes, (Amps), A
What is the symbol and unit for voltage
Symbol V
Unit V (volts)
What is the symbol and unit for power
P, Watts, W
What is the symbol and unit for resistance
Symbol: R Unit: Ohms (Ω)
How is current shared in series and parallel
Parallel: Is shared through circuit. 12A from start of power output results in 6A to first pathway and 6A to second pathway. It meets back up at end
Series: The same throughout the whole circuit. 12A from one ammeter would result 12A for the whole circuit
How is voltage shared in series and parallel
Parallel: The same all throughout the whole circuit. 12V from power pack would result 12V for each individual branch of the parallel circuit
Series: Its shared. 12V for power pack results in 6V to first bulb and 6V to second bulb
What happens to total current when total resistance goes up
When total resistance goes up, total current goes down, therefore there is less current in the circuit overall for both series and parallel (such as removing a pathway).
In parallel, if another pathway is added, total resistance goes down since there is a new route for the current to flow through therefore total current goes up yet each pathway still receives the same amount of current considering they have equal resistance
Also in parallel, current will always try to take the path with least resistance so paths with less will receive more current.
What happens to voltage when resistance goes up
In a series circuit, if two bulbs have different resistances, the bulb with the higher resistance will shine brighter because it requires more voltage to allow the same current to pass through, meaning it gets a larger share of the total voltage.
Formula for power
P = IV
Variants = I=P/V, V=P/I
P = Power (measured in Watts (W))
I = Current (measured in Amperes (A))
V = Voltage/Potential Difference (measured in Volts (V))
How does power affect brightness of lamps
Power is how bright a bulb glows, the more power, the brighter a bulb. If a bulb has lower current or lower voltage but the other part of the formula stays the same, brightness will still go down.
How to calculate total resistance in a pathway
add up all the components resistance in the pathway
Ohms law
V=IR
Variants= R=V/I, I=V/R
What is a short circuit and how do they work and affect current
A short circuit is a pathway with no resistance. If one pathway contains a lot of resistance and the other is a short circuit, most of the current will flow through the short circuit.