MSCI 324: Comparative Anatomy of Tetrapods Intro
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomical features (mostly bones) common to all tetrapods
Last updated 4:12 AM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
1
New cards
Superior
Anatomical direction referring to the “head” end of an organism.

2
New cards
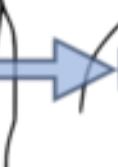
Medial
An anatomical direction going toward the middle line of an organism’s body.
3
New cards
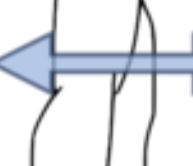
Lateral
Anatomical direction going away from the middle line of an organism’s body.
4
New cards
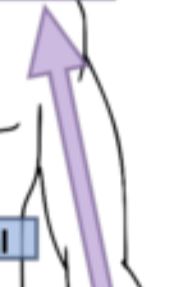
Proximal
The anatomical direction on a limb which leads to its point of attachment/the main body.
5
New cards
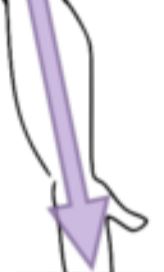
Distal
Anatomical direction on a limb leading away from its point of attachment/the main body.
6
New cards
Anterior
The anatomical direction describing the front/underside of an organism.
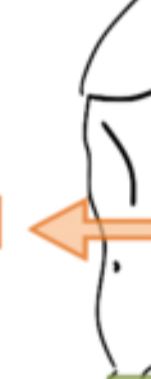
7
New cards
Posterior
The anatomical direction which describes the back or topside of an organism.
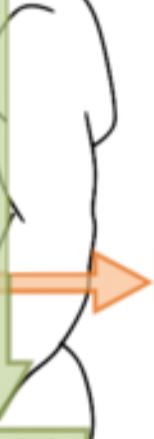
8
New cards
Inferior
The anatomical direction which is away from the head, i.e. at the opposite end.

9
New cards
Cephalic
Alternative term for the anatomical direction going toward the head.
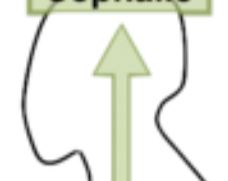
10
New cards
Caudal
Alternative term for the anatomical direction which goes away from the head.
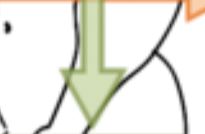
11
New cards
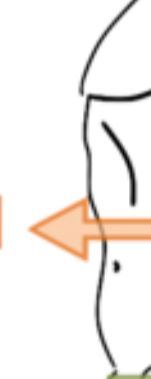
Ventral
Different term for the anatomical direction for the front/underside of an organism.
12
New cards
Dorsal
Alternative term for the anatomical direction of the back or topside of an organism.
13
New cards
Quadrupedal
An organism that walks on four legs.
14
New cards
Bipedal
Organism that walks on two legs.
15
New cards
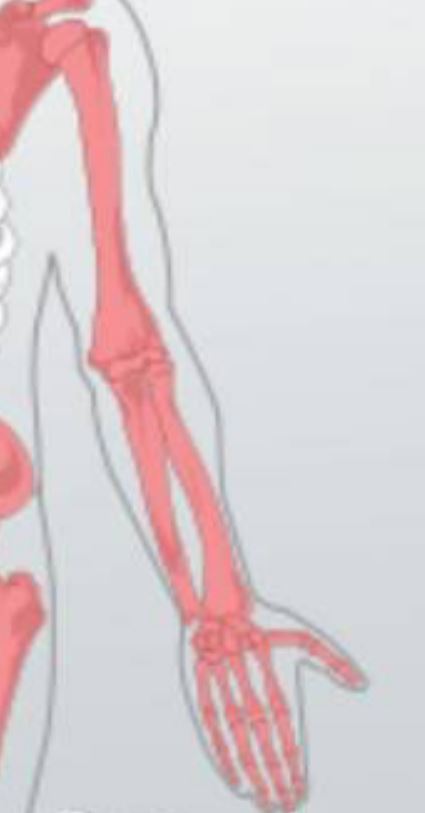
Appendage
A structure that is attached to the main body.
16
New cards
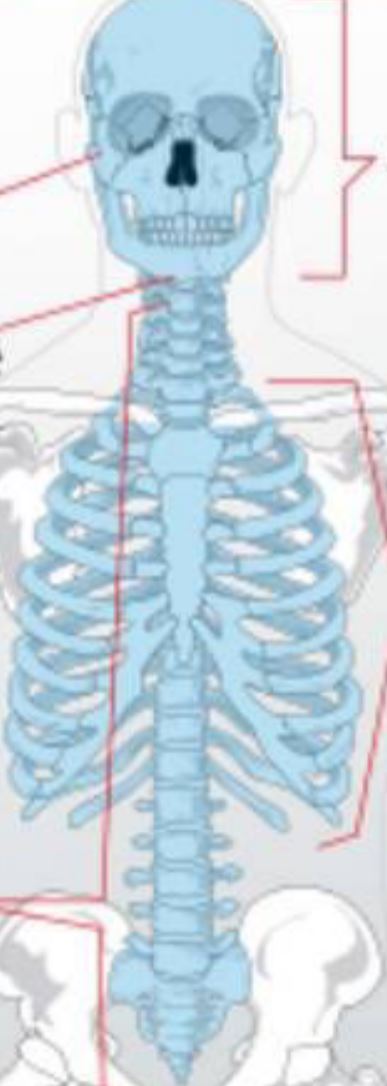
Axial Skeleton
The part of the skeleton composed of bones in the core body, like the skull, ribcage, and vertebra.
17
New cards
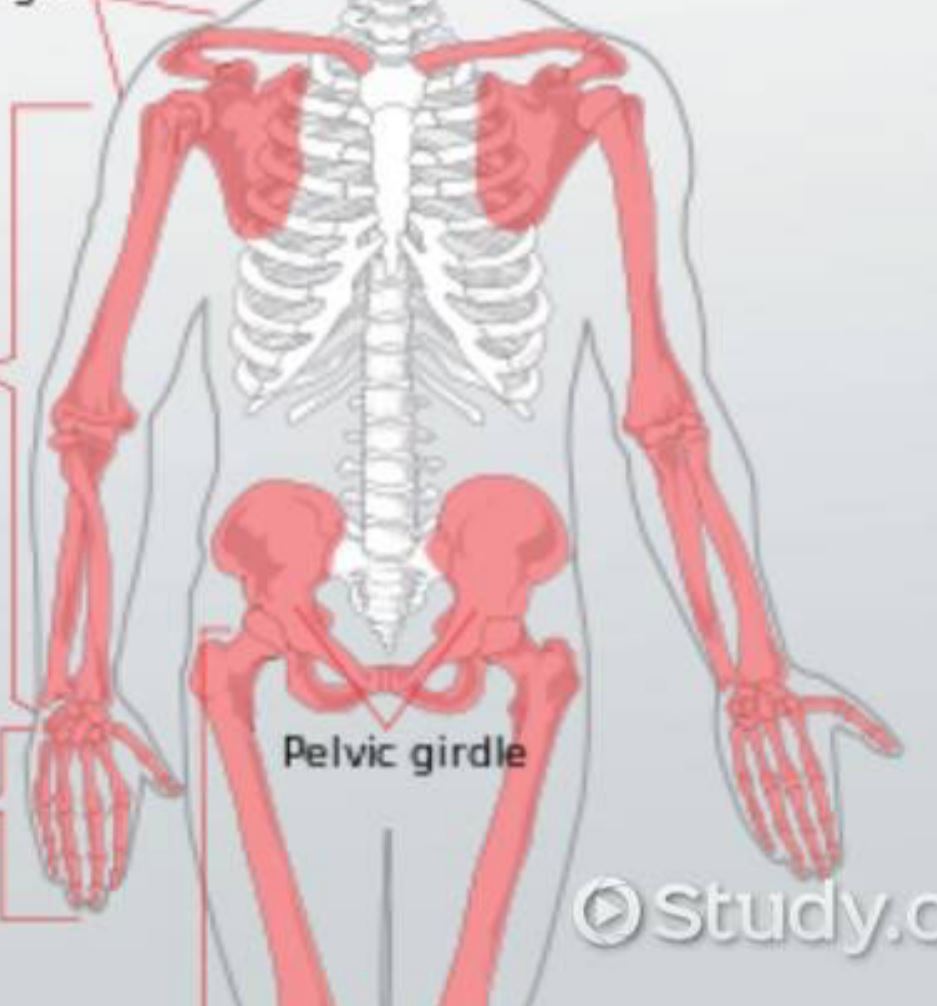
Appendicular Skeleton
A part of the skeleton which consists of appendages.
18
New cards
Ossicles
Inner ear bones.
19
New cards
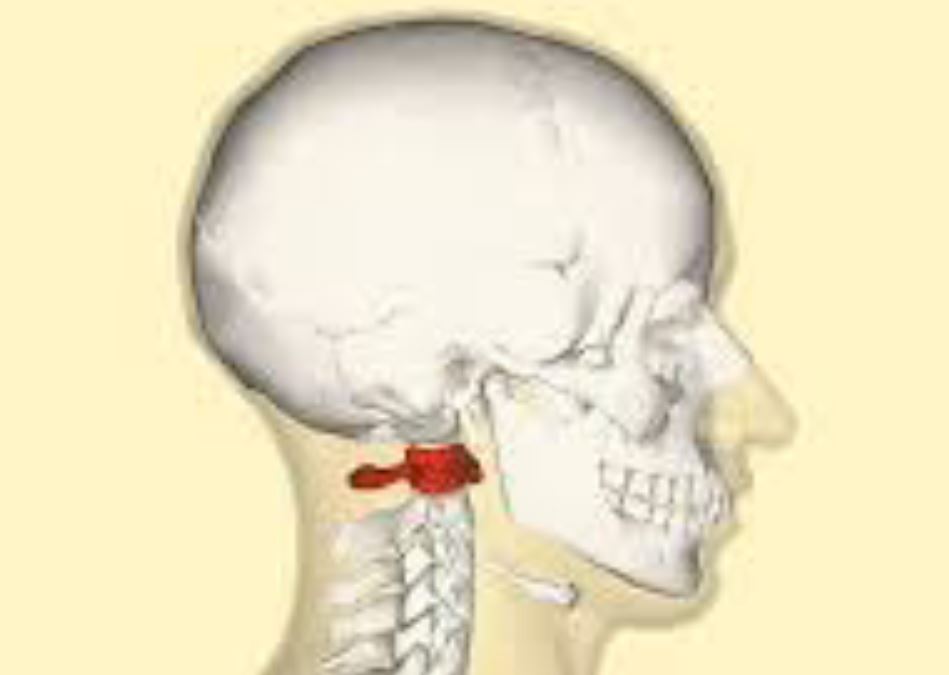
Atlas
Topmost vertebra.
20
New cards
Axis
Second topmost vertebra, forms joint connecting skull and spine.
21
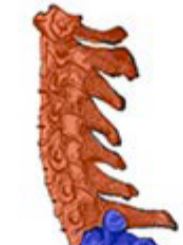
New cards
Cervical vertebrae
Top section of vertebrae, usually 7 in number.
22
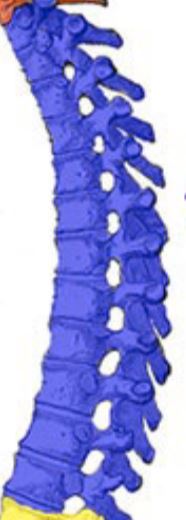
New cards
Thoracic vertebrae
Long section of vertebrae, making up the upper back of the organism.
23
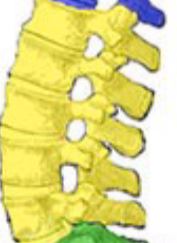
New cards
Lumbar vertebrae
Relatively short section of vertebrae, forms the lower back.
24
New cards
Sacrum
A structure composed of fused vertebrae, the base of the spine.
25
New cards
Coccyx
The base of the tail, or a vestigial tail structure.

26
New cards
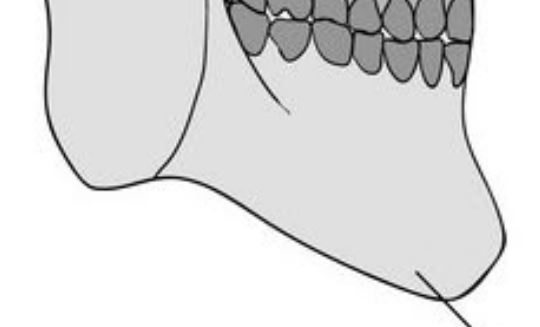
Mandible
Lower jawbone.
27
New cards
Maxilla
Upper jawbone.

28
New cards
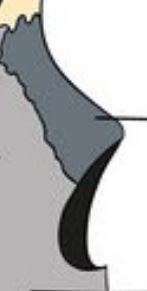
Nasal bone
Bone which forms the bridge of the nose.
29
New cards
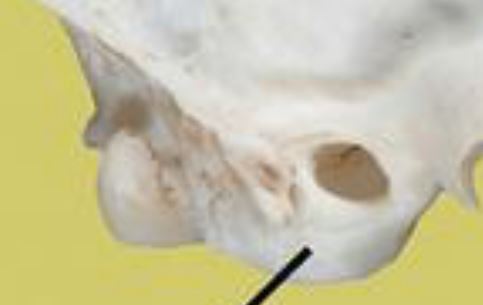
Auditory bulla
Hollow, rounded structure in the skull partly enclosing the middle and inner ear.
30
New cards
Supraorbital process
A bony elongation located above the eye socket
31
New cards
Zygomatic arch
Bridge of bone extending from the temporal bone (side of the skull) to the maxilla.

32
New cards
Sagittal crest
Ridge of bone running lengthwise along the midline at the top of the skull.

33
New cards
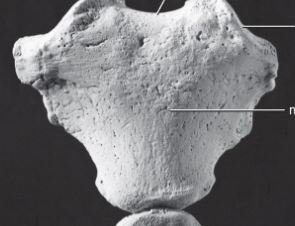
Sternum
Long, flat bone located in the center of the chest.

34
New cards
Manubri sterni
Upper part of the sternum.
35
New cards
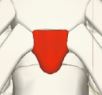
Xiphoid process
Cartilaginous extension of the lower part of the sternum.
36
New cards
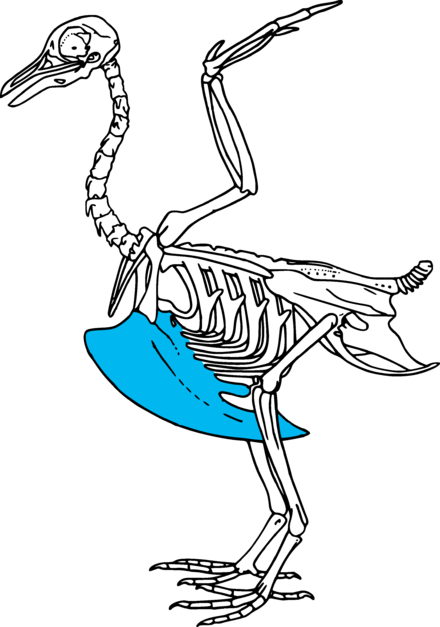
Keel
Extension of the sternum found in birds.
37
New cards
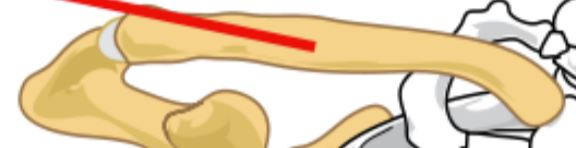
Clavicle
Bones that stretch ventrally across the shoulders, help form the shoulder girdle.
38
New cards
Scapula
A pair of bones that lie dorsally along the chest cavity, help form the shoulder girdle.
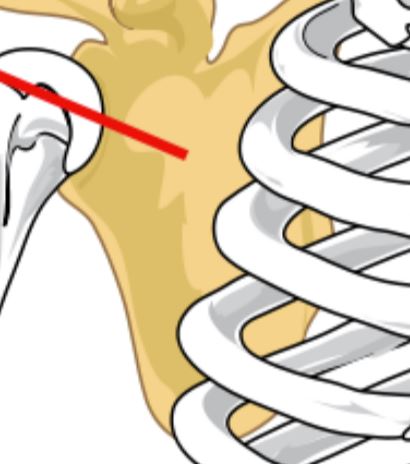
39
New cards
Humerus
Long bone in the upper arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow.
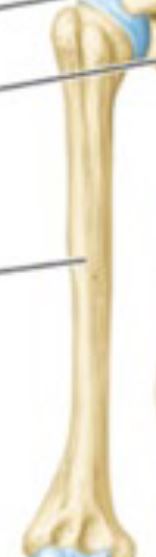
40
New cards
Radius
One of two bones that makes up the forearm, on the lateral side.
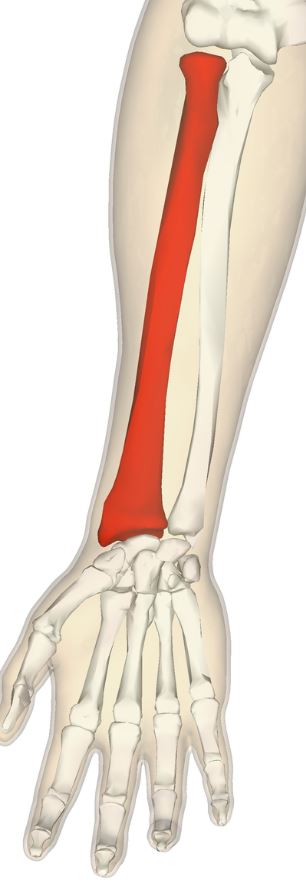
41
New cards
Ulna
One of two bones that makes up the forearm, on the medial side.
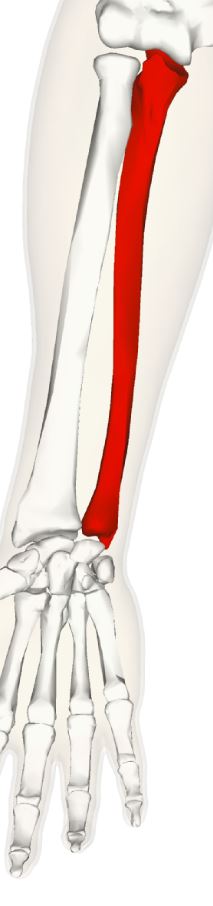
42
New cards
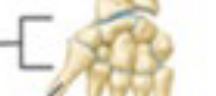
Carpals
Bones of the wrist, connect the bones of the forearm to hand bones.
43
New cards
Metacarpals
Bones of the hand.

44
New cards
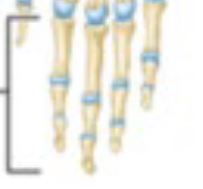
Phalanges
Bones of the fingers.
45
New cards
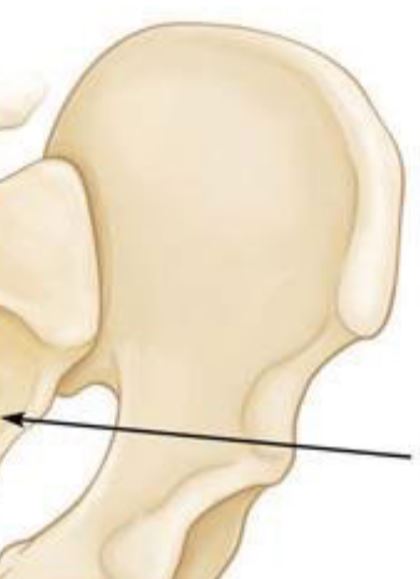
Ilium
Large, broad pair of bones forming each half of the pelvis.
46
New cards
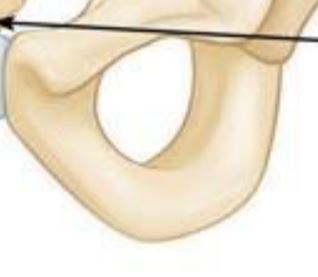
Ischium
Curved bone forming the base of each half of the pelivs.
47
New cards
Pubis
Pubic bones, at the front of the pelvis.
48
New cards
Femur
Superior bone in the leg, forms the thigh.

49
New cards
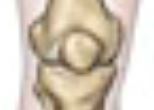
Patella
The knee cap, protects the joint between the upper and lower leg bones.
50
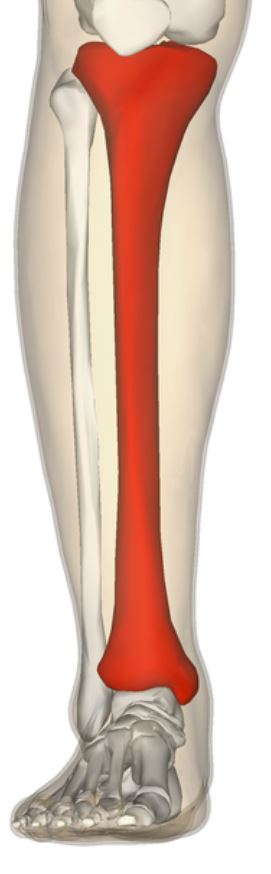
New cards
Tibia
Larger of the two bones in the lower leg, connected to the knee and ankle joints.
51
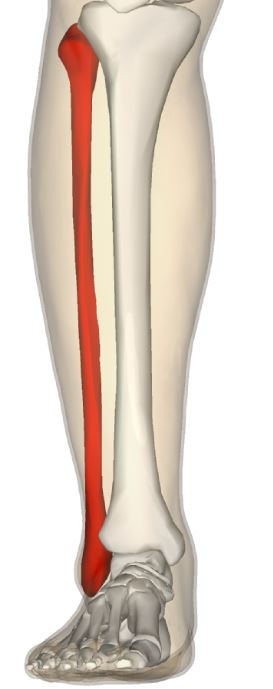
New cards
Fibula
Smaller of the two bones in the lower leg, supports the tibia.
52
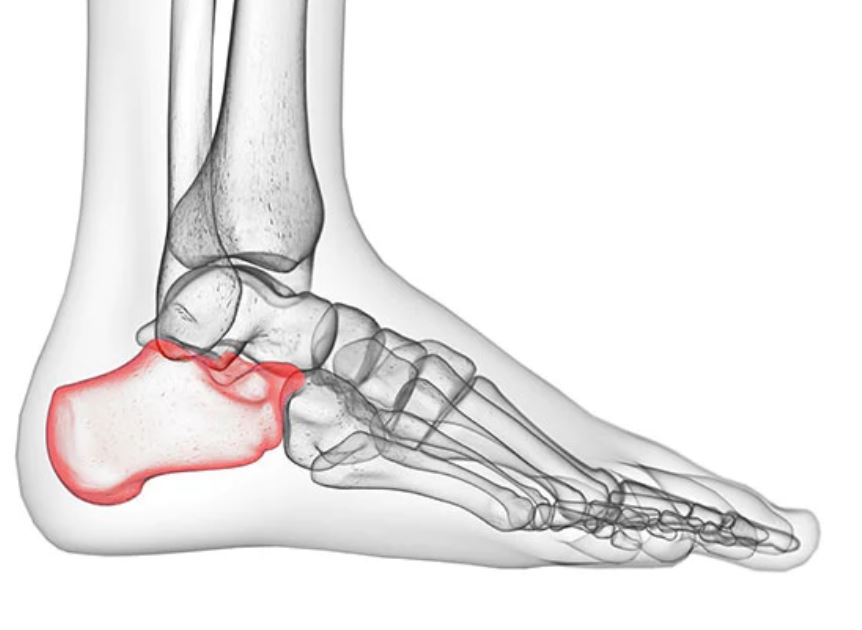
New cards
Calcaneus
Bone of the tarsus which constitutes the heel in primates and the hock in some other species.
53
New cards
Tarsals
Short, angular bones that make up the ankle.
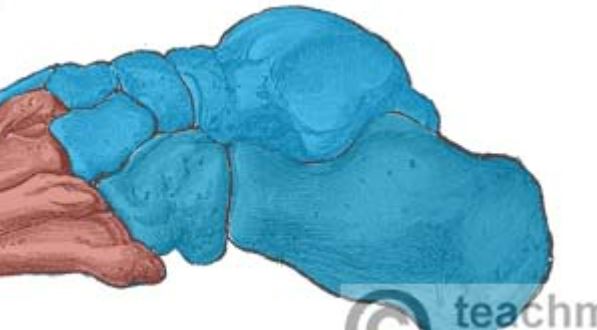
54
New cards
Metatarsals
Five bones that make up the feet.
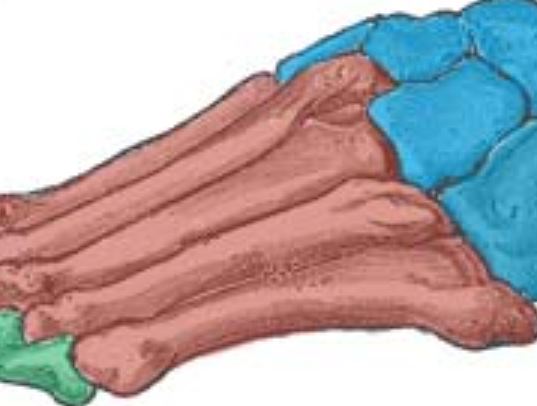
55
New cards
Phalanges (feet)
The bones that make up the toes.
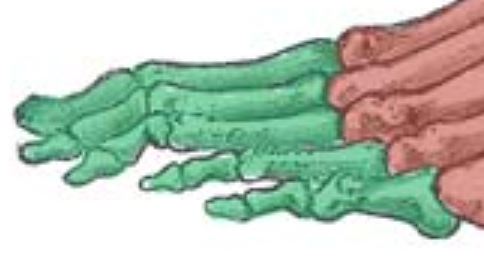
56
New cards
Plastron
Ventral side of a turtle’s shell.

57
New cards
Carapace
Dorsal side of a turtle’s shell.
