IOA2 Exam 3 - Pupillary Pathway
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
What is required for autonomic control of the iris muscles during normal visual activities?
Balanced activation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
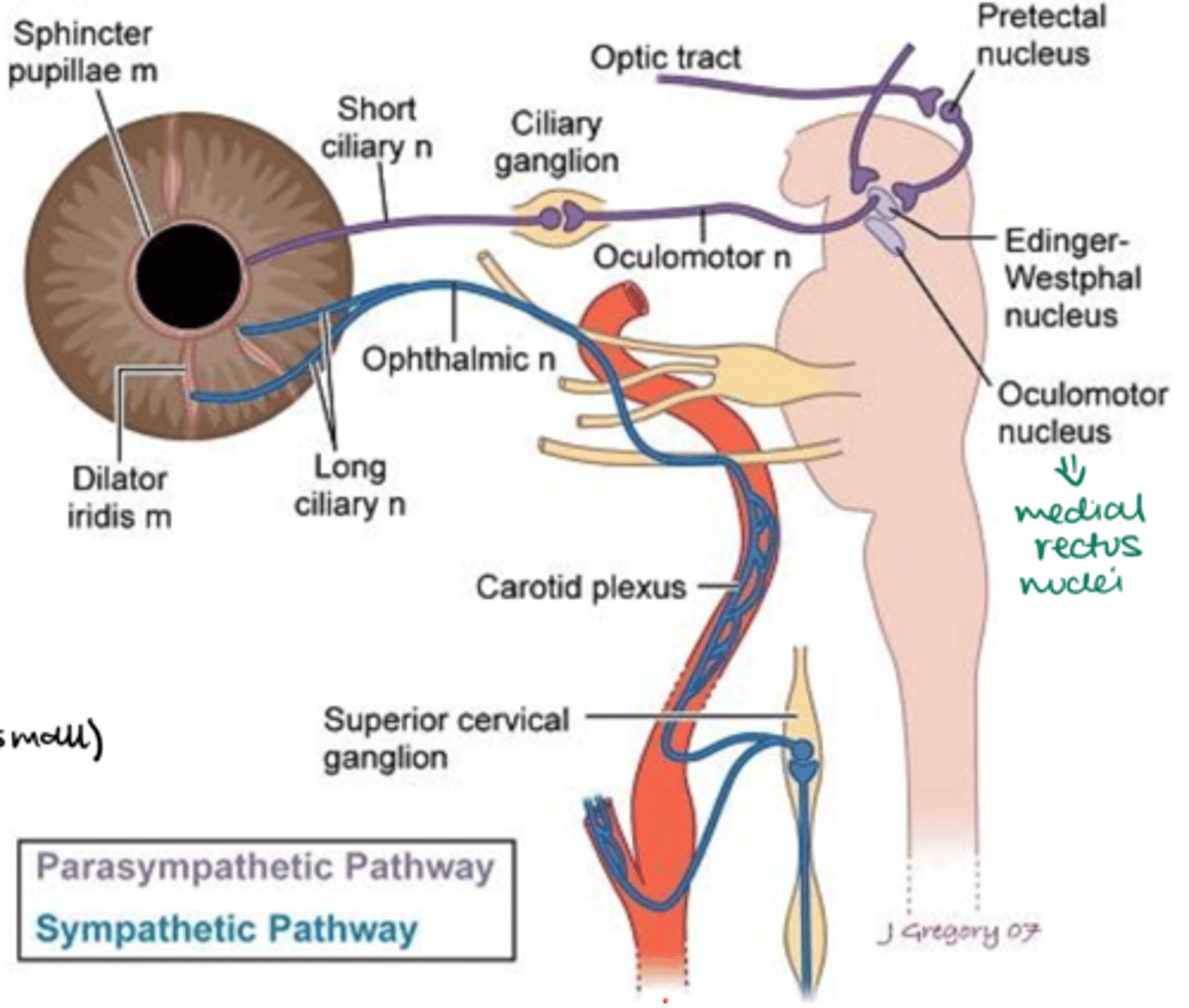
Which muscle does the sympathetic system control in the iris?
Dilator pupillae muscle
What is the location of the dilator pupillae muscle fibers?
Radial muscle fibers distal to the pupillary entrance
Where is the origin of the sympathetic pathway of the iris?
T1-T3 levels of spinal cord
Which muscle does the parasympathetic system control in the iris?
Sphincter pupillae muscle
What is the location of the sphincter pupillae muscle fibers?
Circular muscle proximal to the pupillary entrance
Where is the origin of the parasympathetic pathway of the iris?
Midbrain/Pons
What are the sympathetic fibers of the iris controlled by?
Hypothalamus projections (descending pathway)
Where do the sympathetic fibers synapse in the spinal cord?
Laternal horn column of the cervical spinal cord (T1-T3)
How do the fibers from preganglionic neurons leave the spinal cord?
Thru the ventral root in one of the first 3 thoracic nerves
How do preganglionic fibers enter the sympathetic ganglion chain?
Thru the spinal nerve and white ramus communicante
Preganglionic fibers leave the 1)_________ in one of the first three thoracic nerves via the 2)___________, and enter the 3)___________ thru the 4)_________ and _________.
1) Spinal cord
2) Ventral root
3) Sympathetic ganglion chain
4) Spinal nerve & White ramus communicante
Where do preganglionic fibers synapse after ascending in the sympathetic chain?
Superior cervical ganglion
1)__________ ascend in the sympathetic chain to synapse in the 2)___________.
1) Preganglionic fibers
2) Superior cervical ganglion
Where is the superior cervical ganglion located?
At the level of the 2nd and 3rd cervical vertebrae (C2 and C3)
________ fibers leave the superior cervical ganglion.
Postganglionic
What do postganglionic fibers form after leaving the superior cervical ganglion?
The carotid plexus around the internal carotid artery
How do postganglionic fibers enter the skull?
Thru the carotid canal
Where do sympathetic fibers go after leaving the plexus in the cavernous sinus?
They take multiple pathways to target structures
Networks of sympathetic fibers leave the ____________ and take multiple pathways to the target structures.
plexus in the cavernous sinus
With which division of the trigeminal nerve do some sympathetic fibers travel?
Ophthalmic division
Once in the orbit, which nerve do sympathetic fibers follow?
Nasociliary nerve
Which nerves do sympathetic fibers travel with to innervate the dilator pupillae and ciliary muscle?
Long ciliary nerves
Sympathetic fibers travel with the 1)_________ to innervate the 2)___________ and 3)__________.
1) Long ciliary nerves
2) Dilator pupillae
3) Ciliary muscle
What is the effect of sympathetic stimulation on the iris dilator muscle?
Mydriasis (pupil dilation)
What is the effect of sympathetic stimulation on the ciliary muscle?
Relaxation (inhibitory effect- flattens the lens to see distance objects)
What does sympathetic stimulation do to the iris dilator muscles?
Activates them, causing pupillary dilation (mydriasis)
What is the effect of pupil dilation (mydriasis)?
Increases retinal illumination
What effect does sympathetic stimulation have on the ciliary muscle?
Inhibitory effect, causing relaxation
What role does the sympathetic pathway play in vision?
Imp for
-distant vision as part of the accommodation reflex
-dim light response
During distance vision, what happens to the ciliary muscles?
They relax, and the border of the choroid moves away from the lens
During distance vision, what happens to the suspensory ligaments?
They pull against the lens
What shape does the lens become during distance vision and why?
Lens becomes flatter to focus on distant objects
PLS SUMMARIZE THE SYMPATHETIC PATHWAY TO THE IRIS
1) Sympathetic fibers are controlled by the hypothalamus projections (descending pathway).
2) The fibers synapse in the laternal horn column of the cervical spinal cord (T1-T3).
3) Fibers from preganglionic neurons leave the spinal cord thru one of the first three thoracic nerves.
4) Fibers exit via the ventral root and enter the sympathetic ganglion chain thru the spinal nerve and white ramus communicante.
5) Preganglionic fibers ascend in the sympathetic chain to synapse in the superior cervical ganglion (C2 & C3).
6) Postganglionic fibers leave the superior cervical ganglion.
7) Postganglionic fibers form the carotid plexus around the internal carotid artery and enter the skull thru the carotid canal.
8) Postganglionic fibers may leave the plexus in the cavernous sinus, taking multiple pathways to the target structures.
9) Some sympathetic fibers travel with the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve.
10) Once in the orbit, they follow the nasociliary nerve.
11) Finally, they travel with the long ciliary nerve to innervate the dilator pupillae and the ciliary muscle.
Effects:
-Sympathetic stimulation activates the dilator muscle, causing pupillary dilation (mydriasis), which increases retinal illumination.
-Sympathetic stimulation also has an inhibitory effect on the ciliary muscle, resulting in relaxation, and causing the lens to flatten to see distant objects.
Where does the sympathetic pathway to the iris originate?
T1-T3 levels of the spinal cord
Where do the preganglionic fibers exit?
Via the ventral root
Where do preganglionic fibers synapse?
Superior cervical ganglion
How do postganglionic fibers leave the superior cervical ganglion?
They travel through the internal carotid plexus, and some travel with ophthalmic division
Once in the orbit, what do the postganglionic fibers follow?
Nasociliary nerve
Finally, the postganglionic fibers travel with the 1)_________ to activate the 2)__________, causing 3)________.
1) Long ciliary nerve
2) Iris dilator
3) Mydriasis
What may the postganglionic fibers travel through instead of the long ciliary nerve, causing interruption?
Sympathetic root --> ciliary ganglion (no synapse) --> short ciliary nerves --> choroidal and conjunctival blood vessels --> vasoconstriction
Where are the preganglionic neuron fibers for the parasympathetic pathway to the iris located?
In the midbrain
Specifically where in the midbrain are the preganglionic fibers for the parasympathetic pathway to the iris located?
Edinger Westphal nucleus (In the parasympathetic accessory third-nerve nucleus)
The Edinger-Westphal nucleus is what type of component of the Oculomotor Nerve (CNIII)?
General visceral efferent (GVE)
With which nerve do preganglionic parasympathetic fibers leave the Edinger-Westphal nucleus?
Oculomotor nerve
After the preganglionic parasympathetic fibers leave the Edinger-Westphal nucleus, what do they follow to reach the orbit?
They follow the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve into the orbit
Preganglionic parasympathetic nerve fibers follow the 1)___________ into the 2)_________.
1) Inferior division of the oculomotor nerve
2) Orbit
Where do the parasympathetic fibers enter when they leave the inferior division?
Ciliary ganglion (where they synapse)
What is the size and shape of the ciliary ganglion?
-Small, flattened structure
-2x1mm
Where is the ciliary ganglion located?
Within the muscle cone, between the lateral rectus muscle and the optic nerve, approximately 1cm anterior to the optic canal (and slightly lateral)
How many roots does the ciliary ganglion have?
3
Name the 3 roots of the ciliary ganglion
1) Parasympathetic root
2) Sensory root
3) Sympathetic root
Where are the roots of the ciliary ganglion located?
At the posterior edge of the ciliary ganglion
Which root of the ciliary ganglion do parasympathetic fibers use to synapse?
Parasympathetic root
Where do the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers from the ciliary ganglion go? (ie. Where does the parasympathetic root carry information to?)
Sphincter pupillae muscle
Where does the sensory root carry information from?
-Cornea
-Iris
-CB
Do sympathetic fibers synapse in the ciliary ganglion?
NO, they pass thru the sympathetic root
Where does the sympathetic root carry information to?
Dilator pupillae muscle
What emerges from the anterior edge of the ciliary ganglion?
Short ciliary nerves
Which type of fibers are carried by the short ciliary nerves?
-Parasympathetic fibers
-Sensory fibers
-Sympathetic fibers
Which muscles do the parasympathetic fibers target?
Sphincter pupillae muscle
Which muscles do the sensory fibers target?
-Cornea
-Iris
-Ciliary muscle
Which muscles do the sympathetic fibers target?
Dilator pupillae muscle
Are postganglionic parasympathetic neurons myelinated?
Yes
Where are the soma (cell bodies) of postganglionic parasympathetic neurons located?
Ciliary ganglion
Where do postganglionic parasympathetic fibers project?
Towards the short ciliary nerves
Which part of the eye do the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers synapse?
Anterior segment
What structures in the anterior segment of the eye do postganglionic parasympathetic neurons innervate?
-Ciliary muscle
-Sphincter pupillary muscle
What is the effect of parasympathetic innervation on the ciliary muscle?
Contraction, leading to accommodation
What happens to the lens during parasympathetic stimulation of the ciliary muscle?
Lens thickens
What is the effect of parasympathetic innervation on the sphincter pupillary muscle?
Miosis (pupil constriction)
What are the effects of parasympathetic stimulation?
-Pupillary constriction
-Contraction of the ciliary muscle
What is the effect of parasympathetic stimulation on the pupil?
Pupillary constriction (miosis)
What is the effect of pupillary constriction due to parasympathetic stimulation?
Decreases intraretinal illumination
When does parasympathetic stimulation cause pupillary constriction?
During sleep and accommodation
What is the effect of parasympathetic stimulation on the ciliary muscle?
Contraction
What does contraction of the ciliary muscle enable the eye to do?
Enables the eye to focus on near objects in accommodation
During near vision, what happens to the ciliary muscles?
They contract, pulling the border of the choroid towards the lens
During near vision, what happens to the suspensory ligaments?
They relax
What shape does the lens become during near vision and why?
Lens becomes thicker and rounder, to focus on near objects
Where do preganglionic parasympathetic fibers originate?
Edinger-Westphal nucleus in the midbrain
Which cranial nerve do preganglionic parasympathetic fibers travel with?
Oculomotor nerve
Which division of the oculomotor nerve do the preganglionic parasympathetic fibers follow?
Inferior division of oculomotor nerve
Where do preganglionic parasympathetic fibers synapse?
Ciliary ganglion
The ciliary ganglion is located within the 1)_________, between the 2)_________ and ________.
1) Muscle cone
2) Lateral rectus muscle and optic nerve
How do postganglionic parasympathetic fibers leave the ciliary ganglion?
Via short ciliary nerves
What muscles do the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers innervate?
-Iris sphincter
-Ciliary muscle
What is the effect of parasympathetic innervation on the iris sphincter muscle?
Miosis (pupillary constriction)
What's the effect of parasympathetic innervation on the ciliary muscle?
Accommodation (to focus on near objects)
PLS SUMMARIZE THE PARASYMPATHETIC PATHWAY TO THE IRIS
1) Preganglionic neuron fibers originate in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus in the midbrain.
2) Preganglionic fibers leave the midbrain as part of the oculomotor nerve (CNIII).
3) These fibers travel within the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve.
4) Preganglionic fibers enter the ciliary ganglion.
5) Preganglionic fibers synapse within the ciliary ganglion.
6) Postganglionic fibers leave the ciliary ganglion via the short ciliary nerves.
Effects:
7) Postganglionic fibers innervate the iris sphincter muscle, causing pupillary constriction (miosis).
8) Postganglionic fibers innervate the ciliary muscle, causing contraction for accommodation (focusing on near objects)
T/F: In normal awake individuals, parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves are in balance.
True
To reflect the balance in parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves, the size of the pupil ________.
changes constantly and rhythmically
Physiologic pupillary unrest
Hippus
What happens to pupil size during sleep, and why?
Pupils are small during sleep.
-The sympathetic system shuts down so the parasympathetic system predominates
During sleep, the pupils are small because the 1)___________ system shuts down and the 2)_________ system predominates.
1) Sympathetic
2) Parasympathetic
What does disruption of the sympathetic pathway lead to?
Miosis
What happens to the dilator pupillae during disruption in the sympathetic pathway?
Loses tone
What is the result of the dilator pupillae muscle losing tone?
There is no counteracting pull against the sphincter muscle, leading to a smaller pupil
Which abnormality is characterisitic of sympathetic pathway disruption?
Anisocoria
What is anisocoria?
Difference in pupil size