Academic Team State Science 2017-2023 and Regionals 2023 Science plus 2015 state
1/1113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1114 Terms
Lorentz factor
a term that designates how much an object's time, space, & mass are altered as a result of its motion. The factor is very close to 1 except at speeds approaching the speed of light.
equal to 1 when velocity is zero. Used to make relativistic corrections in measurements. Time slows down the faster you go so try to find that in relation to Earth's time. so if time of moving object asked, then denominator, if time of earth object, then 1/. it could be 1 in the numerator or whatever time the mover perceives has passed.
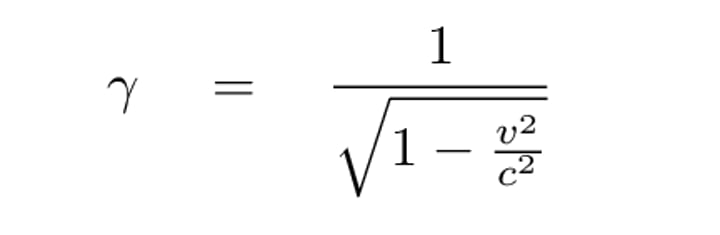
2021 State Written Assesment
N/A
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
Stimulates adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids (cortisol). THis hormone is produced by the master gland though. Overproduction of this hormone reuslts in Cushing's disease.
Cortisol
stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex and stimulated by ACTH
Gherin
a hormone released by the stomach that signals the hypothalamus of the brain to stimulate eating
IGF-1
insulin-like growth factor 1 This has immediate effects, whereas HGH has a longer loading period. increases lean body mass,1 helping you burn fat, and builds up physical endurance.
Buccinator
Used to suck in your cheeks, compresses them
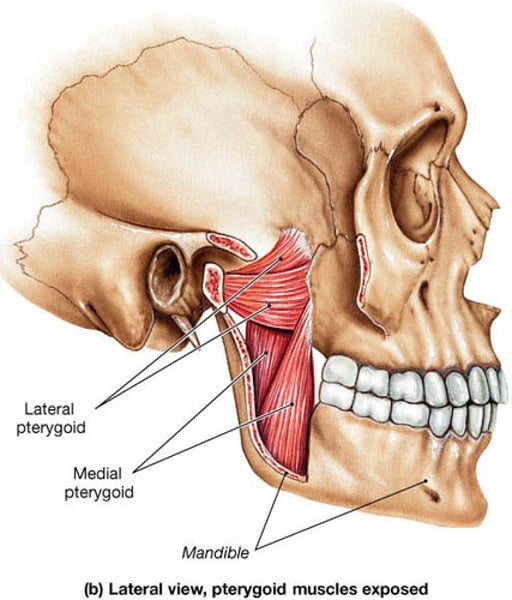
Medial Pterygoid
elevates mandible and moves it from side to side
Zygomaticus major
retracts and elevates corner of mouth for smiling
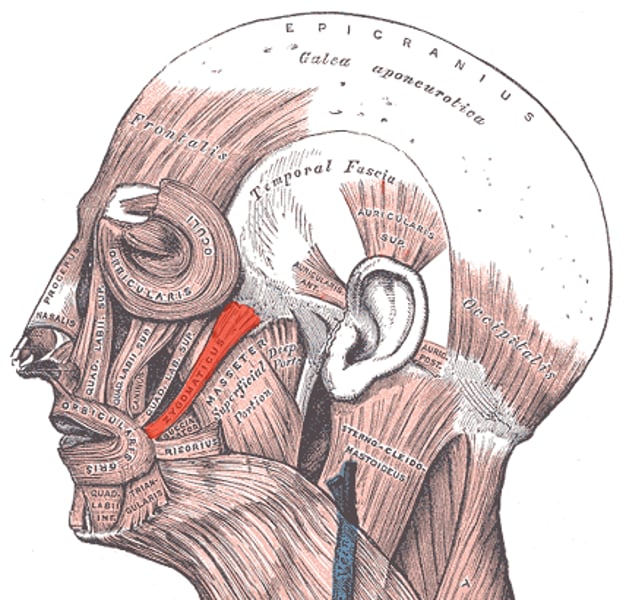
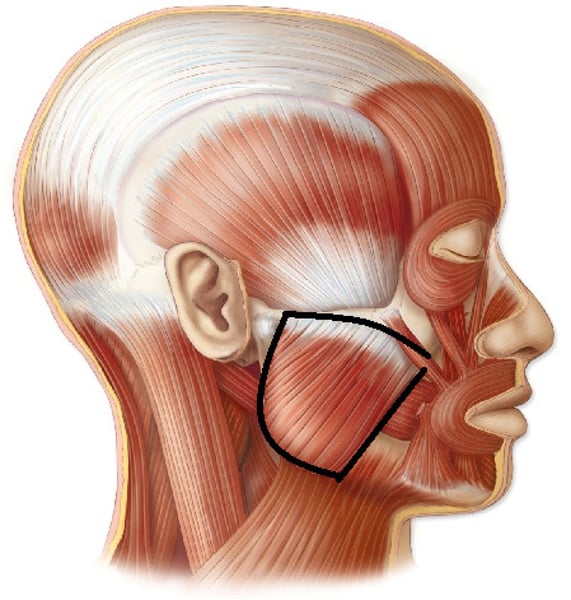
Masseter
one of the primary muscles of mastication (chewing). This is primarily responsible for the elevation of the mandible and some protraction of the mandible.
L-Dopa
A drug for Parkinson's disease that contains the precursors to dopamine and catecholamine neurotransmitters (dopanime, epinephrine etc.) THis is hydroxylated tyrosine. Easily passes through blood brain barrier
GABA
An inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. γ-Aminobutyric acid, or this, is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
5-HTP
precursor of serotonin, used by people who want to self-medicate for insomnia, depression and anxiety
Monoamine Oxidase
an enzyme that breaks down and thereby inactivates monoamine transmitters. a class of enzymes that destroy the monoamines: dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. Monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin and the catecholamines dopamine, adrenaline, and noradrenaline.
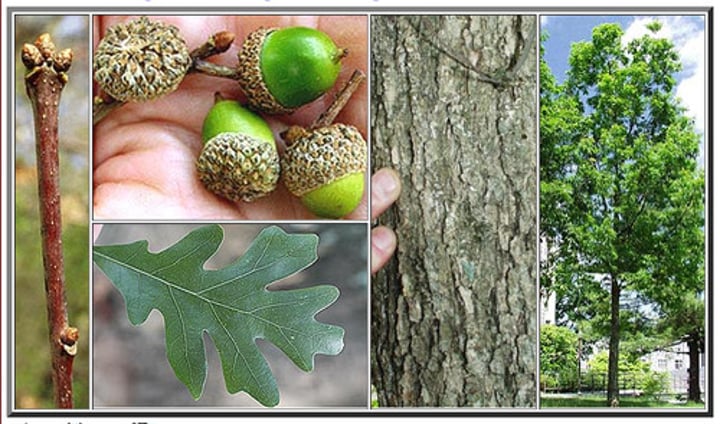
Quercus
genus of oaks that produce acorn seeds and are in the north

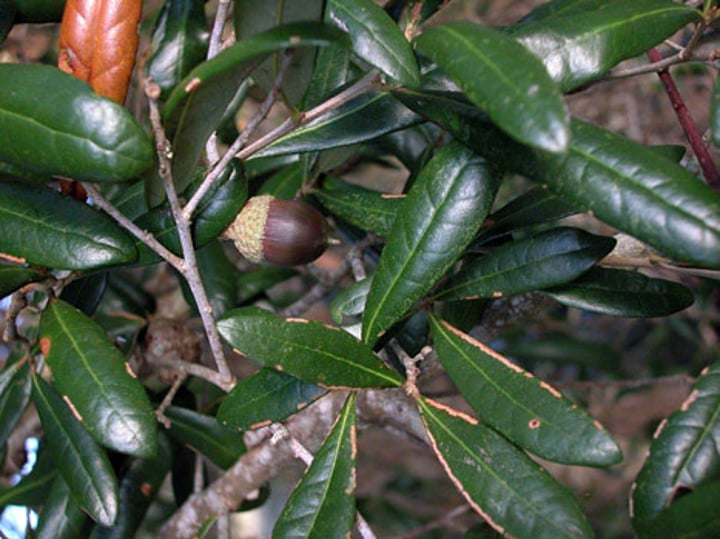
Fagaceae
Beech Family
Beech, oak, chestnuts, AMericanc chestnut, pin oak, and chinkapin

Acer genus
maple's genus
Prunus
Plum plant genus
Odnata
taxon of dragonflies and damselflies (suborder of damsel is zygoptera)
hemiptera
taxon of true bugs including bed bugs, assassin bugs, and shield bugs
Hymenoptera
A family of insects that includes bees, wasps, ants, and yellow jackets.
Diptera
flies and mosquitoes
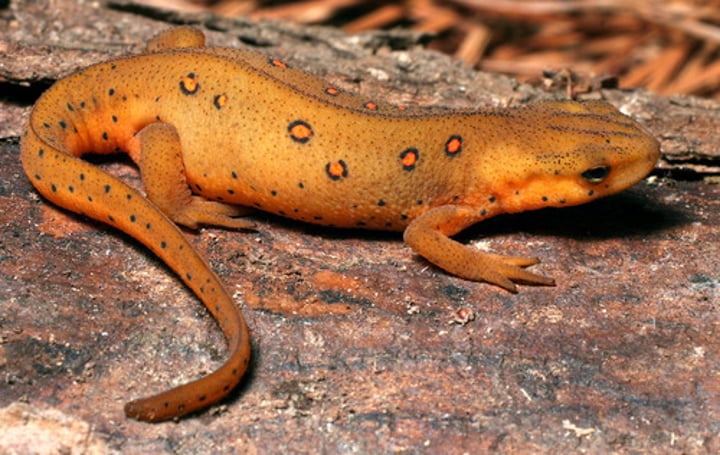
Newts
amphibious salamanders that live on land but return to the water for breeding

Caecilians
Worm-like, legless amphibians found in the tropics, gymnophiona. Segmented

homeobox
a DNA sequence, around 180 base pairs long, that regulates large-scale anatomical features in the early stages of embryonic development.
HER2
growth factor PROTEIN highly activated in cells of certain types of breast cancer. Helps the cells grow quickly. Actually an over-stimulated protein kinase on cell membrane
ras gene
a G protein that relays a signal from a growth factor receptor on the plasma membrane to a cascade of protein kinases. A gene that codes for namesake protein, a G protein that relays a growth signal from a growth factor receptor on the plasma membrane to a cascade of protein kinases, ultimately resulting in stimulation of the cell cycle.
Hemizygous
the presence of only one allele for a characteristic, as in X-linkage; makes descriptions of dominance and recessiveness irrelevant. an individual who has only one member of a chromosome pair or chromosome segment rather than the usual two.
pyruvate dehydrogenase
converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA.
- stimulated by insulin
- inhibited by acetyl-CoA
G3P dehydrogenase
G3P to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. an enzyme that catalyzes the sixth step of glycolysis and thus serves to break down glucose for energy and carbon molecules.
chiasmata
The X-shaped, microscopically visible region representing homologous chromatids that have exchanged genetic material through crossing over during meiosis. Visible is diplotene stage of prohase I
synaptonemal complex
A zipper-like protein structure that causes replicated homologs to become physically connected during prophase of meiosis I; sets the stage for crossing over.
Centromeres
Located in the center of the "X", they hold the chromatids together in a chromosome. They also help the chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers.
Capsomeres
identical protein subunits that spontaneously self assemble to form the capsid. Subunits. in an icosahedral shape
Proteomes
all of the proteins that a given cell makes; a set of proteins produced in an organism, system, or biological context
Spikes on virus
They are essential for attachment of the virus to the host cell [glycoprotein keys]. not only play a critical role in attachment to host cell surfaces via receptor-specific interactions, as shown above, but they also facilitate the approach of viruses to cell surfaces before the attachment
spongiform encephalopathy
Degenerative disease due to prion protein. 4 types are Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD), Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome, fatal familial insomnia, and kuru.
Scrapie
prion disease in sheep
Kuru
Prion disease suffered by the Fore due to consuming humans through cannibalism specifically by consuming the brains/nervous system of the dead. Symptoms include insomnia, lack of coordination/balance, eventually death. Contracted from infected beef. Spongifrom enephalopy
Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome
Prions Inheritable transmissible spongiform encephalopathy misfolded prion proteins general: long incubation periods, neuronal loss, lack of inflammation response; Early stages: failing memory and lack of coordination; Late stages: involuntary movements, dementia, seizures, coma, blindness, loss of coordination
blackwater
Water that contains feces and urine; also called "sewage". Water from toilets and urinals that is considered under all codes to be wastewater. Some states also consider water from kitchen sinks, showers, and bathtubs to this.
Lentic Ecosystems
still water (ponds, lakes and wetlands); aquatic ecossytem
Lotic Ecosystems
flowing water (streams and rivers); an aquatic ecosystem
Riparian ecosystem
Transition zone between a terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem
Kroll process
a pyrometallurgical industrial process used to produce metallic titanium from titanium tetrachloride. This process replaced the Hunter process for almost all commercial production.
Electron affinity
the amount of energy that is liberated whenever a molecule or a neutral atom tends to acquire an electron from the other elements.
bond-dissociation energy
the energy required to break the bond between two covalently bonded atoms
Fugacity
Tendency to escape a certain phase; at vapor liquid equilibrium, this quantity of both phases are equal
critical pressure
the lowest pressure at which a substance can exist as a liquid at the critical temperature. the temperature above which, a gas cannot be converted to liquid even by application of pressure. At the critical temperature, the pressure required to convert the gas into liquid is known as this
Fermi energy
For a metal, the energy corresponding to the highest filled electron state at 0 K. By the Pauli exclusion principle, we know that the electrons will fill all available energy levels, and the top of that "Fermi sea" of electrons is called this. the energy difference between the highest and lowest occupied single-particle states in a quantum system of non-interacting fermions at absolute zero temperature.
Critical temperature
the temperature above which a substance cannot exist in the liquid state. the temperature above which vapor cannot be liquefied no matter what pressure is applied
pKa and Ka
Strong acids have this as less then -1.74 and a high this
Weak acids have high this and low this
Strontium
87-isotope is stable of this. 90-isotope=nuclear fallout. Abosrbed by bone, 30 unstable isotopes
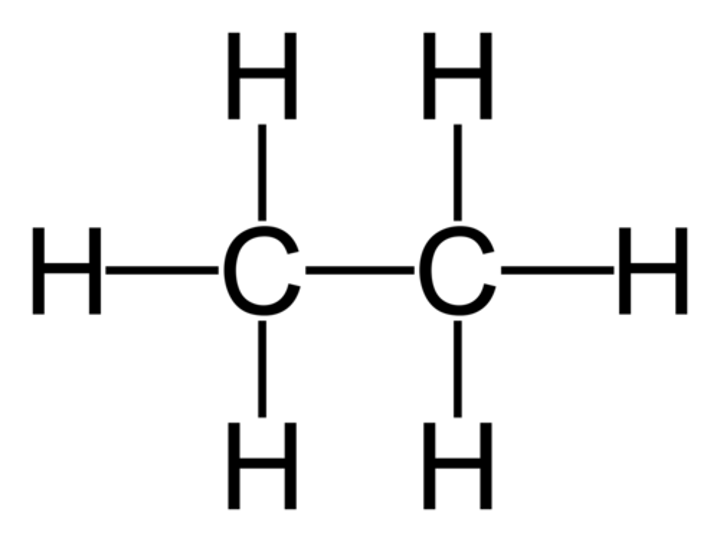
Aliphatic
A compound containing carbon and hydrogen joined together in straight chains, branched chains or non-aromatic rings. Can be a ring but must be single bonds unlike benzene
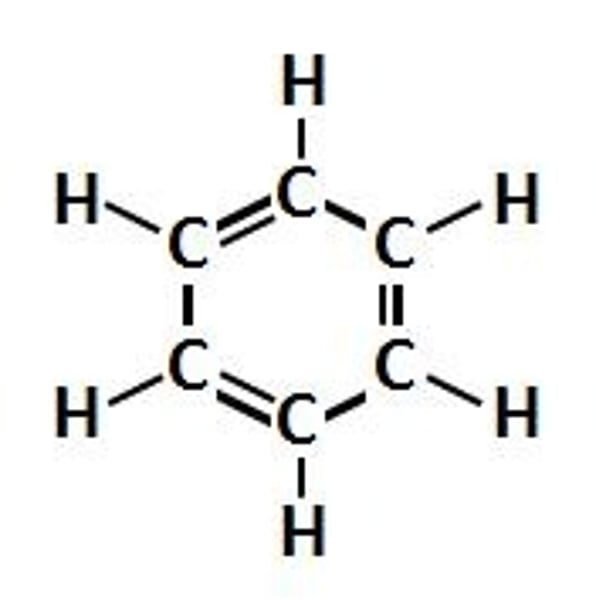
aromatic compound
a compound that contains the ring structure of benzene. must have a benzene ring of alternating single and double bonds.
Amphiphatic
A molecule that has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions.
olefin
also called alkene, compound made up of hydrogen and carbon that contains one or more pairs of carbon atoms linked by a double bond.
Grignard Reaction
A carbonyl addition reaction between a Grignard reagent (R-MgX) with an aldehyde or ketone to produce an alcohol.
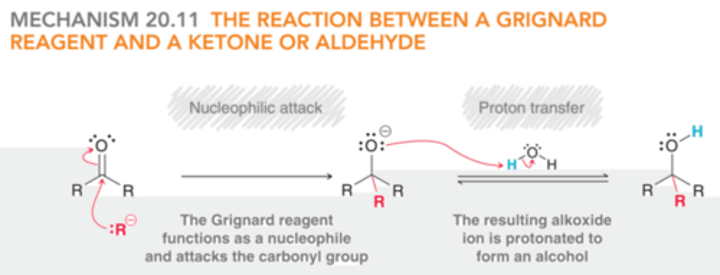
benzaldehyde
benzene with aldehyde
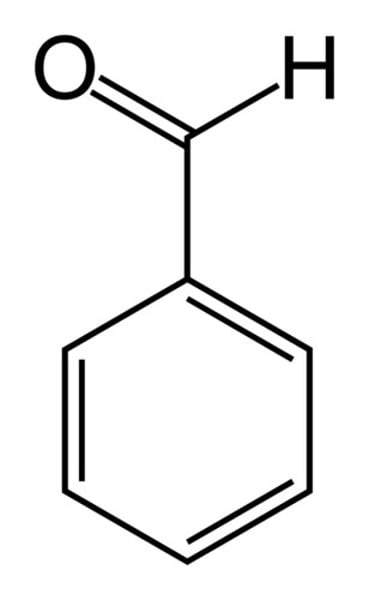
chlorobenzene
IUPAC rules for aromatic compounds
1. the substituent name is placed as a prefix to the name of aromatic compounds. For example, a benzene ring attached to a one-nitro group is named as nitrobenzene.
2. If two bromo- groups are attached to the adjacent carbon atoms of the benzene ring, it is named as 1,2-dibromobenzene. applicable to other groups too.
3.When different substituted groups are attached to the aromatic compounds, the substituent of the base compound is assigned number one and then the direction of numbering is chosen such that the next substituent gets the lowest number. Substituents are named in alphabetical order. For example: when chloro and nitro groups are attached to the benzene ring, we first locate the chloro group then nitro groups.
Also, for IUPAC, the alkanes/methyl groups have the lowest priority and so you must start from the other side that has more priority
block and tackle pulley
a system of pulleys made of fixed and moveable pulleys; can have large mechanical advantages
Hero's engine
The earliest steam engine; it was able to actually do work, but it was a revolutionary idea.
Atwood's machine
2 masses attached by a string that is threaded through a pulley; a system of pulleys made of fixed and moveable pulleys; can have large mechanical advantages. masses connected by a massless string on massless pulleys. Eiffel tower ex.
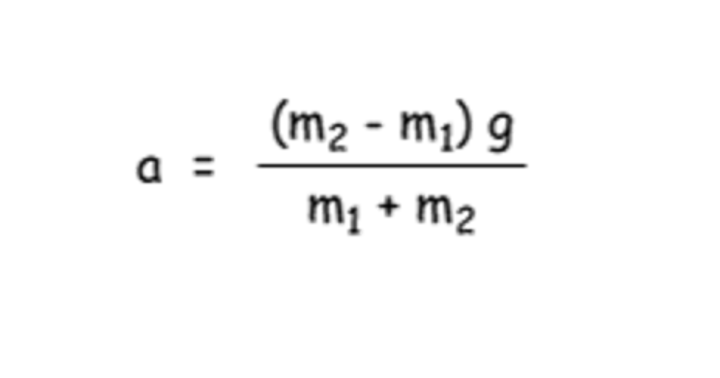
Brownian ratchet
a class of models for directed transport using Brownian motion that is rectified through the input of energy. For a diffusing particle, the energy is used to switch between two states that differ in their diffusive transport processes. This behavior results in biased diffusion.
Feynman's sprinkler
a sprinkler-like device which is submerged in a tank and made to suck in the surrounding fluid. The question of how such a device would turn was the subject of an intense and remarkably long-lived debate
Chinese Room
: a thought experiement devised by john Searle to show that computers lack intentionality ( two doors, a book that translates symbols from English to Chinese, cant understand what the symbols mean though, convince two people outside the room that you understand Chinese)
Szilard's engine
does not allow us to generate energy out of nothing, but it does provide that subtle link between energy and information.
elastic collision formula
m1v1+m2v2=m1v′1+m2v′2,m1v1+m2v2=m1v′1+m2v′2,
where the primes (') indicate values after the collision

inelastic collision formula
m₁v₁ᵢ+m₂v₂ᵢ=(m₁+m₂)vᶠ

lens equation
1/f = 1/do + 1/di
relates the distance of the object from the lens, the distance of the image from the lens, and the focal length of the lens.
do is the distance of the object from the lens, di is the distance of the image from the lens, and f is the focal length of the lens.
Mitscherlich's law
predicts which chemical compounds have the same crystal structures.
Paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and ferromagnetism IN A magnetic field
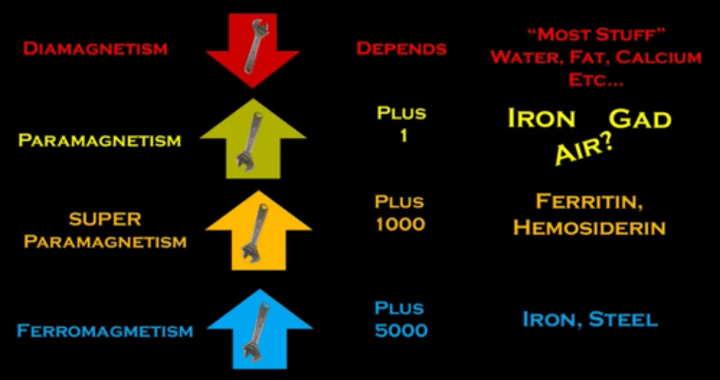
No applied magnetic field for paramagnetism, diamagnetims, and ferromagnetsm
Para: random motion
Ferro: up
Dia: none
Centaurs
Icy planeotids originated from the Kuiper belt found between Jupiter an neptune. Ex. Hidalgo, Echidna, Typhon
Plutinos
Objects by Pluto but far enough from Neptune, that they are able to maintain an orbit around the sun.. One of the icy Kuiper belt objects that, like Pluto, are caught in a 3:2 orbital resonance with Neptune.
Trojans asteroids
Asteroids that circle the Sun following Jupiter's orbit. a small celestial body (mostly asteroids) that shares the orbit of a larger body
Phosphine
Detected this substanxe in the clouds of Venus. the biosignature gas that may be present in Venus
Enceladus
A moon of Saturn, has been seen shooting out plumes of liquid water so it is thought to be habitiable
Kaolinite
a white to cream-colored clay produced by the weathering of feldspar
Spodsol
1. more acidic
2. type of forest soil
3. conifer cover
4. coniferous forests
type of soil in taiga biomes
mollisol
Soils with thick (usually 10 inches or more), dark surfaces that have a base
saturation of 50 percent or more in the surface soil.
-found in Florida
grassland soil
Alfisol
Soil type found in deciduous forests. moderately leached soils that have relatively high native fertility. These soils have mainly formed under forest and have a subsurface horizon in which clays have accumulated. are primarily found in temperate humid and subhumid regions of the world.
Found in temperate forests
Histosols
High organic content and wet
water saturated, organic soils, like those found in a swamp or marsh
- EX: Okefenokee Swamp of GA
oxisol
a thick, weathered soil of the humid tropics that is largely depleted of fertility and nutrients
found in tropical rainforests
Cygnus X-1
Binary System with a Blue Supergiant and a compact Object which is likely a Black Hole. The Blue Supergiant is a variable star. - nearest black hole to earth
- about 6,070 light years distant from earth
First proposed black hole. It is an intense x-ray source neat Eta Cygni and is thought to be a black hole in orbit around the 9th-magnitude blue supergiant about 8,000 light-years away in our own galaxy. First such source widely accepted to be a black hole
Ton 618
a hyperluminous, broad-absorption-line, radio-loud quasar and Lyman-alpha blob[2] located near the border of the constellations Canes Venatici and Coma Berenices
Messier 31
AKA andromeda galaxy
bright enough to be seen by the naked eye on dark, moonless nights. The Andromeda Galaxy is the only other (besides the Milky Way) spiral galaxy we can see with the naked eye.
Sagittarius A
The powerful radio source located at the core of the Milky Way Galaxy. An objecy that possesses a supermassive black hole. 2020 nobel prize in physics for this.= for Ghenzel and Ghez
FarFarOut
The most distant verified object in our solar system. 20 billion km.
Oumuamua
An Asteroid from another solar system that passed into our solar system in 2018. Looks oddly like a Baguette. The first confirmed object from another star to visit our solar system, this interstellar interloper appears to be a rocky, cylinder-shaped object with a somewhat reddish hue. The object, by its discoverers, is up to one-quarter mile (400 meters) long and highly-elongated—perhaps 10 times as long as it is wide.
Labrynthodonts
earliest amphibians; carboniferous period, considered to be the common ancestors of terrestrial vertebrates
Acanthodians
Any of a group of ancient jawed aquatic vertebrates from the Silurian and Devonian periods. Group of jawed fishes, characterized by large spines in their fins from which sharks may have originated and that represents Chondrichthyes, which includes living sharks, rays, and chimaeras.
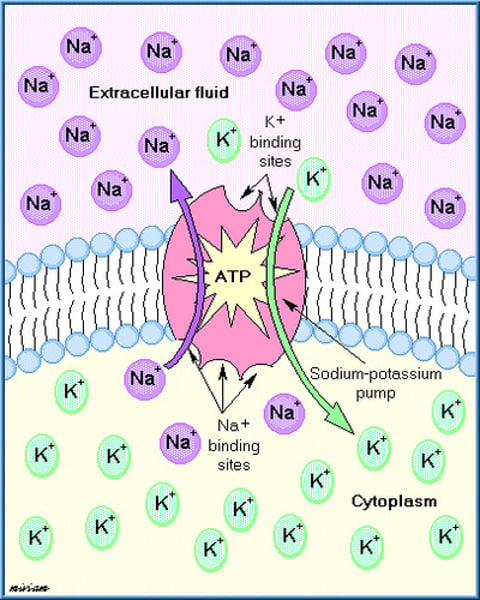
sodium potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell. Net charge outside the membrane is +1 because 3 Na are pushed out for 2 K
Tinea
infection of the skin caused by a fungus. Ex. ringwomr causing athlete's foot and jock itch
Thrush
a fungal infection in the mouth and/or throat caused by Candida albicans and manifesting as white patches and ulcers
Impetigo
inflammatory skin disease with pustules that rupture and become crusted. bacterial skin infection characterized by isolated pustules that become crusted and rupture. caused by one or both of the following bacteria: group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus.
Mass spectrum
a graph of the data from a mass spectrometer, where m/z ratios of the deflected particles are plotted against the number of particles with a particular mass
End face centered monoclinic
A slanted cube type of cell
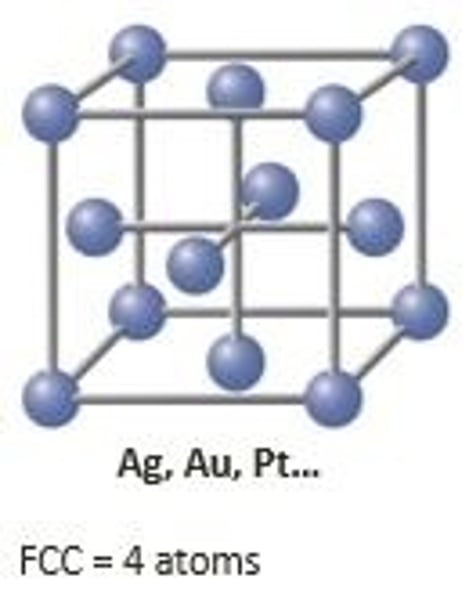
face centered cubic
include aluminum, copper, nickel, gamma iron, gold, and silver.