Renaissance Art
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:13 AM on 11/29/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
Renaissance Art
2
New cards
What was the Renaissance?
- Began around 1350 in Italy
- French word that means "rebirth."
- A revival of classical forms originally developed by ancient Greeks and Romans; concerned with secular life—interest in humanism and assertion of the importance of the individual (Humanists).
- French word that means "rebirth."
- A revival of classical forms originally developed by ancient Greeks and Romans; concerned with secular life—interest in humanism and assertion of the importance of the individual (Humanists).
3
New cards
The top four Breakthroughs in art skills during the Renaissance:
- Oil on Canvas
- Perspective
- Chiaroscuro
- Pyramid Configuration
- Perspective
- Chiaroscuro
- Pyramid Configuration
4
New cards
New Techniques
1. Realism & Expression
2. Perspective
3. Classicism
4. Emphasis on Individualism
5. Geometrical Arrangement of Figures
6. Light & Shadowing/Softening Edges
2. Perspective
3. Classicism
4. Emphasis on Individualism
5. Geometrical Arrangement of Figures
6. Light & Shadowing/Softening Edges
5
New cards
1. Realism & Expression
i) Showing scenes as they actually appear
ii) Expression is different depending on the individual and the scene
Left: 'Christ Pantocrator', Byzantine Mosaic (6th century)
Right: 'Christ Blessing' by Antonello da Messina (1465)
ii) Expression is different depending on the individual and the scene
Left: 'Christ Pantocrator', Byzantine Mosaic (6th century)
Right: 'Christ Blessing' by Antonello da Messina (1465)

6
New cards
2. Perspective
i) A graphic system that creates the illusion of depth and volume on two-dimensional surfaces
Example: 'The Trinity' by Masaccio (1427)
Example: 'The Trinity' by Masaccio (1427)
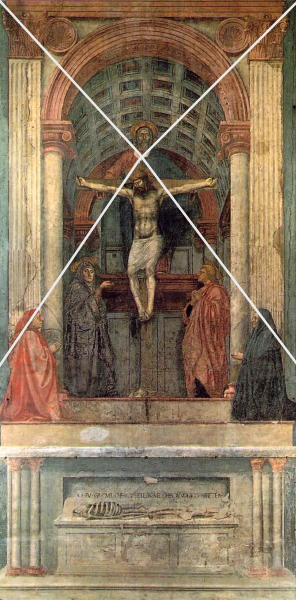
7
New cards
3. Classicism
i) Greek and Roman influence where perfect proportion is the ideal
ii) Secularism: Without religious influence
Humanism: Emphasizes reason and human fulfillment
Example: Venus de' Medici/The Classical Pose
ii) Secularism: Without religious influence
Humanism: Emphasizes reason and human fulfillment
Example: Venus de' Medici/The Classical Pose

8
New cards
4. Emphasis on Individualism
i) Highlighting specific characteristics to show how one subject is unique from another
Painting: '~~The~~ Duke & Duchess of Urbino' by Piero della Francesca (1465-1466)
Painting: '~~The~~ Duke & Duchess of Urbino' by Piero della Francesca (1465-1466)
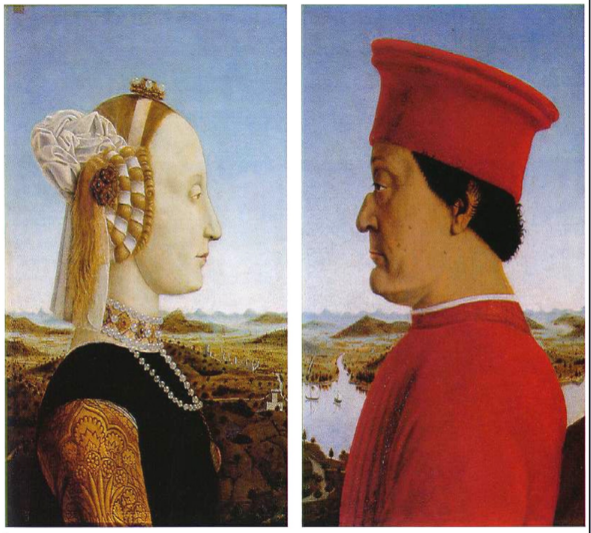
9
New cards
5. Geometrical Arrangement of Figures
i) The arrangement of figures to form geometric shapes
Painting: 'The Dreyfus Madonna with the Pomegranate' by Leonardo da Vinci (1469)
Painting: 'The Dreyfus Madonna with the Pomegranate' by Leonardo da Vinci (1469)
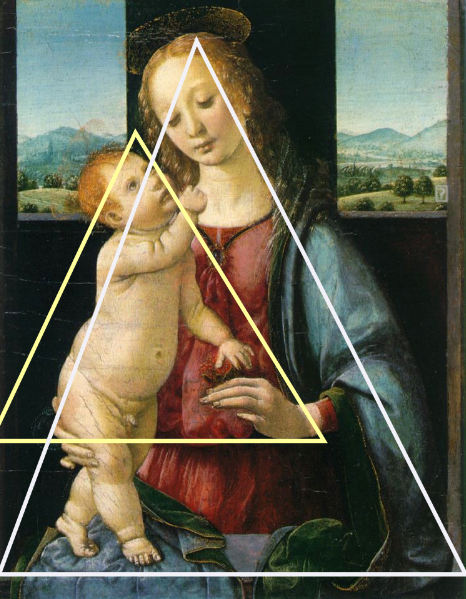
10
New cards
6. Light & Shadowing/Softening Edges
i) Chiaroscuro: The use of extreme contrast between light and dark to create a dramatic effect
ii) Sfumato: The blurring or softening of sharp outlines by gradually blending one tone into another
Painting: 'Ginevra de' Benci' by Leonardo da Vinci (1474-1478)
ii) Sfumato: The blurring or softening of sharp outlines by gradually blending one tone into another
Painting: 'Ginevra de' Benci' by Leonardo da Vinci (1474-1478)
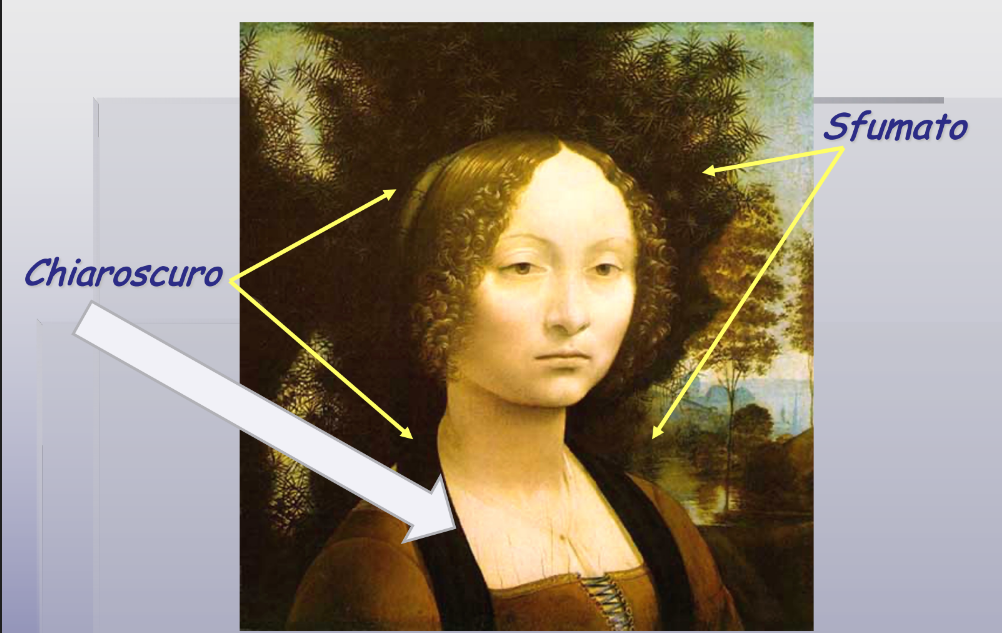

11
New cards
Early Renaissance Artists
1. Masaccio (1401-1428)
2. Donatello (1386-1466)
3. Sandro Botticelli (1445-1510)
4. Leonardo Da Vinci (1452-1519)
5. Raphael Sanzio (1483-1520)
6. Michelangelo (1475-1564)
2. Donatello (1386-1466)
3. Sandro Botticelli (1445-1510)
4. Leonardo Da Vinci (1452-1519)
5. Raphael Sanzio (1483-1520)
6. Michelangelo (1475-1564)
12
New cards
Masaccio (1401-1428)
- His frescoes are the earliest monuments of Humanism
- One of the first to use perspective
- All of his works are religious in nature—altarpieces or church frescoes
Painting: Trinity (1425-1428)
- One of the first to use perspective
- All of his works are religious in nature—altarpieces or church frescoes
Painting: Trinity (1425-1428)
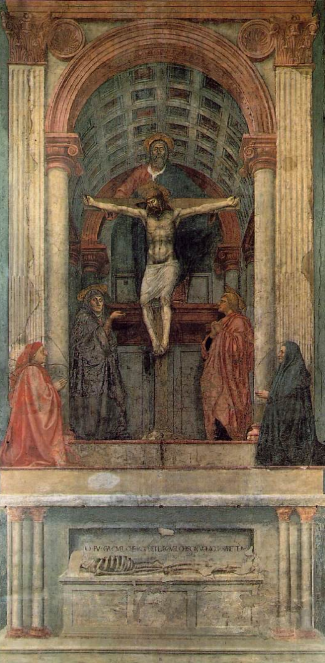
13
New cards
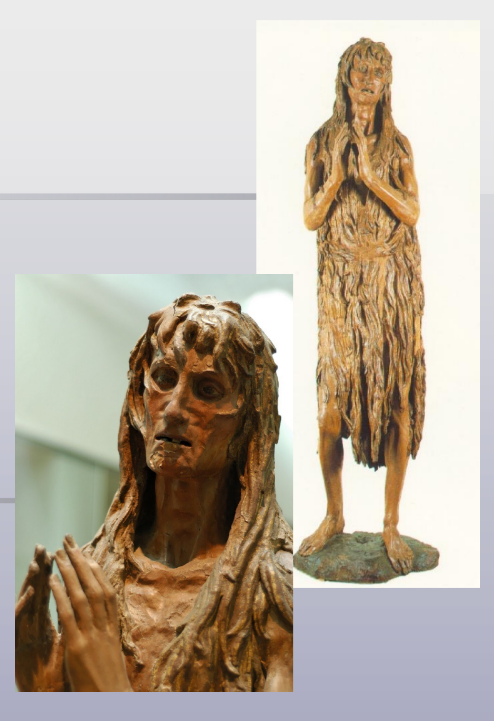

Donatello (1386-1466)
- Recaptured the central discovery of Classical sculpture
- Contrapossto
- Inspired by ancient visual examples
Paintings:
Mary Magdalene, c.1453- 1455, Wood
- Emphasizes her physical and mental anguish and also her strength and determination
- Recognized for the astonishing realism
David, circa 1435-1440, Bronze
- David is shown standing and resting his foot resting on the severed head of Goliath.
- Victorious attitude
- Contrapossto
- Inspired by ancient visual examples
Paintings:
Mary Magdalene, c.1453- 1455, Wood
- Emphasizes her physical and mental anguish and also her strength and determination
- Recognized for the astonishing realism
David, circa 1435-1440, Bronze
- David is shown standing and resting his foot resting on the severed head of Goliath.
- Victorious attitude

14
New cards
Sandro Botticelli (1445-1510)
- Decorative linear style
- Influence of Byzantine Art
- Biblical Subject Matter
Paintings:
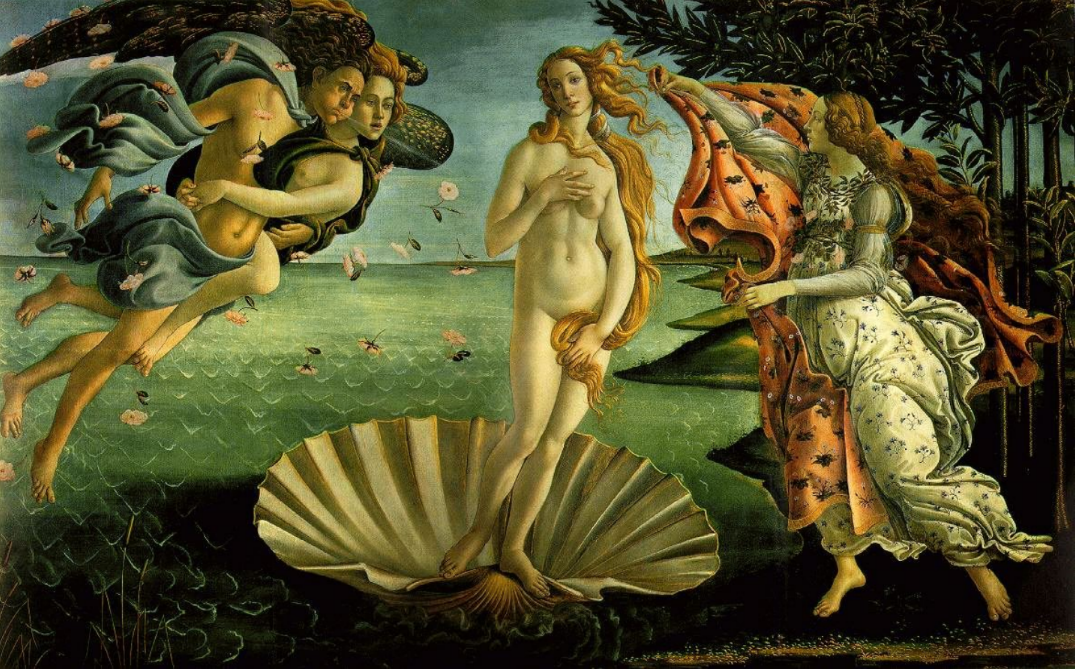
The Birth of Venus c. 1485
- Symbol of the coming spring
- Her depiction as a nude is noteworthy in itself, given because during Renaissance period rarely were nudes ever painted mostly themes of Christianity
- Influence of Byzantine Art
- Biblical Subject Matter
Paintings:
The Birth of Venus c. 1485
- Symbol of the coming spring
- Her depiction as a nude is noteworthy in itself, given because during Renaissance period rarely were nudes ever painted mostly themes of Christianity

15
New cards
Leonardo Da Vinci (1452-1519)
- A scientist, inventor, and an artist
- Considered one of the greatest painters of the Italian Renaissance
Paintings:
Mona Lisa, 1506
The Last Supper, 1498, Fresco
- Disciples are all displaying very human, identifiable emotions
- Every single element of the painting directs one's attention straight to the midpoint of the composition, Christ's head.
- Considered one of the greatest painters of the Italian Renaissance
Paintings:
Mona Lisa, 1506
The Last Supper, 1498, Fresco
- Disciples are all displaying very human, identifiable emotions
- Every single element of the painting directs one's attention straight to the midpoint of the composition, Christ's head.

16
New cards
Raphael Sanzio (1483-1520)
- Expressed all qualities of High Renaissance art and the use of light and shadow
Paintings:
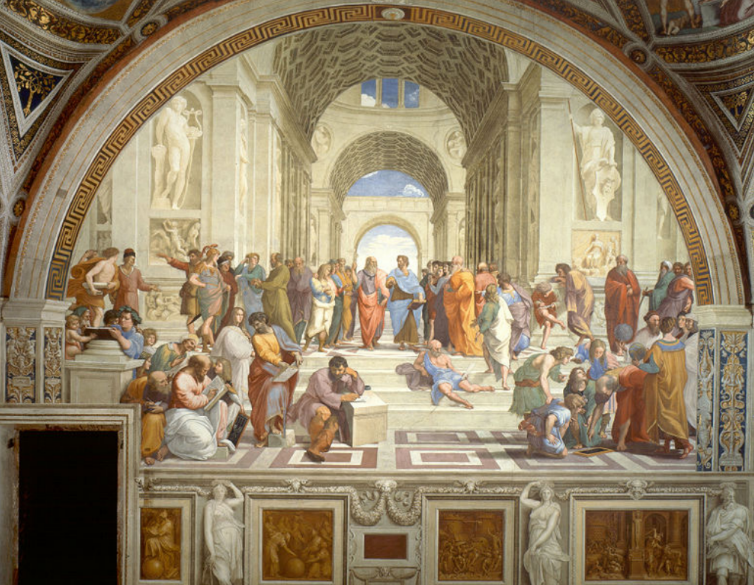
The School of Athens, 1511
- Subject matter is classical
- Painting depicts philosophers from the ancient world, such as Plato, Aristotle and Socrates assembled in the center
- Figures have idealized bodies, graceful gestures and a beautiful spacious environment
Paintings:
The School of Athens, 1511
- Subject matter is classical
- Painting depicts philosophers from the ancient world, such as Plato, Aristotle and Socrates assembled in the center
- Figures have idealized bodies, graceful gestures and a beautiful spacious environment

17
New cards
Michelangelo (1475-1564)
- Architect, sculptor, painter, poet and engineer
- Carved his sculptures from one block
- Pieta means pity
- Pyramid configuration
Examples:
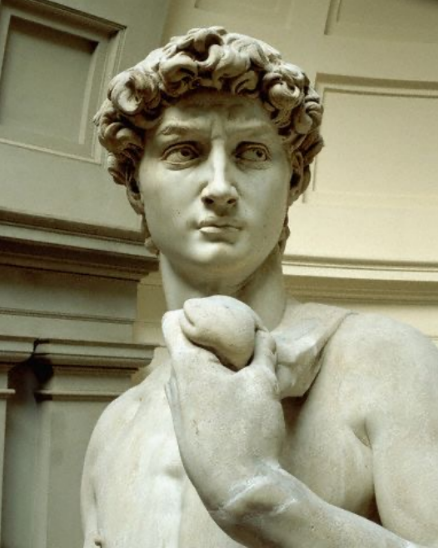
David, marble, 1501-1504
- "Triumphant David" in that he shows him after he has already killed Goliath and his foot rests upon the giant's severed head.
- Contrapposto pose
- Carved his sculptures from one block
- Pieta means pity
- Pyramid configuration
Examples:
David, marble, 1501-1504
- "Triumphant David" in that he shows him after he has already killed Goliath and his foot rests upon the giant's severed head.
- Contrapposto pose

18
New cards
Renaissance Portraits with a Modern Twist
Alan Macdonald (b. 1962)
- His portraits are in the Renaissance style however, emphasize a sense of consumerism (the void in our lives we are trying to fill on a superficial level)
- His portraits are in the Renaissance style however, emphasize a sense of consumerism (the void in our lives we are trying to fill on a superficial level)
