Chemistry B Exam Review
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/88
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
1
New cards
VSEPR
the repulsion of electron pairs which may cause different shapes.
Valance shell electron pair reduction, the repulsion of electon pairs surrounding an atom causes the pairs to be oriented as far apart as possible.
\
Valance shell electron pair reduction, the repulsion of electon pairs surrounding an atom causes the pairs to be oriented as far apart as possible.
\
2
New cards
AXe Notation
A= element, X= # of atoms bonded to central atom, E= pair of unshared electrons.
3
New cards
Metallic bonds are
bonds between two metal atoms.
4
New cards
Ionic bonds are
attractions between oppositely charged ions (metal and nonmetal)
5
New cards
covalant bond
a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Two nonmetals.
6
New cards
Hydrogen bonds are
weaker molecule bonding. Involves Nitrogen, ,oxygen, and flourine. hydrogen bonding is weaker than an ionic or covalent bond
7
New cards
Group
A column on the periodic table (vertical, up & down) determines number of valance electrons
8
New cards
Period
A horizontal row of elements in the periodic table. Shows energy level.
9
New cards
octet rule
States that atoms lose, gain or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons
10
New cards
duet rule
Hydrogen and Helium only want two electrons
11
New cards
Enthalpy
Measure of heat that is produced or absorbed in a chemicle reaction
12
New cards
Polar dissolves
polar
13
New cards
nonpolar dissolves
nonpolar
14
New cards
Bond strenght least to greatest
Hydrogen, Nonpolar covalant, polar covalant, ionic
15
New cards
Hydrogen bonds and Ice
The hydrogen bonds to the oxygen atoms. causing ice to form. allows ice to be less dense than liquid water.
16
New cards
1 calorie = ____ joules
4\.184
17
New cards
1000 calories = ___ kcal
1 kcal
18
New cards
1000 Joules is _______________ KJ
1 kJ
19
New cards
1000 calories = __ Calories
1 Calorie
20
New cards
STP (standard temperature and pressure)
temp: 0 celcius = 273 kalvin. \n PRessure: 22.4 l \n 22.4 l =
21
New cards
Pressure, temperature, and volume relationships
When pressure goes up, volume goes down: \n volume goes up, temp goes up.
\
\
22
New cards
Daltons law of partial pressure
the total pressure exerted by a mixture of gasses is the same as the particle pressures of all the gasses present. pTotal = P1 + P2.
23
New cards
homogeneous solution
mixture (all parts look the same)
24
New cards
heterogeneous solution
A mixture in which different parts can be easily distinguished
25
New cards
aqueous solution
a solution in which water is the solvent
26
New cards
Solvent
Substance present in the largest amount
27
New cards
solute
other substances in the solution.
28
New cards
Titrations
method of finding normalty of adding another substance with a known molarity. NaVa = NbVb. If finding molarty, convert N to M before doing caluclation so the units are the same
29
New cards
Oxidization
Lose electrons (+)
30
New cards
Reduction
Gains electrons (-)
31
New cards
Arrenenius acid and base
Produces (H+) and (OH-)
32
New cards
Brownsted acid and base
Donates Protron(acid) and accepts protron(base)
33
New cards
what kind of compound is a salt
ionic compound
34
New cards
electronegativity trends on the perioic table are the same as
ionization energy
35
New cards
0-0.4
nonpolar covalent
36
New cards
0\.5-1.7
polar covalent
37
New cards
1\.8+
ionic
38
New cards
nonpolar covalent
electrons shared between nonmetals, often the same element (02), electronegativity differnece 0-0.4
39
New cards
polar covalent
unequal sharing of electrons between nonmentals, electronegativity difference 0.5-1.7
40
New cards
valance electrons
electrons in the outermost energy level, can be found based on group number on the periodic table
41
New cards
pauli exculusion principle
each orbital can have a maximum of 2 electrons and they must have opposite spins
42
New cards
hunds rule
if a sublevel has more than 1 orbital, then the electrons will not “pair up” until all the orbitals have one electron.
43
New cards
Atomic size increases
as you move left and down
44
New cards
ionization energy increases
as you move up and right
45
New cards
chemical activity in metals increases
as you move left and down
46
New cards
chemical activity in nonmentals increases
as you move up and right
47
New cards
electronegativity increases
as you move up and right
48
New cards
delta H
change in enthelapy
49
New cards
to calculate delta H
T Chart:
\-take grams of element/compound in the problem
\-take the molar mass of that compound
\-Put one mole above the molar mass
\-put the number of moles in the problem below and across the 1
\-Put the delta H or KJ of heat above the number of moles in the problem
\-multiply the numbers on top and divide each number in the bottom
\-take grams of element/compound in the problem
\-take the molar mass of that compound
\-Put one mole above the molar mass
\-put the number of moles in the problem below and across the 1
\-Put the delta H or KJ of heat above the number of moles in the problem
\-multiply the numbers on top and divide each number in the bottom
50
New cards
specific heat capacity
Q (energy in J) = s (specific heat capacity) x m (mass in g) x (Tfinal-Tinital) (temperature in degrees c)
51
New cards
bond strength
amount of energy needed to break a chemical bond,
triple double single (greatest to weakest)
Hydrogen, Nonpolar covalant, polar covalant, ionic (weakest to greates)
triple double single (greatest to weakest)
Hydrogen, Nonpolar covalant, polar covalant, ionic (weakest to greates)
52
New cards
Boyle’s Law
P1V1 = P2V2
inversley related, one goes up other goes down
temperature constant
inversley related, one goes up other goes down
temperature constant
53
New cards
Charels’s Law
V1/T1 = V2/T2
Directly related, one goes up other goes up
pressure constant
Directly related, one goes up other goes up
pressure constant
54
New cards
combined gas law
(P1V1)/T1 = (P2V2)/T2
55
New cards
ideal gas law
pv=nrt
r=0.08206, universal gas constant
r=0.08206, universal gas constant
56
New cards
Dalton’s Law Calculation
\-Find number of moles of each substance using molar mass and t charts
\-Find partial pressures of each using P = nrt/v
\-Add the partial pressures together to find the total pressure
\-Find partial pressures of each using P = nrt/v
\-Add the partial pressures together to find the total pressure
57
New cards
to find kelvin
add 273 to c
58
New cards
to find celcius
subtract 273 from k
59
New cards
concentrated
lots of solute in it
60
New cards
dilute
little solute in it
61
New cards
Molarity =
moles of soulute/liters of soultion
62
New cards
finding mass of the solution using molarity
times the volume by molairty
63
New cards
finding volume of the solution using molairty
divide the mass by the molarity
64
New cards
solubility
how much solute can complelty dissolve in a solvent
65
New cards
saturated
solution that has dissolved all the solute it can at a specific temperature
66
New cards
unsaturated
solution that has NOT dissolved all the solute it can at a specfic temperature
67
New cards
supersaturated
a solution that has more solute dissolved in it than normally possible at a given temperature
68
New cards
solubility usually increases as
the temperature of the solution increases
69
New cards
how to speed up the process of dissolving
\-stir
\-raise the temperature
\-increase the surface area
\-raise the temperature
\-increase the surface area
70
New cards
Absolute zero
0 Kelvin
\-273 Celcius
\-273 Celcius
71
New cards
Acids
\-H+
\-taste sour
\-Ph 0-6
\-Proton Donor
\-taste sour
\-Ph 0-6
\-Proton Donor
72
New cards
Bases
\-OH-
\-taste bitter
\-Ph 8-14
\-Proton Acceptor
\-Soapy/Slippery
\-taste bitter
\-Ph 8-14
\-Proton Acceptor
\-Soapy/Slippery
73
New cards
the subscript of H or OH tells
if the acid or base is mono, di, or triprotic.
The larger the subscript, the more acdic or basic the substance will be.
The larger the subscript, the more acdic or basic the substance will be.
74
New cards
Normality
moles of H or OH/liters of solution
75
New cards
if you already have the molarity
multiply by the mono, di, or tri for the normality (if given normality, divide by these to find molarity)
76
New cards
when doing oxidation and reduction problems
single elements = 0
compounds = charges on pink sheet
compounds = charges on pink sheet
77
New cards
Balancing half reactions
2 products = oxidation (smaller to bigger)
1 product= reduction (bigger to smaller)
1 product= reduction (bigger to smaller)
78
New cards
reactions occur when activation energy is
supplied by collisions
79
New cards
catalysts work by
lowering activation energy
80
New cards
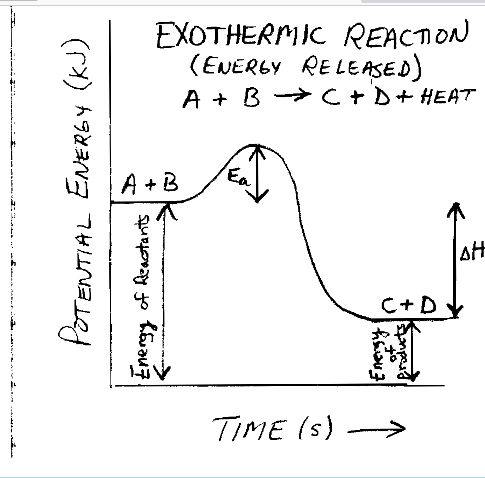
be able to know and label this
exothermic energy diagram
81
New cards
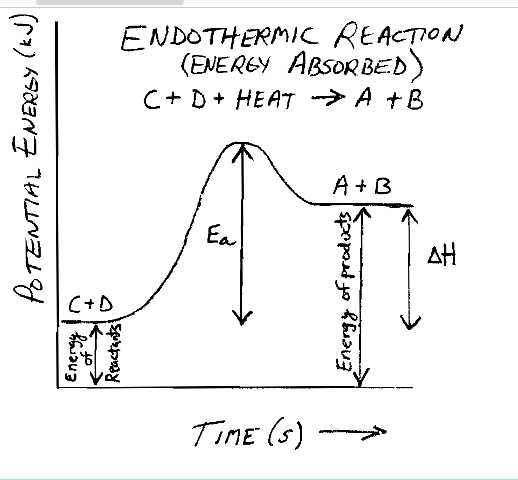
be able to know and label this
endothermic energy diagram
82
New cards
exothermic energy
\-detla H, heat is released
83
New cards
endothermic energy
\+delta H, heat is absorbed
84
New cards
homogeneous equllibrilluim
substances that are present in the same physical state
85
New cards
heterogeneous equllibrilluim
involves substances in more than 1 physical state
86
New cards
noble gases are
not reactive
87
New cards
pressure
the constant bombardment of the walls of a container by the moving molecules of a gas
88
New cards
factors that affect the speed of a reaction
\-nature of reactants
\-temperature of reactants
\-presence of a catalyst
\-temperature of reactants
\-presence of a catalyst
89
New cards
Nuteralized subatances (H20 and salt)
have a ph of 7