VS331: Module 37: Male, Testes
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
1. Testes - Produce sperm
2. Epididymis - Matures sperm
3. Ductus deferens - Carry sperm
4. Accessory sex glands - Contribute to ejaculate
5. Penis - Carries urine & ejaculate out of the body
List the 5 organs that make up the male reproductive system & their general function
Scrotum
Black arrows = smooth muscle
Helps to maintain a constant temperature for the development & storage of sperm
Identify the structure, what is indicated by the black arrows, and its function.
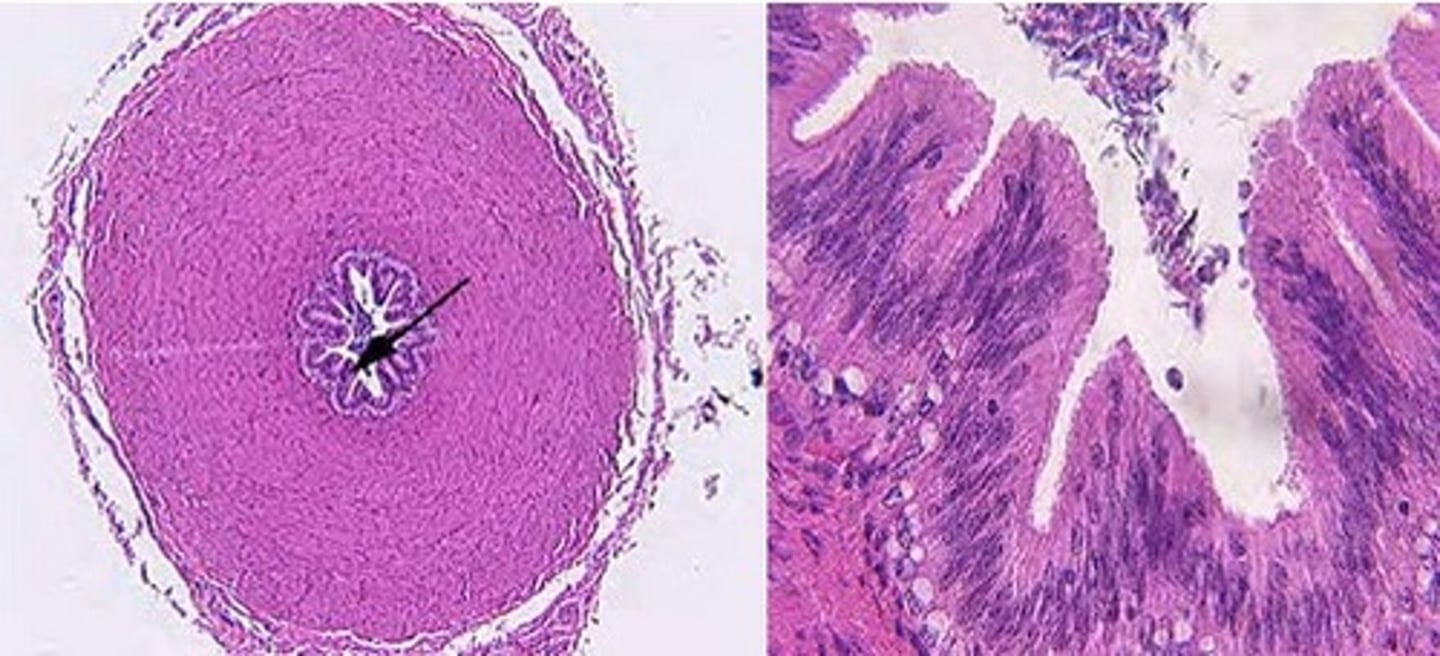
Exocrine: Production & secretion of sperm
Endocrine: Synthesis of hormones, primarily testosterone
Describe the exocrine & endocrine functions of the testes.
1. Seminiferous tubules - Tubular exocrine gland that secretes via holocrine method
2. Interstitial cells (Leydig cells) - Produce testosterone
3. Tunica albuginea - Dense irregular connective tissue, penetrates into the parenchyma to form septa
Identify the #1-3, describe their characteristics & functions
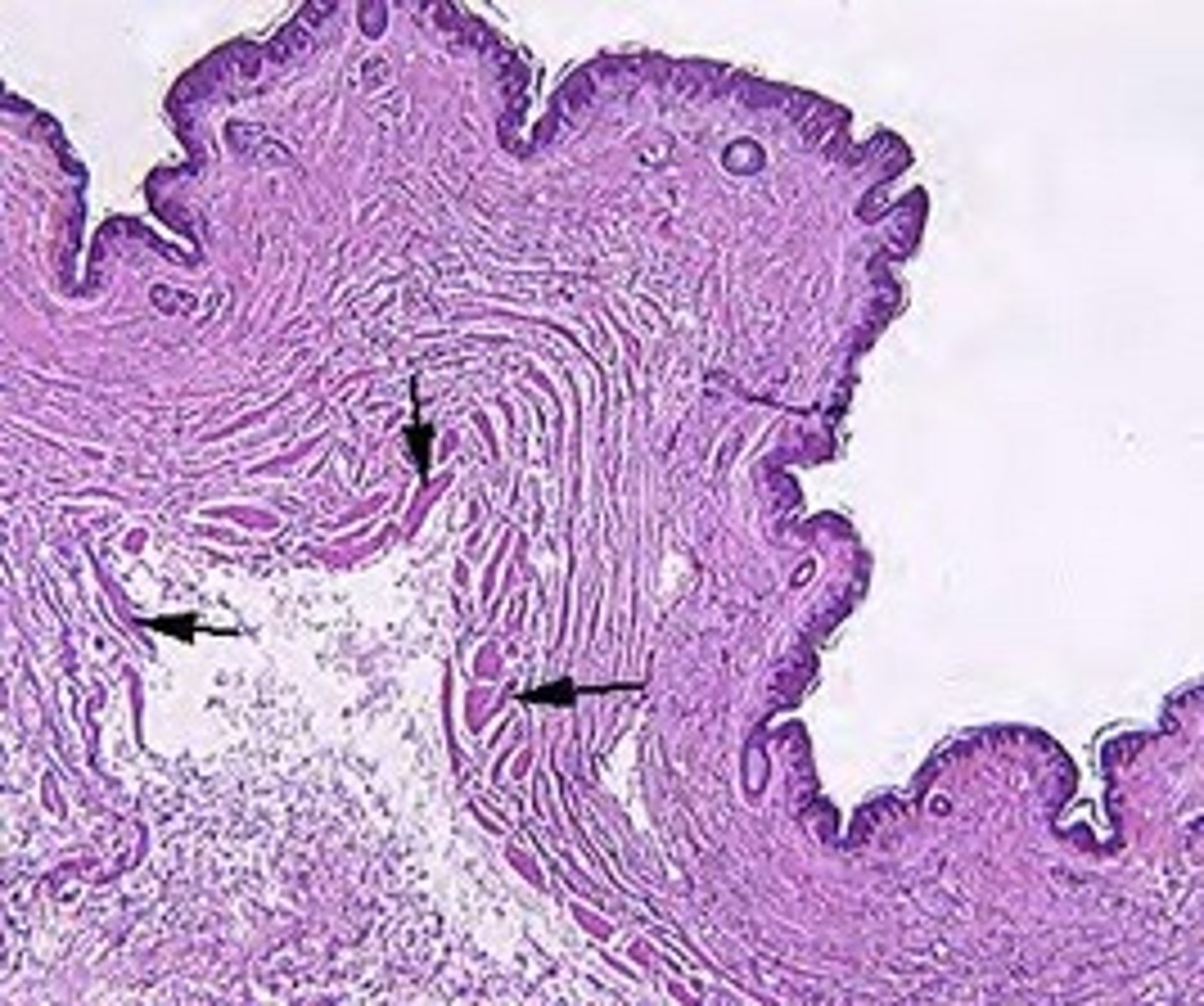
1. Spermatogenic cells - Differentiate to mature sperm
2. Sertoli cells - Support cells: Produce small amount of estrogen, provide physical support of sperm cells, participate in the "blood-testis barrier"
Describe the two basic cell types in the seminiferous tubule.
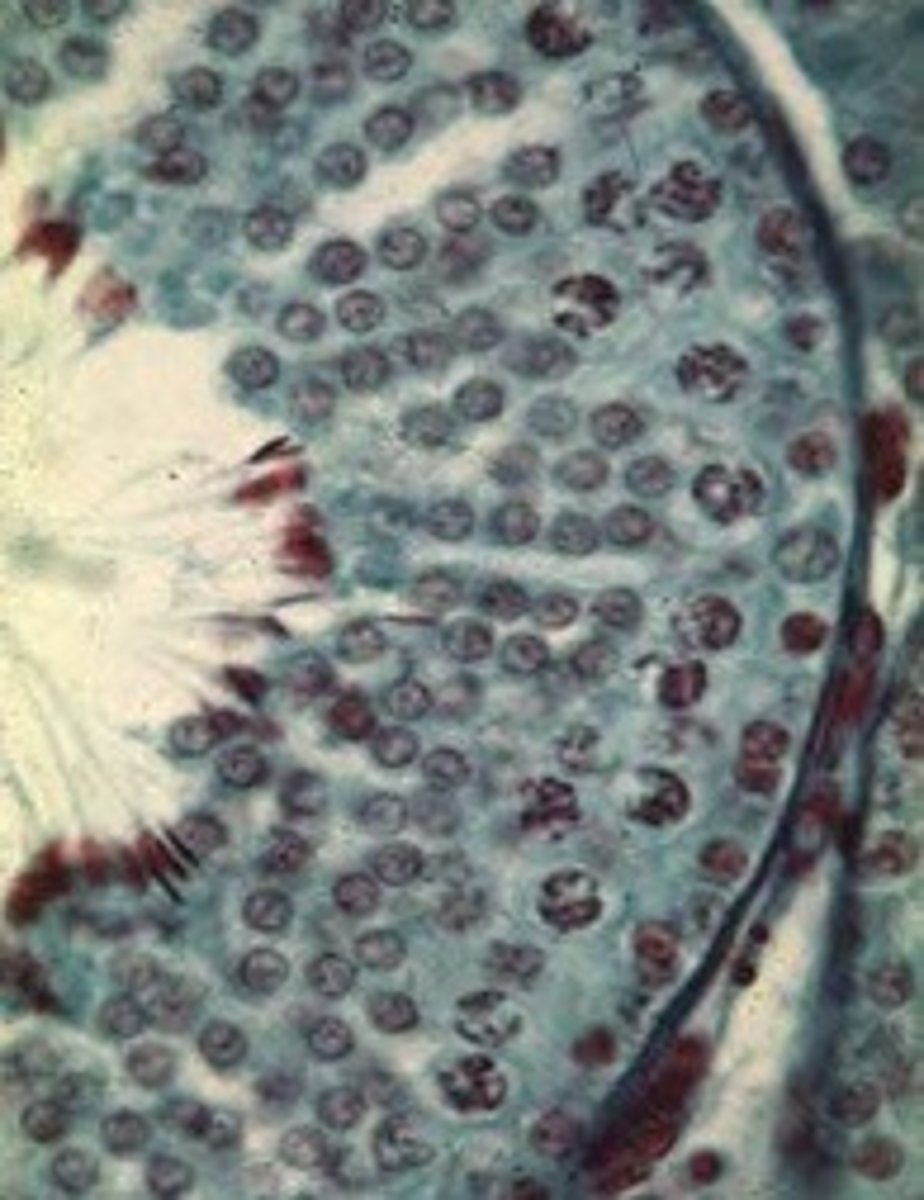
1. Interstitial/Leydig cells - endocrine cells that produce testosterone
2. Peritubular cells - 2-3 layers of contractile cells & collagen fibers outside the basal lamina
3. Sertoli cells - Physical support of sperm cells, secrete androgen binding hormone & inhibin
4. Developing sperm - Youngest at the base, mature sperm near the lumen
- 1. Spermatocytes - Primary, diploid
- 2. Spermatids - Haploid, near lumen
- 3. Spermatazoa
Describe the 4 cells found in the testis
1. Spermatogonial phase - Spermatogonia: Needs hormonal influence, supported by Setoli cells that form the blood-testis barrier
2. Spermatocyte Phase - Primary spermatocytes: Loose half of its chromosomes, become secondary spermatocytes, & the spermatids
3. Spermatid Phase - Spermatids differentiate into sperm developing flagellum & and mature appearance
List the 3 phases of spermatogenesis, name the cell types found in each phase.
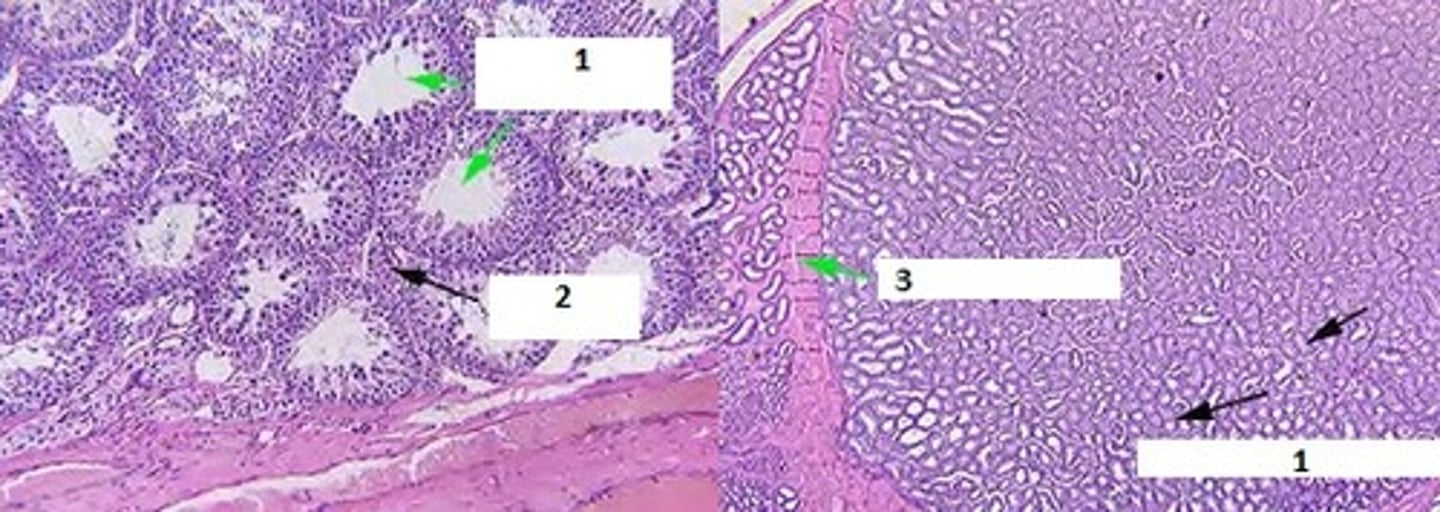
1. Rete Testis - Point where seminieferous tubules converge.
2. Mediastinum Testis - Connective tissue core surrounding rete testis
3. Straight tubules/ Efferent ductules - Lined by pseuodstratified columnar epithelium. Tall ciliated cells & short nonciliated cells. Has thin layer of smooth muscle & elastic fibers
Identify & describe #1-3. List common characteristics.
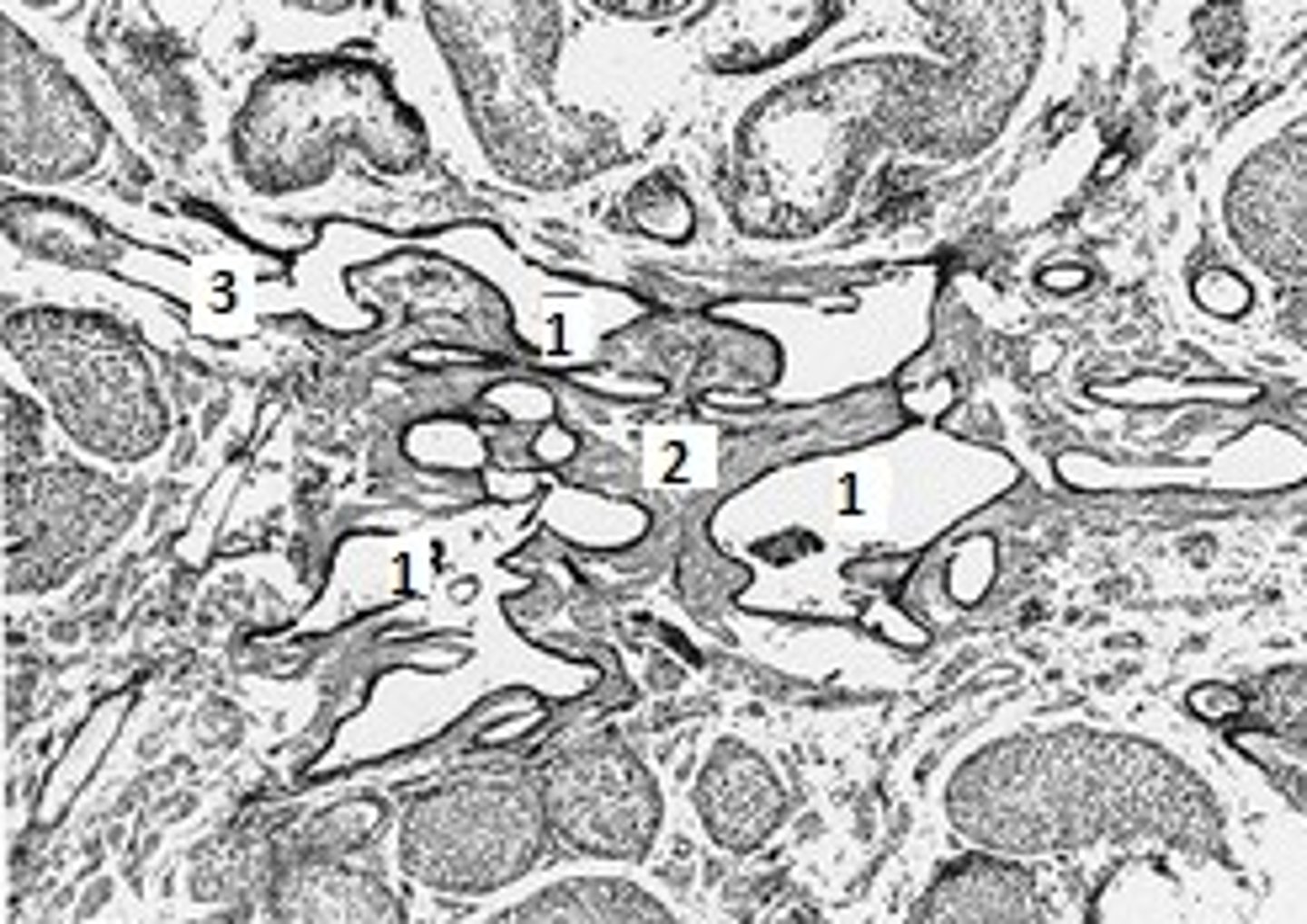
Epididymis - Lumen lined with pseudostratified sterociliated columnar epithelium
1. Smooth muscle
2. Connective tissue - Highly vascularized
3. Tunica albuginea - Dense connective tissue capsule
Identify the organ, & #1-3.
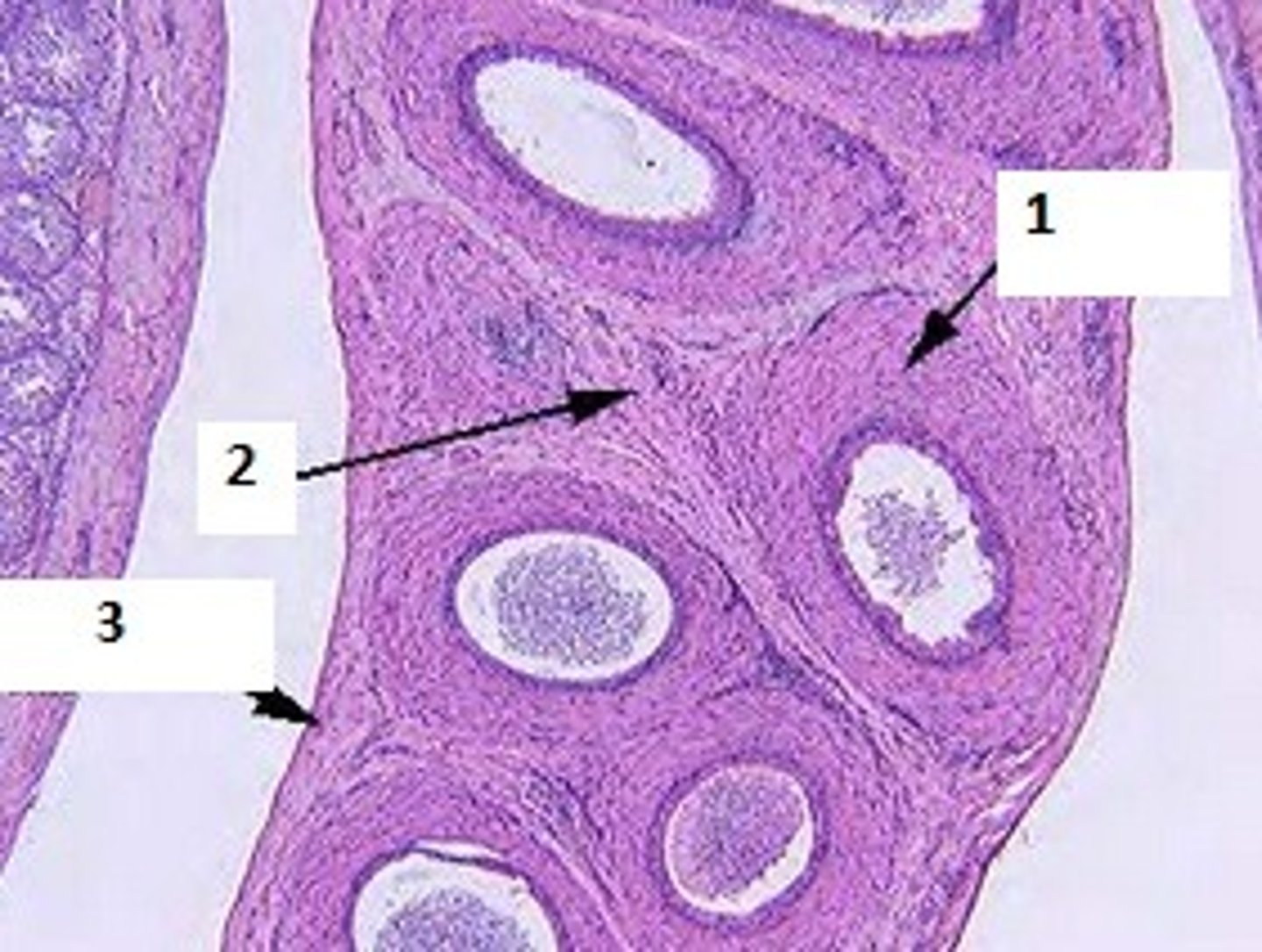
Ductus Deferens
- Function: carries sperm to pelvic urethra
- Epithelium: Pseudostratified sterociliated columnar epithelium
- Thick tunica muscularis
- Tunica serosa
Identify the organ, its function, the epithelium, and any tunica.