n471 final
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
patient protection and affordable care act
reduce uninsured, increase access to care, help for preexisting conditions, changes with governmental changes
value based purchasing
decreases costs, work with vendors
accountable care organizations
group of providers working together to take care of patient groups, goal of seamless, quality care, coordination of care
bundled payments
payment model that combines the cost of multiple services into a single payment — paid per diagnosis and all associated costs
medical home
team-like process for improved access to services, quality, and outcomes of patient care, reduce hospitalizations and high-cost medical services
cost containment
(hospital inpatient care)
focus on effective, efficient and quality services
equals out in revenue
everyone is responsible
unit manager considers each unit’s budget
hospital budgeting
expenses and income for a certain time period
must be as accurate as possible
fixed expenses — mortgages, salaries
variable expenses — payroll of hourly employees, costs of supplies
controlled expenses — how many people work during a shift
uncontrollable expenses — emergencies, needing more staff/time, specific supplies needed to care for patients
budgeting steps
assess — what are the needs
diagnosis — what needs are priority
plan — set time/goals
implementation — continue to assess for change
evaluation — review, add, remove
budget types
personnel - largest expenditure
operating - expenses that change (electricity, repairs, maintenance, supplies)
capital - buildings, major equipment
medicare
federally funded program for seniors over age 65 or disabled recipient pays into insurance plan; several plans of MC cover a variety of services
medicaid
federal/state plan to assist indigent population, disabled, long term care
prospective payment system
regulations as to what providers/healthcare agencies can charge based on a diagnosis rather than patient specific
managed care organization
health program that looks at efficiency, access and cost, PCP as gatekeeper
budgeting RN opportunities
staff nursing
managers/leaders
quality department
technology department
fiscal budget
supply allocation/distribution buyer/manager
vendor representative
insurance nurse
interprofessional communication
communication with
patients, families, colleagues, leadership
necessary for continuity and productivity
organizational communication
more complex than interpersonal
more communication channels
more individuals
more information
new technology
communication process
internal and external climate
effective communication requires sender to validate what receivers see/hear
differences in gender, power, status can affect organization and unit org
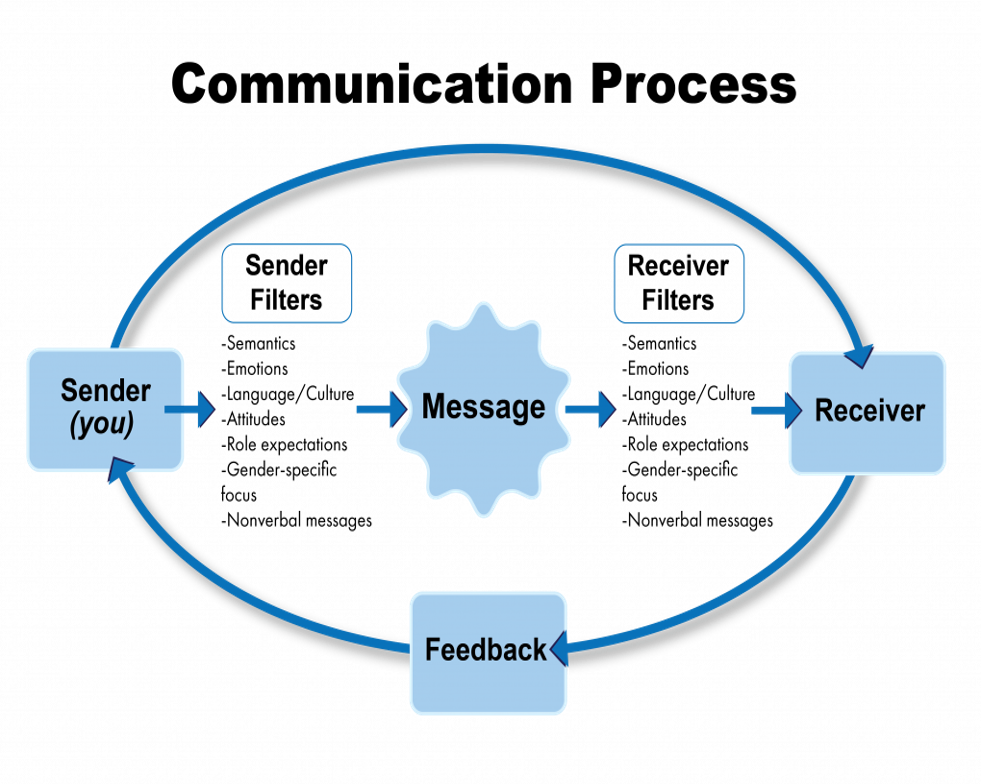
internal climate
includes values, feelings, stress levels of both sender and receiver
external climate
status, power, authority of sender/receiver, timing and organizational climate
assess org communication
formal vs. informal
who communicates with who
what is the pace of communication
understand structure & who’s affected by decisions
use clear, simple, precise communication
seek feedback on whether communication received is accurate
use multiple modes of communication
don’t overwhelm people with unnecessary info
upward communication
manager makes needs/wants known to higher level
downward communication
manager communicates info to colleagues under them
horizontal communication
manager communicates with others on same hierarchical level
diagonal communication
manager interacts with other managers or physicians on different hierarchical levels
grapevine communication
info flows quickly and haphazardly among people at levels
written communication
use when documentation is needed
can be formal or informal
tone can be mistaken
face to face communication
formal or informal
depends on intent, sender/receiver needs
watch body language
telephone/text
rapid communication, formal or informal
assertive verbal
direct, honest, does not infringe on rights
passive verbal
person remains silent about issue even though they have strong feelings; “suffer in silence”
aggressive verbal
direct, threatening, condescending, infringes on rights
passive aggressive verbal
an aggressive message presented in a passive way (incongruent message)
SBAR
standardized professional communication to provide quality patient care and reduce errors
situation, background, assessment, response
listening skills
understanding own emotional intelligence — values, beliefs, past experiences, biases, limits, emotional awareness and control
balance the needs around you
understand conversation coming in, interpret meaning, restate misunderstandings
group - forming
way of establishing behaviors in groups
who are leaders and dependents
what behaviors are among the group
identify rules, tasks, responsibilities
group - storming
resistance is normal when forming groups
see what influences come within the group, how they resolve, or rebel
how are demands of tasks resolved
group - norming
group starts to develop more efficiently, conflict resolves, cooperation develops
group - performing
group completes tasks, members perform in their roles, problems are resolved
leadership and emotional intelligence
know self first before leading others
know the team
know the unit culture
see the bigger picture
communication
live by virtues/values
motivation
process of inducing, inspiring, and energizing people to work willingly with zeal, initiative, confidence, satisfaction and an integrated manner to achieve desired goals
moral boosting activity
intrinsic motivation
comes from within a person
often influenced by upbringing, family structure, culture, values, beliefs are formed at a young age
can be developed and change over time
extrinsic motivation
comes from outside the person
financial, emotional, self, personal, relational factors
can develop and change over time
team building
encourages trust
goal attainment
cooperation
see other views
improves efficiency
resolves conflict
role model desired behaviors
listen
take action about concerns
uphold values when challenges arise
stay positive
encourage others
demonstrate care at the bedside
accountability
remember our purpose
don’t make excuses
synergy
the cooperative working together of 2+ people or orgs, when their combined effect is greater than sum of their individual efforts
creating synergism
hire the right people
stay positive when challenged
go the extra mile
share common interests, values
compliment skills
stronger as a group
empower group members
be committed
worker engagement
active in their work
increases performance/outcomes
more than “just a job”
employees love what they do
committed
balancing work life
make decisions
creative thinking/innovation
know job expectations
positive reinforcement
validation of work effort
be specific
recognition of extra effort
hire for the fit, not just to fill a vacancy
show trust in decision
let employees “create” at work
external rewards are not always positive
give praise during huddles, unit or personnel specific
encourage one another
leaders can motivate by
set clear expectations
be fair/consistent
be strong in decision making
create a team atmosphere
rave individual uniqueness
encourage diversity, equity, inclusion
provide growth opportunities
give credit for ideas
communicate org needs
don’t micromanage
create trust/being part of team
be a positive role model
listen intently
take self care seriously
delegation
transferring authority and responsibility to perform a specific activity from their own practice, to an individual qualified to perform that task but retains accountability for the task
delegation benefits
allows time to focus initiatives
increases flexibility
gain trust in staff performance
earn respect from staff
improves communication
achieves goals in cooperative group effort
balances workload and time
decreases stress
increased productivity
more ideas/creativity/solutions
better use of human resources
builds on leadership skills
delegation staff benefits
improves the level of trust and communication
achieves goals that require cooperative group effort
personal and professional development
increased job satisfaction
know-how, experience
increased productivity
delegation org benefits
saves money for the organization because it makes the best use of organization resources since it increases overall productivity and efficiency
ensures tasks are assigned to the right person at the right level
more motivated staff and improved retention
effective delegation
identify the necessary skills/education level to complete task
NPA — determines RNs’ scope in each state
RN must understand scope of practice of others on nursing team
different rules apply in each state and organization for delegation to unlicensed personnel
nurse practice act
state’s definition of delegation
items that can’t be (routinely) delegated
guidelines for RNs about tasks that can be delegated
description of professional nursing practice
description of RN, LPN/LVN, UAP scope
degree of supervision required for task
guidelines for lowering delegation risks
warnings about inappropriate delegate
if there is a restricted use of the word “nurse” to licensed staff
RNs in NYS
RNs are independent practitioners and don’t require supervision when providing care
prepared to assess, diagnose, plan, implement, evaluate
LPN scope
dependent practitioners that must practice under supervision of RN or other licensed provider
RN needs to be on premises or immediately available by telephone when professional services are rendered
degree of supervision should be appropriate to the circumstances
home care → RN available by phone
LTC → RN on site at least 8 hours per day and available by phone at other times
UAP scope
unlicensed healthcare provider permitted to perform in a limited manner some activities that fall within nursing scope
supervising RN still responsible for assessment, evaluation, judgment
UAP functions
non nursing: housekeeping, clerical, transportation, dietary
health related:
doesn’t require professional judgment/critical thinking and can be completed using standard procedure
NOT within legally protected scope
must have demonstrated competency
scope exceptions
permits nursing activities/tasks to be performed by non-nurses under very specific conditions
family members
nursing students
OMH/OMRDD attendants
caregivers for self-directing individuals in special state-authorized home care programs
delegation in NYS
Rule of Board of Regents states
delegating professional responsibilities to a person when the license delegating such responsibilities knows/has reason to know that such person is not qualified = unprofessional conduct
crime to permit unauthorized practice
class E felony
violations reportable to State Education Department, Office of Professions, State Attorney General
what can be delegated
LPNs/UAPs must be supervised by RN or other authorized licensed professional
RNs can delegate to RNs/LPNs
LPNs can delegate to LPNs
non-nursing tasks can be assigned to UAPs
RN must
be familiar with job descriptions
know competency level
have supervisory authority
delegation - potential for harm
the greater the potential for harm, the more necessary it may be to have a professional nurse render care
delegation - condition/stability
an UAP should be assigned no more than minimal health-related activities for unstable patients
delegation - complexity of task
activities involving complex psychomotor skills and requiring expert nursing assessment/judgment should only be performed by professional nurse
as required skills increase in complexity, greater consideration must be given to prior training and demonstrated competency
delegation - problem solving/innovation
adapting an activity and evaluating its outcome is professional nurse’s responsibility
delegation - unpredictability
when a patient’s response is unpredictable or unknown, it is advisable to delegate activity to RN/LPN
delegation - coordination/consistency
the nurse’s ability to plan, coordinate and evaluate a patient’s care is restricted when support personnel engage in most of direct patient contact
delegation - 1. define the task
complexity and components
what areas of authority or what resources must the person control to achieve expected results
what are the limits, boundaries, or parameters for each area of authority or resource to be used?
NEVER delegate: discipline, situation that involves confidentiality, controversy
delegation - 2. decide on delegate
match task to individual
who has requisite capabilities?
who is allowed to do the task legally and by organizational policy?
who is willing to accept responsibility?
delegation - 3. determine the task
clearly define expectations
describe the task, provide a reason for the task, inform about standard of evaluation and how often, identify constraints as well as risks, validate understanding by eliciting questions and providing feedback
delegation - 4. reach agreement
empower delegate
anticipate areas of negotiation, identify what you are prepared and able to provide
delegation - 5. monitor performance and provide feedback
reward accomplishment
mechanism for feedback and control that ensures tasks are carried out as agreed
rights of delegation
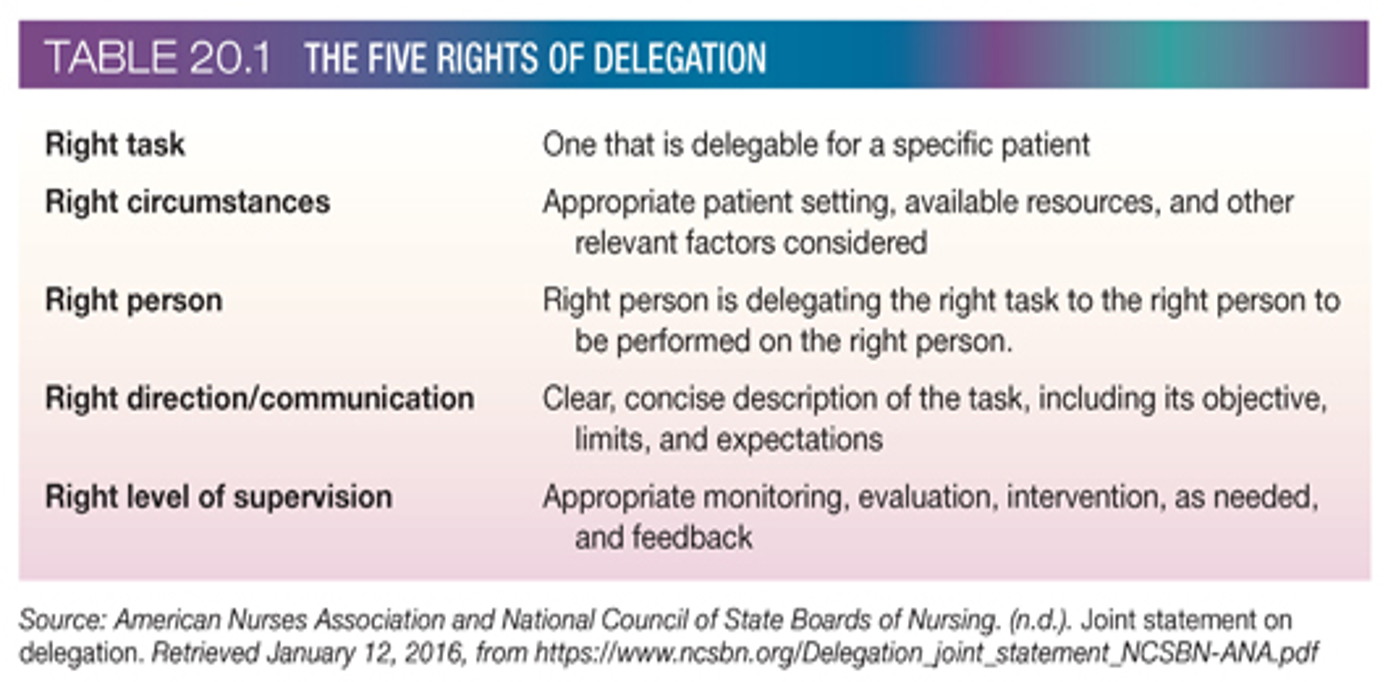
successful delegation
define task
select individual
assess ability and training needs
explain why
state required results
agree on schedule
support and communication
provide feedback on results
repeat process
effective delegation - plan ahead
delegate before you get overwhelmed
assess situation to identify tasks that can be delegated
effective delegation - select/empower
identify the right individuals for the task
be aware of job descriptions and allowed tasks per hospital
delegate authority and responsibility to complete the task
effective delegation - communicate goals
purpose of task, any limitations or qualifications imposed on task including a timeline, expectations for reporting
effective delegation - set deadlines
monitor progress
shows interest of delegator, provides review of progress and encourages ongoing communication
final responsibility belongs to delegator but delegate accepts responsibility for completing task appropriately and is accountable
effective delegation - be a role model
provide guidance
as a resource to delegate to identify alternate solutions
be willing to answer questions, clarify desired outcomes
reassuming task is a last resort as it fosters sense of failure and demotivates
effective delegation - evaluate
provide feedback including positive and negative
ask what you could have done differently to help
effective delegation - reward
reward successfully completed accomplishment
leaders are often measured by successes of those on their teams
can delegate to UAP
feeding w/o swallowing precautions, drinking, ambulating/turning, grooming, toileting
collecting vitals, I/O, glucometer (not in NYS)
apply clean dressings
perform oral suctioning/mouth care
taking EKGs
giving enemas
doing venipuncture
carrying out non-nursing functions
reporting to RN/LPN
cannot delegate to UAP
assessing, evaluating, problem solving
determining nursing dx
developing nursing plan of care
providing patient education or health counseling
performing sterile or invasive procedures
feeding through NG tube
admin O2
trach suctioning or resp care
admin meds
appropriate tasks to assign to UAP
non-invasive/nonsterile tx
collecting, reporting, documenting data (VS, height/weight, I/O, urine tests)
ambulation, positioning, turning, transfers
transportation of patient within facility
personal hygiene, elimination (vaginal irrigations and cleansing enemas)
feeding, cutting up food, placing of meal trays
socialization activities
activities of daily living
RN to LPN - can delegate
monitoring client findings as input to RN’s ongoing assessment
reinforcement of client teaching from standard care plan
routine dressing changes
tracheostomy care
suctioning
checking NG tube patency
admin of enteral feedings
ostomy care
insertion of urinary cath
med admin (excluding IVs)
RN to LPN - cannot delegate
assess, evaluate, problem solve
independently develop nursing care plan
admin chemo
admin direct IV push except saline/heparin flushes
admin IV fluid bolus for plasma volume
access any form of central line or venous chest or arm port line device (except in outpatient chronic hemodialysis)
triage, case management, mental health teaching
under delegation
“i like to have things done my way”
“my staff will resent the additional work”
“my staff expect me to be the problem solver and decision maker”
“i can do this better and quicker than my staff”
“i don’t have confidence in my staff”
“it’s easier to do it myself than organize, explain and monitor it”
over delegation
poor time management
unorganized
insecure in ability to do task
do not know laws/regulations
assignment too heavy
improper delegating
delegating at wrong time
to the wrong person
for the wrong reason
delegating tasks/responsibilities beyond capabilities of delegate
delegating w/o providing adequate information
resistance to delegation
current workload is overwhelming
believe they are incapable of performing task or lacks confidence
inherent resistance to authority
tasks are overdelegated in terms of specificity
performance appraisal
determines how well employee carries out duties
should encourage/motivate staff
objective manner
determines area for professional growth, strength, projects, committee involvement
how is employee working toward organizational goals
motivate through appraisal
have a positive outcome
have a standardized process
shows accountability
appraisal tool must accurately assess the performance
employee input
known standards
should be completed with direct supervisor
appraisal - accuracy/fairness
be objective
be aware of personal biases
seek other managers’ input as needed
gather and keep accurate data
obtain positive data about performance, growth, achievement
note areas of improvement
self appraisal needed
work toward goals
appraisal day
employee should know reason for meeting
choose a time not rushed and provide advanced notice
be ready to give unbiased appraisal
watch body language
begin positive, have employee give self-assessment
listen and give full attention, avoid distraction
be specific
set goals
agree/disagree on terms
peer review
provides feedback and growth opportunities
must orient staff to process
standard tools available
ongoing support, resources
how should the information be used
increase professionalism
performance appraisal components
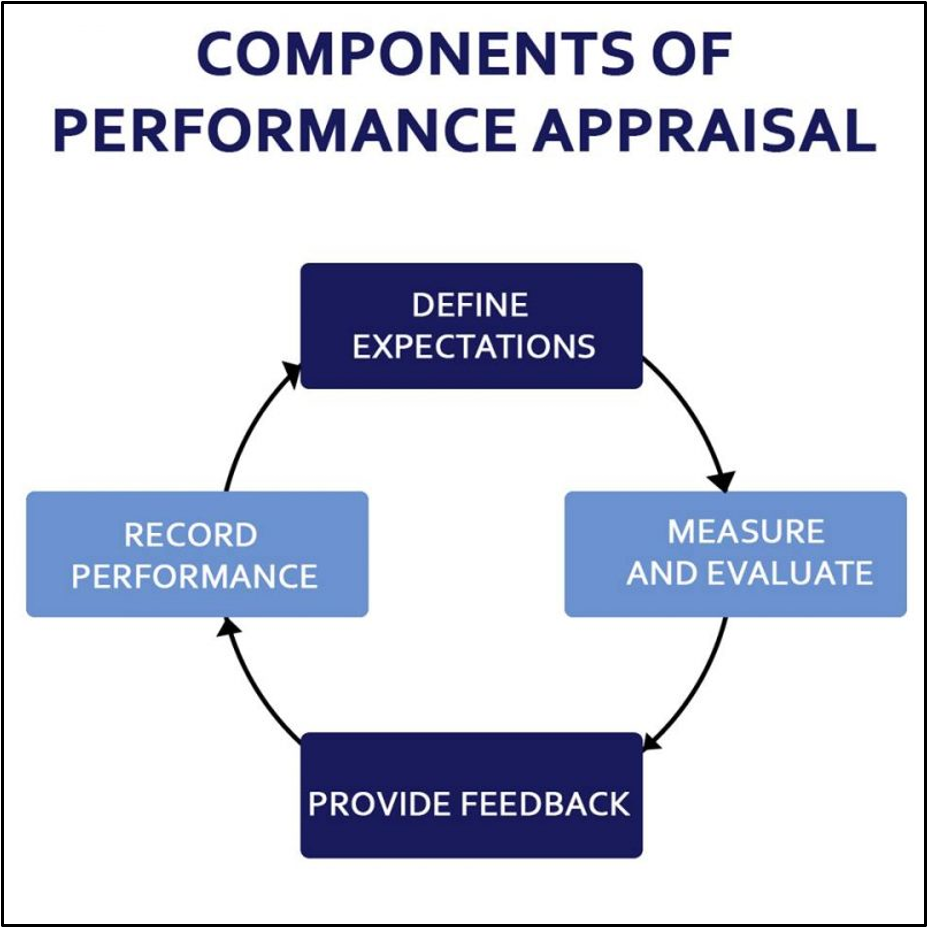
how to manage employee problems
understand personalities
communication is key
adequate employee training
regularly scheduled performance evaluations
be constructive vs. destructive
support mental health of overworked
employee understands expectations and manager needs them to develop skills/job performance
self discipline - values/beliefs, self worth, integrity, emotional intelligence
does employee fit in with the group, is there social pressure
mutual trust among colleagues, with management, with administration
McGregor’s Hot Stove Rules
forewarning
immediate consequences
consistency
impartiality