glucose regulation 1/2 DM 1
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
endocrine organs fx
synthesize and secrete hormones
endocrine
hormones released into bloodstream
paracrine
into adjacent tissue only
hormones
many have long half life = likely high ppb like t4 hormone
secretions triggered by
-concentrations of specific substance (glucose)
-neural stimulation (SNS & epi)
-endocrine sequences (epi → aldosterone)
regulate secretions
negative feedback mechanisms
function tests
hormone level or the affector substance level
-like glucose (indirect test of insulin fx); t4 (direct hormone level test)
endocrine dysfunctions
hyposecretion or hypersecretion (s&s will be directly related to excess or deficit of the expected hormone level)
-d/t primary endocrine disorder; signaling disorder; sequence disorder
hyposecretion
congenital defect, disease/inflammation, hypoperfusion, ageing
hypersecretion
genetic, tumours, environmental stimuli
primary energy sources
glucose, fatty acids (fats)
glucose
is readily distributed
needed for brain (cns)
extra stored as glycogen and triglycerides
-cannot store it as regular glucose for later
cns
needs constant supply of glucose (broken down: CO2 and H20)
glycogen and triglycerides
in liver and muscles and adipose cells
-fall in BG → glycogen breakdown via glycogenolysis (triggered in glucagon hormone) → for when extra glucose needed
gluconeogenesis
formation of more glucose from other sources, released prn
fatty acids
distributed via lymph to circulation
-cns and rbcs cannot use fatty acids
triglycerides
extra fatty acids stored as
-broken down into 3 fatty acids and glycerol
glycerol
glycolytic pathway into glucose
fatty acids
are not converted into glucose - cannot be used by the brain for energy
ketone metabolites
fatty acid metabolism in liver
insulin
pancreatic hormone (endocrine)
-synthesized in Beta cells (Langerhans)
insulin actions
glucose’ cellular uptake
promotes storage formation
amino acid cellular uptake; triglyceride adipose cell uptake
promotes storage formation
insulin action
-glycogen synthesis
-triglyceride synthesis
-protein synthesis
-prevents: glycogen and fat lysis (in order 1st use glucose) & protein lysis (to preserve tissue)
glucagon
synthesized in alpha cells = opposite of insulin
promotes mobilization of stores
glucagon
-glycogenolysis; gluconeogenesis (amino acid conversion into glucose); lipolysis (triglyceride breakdown)
glucagon triggered by
low plasma glucose levels (between meals; hypoglycemia) → mobilize stores and replenish blood glucose for cellular use
pancreas to release insulin
high blood glucose triggers
the beta cell in isle of langerhans
insulin released from
take up glucose from blood
blood glucose falls because cells
produces glycogen
blood glucose falls because liver
pancreas to release glucagon
low blood glucose triggers
glucagon
alpha cells secrete this (in islet of lagerhans)
down glycogen
glucagon released and liver breaks
liver breaking down glycogen
blood glucose rises due to
beta cells secrete insulin
glucose enter pancreatic beta cell via glucose transporter → metabolized via glucokinase into ATP → closes K channels (on beta cell) → depolarization → insulin secretion
insulin synthesis
stimulant is high serum glucose
50% 1st pass metabolized
insulin from pancreas enters hepatic circulation
metabolites
are renally excreted
tyrosine kinase
insulin binds to this cellular membrane receptor
kinase enzyme
tyrosine kinase activates this enzyme within cell
channels
kinase enzyme within cell stimulates these glucose transporter _____ to open to glucosse
somatostatin
is d cell produced
inhibits glucose and insulin
immediate effects of beta cell destruction
disabled transport of glucose into cells → dysfunction of glucose, fat, and protein metabolism
results from beta cell destruction
hyperglycemia, polydipsia (high solute [ ]), cellular dehydration, polyuria, glycosuria, fat for energy, ketones, metabolic acidosis
polydipsia
thirst triggered -really high solute in serum = high osmotic pressure, dictates h2o into blood
osmotic shift into filtrate
high urine production
-due to beta cell destruction
fat for energy
due to beta cell destruction
= breakdown of triglycerides and glycerol
ketones
from hepatic metabolism of fatty acids
due to beta cell destruction
metabolic acidosis
occurs from ketones which are result of hepatic metabolism of fatty acids
-drop ph of blood less than 7.35
-lactate byproduct of aerobic metabolism also increases acidity
-also produces acetone (sweet breath)
results from beta cell destruction
ketonuria, changes in loc, acetone breath, metabolic acidosis, coma, death
acetyl CoA
from free fatty acids which leads to ketone bodies synthesis which leads to ketone bodies which produce acetone and ketonuria
energy substitutes
lipolysis and proteolysis
lipolysis
fatty acid breakdown
liver metabolism fatty acids (fatty acid oxidation) = ketones and ketonuria
proteolysis
weight loss and muscle wasting (smooth muscle too which can have severe s/e)
altered cell fx due to reduced glucose uptake consequences
insulin resistance (due to lowered fx of cells)
altered cellular repair
endothelial dysfunction and decreased angiogenesis
organ injury
endothelial dysfunction causes
increased oxidative stress → inflammatory consequences = risk of clotting
organ injury from reduced glucose uptake
retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, CV
DM dx
fasting glucose >7mmol/L (normal <6)
type 1a dm
genetic predisposition + triggering event (infection, trauma) → immune rxn to beta cell antigens = autoimmune
type 1b dm
idiopathic (familial), rare
dm
total detruction of beta cells: IDDM (insulin dependent)
when is iddm dx
usually pre 30yrs of age (toddler and teens) - rapid growth and hormonal changes
iddm tx
insulin
-if no tx: diabetic ketoacidosis = death
basal insulin level
5-15 IU/mL
-always present ongoing secretion
-cruise control
peak level insulin
60-90 IU/mL
booster at meals to match glucose content
normal levels
4-8mmol/L
tx w/ insulin goal
restore normal glucose patterns
mimic basal & peak endogenous levels
minimize risk of hypoglycemia
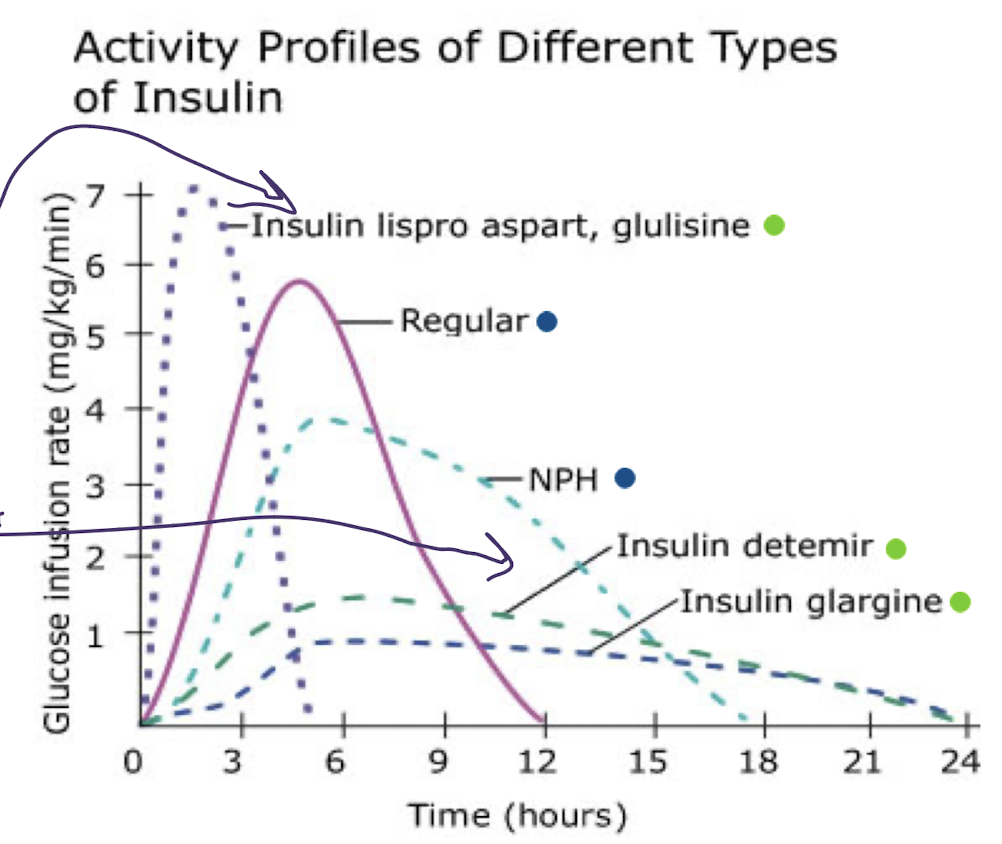
4 basic insulin categories
rapid acting (10-15 min onset)
long acting (up to 24hrs cruise control always present)
short acting (regular) peak and duration slightly longer
intermediate acting (NHP) slightly higher peak
SC insulin
injections, portable pen injectors, insulin pumps (basal and bolus delivery)
IV insulin
utilized in critically ill patients
drug admin rights
dose double checked by 2 rns
check dose carefully (units)
injection sites
upper outer arms
abdomen
buttocks
upper outer thighs
need to rotate sites
rapid acting insulin
onset 10-15 mins
peak 1-2 hr
duration 3-5 hrs
-ideal for meal time bolus, pt can eat right away, insulin for insulin pumps
-dose per carb contnent
check bg 1-2hr post
rapid acting insulin drugs
lispro
Aspart
Glulisine
Fiasp (Aspart) faster onset of 4min
rapid acting insulin in pumps
meal time boluses
per carb content
check bg pre meal and 1-2 hr post
basal insulin requirements in pumps
always slowly given over 24 hrs
or given once to twice in hospital
check bedtime bg, if lowers too much overnight risk for hypoglycaemia = adjust basal insulin dose
endocrinology appts
long acting insulin
onset 90 min
plateaus for up to 24hrs (depends on how often you give it)
ideal for: background admin 1-2x daily consistency is important - never IV
adjust dose according to bedtime bg level
long acting insulin drugs
Detemir
Glargine
Degludec ultra long acting
short acting insulin (regular)
onset 30 mins
peak 2-3 hrs
duration 6.5 hrs (dose dependent)
ideal for: meals (30-45 min pre meal)
issues with hypoglycemia and balancing dose w intake, ensure pt eats
short acting insulin iv
used if ketoacidosis, new dx, stabilizing pt in hospital
short acting insulin drugs
Novolin ge Toronto
Humulin R
Entuzity (KwikPen) 5x more [ ]
intermediate acting insulin
onset 1-3 hrs
peak 5-8hrs hypoglycemia at peak, why not as popular
duration up to 18hrs (dose dependent)
ideal for: background replacement, admin 1-2x daily if pt on steroids
never iv
monitor night for hypoglycemia
intermediate acting insulin drugs
Humulin N
Novolin ge NHP
intensive insulin tx req
estimated daily insulin reqd: 0.55 U x Pt. wt (kg)
-doesnt factor in BMR, activity/stress, food, starting point only
-approx 40% of estimate = basal
other 60% = boluses
bolus insulin dosage based on
BG pre meal
carb content/meal
basal insulin dosage based on
estimate, bedtime bg level
am admin preferred, avoids nighttime hypoglycemia
similar amt each day, as long as bedtime bg is normal
given even if pt is npo
if pt on insulin pump, the basal dose is continuously delivered (fast acting insulin)
BBIT
basal (long acting) in am
bolus (short/rapid) @ meals
insulin correction (short/rapid) if necessary (based on bg post meal)
titrate doses to achieve glucose levels 4-8 (monitor bg through day)
bg checks recommended
pre meal, post meal (1-2 hr for new dx), at bedtime
4x day minimum
8x for newly dx pts