Psych Brain&Behavior INCOMPLETE
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Neurotransmission
the process that occurs when
a neurotransmitter is released from a presynaptic
neuron and binds to a receptor on the postsynaptic
neuron
Neurotransmitter Receptors
Neurotransmitters evoke postsynaptic potentials by binding to members of a
diverse group of transmembrane proteins called…
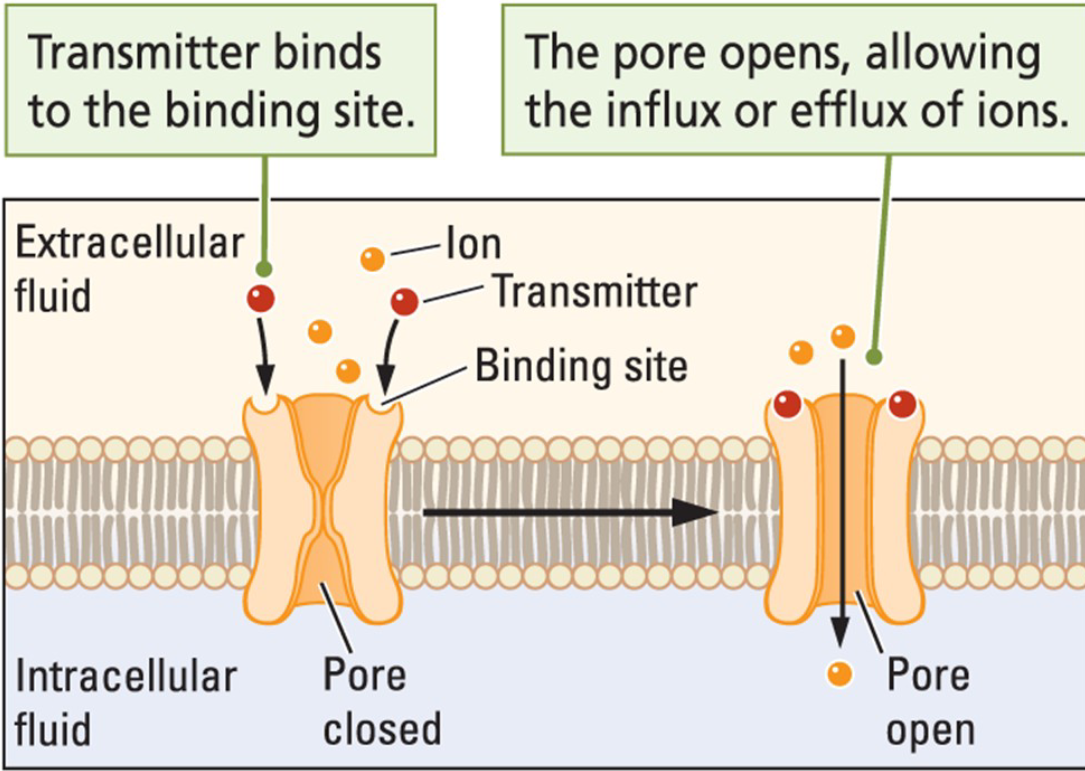
Ionotropic
Ligand-gated ion channels that rapidly open when a chemical messenger, such as a neurotransmitter, binds to them, allowing specific ions (like Na⁺, K⁺, Ca²⁺, or Cl⁻) to pass through the cell membrane
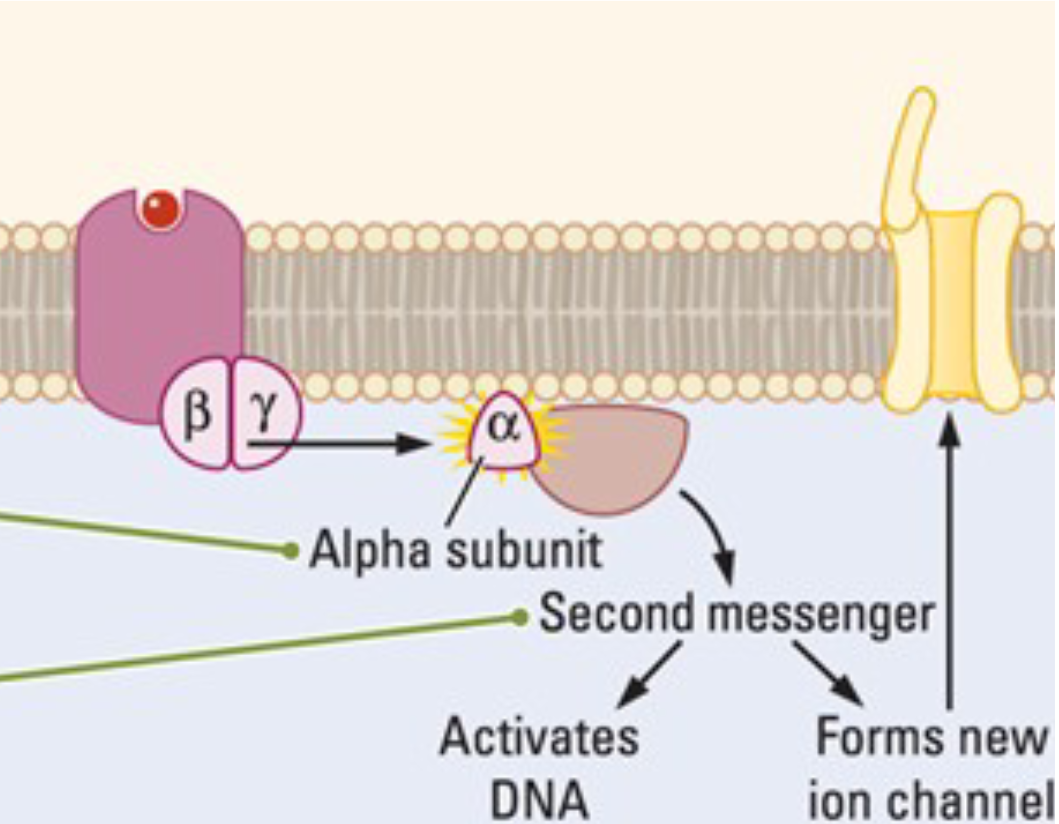
Metabotropic
A class of cell surface receptors, most commonly G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), that do not directly open ion channels
Neurochemicals (Neurotransmitters) include
Small Molecules, Neuropeptides and Gasotransmitters
Small Molecule include
Acetylcholine, Monoamines, Amino Acids, ATP and its byproducts
Monoamides include
Catecholamines - dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine
Indoleamines - Serotonin and Melatonin
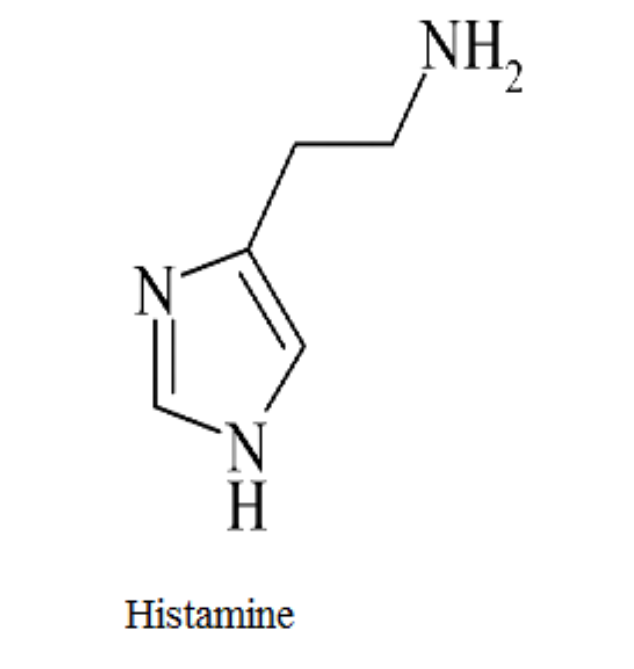
Histamine
Amino Acids include
Glutamate, GABA, Glycine and five others
Neuropeptides include
Endorphins, Substance P, and Insulin and 43 others
Gasotransmitters
Nitric Oxide, Carbon Monoxide
Small Molecule: Acetycholine
Plays a role in memory, learning, attention, arousal and involuntary muscle movement mostly contained in the brainstem and basal forebrain and can be broken up into Acetate and Choline.
Acetate
A compound found in acidic foods (e.g. vinegar and lemon juice)
Choline
A breakdown products of fats present in foods (e.g. egg yolk, avocado salmon, olive oil)
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE, enzyme)
Breakdown acetylcholine into acetate and choline for reuptake back into presynaptic cell.
Nicotinic-ACh Receptor
Ionotropic receptor for Na+, K+ , Ca 2+ ion channel (typically net +
change). fast acting and named after it’s ability to stimulate nicotine.
Used at the neuromuscular junction (connection
between nerves and muscles) and CNS
Muscarinic ACh Receptor
Metabotropic receptor thus slower acting. Implicated in higher brain functions such as learning and memory. Related to Alzheimer’s disease
Catecholamines
Named on the basis of the hydroxylated
phenol ring termed a catechol nucleus. Dopamine, Norepinephrine, and Epinephrine. All share similar chemical structure.
Indolamines
Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) and Melatonin
Histamine
Control of arousal and waking and Regulation of immune response
Tyrosine
The catecholamines synthesis precursor chemical. Foods high in this chemical
include cheese, soybeans, beef, lamb etc.
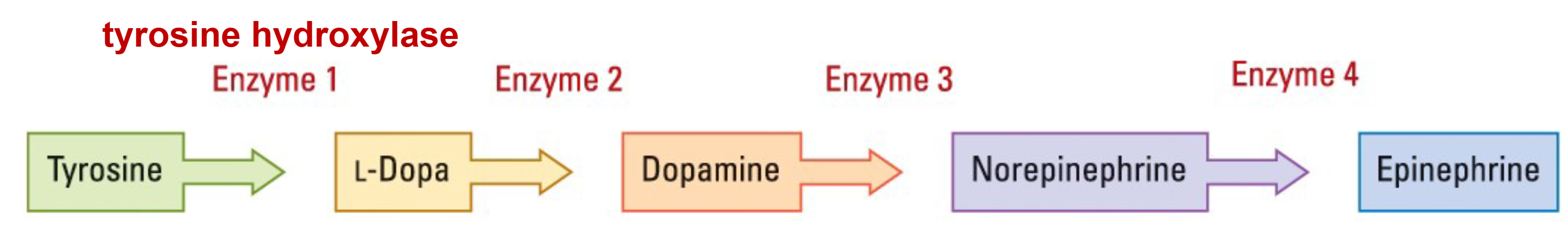
Tyrosine hydroxylase
This enzyme changes tyrosine into L-dopa, which other enzymes convert
first into dopamine, then into norepinephrine, and finally into epinephrine
The Dopamine pathways are…
substantia nigra → striatum (caudate and putamen),
Mesolimbic DA pathway,
the ventral tegmental area (VTA) → the limbic system,
Mesocortical DA pathway
Nigrostriatal dopamine pathway
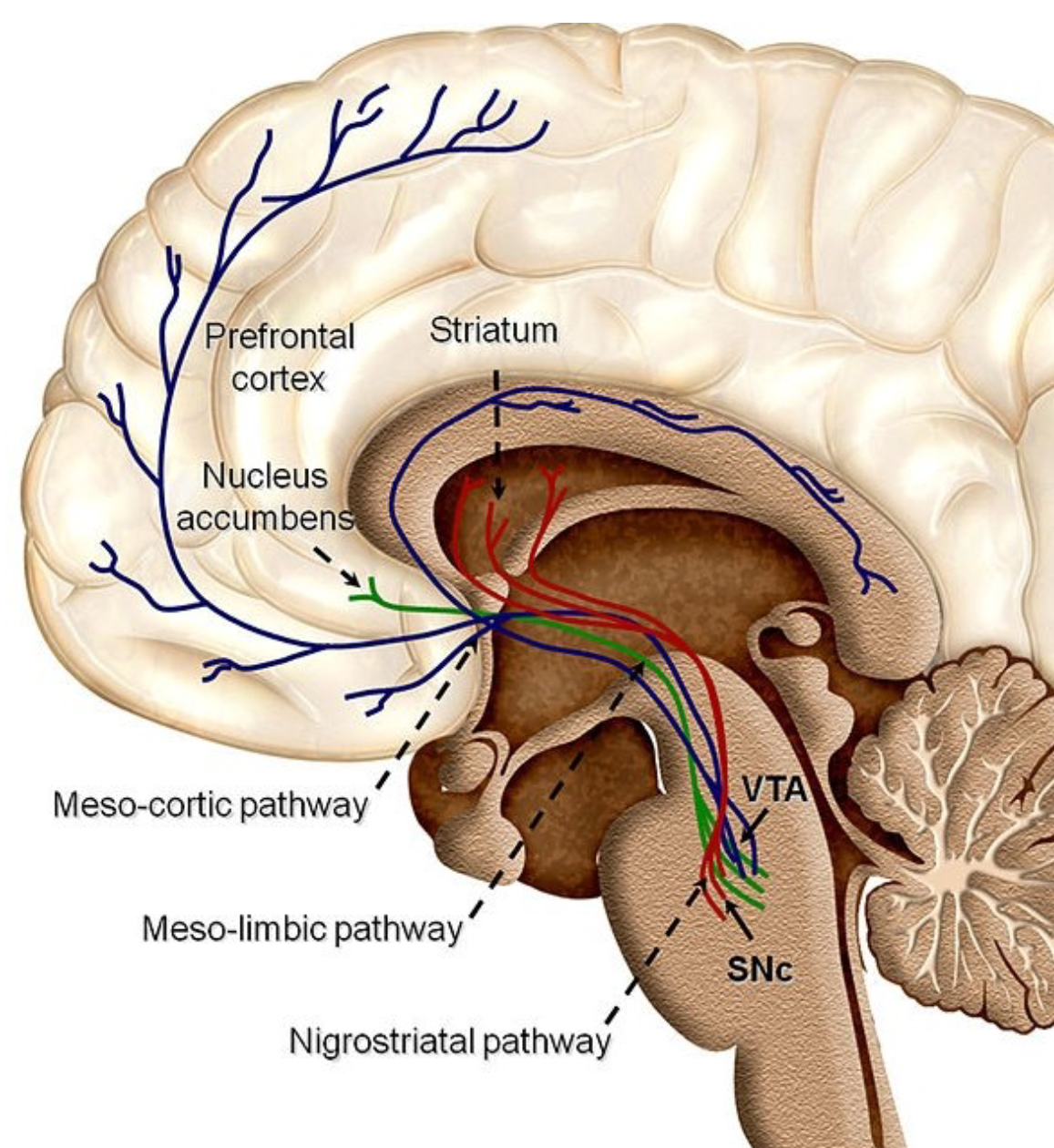
substantia nigra → striatum
Movement-related activities and Parkinson’s disease
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) the limbic
system
Reward and pleasure, Addiction & Schizophrenia
Mesocortical DA pathway
important for cognition and the regulation of
executive functions (e.g., attention, working
memory, inhibitory control, planning, etc.)
Dopamine (DA) Receptors & DA removal
5 different types of DA receptors (D1-D5),
and all are metabotropic
DA is actively re-uptaken by dopamine
transporters (DAT) in the presynaptic
terminal → destroyed by an enzyme called
monoamine oxidase (MAO)
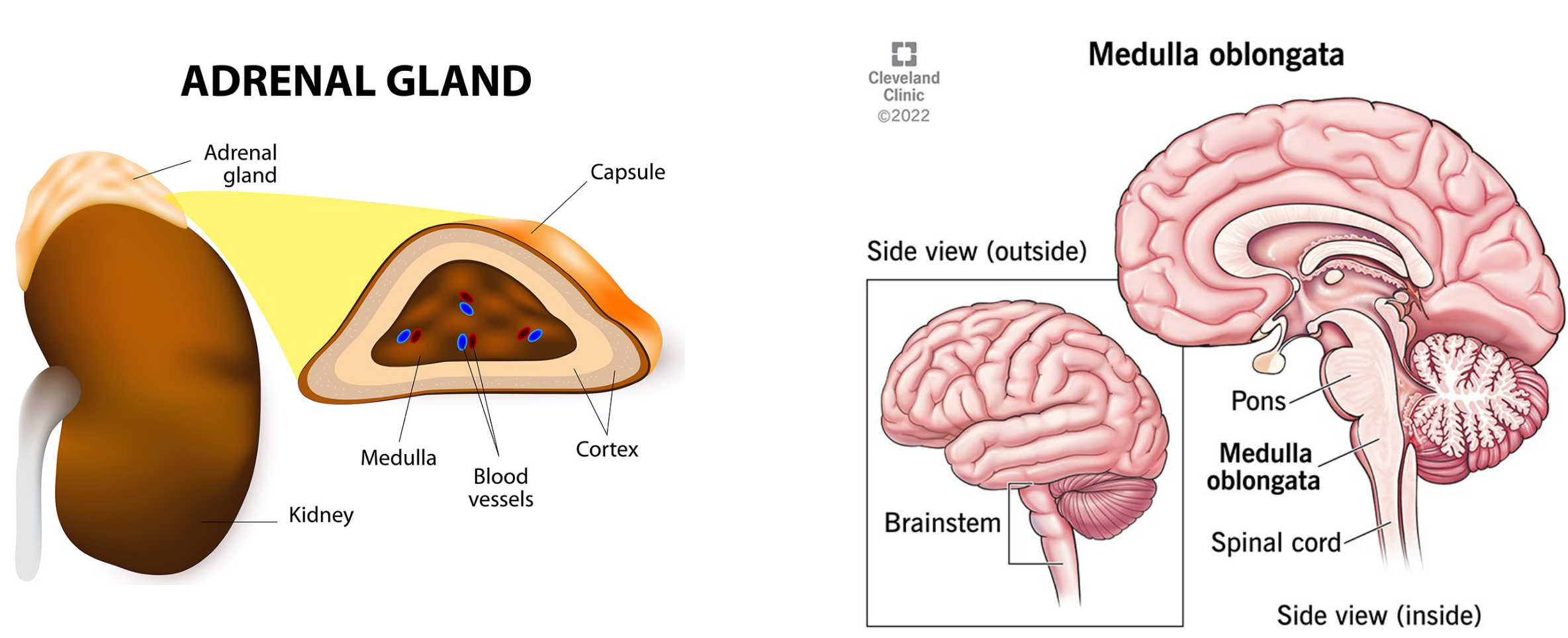
Adrenalin (epinephrine)
synthesized in the adrenal gland (adrenal medulla) → involved in fight or flight response. activating adrenergic receptors throughout the body
also synthesized in the brain (medulla oblongata)
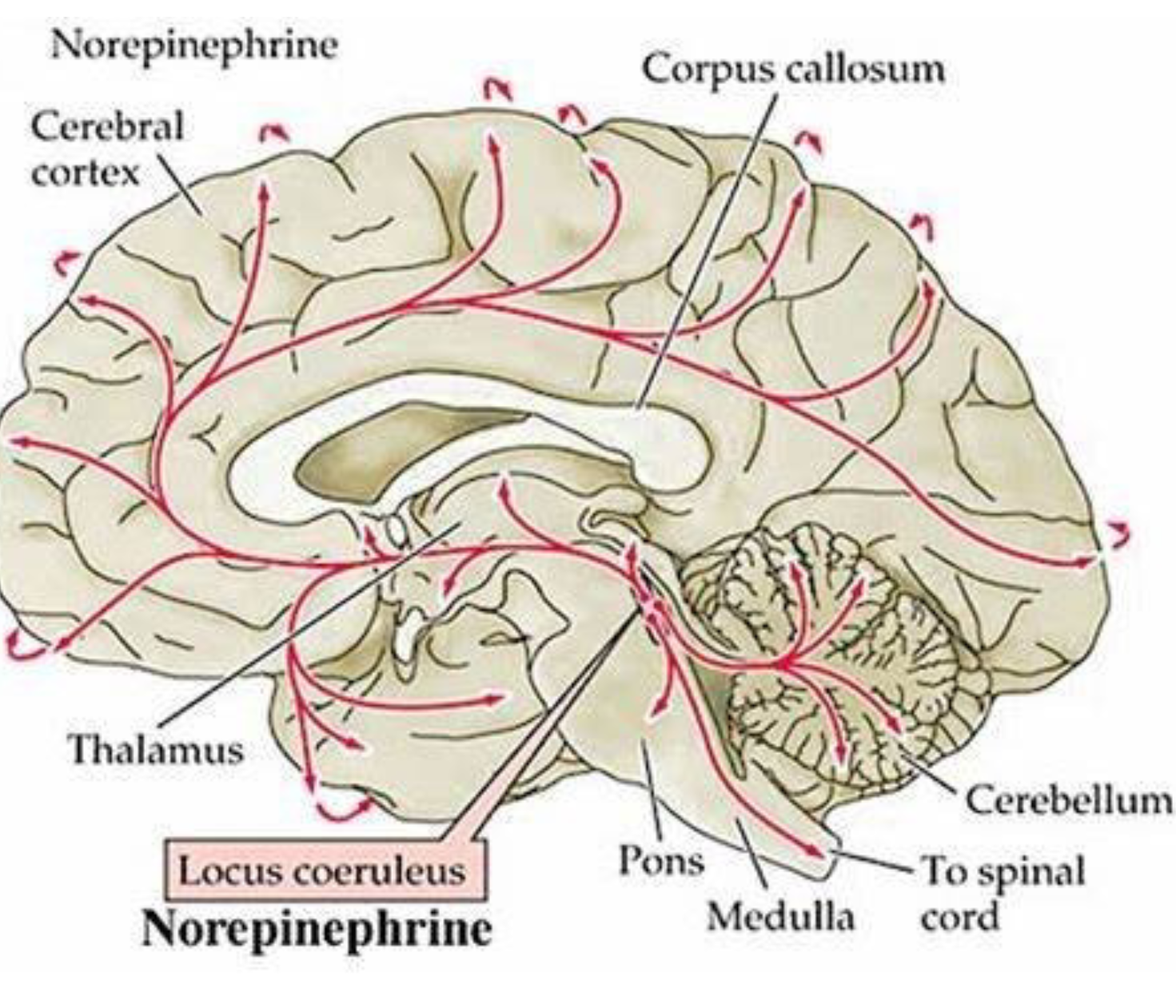
Noradrenalin (= norepinephrine, NE)
Mediate fight or flight response
• Increases arousal and vigilance
• Enhances sensory processing
• Strengthens memory encoding in the
amygdala and hippocampus
• Prepares motor systems for fast reaction
most NE neurons are clustered in
the brainstem in a region called the locus
coeruleus (LC)
Metropic receptors
Serotonin(5-HT, for 5-hydroxytryptamine)
Plays an important role in many psychological
processes - regulation of mood, control of eating, sleep,
and arousal
Major source of 5-HT in the brain is the raphe
nuclei in the brainstem
Synthesized from the amino acid, L-tryptophan
Amino Acid
The transmitters of this small molecule are the workhorses of the brain because so many synapses use them.
Glutamate, Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
Glutamate (glutamic acid, Glu)
typically opens Na + and Ca 2+ channels →
excites neurons!
the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain &
spinal cord
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
typically opens Cl – channels → inhibits neurons!
the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain
Glutamate Receptors
Both ionotropic. AMPA Receptor and NMDA Receptor
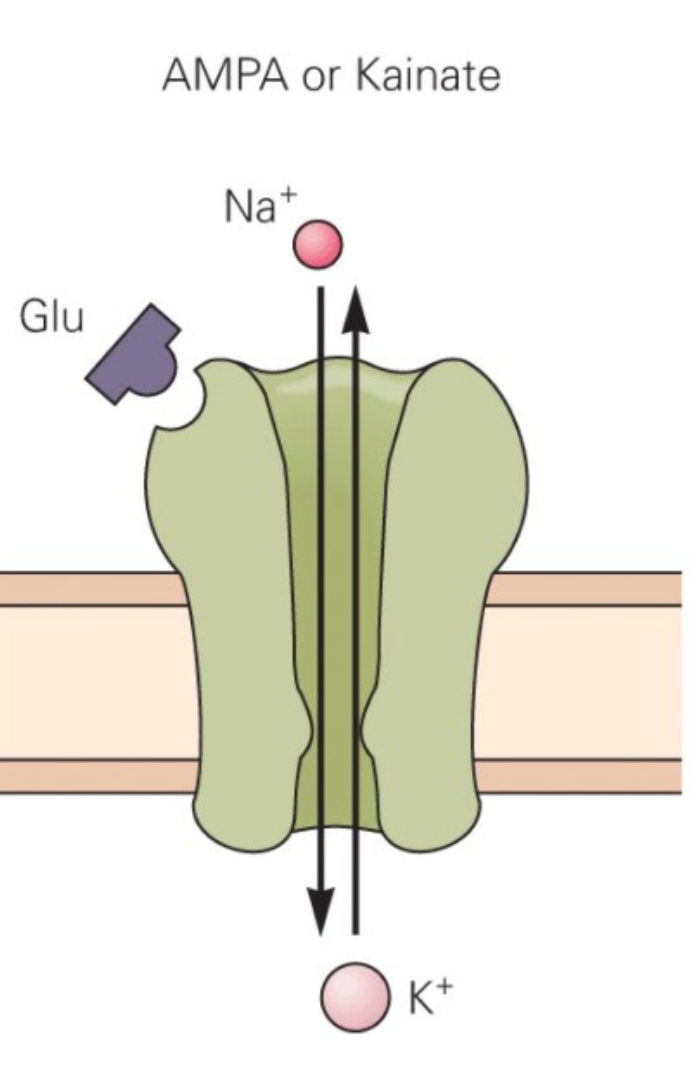
AMPA Receptor
This is the most common glutamate receptor. Used in most types of excitatory synaptic transmission. Passes Na+ ions
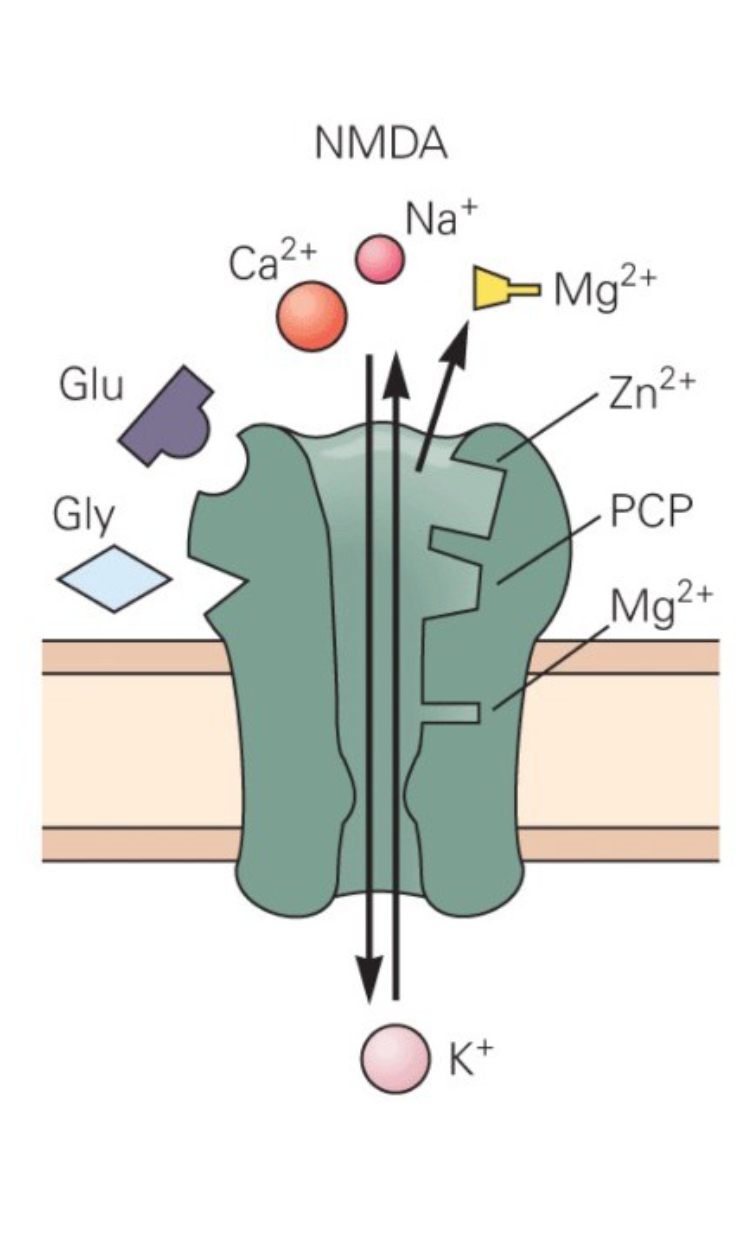
NMDA Receptor
Permits Na+ and Ca2+ to enter the cell. Important for learning and memory. Mg2+ ion must be removed for the channel to pass
ions.
Receptor only opens when glutamate is bound OR when the cell is depolarized (less negative on the inside compared to its resting state)
ligand and voltage-dependent
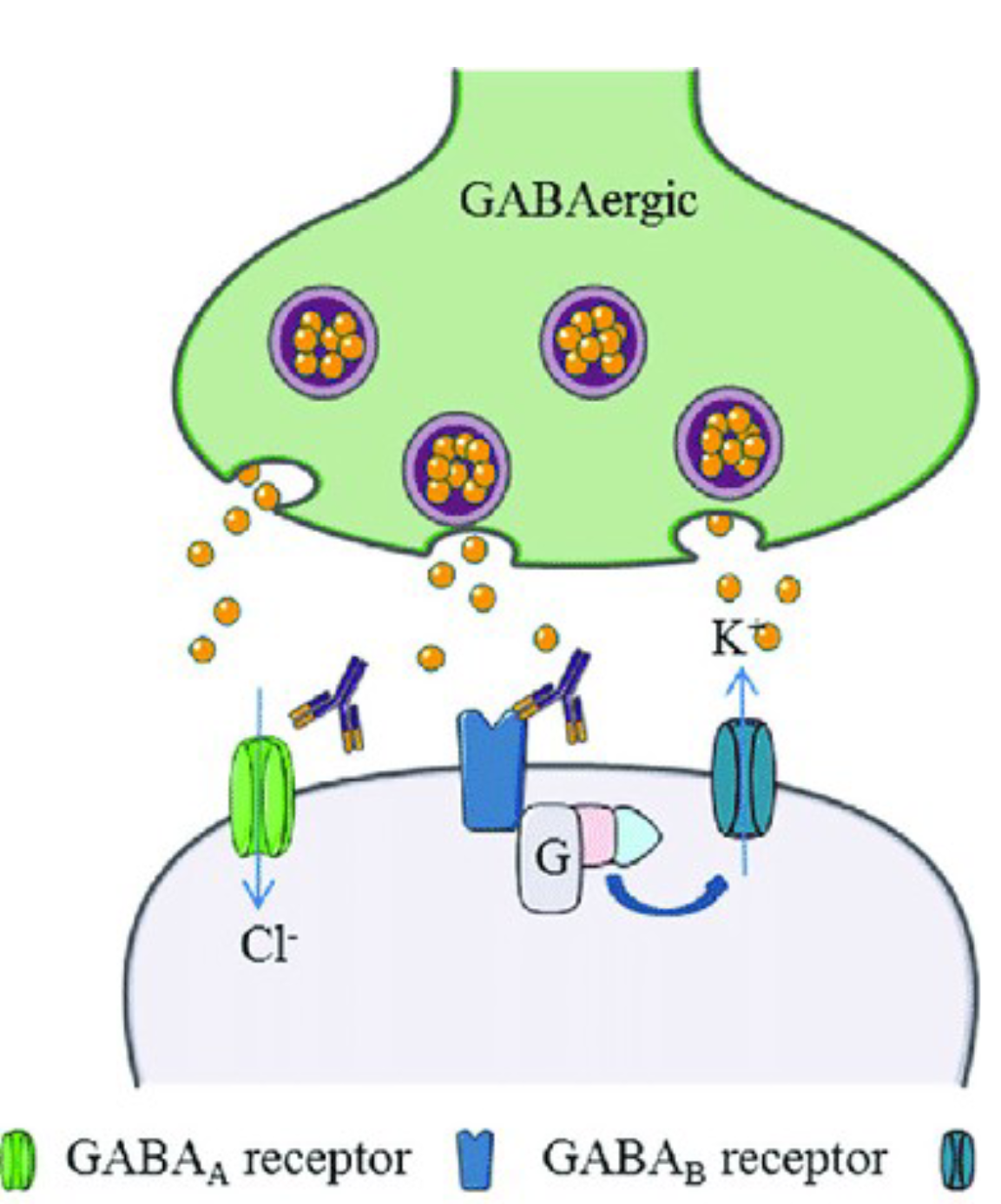
GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)
Produced from glutamate is a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. Enzymatic reaction: Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD).
2 types of GABA receptors both create IPSPs
GABA-A receptor: ionotropic; passes Cl-
GABA-B receptor: metabotropic; controls a K+ channel
Peptide Transmitters: Neuropeptides (Chain of amino acids)
Synthesized through translation &transcription - instructions in DNA
Over 100 distinct neuropeptides
Opioid peptides: endorphin, dynorphin, enkephalins - pain modulation, reward, stress relief
Hypothalamic releasing hormones: control pituitary
hormone release
Social/affective peptides: oxytocin, vasopressin
Endocannabinoids
a class of neuromodulators derived from lipid molecules, rather than amino
acids or peptides
Acts on cannabinoid receptors
• CB1 receptors
• CB2 receptors
• Metabotropic
Affect appetite, pain, sleep, mood, memory, anxiety, and the stress
response
Cannabis and the Endocannabinoid System
Cannabis refers to all products derived from the plant Cannabis sativa
main cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD)

Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
Act on cannabinoid receptor CB1 receptors and CB2 and the principal psychoactive effect

Cannabidiol (CBD)
Reduce the number of seizures
• Reduce anxiety
• Effect on insomnia
• helps control pain
Drugs
Chemical compounds administered to produce a desired change. Three different names. chemical, generic, and branded names
Psychopharmacology
Study of the ways drugs affect the nervous system and behavior
Chemical name
Describes the drug's complex molecular structure
Generic name
Name of the drug's active ingredient
Brand name
Unique, trademarked name given by the
manufacturer (Tylenol, Advil, Midol etc.)
Intracerebral
Administered between the two cerebral hemispheres of the brain
Oral Administration
Most common and safest route for taking a substance by mouth for systemic absorption. Weak acids pass from stomach into bloodstream. Weak bases pass from intestines into bloodstream.
Intramuscular
Drugs injected into muscles encounter more barriers
Inhalation
Drugs inhaled into lungs encounter fewer barriers
Intravenous (IV)
Drugs injected into bloodstream encounter fewest barriers to the brain but must be liquid
Blood Plasma
The liquid component of your blood. 55% of bloods total volume
Absorption rate
The time to reach maximum plasma concentration. Faster rate of absorption higher
and earlier peak concentration.
Circumventricular organs (CVOs)
Specialized brain regions where the BBB is weak or absent. “windows” for the brain to communicate with the blood. 7 areas are considered as CVOs such as...
• Pineal gland: Entry of chemicals that affect day-night cycles
• Pituitary gland: Entry of chemicals that influence pituitary hormones
• Choroid plexus
• Area postrema: entry of toxic substances that induce vomiting
The body eliminates drugs mainly through
Metabolism (Biotransformation) and Excretion
Metabolism (Biotransformation)
Occurs mostly in the liver, Drugs are broken down into more water-
soluble compounds for easier excretion, cytochrome P450 enzyme family is involved
Excretion
Metabolized drugs are excreted through urine,
feces, sweat, breast milk, and exhaled air
Most psychoactive drugs primarily affect
neurotransmitter release, receptor activation,
and removal from the synaps
Agonist
Mimics or enhances
A substance that binds to a receptor and
activates it, producing a biological response
similar to the natural neurotransmitter
Antagonist
Prevents or weaken receptor
A substance that binds to a receptor but
does NOT activate it, instead blocking or
reducing the effect of the natural
neurotransmitter
2 kinds of drug-receptor interaction
Competitive binding
and Non-competitive binding
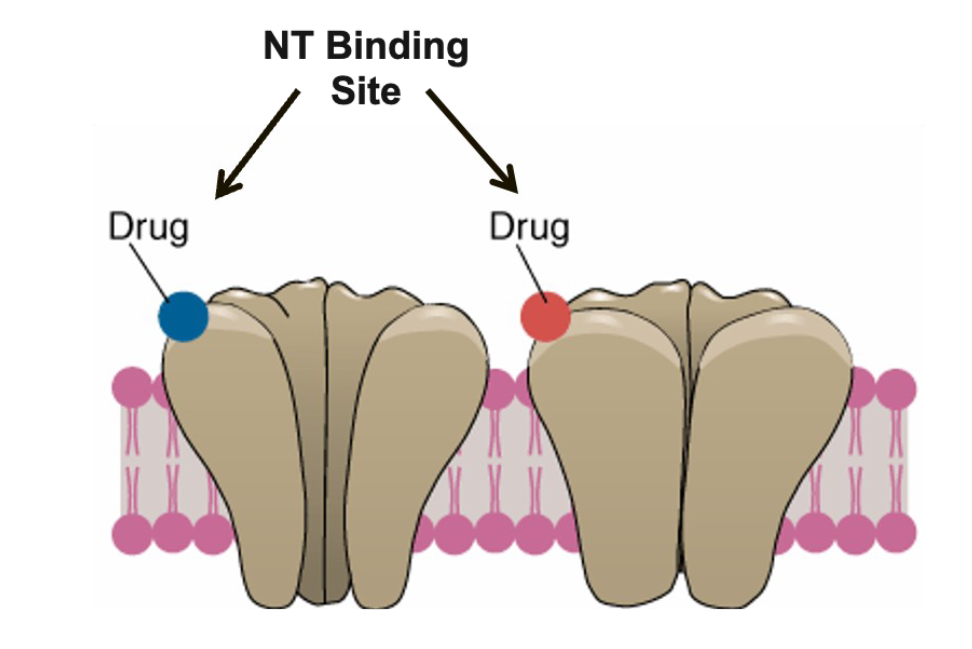
Competitive binding
occurs at a neurotransmitter binding site = drug compete with the
neurotransmitter to bind to the receptor
• Direct agonist
• Direct Antagonist
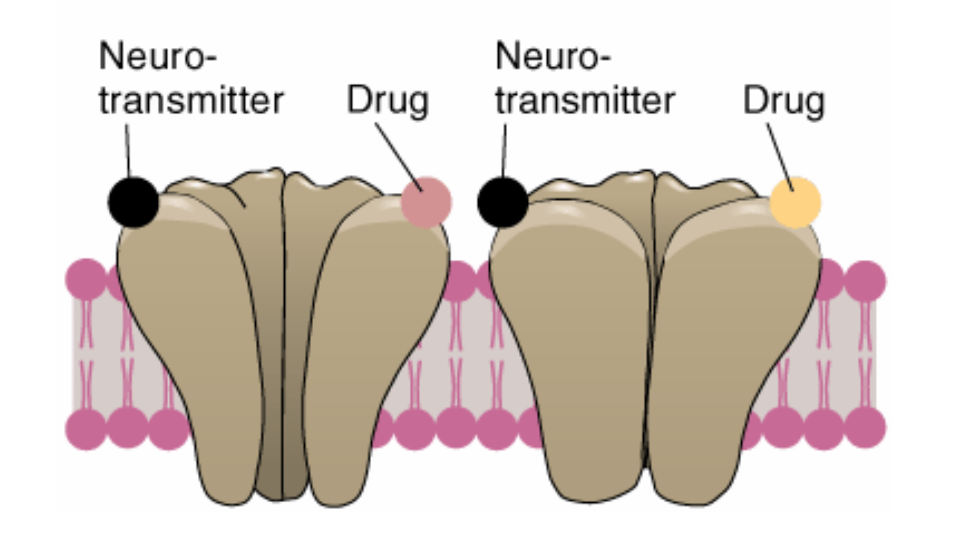
Non-competitive binding
occurs at an alternate binding site on the same receptor
• Indirect agonist
• Indirect
antagonist
Psychoactive Drugs
Chemical substance that
changes the function of the nervous system and
results in alterations of perception, mood,
cognition, and behavior
Barbiturates
Indirect agonist of GABA-A
receptors
• Sedative-hypnotics properties
• Sleeping medication or anesthesia
induction
Benzodiazepines
Indirect agonist of
GABA-A receptors
Anti-anxiety properties
Ketamine
Used medically for induction and maintenance of
anesthesia or pain management
• NMDA receptor indirect antagonist
• Binds to PCP binding site
• Prevent Ca2+ influx NMDA receptor
Esketamine
approved in conjunction with oral
antidepressant in March of this year
Sedative : Xylazine
is a non-opioid sedative or tranquilizer. Used for sedation, anesthesia, muscle relaxation, and analgesia in animals such as horses, cattle,
and other non-human mammals
First-generation antipsychotics
Mainly D2 receptor antagonist, Also block noradrenergic, cholinergic, and histamine
receptors unwanted side effects
Second-generation antipsychotics:
D2 and 5-HT2 receptor antagonist, Increase selectivity
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD, depression)
• Prolonged feelings of worthlessness and guilt
• General slowing of behavior
• Frequent thoughts of suicide