Oc pham: ocular anesthetics
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
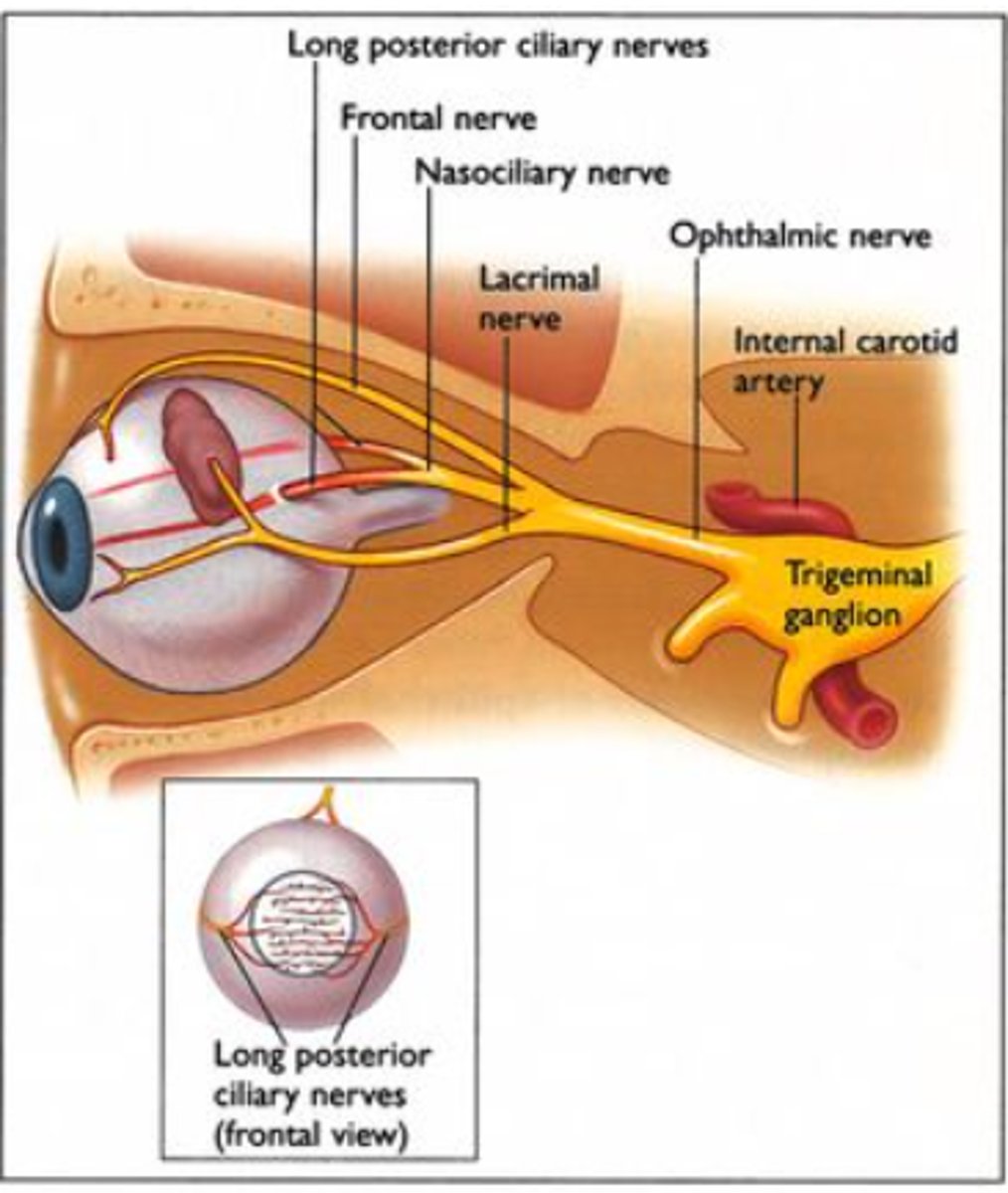
cornea is innervated by what nerve
nasociliary branch of ophthalmic nerve
ability to sense pain
algesia
ability to perceive sensation
esthesia
movement
kinesia
list 3 parts of anesthetic chemical structure
amine = hydrophilic
aromatic = hydrophobic
intermed chain = potency/tox
Aromatic and Amine groups help with absorption
Ester anesthetics :
what metabolizes them, longer/shorter duration vs amide?
Benoxinate
tetracaine
proparacaine
plasma cholinesterase
shorter duration
amide anesthetics :
what metabolizes them, longer/shorter duration vs amide?
lidocaine
liver
longer
ester/amide which more likely allergic
ester --> karaan allergic proparacaine
pH anesthetics, how do tears impact penetration?
weak base
Instillation into the tears (ocular surface)
• Tears are neutral to slightly basic pH which increases non-ionized form
of the molecule
• Enhancing ability to penetrate the nerve cell membrane
• pH of instillation site may increase/decrease effects of
anesthetic
Anesthetics- Mechanism of Action
Na+ channel blocker
• Prevents Na+ from entering the nerve cell
• Prevents depolarization- no action potential formation
• No generation of nerve impulse
anesthesia • Onset: ___ after instillation
15-20 seconds
anesthetic Prolonged duration when paired with ____
epinephrine --> vessel constriction so slow breakdown.
anesthetics are pre cat ___
C --> no human studies may be risk
• Most used topical anesthetic
0.5% Proparacaine HCl solution
duration of 0.5%, 1% tetracaine, 0.5% proparacaine, 0.25% benoxinate/fluoroscein, lidocaine
Tetracaine HCl 0.5%
Duration: 20 min
Tetracaine HCl 1.0%
Duration: 1 hour
Proparacaine HCl 0.5%
Duration: 15 min
Proparacaine HCl 0.5%/Sodium Fluorescein 0.25% - 15 minutes
lidocaine
30-60 min
May be good option for tonometry on contact lens wearers
0.35% Disodium Fluorexon/0.4% Benoxinate HCl solution
vs normally use 0.25% sodium fluoroscein/0.4% benoxinate HCL
Only amide topical anesthetic available
0.35% Lidocaine HCl solution
longest duration topical anesthetic
1.0% tetracaine --> 1 hr (cataract surgery_
ADR ocular anesthetics (esters)
Desquamation of corneal epithelial cells
• Occurs within minutes after topical instillation
• Can reduce visual acuity
• Results in corneal staining
• Conjunctival injection/hyperemia
• Lacrimation
• Photophobia
• Induce dry eye signs/alter dry eye
measurements
Limit drop use:
• Tetracaine: 7 drops
• Proparacaine: 14 drops
treatment for blepharoconjunctivitis, potential cause?
topical steroid --> note allergy to ester anesthetics in chart
_____ is added to anesthetic to prolong anesthetic
action and promote hemostasis
epinephrine
local anesthesia contraindicated in what conditions?
• Angle closure glaucoma
• Brain injury
• Coronary insufficiency
• Peripheral vascular disease
• Labor and delivery
DO NOT USE EPINEPHRINE IN:
contaminated wounds
MAO inhibitors
peripheral vascular disease
disorders that Epinephrine should be used with caution
• Stable Diabetics
• Hypertension
• Ateriosclerosis
• Thyrotoxicosis
• Heart Block
• Cerebrovascular disease
what local anesthetic can be used for contaminated wounds and vascular diseases,
lidocaine --> cause vasodilate not constrict like others w epinephrine
what local anesthetic can be used for cardivacular risk, cerebrovascular risk?
lidocaine --> cause vasodilate not constrict like others w epinephrine
what local anesthetic can be used for nerve block?
lidocaine --> cause vasodilate not constrict like others w epinephrine
what local anesthetic Useful in highly vascular areas like the eyelids
Lidocaine + Phenylephrine
Lidocaine + Phenylephrine duration
60-400 minutes