MCAT Biochemistry - Lipid Structure and Function
1/54
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Lipids
characterized by insolubility in water and solubility in nonpolar organic solvents; serving vital structural, signaling, and energy storage roles
amphipathic
molecule with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
Phospholipids
a phosphate and alcohol that comprise the polar head group, joined to hydrophobic fatty acid tail(s) by phosphodiester linkages; further classified according to the backbone on which the molecule is built
glycerol
three-carbon alcohol; forms phosphoglycerides or glycerophospholipids
saturated fatty acid
have only single bonds; have greater van der Waals forces and a more stable overall structure; form solids at room temperature
ex. animal fat, butter
unsaturated fatty acid
includes one or more double bonds; introduces kinks into the fatty acid chain; tend to be liquids at room temperature; make up more fluid regions of the phospholipid bilayer
ex. plant oils
Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides)
contain a glycerol backbone bonded by ester linkages to two fatty acids and by a phosphodiester linkage to a highly polar head group (can be positively, negatively, or neutrally charged)
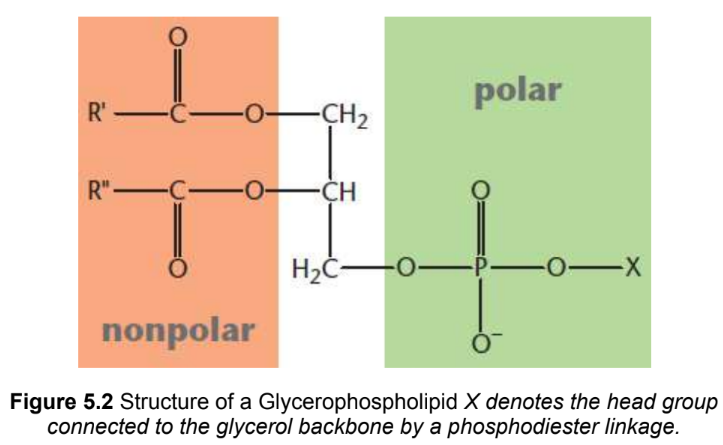
phosphatidylcholine
glycerophospholipid with a choline head group
phosphatidylethanolamine
glycerophospholipid with an ethanolamine head group
Sphingolipids
have a sphingosine or sphingoid backbone; long-chain, nonpolar fatty acid tails and polar head groups, many but not all are phospholipids
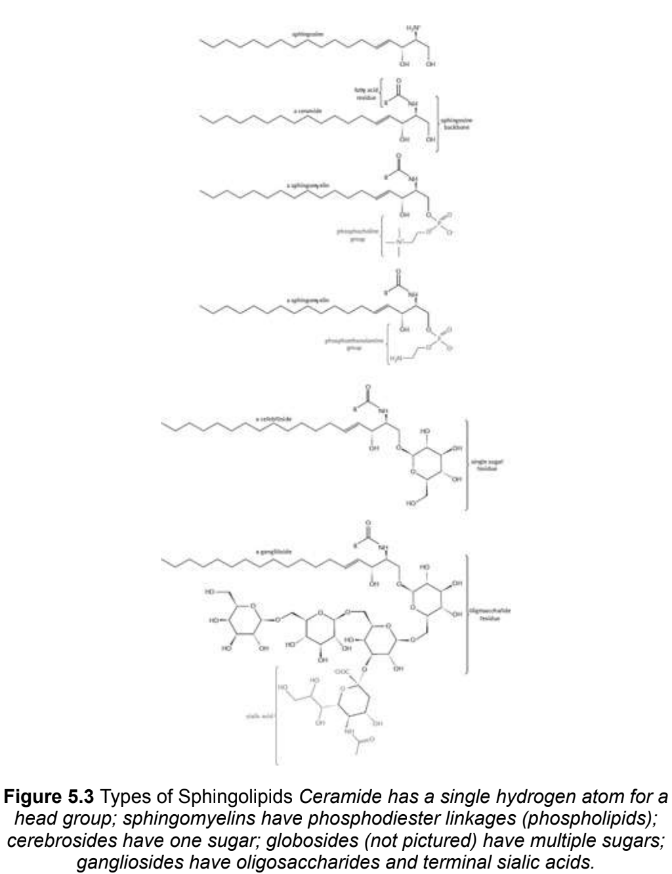
glycolipid
any lipid linked to a sugar
ceramide
the simplest sphingolipid is ceramide; has a single hydrogen atom as its head group
Sphingomyelins (sphingophospholipids)
also phospholipids; either phosphocholine or phosphoethanolamine as a head group; no net charge; major components in the plasma membranes of cells producing myelin
glycosphingolipids
Sphingolipids with head groups composed of sugars bonded by glycosidic linkages; found mainly on the outer surface of the plasma membrane
Cerebrosides
glycosphingolipids with single sugar
globosides
glycosphingolipids with two or more sugar; neutral glycolipids, no charge at normal pH
Gangliosides
glycolipids that have polar head groups composed of oligosaccharides with one or more N-acetylneuraminic acid molecules at the terminus and a negative charge; play a major role in cell interaction, recognition, and signal transduction
N-acetylneuraminic acid (NANA; sialic acid)
negatively charged at physiological pH
Waxes
esters of long-chain fatty acids with long-chain alcohols; pliable solids at room temperature; protection for both plants (surface coating to prevent excessive evaporation and to protect against parasites) and animals (prevent dehydration, as a water-repellant to keep skin and feathers dry, and as lubricant).

Terpenes
a class of lipids built from isoprene (C5H8) moieties and share a common structural pattern with carbons grouped in multiples of five: a single terpene unit contains two isoprene units; the metabolic precursors to steroids and other lipid signaling molecules; produced mainly by plants and also by some insects; generally strongly scented
ex. turpentine, a derivative of resin
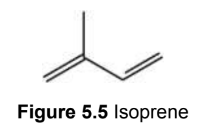
Monoterpenes (C10H16)
contain two isoprene units
ex. essential oils and turpentine
Sesquiterpenes
contain three isoprene units
diterpenes
contain four isopreneex. vitamin A
Triterpenes
six isoprene units, can be converted to cholesterol and various steroids
tetraterpenes
eight isoprene units
ex. Carotenoids, like β-carotene and lutein
polyterpene
isoprene chains between 1000 and 5000 units long
ex. natural rubber
Terpenoids (isoprenoids)
derivatives of terpenes that have undergone oxygenation or rearrangement of the carbon skeleton; share similar characteristics with terpenes in terms of both biological precursor function and aromatic properties
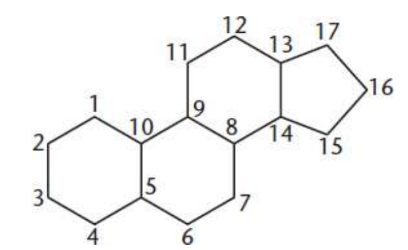
steroids
metabolic derivatives of terpenes; four cycloalkane rings fused together: three cyclohexane and one cyclopentane; functionality is determined by the oxidation status of these rings, as well as the functional groups they carry
Steroid hormones
steroids that act as hormones, meaning that they are secreted by endocrine glands into the bloodstream and then travel on protein carriers to distant sites, where they can bind to specific high-affinity receptors and alter gene expression levels
ex. testosterone, estrogens, cortisol, aldosterone
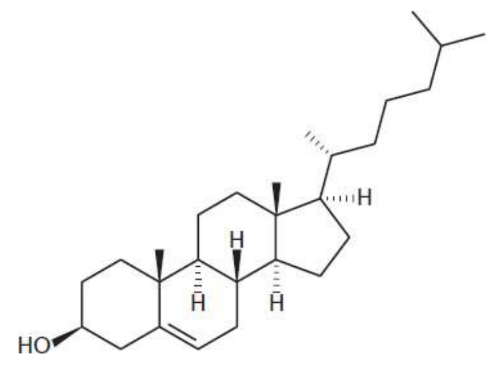
Cholesterol
is a steroid of primary importance
major component of the phospholipid bilayer responsible for mediating membrane fluidity; amphipathic molecule containing both hydrophilic and hydrophobic components; At low temperatures, it keeps the cell membrane from solidifying; at high temperatures, it holds the membrane intact and prevents it from becoming too permeable
precursor to many important molecules, including steroid hormones, bile acids, and vitamin D
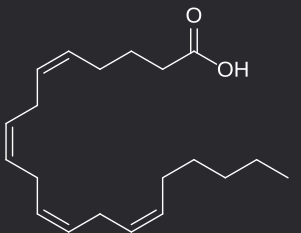
Prostaglandins
20-carbon molecules are unsaturated carboxylic acids derived from arachidonic acid and contain one five-carbon ring; paracrine or autocrine signaling molecules; to regulate the synthesis of cAMP
arachidonic acid
polyunsaturated omega−6 fatty acid; precursor in the formation of prostaglandins
vitamin
essential nutrient that cannot be adequately synthesized by the body and therefore must be consumed in the diet; divided into water-soluble and lipid-soluble
Vitamin A (carotene)
unsaturated hydrocarbon that is important in vision, growth and development, and immune function
retinal
a component of the light-sensing molecular system in the human eye; most
significant metabolite, the aldehyde form of vitamin A
Retinol
the storage, alcohol form of vitamin A, ingredient in skin-care products used to reduce wrinkles and other effects of skin aging
retinoic acid
carboxylic acid form of vitamin A; a hormone that regulates gene expression during epithelial development
Vitamin D (cholecalciferol)
can be consumed or formed in a UV light–driven reaction in the skin
calcitriol
the biologically active form of vitamin D; converted from cholecalciferol in liver and kidneys; increases calcium and phosphate uptake in the intestines, which promotes bone production
rickets
vitamin D defienciency; a condition seen in children characterized by underdeveloped, curved long bones as well as impeded growth
Vitamin E
a group of closely related lipids called tocopherols and tocotrienols; characterized by a substituted aromatic ring with a long isoprenoid side chain; hydrophobic
Tocopherols
biological antioxidants; aromatic ring reacts with free radicals, destroying them.; prevents oxidative damage, an important contributor to the development of cancer and aging
Vitamin K
actually a group of compounds, including phylloquinone (K1) and the menaquinones (K2); vital to the posttranslational modifications required to form prothrombin, an important clotting factor; aromatic ring of vitamin K undergoes a cycle of oxidation and reduction during the formation of prothrombin; also required to introduce calcium-binding sites on several calcium-dependent proteins
warfarin
anticoagulant; blocks the recycling of vitamin K, causing a deficiency or lowering of the active amount
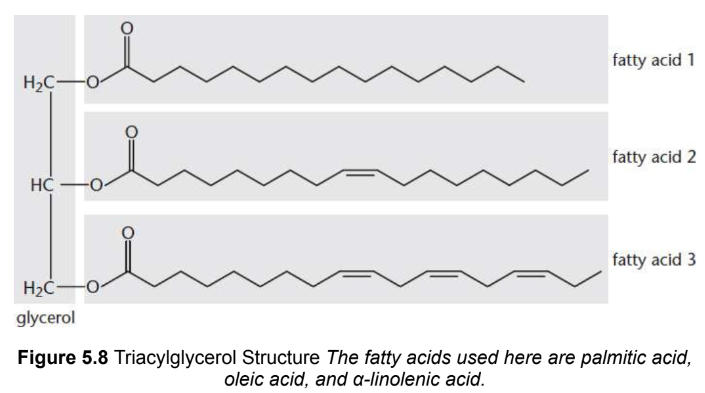
Triacylglycerols (triglycerides)
three fatty acids bonded by ester linkages to glycerol; rare for all three fatty acids to be the same; nonpolar and hydrophobic
animals store in apipocytes; plants store as oil
adipocytes
Special cells in animals store large amounts of fat and are found primarily under the skin, around mammary glands, and in the abdominal cavity
Saponification
ester hydrolysis of triacylglycerols using a strong base, i.e. lye; basic cleavage of the fatty acid, leaving the sodium salt of the fatty acid and glycerol
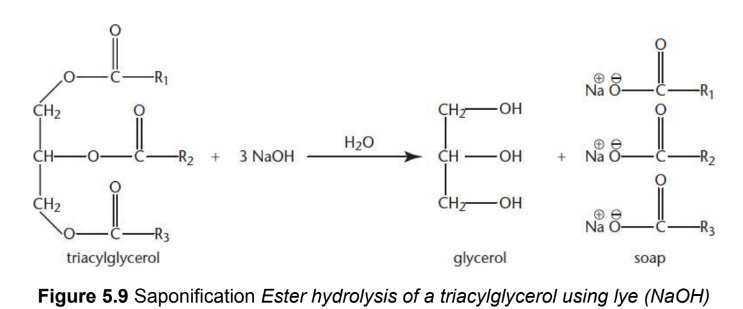
lye
common name for sodium or potassium hydroxide
surfactant
lowers the surface tension at the surface of a liquid, serving as a detergent or emulsifier
colloid
the two phases appear to combine into a single phase
micelles
tiny aggregates of soap with the hydrophobic tails turned inward and the hydrophilic heads turned outward, thereby shielding the hydrophobic lipid tails and allowing for overall solvation

adipocere
natural saponification in corpses as triacylglycerols are hydrolyzed by naturally occurring bases
lecithins
complicated lipids, generic term to designate any group of yellow-brownish fatty substances occurring in animal and plant tissues which are amphiphilic