GGR321 - Quiz 3 + 4 questions
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Cost distance algorithm
create a source grid with 0 at starting point and some other value for all other cells
create a cost grid with same size and resolution but containing the costs for each cell
run the cost distance facility in GIS on these two input grids, output ACS grid along with tracking grid
To create the least cost paths, a target grid containing the target/destination points
Historically, the pioneer of Spatial Analysis is considered to be _________ in his study of the cholera outbreak in London, Soho area, in 1850s .
Dr. John Snow
Spatial analysis types:
Inductive
examining empirical evidence in the search for patterns that might support new theories or general principles
Deductive
focusing on the testing of known theories or principles against data
Normative
Using spatial analysis to develop or prescribe new or better designs
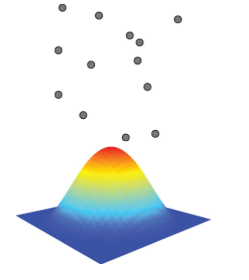
In density estimation, as a form of spatial analysis based on distance, the kernel’s shape depends on a distance parameter;
Increasing the value of the parameter results in
a broader and lower kernel
Reducing the value of the (distance) parameter results in
a narrower and sharper kernel
The method of spatial interpolation of rainfall estimates from a few rain gauges to obtain estimates at other locations where rainfall had not been measured:
Inverse-distance weighting,
Kriging,
Thiessen polygons
Thiessen polygons
Short script in ArcPy to set up a workspace in ArcGIS Pro for data located at C:/PythonStart
arcpy.env.workspace = "C:/PythonStart"
Geoprocessing tools; parameters and their properties:
Name
a unique name for each tool parameter
Type
the type of data expected, such as feature class, string, integer, raster
Direction
whether the parameter defines input or output values
Required
whether a value must be provided for a parameter or is optional
3D Analyst
Analyzes and creates 3D GIS data and performs 3D surface operations using rasters, TINs, terrains, and LAS datasets (lidar)
Network Analyst
Measures distances and travel times along a network to find a route between multiple locations, creates drive-time buffers or service areas, and finds the best locations for facilities to serve a set of locations
Image Analyst
Interprets and uses imagery, performs feature extraction and measurement, and performs classification and object detection using machine learning
Spatial Analyst
Finds the most suitable locations, calculate distance and determine optimal paths by incorporating the cost of travel, analyze and interpolate surfaces, calculate density, conduct hydrologic analysis, perform statistical analysis, and perform various raster-based mathematical operation
In spatial analysis hypothesis testing, randomization tests are uniquely adapted to testing hypotheses about spatial patterns - True or False?
True
Geoprocessing in ArcGIS Pro allows to perform spatial analysis and modeling with the use of _____ , ______and , _______ as well as automate GIS tasks.
tools, models, and scripts
Availability of geoprocessing tools in ArcGIS Pro depends in part on license level: Basic, Standard, or Advanced and license for extensions, such as ArcGIS 3D Analyst™, ArcGIS Network Analyst™, and ArcGIS Spatial Analyst™. T or F
True
Assume you're using Python to find areas of suitable vegetation that exclude areas heavily impacted by major roads. Please match accordingly the name of the step with the corresponding line(s) of the script:
import system modules, set environment settings, select suitable vegetation patches from all vegetation
Types of geoprocessing tools:
Built-in tools
These tools are built using ArcObjects and a compiled programming language such as C++.
Model tools
These tools are created using ModelBuilder.
Script tools
These tools consist of Python scripts that are accessible using a tool dialog box.
ArcPy modules:
arcpy.da
a module for working with data
arcpy.sa
a module for map algebra and raster analysis
arcpy.ia
a module for image analysis and interpretation
arcpy.mp
a map scripting module
Please match the method of accessing Clip tool with correct line of Python code:
by corresponding function:
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = “C:/Data”
arcpy.Clip_analysis(“streams.shp”, “study.shp”, “result.shp”)
Please match the method of accessing Clip tool with correct line of Python code:
by using modules that match the toolbox alias name:
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = “C:/Data”
arcpy.analysis.Clip(“streams.shp”, “study.shp”, “result.shp”)
The Buffer tool has three required parameters and five optional parameters. To specify a dissolve option (e.g., LIST) and the field to use in this dissolve (e.g., CODE), two optional parameters must be skipped. This can be done in several ways. Please choose ALL correct answers:
arcpy.Buffer_analysis("roads", "buffer", "100 METERS", dissolve_option="LIST", dissolve_field="CODE")
arcpy.Buffer_analysis("roads", "buffer", "100 METERS", "#", "#", "LIST", "CODE")
arcpy.Buffer_analysis("roads", "buffer", "100 METERS", "", "", "LIST", "CODE")
arcpy.Buffer_analysis("roads", "buffer", "100 METERS", None, None, "LIST", "CODE")