GV black classification, principles of amalgam
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
GV blacks classification was based on?
location (anterior vs posterior)
Origin (pit and fissure vs smooth surface)
Extent (involving proximal surfaces or incisal edges)
which class did black not include?
VI: added in 1956 by simon
class I
anterior and posterior:
pits and fissures (occlusal, buccal and lingual surfaces, including cingulum pits)
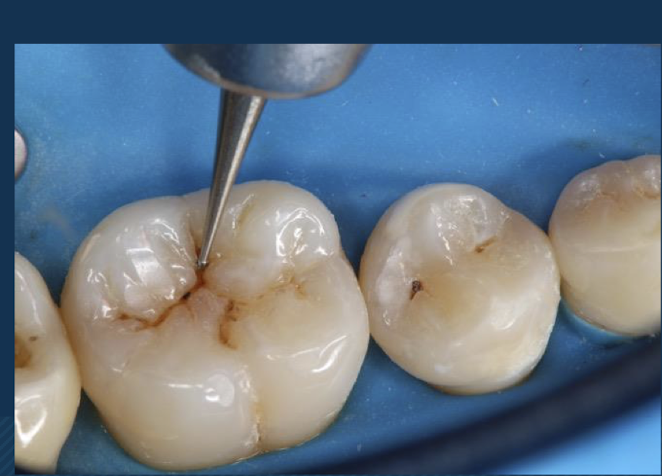
class I
class I
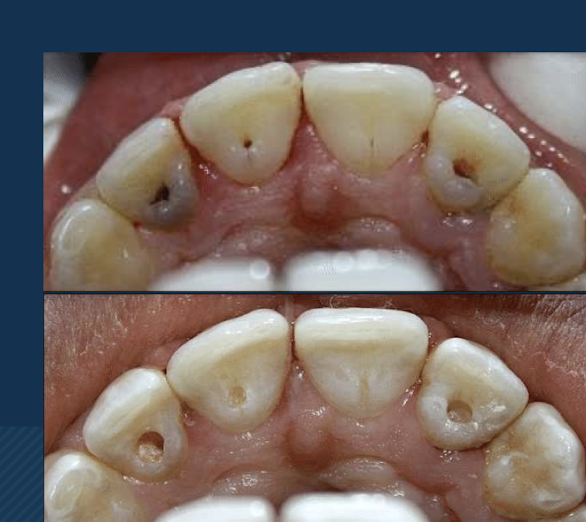
class II
Proximal surfaces of molars and premolars (posterior only)
mesial or distal
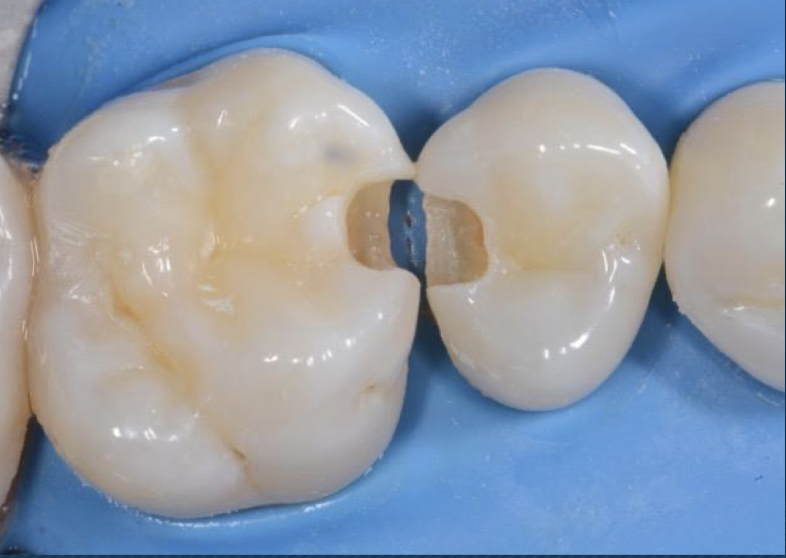
class II
class II
class III
proximal surfaces of ANTERIOR teeth that do not involved incisal edges
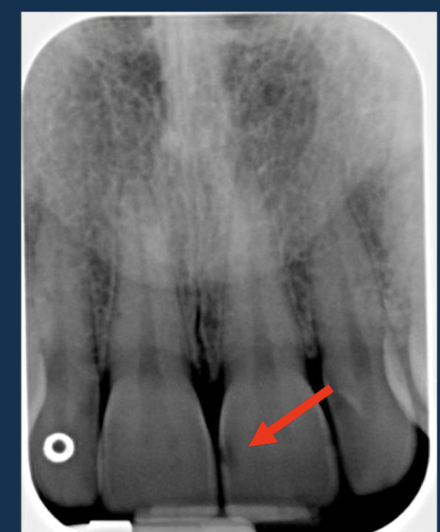
class III
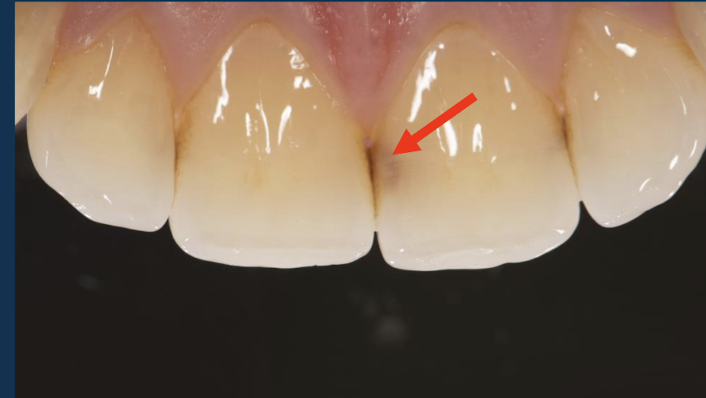
class III
class IV
proximal surfaces of anterior teeth that involve incisal edge
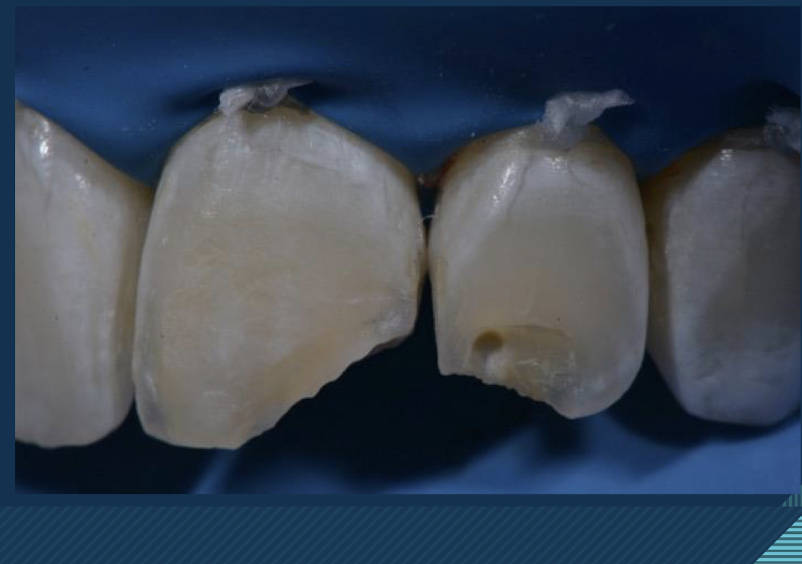
class IV
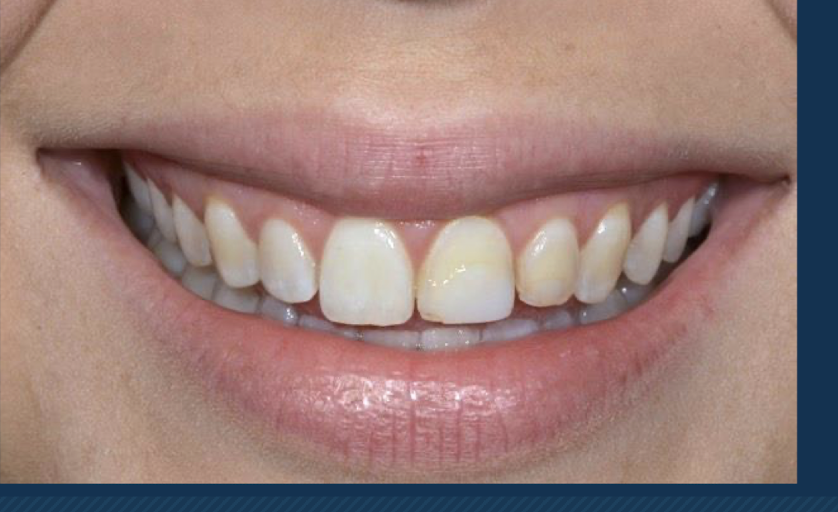
class IV
class V
Cervical (gingival) third of
anterior
facial (or palatal)
posterior
Buccal (lingual)
class VI
incisal edges
ant teeth
Occusal cusp tips
Posterior teeth
no interproximal or pits and fissures
class IV vs Anterior class VI?
proximal surfaces involved in class IV
Definition of amalgam? dental amalgam?
any material that contains mercury as the main ingredient on its composition
specific combo based on the mixture of silver-tin alloy with mercury is called dental amalgam
Dental Amalgam pros
excellent strength
Proven longevity (evidence based)
Low cost
self sealing
not as technique sensitive
dental amalgam cons
esthetics, bonding to tooth structure?, mroe demanding cavity prep design when compared to composite
Threshold limit value of mercury
Amt of mercury vapor that can be allowed in air for workers who spend 8/day, 40 hrs a week in that enviroment
OSHA 50 ug / m
WHO: 25 u
the worst dose a patient could from 10 or 12 amalgam restorations would be about 1/100 TLV
outline form of amalgam
min depth
Facolingual width
remaining marginal ridge thickness
internal line angles
Buccal and lingual walls
mesial and distal walls
cavosurfarce angle
acesss
min depth: 1.5-2 mm or 0.2 mm into dentin (to avoid amalgam fracture)
Facolingual width: 1/3 - ½ intercuspal width (1-1.5 mm)
remaining marginal ridge thickness: greater or equal to 1.6 mm
internal line angles: rounded
Buccal and lingual walls: convergent occlusally
mesial and distal walls: follow the orientation of enamel rods
cavosurfarce angle: 90-100 degree exist
acesss: parallel to long axis of tooth
outline form helpers
#245:
length: 3 mm
width: 0.8 mm
convergent towards shank
rounded corners
330
shorter 1.6 mm
between cusp ridges, aim for …
1-1.5 mm (not less than 1)
the smallest amalgam condenser width?
1 mm
mesial and sital walls at > 1.6 mm
mesial and distal walls at 1.6 mm marginal rideg
convergent, 1.6 = divergent
cavosurface angle of amalgam
90-100 degrees: formed between an internal wall and non prepared surface of tooth
4 things resistance form is achieved by
Sufficient area of flat pulpal floor (peripheral seat)
conservation of healthy tooth
strong ideal enamel margins (no unsupported enamel)
sufficient depth (1.5 mm) for adequate thickness of restoration
retention form: prevents what?
primary?
secondary?
dislodgement of restoration
retentive features: facial and lingual walls - converging occlusally
secondary: pins and grooves (#1/4 round of 169 L)
convenience form
convenience form requires that the extent of prep be adjusted to provide adequate access and visability
Resistance form: no unsupported enamel:
enamel rods?
Rods: ?
enamel margin?
from DEJ to external surface of ename;
converge toward center of developmental grooves
Perpendicular to tooth surface