Biology module 1+2
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
foundations of biology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
eukaryotic cell structure and function (animal+plant) 10 terms
Nucleus= chromosomes that are wound up and enclosed in a nuclear envelope controls cell activity and make ribosomes
Plasma membrane= made from lipids and proteins controls the movement of things going in and out the cell
Mitochondria= double membrane, contains the enzymes for respiration and produces ATP for aerobic respiration
Ribosomes= very small organelle found in the cytoplasm or endo plasma reticular where proteins are made
Golgi apparatus = fluid filled membrane that packages and process proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles
Golgi vesicles= transports the proteins and lipids
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) = lots of ribosomes around it and processes the proteins made
Smooth endoplasmic rectum = synthesises and processes lipids
Cytoplasm = where most of the chemical reactions take place
Lysosome = contains digestive enzymes that break down waste materials in the cell
eukaryotic cell structure and function (plant only) 6terms
Chloroplast = where photosynthesis occurs and contains chlorophyl double membrane
Cell wall = provides structural support and protection; made of cellulose.
Vacuole = large sac that stores water, nutrients, helps maintain pressure inside the cell
Adaptations of eukaryotic cells
RBC:
Biconcave shape for increased SA and o2 diffusion
No nucleus so they can store more haemoglobin and bind more o2
small intestines + lungs
SI have microvilli that increase surface area Lungs have alveoli which increase surface area for gas exchange.
they also have a large blood supply through capillaries that are 1 cell thick
Storgage
fat cells have large lipids store
Energy requirements
Muscle cells have large amounts of mitochondria to carry out lots of respitation and ATP for areobic respiration in the joints
nerve cells are the same
Secretion
cells that secrete substances need a large golgi apperatuss need lots of ribosomes
Transport
active transport need carrier proteins and channel proteins and ribosomes
Prokaryotic cells
no membrane bound organelles
ribosomes are 70s
cell wall made of murine
flagella help its mobility
DNA in soiled strands and plasmids
may have capsules that secrete substances to protect it
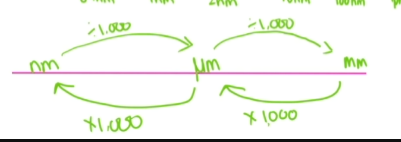
units and conversions

Microscopes
light microscope | transmission electron microscope | scanning electron microscope |
res 200nm | 0.2-0.5 nm (highest res) | 0.3-0.5 nm |
x1800 | x500,000 | x500,000 |
uses light to see the object in colour | beams of electrons pass thru it and is dispersed by the structures forming an image | thin layer of metal, electrons then bounce off it |
image 2d with limited depth | 2d image black and white | 3d image |
alive or dead | dead | dead |
formular for magnification and how to do graticule calc
magnification= size of image/ actual size (I AM)
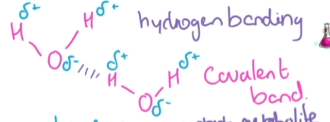
Bonding in molecules (water)
Hydrogen bonding and polar lots of energy needed to break the bonds

Water and its uses (6)
its polar = good solvent and can bond with other polar molecules
high latent heat of evaporation = helps cool down organisms
high specific heat capacity= helps regulate temperature making it a good habitat
cohesion= allows water to travel up stems and plants
surface tension= allows organisms to live on water
when it freezes ice has a lower density than liquid water, causing it to float and insulate aquatic life and provide habitat
monomers examples
amino acids → proteins
nucleotides → DNA
glucose → polysaccharide
Monosaccharides
monomers for carbohydrates
eg: glucose, fructose, galactose all with the formular C6H12O6
general formular is (CH2O)n
Alpha and beta glucose
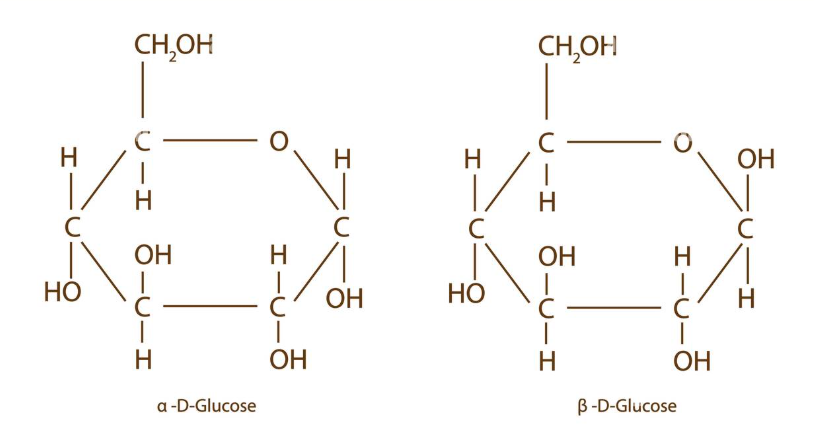
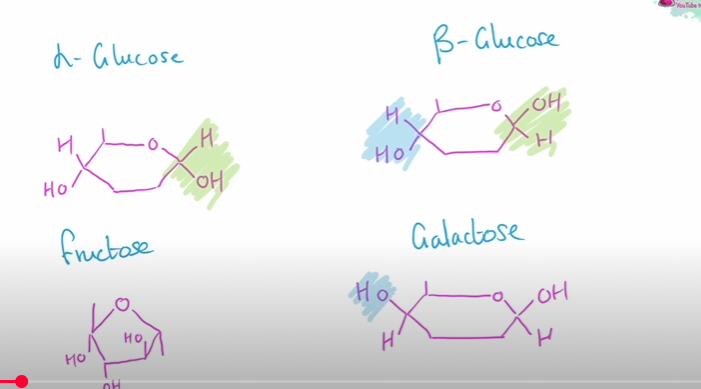

disaccharides and condensation reaction
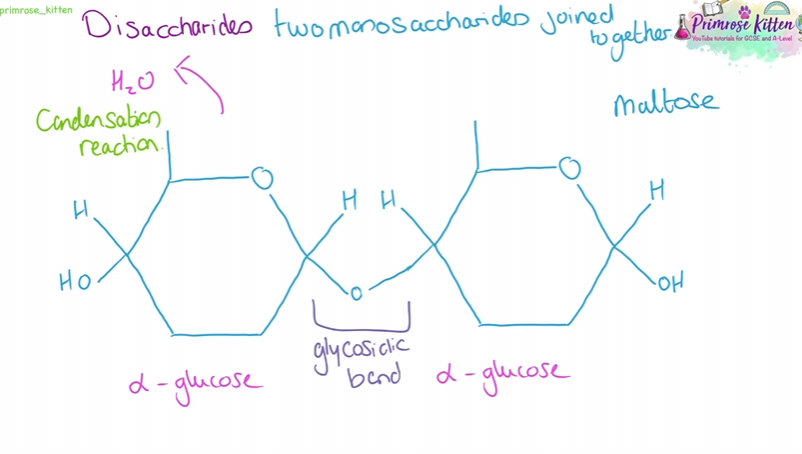

types of disaccharides
Maltose = 2 glucose monosaccharides
Sucrose= glucose and fructose
Lactose = glucose and galactose
polysaccharides definition
long chain of monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds in condensation reactions
alpha glucose and starch (plant only)
long chain of glucose
chains can be coiled into an alpha helix - compact
insoluble - makes it good for storage
branched - increases sa so enzymes HYDROLYSE quicker to provide glucose for respiration
Amylose is the straight chain (1,4 glycosidic bonds) amylopectin is the branches (1,4 + 1,6 glyco bonds)
alpha glucose and glycogen (liver +muscle cells)
long chains of a-glucose has more branches than starch
branched - increases sa so enzymes HYDROLYSE quicker to provide glucose for respiration
insoluble - makes it good for storage + no effect on osmosis
beta glucose and cellulose
long chains of cellulose
Straight, unbranched chains that are parallel to each other
have hydrogen bonds
found in the walls of plant cells
used for structure
Lipids
Insoluble in water
soluble in organic solvents (alcohol)
triglycerides 9FATS AND OILS)
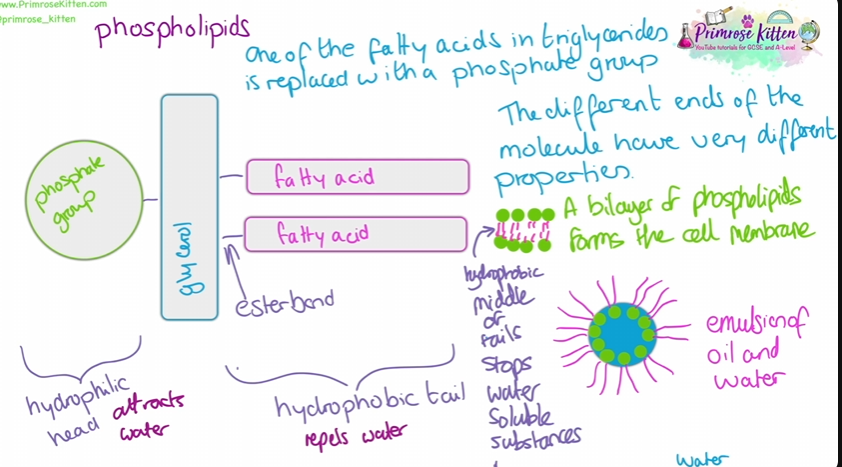
phospholipids
energy released twice as much as carbohydrates
waxy cuticles conserve water
insulation - like in sea animals
protection
Triglycerides


Phospholipids

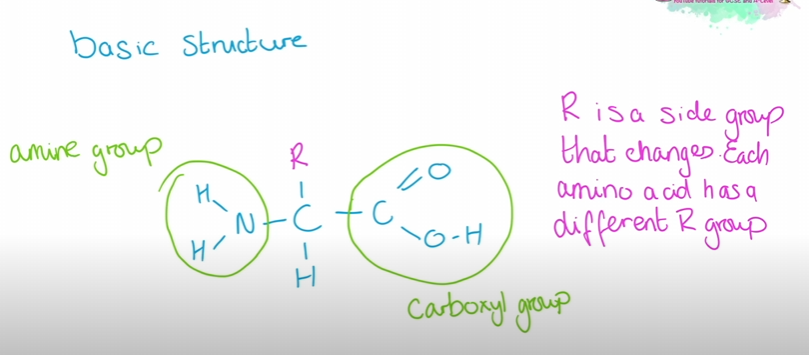
amino acids structure

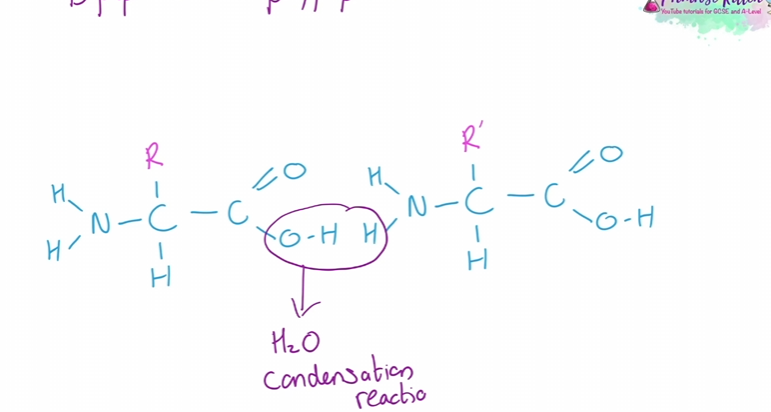
dipeptides and polypeptides
made from chains of amino acids
2 steps in making them
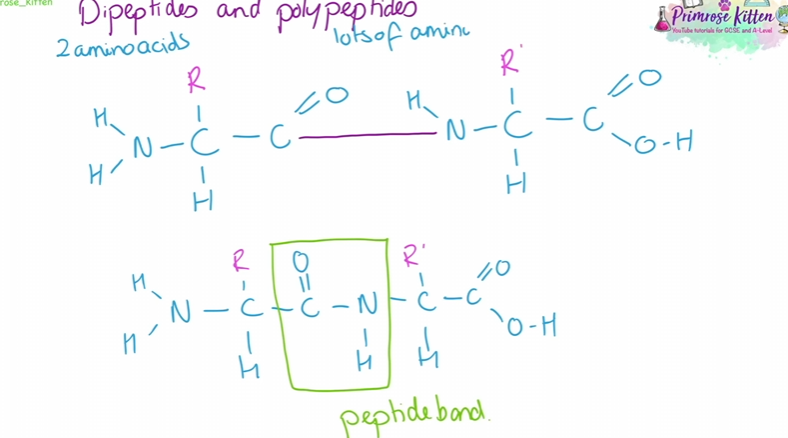
the roles of proteins
polypeptide chains can fold up to make proteins
examples of proteins
Enzymes- break down large molecules into smaller ones
structural proteins - long parallel peptides chains
Antibodies- immune response 2 short polypeptide chains highly variable
Transport proteins- channel proteins in cell membranes contains hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids
protein structure
Primary structure | the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. peptide bonds |
secondary structure | hydrogen bonds form between the polypeptide chains makes: alpha helix or beta pleated sheets |
tertiary structure | increased bonding leads to further bonding hydrogen bonding(weak) , disulphate bonding(strong), ionic bonding (between carboxyl + amino groups , broken by PH ) 3d shape |
quaternary structure | found in larger complex proteins that have MORE than 1 polypeptide chain eg globular and fibrous protiens’ |
globular and fibrous proteins
fibrous protein
are insoluble
used for structure
collagen(strong)
keratin (waterproof)
elastin (stretchy)
globular protein
used in enzymes and metabolic functions
spherical
soluble hydrophilic r groups face outwards
haemoglobin (haem prosthetic group)
insulin (hydrophilic r groups)
pepsin (lots of acidic r groups)
Nucleotides structure
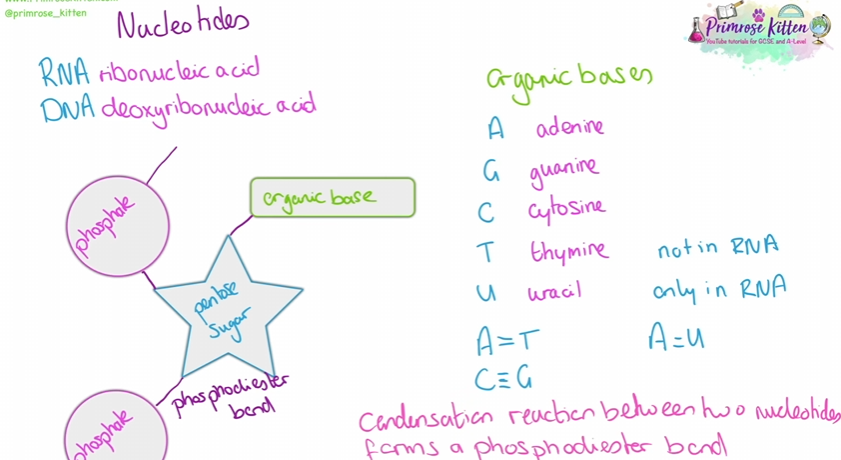
A and G are purines (contains 2 carbon rings) T and C are pyrimidines (contain 1 carbon ring)

RNA
uses RIBOSE not deoxyribose like DNA and uses uracil not thymine shorter and single stranded
3 types of RNA
mRNA (messenger RNA) codes the amino acids
rRNA (ribosomal RNA) translates the mRNA
tRNA(transfer RNA) carries amino acids to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
DNA replication
DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the 2 strands of DNA unwinding the double helix making 2 separate strands
Free nucleotides bind to their complementary bases
DNA polymerase joins the new nucleotides together creating the phosphodiester bonds
2 identical strands of DNA are formed semi-conservative
Transcription and mRNA
DNA helicase separates the hydrogen bonds and RNA polymerase works on a section of DNA
nucleotides in the nuclues pair with their complementary base on the template strand
coding and non coding DNA
gene : section of DNA that codes for functional RNA or polypeptide Locus: position of the gene with in the DNA
Allele: different versions of the same gene
Introns: bits of a gene that dosen’t code for anything
Exon: bits of a gene that do code for something
homologous chromosome: Matching pair that might contain different alleles
Triplet: 3 base pairs that code for an amino acid
Degenerate code: more than 1 triplet can code an amino acid
Non-overlapping: each base pair is only read once
Proteome: all the protein that a cell can make
ATP + ADP + AMP
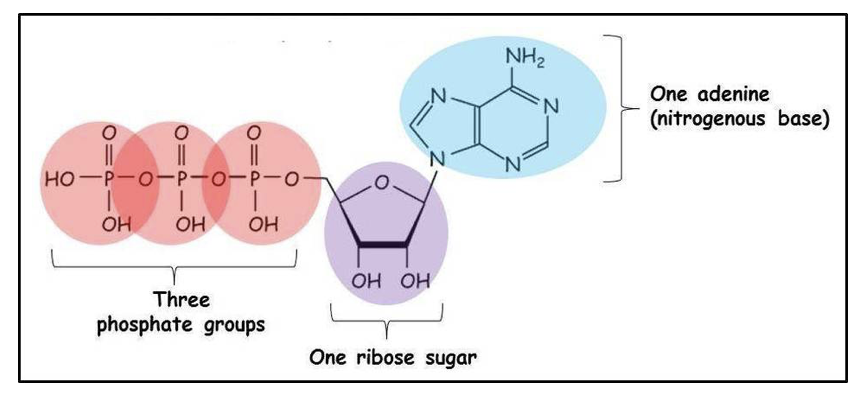
ADP: 2 phosphates and AMP: 1 phosphate
bonds between the phosphates are unstable and low activation energy so they are easily broken down for energy
APT + H20 → ADP + phosphate + energy
enzyme that breaks it down: ATP hydrolase
enzyme that forms it : ATP synthase
process in cells that require
metabolism
movement
active transport
secretion
Enzymes
are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reaction by lowering activation energy
they don’t get used up and are specific to the substate they work on can break down or build a molecule
lock and key - enzymes (old model)
enzyme with a tertiary structure has an active site that is specific to the substate that it wants to bind to. exact match
the substate is complementary to the enzyme creating an enzyme-substate complex that breaks it down
induced fit - enzymes (new modle)
it suggests that the shape of the active site changes slightly to better accommodate the substate to it can be complementary
Enzyme - rate of reaction
we can measure the product being made or the substate being used up.
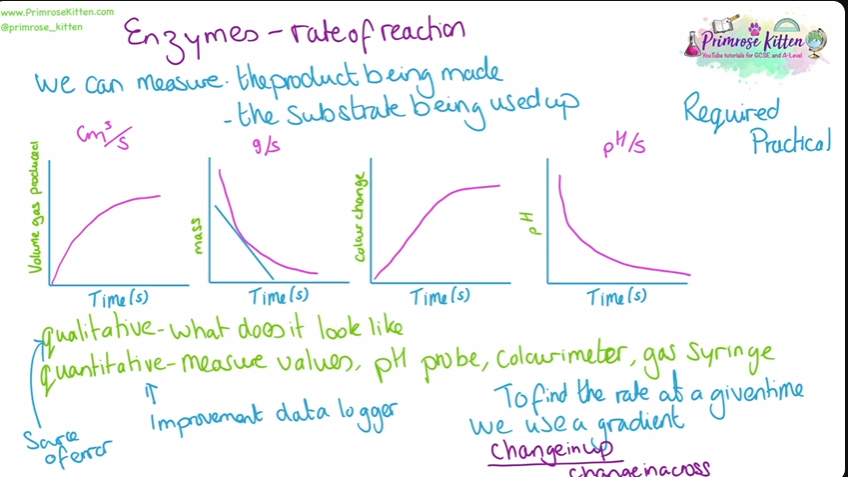
Enzyme - affect of temperature
as the temperature increases the particles move more so more frequent collisions so a reaction is more likely to happen , the enzyme is more likely to make enzyme-substrate complex
the tertiary structure starts to change due to the enzyme breaking at high temps this denatures it as the active site is no longer complementary
temperature coefficient : rate of reaction +10c / rate of reaction at T
Enzymes - PH
PH is the conc of H+ ions
the H+ and OH - ions interfere with the ionic bonds in the tertiary structure changing the shape of the active site
each enzyme has a different optimal PH
Enzyme -concentration
the higher the conc the more frequent it finds the substrate increasing the rate of reaction until it reaches saturation point.
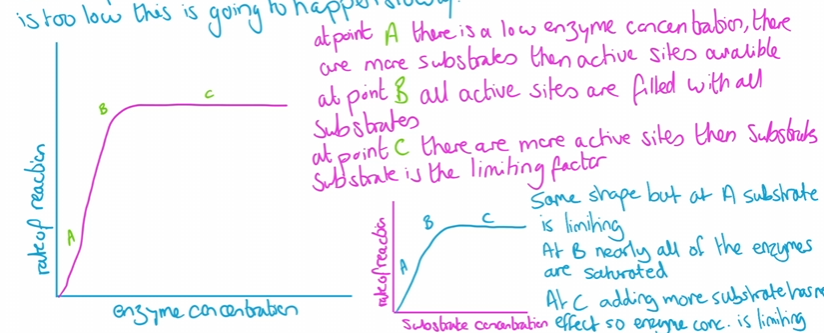
how to measure it
using indicator to show change in PH as product is produces
colorimeter to measure colour change
rate= absorbance/time taken

Enzymes- Inhibition
Competitive inhibition
inhibitors is a similar shape to the substrate and will occupy the active site stopping the formation of an Enzyme-substrate complex, the time they bind to it varies (slows down the rate of reaction)
Non competitive inhibitors
A molecule will bind to the Enzyme in a location away from the active site. this changes the shape of the active site so it is no longer complementary and no ES complexes form ( denatures it)
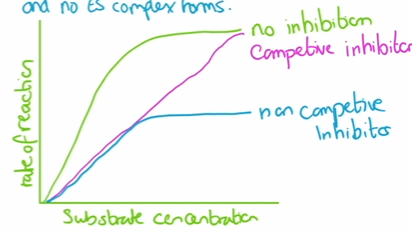

Enzyme- cofactors
Prosthetic groups
small non protein molecules that permanently bond with covalent bonds
E.g. haem group in haemoglobin.
Temporary co-factors
Ease the formation of ES complexes - binds to substrate to form the correct shape OR change charge distribution on enzyme/substrate
Bind temporarily to the enzymes to help break it down
E.g. amylase needs Cl- ions to digest starch into maltose
Enzymes - Co-enzymes (type of cofactors)
Organic non proteins that temporarily bind to the active site
chemically charged in the reaction (reduced/oxidised) need top be recycled back to og form
some need vitamins are needed to make them
Structure of cell membranes
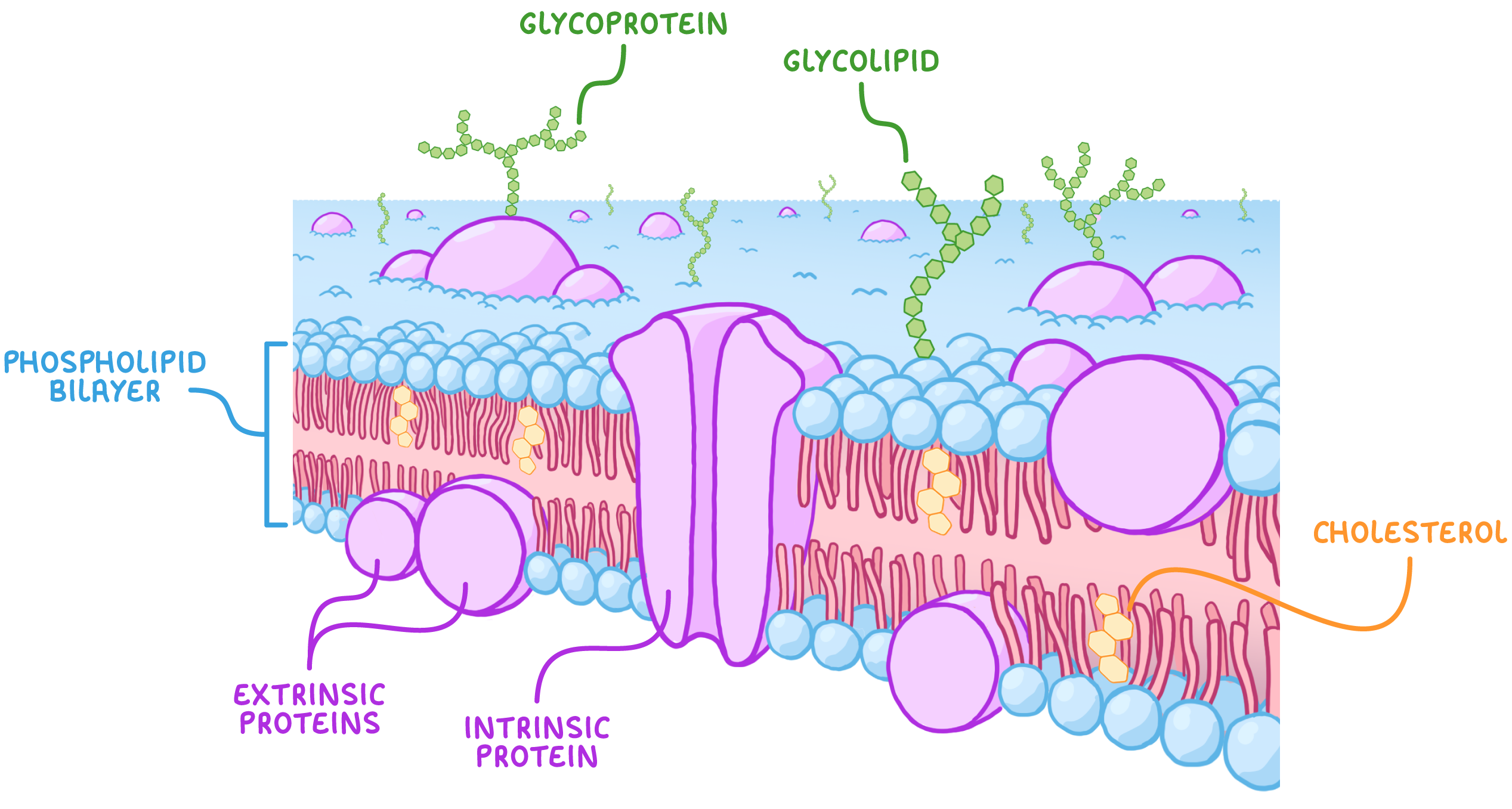
Phospholipids
the hydrophilic heads point outside the membrane whereas the hydrophobic tails are inside - this allows lipid soluble materials can move through. the phobic tails stop water soluble materials from exiting
Proteins
CARRIER PROTIENS and CHANELL PROTIENS help molecules + ions move through the membrane ( intrinsic aka inside)
extrinsic proteins only found on one side help with cell signalling
GLYCOPROTIENS - have intrinsic proteins attached to carbohydrates and help in cell adhesion, signalling and recognition (for hormones or neurotransmitters’ etc)
Cholesterol
found within the phospholipid bilayer and gives the strength and stability
its hydrophobic properties helps the tails of the phospholipids hold together further preventing water loss.
GLYCOLIPIDS : lipids combined with carbohydrates helps in cell adhesion, signalling and recognition
Fluid mosaic model
developed in the 1970s as a way to describe the movement within the plasma membrane
its a fluid because the phospholipid bilayer and other parts are not fixed in place and can move past each other
its a mosaic due to the wide range of shapes and sizes that make up the membrane
Cell membrane - factors effecting it
increasing temp - increases the phospholipid bilayer fluidity making it more preamble
( solvents , detergents , freezing can increase permeability)
Osmosis
the diffusion of water molecules from a region of high water potential to a region of low water potential across a partially permeable membrane
osmosis in animal cells (RBC)
Isotonic solution - no net movement
Hypotonic solution - water enters, cell swells/bursts
Hypertonic solution - water leaves, cell shrinks
osmosis in plants
In a hypotonic solution, plant cells become turgid as water enters, creating pressure against the cell wall/ cell swells
In a hypertonic solution, plant cells undergo plasmolysis as water leaves, leading to wilting and cell shrinks
isotonic solutions- no net movement
factors effecting osmosis
temperature - more kinetic energy = diffuse faster
Water potential gradient = the steeper the faster the rate of osmosis
Thickness of cell membrane - thinner means less distance = diffuse faster
Surface area - larger sa means more water can cross at once = osmosis faster
Diffusion
The net movement of molecules from a region where they’re more highly concentrated to where they’re less concentrated until evenly distributed
only small particles and nonpolar molecules can diffuse directly
Facilitated diffusion
Charged ions and polar molecules need help passing through the lipid bilayer
CHANNEL PROTIENS allow the particles to pass through via diffusion ( No ATP is needed its passive)
each ion has it sown channel protein
Active transport
The movement of molecules or ions into or out of a cell from a region of lower concentrations to a region of higher concentration. using ATP or carrier proteins
A molecule enters the carrier protein and APT will turn into ADP triggering the shape of the protein to move the molecule to the other side
Endo and Exocytosis
bulk transport ( large molecules or amt)
requires ATP to move vesicles along the cytoskeleton
adaptations of the cell membrane
micro villi on the epithelial cells increase SA
brush border- lots more carrier proteins for more diffusion and co active transport
The cell cycle
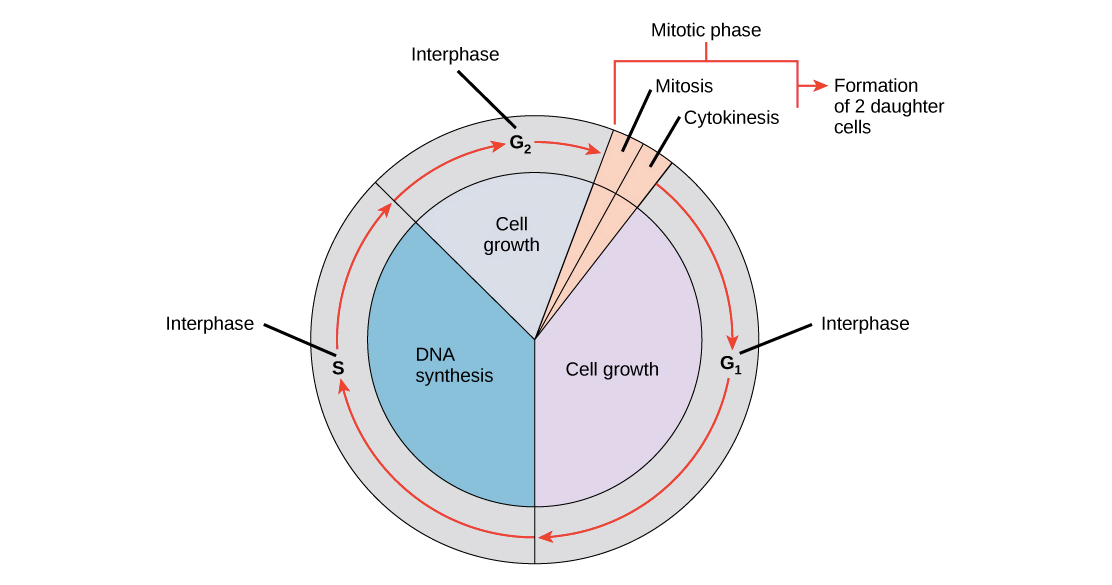
Interphase - This occupies the majority of the cycle as cells prepare for division.
Mitosis - This is when the nucleus of the cell divides in two.
Cytokinesis - This is when the whole cell and cytoplasm divides in two to produce
G1 phase is when cell grown + makes new proteins
S phase - where DNA is replicated
G2 phase- where it continues to grow and replicated DNA is checked for errors
G1 checkpoint - to see if the cell has all the chemicals needed + for damage
G2 checkpoint - check to see if its been replicated without DNA error
Metaphase checkpoint - chromosomes are checked to see if they are attached to the spindle
mitosis
Interphase | the cell prepares for division by growing replicating its DNA and organelles |
Prophase | chromosomes become visible and condense, centrioles develop these are spindle poles that move to opposite ends of the cell |
Metaphase | the chromosomes can be visualised as 2 chromatids joined by centromere the spindle fibres attach to them and the chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell |
Anaphase | the centromere split and the individual chromatids separate and move to opposite sides of the cell |
Telophase | when the chromosomes reach the opposite poles they are uncoiled and a nuclear envelope forms |
Cytokinesis | cytoplasm and cell membranes divide the cell membrane reforms around it these are the TWO identical daughter cells |
Meiosis
first division | second division |
P1: DNA duplicates and the chromosomes copy to form CHROMATIDS and arrange themselves with their homologous pair | P2: the TWO daughter cells start the process of division. |
M1: chromatids line up at the cell's equator and pulled to opposite sides | M2: they are lined up in the equator of the cell |
A1: the cell starts to divide | A2: the CHROMOSOMES are separated with each arm being pulled in a different direction |
T1: New cells formed cytoplasm divided | T2: each daughter cell will be a haploid and are not identical |
Meiosis crossing over
increase in genetic variation
homologous chromosomes twist around each other and re-join the other chromatid swapping genetic info
this point where they touch is called chiasma
this leads to maternal and paternal genes in the same place
Independent segregation
Homologues pairs are lined up at random resulting in different combinations of chromosomes
(12n)2
mitotic index
number of cells in mitosis/ number of cells in the sample examined.
why are the cell cycles important
Mitosis | Meiosis |
growth | increases genetic variation through fertilisation of two random gametes |
tissue repair | creates haploid cells which make a diploid organism |
asexual reproduction | genetic variation increases the organisms chance of survival during evolution |
Stem cells and differentiation
multicellular eukaryotic organisms start off as single undifferentiated cells which divides by mitosis
eg: A zygote (embryo cell) undergoes differentiation to become various specialized cell types. as gene expression is changed
cell shape changes
cell contents change
proportion of organelles change
Specialised cells
Erythrocytes (rbc): carry oxygen to lungs to respiring cells
biconcave shape = higher SA:V
no nucleus + few organelles = more space for haemoglobin to bind to oxygen
small and flexible so they easily pass through capillaries
Neutrophils (type of wbc)
much larger then rbc and multilobed making it flexible and stretch
can move by chemotaxis = detect and follow chemical trails (receptors)
this allows it to be efficient in phagocytosis of pathogens
Spermatozoa (sperm cell)
acrosome contains enzymes that digest the egg cell
haploid nucleus allows it to fertilize
many mitochondria for ATP for energy
tail/flagella to help it move and its thin + narrow
Specialised plant cells
Palisade cells
adapted for photosynthesis
long and cylindrical allows for compactness
large vacuole pushes chloroplast to the edge of the cells
many chloroplast
cytoskeleton allows to move the chloroplasts
Guard cells
controls opening and closing of the stomata -gas exchange + transpiration
no photosynthesis BUT contains chloroplasts
cell wall around stomata thicker more cellulose
Root hair cell
large SA
lots of carrier proteins for active transport e.g. ions
lots of mitochondria for ATP for active transport
large vacuole to control water volume
Xylem + Phloem
PHLOEM
Living cells joined end to end
reduced cytoplasm
no nucleus
cytoplasm connects through sieve plates
companion cells for each sieve tube provide ATP and carry out living functions for the sieve tubes
XYLEM
xylem vessel= joined end to end
no cytoplasm = ease of flow
boarded pits = gaps in lignin allow lateral movement of water between vessels and to cells
lignin forms in spirals to allow flexibility + keeps xylem open during high pressure
Animal tissues
a group of similar cells working together to carry out a certain function
1) Epithelial tissue
function: lining free surfaces
close cells
no blood vessels
smooth or projections (villi and cilia)
short cell cycles
can do : adsorption , filtration , secretion , excretion
2) Connective tissue
Function: to hold structures together
matrix of non living proteins and polysaccharides separates cell
can withstand forces
Example = cartilage
hyaline cartilage - bones
fibrocartilage - vertebral disc
elastic cartilage - ear
Muscle tissue
lots of blood vesse,s - formed of cells called fibers - specialised organelles called microfilaments
skeletal muscle = causes bones to move
cordiac muscle = causes walls of the heart to connect
smooth/ involuntary muscle - causes walls of inactive blood vessels to contract
Plant tissues
Epidermal tissues
flattened cless , lack chloroplasts
protectiv covering of leaves
some prodice waxy cuticle to prevent water loss
Vascular tissue
carries water and mineral ions (xylem)
transports sucrose from leaves to roots /floers/shoots (phloem)
meristem tissue
contains stem cells
found in the root shoots and tips and cambium of vascular bundles
thin walls , no chloroplasts. small vacuole. many dividing cells
meristems in the CAMBIUM produce xylem cells , loses the end walls so no interruption to flow of lignin, provides strength and waterproofing
meristems in phloem: looses organelles and develop sieve plates
associate with companion cells which can provide ATP
Stem cells in medicine
stem cells are pluripotent

