Basic Microbiology - Ch. 10
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
What are drugs that act against diseases?
Chemotherapeutic agents
Who invented “magic bullets” and the concept of chemotherapy?
Paul Ehrlich
Who invented penicillin released from Penicillium (1st true)?
Alexander Fleming
Who discovered sulfanilamide (that was the 1st widely available kind)?
Gerhard Domagk
Who found out about antibiotics, and that antimicrobial agents are produced naturally by organisms?
Selman Waksman
What are semi-synthetics?
Chemically altered natural antibiotics that are more effective, longer lasting, or easier to administer.
What generation of antibiotics are semi-synthetics considered?
Second generation.
What kind of antimicrobials are completely made in a lab?
Synthetics
Successful chemotherapy requires __________ __________.
Successful chemotherapy requires selective toxicity.
What is selective toxicity?
Taking advantage of structural and/or metabolic differences between host and pathogen.
What group of drugs is most prominent in inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis?
Beta-lactams
What functional group defines beta-lactam antibiotics? Give an example.
The beta-lactam rings (e.g. Penicillin)
Beta-lactams _______ to and _________ enzymes that cross-link ________ subunits.
Beta-lactams bind to and inhibit enzymes that cross-link NAM subunits.
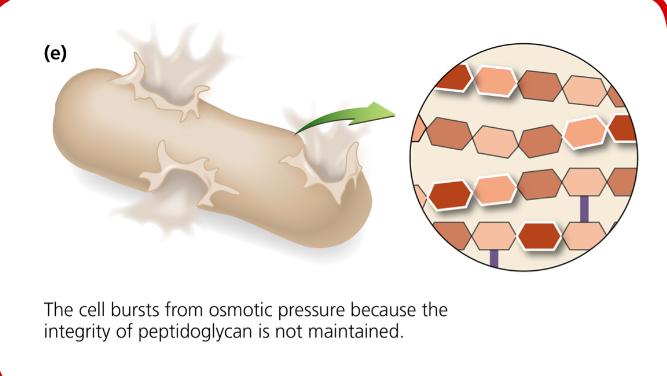
What does this image show?
The cell bursts from osmotic pressure because the integrity of peptidoglycan is not maintained.
True or false: Vancomycin has a beta-lactam ring.
False. Vancomycin does NOT have a beta-lactam ring.
What disrupts mycolic acid formation in mycobacterial species?
Isoniazid
Why does isoniazid (treats leprosy/tuberculosis) require a long treatment?
Mycobacteria reproduce slowly.
What size are prokaryotic ribosomes and their subunits?
70S ribosomes (made of 30S + 50S subunits)
What size are eukaryotic ribosomes and their subunits?
80S ribosomes, made of 40S + 60S subunits.
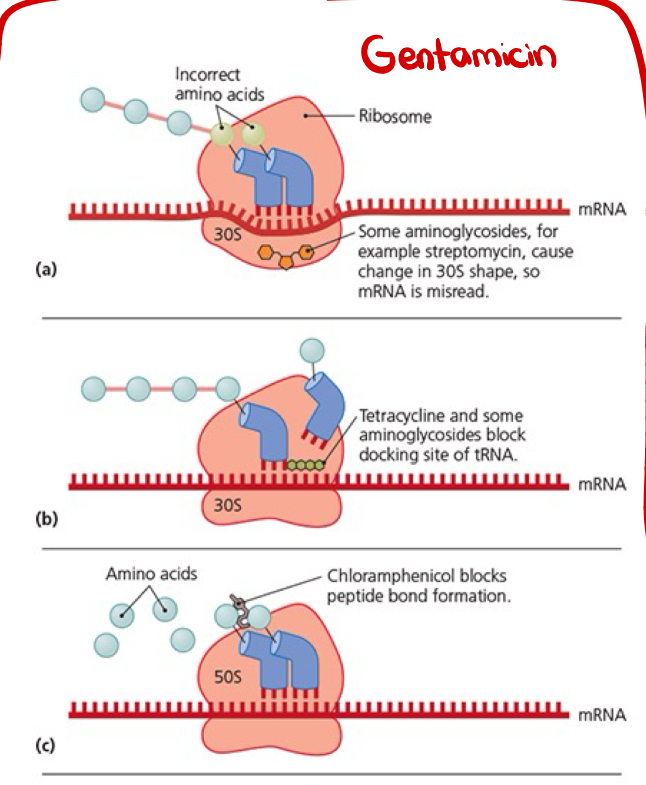
Explain the process the image shows.
.
What selectively binds to isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase?
Mupirocin
Mupirocin prevents loading of isoleucine only in Gram-___________ bacteria.
Mupirocin prevents loading of isoleucine only in Gram-positive bacteria.
What does oxazolidinone do?
Prevents the early steps of protein synthesis
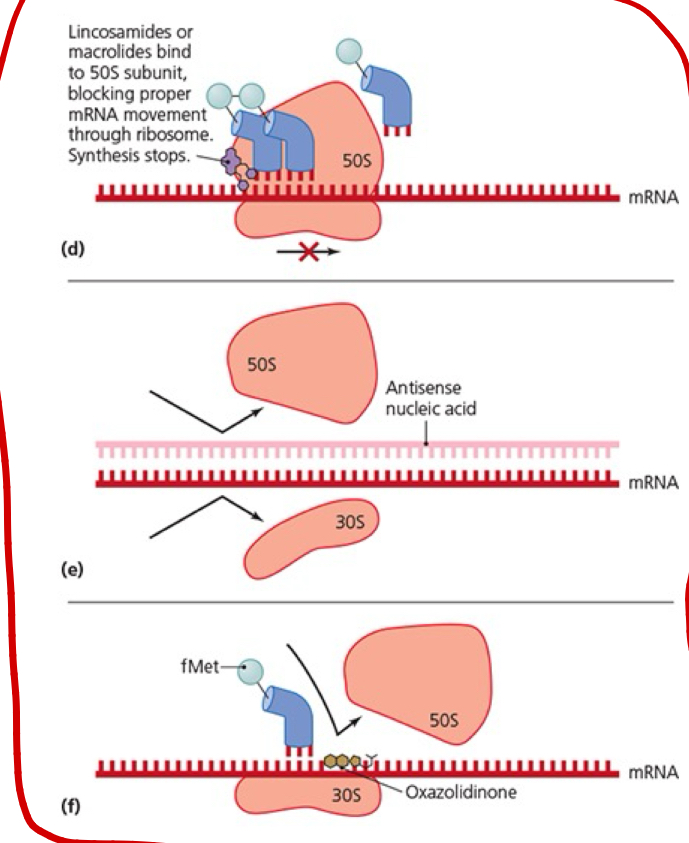
Explain the process this image shows.
.
__________ and _____________ attach to __________ in FUNGAL membranes.
Nystatin and amphotericin B attach to ergosterol in FUNGAL membranes.
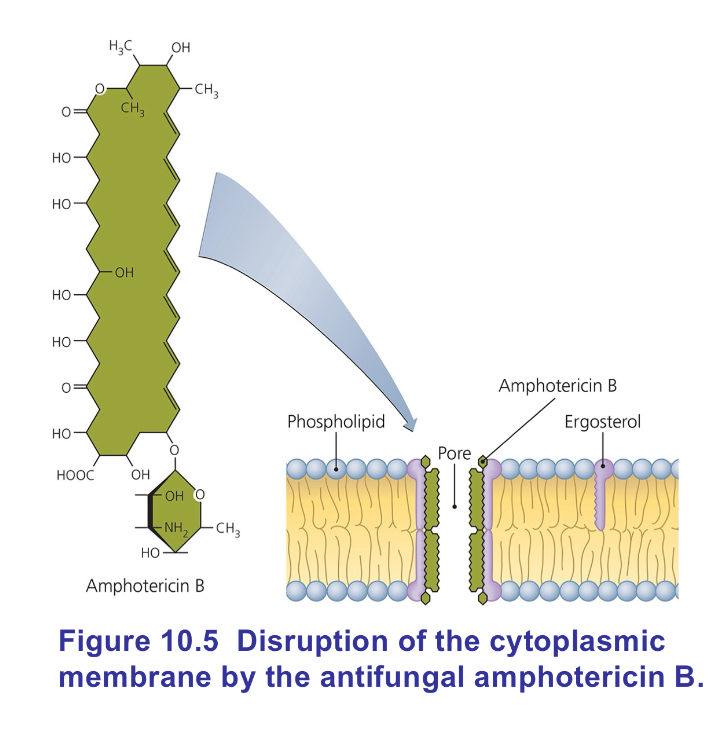
What class is nystatin and amphotericin B considered?
Polyenes
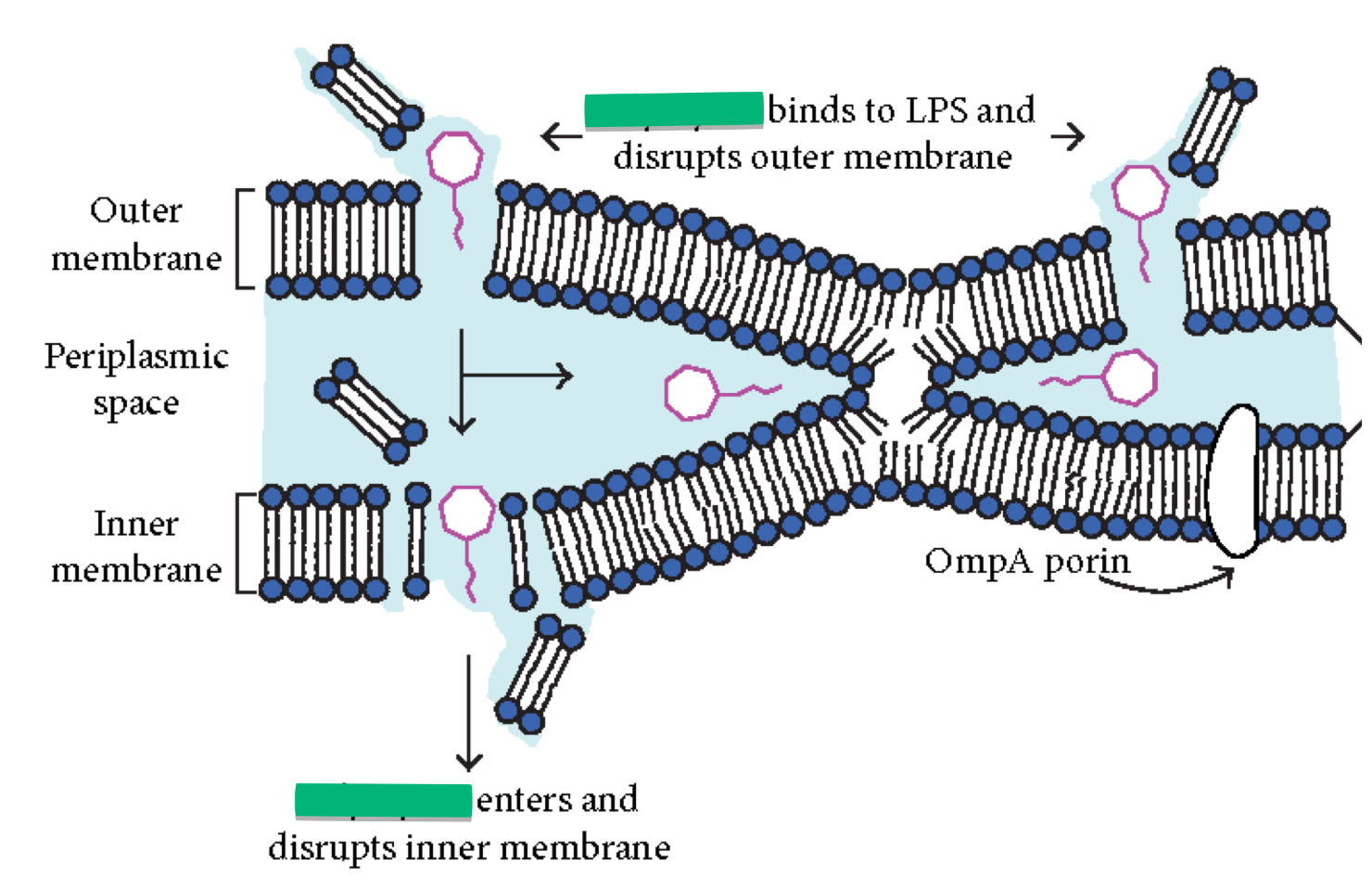
What does polymyxin do?
Disrupts cytoplasmic membranes of gram-negative BACTERIA
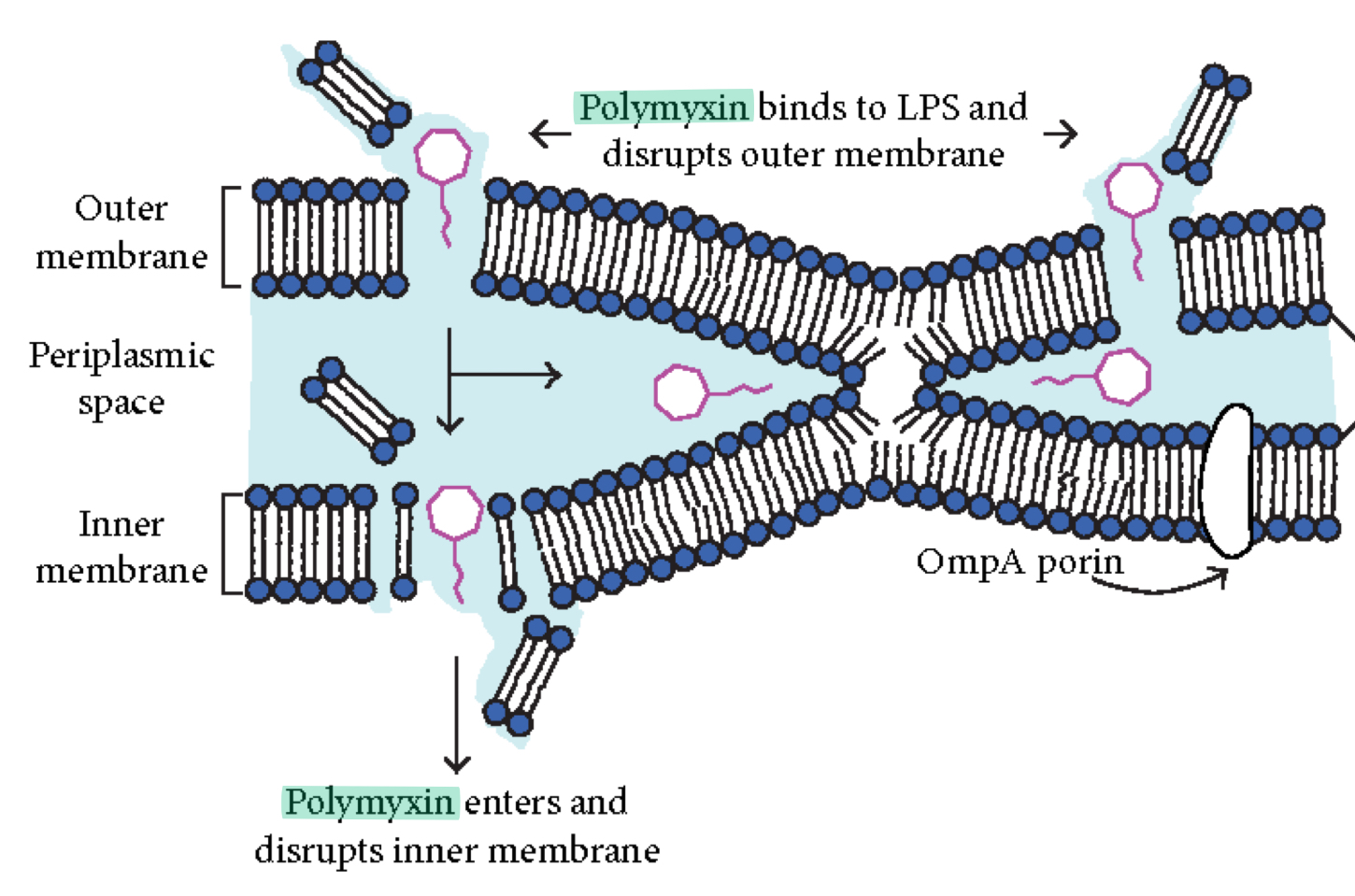
Why is Polymyxin limited in use?
It is toxic to human kidneys (nephrotoxic)
Anti metabolic agents disrupt _________ _____________ and glucose uptake by many protozoa and parasitic worms.
Anti metabolic agents disrupt tubulin polymerization and glucose uptake by many protozoa and parasitic worms.
What do sulfonamides do?
Inhibit nucleic acid synthesis
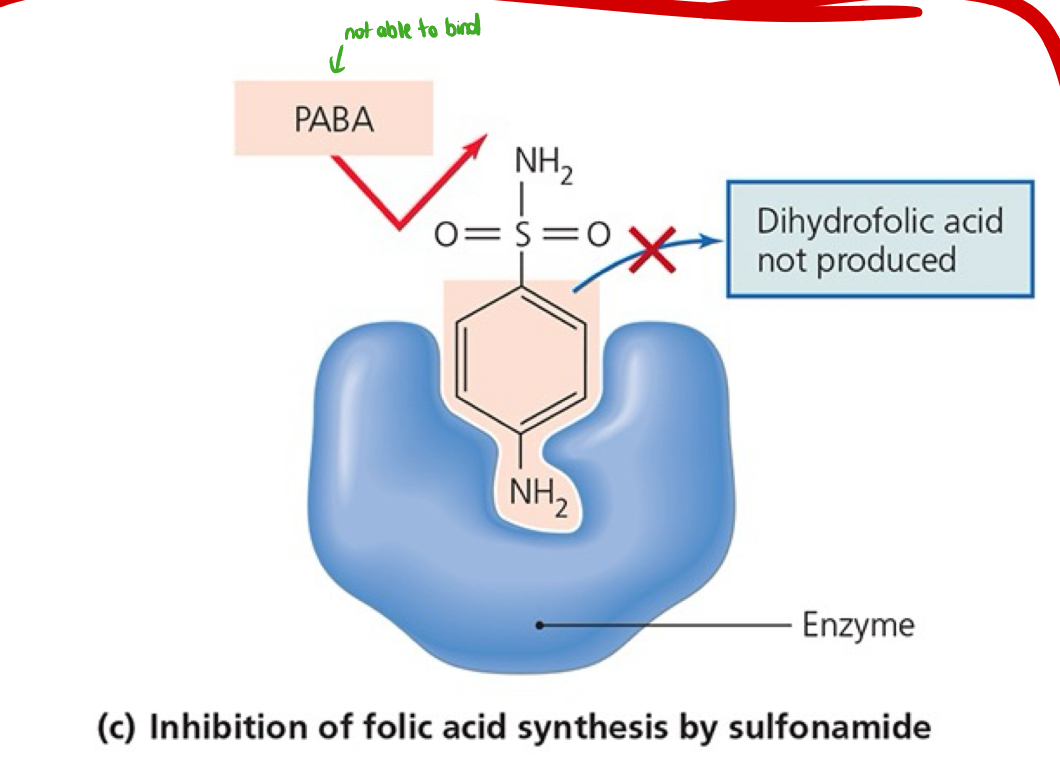
Be able to explain the inhibition of folic acid synthesis by sulfonamide (shown in the image).
The PABA is unable to bind to the enzyme due to sulfonamide, so dihydrofolic acid is not produced.
True or false: Drugs often affect both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
True. Drugs often affect both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
What are two examples of drugs that help with inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis?
Quinolones and fluoroquinolones
What are analogs?
Similar molecules
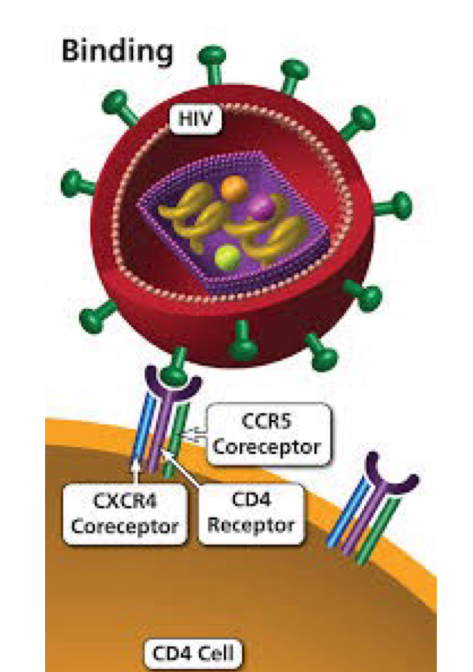
What blocks viral attachment or receptor proteins?
Attachment antagonists
What are two drugs that inhibit protein synthesis?
Mupirocin and oxazolidinone
What are two drugs that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis?
Vancomycin and Isoniazid
What does vancomycin do?
Interferes with bridges that link NAM subunits in Gram-positive bacteria
What does isoniazid do?
Disrupts mycolic acid formation in mycobacterial species.
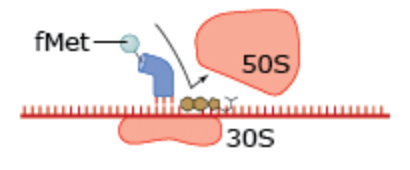
What drug blocks the initiation in this process?
Oxazolidinones
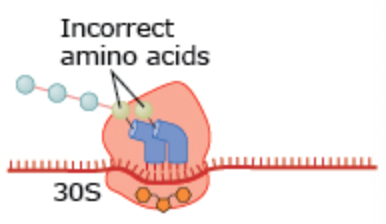
What drug changes the 30S subunit in this process?
Aminoclycosides
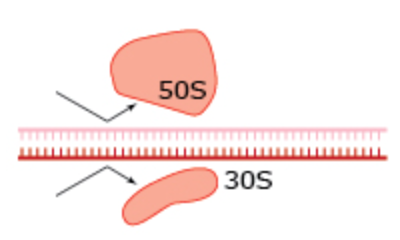
What drug blocks ribosome attachment in this process?
Antisense nucleic acids
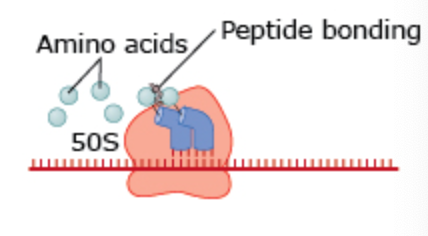
What drug inhibits peptide bonding in this process?
Chloramphenicol
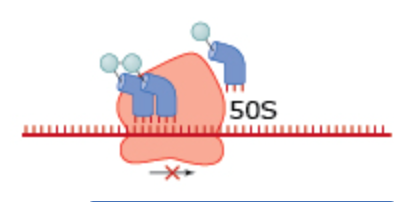
What drug blocks ribosome movement in this process?
Lincosamides and macrolides
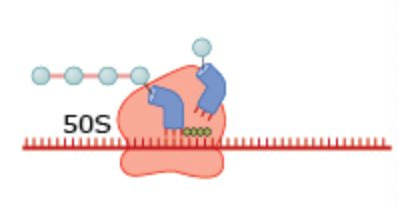
What drug blocks tRNA docking in this process?
Tetracyclines
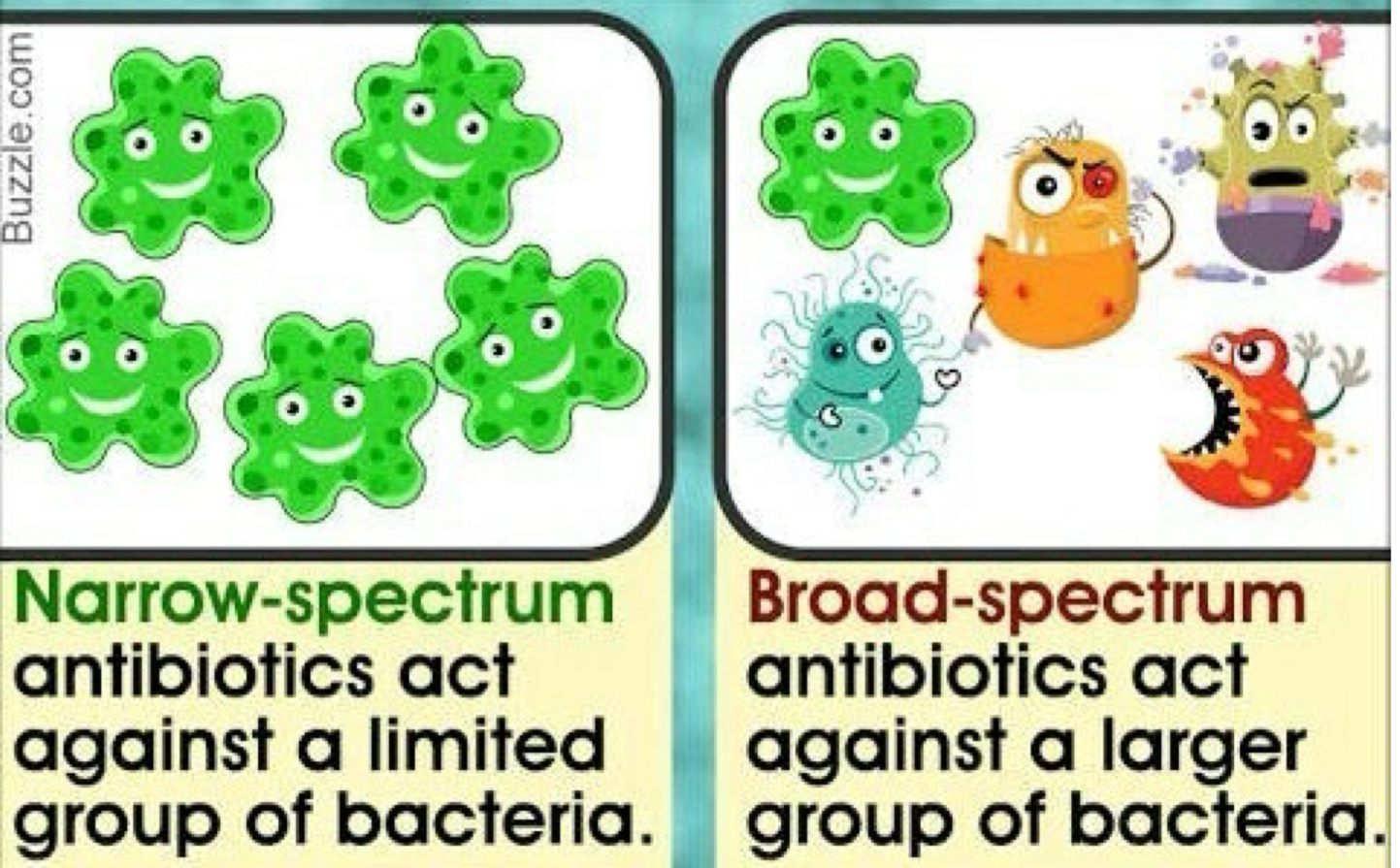
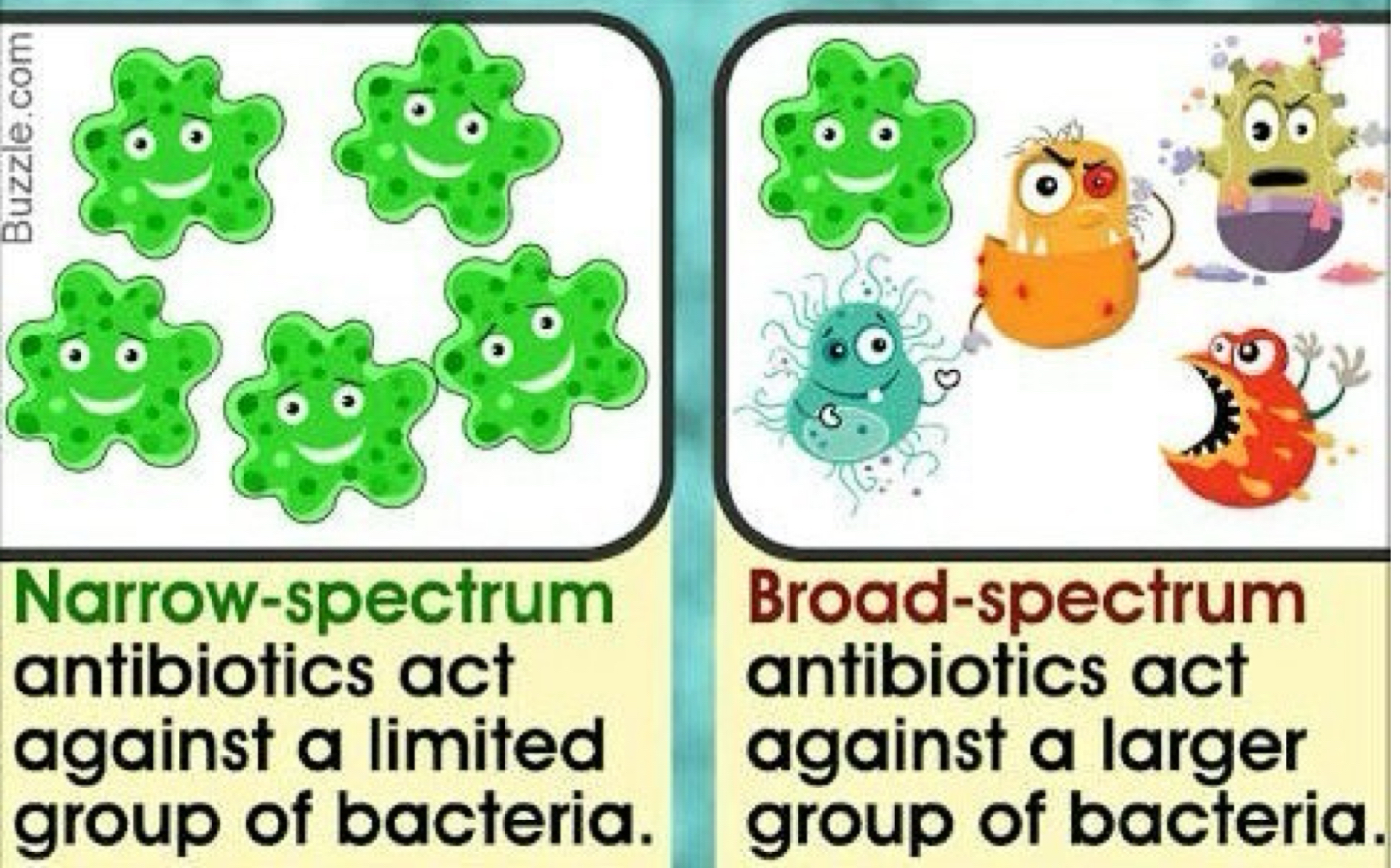
What is a narrow-spectrum effective against?
Few bacteria
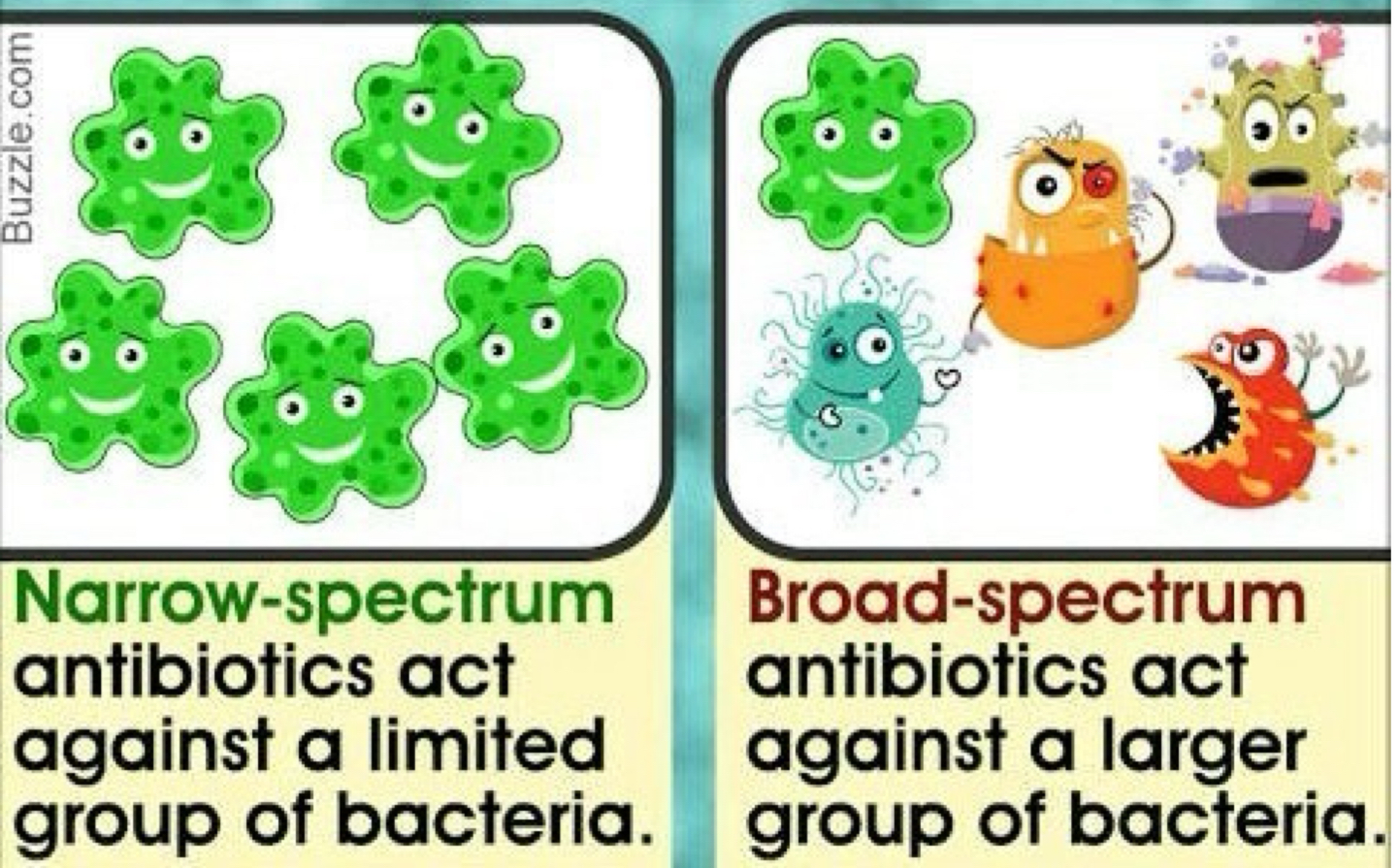
What is a broad-spectrum effective against?
Many organisms.
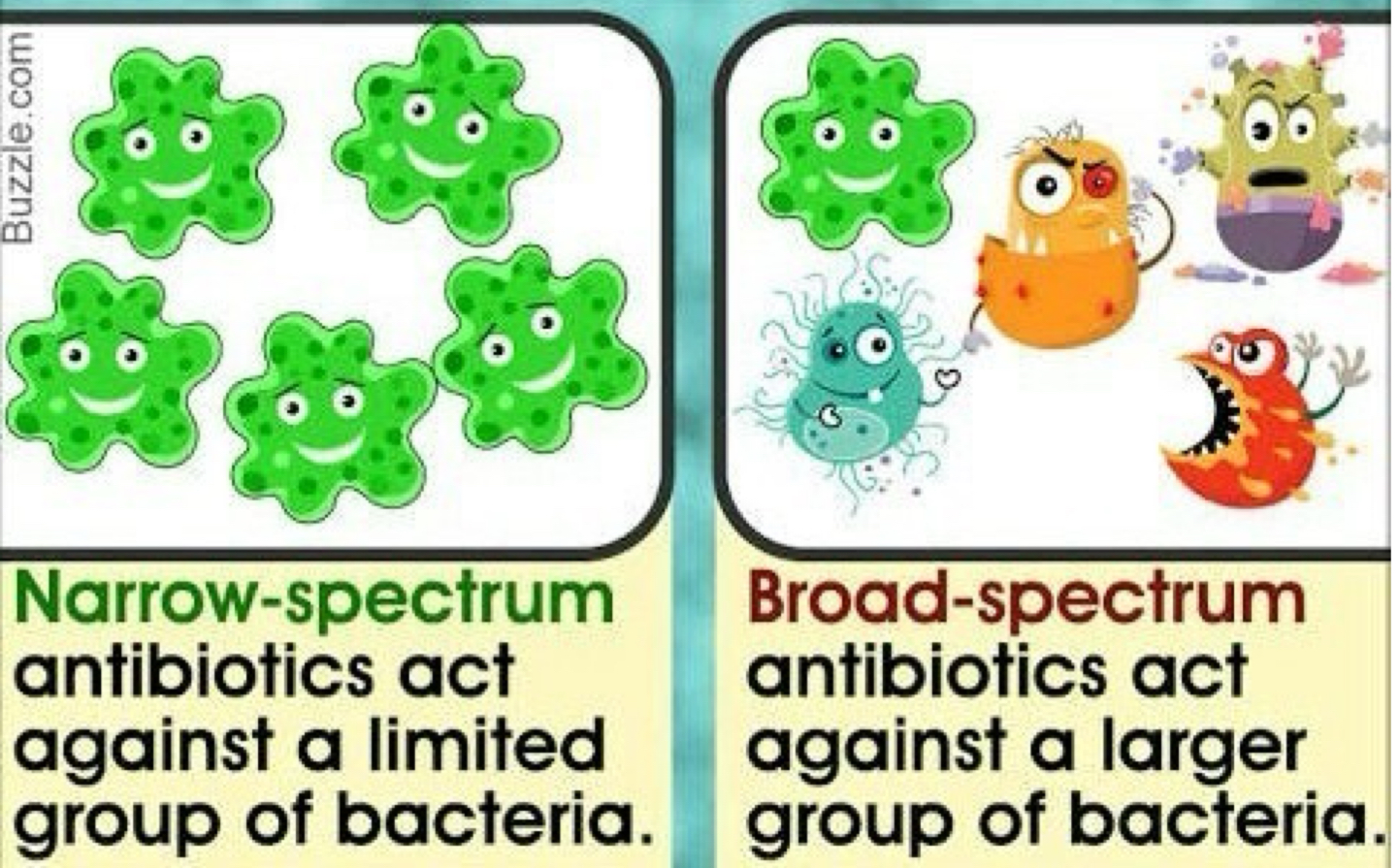
Using a broad-spectrum may allow for secondary or ____________ to develop.
Using a broad-spectrum may allow for secondary or superinfections to develop.
Using a broad-spectrum kills normal flora which reduces _________ __________.
Using a broad-spectrum kills normal flora which reduces microbial antagonism.
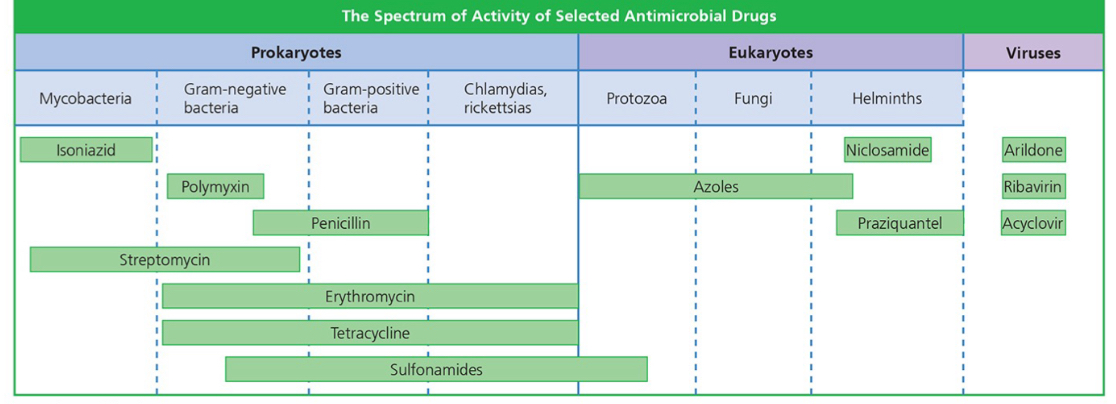
Know how to interpret this graph.
The larger the space one antibiotic takes up on the graph, the broader the spectrum of the antibiotic.
What does the minimum inhibitory concentration test determine?
Whether a drug is bactericidal OR bacteriostatic
What does the minimum bactericidal concentration test determine?
The lowest concentration that kills bacteria (bactericidal)
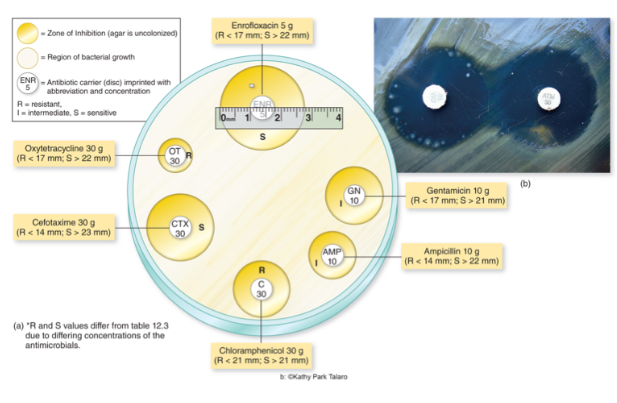
What technique is shown in the image?
Kirby-Bauer technique
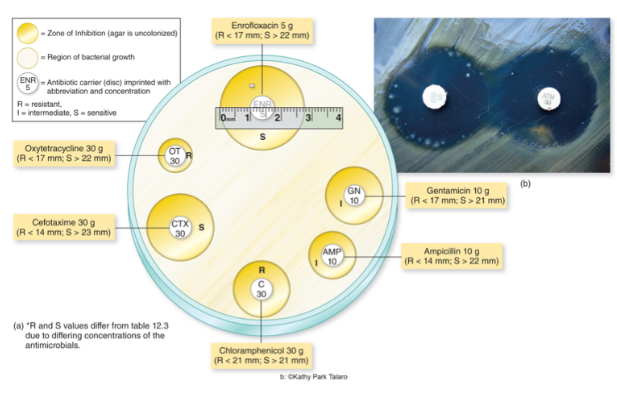
Within the Kirby-Bauer technique, what is the zone of inhibition?
Area formed during incubation that’s measured and compared with standard for each drug.
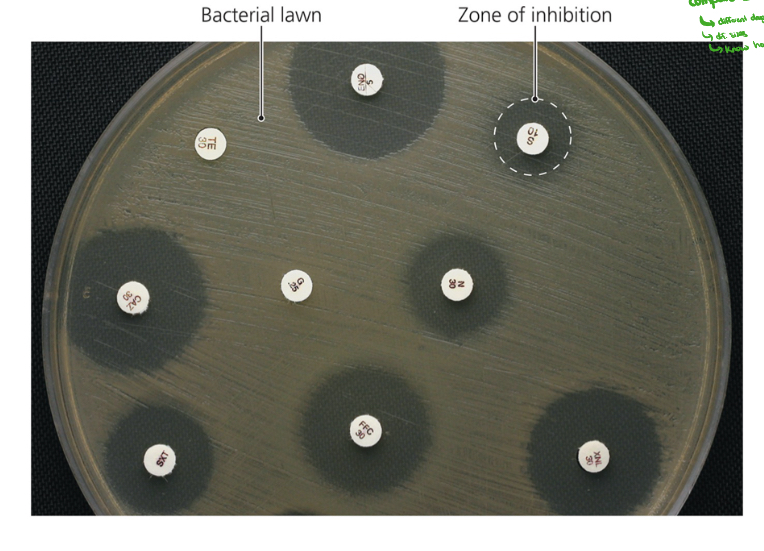
What test is shown in the image?
Kirby-Bauer test
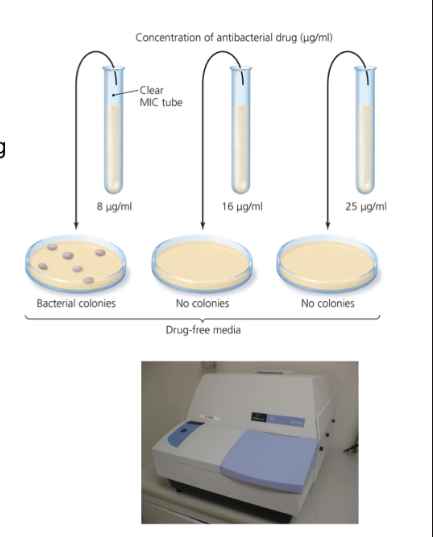
What does the minimum inhibitory concentration test determine?
The smallest concentration (highest dilution) of drug that visibly inhibits growth.
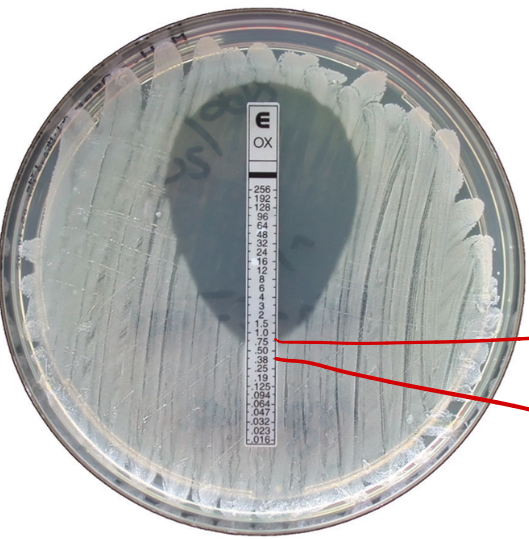
What test is shown in the image?
Etest
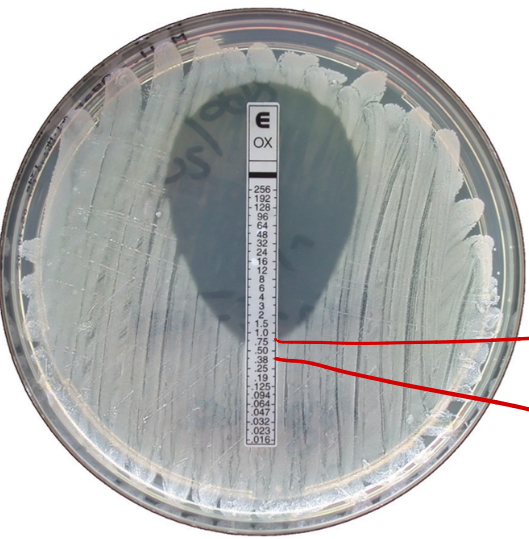
What two points are being pointed out in the image within the Etest?
Actual concentration
2-fold increased
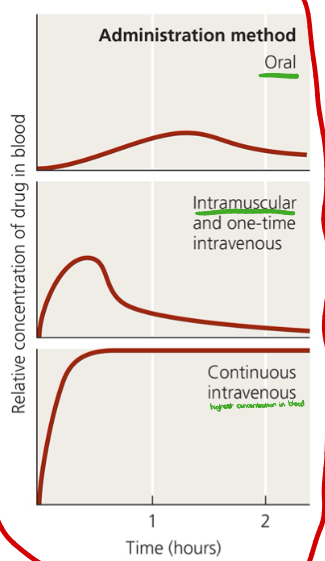
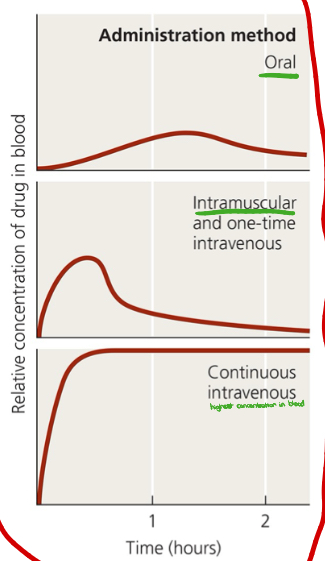
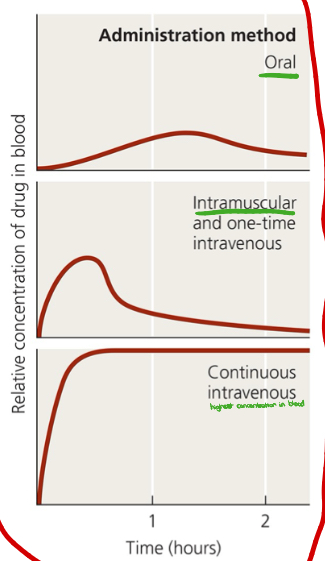
What are four different routes of administering antimicrobial drugs? Which route has the highest concentration?
Topical
Oral
Intramuscular
Intravenous (highest concentration
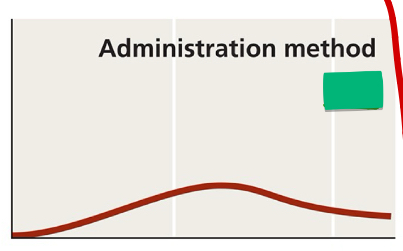
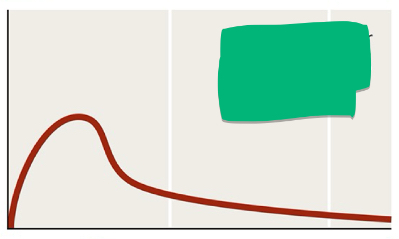
What administration method is shown in the image?
Oral
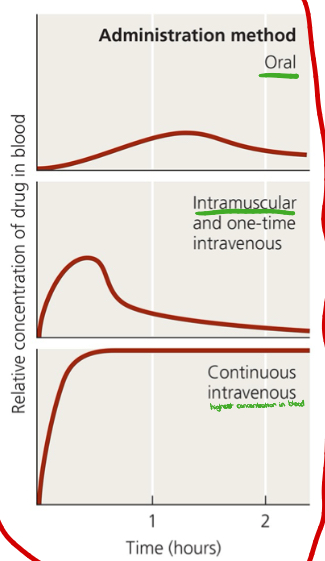
What administration method is shown in the image?
Intramuscular
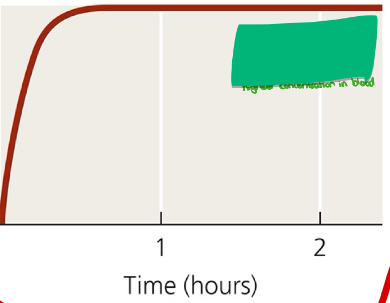
What administration method is shown in the image?
Intravenous
What are three things to consider when prescribing antimicrobial drugs?
Toxicity
Allergies
Disruption of normal microbiota.
Drugs may be toxic to what three parts of the body?
Kidneys, liver, or nerves
What do tetracyclines do?
Cross the placenta and are deposited in fetal bones and teeth.
If treatment fails, the failure is due to what?
The inability of the drug to diffuse into that body compartment.
What is therapeutic index (TI)?
The ratio of the dose of the drug that is toxic to humans compared to its minimum effective dose.
What is the therapeutic window?
The range of concentrations at which the antimicrobial is both effective and non-toxic.

Out of these numbers, which is the BEST/Safest?
10/1

Out of these numbers, which is the WORST/least safest?
1.5/1
1/2
What is an example of an allergy side effect to antimicrobial drugs? (hint: SEVERE!)
Anaphylactic shock
What are the two ways bacteria acquires resistance?
Mutation and gaining R-plasmids from transformation, transduction, and conjugation.
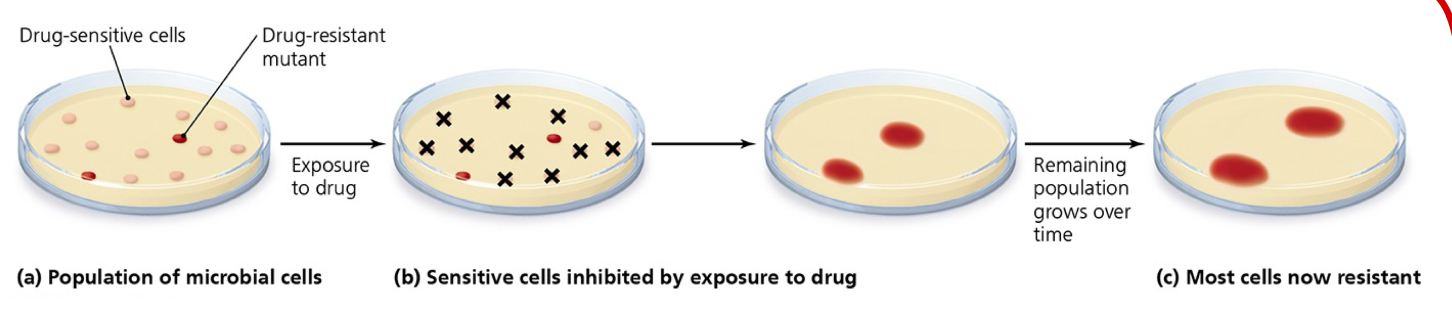
Be able to explain this image of the development of resistance in bacteria.
A population of microbial cells has drug-sensitive cells and drug-resistant cells due to mutation. When the population is exposed to the drug, the drug-sensitive cells are inhibited/killed, leaving only the drug-resistant cells. The remaining cells (drug-resistant cells) grow in number and most of the cells of the population are now resistant.
What are 4 mechanisms of resistance?
Beta-lactamases - enzyme that destroy/deactivate drugs
Porins - pumps antimicrobial drug out of cell before it can act
Bacteria in biofilms can resist antimicrobials
MfpA protein produced by mycobacterium tuberculosis
When is multiple drug resistance (MDR) common?
When resistance plasmids are exchanged between species.
What are MDR pathogens resistant to?
At least three antimicrobial agents.
When can cross-resistance occur?
When drugs are similar in structure.
What is synergism?
When one drug enhances the effect of a second drug.
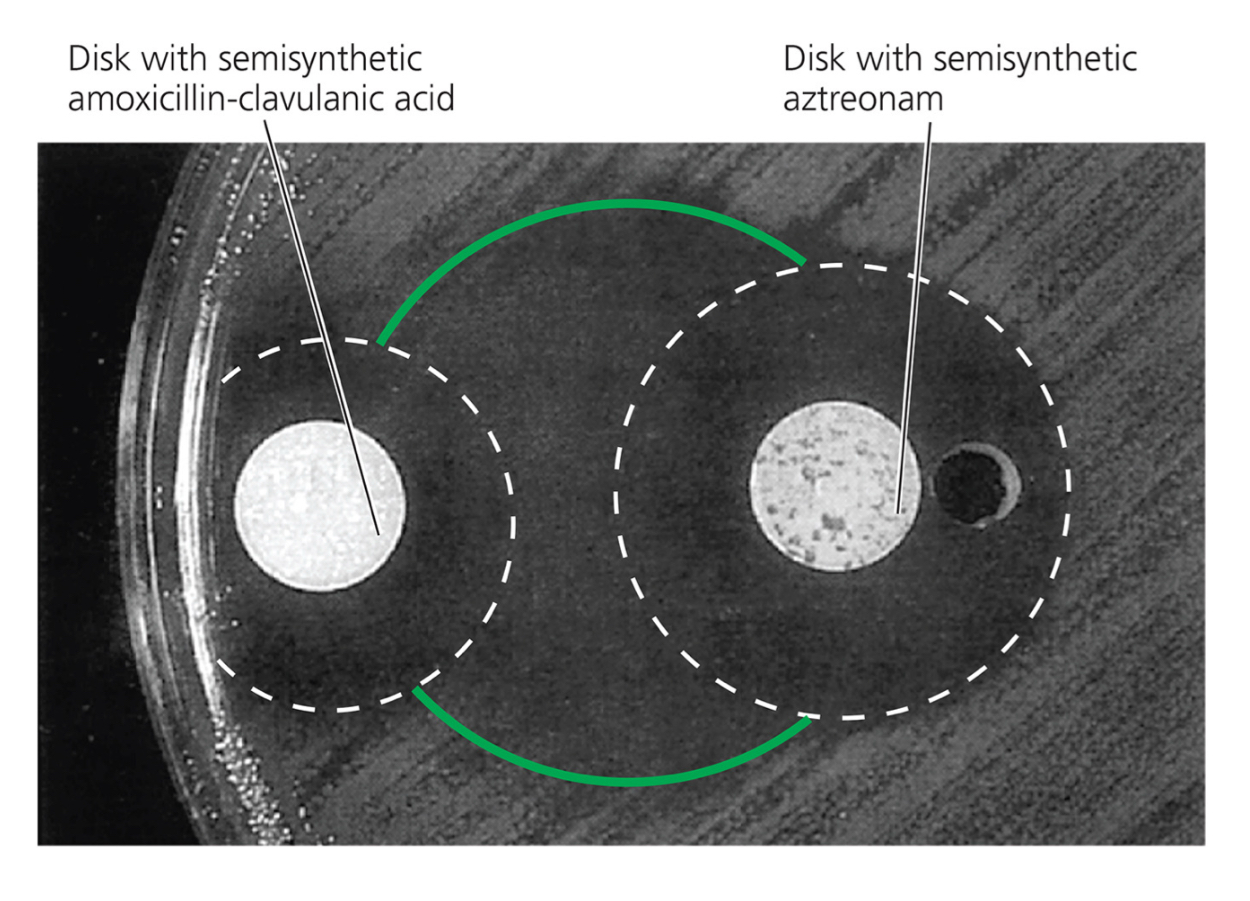
True or false: You should only use antimicrobials when necessary.
True.
A patient shows up to you with a viral infection. Should you give them antibiotics? Explain.
No, antibiotics are only used for bacterial infections.