Health Assessment Unit 6
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Muscles
Over 600 muscles in the human body protect our bones.
Responsible for body movement
Three types of muscle
Cardiac
Smooth
Skeletal
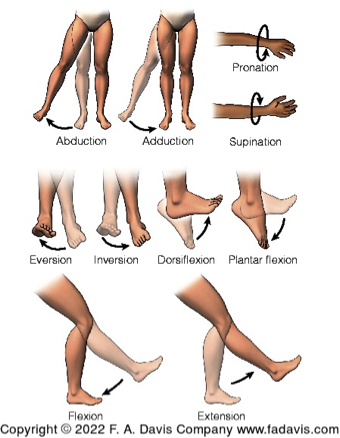
Types of Muscle and Joint Movements (Photo)
Be able to describe in words
Tendons
Tendons allow for the attachment of muscle to bones.
Tendon Injury Type
Strain
Ligaments
Ligaments attach bone to bone
Ligaments Injury Type
Sprain
Diagnostics (MSK System)
Blood test
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK)
X-ray
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Computed tomography (CT scan)
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan
Health History (MSK System)
Family history
Past surgical history
Past medical history
Nutrition
Pain assessment
Risk factors
Cultural considerations
Sequence of Assessment (MSK System)
Inspection
Palpation
Assessing range of motion
Assessing strength
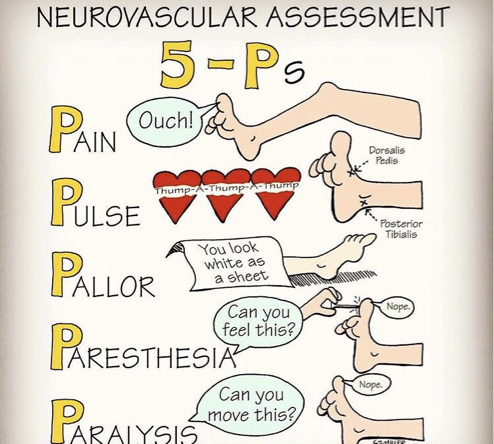
The Five “Ps”
“Five Ps” will help you to focus on specific musculoskeletal symptoms or injuries.
Pain
Paralysis
Paresthesia
Pallor
Pulselessness
Inspecting Gait
Technique
Have the patient walk away from you first and then back toward you.
Inspect any differences in leg swing and arm swing.
Assess the patient’s ability or inability to control any joints.
Assess if the patient uses any assistive devices.
Inspecting Gait
Findings
Normal Findings
Gait length is approximately 1.5 m for adults
Equal leg and arm swing
Arm swing contralateral
Smooth, even pattern
No assistive devices
Maintains balance easily
No limp
Expected motion
Abnormal Findings
Unequal leg and/or arm swing
Arm swing not contralateral
Pattern is not smooth or even
Using assistive device
Unable to maintain balance
Limping
Alterations in motion
Limited
Increased
Ataxia
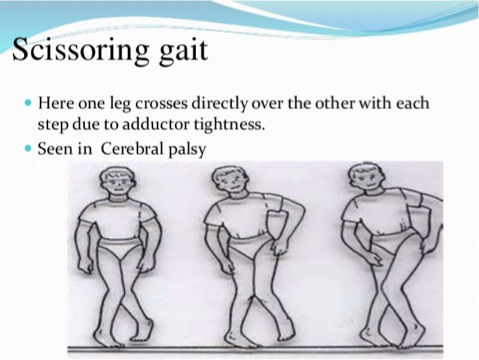
Scissors
Shuffling
Foot drop
Scissoring Gait
Foot Drop
A weakness or paralysis of the muscles of the lower leg or the inability to control plantar flexion of the ankle; it may indicate peroneal nerve injury or muscle or neurological disorders.
In this condition, the patient is unable to use the muscles to bring the foot into the neutral position (Fig. 16-10A).
This is where the foot is at 90 degrees to the lower leg, much like the letter L.

Inspecting Posture
Techniques
Inspect the patient’s posture while the patient is walking.
Is the head centered on the axial skeleton?
Is there an alteration in balance, ability to ambulate or stand?
Have patient sit in a chair and get up from a chair; note any difficulties in lowering or raising him- or herself.
Assess position of shoulders and head.
Ask patient to rotate (turn) the head to the right and then to the left.
Ask patient to tip the head to the right and then to the left.
Ask patient to flex and extend the neck.
Assess patient’s ability to stand and sit.
Ask the patient to bend forward at the waist; inspect the spinal curvature.
Ask patient to bend at the waist to the right and left, forwards and backwards.
Inspecting Posture
Findings
Normal Findings
When standing, feet are shoulder width apart
When standing and sitting, head centered on axial skeleton
When standing, weight is distributed evenly on both lower extremities
ROM of the neck and back are symmetrical
Abnormal Findings
Numbness or tingling
Head not centered on the axial skeleton
Limitations in ROM
Shoulders are not level
Motion of trunk is not symmetrical
Inspecting and Palpating Vertebral Column
Technique
Purpose: To assess for abnormalities in the structure of the vertebral column
Have patient stand.
Inspect alignment of vertebral column.
Using two or three finger pads, starting at the top of the vertebral column, palpate the vertebral column for tenderness, deviations, or protrusions.
Inspecting and Palpating Vertebral Column
Findings
Normal Findings
Vertebral column is straight
No pain or alteration of sensation
No deviations in any plane
No deformities found
Abnormal Findings
Presence of pain, tenderness, altered sensation
Deformities found
Scoliosis
Kyphosis
Lordosis
Protrusions or depressions
Scoliosis
An abnormal curvature of the spine that occurs in a lateral manner; it may look like a C or S on visualization and be palpable

Kyphosis
A curvature of the spine that looks like a slouching, or hunchback, posture; this can lead to problems with the contents of the thorax. This occurs in the thoracic spine

Lordosis
A curvature of the spine that looks like an arched lower back: it is an increased inward curvature of the lumbar spine

Inspecting and Palpating Upper Extremities
Technique
Always compare the right with the left side
Assess
Shoulder
Elbow
Wrist
Hand/fingers and joints
Using two or three finger pads, gently palpate the upper extremity on the right side.
Assess for
Tenderness
Depressions
Bulges
Changes in temperature
Repeat on the left side and compare sides.
Inspecting and Palpating Upper Extremities
Findings
Normal
Symmetry between right and left
No pain or alteration of sensation
No deformities found
Full range of motion
Some flexion of the fingers
No forward rounding of shoulders
Upper arms straight
Slight bend at elbow
Wrists in alignment with lower arm
Abnormal
Presence of pain, altered sensation
Deformities found
Limited range of motion
No symmetry between right and left
Forward rounding of shoulders
Upper arms not straight
No, or excessive, bend at elbow
Wrists not in alignment with lower arm
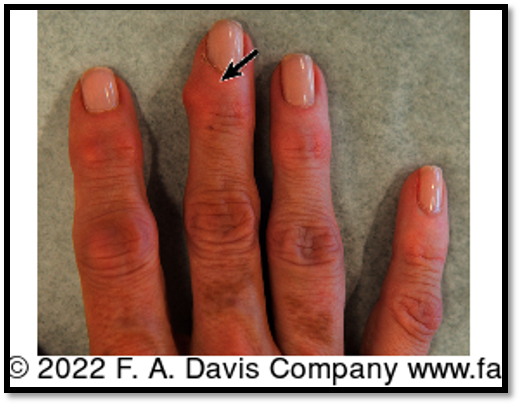
Bouchard’s Nodes
Bony enlargements on the proximal interphalangeal joints (PIP) joints; commonly seen in osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis

Heberden’s node
Bony enlargements on the distal interphalangeal joints (DIP); commonly seen in osteoarthritis

Assessing ROM and Muscle Strength of Upper Extremities
Technique
Ask the patient to perform specific motions independently first and then against resistance.
Assess ROM before strength.
Shoulder Movement
Flexion
Flexion against resistance
Extension
Extension against resistance
Abduction
Abduction against resistance
Adduction
Adduction against resistance
Internal rotation
Internal rotation against resistance
External rotation
External rotation against resistance
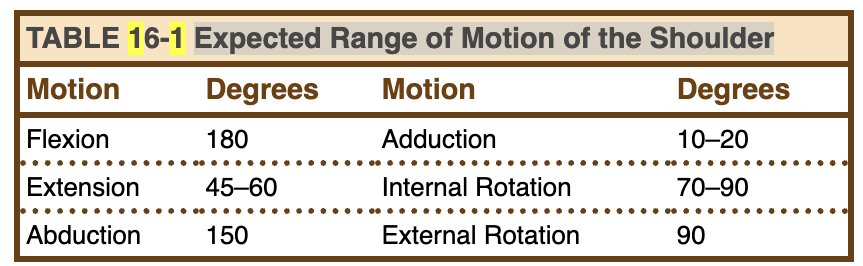
See Table 16-1 for expected ROM.
Expected Range of Motion of the Shoulder Table
Expected Range of Motion at the Elbow and Forearm Table

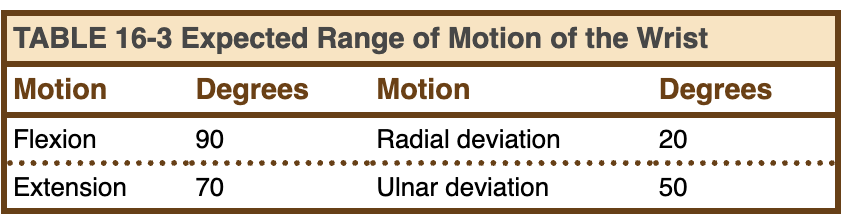
Expected Range of Motion of the Wrist Table
Elbow motion
Flexion
Flexion against resistance
Extension
Extension against resistance
Hand motion
Pronation of hand
Pronation of hand against resistance
Supination of hand
Supination of hand against resistance
Wrist Motion
Flexion
Flexion against resistance
Extension
Extension against resistance
Radial deviation
Radial deviation against resistance
Ulnar deviation
Ulnar deviation against resistance
Finger Motion
Flexion
Flexion against resistance
Extension
Extension against resistance
Assessing for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Tinel’s Test

Assessing for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Phalen’s Test

Grading Muscle Strength
0: Unable to contract muscle in a gravity eliminated position
1: Able to contract muscle slightly
2: Able to move joint in a gravity eliminated position
3: Able to move joint against gravity
4: Able to move joint with some resistance through range of motion.
5: Able to move joint with full resistance through range of motion
Assessing ROM and Muscle Strength of Upper Extremities
Findings
Normal
Symmetric ROM from right to left
Absence of pain or altered sensation
Strength equal from right to left
Strength between 4 and 5
Abnormal
Asymmetric ROM from right to left
Presence of pain or altered sensation
Unequal strength between right and left
Strength < 4
+Tinel’s or Phalen's test
Inspecting and Palpating Lower Extremities
Technique
Purpose: To assess for any abnormalities within the lower extremity
Ask patient to perform specific motions independently first and then against resistance.
Ask patient to perform the following ROM activities of the right and left lower extremity.
Inspect each extremity and compare the right side with the left side.
Palpating Lower Extremities
Hip
Knee
Ankle
Foot
Toes
Palpating Lower Extremities
Assess the presence of:
Tenderness
Depressions
Bulges
Temperature change
Inspecting and Palpating Lower Extremities
Findings
Normal
No pain or alteration of sensation
No deformities found
Symmetry between right and left
Weight placed on both legs evenly
Hips in neutral position
Slight bend at knee, pointed forward
Ankle is perpendicular to lower leg
Foot straight forward
Abnormal
Presence of pain, altered sensation, temperature change
Deformities found
Hallux Valgus
Hammertoe
No symmetry between right and left
Weight unevenly distributed to one side
Hips not in neutral position
No, or excessive bend at knee
Ankle not perpendicular to lower leg
Assessing ROM and Strength of Lower Extremities
Technique
Tell the patient you will be assessing each lower extremity separately and he or she will have to perform specific motions without assistance.
Assess any differences in symmetry of motion and the fluid nature of the motion.
Assess strength: Graded 0–5
Grading Strength of Muscle Chart

Hip Motion
Flexion
Flexion against resistance
Extension
Extension against resistance
Abduction
Abduction against resistance
Adduction
Adduction against resistance
Knee Motion
Flexion
Flexion against resistance
Extension
Extension against resistance
Foot Motion
Inversion
Inversion against resistance
Eversion
Eversion against resistance
Ankle Motion
Dorsiflexion
Dorsiflexion against resistance
Plantar flexion
Plantar flexion against resistance
Assessing ROM and Strength of Lower Extremities
Findings
Normal
Symmetric ROM from right to left
Motion is fluid and without pain
Absence of pain or altered sensation
Strength equal from right to left
Strength between 4 and 5
Abnormal
Asymmetric ROM from right to left
Motion is not fluid
ROM limitation
Presence of pain or altered sensation
Unequal strength between right and left
Strength < 4
Healthy People 2030 (MSK System)
Arthritis Goal:
Reduce pain and disability from arthritis (ODPHP, 2020)
Osteoporosis Goal:
Prevent fractures and disabilities related to osteoporosis (ODPHP, 2020)
Workplace Goal:
Promote the health and safety of people at work (ODPHP, 2020)
Chronic Pain Goal:
Reduce chronic pain and misuse of prescription pain relievers (ODPHP, 2020)
Ataxia
An unsteady gait that may be used to compensate for an injury or pain in the extremities. This may also indicate a problem with cerebellar function.
Scissors or Diplegic Gait
Most commonly seen in cerebral palsy. The legs cross the midline in a swinging fashion to compensate for lack of motion.
Female Reproductive System
Diagnostics
Mammogram
Needle biopsy
Sonogram
Papanicolaou test (Pap smear)
Human papillomavirus (HPV) test
Vaginal specimens
Menstrual History
Age of the start of menstruation
Date of last menstrual period
Regular or irregular
Menstrual cycle is expressed as X/Y
X = Duration
Y = Cycle
Number of days of bleeding
Type of absorbent products used
Amount of bleeding
Duration
Menstrual cramps
Primary dysmenorrhea
Secondary dysmenorrhea
Bleeding between cycles
Premenstrual syndrome
Bleeding after sexual intercourse
Menopause
Perimenopause
Post menopause
Amenorrhea
Metrorrhagia
Menorrhagia
Oligomenorrhea
Sexual Health
Ask questions about the “P’s”
New sex partners
Practices
Protection
Past history of STIs
Prevention of pregnancy
Additional questions: “Is there anything else about your sexual practice that I need to know about?”
Contraceptive History
Ask patient about contraceptive method
Birth control pills
Transdermal patch
NuvaRing
Subdermal hormonal methods
Diaphragm
Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
Cervical cap
Female/Male condom
Spermicide
Rhythm method
Breast Health
Breast surgeries
Mastectomy
Breast reduction
Breast examinations
Clinical breast exam (CBE)
Breast self-examination (BSE)
Mammogram – date of last test
Family history of breast cancer or breast disease
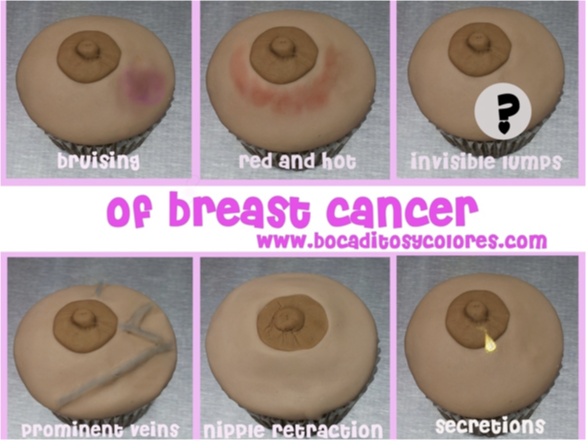
See Box 18-3 for Warning signs of breast cancer
Fibrocystic breast disease/cysts
Warning Signs for Breast Cancer
Lump.
Thickening or dense tissue felt inside the breast or underarm area.
Swelling, warmth, inflammation, or color changes.
Change in the size or shape of the breast.
Dimpling or puckering of the skin.
Itchy, scaly sore or rash on or around the nipple.
Retraction of the nipple or other parts of the breast.
Nipple discharge.
Pain in an area of the breast.
Risk factors for breast cancer
See Box 18-4.
Family history of one or more first-degree relatives.
• Inherited mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes.
• Advancing age.
• Obesity in advancing age.
• Moderate levels of alcohol.
• Combined hormonal therapy of estrogen and progesterone.
• Physical inactivity.
• Increased breast tissue density.
• Long menstrual period (periods that start early and/or end later in life).
• Oral contraceptives.
• Never having children.
• Having a child after age 30.
Breast concerns
Lumps
Pain in one or both breasts
Mastalgia is breast pain that usually is correlated to a woman’s menstrual cycle.
Tenderness
Breast nipple discharge
Skin changes
Axillary changes
Gynecological History
Past and present gynecological symptoms
Gynecologic cancers
Vaginal discharge, bleeding, or itching
Genital sores
Abdominal or pelvic pain
Painful urination
Infertility
Gynecological surgeries or procedures
Infertility
Vaginal discharge
Onset, duration, frequency, volume, and odor of discharge.
Normal vaginal discharge is clear but may turn white or yellow when exposed to the air.
Abnormal discharge
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Pelvic exam and PAP smear
Ask date of last exam/test
Gynecologic cancers
Gynecological symptoms
Use of external products such as douches
Pelvic pain
Gynecological History
Abnormal Discharge
Inspecting Female Breasts
Purpose: To assess the breasts for size, shape, color and abnormalities
Inspect the breasts in four different positions:
Seated with the arms hanging by each side
Seated with the arms placed over the head
Seated with the hands on the hips
Standing and leaning forward
Inspecting Female Breasts
Inspect the skin
Color
Contour
Edema
Lesions
Ulcerations
Texture of skin
Vascularity
Venous patterns
Inspecting Female Breasts
Inspect the areola
Shape
Color
Hair
Visible lumps
Inspecting Female Breasts
Inspect the nipples
Size
Position
Shape
Discharge
Crusting
Presence of accessory nipples
Inspecting Female Breasts
Inspect the signs of retraction
Dimpling
Puckering
Furrows
Eversion of Nipple

Inversion of Nipple
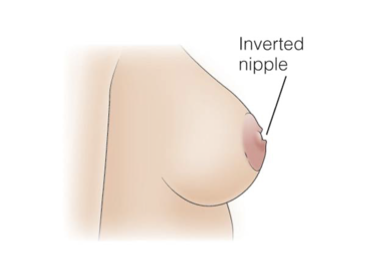
Paget’s Disease of the Breast
Picture
General Breast Assessment
Picture

Breast Appearances
Picture
Inspecting Female Breasts
Inspect the lower aspect of breasts
Symmetry
Skin changes
Nipple deviations
Inspecting Female Breasts
Inspect the axilla
Hair distribution
Skin texture
Protrusion of lumps or masses
Inspecting Female Breasts
Ask Patient before inspecting
Ask the patient to press her hands against her hips contracting the pectoral muscles and inspect:
Symmetry
Skin changes
Retraction areas
Nipple deviations
Ask the patient to stand and bend forward and inspect from the front and laterally:
Symmetry
Skin changes
Retraction areas
Nipple deviations
Inspecting Female Breasts
Normal Findings
Breasts are symmetrical
Color of skin is uniform
Areola is round or oval, uniform color
Montgomery tubercles are present
Nipples are centered, round, without discharge or crusting
Venous patterns are the same on both breasts
Inspecting Female Breasts
Abnormal Findings
Asymmetrical breasts
Erythema or signs of inflammation
Mastitis
Breast tissue retraction, lumps, or dimpling
Unilateral venous pattern
Peau d’orange
Palpating Female Breasts
Purpose: To assess for lumps, density of breast tissue, or breast masses
Equipment: Gloves (if needed)
Three pattern techniques:
Circular
Radial spoke
Vertical strip
The vertical strip method is superior for ensuring that all breast tissue is examined.
Palpating Female Breasts
Ask Patient before palpating
Assist or ask the patient to assume the supine position.
Ask the patient to take her right arm out of the gown sleeve and raise it above her head.
Stand on the patient’s right side.
Following one of the three patterns, using the finger pads of three fingers of your dominant hand, palpate the right breast and corresponding axillary area.
Palpating Female Breasts
While palpating, assess for:
Tissue density
Lumps, masses, or increased density
Shape
Consistency
Location (use a clock face to identify location, i.e., 1:00 o’clock)
Size
Moveable or fixed
Tenderness
Palpating Female Breasts
While palpating
Wear gloves if any history or nipple drainage or reports of nipple drainage.
Gently palpate the nipple and compress the nipple and areola between your thumb and index finger to assess for any discharge.
If discharge, note
Amount
Color
Odor
Consistency
Repeat steps on the left side.
Palpating Female Breasts
Normal Findings
No tenderness
No lumps
No increased tissue density
No nipple discharge
Palpating Female Breasts
Abnormal Findings
Tenderness or pain
Lumps or masses
Nipple discharge
Paget’s disease
Breast Self-Examination (BSE)
Breast cancer mortality can be effectively reduced through screening and awareness (ACOG, 2016).
Assess the patient’s understanding of
Breast self-awareness (BSA)
Breast self-exam (BSE)
How and when the patient is doing BSE
Male Reproductive System
Diagnostics
Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test is a blood test that measures the amount of PSA, a protein secreted by prostate epithelial cells.
Prostate biopsy procedure removes a sample of body tissue.
Urethral specimens are obtained in men with penile discharge.
Male Reproductive System
Health History
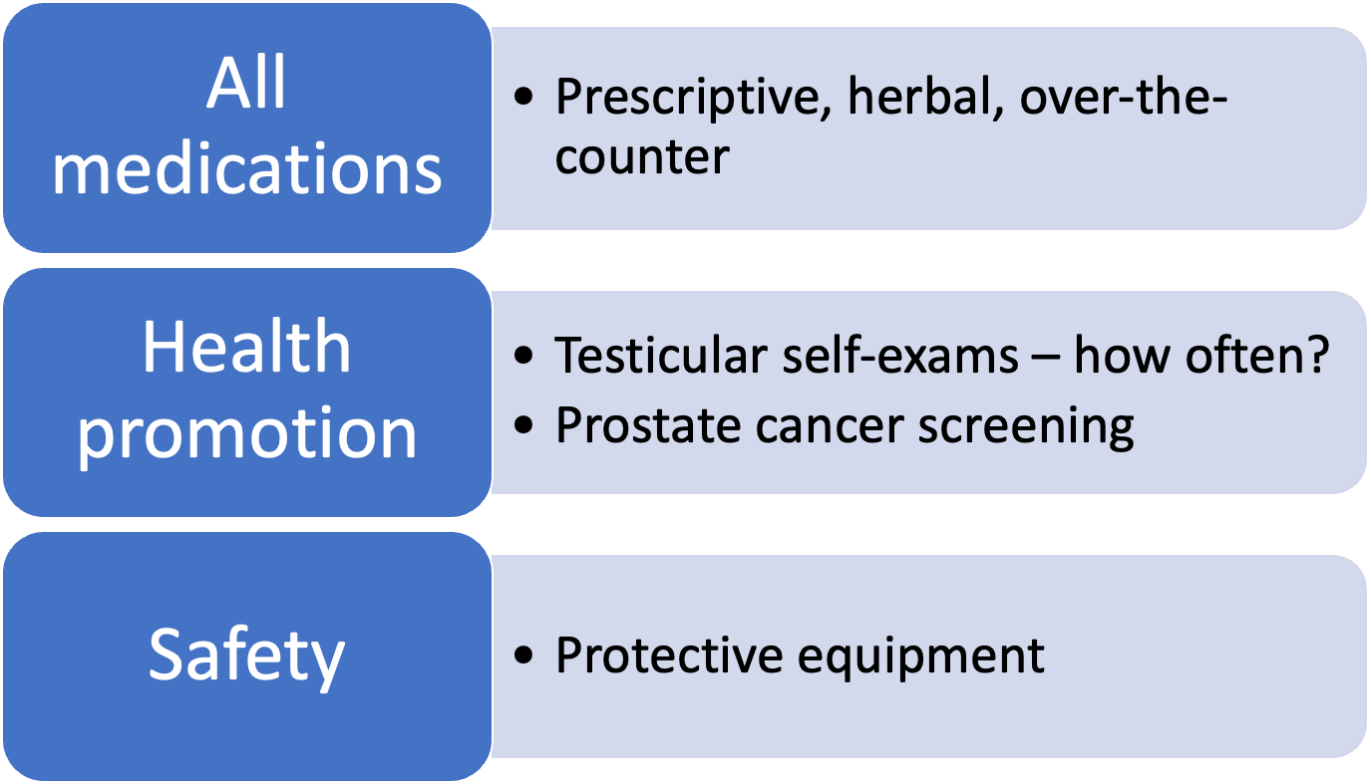
See Table 19-1 for risk factors for male cancers.
Testicular
Penile
Prostate
Male breast
Past medical or surgical history of conditions related to kidneys, bladder, rectum, genital area
Family history of bladder, breast, kidney, penis, prostate, and testicular cancers
Risk Factors for Male Cancers
Testicular Cancer
Family history (brother or father)
Undescended testicle (cryptorchidism)
Cancer in the other testicle
Carcinoma in situ of the testicle
Men infected with HIV and AIDs
Body size – tall men (ACS, 2020a)
Penile Cancer
Not being circumcised
HPV infection
AIDS
Phimosis
Smoking and tobacco use
Advancing age
Ultraviolet light treatment for psoriasis (ACS, 2018b)
Prostate Cancer
African American men
Advancing age
BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene changes
Family history (ACS, 2020b)
Male Breast Cancer
Advancing age
Radiation exposure to chest area
High estrogen levels
Family history of breast cancer
Inherited gene mutation (BRCA1, BRCA2)
Klinefelter syndrome
Alcohol
Testicular conditions
Liver disease
Obesity
(ACS, 2018a)
Common Sexually Transmitted Infections
Sexually transmitted infection (STI) occurs when either bacteria or viruses enter the body; patient asymptomatic
STIs disrupt the normal body function or structure, and signs and symptoms appear.
Common STIs
Gonorrhea
Chlamydia
Genital herpes
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Syphilis
Male Reproductive System
Pain
Use the OLDCARTS mnemonic
Dysuria
Bladder pain
Costovertebral pain
Testicular pain
Inguinal pain
Male Reproductive System
Urinary Symptoms
Difficulty starting the stream
Hesitancy or urinary retention
Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)
Frequency
Penile sores, lesions, or discharge
Color
Amount
Consistency
Odor of discharge
Male Reproductive System
Scrotum
Male Reproductive System
Sexual Health
World Health Organization (WHO) has defined sexual health as a state of physical, mental, and social well-being in relation to sexuality.
Four P’s of sexual history:
Partners – sexual relationship, number and type of sexual partners.
Practices – types of sexual practices
Protection – precautions and protection
Past STIs – time frame, treatment
Male Reproductive System
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) occurs when a consistent inability to get or maintain an erection prevents a man from having satisfying sex.
Linked to several common diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, hypertension
Ask the patient: “Are you able to achieve or maintain an erection?”
Symptoms
Length of time, occur gradually or suddenly
Male Reproductive System
Preparation for Assessment
Sequence of Assessment
Inspecting and palpating the male breasts
Inspecting the male genitalia
Provide a warm and comfortable room.
Reassure the patient that confidentiality will be maintained.
Encourage the patient to empty his bladder.
Expose only the area being assessed.
Inspecting/Palpating Male Breasts
Purpose: To assess for lumps, nipple discharge or abnormalities
Equipment: Gloves, additional PPE (if needed)
With the patient lying in the supine position, inspect the male breasts.
Symmetry
Color
Contour (dimpling or retraction)
Edema
Lesions
Ulcerations
Texture of skin
Inspecting/Palpating Male Breasts
Inspecting Areola
Shape
Color
Inspecting/Palpating Male Breasts
Inspecting Nipples
Size
Position
Shape
Discharge
Scaling or crusting
Inspecting/Palpating Male Breasts
Ask patient while inspecting/palpating
Ask the patient to raise his arms to over his head.
Inspect the lateral aspect of the breasts toward the mid-axillary line for skin changes.
Gently palpate each breast and axillary area using the finger pads of your second, third, and fourth fingers using the vertical strip pattern assessment techniques.
Palpating Male Breasts
Palpate any lump or mass and note the following:
Shape
Size
Consistency
Mobility
Location
Put on gloves and palpate each areola.
Palpate and press each nipple and note any discharge.
Color
Consistency
Odor