year 13 organic 1
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
optical isomerism, aldehydes and ketones, carboxylic acid
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
what are optical isomers?
non- superimposable mirror images
how do optical isomers arise ?
arises when a molecules mirror image is non-superimposable
also called enantiomers
this happens when a molecule contains a carbon atom with 4 different groups attach to it
that carbon can be called the ‘chiral centre’ therefore the whole molecule can be referred to as ‘chiral’
we can also refer to these types of molecules as ‘optically active’
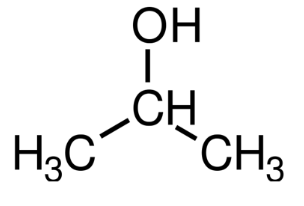
is this optically active ?
not optically active
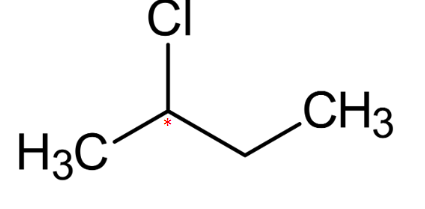
is this optically active ?
optically active
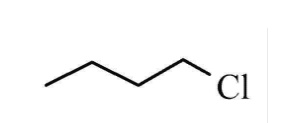
is this optically active ?
not optically active
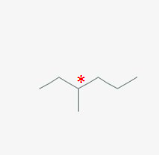
is this optically active?
optically active
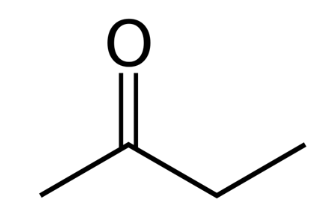
is this optically active ?
not optically active
properties of optically active compounds?
identical chemical and physical properties
effect of plane polarised light, one optical isomer will rotate the plane of polarisation clockwise, the other will rotate it anticlockwise
reaction with other chiral molecules ? (mention drugs)
chiral molecules react differently
many drugs are optically active with one enantiomer only having the beneficial effect
in other cases, the other enantiomer can be harmful (thalidomide)
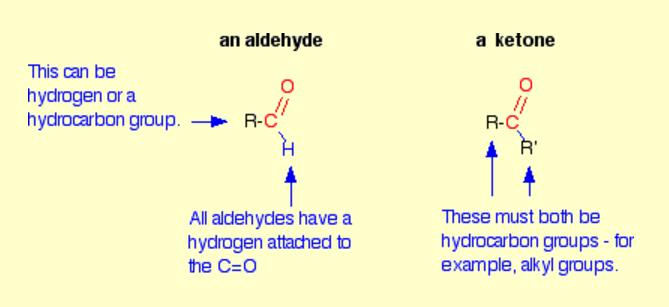
how to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones?
fehling’s/ tollenes reagent
aldehydes/ketones are a better oxidising/reducing agent than the other due to the presence of a ….. atom attached to the …. double bond therefore is easier to get oxidised/ reduced.
aldehydes are a better reducing agent than the other due to the presence of a hydrogen atom attached to the carbon-oxygen double bond therefore is easier to get oxidised
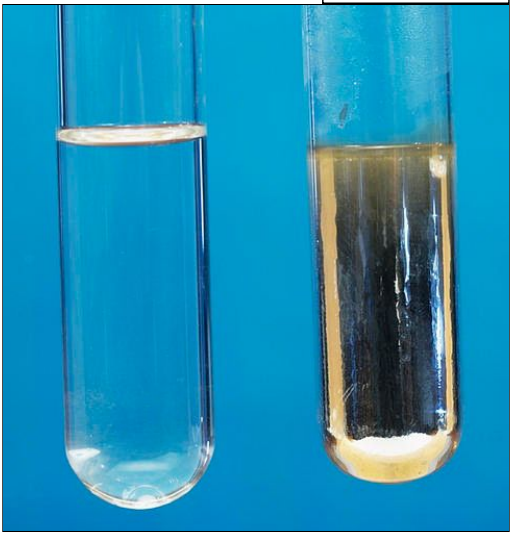
describe test to differentiate aldehydes and ketones. (describe tollens)
Tollen’s reagent can be used to identify aldehydes. It is added to the solution being tested and warmed gently.
If an aldehyde is present, a silver mirror will form in the test tube. If not, the solution will remain colourless.

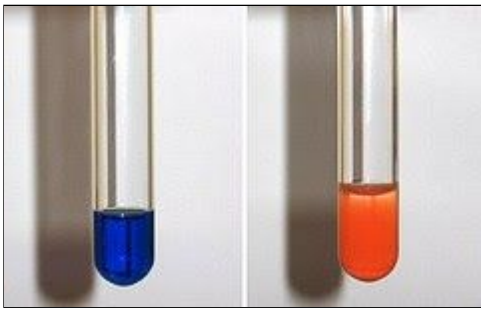
describe test to differentiate aldehydes and ketones. (describe fehling’s solution)
Fehling's solution is another way of testing for aldehydes. It is added to the solution being tested and heated.
A brick red precipitate will form if an aldehyde is present and if not, the solution remains blue and there is no observed change.
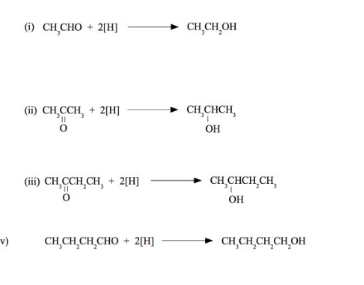
what is formed when an aldehyde and ketone is reduced ?
aldehydes - primary alcohol
ketones - secondary alcohol
what reducing agent is used to reduce aldehydes and ketones and how does it allow this? (what is it dissolved in as well to allow it to work )
whats the name of the mechanism that takes place ?
NaBH4/ LiBH4
provides a source of hydride ions (H-) which is the nucleophile
dissolved in water/ ethanol which is the source of H+ ions
nucleophilic addition
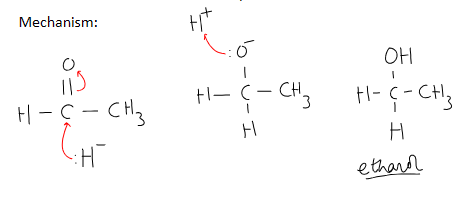
outline the mechanism of reduction of an aldehyde ethanal

what else can be used as a reducing agent other than NaBH4 / LiBH4?
state conditions and what it produces and why its not preferred over the other reducing agent
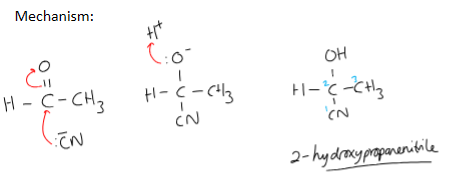
KCN
acidified KCN as thats a good source of H+ ions
produces hydroxy nitriles
HCN not used as its a toxic gas
outline mechanism of an aldehyde with KCN ethanal
what happens if unsymmetrical ketone/ any aldehyde undergoes nucleophilic addition?
a racemic mixture would be formed
C=O bond is flat/planar
nucleophile can attack from above or below with equal probability
racemic mixture forms (equal amount of two enantiomers of an optically active substance)
no optical activity/ no effect on plane polarised light as half would rotate it clockwise and the other half anticlockwise
carboxylic acid + metal
carboxylic acid + carbonates
carboxylic acid + bases and alkalis
salt + hydrogen
salt + water + CO2
salt + water
how are esters formed ? what catalyst is used ?
carboxylic acid + alcohol
sulfuric acid catalyst - H2SO4
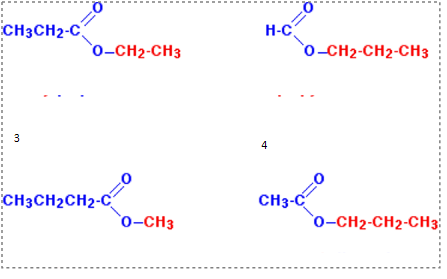
name these esters
ethyl propanoate
propyl methanoate
methyl butanoate
propyl ethanoate
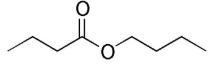
name this ester
butyl butanoate
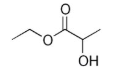
name this ester
ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate
outline acid hydrolysis of esters - methyl propanoate
CH3CH2COOCH3 + H2O ~ CH3CH2COOH + CH3OH
~ = reversible reaction sign
! remember H+ acid catalyst on top of reversible reaction sign
acid hydrolysis of an ester would form a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
this is a reversible process so if this is done in a closed system an equilibrium mixture of reactants and products is obtained
outline base hydrolysis of esters - methyl propanoate
what is the product called
CH3CH2COOCH3 + H2O CH3CH2COOH + CH3OH
then with NaOH it forms:
CH3CH3COONa + H2O
overall: CH3CH2COCH3 + NaOH —> CH3CH2COONa + CH3OH
CH3CH2COONa - carboxylate salt
why do scientists make esters? what can they be used for?
esters give fruits their smell
they are sweet smelling which are added to foods/perfumes
they are used as solvents
they are used plastics to make plastics softer and more flexible
- soaps and biodiesel
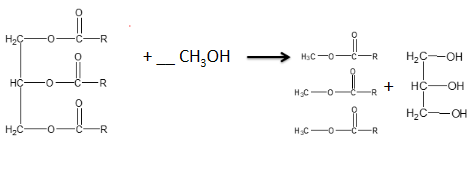
how are triesters formed? and what is the IUPAC name for glycerol ?
they’re formed when 3 carboxylic acids react with the alcohol (aka glycerol)
glycerol - propan- 1,2,3 - triol
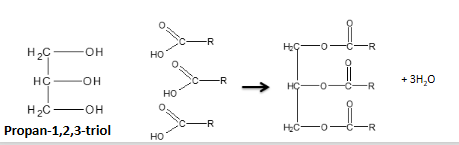
show how glycerol reacts with carboxylic acid to form a triester
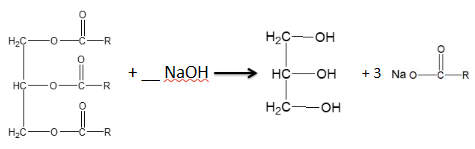
how would you form soap from a triesters ?
hydrolysing triesters is done using conc. NaOH
glycerol (propane-1,2,3 - triol) and sodium carboxylate salts are made
how can triesters be used to make biodiesel ?
triesters react with methanol in the presence of a base catalyst
methyl esters and propan- 1,2,3 triol are produced
what are acyl chlorides?
an acid derivatives where the OH group has been replaced by a chlorine atom
how can you produce an acyl chloride?
mix a carboxylic acid with phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5)
Ethanoyl chloride + water
ethanoic acid + HCl
ethanoyl chloride + methanol
methyl ethanoate + HCl
ethanoyl chloride + ammonia
ethanamide + HCl
ethanoyl chloride + propylamine
n- propylethanamide + HCl
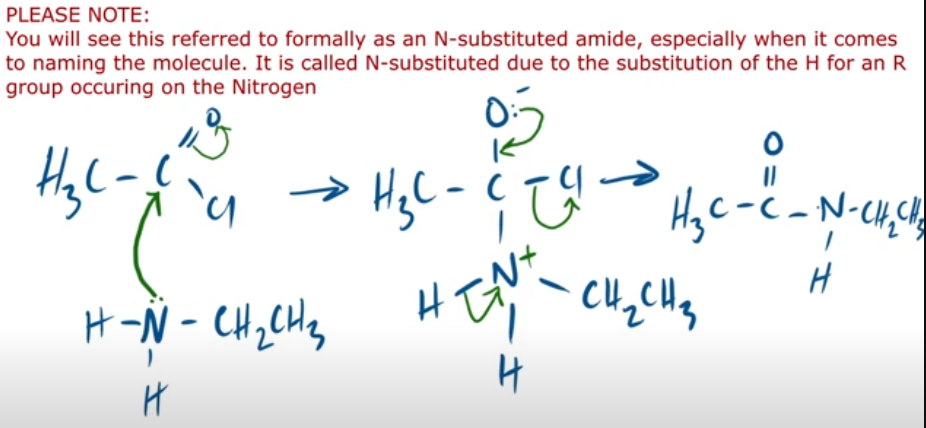
what’s the name of the mechanism which would take place in an ethanoyl chloride ?
nucleophilic addition- elimination
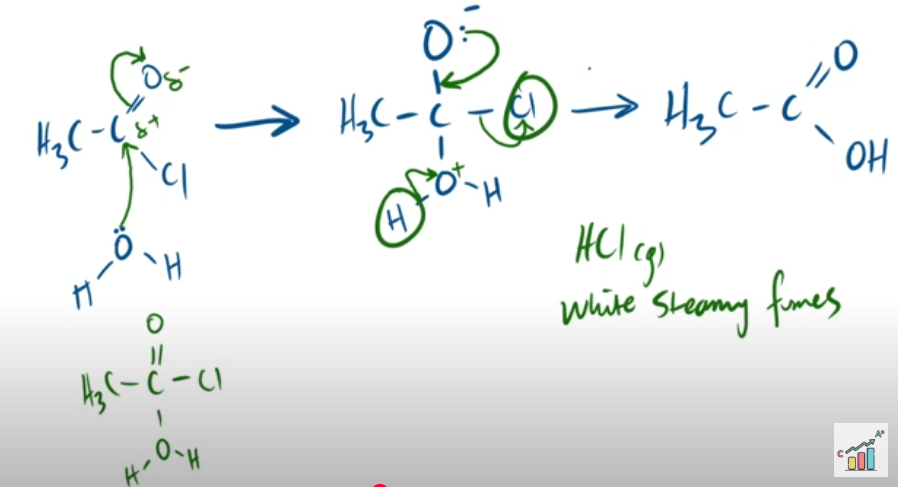
outline the mechanism between ethanoyl chloride and water. and state observation made.
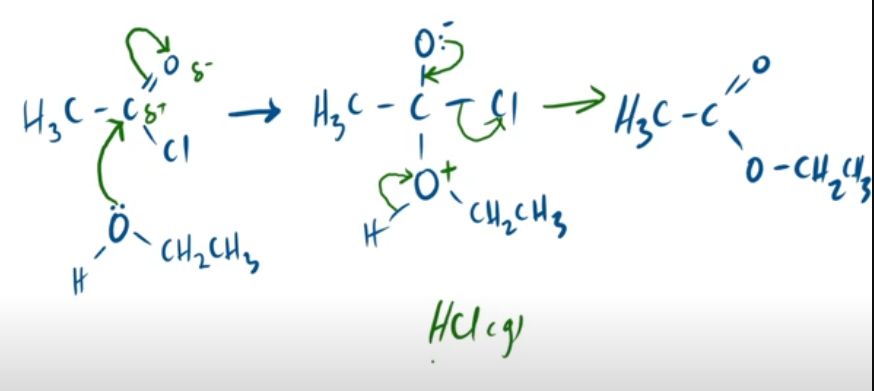
outline the mechanism between ethanoyl chloride and alcohol. and state observation made.
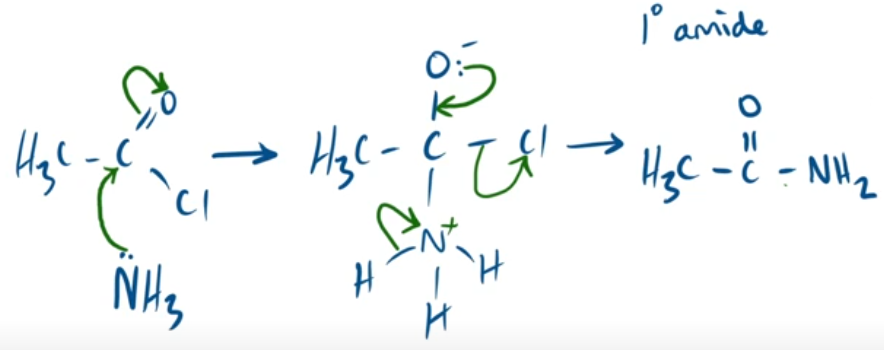
outline the mechanism between ethanoyl chloride and ammonia. and state observation made
outline the mechanism between ethanoyl chloride and primary amine. and state observation made
ethanoic anhydride + water
2x ethanoic acid
ethanoic anhydride + methanol
methyl ethanoate + ethanoic acid
ethanoic anhydride + ammonia
ethanamide + ethanoic anhydride
ethanoic anhydride + methylamine
n- methylethanamide + ethanoic acid
compare acyl chloride and acid anhydride reactions
